Multidimensional Profiling of Senescence in Eastern Honey Bee, Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae), Workers: Morphology, Microstructure, and Transcriptomics
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rearing and Sample Collection of Apis cerana
2.2. Observation of Morphological Characteristics
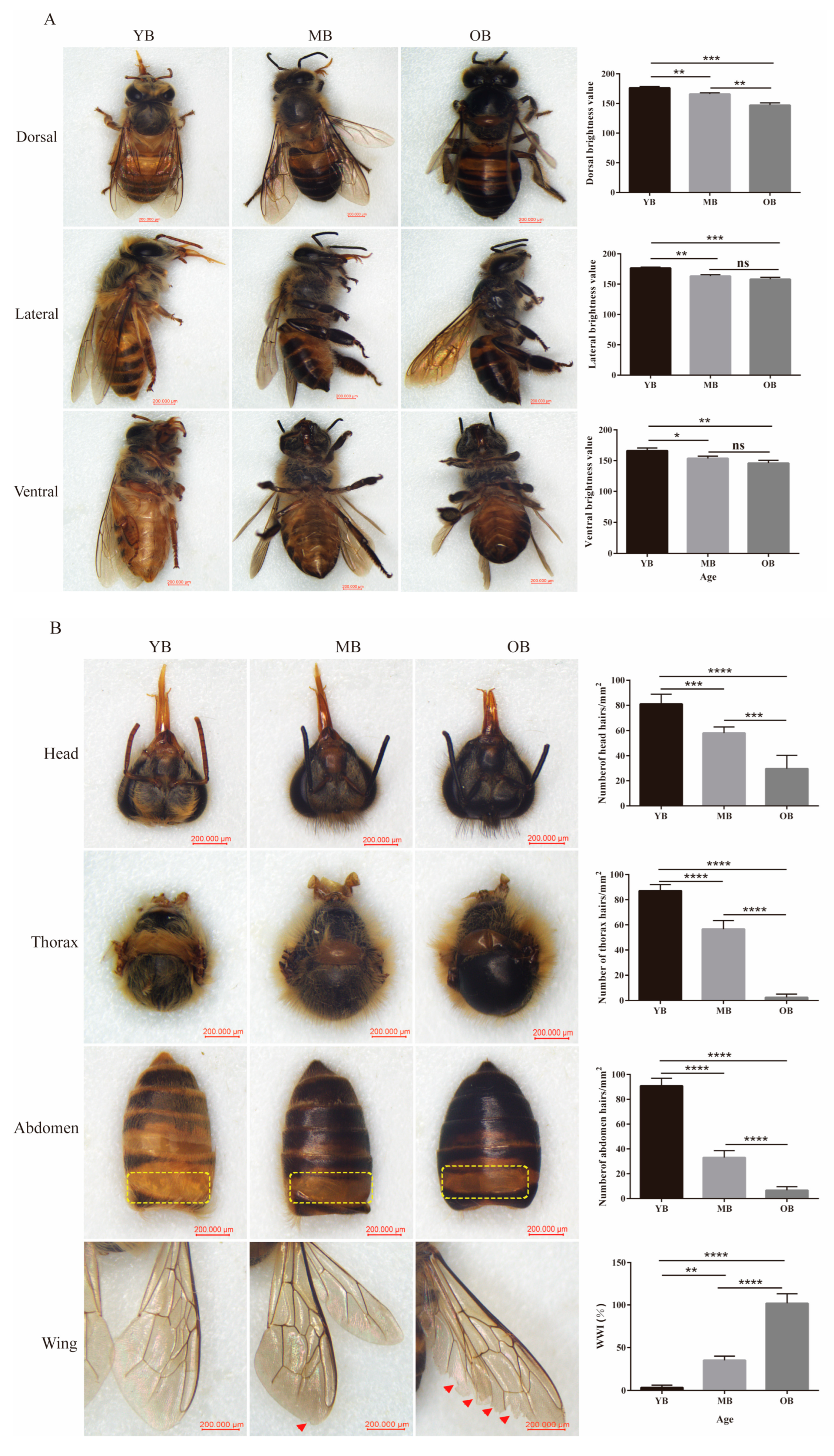
Measurement of Dorsal Brightness
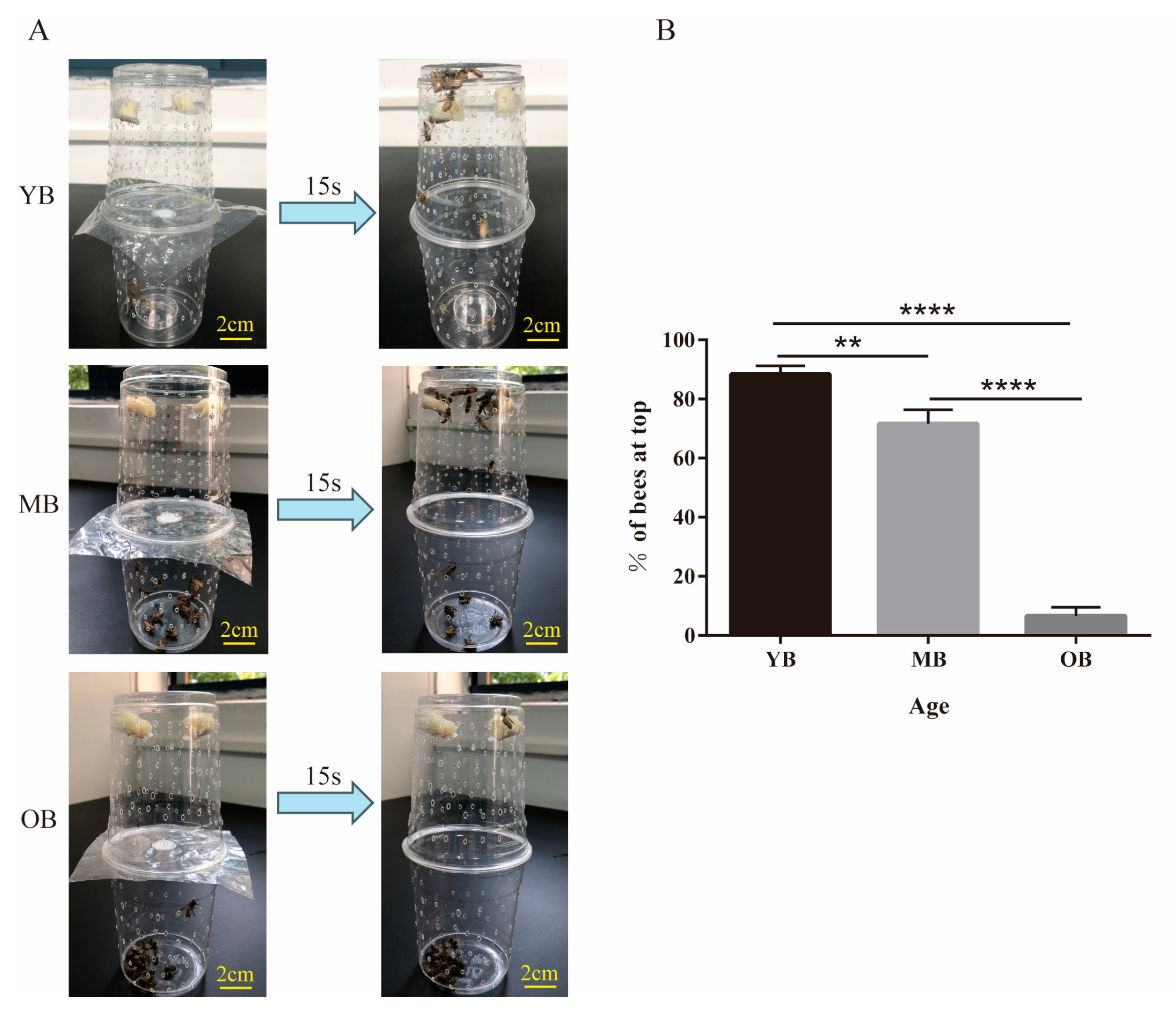
2.3. Assessment of Locomotive Abilities
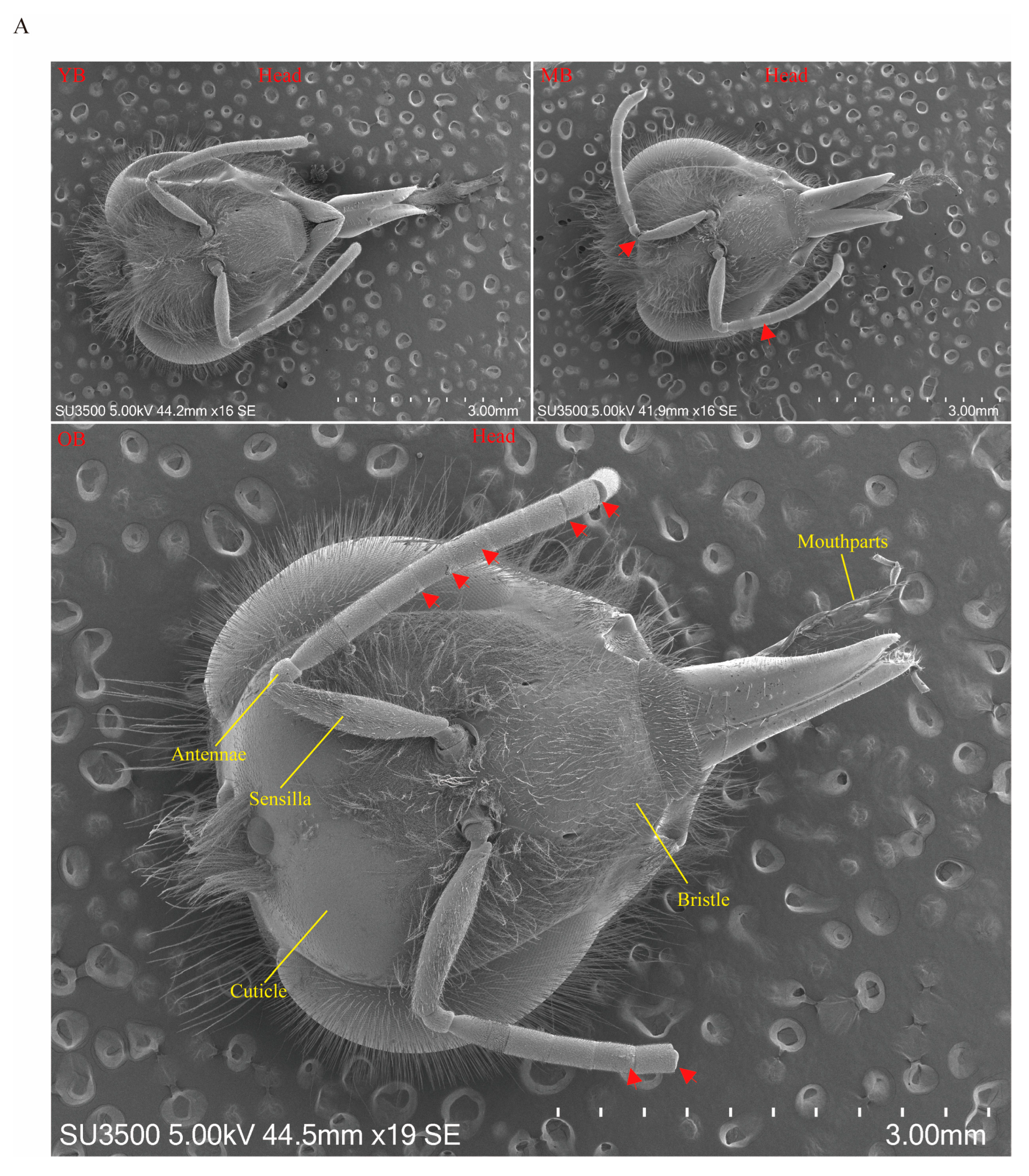
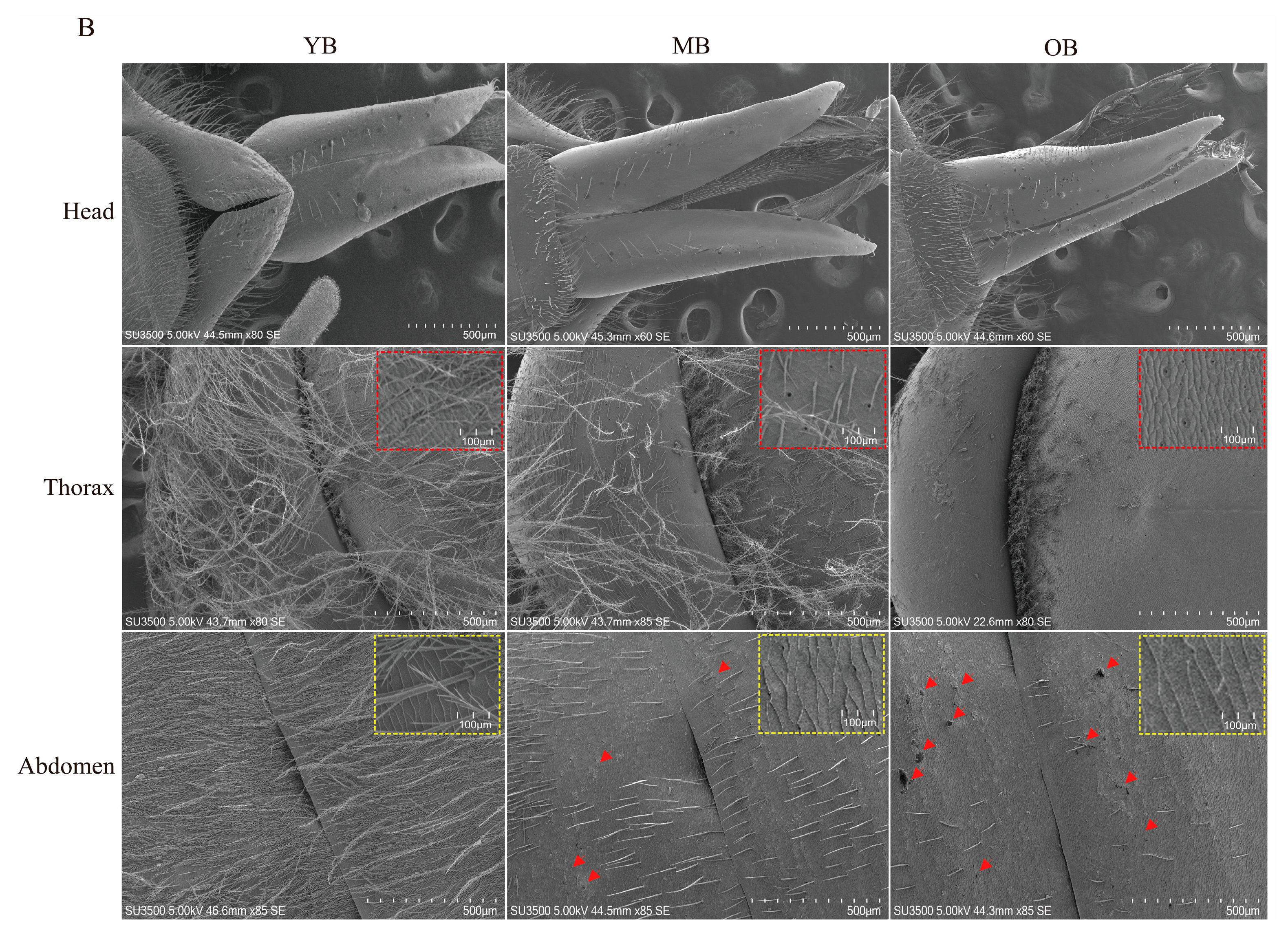
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Observation
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Observation
2.6. Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis
2.7. Validation of DEGs by qRT-PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Age-Dependent Morphological Degeneration in Worker Bees
3.2. Age-Dependent Decline in Locomotor Performance of Worker Bees
3.3. Age-Dependent Degradation of Cuticular Structures in Worker Bees
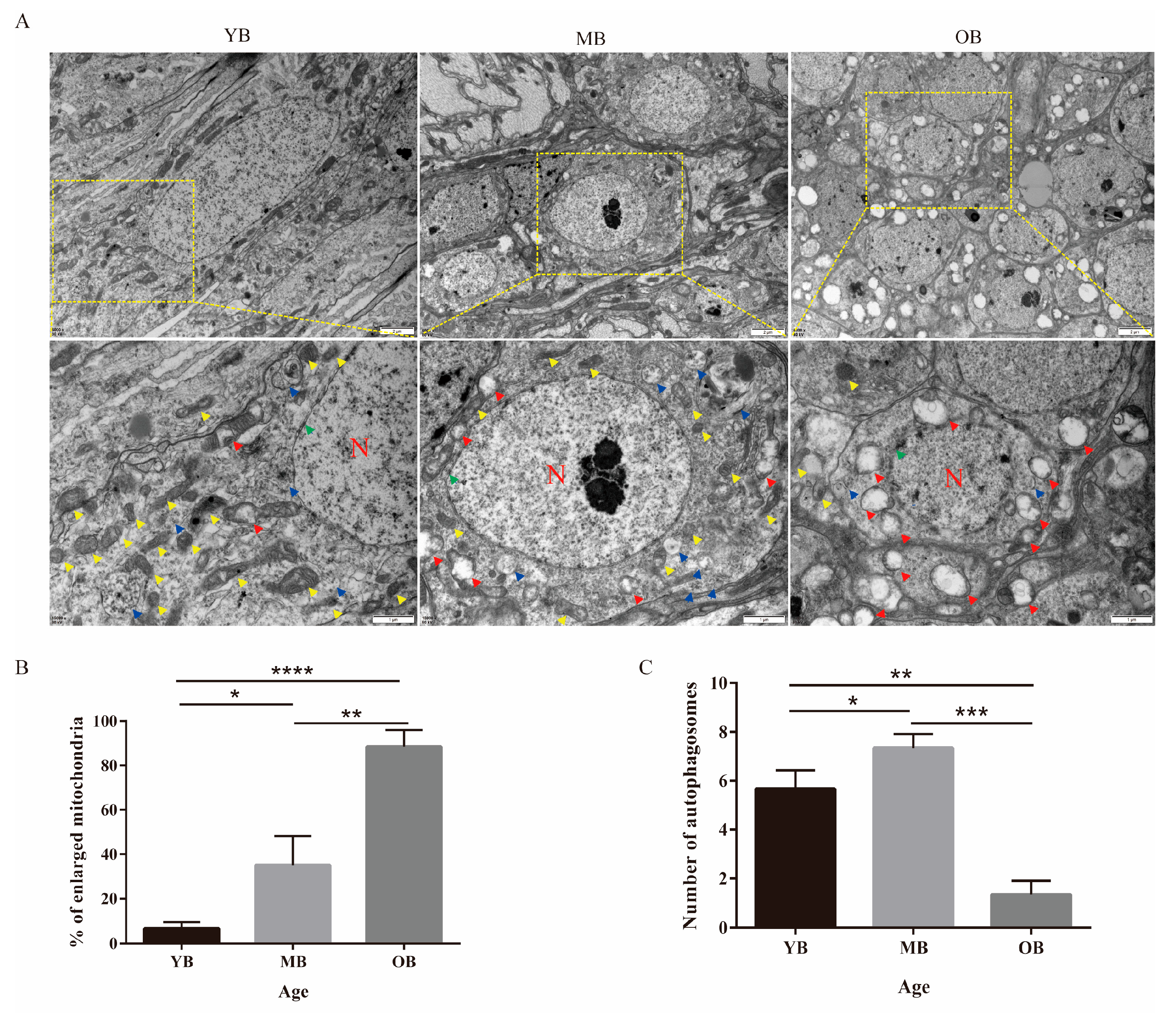
3.4. Age-Dependent Ultrastructural Alterations in the Brain Tissue of Worker Bees
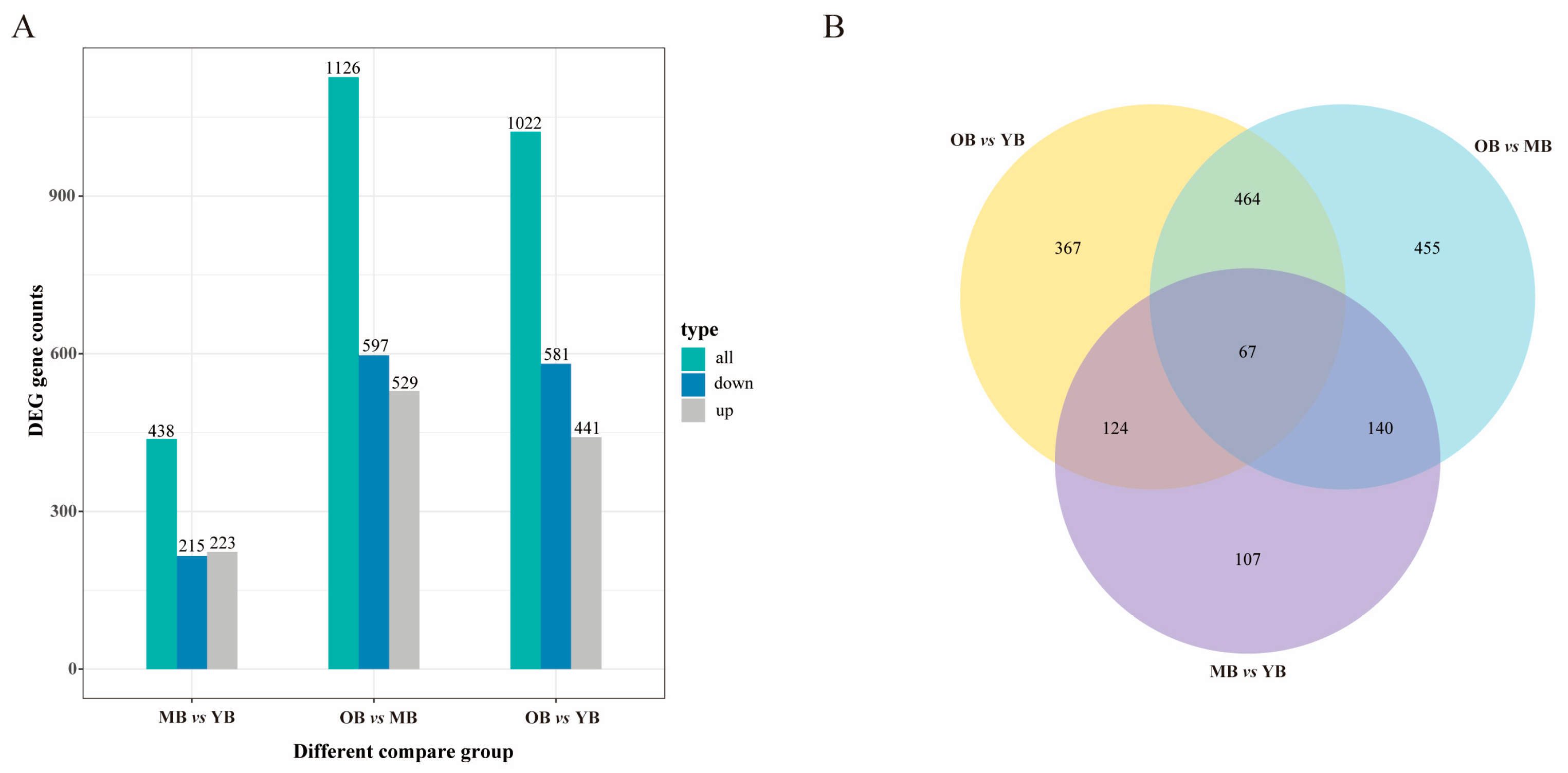
3.5. Transcriptomic Analysis of Aging-Related Genes
3.5.1. Screening of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Related to Aging
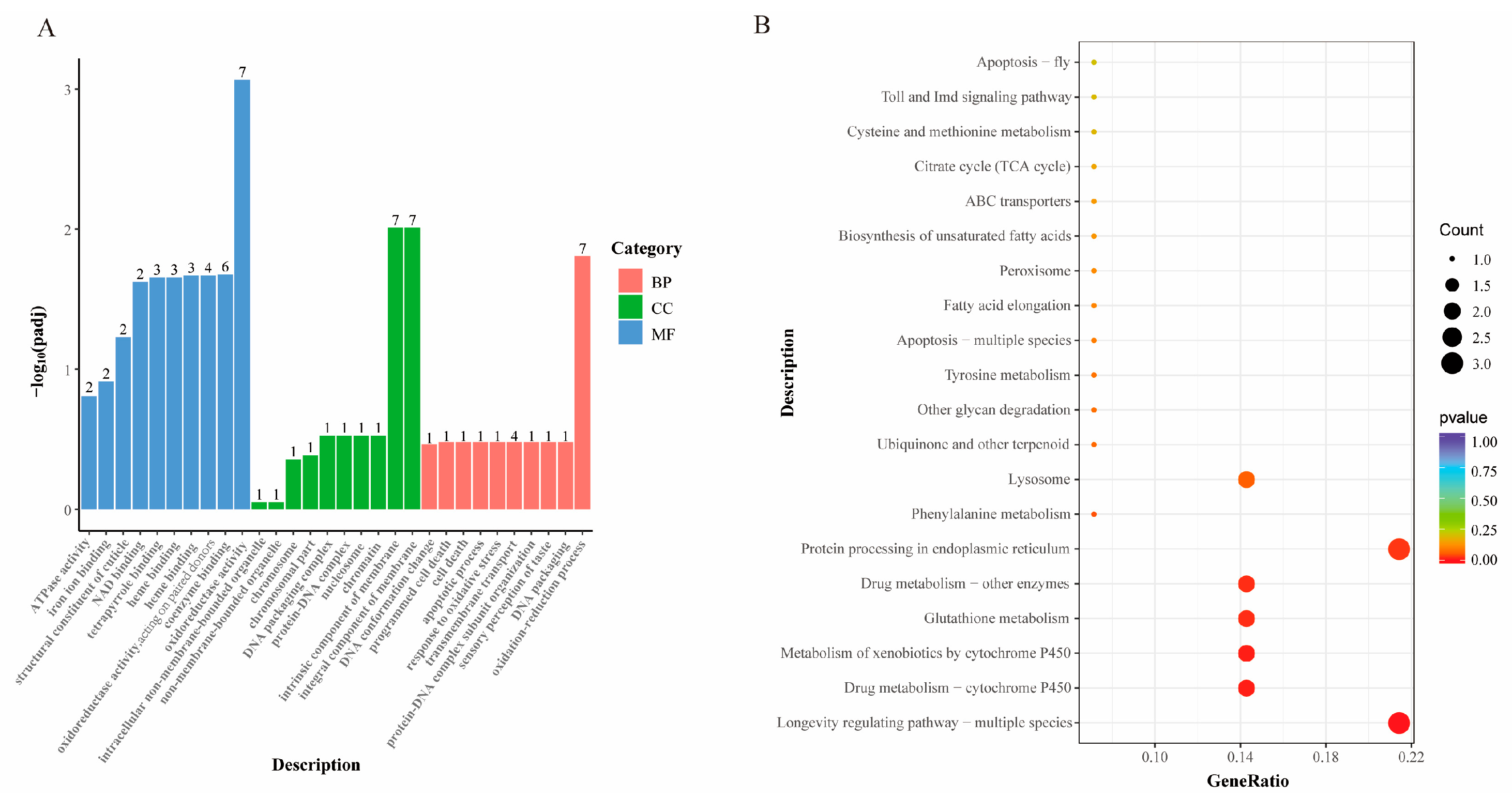
3.5.2. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Aging-Related DEGs
3.5.3. Identification of Genes Related to Aging
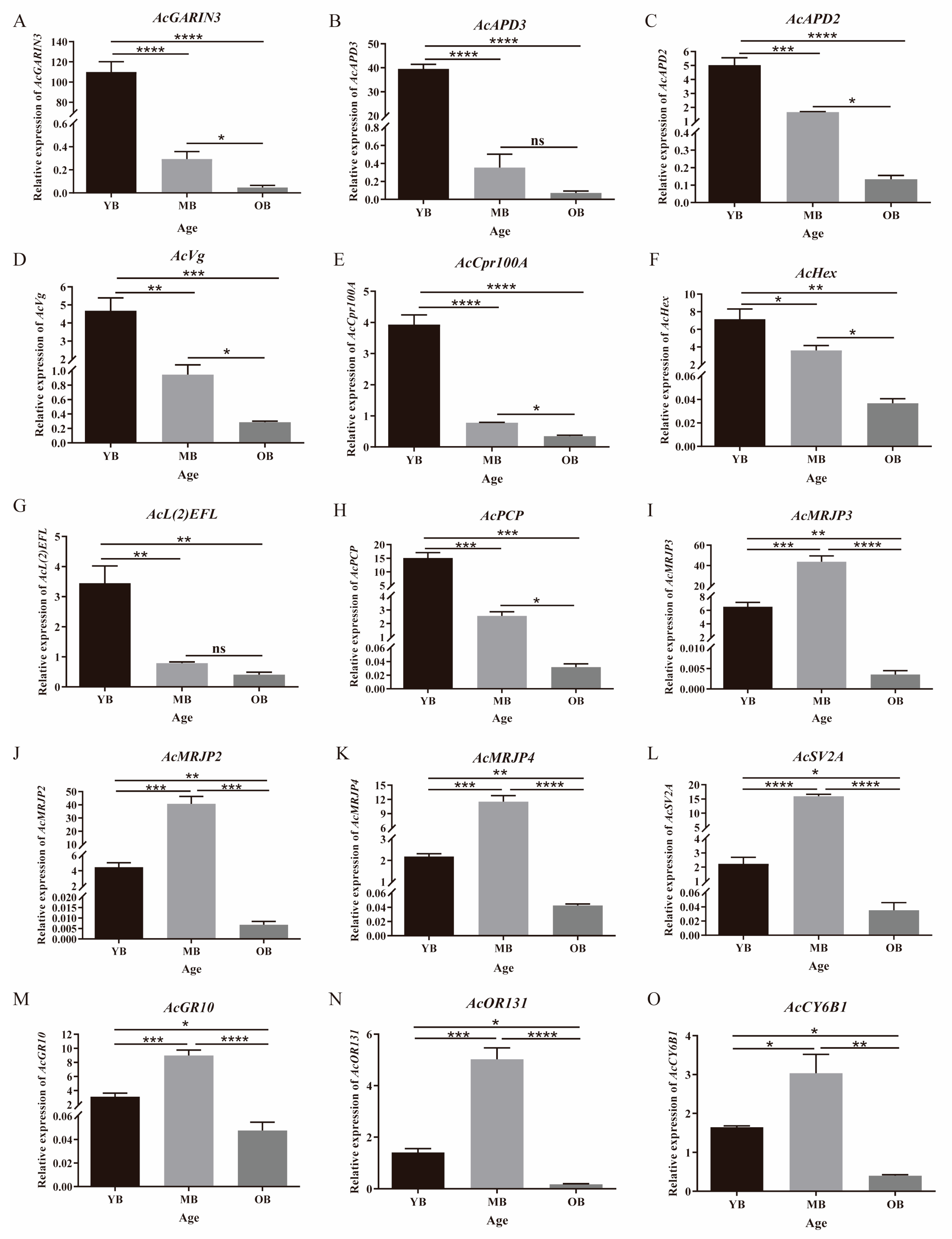
3.6. Expression Level Analysis of Aging-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| YB | Young bee |
| MB | Mid-aged bee |
| OB | Old bee |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| SE | Mean ± standard error of the mean |
| FPKM | Fragments per Kilobase of Exon per million Mapped Fragments |
| Log2FC | log2Fold Change |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
References
- Klein, A.M.; Vaissiere, B.E.; Cane, J.H.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Cunningham, S.A.; Kremen, C.; Tscharntke, T. Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulyshen, M.; Urban-Mead, K.R.; Dorey, J.B.; Rivers, J.W. Forests are critically important to global pollinator diversity and enhance pollination in adjacent crops. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2023, 98, 1118–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, A.L.; McCarty, G.; Du, L.; Sichko, C.; Maguire, K. Native bee pollination ecosystem services in agricultural wetlands and riparian protected lands. Wetlands 2024, 44, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, E.; Potts, S.G.; Senapathi, D.; Albrecht, M.; Arafah, K.; Askri, D.; Bocquet, M.; Bulet, P.; Costa, C.; Rúa, P.; et al. Beekeepers’ perceptions toward a new omics tool for monitoring bee health in Europe. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0316609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; Mazzoni, L.; Giampieri, F. The composition and biological activity of honey: A focus on Manuka honey. Foods 2014, 3, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindrod, I.; Martin, S.J. Varroa resistance in Apis cerana: A review. Apidologie 2023, 54, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Mendieta, S.; Tan, K.; Christmas, M.J.; Olsson, A.; Vila, C.; Wallberg, A.; Webster, M.T. The genomic basis of adaptation to high-altitude habitats in the eastern honey bee (Apis cerana). Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Niu, Q.; Zhao, H.; Du, Y.; Jiang, Y. Transcriptomic analysis to uncover genes affecting cold resistance in the Chinese honey bee (Apis cerana cerana). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179922. [Google Scholar]
- Goulson, D.; Nicholls, E.; Botías, C.; Rotheray, E.L. Bee declines driven by combined stress from parasites, pesticides, and lack of flowers. Science 2015, 347, 1255957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Jin, S.S.; He, Y.; Luo, J.H.; Xu, C.Q.; Wu, Y.Y.; Hou, C.S.; Wang, Q.; Diao, Q.Y. Physiological analysis and transcriptome analysis of asian honey bee (Apis cerana cerana) in response to sublethal neonicotinoid imidacloprid. Insects 2020, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stindl, R.; Stindl, W., Jr. Vanishing honey bees: Is the dying of adult worker bees a consequence of short telomeres and premature aging? Med. Hypotheses 2010, 75, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hristov, P.; Shumkova, R.; Palova, N.; Neov, B. Factors associated with honey bee colony losses: A mini-review. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Ji, C.; Shi, W.; Su, S.; Xue, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C. Survey results of honey bee colony losses in winter in China (2009–2021). Insects 2023, 14, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.E., Jr.; Peng, C.Y. Aging and development in social insects with emphasis on the honey bee, Apis mellifera L. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 695–711. [Google Scholar]
