Exploring the Intersection of Microplastics and Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Comprehensive Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Selection of Studies
3. Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Sources, Types, and Environmental Impact
3.1. Environmental Distribution and Bioaccumulation
3.2. Characteristics Influencing Environmental Impact
3.3. Toxic Impacts of Microplastics on Living Organisms
4. Black Soldier Fly Larvae: Biology and Applications
4.1. BSFL as a Sustainable Waste Management Solution and Bioremediation
4.2. Life Cycle and Biology of BSFL
5. Interaction Between Microplastics and Black Soldier Fly Larvae
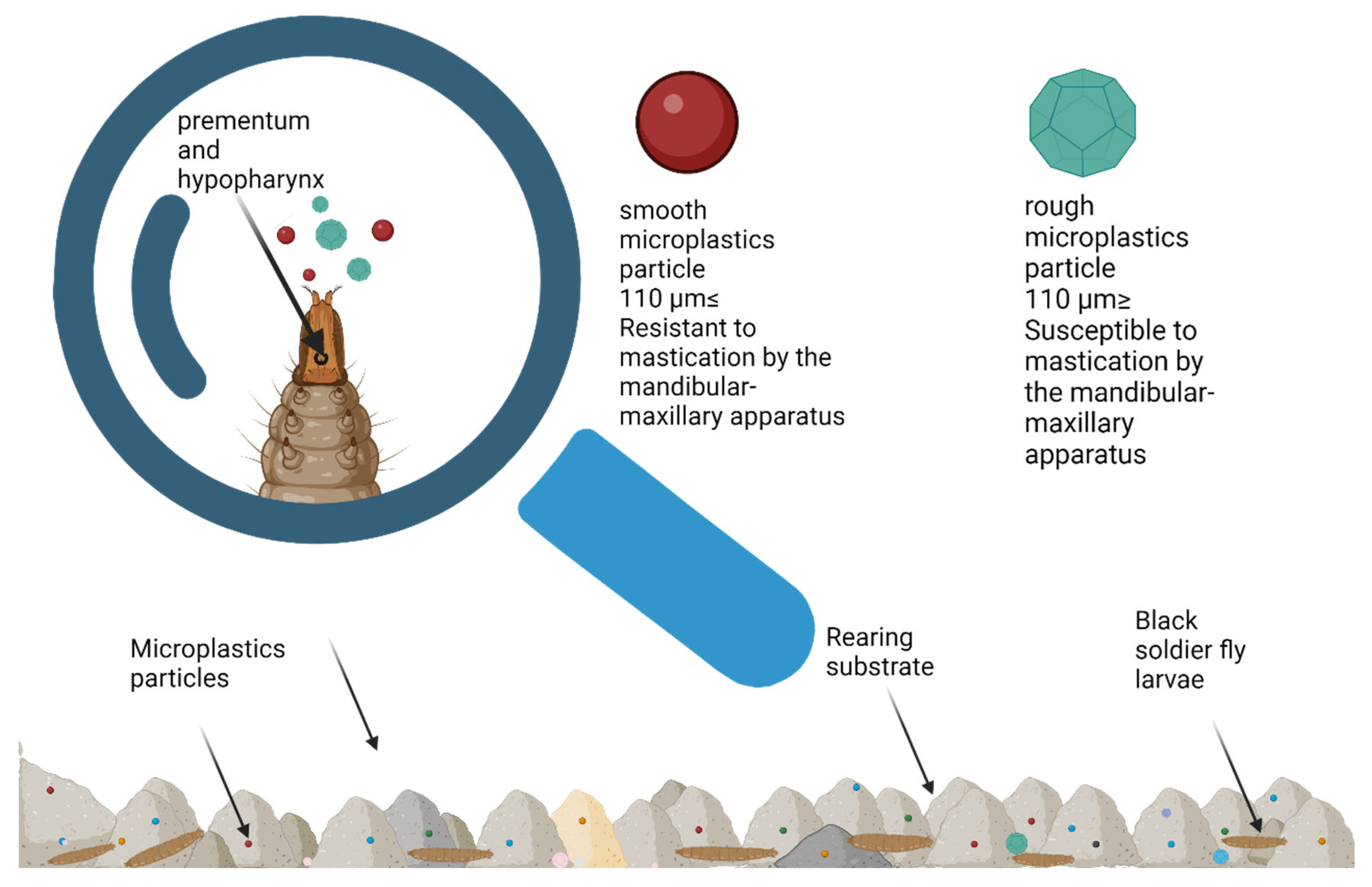
5.1. Ingestion of Microplastics by BSFL
5.2. Digestion, Degradation, and Microbiome Dynamics in Black Soldier Fly Larvae Exposed to Microplastics
5.2.1. Digestion and Degradation of Microplastics by BSFL
5.2.2. Microbiome Alterations Induced by Microplastic Ingestion
5.2.3. Impact of Microplastics on BSFL Growth and Development
6. Current Research and Findings
6.1. Effects of Microplastics on Insect Larvae: Retention, Growth, and Survival Across Diverse Environmental Conditions
6.2. Challenges and Limitations in Current Research
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSFL | Black Soldier Fly Larvae |
| BSF | Black Soldier Fly |
| MPs | Microplastics |
| MINP | monoisononyl phthalate |
| DINP | diisononyl phthalate |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| EDX | energy-dispersive X-ray microanalysis |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| qPCR-Total | DNA extraction and quantification |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PLA | polylactic acid |
| DEHT | di(2-ethylhexyl) terephthalate |
| PVC | polyvinyl chloride |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| DOP | dioctyl phthalate-phthalic acid esters |
References
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Sarker, A.; Ram, K.; Uddin, M.G.; Walker, T.R.; Chowdhury, T.; Uddin, J.; Khandaker, M.U.; Rahman, M.M.; Idris, A.M. Microplastic Toxicity in Aquatic Organisms and Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H.; Fu, L.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X.; Xu, Y.; Du, X. A Review of Microplastics in the Aquatic Environmental: Distribution, Transport, Ecotoxicology, and Toxicological Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11494–11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obbard, R.W. Microplastics in Polar Regions: The Role of Long Range Transport. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Fadare, O.O.; Paredes, M.; Wang, Q.; Verla, A.W.; Shafea, L.; Chowdhury, T. An Overview of Physical, Chemical and Biological Methods for Removal of Microplastics. In Microplastics Pollution in Aquatic Media: Occurrence, Detection, and Removal; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 273–289. [Google Scholar]
- Thacharodi, A.; Hassan, S.; Meenatchi, R.; Bhat, M.A.; Hussain, N.; Arockiaraj, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Sharma, A.; Nguyen, H.T.; Pugazhendhi, A. Mitigating Microplastic Pollution: A Critical Review on the Effects, Remediation, and Utilization Strategies of Microplastics. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Vinnerås, B. Effects of Feedstock on Larval Development and Process Efficiency in Waste Treatment with Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Senecal, J.; Calvo, M.G.; Ahrens, L.; Josefsson, S.; Wiberg, K.; Vinnerås, B. Fate of Pharmaceuticals and Pesticides in Fly Larvae Composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, B.; Scheibelberger, R.; Axmann, S.; Adler, A.; Jäger, H. Impact of Substrate Contamination with Mycotoxins, Heavy Metals and Pesticides on the Growth Performance and Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) for Use in the Feed and Food Value Chain. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.U.; Hollah, C.; Wiesotzki, K.; Rehman, R.U.; Rehman, A.U.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Nienaber, T.; Heinz, V.; Aganovic, K. Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens as a Potential Innovative and Environmentally Friendly Tool for Organic Waste Management: A Mini-Review. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, S.; Vervoort, E.; Bruno, D.; Van der Donck, T.; Tettamanti, G.; Seo, J.W.; Poma, G.; Covaci, A.; De Smet, J.; Van Der Borght, M. Ingestion and Excretion Dynamics of Microplastics by Black Soldier Fly Larvae and Correlation with Mouth Opening Size. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, C.; Priya, A.; Singh, S.B.; Bahuguna, V.; Daverey, A. Potential Strategies for Bioremediation of Microplastic Contaminated Soil. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2024, 6, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragone, N.B.; van Hamelsveld, S.; Nazmi, A.R.; Stott, M.; Hatley, G.A.; Moloney, K.; Bohm, K.; Gutierrez-Gines, M.J.; Weaver, L. Examining the Potential of Plastic-Fed Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) as “Bioincubators” of Plastic-Degrading Bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 136, lxaf085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, F.; Bonelli, M.; Bruno, D.; Sequino, G.; Montali, A.; Reguzzoni, M.; Pasolli, E.; Savy, D.; Cangemi, S.; Cozzolino, V. Plastics Shape the Black Soldier Fly Larvae Gut Microbiome and Select for Biodegrading Functions. Microbiome 2023, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lievens, S.; Yin, S.; Belova, L.; Fujii, Y.; Bombeke, J.; De Smet, J.; Van Der Borght, M.; Covaci, A.; Poma, G. Bioaccumulation and Biotransformation of Plasticisers Diisononyl Phthalate and Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Terephthalate in Black Soldier Fly Larvae Reared on (Micro)Plastic-Contaminated Food Waste. J. Environ. Expo. Assess. 2024, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Cao, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Qin, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Enhanced Biodegradation of Microplastic and Phthalic Acid Ester Plasticizer: The Role of Gut Microorganisms in Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazour, M.; Terki, S.; Rabhi, K.; Jemaa, S.; Khalaf, G.; Amara, R. Sources of Microplastics Pollution in the Marine Environment: Importance of Wastewater Treatment Plant and Coastal Landfill. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Wu, W.; Gao, Y.; Ling, W. Sources of Microplastic in the Environment. Microplastics Terr. Environ. Emerg. Contam. Major Chall. 2020, 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Golwala, H.; Zhang, X.; Iskander, S.M.; Smith, A.L. Solid Waste: An Overlooked Source of Microplastics to the Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Mirande, C.; Tassin, B. Synthetic Fibers in Atmospheric Fallout: A Source of Microplastics in the Environment? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolsky, C.; Kelkar, V.; Driver, E.; Halden, R.U. Municipal Sewage Sludge as a Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 14, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Agricultural Plastic Mulching as a Source of Microplastics in the Terrestrial Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrenfeld, N.L.; Arbuckle-Keil, G.; Naderi Beni, N.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L. Source Tracking Microplastics in the Freshwater Environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Dietze, V.; Baum, A.; Sauer, J.; Gilge, S.; Maschowski, C.; Gieré, R. Tire Abrasion as a Major Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Chen, L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.; Lü, F. Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Landfill: A Source of Microplastics? -Evidence of Microplastics in Landfill Leachate. Water Res. 2019, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Xing, B. Environmental Source, Fate, and Toxicity of Microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrini, K.; Pereira, T.C.B.; Maraschin, T.G.; Teodoro, L.D.S.; Basso, N.R.D.S.; De Galland, G.L.B.; Ligabue, R.A.; Bogo, M.R. Micro-and Nanoplastic Toxicity: A Review on Size, Type, Source, and Test-Organism Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 162954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Lozano, Y.M.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics Increase Soil PH and Decrease Microbial Activities as a Function of Microplastic Shape, Polymer Type, and Exposure Time. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 675803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, Y.M.; Lehnert, T.; Linck, L.T.; Lehmann, A.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastic Shape, Polymer Type, and Concentration Affect Soil Properties and Plant Biomass. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 616645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P. A Review on the Impacts of Microplastic Beads Used in Cosmetics. Acta Biomed. Sci. 2016, 3, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Synthetic Fibers as Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review from Textile Perspective with a Focus on Domestic Washings. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelein, A.; Int-Veen, I.; Kammann, U.; Scharsack, J.P. Microplastic Fibers—Underestimated Threat to Aquatic Organisms? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deocaris, C.C.; Allosada, J.O.; Ardiente, L.T.; Bitang, L.G.G.; Dulohan, C.L.; Lapuz, J.K.I.; Padilla, L.M.; Ramos, V.P.; Padolina, J.B.P. Occurrence of Microplastic Fragments in the Pasig River. H2Open J. 2019, 2, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Jia, W.; Qin, X. LDPE Microplastic Films Alter Microbial Community Composition and Enzymatic Activities in Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cui, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X. An Evaluation Model to Predict Microplastics Generation from Polystyrene Foams and Experimental Verification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.M.; Mahamuni-Badiger, P.; Ingavale, R.R.; Patel, P.R.; Dhanavade, M.J. Usage of Microplastic Beads in Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics Industry: A Review. Microplastic Pollution, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Duan, C.; Cao, N.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Effects of Microplastics on Soil Microbiome: The Impacts of Polymer Type, Shape, and Concentration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vdovchenko, A.; Resmini, M. Mapping Microplastics in Humans: Analysis of Polymer Types, and Shapes in Food and Drinking Water—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digka, N.; Tsangaris, C.; Kaberi, H.; Adamopoulou, A.; Zeri, C. Microplastic Abundance and Polymer Types in a Mediterranean Environment. In Proceedings of the international conference on microplastic pollution in the Mediterranean Sea, Capri, Italy, 26–29 September 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Zhai, W.; Liu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, P. The Influence of Polyethylene Microplastics on Pesticide Residue and Degradation in the Aquatic Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
