Black Soldier Fly: A Keystone Species for the Future of Sustainable Waste Management and Nutritional Resource Development: A Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
Methodology
2. Biological and Genomic Foundations
2.1. BSF Life Cycle
2.2. Genomic Insights
| Factor | Traits | Organism | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic | Genomic expansion (immune genes, CYP450s, olfactory receptors) | BSF | Enhanced detoxification, pathogen resistance, and detection of decaying matter via expanded gene families. | [33,75] |
| Rapid evolutionary adaptation to diet | BSF | Stronger adaptive responses to low-quality diets (e.g., wheat bran) due to selection pressure. | [77] | |
| Genotype-by-diet interactions | BSF | Genetic strains show varied growth and nutrient composition depending on substrate. | [79] | |
| Metabolic gene enrichment (amino acid/fatty acid metabolism) | BSF | Efficient conversion of decaying matter into biomass via enriched metabolic pathways. | [76] | |
| Environmental | Diet-dependent midgut adaptations | BSF | Enzyme activity, cell morphology, and nutrient storage adjust to low-quality diets (e.g., fruit/vegetable waste). | [80] |
| Microbiome shifts (Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria) | BSF | Gut microbiota degrades complex organics; composition changes with substrate type. | [81] | |
| Behavioral response to VOCs | BSF | Odorant-binding proteins detect volatile organic compounds to locate decay. | [82] | |
| Waste storage conditions | BSF | Refrigeration promotes beneficial yeasts (e.g., Pichia), while open storage increases spoilage fungi. | [83] | |
| Morphology/Physiology | Midgut enzyme plasticity | BSF | Transcriptome shifts in digestion/absorption genes under different diets. | [80] |
| Fat body metabolism | BSF | Alters lipid/protein storage in response to nutrient availability (e.g., protein-poor diets). | [84] | |
| Heavy metal tolerance | BSF | Accumulates Cd/Pb but thrives on non-hazardous waste; limited tolerance to extreme pollution. | [85] | |
| Microbiome Interactions | Lignocellulose degradation | BSF | Corynebacterium and Brevibacterium in residues break down lignin; gut bacteria synergize with host enzymes. | [86,87,88] |
| Protein/lipid digestion | BSF | Pseudomonas and Campylobacter produce proteases/lipases; microbiota–host synergy enhances nutrient extraction. | [89,90] | |
| Applications | Waste conversion strategies | BSF | Pretreatment (e.g., hydrothermal) and microbiota engineering improve bioconversion efficiency. | [44] |
| Genetic breeding/CRISPR | BSF | Enhanced traits (e.g., flightlessness, detoxification) via selective breeding or gene editing. | [33,91] | |
| Genome Insights | Genome size (~1.01–1.68 Gb) and complexity | BSF | Large genome with 14,000–17,000 protein-coding genes, repetitive elements (67%), and expanded immune/metabolic gene families. | [76,92] |
| Antimicrobial peptides (defensins, cecropins) | BSF and Other Insects | Protect against pathogens in decay-rich environments via membrane disruption; developmentally regulated expression. | [93] |
3. Environmental Protection and Waste Management
3.1. BSF Digestive System and Bioconversion Efficiency
3.2. Comparison of BSF Bioconversion and Traditional Waste Treatment Methods
| Method | Description | Environmental Impact | Byproducts | Advantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSF Bioconversion | Using BSF larvae to convert organic waste into biomass and frass. | Reduces waste volume by up to 50% and lowers CO2 emissions. | Larvae (for feed), frass (for fertilizer), insect oils, and chitin. | Reduce ARGs in biosolids up to 99% in certain pathogens, minimizing heavy metal accumulation. Zinc and cobalt are not significantly retained. | [15,133] |
| Composting | Biological decomposition of organic matter into compost. | Reduces landfill waste, lowers methane emissions, and returns nutrients to the soil. | Nutrient-rich compost, potential liquid leachate. | Peroxydisulfate, Calcium Peroxide, and Attapulgite–Activated Carbon Composite (AACC) amendments reduce ARGs. | [137,138,139,140,141] |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas. | It captures methane, reduces CO2 gas emissions, and lowers odours and pathogens. | Biogas (energy), digestate (fertilizer), and small liquid effluent. | Heavy metals and antibiotics can inhibit the activity of anaerobic microorganisms. | [142,143] |
| Vermicomposting | Using earthworms to convert organic waste into vermicompost. | It has a low environmental impact, reduces waste, and minimizes CO2 gas emissions. | Vermicompost (fertilizer), worm biomass (animal feed). | Decreases ARGs in organic waste by up to 40% in specific genes. | [137,144,145] |
3.3. Environmental and Economic Benefits and Health Risks
Carbon Footprint Claims of Commercial BSF Products
4. Nutritional and Functional Applications of BSF
4.1. Nutritional Composition and Feed Value
4.1.1. Macronutrient Composition
4.1.2. Micronutrients
4.1.3. Mineral Content
4.1.4. Bioactive Compounds
4.1.5. Comparative Context
| Nutrient | BSFL | SBM | FM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude Protein% | 30–53 (dry matter) | 41.39 | 56 |
| Crude Fat% | 20–41 | 1.18 | 8.6 |
| Crude Fiber% | 2–9 (due to chitin) | 0.87 | 0 |
| Ash% | 2–9 | 6.3 | 15 |
| Calcium (Ca)% | 3.85 | 0.29 | 7.38 |
| Phosphorus (P)% | 0.94 | 0.56 | 3.97 |
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl)% | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.7 |
| Amino Acids% | Comparable to FM; higher than SBM | Lower levels | Higher levels |
| Fatty Acids% | Lauric (21%), Oleic (32%), Palmitic (16%). | Lauric (trace), Oleic (18%), Palmitic (11%). | Lauric trace, Oleic (19.8–27.1%), Palmitic (21.2–26.6%). |
| Insect | Protein (%) | Carbohydrates (%) | Fats (%) | Ash (%) | Micronutrients (%) | Chitin (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crickets (Acheta domesticus) | 65 | 21 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | [209] |
| Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) | 50 | 38 | 13 | 1 | 3 | 1 | [210,211,212] |
| Grasshoppers (Caelifera) | 70 | 15 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | [213,214,215] |
| Silkworms (Bombyx mori) | 64 | 21 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 2 | [216,217,218] |
| Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) | 42 | 30 | 35 | 3 | 2 | 1 | [54] |
| Ants (Formicidae) | 42 | 25 | 16 | 2 | 4 | 1 | [219] |
| Termites (Isoptera) | 35 | 23 | 28 | 3 | 4 | 3 | [220,221] |
| Locusts (Locusta migratoria) | 60 | 20 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 3 | [215,222] |
5. Industrial Applications of the BSF
5.1. Animal Feed
5.2. Sustainable Waste Management
5.3. Bioremediation and Soil Enhancement
5.4. Bioplastics
5.5. Circular Economy
5.6. Bioconversion
5.7. Sustainable Protein Source
5.8. Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) and Species-Specific Applications
| Type of AMP | Mechanism of Action | Effective Against | Uses | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defensins | Disrupt bacterial cell membranes, broad-spectrum activity | Effective against Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli | Potential use in agriculture and medicine as natural antimicrobial agents | [307,308,309] |
| Cecropins | Disrupt bacterial cell membranes | Effective against a broad range of bacteria, including E. coli and S. aureus | Useful as natural antimicrobial agents in agriculture and medicine | [310,311,312] |
| Diptericins | Target Gram-negative bacteria by binding to cell wall components | Highly effective against Gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas spp. | Potential use in agriculture and medicine as natural antimicrobial agents | [307,311,313] |