- Behrends, A.; Scheiner, R.; Baker, N.; Amdam, G.V. Cognitive aging is linked to social role in honey bees (Apis mellifera). Exp. Gerontol. 2007, 42, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speth, M.T.; Kreibich, C.D.; Amdam, G.V.; Munch, D. Aging- and task-related resilience decline is linked to food responsiveness in highly social honey bees. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 65, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.; Jemielity, S. Social insects as a model to study the molecular basis of ageing. Exp. Gerontol. 2006, 41, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdam, G.V.; Omholt, S.W. The regulatory anatomy of honeybee lifespan. J. Theor. Biol. 2002, 216, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, M.; Velarde, R.A.; Remolina, S.; Moran-Lauter, A.; Wang, Y.; Hughes, K.A.; Robinson, G.E. Vitellogenin, juvenile hormone, insulin signaling, and queen honey bee longevity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7128–7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ament, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Robinson, G.E. Nutritional regulation of division of labor in honey bees: Toward a systems biology perspective. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2010, 2, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantaphanwattana, T.; Houdelet, C.; Sinpoo, C.; Voisin, S.N.; Bocquet, M.; Disayathanoowat, T.; Chantawannakul, P.; Bulet, P. Proteomics and immune response differences in Apis mellifera and Apis cerana inoculated with three Nosema ceranae isolates. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 2030–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhao, H.; Guo, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Q.; Xu, B.; Guo, X. Distinct molecular impact patterns of abamectin on Apis mellifera ligustica and Apis cerana cerana. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, T.; Shen, F.; Liu, Z.; Yin, L.; Shen, J.; Liang, Q.; Luo, Y.X. Comparative proteomic analysis reveals mite (Varroa destructor) resistance-related proteins in Eastern honeybees (Apis cerana). Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 10103–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Ray Hajong, S.; Talukdar, N.; Chetria, S.; Chakrabartya, S. Task specific behavior of Indian honey bee (Apis cerana indica) workers. J. Apicult. Res. 2024, 64, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Kuang, H.O.; Kuang, B.Y.; Qin, Y. Juvenile hormone and division of labor in Apis cerana. J. Apicult. Res. 2001, 40, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Corona, M.; Robinson, G.E. Genes of the antioxidant system of the honey bee: Annotation and phylogeny. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinello, M.; Mutinelli, F. Antioxidant activity in bee products: A review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwood, R.W. Pain and suffering in invertebrates? ILAR J. 2011, 52, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollo, S.; Vitale, A. Invertebrates and Humans: Science, Ethics, and Policy. In The Welfare of Invertebrate Animals. Animal Welfare; Carere, C., Mather, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Vanengelsdorp, D.; Evans, J.D.; Saegerman, C.; Mullin, C.; Haubruge, E.; Nguyen, B.K.; Frazier, M.; Frazier, J.; Cox-Foster, D.; Chen, Y.; et al. Colony collapse disorder: A descriptive study. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, S.; Feller, C.; Forne, I.; Schiller, E.; Sevin, D.C.; Schauer, T.; Regnard, C.; Straub, T.; Prestel, M.; Klima, C.; et al. Life span extension by targeting a link between metabolism and histone acetylation in Drosophila. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Morton, G.; Hadi, S. Analysis of rpoS and bolA gene expression under various stress-induced environments in planktonic and biofilm phase using 2−△△CT method. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 357, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Xie, L.X.; Tang, X.Y.; He, Y.Y.; Song, H.L.; Xiong, R.Y.; Hu, B.S.; Ma, Z.G.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Xu, J.S. Environmental stressor-induced functional and expression dynamics of glutathione S-transferase genes in bees. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2025, 214, 106581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, V.K.; Madsen, K.L.; Kjaerulff, O. Drosophila Rab2 controls endosome-lysosome fusion and LAMP delivery to late endosomes. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1520–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Tian, Y.; Han, M.; Miao, X. Longevity extension of worker honey bees (Apis mellifera) by royal jelly: Optimal dose and active ingredient. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promislow, D.E.L.; Flatt, T.; Bonduriansky, R. The biology of aging in insects: From drosophila to other insects and back. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 67, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.W.; Zeng, Z.J.; Yan, W.Y. Nutrition affects longevity and gene expression in honey bee (Apis mellifera) workers. Apidologie 2014, 45, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.E., Jr.; Scheiner, R.; Erber, J.; Amdam, G.V. 8. The development and evolution of division of labor and foraging specialization in a social insect (Apis mellifera L.). Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2006, 74, 253–286. [Google Scholar]