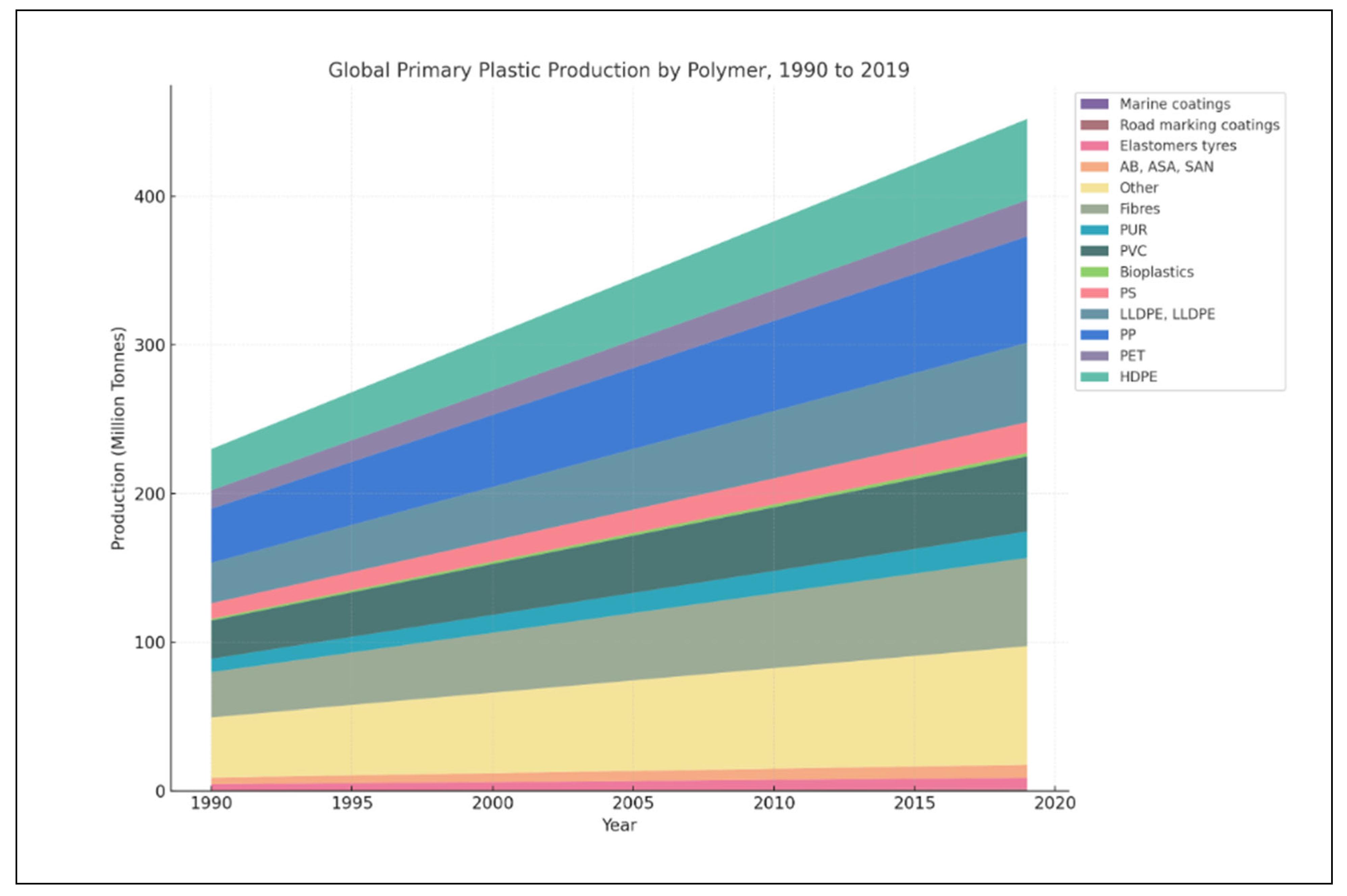
- OECD–Plastic Pollution. Global Primer Plastic Production by Polymer 1990–2019. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/plastic-production-polymer (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of Microplastics in Water and Aquatic Systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. Effects of Microplastics on Agriculture: A Mini-Review. Asian J. Environ. Ecol. 2020, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can-Güven, E. Microplastics as Emerging Atmospheric Pollutants: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Mützel, S.; Primpke, S.; Tekman, M.B.; Trachsel, J.; Gerdts, G. White and Wonderful? Microplastics Prevail in Snow from the Alps to the Arctic. Sci Adv 2019, 5, eaax1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Bhagwat, G.; Oluyoye, I.; Benson, N.U.; Ayejuyo, O.O.; Palanisami, T. Interaction of Chemical Contaminants with Microplastics: Principles and Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Hamid, A.K.; Krebsbach, S.A.; He, J.; Wang, D. Critical Review of Microplastics Removal from the Environment. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbeocha, C.O.; Malek, S.; Emenike, C.U.; Milow, P. Feasting on Microplastics: Ingestion by and Effects on Marine Organisms. Aquat. Biol. 2018, 27, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Baranov, V.; Nel, H.A.; Drummond, J.D.; Kukkola, A.; Hoellein, T.; Smith, G.H.S.; Lewandowski, J.; Bonet, B.; Packman, A.I. Gathering at the Top? Environmental Controls of Microplastic Uptake and Biomagnification in Freshwater Food Webs. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wen, Y.; Marshall, M.R.; Zhao, J.; Gui, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Jones, D.L.; Zang, H. Microplastics as an Emerging Threat to Plant and Soil Health in Agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, W. Cellular Internalization and Release of Polystyrene Microplastics and Nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdessa, R.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Moll, H. Identification of Multiple Cellular Uptake Pathways of Polystyrene Nanoparticles and Factors Affecting the Uptake: Relevance for Drug Delivery Systems. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillaireau, H.; Couvreur, P. Nanocarriers’ Entry into the Cell: Relevance to Drug Delivery. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2873–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, M.; Lee, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, Z.; Wu, P. Environmental Behaviors and Degradation Methods of Microplastics in Different Environmental Media. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarska, E.; Jutel, M.; Zemelka-Wiacek, M. The Potential Impact of Nano-and Microplastics on Human Health: Understanding Human Health Risks. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Duru, C.E.; Ovuoraye, P.E.; Wang, Q. Evaluation of Nanoplastics Toxicity to the Human Placenta in Systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusza, H.M.; Katrukha, E.A.; Nijmeijer, S.M.; Akhmanova, A.; Vethaak, A.D.; Walker, D.I.; Legler, J. Uptake, Transport, and Toxicity of Pristine and Weathered Micro-and Nanoplastics in Human Placenta Cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 097006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Liu, Y.; Chang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Niu, R.; Gao, B.; Guan, Q.; Xia, Y. Micro/Nanoplastic Exposure on Placental Health and Adverse Pregnancy Risks: Novel Assessment System Based upon Targeted Risk Assessment Environmental Chemicals Strategy. Toxics 2024, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Santos-Echeandía, J.; Rocha-Santos, T. Significance of Interactions between Microplastics and POPs in the Marine Environment: A Critical Overview. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, V.; Blázquez, G.; Calero, M.; Quesada, L.; Martín-Lara, M.A. The Potential of Microplastics as Carriers of Metals. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinigopoulou, V.; Pashalidis, I.; Kalderis, D.; Anastopoulos, I. Microplastics as Carriers of Inorganic and Organic Contaminants in the Environment: A Review of Recent Progress. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 350, 118580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.; Braunbeck, T. Bioavailability of Microplastic-Bound Pollutants in Vitro: The Role of Adsorbate Lipophilicity and Surfactants. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 221, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.E.; Hamann, M.; Kroon, F.J. Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification of Microplastics in Marine Organisms: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Current Data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, P.L. Corcoran, P.L. Degradation of Microplastics in the Environment. In Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 531–542. [Google Scholar]