| Attacins | Target the bacterial cell envelope, disrupt cell wall synthesis | Effective against Gram-negative bacteria, including E. coli and Klebsiella spp. | Potential use in agriculture and medicine as natural antimicrobial agents | [293,314,315] |
| Proline-Rich Peptides | Penetrates bacterial cell walls, inhibits intracellular targets such as protein synthesis | Effective against Gram-negative bacteria and certain Gram-positive bacteria | Useful as natural antimicrobial agents in agriculture and medicine | [295,309,316] |
| Lysozyme | Hydrolyze peptidoglycan layer in bacterial cell walls | Highly effective against Gram-positive bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus spp. | Useful as natural antimicrobial agents in agriculture and medicine | [295,317,318] |
| Moricin-Like Peptides | Disrupt bacterial cell membranes | Effective against a wide range of bacteria, including E. coli and certain viral pathogens | Useful as natural antimicrobial agents in agriculture and medicine | [297,310,319] |
| Attacin-Like Peptides | Target bacterial cell envelope, disrupt cell wall synthesis | Effective against Gram-negative bacteria, including Pseudomonas spp. and E. coli | Potential use in agriculture and medicine as natural antimicrobial agents | [309,314,320] |
| Other AMPs | Target bacterial cell membranes | Effective against a variety of bacterial species, including multidrug-resistant strains | Useful as natural antimicrobial agents in agriculture and medicine | [309,314] |
6. Challenges and Prospects
6.1. Regulatory Landscape and Policy Challenges
6.2. Feedstock and Process Engineering
6.3. Product Quality, Safety, and the Consumer
6.4. Environment and Economy
| Application | Key Challenges | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Management | Variable feed quality, contaminant carry-over, high-moisture frass | Sort and blend substrates, rigorous contaminant testing, frass composting/drying |
| Biodiesel/Oil | Diet-dependent lipid, energy-intensive extraction | Use high-fat wastes, green extraction methods, valorize protein/chitin coproducts |
| Animal Feed | Regulatory gaps, nutrient variability, allergenicity | Advocate insect-specific limits, routine safety assays, defatting/fractionation |
| AMP Recovery | Low yields, peptide instability, unclear regulations | Enhance expression (breeding/probiotics), advanced purification and encapsulation, early regulatory engagement |
| Bioremediation | Unpredictable metabolites, residue risks | Closed-loop reactors, coupled secondary treatments, pollutant fate studies |
| Automation and Technology | Manual controls, labor-intensive sorting | IoT-enabled rearing, vision-guided harvesters, modular, open-source hardware |
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSF | Black Soldier Fly |
| BSFL | Black Soldier Fly larvae |
| AMPs | Antimicrobial peptides |
| ARGs | Antibiotic Resistance Genes |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein Kinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids |
| CLA | Conjugated Linoleic Acid |
| VOCs | Volatile Organic Compounds |
| CFP | Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis |
| NPK | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium (used in the context of fertilizers) |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| WDG | Wet distiller’s grains |
| SMS | Spent mushroom substrate |
| CRISPR | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats |
| Gb | Gigabase (one billion base pairs) |
| ACE inhibitors | Inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| IPIFF | International Platform of Insects for Food and Feed |
| DPP-IV-inhibitory | Inhibits dipeptidyl peptidase-IV |
| AAFCO | Association of American Feed Control Officials |
| CO2-eq | Carbon dioxide equivalent |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| FSM | Food Safety Modernization Act |
| LCA | Life cycle assessment |
| EU | European Union |
References
- Benton, T.; Bieg, C.; Harwatt, H.; Pudassaini, R.; Wellesley, L. Food system impacts on biodiversity loss. In Three Levers for food System Transformation in Support of Nature; Chatham House: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Urugo, M.M.; Teka, T.A.; Gemede, H.F.; Mersha, S.; Tessema, A.; Woldemariam, H.W.; Admassu, H. A Comprehensive Review of Current Approaches on Food Waste Reduction Strategies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e70011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.; Meacham, T.; Bhunnoo, R.; Benton, T.G. Food Waste within Global Food Systems. Glob. Food Secur. Program 2013, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamkhar, R.; Hicks, A. Resources, Conservation & Recycling Comparative Environmental Impact Assessment of Aquafeed Production: Sustainability Implications of Forage Fish Meal and Oil Free Diets. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiguobarueghian, I.; Adanma, U.M.; Ogunbiyi, E.O.; Solomon, N.O. Waste Management and Circular Economy: A Review of Sustainable Practices and Economic Benefits. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 22, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, C.J.; Hudson, M.D.; Russell, A.E.; Saluveer, M.; Sidaoui-Haddad, G. Microplastics in Fish and Fishmeal: An Emerging Environmental Challenge? Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.K.; Deepti, M.; Patel, A.B.; Kumar, P.; Angom, J.; Debbarma, S.; Singh, S.K.; Deb, S.; Lal, J.; Vaishnav, A.; et al. Dissecting Insects as Sustainable Protein Bioresource in Fish Feed for Aquaculture Sustainability. Discov. Food 2025, 5, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.R.; Maniruzzaman, K.M.; Dano, U.L.; AlShihri, F.S.; AlShammari, M.S.; Ahmed, S.M.S.; Al-Gehlani, W.A.G.; Alrawaf, T.I. Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices in the Global South. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreoni, I.; Matthews, Z.; Schaafsma, M. The Impacts of Soy Production on Multi-Dimensional Well-Being and Ecosystem Services: A Systematic Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 130182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T.; Tukker, A.; Cucurachi, S. Advancing Waste Valorization and End-of-Life Strategies in the Bioeconomy through Multi-Criteria Approaches and the Safe and Sustainable by Design Framework. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 207, 114907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K.; Chang, J.S. Waste Stream Valorization-Based Low-Carbon Bioeconomy Utilizing Algae as a Biorefinery Platform. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 178, 113245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Orlando, M.; Testa, E.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Pesaro, G.; Miceli, M.; Pollegioni, L.; Barbera, V.; Fasoli, E.; Draghi, L.; et al. Valorization of Organic Waste through Black Soldier Fly: On the Way of a Real Circular Bioeconomy Process. Waste Manag. 2025, 191, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, K.; Halstead, J.; Small, R.; Young, I. Valorisation of Organic Waste By-Products Using Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as a Bio-Convertor. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukchin-Peles, S.; Baker Lozneva, K.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Zilberman, D. From Waste Management to Protein Innovation: Black Soldier Fly as an Embodiment of the Circular Bioeconomy. Future Foods 2025, 11, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Süfer, Ö.; Çalışkan Koç, G.; Lutuf, H.; Rahayu, T.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Fernando, I. Enhancing the Bioconversion Rate and End Products of Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Treatment—A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 27, 9673–9741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetto, A.; Oliva, S.; Riolo, K.; Savastano, D.; Parrino, V.; Cappello, T.; Maisano, M.; Fasulo, S.; Mauceri, A. Waste Valorization via Hermetia illucens to Produce Protein-Rich Biomass for Feed: Insight into the Critical Nutrient Taurine. Animals 2020, 10, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Klammsteiner, T.; Dregulo, A.M.; Kumar, V.