- Keasar, T.; Goubitz, S.; Shmida, A. Age-related sampling of food sources in unsuccessful foraging bumblebees [Hymenoptera: Apidae: Bombus]. Entomol. Gen. 2007, 29, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Tacconi, G.; Polidori, C. Subtle morphological changes in the visual and antennal sensory system of bees and wasps across an urbanisation gradient. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, K.; DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Pruett, M.; Jones, V.P.; Corby-Harris, V.; Pireaud, J.; Curry, R.; Hopkins, B.; Northfield, T.D. Warmer autumns and winters could reduce honey bee overwintering survival with potential risks for pollination services. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlak Gajger, I.; Mutinelli, F. Impact of environmental factors and management practices on bee health. Insects 2024, 15, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, B.; Guo, X. The wisdom of honeybee defenses against environmental stresses. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vommaro, M.L.; Giglio, A. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of a pendimethalin-based herbicide in Apis mellifera. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 280, 116565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, J.H. Structural cuticular proteins from arthropods: Annotation, nomenclature, and sequence characteristics in the genomics era. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, S.; Noh, M.Y.; Dittmer, N.T.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Kramer, K.J.; Kanost, M.R.; Arakane, Y. Cuticular protein with a low complexity sequence becomes cross-linked during insect cuticle sclerotization and is required for the adult molt. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, M.; Gorb, S.N.; Büscher, T.H. The effect of age on the attachment ability of stick insects (Phasmatodea). Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 867–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Jafarpour, M.; Lin, C.P.; Appel, E.; Gorb, S.N.; Rajabi, H. Endocuticle sclerotisation increases the mechanical stability of cuticle. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 8272–8278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrini, N.; Crespo, R.; Juárez, M.P. Biochemistry of insect epicuticle degradation by entomopathogenic fungi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, L.; Hatjina, F.; Ioannidis, P.; Hamamtzoglou, A.; Schoonvaere, K.; Francis, F.; Meeus, I.; Smagghe, G.; de Graaf, D.C. Stress indicator gene expression profiles, colony dynamics and tissue development of honey bees exposed to sub-lethal doses of imidacloprid in laboratory and field experiments. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micas, A.F.; Ferreira, G.A.; Laure, H.J.; Rosa, J.C.; Bitondi, M.M. Proteins of the integumentary system of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 93, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Jin, B.R. Antimicrobial activity of apidermin 2 from the honeybee Apis mellifera. Insects 2022, 13, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melser, S.; Lavie, J.; Benard, G. Mitochondrial degradation and energy metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 2812–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrmacher, V. Mitochondria at work: New insights into regulation and dysregulation of cellular energy supply and metabolism. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uoselis, L.; Nguyen, T.N.; Lazarou, M. Mitochondrial degradation: Mitophagy and beyond. Mol. Cell. 2023, 83, 3404–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Kang, P.; Tatar, M. Drosophila insulin-like peptide-6 (dilp6) expression from fat body extends lifespan and represses secretion of Drosophila insulin-like peptide-2 from the brain. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C.J. The genetics of ageing. Nature 2010, 464, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyer, M.; Dainat, B.; Neumann, P.; Dietemann, V. Social regulation of ageing by young workers in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 87, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R.; Bass, C.; Feyereisen, R.; Vontas, J. The role of cytochrome p450s in insect toxicology and resistance. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 67, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, M.; Gong, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, T. Cytochrome P450s-Their expression, regulation, and role in insecticide resistance. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Xu, B. Characterization of an Apis cerana cerana cytochrome P450 gene (AccCYP336A1) and its roles in oxidative stresses responses. Gene 2016, 584, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, D.; Walter, P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, W.; Guo, D.; Guo, H.; Tan, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, B. Cloning and expression studies on glutathione S-transferase like-gene in honey bee for its role in oxidative stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 2021, 27, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukkar, D.; Wagner, L.; Bonnefoy, A.; Falla-Angel, J.; Laval-Gilly, P. Diverse alterations and correlations in antioxidant gene expression in honeybee (Apis mellifera) hemocytes interacting with microbial pathogen-associated molecular patterns and pesticide cocktails. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 114, 104649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münch, D.; Ihle, K.E.; Salmela, H.; Amdam, G.V. Vitellogenin in the honey bee brain: Atypical localization of a reproductive protein that promotes longevity. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 71, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.G.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Wan, H.; Li, J.; Jin, B.R. Honeybee (Apis cerana) vitellogenin acts as an antimicrobial and antioxidant agent in the body and venom. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 85, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.R.; Nunes, F.M.; Cristino, A.S.; Simoes, Z.L.; Bitondi, M.M. The four hexamerin genes in the honey bee: Structure, molecular evolution and function deduced from expression patterns in queens, workers and drones. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattal, Y.Z.; Alghamdi, A.A. Thermal adaptation involves higher expression levels of the lethal (2)-essential-for-life-like (l (2) efl) among the honeybee Apis mellifera L. subspecies. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2024, 36, 103143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Rupasinghe, S.; Niu, G.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Schuler, M.A. CYP6B1 and CYP6B3 of the black swallowtail (Papilio polyxenes): Adaptive evolution through subfunctionalization. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcock, N.K.; Wakeling, L.A.; Ford, D.; Wright, G.A. Effects of age and nutritional state on the expression of gustatory receptors in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustard, J.A.; Gott, A.; Scott, J.; Chavarria, N.L.; Wright, G.A. Honeybees fail to discriminate floral scents in a complex learning task after consuming a neonicotinoid pesticide. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb217174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, A.; Naef, C.; Albrecht, M. Pesticide hazard, floral resource availability and natural enemies interactively drive the fitness of bee species depending on their crop fidelity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene_ID | Gene Annotation | Average Expression Level | YB/OB | Difference Multiplier | Order | Gene_Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YB | MB | OB | log2(FC) | |||||
| 107993596 | GARIN3 | 3347.207 | 4.524578 | 0.249664 | 13,406.84 | 13.71 | 1 | Golgi-associated RAB2B Interactor protein 3 |
| 107993589 | APD3 | 484.3711 | 3.640512 | 0.359029 | 1349.115 | 10.43 | 2 | Apidermin 3 |
| 107997171 | MRJP3 | 21,312.96 | 109,807.9 | 34.8865 | 610.923 | 9.25 | 3 | Major royal jelly protein 3 |
| 107995056 | Hex | 1137.21 | 375.6247 | 2.319312 | 490.322 | 8.94 | 4 | Hexamerin |
| 107997173 | MRJP2 | 5295.705 | 18,781.23 | 14.57883 | 363.2462 | 8.50 | 5 | Major royal jelly protein 2 |