- Sorasan, C.; Ortega-Ojeda, F.E.; Rodríguez, A.; Rosal, R. Modelling the Photodegradation of Marine Microplastics by Means of Infrared Spectrometry and Chemometric Techniques. Microplastics 2022, 1, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Jiang, B.; Xing, Y.; Ya, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. Recent Advances in the Breakdown of Microplastics: Strategies and Future Prospectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 65887–65903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, F. Microbial Degradation and Other Environmental Aspects of Microplastics/Plastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, M.; Pironti, C.; Motta, O.; Miele, Y.; Proto, A.; Montano, L. Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment: Occurrence, Persistence, Analysis, and Human Exposure. Water 2021, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, J.; Ji, R.; Pan, K.; Miao, A.-J. Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: Occurrence, Accumulation, and Biological Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, F.; Meza, P.; Eguiluz, R.; Casado, F.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Geissen, V. Evidence of Microplastic Accumulation in Agricultural Soils from Sewage Sludge Disposal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Gao, T.; Sillanpää, M. Atmospheric Microplastics: A Review on Current Status and Perspectives. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhen, K.; Sturm, M.T. Microplastic Pollution and Reduction Strategies. In Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, H.C.; Pham, M.H. Ecotoxicological Effects of Microplastics on Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44716–44725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gola, D.; Tyagi, P.K.; Arya, A.; Chauhan, N.; Agarwal, M.; Singh, S.K.; Gola, S. The Impact of Microplastics on Marine Environment: A Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhu, C.; Wang, C.; Gu, C. Occurrence and Ecological Impacts of Microplastics in Soil Systems: A Review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Gorain, S.; Patra, M.; Rajwar, A.K.; Gope, D.; Giri, S.K.; Pal, J.; Mahato, M.; Barik, S.; Biswas, S.J. Microplastics, Their Toxic Effects on Living Organisms in Soil Biota and Their Fate: An Appraisal. In Soil Health and Environmental Sustainability: Application of Geospatial Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Gentili, R.; Quaglini, L.; Cardarelli, E.; Caronni, S.; Montagnani, C.; Citterio, S. Toxic Impact of Soil Microplastics (PVC) on Two Weeds: Changes in Growth, Phenology and Photosynthesis Efficiency. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Qiao, Y.; Klobučar, G.; Li, M. Toxicological Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Zhou, X.; He, J.; Zhang, N.; Shen, X.; Sun, C.; Yan, B.; Shao, Y. Toxic Effects of Acute Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics and Nanoplastics on the Model Insect, Silkworm Bombyx Mori. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Ilyas, M.; Li, R.; Yang, J.; Yang, F.-L. Microplastics and Nanoplastics Effects on Plant–Pollinator Interaction and Pollination Biology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, E.S.; Okoye, C.O.; Atakpa, E.O.; Ita, R.E.; Nyaruaba, R.; Mgbechidinma, C.L.; Akan, O.D. Microplastics in Agroecosystems-Impacts on Ecosystem Functions and Food Chain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Vimalkumar, K. A Review of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Insights into Microplastics as Obesogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 724989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Devi, A.; Kadono, H.; Wang, Q.; Rabin, M.H. The Plastic within: Microplastics Invading Human Organs and Bodily Fluids Systems. Environments 2023, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijagic, A.; Kotlyar, O.; Larsson, M.; Salihovic, S.; Hedbrant, A.; Eriksson, U.; Karlsson, P.; Persson, A.; Scherbak, N.; Färnlund, K. Immunotoxic, Genotoxic, and Endocrine Disrupting Impacts of Polyamide Microplastic Particles and Chemicals. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierżyński, E.; Gawlik, P.J.; Puźniak, D.; Flieger, W.; Jóźwik, K.; Teresiński, G.; Forma, A.; Wdowiak, P.; Baj, J.; Flieger, J. Microplastics in the Human Body: Exposure, Detection, and Risk of Carcinogenesis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Biswas, A.; Sharma, A.; Sarkodie, H.; Tran, I.; Pal, I.; De, S. Mutational Signatures Associated with Exposure to Carcinogenic Microplastic Compounds Bisphenol A and Styrene Oxide. NAR Cancer 2021, 3, zcab004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldschläger, K.; Brückner, M.Z.M.; Almroth, B.C.; Hackney, C.R.; Adyel, T.M.; Alimi, O.S.; Belontz, S.L.; Cowger, W.; Doyle, D.; Gray, A. Learning from Natural Sediments to Tackle Microplastics Challenges: A Multidisciplinary Perspective. Earth Sci. Rev. 2022, 228, 104021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Silva, A.L.P.; Da Costa, J.P.; Mouneyrac, C.; Walker, T.R.