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K. Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Organic Manure Recycling and Its Potential for a Circular Bioeconomy: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camperio, J.; Suarez, J.A.; Simonton, J.; Paresky, E.; Parodi, J.; Benetti, D.D. Valorizing Organic Waste Through Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens): A Sustainable Solution for Aquafeeds with Key Nutrients and Natural Bioactive Polyphenols. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumari, K. An Inclusive Approach for Organic Waste Treatment and Valorisation Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Ristow, B.; Rahayu, T.; Putra, N.S.; Widya Yuwono, N.; Nisa’, K.; Mategeko, B.; Smetana, S.; Saki, M.; Nawaz, A.; et al. Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) and Their Affinity for Organic Waste Processing. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser El Deen, S.; van Rozen, K.; Elissen, H.; van Wikselaar, P.; Fodor, I.; Van Der Weide, R.; Hoek-Van Den Hil, E.F.; Rezaei Far, A.; Veldkamp, T. Bioconversion of Different Waste Streams of Animal and Vegetal Origin and Manure by Black Soldier Fly Larvae Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insects 2023, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirtawijaya, G.; Lee, J.-H.; Bashir, K.M.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, J.-S. Evaluating the Efficiency of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae in Converting Mackerel Head Waste into Valuable Resources. Animals 2024, 14, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Manan, F.; Yeoh, Y.-K.; Chai, T.-T.; Wong, F.-C. Unlocking the Potential of Black Soldier Fly Frass as a Sustainable Organic Fertilizer: A Review of Recent Studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 121997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, I.G.; Yong, J.W.H.; Lalander, C. Frass Derived from Black Soldier Fly Larvae Treatment of Biodegradable Wastes. A Critical Review and Future Perspectives. Waste Manag. 2022, 142, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonaco, G.; Franco, A.; De Smet, J.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P. Larval Frass of Hermetia illucens as Organic Fertilizer: Composition and Beneficial Effects on Different Crops. Insects 2024, 15, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresse, A.; Jordaan, J.; Preez, L.D.; Bhiya, C. Effectiveness of Black Soldier Fly Frass as an Organic Fertilizer. In Change the World; Nelson Mandela University: Port Elizabeth, South Africa, 2024; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/385769294_EFFECTIVENESS_OF_BLACK_SOLDIER_FLY_FRASS_AS_AN_ORGANIC_FERTILIZER?channel=doi&linkId=67347b8268de5e5a3074cf5e&showFulltext=true (accessed on 1 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Mochoge, B.; Korir, N.K.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Khamis, F.M.; Subramanian, S.; Dubois, T.; Musyoka, M.W.; Ekesi, S. Exploring Black Soldier Fly Frass as Novel Fertilizer for Improved Growth, Yield, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Maize under Field Conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 574592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Shahzadi, A.; Zheng, H.; Alam, F.; Nabi, G.; Dezhi, S.; Ullah, W.; Ammara, S.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M. Effect of Different Environmental Conditions on the Growth and Development of Black Soldier Fly Larvae and Its Utilization in Solid Waste Management and Pollution Mitigation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedalmoosavi, M.M.; Mielenz, M.; Veldkamp, T.; Daş, G.; Metges, C.C. Growth Efficiency, Intestinal Biology, and Nutrient Utilization and Requirements of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Compared to Monogastric Livestock Species: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Schmitt, E.; Mathys, A. Sustainable Use of Hermetia illucens Insect Biomass for Feed and Food: Attributional and Consequential Life Cycle Assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 144, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; ur Hollah, C.; Wiesotzki, K.; Rehman, R.U.; Rehman, A.U.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Nienaber, T.; Heinz, V.; Aganovic, K. Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens as a Potential Innovative and Environmentally Friendly Tool for Organic Waste Management: A Mini-Review. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.N.; Niermans, K.; Hoek-van den Hil, E.F.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Effects of Aflatoxin B1 on Metabolism- and Immunity-Related Gene Expression in Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 202, 105944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Fang, G.; Cai, M.; Kou, Z.; Xu, J.; Cao, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, X.; et al. Genomic Landscape and Genetic Manipulation of the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens, a Natural Waste Recycler. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Casartelli, M.; Smet, J.; De Gold, M.; Tettamanti, G. Review: A Journey into the Black Soldier Fly Digestive System: From Current Knowledge to Applied Perspectives. Animal 2025, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, L.; Bouslama, S.; Deschamps, M.H.; Vandenberg, G.; Derome, N. Absence of Microbiome Triggers Extensive Changes in the Transcriptional Profile of Hermetia illucens during Larval Ontogeny. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Bolletta, V.; Meng, Y.; Yakti, W.; Grossule, V.; Shi, D.; Hayat, F. Exploring the Role of the Microbiome of the H. illucens (Black Soldier Fly) for Microbial Synergy in Optimizing Black Soldier Fly Rearing and Subsequent Applications. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippis, D.; Filippis, F.; De Bonelli, M.; Bruno, D.; Sequino, G.; Montali, A.; Reguzzoni, M.; Pasolli, E.; Savy, D.; Cangemi, S.; et al. Plastics Shape the Black Soldier Fly Larvae Gut Microbiome and Select for Biodegrading Functions. Microbiome 2023, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Zhou, S.; Chen, W.; Cao, B.; Sun, Y.; Che, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, T.; Xu, J.; et al. Black Soldier Fly and Microbiome Collaborate to Bioconvert the Tofu Whey Water in an Efficient and Environment-Friendly Manner. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 69, 106888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandi, I.; Öztürk, R.Ç.; Kocabas, M.; Kurtoğlu, İ.Z.; Altinok, I. Nutritional Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Reared on Chicken Waste Meal, Fruit & Vegetable Waste, and Their Mixture. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 9, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumo, M.; Osuga, I.M.; Khamis, F.M.; Tanga, C.M.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Subramanian, S.; Ekesi, S.; van Huis, A.; Borgemeister, C. The Nutritive Value of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Reared on Common Organic Waste Streams in Kenya. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimchan, T.; Hamzeh, A.; Siringan, P.; Thumanu, K.; Hanboonsong, Y.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Antibacterial Peptides from Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae: Mode of Action and Characterization. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai-Foenander, A.S.; Kuppusamy, G.; Manogoran, J.; Xu, T.; Chen, Y.; Tang, S.Y.; Ser, H.-L.; Yow, Y.-Y.; Goh, K.W.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.): A Potential Small Mighty Giant in the Field of Cosmeceuticals. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettamanti, G.; Bruno, D. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Should Be Considered beyond Their Use as Feedstuff. J. Insects Food Feed 2024, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.R.; Mohan, K.; Kandasamy, S.; Surendran, R.P.; Kumar, R.; Rajan, D.K.; Rajarajeswaran, J. Food Waste-Derived Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larval Resource Recovery: A Circular Bioeconomy Approach. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 184, 170–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, C.; Gao, B.; Wu, Y.; Ao, Y.; Ma, S.; Jiménez, N.; Zheng, L.; Huang, F.; Tomberlin, J.K.; et al. Insights into the Reduction of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Mobile Antibiotic Resistance Genes by Black Soldier Fly Larvae in Chicken Manure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Yu, C.; Yang, C.; Gao, B.; Jiménez, N.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Ao, Y.; Zheng, L.; Huang, F.; et al. Mitigation of Antibiotic Resistome in Swine Manure by Black Soldier Fly Larval Conversion Combined with Composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, K.; Taylor, W.; Gyawali, P.; Pattis, I.; Gutiérrez Ginés, M.J. Black Soldier Fly-Based Bioconversion of Biosolids: Microbial Community Dynamics and Fate of Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Elhag, O.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Huang, F.; Jordan, H.R.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Sze, S.-H.; Yu, Z.; et al. Hermetia illucens L. Larvae-Associated Intestinal Microbes Reduce the Transmission Risk of Zoonotic Pathogens in Pig Manure. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 2631–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagappan, S.; Rowland, D.; Barwell, R.; Mantilla, S.M.O.; Mikkelsen, D.; James, P.; Yarger, O. Legislative Landscape of Black Soldier Fly ( Hermetia illucens ) as Feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Zimbelli, A.; Randazzo, B.; Compagni, M.D.; Truzzi, C.; Antonucci, M.; Riolo, P.; Loreto, N.; Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; et al. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Reared on Roasted Coffee by-Product and Schizochytrium sp. as a Sustainable Terrestrial Ingredient for Aquafeeds Production. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva Raman, S.; Stringer, L.C.; Bruce, N.C.; Chong, C.S. Opportunities, Challenges and Solutions for Black Soldier Fly Larvae-Based Animal Feed Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlambo, V.; Richard, S.; Mashiloane, T. Rethinking Food Waste: Exploring a Black Soldier Fly Larvae-Based Upcycling Strategy for Sustainable Poultry Production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odongo, E.E.; Bbosa, W.K.; Kahunde, P.K. Black Soldier Fly (BSF): A Sustainable Solution for Protein, Waste Management, and a Circular Bio-Economy. Eur. J. Theor. Appl. Sci. 2024, 2, 822–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Taethaisong, N.; Meethip, W.; Surakhunthod, J.; Sinpru, B.; Sroichak, T.; Archa, P.; Thongpea, S.; Paengkoum, S.; Purba, R.A.P.; et al. Nutritional Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) and Its Potential Uses as Alternative Protein Sources in Animal Diets: A Review. Insects 2022, 13, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Subhash, A.; Muzaffar, G. Future Opportunities for Products Derived from Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Treatment as Animal Feed and Fertilizer—A Systematic Review; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2024; ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hori, A.; Kawasaki, T.; Hirayasu, H.; Iwase, S.I.; Hashizume, A.; Ido, A.; Miura, C.; Miura, T.; et al. Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae and Pre-Pupae Raised on Household Organic Waste, as Potential Ingredients for Poultry Feed. Animals 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ites, S.; Smetana, S.; Toepfl, S.; Heinz, V. Modularity of Insect Production and Processing as a Path to Efficient and Sustainable Food Waste Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelomi, M. Potential of Black Soldier Fly Production for Pacific. Animals 2020, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyonsaba, H.H.; Höhler, J.; Rumpold, B.A.; Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Meuwissen, M.P.M. Robustness of Business Models for Insect Production for Feed and Food in Europe. J. Insects Food Feed 2024, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korir, L.C.; Ronoh, E.K.; Ondimu, S.N.; Kinyuru, J.N.; Gicheha, M.G. Effects of Temperature Variation on Yield and Quality of Field Crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus) and Black Soldier Flies (Hermetia illucens). J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Conversion of Organic Material by Black Soldier Fly Larvae: Establishing Optimal Feeding Rates. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brichet, N. A Postcolonial Dilemma Tale from the Harbour of St. Thomas in the US Virgin Islands. Itinerario 2019, 43, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devic, E.; Fahmi, M.R. Biology of Hermetia illucens; IPB Press: Marseille, France, 2013; ISBN 9789794936108. [Google Scholar]
- Shumo, M.; Khamis, F.M.; Tanga, C.M.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Subramanian, S.; Ekesi, S.; Huis, A.; Van Borgemeister, C. Influence of Temperature on Selected Life-History Traits of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Reared on Two Common Urban Organic Waste Streams in Kenya. Animals 2019, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomberlin, J.; Sheppard, D.; Joyce, J. Selected Life-History Traits of Black Soldier Flies (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Reared on Three Artificial Diets. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2009, 95, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-X.; Tomberlin, J.; Vanlaerhoven, S. Influence of Resources on Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larval Development. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Addeo, N.F.; Rusch, T.W.; Tarone, A.M.; Tomberlin, J.K. Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larval Heat Generation and Management. Insect Sci. 2023, 30, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, N.S.; Heidelbach, S.; Vestergaard, S.Z.; Nielsen, M.E.; Riisgaard-Jensen, M.; Zeuner, E.J.; Bahrndorff, S.; Eriksen, N.T. Impact of Substrate Moisture Content on Growth and Metabolic Performance of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, D.C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Joyce, J.A.; Kiser, B.C.; Sumner, S.M. Rearing Methods for the Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, S.F.; Flint, C.A.; Bahrndorff, S.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Kristensen, T.N. Reproductive Output and Other Adult Life-History Traits of Black Soldier Flies Grown on Different Organic Waste and by-Products. Waste Manag. 2024, 181, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradabphetrat, P.; Sathawong, S.; Pimsen, M. Effects of Rearing Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) from Organic Wastes. ASEAN J. Sci. Technol. Rep. 2024, 27, e252644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellezza Oddon, S.; Biasato, I.; Resconi, A.; Gasco, L. Black Soldier Fly Life History Traits Can Be Influenced by Isonutrient-Waste-Based Diets. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 23, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranghers, T.; Ottoboni, M.; Klootwijk, C.; Ovyn, A.; Deboosere, S.; De Meulenaer, B.; Michiels, J.; Eeckhout, M.; De Clercq, P.; De Smet, S. Nutritional Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Prepupae Reared on Different Organic Waste Substrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomberlin, J.K.; Adler, P.H.; Myers, H.M. Development of the Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in Relation to Temperature. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalovic, T.N.; McCarthy, S.A.; Warren, I.A.; Wood, J.M.D.; Torrance, J.; Sims, Y.; Quail, M.; Howe, K.; Pipan, M.; Durbin, R. A High-Quality, Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.). G3 2021, 11, jkab085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukmak, R.; Suttinun, C.; Kovitvadhi, U.; Kovitvadhi, A.; Vongsangnak, W. Uncovering Nutrients and Energy Related Gene Functions of Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens Strain KUP. Gene 2024, 896, 148045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gligorescu, A.; Chen, L.; Jensen, K.; Moghadam, N.N.; Kristensen, T.N.; Sørensen, J.G. Rapid Evolutionary Adaptation to Diet Composition in the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). Insects 2023, 14, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorescu, A.; Toft, S.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Axelsen, J.A.; Nielsen, S.A. Development, Metabolism and Nutrient Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in Relation to Temperature and Diet. J. Insects Food Feed 2018, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, C.; Leupi, S.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Kaya, C.; Heuel, M.; Terranova, M.; Blanckenhorn, W.U.; Windisch, W.; Kreuzer, M.; Leiber, F. Genotype-by-Diet Interactions for Larval Performance and Body Composition Traits in the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens. Insects 2022, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.; Bruno, D.; Brilli, M.; Gianfranceschi, N.; Tian, L.; Tettamanti, G.; Caccia, S.; Casartelli, M. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Adapt to Different Food Substrates through Morphological and Functional Responses of the Midgut. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, F.M.; Ombura, F.L.O.; Akutse, K.S.; Subramanian, S. Insights in the Global Genetics and Gut Microbiome of Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens: Implications for Animal Feed Safety Control. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scieuzo, C.; Nardiello, M.; Farina, D.; Scala, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Vogel, H.; Salvia, R.; Persaud, K.; Falabella, P. Hermetia illucens (L.)(Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Odorant Binding Proteins and Their Interactions with Selected Volatile Organic Compounds: An in Silico Approach. Insects 2021, 12, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mašková, Z.; Medo, J.; Kolesár, E.; Tančinová, D.; Ivanišová, E.; Urminská, D.; Hleba, L.; Urminská, J.; Mrvová, M.; Barboráková, Z. Hermetia illucens in the Process of Kitchen Waste Biodegradation: The Effect of Different Approaches to Waste Storage on the Microbiological Profile and Nutritional Parameters of the Larvae. Insects 2025, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.C.; Montali, A.; Bruno, D.; Tettamanti, G. Metabolic Adjustment of the Larval Fat Body in Hermetia illucens to Dietary Conditions. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofroňová, J.; Melliti, A.; Vurm, R. Biogas Digestate and Sewage Sludge as Suitable Feeds for Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Toxics 2024, 12, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, F.; Leier, A.; Xiang, D.; Shen, H.-H.; Marquez Lago, T.T.; Li, J.; Yu, D.-J.; Song, J. Comprehensive Assessment of Machine Learning-Based Methods for Predicting Antimicrobial Peptides. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, N.; Yu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, F.; Huang, F.; Tomberlin, J.K.; ur Rehman, K. Cellulose-Degrading Bacteria Improve Conversion Efficiency in the Co-Digestion of Dairy and Chicken Manure by Black Soldier Fly Larvae. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Recruit Functional Microbiota into the Intestines and Residues to Promote Lignocellulosic Degradation in Domestic Biodegradable Waste. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F.; Fan, M.; Zheng, J.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Huang, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Enhanced Protein Degradation by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) and Its Gut Microbes. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1095025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulida, M.N.; Fatmawati, U. Antifungal, Hydrolytic Enzyme Activity, and Identification of Gut Bacterial in Feces of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Al-Kauniyah J. Biol. 2024, 18, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Z.; Luo, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, B.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y. Establishment of Highly Efficient Transgenic System for Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). Insect Sci. 2022, 30, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalovic, T.N.; Sandrock, C.; Roberts, B.J.; Meier, J.I. Cryptic Diversity and Signatures of Domestication in the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). BioRxiv 2023, 2023, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari, D.; Nayduch, D.; Meisel, R.P. Defensins of the Stable Fly (Stomoxys calcitrans) Have Developmental-Specific Regulation and Evolve at Different Rates. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2024, 64, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; von Allmen, F.; Zurbrügg, C.; Zhang, J.; Mathys, A. Identification of Bacteria in Two Food Waste Black Soldier Fly Larvae Rearing Residues. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 582867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KP, G.; AN, D.; VD, R.; RK, T.; Ganvir, K.P.; Darvekar, A.N.; Raut, V.D.; Thorat, R.K. Effect of Locally Generated Food Waste on Bioconversion and Nutrient Parameters of Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens L. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2022, 10, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.H.; Fidjeland, J.; Diener, S.; Eriksson, S.; Vinnerås, B. High Waste-to-Biomass Conversion and Efficient Salmonella spp. Reduction Using Black Soldier Fly for Waste Recycling. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Cai, M.M.; Xiao, X.P.; Zheng, L.Y.; Yu, Z.N. Research and Industrialisation of Hermetia illucens L. in China. J. Insects Food Feed 2020, 6, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; Egger, J.; Scheidegger, A.; Zurbrügg, C.; Bruno, D.; Bonelli, M.; Tettamanti, G.; Casartelli, M.; Schmitt, E.; Kerkaert, B.; et al. Estimating Black Soldier Fly Larvae Biowaste Conversion Performance by Simulation of Midgut Digestion. Waste Manag. 2020, 112, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Bonacci, T.; Reguzzoni, M.; Casartelli, M.; Grimaldi, A.; Tettamanti, G.; Brandmayr, P. An In-Depth Description of Head Morphology and Mouthparts in Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2020, 58, 100969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, F.; Yu, C.; Yuan, R.; Zhou, B.; Ren, Z.; Yu, Z.; et al. Morphometric Characteristic of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Wuhan Strain and Its Egg Production Improved by Selectively Inbreeding. Life 2022, 12, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.K.-H.; Kim, W.-T.W.; Lee, S.S.-B.; Choi, Y.Y.-C.; Nho, S.S.-K. Seasonal Pupation, Adult Emergence and Mating of Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in Artificial Rearing System. Int. J. Ind. Entomol. 2010, 21, 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Wu, M.; Bao, Y.; Tong, H.; Ren, M.; Jin, N.