| 107997172 | MRJP4 | 21,093.77 | 99,826.85 | 102.1779 | 206.4416 | 7.69 | 6 | Major royal jelly protein 4 |
| 108002484 | SV2A | 92.92831 | 333.0887 | 0.754609 | 123.1476 | 6.94 | 7 | Synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A |
| 107996070 | GR10 | 25.42094 | 60.81404 | 0.360529 | 70.51007 | 6.14 | 8 | Gustatory receptor 10 |
| 107993585 | APD2 | 1964.391 | 632.1537 | 38.80771 | 50.61858 | 5.66 | 9 | Apidermin 2/cuticle protein 1 |
| 108002602 | PCP | 113.7687 | 11.70071 | 0.297192 | 39.37086 | 5.27 | 10 | Pupal cuticle protein |
| 108003970 | CYP6B1 | 99.4837 | 258.644 | 8.422693 | 30.70799 | 4.94 | 11 | Cytochrome P450 6B1 |
| 107999079 | Cpr100A | 29.13097 | 4.140551 | 1.183832 | 24.60733 | 4.62 | 12 | Cuticular protein 100A |
| 108000069 | Vg | 2362.827 | 437.8775 | 134.7151 | 17.53944 | 4.13 | 13 | Vitellogenin |
| 107996978 | OR131 | 18.87142 | 43.73428 | 1.119135 | 16.86251 | 4.08 | 14 | Odorant receptor 131 |
| 107996027 | L(2)EFL | 2249.161 | 516.4503 | 155.335 | 14.47942 | 3.86 | 15 | Protein lethal (2) essential for life |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Q.; Huang, Z.Y.; Hai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Dang, X.; Xu, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, Z. Multidimensional Profiling of Senescence in Eastern Honey Bee, Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae), Workers: Morphology, Microstructure, and Transcriptomics. Insects 2025, 16, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090902
Ma Q, Huang ZY, Hai Q, Zhang J, Tang X, Dang X, Xu J, Ma Z, Zhou Z. Multidimensional Profiling of Senescence in Eastern Honey Bee, Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae), Workers: Morphology, Microstructure, and Transcriptomics. Insects. 2025; 16(9):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090902
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Qiang, Zachary Y. Huang, Qianmin Hai, Jun Zhang, Xiangyou Tang, Xiaoqun Dang, Jinshan Xu, Zhengang Ma, and Zeyang Zhou. 2025. "Multidimensional Profiling of Senescence in Eastern Honey Bee, Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae), Workers: Morphology, Microstructure, and Transcriptomics" Insects 16, no. 9: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090902
APA StyleMa, Q., Huang, Z. Y., Hai, Q., Zhang, J., Tang, X., Dang, X., Xu, J., Ma, Z., & Zhou, Z. (2025). Multidimensional Profiling of Senescence in Eastern Honey Bee, Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae), Workers: Morphology, Microstructure, and Transcriptomics. Insects, 16(9), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090902