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Solutions and Integrated Strategies for the Control and Mitigation of Plastic and Microplastic Pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, S.M. Exploring Public Awareness, Influencing Factors and Policy Implications towards Microplastic Pollution: Perspectives from Malaysia. Mar. Policy 2024, 161, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumari, K. An Inclusive Approach for Organic Waste Treatment and Valorisation Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, G.; Van Zanten, H.H.E.; Zamprogna, A.; Veenenbos, M.; Meijer, N.P.; Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Van Loon, J.J.A. Conversion of Organic Resources by Black Soldier Fly Larvae: Legislation, Efficiency and Environmental Impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Mathys, A. Decomposition of Biowaste Macronutrients, Microbes, and Chemicals in Black Soldier Fly Larval Treatment: A Review. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-H.; Ryu, J.; Lee, J.; Ko, K.; Lee, J.; Park, K.Y.; Chung, H. Use of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Food Waste Treatment and Energy Production in Asian Countries: A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyers, M.; Coudron, C.; Ravi, R.; Meers, E.; Bruun, S. Black Soldier Fly Larvae as an Alternative Feed Source and Agro-Waste Disposal Route–A Life Cycle Perspective. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 192, 106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzy, R.R.; El-Dakar, M.A.; Wang, D.; Ji, H. Conversion Efficiency of Lignin-Rich Olive Pomace to Produce Nutrient-Rich Insect Biomass by Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragan-Fonseca, K.B.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Nutritional Value of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) and Its Suitability as Animal Feed–a Review. J. Insects Food Feed 2017, 3, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Jung, J.-M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Bhatnagar, A.; Chen, W.-H.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Kwon, E.E. Biodiesel Production from Black Soldier Fly Larvae Derived from Food Waste by Non-Catalytic Transesterification. Energy 2022, 238, 121700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.X.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Vanlaerhoven, S. Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.; Ireri, D.; Zurbrügg, C.; Fowles, T.; Mathys, A. Efficient and Safe Substrates for Black Soldier Fly Biowaste Treatment along Circular Economy Principles. Detritus 2021, 16, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang-Jie, D.; Xiang, F.-M.; Tao, X.-H.; Jiang, C.-L.; Zhang, T.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-J. A Full-Scale Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Bioconversion System for Domestic Biodegradable Wastes to Resource. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Tabinda, A.B.; Ali, A.; Zurbrügg, C. Reducing the Space Footprint of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Waste Treatment by Increasing Waste Feeding Layer Thickness. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Hou, D.; Chen, J.; Nowar, E.E.; Li, Z.; Hu, R.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, S. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Enhancing Carbon and Nitrogen Conversion in Food Wastes by the Black Soldier Fly. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Negi, S.; Mandpe, A.; Singh, R.V.; Hussain, A. Rapid Composting Techniques in Indian Context and Utilization of Black Soldier Fly for Enhanced Decomposition of Biodegradable Wastes-A Comprehensive Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 227, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Awasthi, M.K.; Chen, H.; Duan, Y.; Awasthi, S.K.; Zhang, Z. Performance of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) for Manure Composting and Production of Cleaner Compost. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkayastha, D.; Sarkar, S. Sustainable Waste Management Using Black Soldier Fly Larva: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 12701–12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakeri, E.M.; Ogola, H.J.; Ayieko, M.A.; Amimo, F.A. An Open System for Farming Black Soldier Fly Larvae as a Source of Proteins for Smallscale Poultry and Fish Production. J. Insects Food Feed. 2017, 3, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, K.; Edwards, O.; Sunna, A.; Paulsen, I.T.; Maselko, M. Diverting Organic Waste from Landfills via Insect Biomanufacturing Using Engineered Black Soldier Flies (Hermetia illucens). Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lievens, S.; Poma, G.; De Smet, J.; Van Campenhout, L.; Covaci, A.; Van Der Borght, M. Chemical Safety of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens), Knowledge Gaps and Recommendations for Future Research: A Critical Review. J. Insects Food Feed. 2021, 7, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Cai, R.; Xie, S. Effects of Heavy Metals on the Bioaccumulation, Excretion and Gut Microbiome of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Liu, N.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Cai, M. Tolerance and Removal of Four Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Compounds (PAHs) by Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, S.; Li, F.; Zheng, L.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, C.; Fan, M.; Cai, M. Characteristics and Mechanisms of Ciprofloxacin Degradation by Black Soldier Fly Larvae Combined with Associated Intestinal Microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Camenzuli, L.; Van Der Lee, M.K.; Oonincx, D. Uptake of Cadmium, Lead and Arsenic by Tenebrio Molitor and Hermetia illucens from Contaminated Substrates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghit, I.; Liland, N.S.; Lundebye, A.-K.; Tibon, J.; Sindre, H.; Nilsen, H.; Hagemann, A.; Sele, V. Aquaculture Sludge as Feed for Black Soldier Fly: Transfer of Chemical and Biological Contaminants and Nutrients. Waste Manag. 2024, 187, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbokou Foukmeniok, S.; Ogbon, A.; Bougna Tchoumi, H.H.; Dzepe, D.; Santos, J.C.C.; Riggi, L.; Tonle Kenfack, I.; Djouaka, R. Effect of the Rearing Substrate Contamination with λ-Cyhalothrin Pesticide on the Growth Performance and Survival of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae: A Study of Biodegradation Kinetics. Chem. Afr. 2024, 7, 2833–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagappan, S.; Rowland, D.; Barwell, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Mikkelsen, D.; Mantilla, S.M.O.; James, P.; Yarger, O.; Hoffman, L. Organic Side Streams (Bioproducts) as Substrate for Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Intended as Animal Feed: Chemical Safety Issues. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2022, 62, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piersanti, S.; Rebora, M.; Turchetti, B.; Salerno, G.; Ruscetta, M.; Zucconi, L.; D’Alò, F.; Buzzini, P.; Sannino, C. Microplastics in the Diet of Hermetia illucens: Implications for Development and Midgut Bacterial and Fungal Microbiota. Waste Manag. 2024, 186, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-G.; Choi, Y.-C.; Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, W.-T.; Jeong, G.-S.; Park, K.-H.; Hwang, S.-J. Ecology of the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratmyidae) in Korea. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2008, 47, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, J.; Wynants, E.; Cos, P.; Van Campenhout, L. Microbial Community Dynamics during Rearing of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) and Impact on Exploitation Potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02722-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boakye-Yiadom, K.A.; Ilari, A.; Duca, D. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Life Cycle Assessment on the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.). Sustainability 2022, 14, 10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaru, A.; Vig, A.; Ladoși, D.; Păpuc, T.; Struți, D.; Georgescu, B. The Use of Various Oviposition Structures for the Black Sol-dier Fly, Hermetia illucens L.(Diptera: Stratiomydae) in Improving the Reproductive Process in Captivity. ABAH Bioflux 2019, 11, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Boafo, H.A.; Gbemavo, D.; Timpong-Jones, E.C.; Eziah, V.; Billah, M.; Chia, S.Y.; Aidoo, O.F.; Clottey, V.A.; Kenis, M. Substrates Most Preferred for Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens (L.) Oviposition Are Not the Most Suitable for Their Larval Development. J. Insects Food Feed. 2023, 9, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, N.B.; Dickerson, A.J.; Tomberlin, J.K. No Neonates without Adults: A Review of Adult Black Soldier Fly Biology, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). BioEssays 2023, 45, 2200162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros-Cordeiro, K.B.; Báo, S.N.; Pujol-Luz, J.R. Intra-Puparial Development of the Black Soldier-Fly, Hermetia illucens. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Ristow, B.; Rahayu, T.; Putra, N.S.; Yuwono, N.W.; Mategeko, B.; Smetana, S.; Saki, M.; Nawaz, A.; Nagdalian, A. Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) and Their Affinity for Organic Waste Processing. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwono, A.S.; Permana, I.G.; Nurulalia, L.; Mentari, P.D. Decomposition Characteristics of Selected Solid Organic Wastes by Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Larvae as Affected by Temperature Regimes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Bonacci, T.; Reguzzoni, M.; Casartelli, M.; Grimaldi, A.; Tettamanti, G.; Brandmayr, P. An In-Depth Description of Head Morphology and Mouthparts in Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2020, 58, 100969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Bae, S.; Park, K.