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. Effects of Different Nitrogen Sources and Ratios to Carbon on Larval Development and Bioconversion Efficiency in Food Waste Treatment by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). Insects 2021, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguz, M.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F.; Dama, A.; Lussiana, C.; Renna, M.; Gasco, L. Effect of Rearing Substrate on Growth Performance, Waste Reduction Efficiency and Chemical Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5776–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Peng, P.; Xue, C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Hu, W.; Cao, Y. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Larval Diet Improves CD8+ Lymphocytes Proliferation to Eliminate Chicken Coronavirus at an Early Infection Stage. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 260, 109151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Significantly Change the Microbial Community in Chicken Manure. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhag, O.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Jordan, H.R.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Huang, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Inhibition of Zoonotic Pathogens Naturally Found in Pig Manure by Black Soldier Fly Larvae and Their Intestine Bacteria. Insects 2022, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, U.K.; Lando, A.T.; Djamaluddin, I. Potential of Black Soldier Fly Larvae in Reduction Various Types Organic Waste. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2024, 25, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklicky, V.; Guidini Lopes, I.; Lalander, C. Enhancing Reproducibility in Black Soldier Fly Research. J. Insects Food Feed. 2024, 10, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Lopes, I.G. Advances in Substrate Source Composition for Rearing Black Soldier Fly Larvae as a Protein Source; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.G.; Wiklicky, V.; Vinnerås, B.; Yong, J.W.H.; Lalander, C. Recirculating Frass from Food Waste Bioconversion Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae: Impacts on Process Efficiency and Product Quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, R.; Muñoz, H.M.B.; Jawiarczyk, N.; Vaya, A.M. Chapter 21—Black Soldier Fly Biorefinery: A Novel Upcycling Route for Municipal Biosolids. In Clean Energy and Resources Recovery; Tyagi, V., Aboudi, K.B.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 487–500. ISBN 978-0-323-85223-4. [Google Scholar]
- Eggink, K.M.; Donoso, I.G.; Dalsgaard, J. Optimal Dietary Protein to Carbohydrate Ratio for Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.G.; Lalander, C.; Vidotti, R.M.; Vinnerås, B. Using Hermetia illucens Larvae to Process Biowaste from Aquaculture Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzepe, D.; Magatsing, O.; Kuietche, H.M.; Meutchieye, F.; Nana, P.; Tchuinkam, T.; Djouaka, R. Recycling Organic Wastes Using Black Soldier Fly and House Fly Larvae as Broiler Feed. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2021, 1, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseindoust, A.; Ha, S.H.; Mun, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Substrates, D.; Hosseindoust, A.; Ha, S.H.; Mun, J.Y.; Kim, J.S. Quality Characteristics of Black Soldier Flies Produced by Different Substrates. Insects 2023, 14, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuso, A.; Barbi, S.; Macavei, L.I.; Luparelli, A.V.; Maistrello, L.; Montorsi, M.; Sforza, S.; Caligiani, A. Effect of the Rearing Substrate on Total Protein and Amino Acid Composition in Black Soldier Fly. Foods 2021, 10, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; ur Rehman, A.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, X.; Somroo, A.A.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Conversion of Mixtures of Dairy Manure and Soybean Curd Residue by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 154, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luparelli, A.V.; Saadoun, J.H.; Lolli, V.; Lazzi, C.; Sforza, S.; Caligiani, A. Dynamic Changes in Molecular Composition of Black Soldier Fly Prepupae and Derived Biomasses with Microbial Fermentation. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, N.; Utterback, P.; Parsons, C.M. True Metabolizable Energy and Amino Acid Digestibility in Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meals, Cricket Meal, and Mealworms Using a Precision-Fed Rooster Assay. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, D.-H.; Jeong, S.-B.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, H.-G.; Lee, K.-W. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Oil as an Alternative Fat Source in Broiler Nutrition. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3133–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, S.K.; Schokker, D.; Harms, A.C.; Kruijt, L.; Smits, M.A.; Jansman, A.J.M. Local Intestinal Microbiota Response and Systemic Effects of Feeding Black Soldier Fly Larvae to Replace Soybean Meal in Growing Pigs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foysal, M.J.; Gupta, S.K. A Systematic Meta-Analysis Reveals Enrichment of Actinobacteria and Firmicutes in the Fish Gut in Response to Black Soldier Fly (Hermetica illucens) Meal-Based Diets. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Srikanth, B.H.; Kumari, K. Determining the Black Soldier Fly Larvae Performance for Plant-Based Food Waste Reduction and the Effect on Biomass Yield. Waste Manag. 2021, 130, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossule, V.; Lavagnolo, M.C. The Treatment of Leachate Using Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Larvae: Adaptability and Resource Recovery Testing. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dakar, M.A.; Ramzy, R.R.; Ji, H. Influence of Substrate Inclusion of Quail Manure on the Growth Performance, Body Composition, Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Profiles of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortmans, B.; Diener, S.; Verstappen, B.; Zurbrügg, C. Black Soldier Fly Biowaste Processing—A Step-By-Step Guide; Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-906484-66-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Hou, D.; Pang, W.; Nowar, E.E.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Hu, R.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; et al. Effect of Moisture Content on Greenhouse Gas and NH3 Emissions from Pig Manure Converted by Black Soldier Fly. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 133840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michishita, R.; Shimoda, M. Inoculation with Black Soldier Fly Larvae Alters the Microbiome and Volatile Organic Compound Profile of Decomposing Food Waste. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renninger, B.; Mccreary, C.; Williams, C.; Troncoso, W. Compost Emission Factors—Volatile Organic Compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 131, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Beskin, K.V.; Holcomb, C.D.; Cammack, J.A.; Crippen, T.L.; Knap, A.H.; Sweet, S.T.; Tomberlin, J.K. Larval Digestion of Different Manure Types by the Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Impacts Associated Volatile Emissions. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.; Guerra, N.; Colón, J.; Gabriel, D.; Ponsá, S.; Sánchez, A. Characterization of the Gaseous and Odour Emissions from the Composting of Conventional Sewage Sludge. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemes, Y.M.; Nyord, T.; Feilberg, A.; Hafner, S.D.; Pedersen, J. Effect of Anaerobic Digestion on Odor and Ammonia Emission from Land-Applied Cattle Manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, G.D.P.; Hesselberg, T. A Review of the Use of Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), to Compost Organic Waste in Tropical Regions. Neotrop. Entomol. 