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Han, S.; Koh, Y. Biochemical Characterization of Digestive Enzymes in the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2011, 14, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, L.; Fernandez-Bayo, J.; Niemeier, D.; Pitesky, M.; VanderGheynst, J.S. Managing High Fiber Food Waste for the Cultivation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. npj Sci. Food 2019, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Klammsteiner, T.; Dregulo, A.M.; Kumar, V.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K. Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Organic Manure Recycling and Its Potential for a Circular Bioeconomy: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorescu, A.; Toft, S.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Axelsen, J.A.; Nielsen, S.A. Development, Metabolism and Nutrient Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in Relation to Temperature and Diet. J. Insects Food Feed. 2018, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Jin, W.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, S.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Strengthen the Metabolic Function of Food Waste Biodegradation by Gut Microbiome. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzepe, D.; Nana, P.; Mube, K.H.; Fotso, K.A.; Tchuinkam, T.; Djouaka, R. Role of Pupation Substrate on Post-Feeding Development of Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 760–764. [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel, G.; Bhaskaran, G. Pupariation and Pupation in Cyclorrhaphous Flies (Diptera): Terminology and Interpretation. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1973, 66, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Vanin, S.A. On the Concepts of" Pre-Pupa", with Special Reference to the Coleoptera. Rev. Bras. Zool. 1984, 2, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Vanlaerhoven, S.L.; Tomberlin, J.K. Substrate Effects on Pupation and Adult Emergence of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguz, M.; Miranda, C.D.; Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K. Adult Behaviour as the next Frontier for Optimising Industrial Production of the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens (L.)(Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J. Insects Food Feed. 2023, 9, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, D.C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Joyce, J.A.; Kiser, B.C.; Sumner, S.M. Rearing Methods for the Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.D.; Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K. Interspecific Competition between the House Fly, Musca Domestica L.(Diptera: Muscidae) and Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) When Reared on Poultry Manure. Insects 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, E.; Villazana, J.; Alyokhin, A.; Rose, J. Colonisation of Finfish Substrate Inhabited by Black Soldier Fly Larvae by Blow Flies, Bacteria, and Fungi. J. Insects Food Feed. 2020, 6, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Yao, H. Comprehensive Resource Utilization of Waste Using the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens (L.))(Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Animals 2019, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-T.; Bae, S.-W.; Park, H.-C.; Park, K.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Choi, Y.-C.; Han, S.-M.; Koh, Y. The Larval Age and Mouth Morphology of the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Int. J. Indust Entomol. 2010, 21, 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C. A Toxicological Perspective of Plastic Biodegradation by Insect Larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 248, 109117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, P.; Xu, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, H. Microplastics Existence Intensified Bloom of Antibiotic Resistance in Livestock Feces Transformed by Black Soldier Fly. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, D.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Lin, H.; Bi, Q.; Zhao, Y. Biodegradation of Polyethylene Microplastic Particles by the Fungus Aspergillus Flavus from the Guts of Wax Moth Galleria Mellonella. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miravalle, E.; Balboa, S.; Zanetti, M.; Otero, A.; Lazzari, M. New Insights on the Degradation of Polystyrene and Polypropylene by Larvae of the Superworm Zophobas Atratus and Gut Bacterial Consortium Enrichments Obtained under Different Culture Conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Fischer, H. Microplastics Affected Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Pupation and Short Chain Fatty Acids. J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 145, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heussler, C.D.; Klammsteiner, T.; Stonig, K.T.; Insam, H.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M. Decrypting the Microbiota on the Black Soldier Fly’s (Hermetia illucens L., Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Egg Surface and Their Origin during Development. bioRxiv 2022, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heussler, C.D.; Dittmann, I.L.; Egger, B.; Robra, S.; Klammsteiner, T. A Comparative Study of Effects of Biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable Microplastics on the Growth and Development of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). Waste Biomass Valorization 2024, 15, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Chung, H. Effects of Microplastics and Salinity on Food Waste Processing by Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, B.; Gu, C.; Shen, C.; Yin, S.; Aamir, M.; Li, F. Are We Underestimating the Sources of Microplastic Pollution in Terrestrial Environment? J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, S.; Poma, G.; Frooninckx, L.; Van der Donck, T.; Seo, J.W.; De Smet, J.; Covaci, A.; Van Der Borght, M. Mutual Influence between Polyvinyl Chloride (Micro)Plastics and Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). Sustainability 2022, 14, 12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
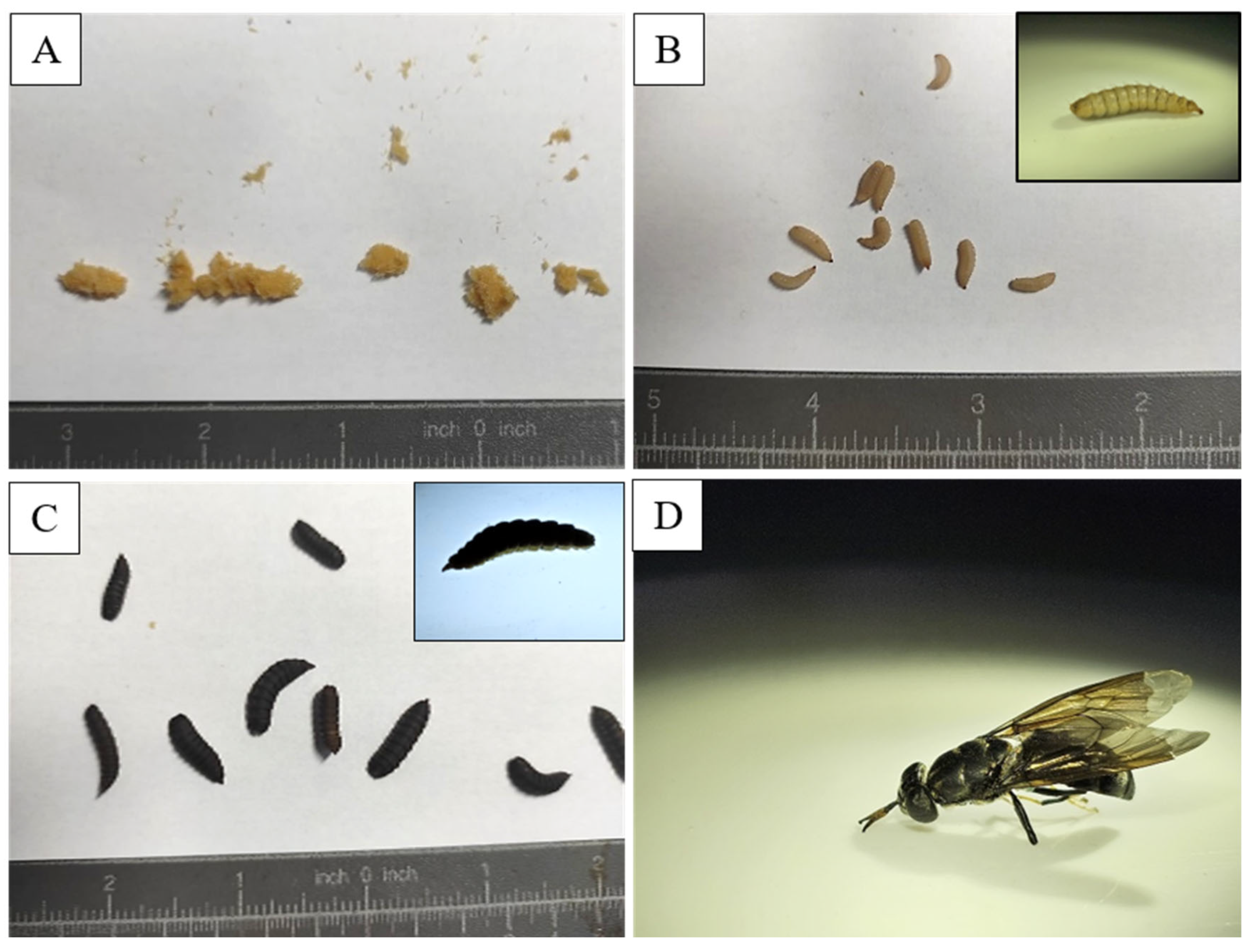


| No. | Environmental Conditions | Types of Microplastics Analyzed | Size Range of Microplastics | Analytical Techniques | Microplastic Retention and Excretion | Effects on Growth and Survival | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 27 °C and 60% relative humidity | PA | (<150 μm) | Histology Fluoroscopic microscopy | MPs only in gut MPs excrete before pupation | Growth unaffected | [150] |
| 2. | 27 °C and 60% relative humidity | PLA | (<150 μm) | Histology Fluoroscopic microscopy | MPs only in gut MPs excrete before pupation | Growth unaffected | [150] |
| 3. | 27 °C with a relative humidity of 60% | DINP | Not specified | Gas chromatographic Liquid chromatographic | Moderate DINP intake, converted to MINP | Not specified | [17] |
| 4. | 27 °C with a relative humidity of 60% | DEHT | Not specified | Gas chromatographic Liquid chromatographic | no clear biotransformation pattern | Not specified | [17] |
| 5. | 27 °C with a relative humidity of 60% | PVC | Not specified | Gas chromatographic Liquid chromatographic | Not specified | Not specified | [17] |
| 6. | Temp: 27–28°C, Humidity: 50%+ | PE | 400 μm | Quantifying | Not specified | Lower weight on PE Increased pupation, reduced consumption | [151] |
| 7. | Temp: 27–28°C, Humidity: 50%+ | PS | 500 μm | Quantifying | Not specified | Higher weight on PS Lower survival, less substrate | [151] |
| 8. | Stable Conditions | PE | 125–50 μm | Measurements Larval gut DNA Extraction | Not specified | Larval stage prolonged | [18] |
| 9. | Stable Conditions | PP | 125–150 μm | Measurements Larval gut DNA Extraction | Not specified | Larval stage prolonged | [18] |
| 10. | Stable Conditions | DMP | Not specified | Measurements Larval gut DNA extraction | Not specified | Minimal impact | [18] |
| 11. | Stable conditions | DOP | Not specified | Measurements Larval gut DNA extraction | Not specified | Minimal impact | [18] |
| 12. | At 27 °C and 60% humidity | PE | (Dv(50) = 61.5 μm) | Fluorescent microscopy SEM | No gut accumulation, particles excreted | Growth unaffected | [13] |
| 13. | 14-h photoperiod, 28 ± 3 ◦C, relative humidity 60 ± 10 %) | PVC | 150–190 μm | SEM, EDX, TEM, qPCR, Bacterial and fungal DNA amplification and metabarcoding sequencing | No gut changes | No mortality rise, smaller pupae | [118] |
| 14. | 30–40% humidity & 25°C. Temp. | PP | 55 ± 4 μm | Measurement SCFA profile gas chromato-Graphy | Not specified | Lower pupation, higher fatty acid levels | [148] |
| 15. | 27.0 ± 0.5 °C, 70 ± 5% relative humidity, in the dark | PE | 400–1000 μm | SEM Metagenomic analyses of the midgut | Not specified | Delayed development | [16] |
| 16. | 27.0 ± 0.5 °C, 70 ± 5% relative humidity, in the dark | PS | 400–800 μm | SEM Metagenomic analyses of the midgut | Not specified | Delayed development | [16] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ionica, C.-N.; Pop, R.; Popa, R.P.; Tabaran, A.-F.; Hodor, D.; Condor, S.; Daina, S.; Szakacs, A.-R.; Macri, A. Exploring the Intersection of Microplastics and Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Comprehensive Review. Insects 2025, 16, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090913
Ionica C-N, Pop R, Popa RP, Tabaran A-F, Hodor D, Condor S, Daina S, Szakacs A-R, Macri A. Exploring the Intersection of Microplastics and Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Comprehensive Review. Insects. 2025; 16(9):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090913
Chicago/Turabian StyleIonica, Claudiu-Nicusor, Romelia Pop, Raluca Paula Popa, Alexandru-Flaviu Tabaran, Dragos Hodor, Sergiu Condor, Sorana Daina, Andrei-Radu Szakacs, and Adrian Macri. 2025. "Exploring the Intersection of Microplastics and Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Comprehensive Review" Insects 16, no. 9: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090913
APA StyleIonica, C.-N., Pop, R., Popa, R. P., Tabaran, A.-F., Hodor, D., Condor, S., Daina, S., Szakacs, A.-R., & Macri, A. (2025). Exploring the Intersection of Microplastics and Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Comprehensive Review. Insects, 16(9), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090913