2020, 49, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, S. Valorisation of Organic Solid Waste Using the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens, in Low and Middle-Income Countries; ETH Zurich: Zürich, Switzerland, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Amrul, N.; Ahmad, I.; Basri, N.; Suja, F.; Jalil, N.; Azman, N. A Review of Organic Waste Treatment Using Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). Sustainability 2022, 14, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-L.; Jin, W.-Z.; Tao, X.-H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, S.-Y.; Xu, X.-H.; Li, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.-J. Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Strengthen the Metabolic Function of Food Waste Biodegradation by Gut Microbiome. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges Silva, L.R.; Kardos, L. Composting of Distillery Spent Wash. J. Environ. Geogr. 2023, 17, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbenko, A.D.; Kaplan, M.A.; Tihomirov, N.E.; Andreevskaya, V.M.; Morozova, Y.A.; Sevostyanova, E.P.; Konushkin, S.V.; Baikin, A.S.; Sergiyenko, K.V.; Nasakina, E.O. Proven Methods of Active Biological Processing. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2929, 030010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Wen, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Q. The Removal Performances and Evaluation of Heavy Metals, Antibiotics, and Resistomes Driven by Peroxydisulfate Amendment during Composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Fu, Q. Simultaneous Passivation of Heavy Metals and Removal of Antibiotic Resistance Genes by Calcium Peroxide Addition during Sewage Sludge Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Sun, W.; Yu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J. Simultaneous Reductions in Antibiotics and Heavy Metal Pollution during Manure Composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Niu, Q.; Nie, W.; Li, X.; Yang, C. Effects of Heavy Metals and Antibiotics on Performances and Mechanisms of Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velivela, A.; Barham, H.; Bauer, J.; Roschke, J.; Daim, T.U.; Meissner, D. Biogas: Converting Waste to Energy. In Innovation Management in the Intelligent World. Science, Technology and Innovation Studies; Daim, T.U., Meissner, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saapi, S.S.Y.; Andrianisa, H.A.; Zorom, M.; Mounirou, L.A.; Kouassi, H.A.A.; Ahossouhe, M.S. New Developments on Vermifiltration as a Bio-Ecological Wastewater Treatment Technology: Mechanism, Application, Performance, Modelling, Optimization, and Sustainability. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, M.; Zhang, B.; Wan, S.; Huang, J. Exploring the Effects of Zeolite, Biochar, and Diatomite as Additives for Enhancing Heavy Metals Passivation and Eliminating Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Composts during Vermicomposting of Dewatered Sludge and Green Waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elissen, H.; van der Weide, R.; Gollenbeek, L. Effects of Black Soldier Fly Frass on Plant and Soil Characteristics: A Literature Overview; Wageningen Plant Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alciatore, G.; Peguero, D.A.; Gold, M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Niu, M.; Bargetze, F.; Mathys, A. Preservation of Agri-Food Byproducts by Acidification and Fermentation in Black Soldier Fly Larvae Bioconversion. Waste Manag. 2024, 186, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelomi, M. Mitigation Strategies against Food Safety Contaminant Transmission from Black Soldier Fly Larva Bioconversion. Animals 2024, 14, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, T.; Meziane, K.Z.; Megateli, S.; Moussaoui, B.; Guemou, L.; Reghioui, B. Bio-Treatment of Cheese Whey by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Reared in Algeria. J. Agric. Appl. Biol. 2024, 5, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, K.C.W.; de Lange, E.; van Asseldonk, L.L.M.; Zoet, L.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Safety and Transfer of Veterinary Drugs from Substrate to Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Animal 2024, 18, 101214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrina, D.N.; Mutia, R.; Dharmajati, K. Substitution Potential of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal (Hermetia illucens) for Meat Bone Meal in IPB-D1 Chicken Diets. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1359, 012117. [Google Scholar]
- Batool, M.; Tabinda, A.B.; Tahir, A. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Feed Suitability for Chicken and Prospects for Economic Valuation and Viability Aspects. J. Insects Food Feed 2024, 10, 1747–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chineme, A.; Assefa, G. Open and Closed Black Soldier Fly Systems Tradeoff Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, G.; Nikiema, J. Global Experiences on Waste Processing with Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia Illucens): From Technology to Business; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2019; Volume 16, ISBN 9290908939. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, D.; Devic, E.; Subamia, I.W.; Talamond, P.; Baras, E. Technical Handbook of Domestication and Production of Diptera Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Hermetia illucens, Stratiomyidae; IRD Edition/IPB Presse: Kota Bogor, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pleissner, D.; Smetana, S. Estimation of the Economy of Heterotrophic Microalgae-and Insect-Based Food Waste Utilization Processes. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.J.W.; Pieterse, E. Markets, Money and Maggots. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffeis, M.; Wakefield, M.E.; Almeida, J.; Alves Valada, T.R.; Devic, E.; Koné, N.; Kenis, M.; Nacambo, S.; Fitches, E.C.; Koko, G.K.D.; et al. Life Cycle Cost Assessment of Insect Based Feed Production in West Africa. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgett, A.; Newes, E.; Milbrandt, A. Economic Analysis of Wet Waste-to-Energy Resources in the United States. Energy 2019, 176, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazan, D.M.; Fraccascia, L.; Mes, M.; Zijm, H. Cooperation in Manure-Based Biogas Production Networks: An Agent-Based Modeling Approach. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, T. Disposal Is Not Free: Fiscal Instruments to Internalize the Environmental Costs of Solid Waste. Int. Tax Public Financ. 2022, 29, 1047–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, N.; Jamuda, M.; Panda, A.K.; Samal, K.; Nayak, J.K. Emission of Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) during Composting and Vermicomposting: Measurement, Mitigation, and Perspectives. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganaro, M.; Bahrndorff, S.; Eriksen, N.T. Growth and Metabolic Performance of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Grown on Low and High-Quality Substrates. Waste Manag. 2021, 121, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye-Yiadom, K.A.; Ilari, A.; Duca, D. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Life Cycle Assessment on the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.). Sustainability 2022, 14, 10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leni, G.; Del Vecchio, L.; Dellapina, C.; Moliterni, V.M.; Caligiani, A.; Cirlini, M. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Grown on Hemp Fiber: Nutritional Composition and Production of Potential Bioactive Peptides. Macromol 2024, 4, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaiah, G.M.; Kumar, R.; Kumari, R.; Chandan, N.K.; Debbarma, J.; Damle, D.K.; Das, A.; Giri, S.S. Dietary Fishmeal Replacement with Hermetia illucens (Black Soldier Fly, BSF) Larvae Meal Affected Production Performance, Whole Body Composition, Antioxidant Status, and Health of Snakehead (Channa striata) Juveniles. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2023, 297, 115597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, A.A.; Rehman, K.; ur Cai, M.; Laghari, Z.A.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Larval Biomass Production from the Co-Digestion of Mushroom Root Waste and Soybean Curd Residues by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 30112–30125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, S.Y.; Tanga, C.M.; Osuga, I.M.; Cheseto, X.; Ekesi, S.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Nutritional Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Feeding on Agro-Industrial by-Products. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2020, 168, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, I.; Newman, L.P.; Gill, H.; Danaher, J. The Influence of Food Waste Rearing Substrates on Black Soldier Fly Larvae Protein Composition: A Systematic Review. Insects 2021, 12, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, N.; Ramesh, N.; Prashantha, C.N. Isolation and Characterization of Hermetia illucens Larval Protein for the Assessment of Inhibitory Activity against MCF7 and HeLa Cell Lines. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2020, 3075, 3045–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryvak, H.P.; Levitskyy, T.R.; Boyko, G.I.; Nedilka, G.Y.; Vilha, O.M. Alternative Non-Traditional Sources of Feed Protein and Amino Acids. Sci. Tech. Bull. State Sci. Res. Control Inst. Vet. Med. Prod. Fodd. Addit. Inst. Anim. Biol. 2024, 25, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, N.; Vidakovic, A.; Langeland, M.; Kiessling, A.; Sampels, S.; Lalander, C. Fatty Acid Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens)—Possibilities and Limitations for Modification through Diet. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryati, T.; Julaeha, E.; Farabi, K.; Ambarsari, H.; Hidayat, A.T. Lauric Acid from the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) and Its Potential Applications. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniers, J.J.A.; Graham, R.I. Effect of Protein and Carbohydrate Feed Concentrations on the Growth and Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2019, 5, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liland, N.S.; Biancarosa, I.; Araujo, P.; Biemans, D.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbø, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lock, E.J. Modulation of Nutrient Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae by Feeding Seaweed-Enriched Media. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pliantiangtam, N.; Chundang, P.; Kovitvadhi, A. Growth Performance, Waste Reduction Efficiency and Nutritional Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae and Prepupae Reared on Coconut Endosperm and Soybean Curd Residue with or without Supplementation. Insects 2021, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; ur Rehman, K.; Li, W.; Cai, M.; Li, Q.; Mazza, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Dynamic Changes of Nutrient Composition throughout the Entire Life Cycle of Black Soldier Fly. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin Tan, P. Study of the Oviposition Response of Black Soldier Fly (BSF) in the Presence of Banana and Pupal Remains. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2020, 8, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnamasari, L.; Lopez, Z.P.; dela Cruz, J.F. A Review: Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal as a Dietary Protein Source in Poultry Diets. Biotropika J. Trop. Biol. 2022, 10, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Gutiérrez, F.M.A.; Fomich, M.; Metzcar, C.; Saad, J.; Dia, V.P.; Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Wang, T. Compositional Analysis of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Larvae and Adults. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 1411–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, N.F.N.M.; Seok-Kian, A.Y.; Seng, L.L.; Mustafa, S.; Kim, Y.-S.S.; Shapawi, R. Nutritional Value of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Processed by Different Methods. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boykin, K.L.; Mitchell, M.A. Evaluation of Vitamin A Gut Loading in Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). Zoo Biol. 2021, 40, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Romano, N.; Renukdas, N.; Kumar, V.; Sinha, A.K. Comparing Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae versus Prepupae in the Diets of Largemouth Bass, Micropterus Salmoides: Effects on Their Growth, Biochemical Composition, Histopathology, and Gene Expression. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, D.N.; Silva, A.R.R.; Morgado, R.G.; Mostafaie, A.; Pereira, A.; Pinto, J.; Lopes, I.G.; Murta, D.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Brooks, B.W.; et al. Improving Product Safety for Edible Insects: Toxicokinetics of Hg in Tenebrio Molitor and Hermetia illucens. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Rijo, P.; Rosado, C. Bioactive Compounds from Hermetia illucens Larvae as Natural Ingredients for Cosmetic Application. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, P.; Ameixa, O.M.C.C.; Palma, M.; Louzado, M.; Rodrigues, D.; Pinho, M.; Viegas, I. Tracking Lipid Synthesis Using 2H2O and 2H-NMR Spectroscopy in Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Fed with Macroalgae. J. Exp. Biol. 2024, 227, jeb247941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renna, M.; Gasco, L.; Livorsi, L.; Mele, M.; Conte, G.; Meneguz, M.; Lussiana, C. Growth Performance, Proximate Composition and Fatty Acid Profile of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Reared on Two Grape Pomace Varieties. Animal 2024, 18, 101240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Hilaire, S.; Cranfill, K.; McGuire, M.A.; Mosley, E.E.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Newton, L.; Sealey, W.; Sheppard, C.; Irving, S. Fish Offal Recycling by the Black Soldier Fly Produces a Foodstuff High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 38, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslykhah, U.; Phupaboon, S.; Suriyapha, C.; Matra, M.; Wanapat, M. Encapsulation of Protein-Based Bioactive from Black Soldier Fly for Ruminant Feeding. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mu, L.; Zhuang, L.; Han, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wei, L. A Cecropin-like Antimicrobial Peptide with Anti-Inflammatory Activity from the Black Fly Salivary Glands. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, M.K.; Li, C.M.; Furtado, W.E.; Huang, Q.; St-Hilaire, S.; Kenéz, Á. Antibacterial Properties of Oil Extracts of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Reared on Bread Waste. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2024, 64, AN23394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.; Marusich, E.; Leonov, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Extract from Hermetia illucens (Black Soldier Fly) Larvae against Multi Drug-Resistant (MDR) Human Pathogenic Bacteria. In Proceedings of the 1st International Electronic Conference on Antibiotics, Basel, Switzerland, 8–17 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Elkadaoui, S.; Azzi, M.; Desbrieres, J.; Zim, J.; El Hachimi, Y.; Tolaimate, A. Valorization of Hermetia illucens Breeding Rejects by Chitins and Chitosans Production. Influence of Processes and Life Cycle on Their Physicochemical Characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirwandhono, E.; Yunilas; Ginting, N.; Siregar, G.A.W.; Nasution, M.I.A.; Wahyuni, S. Siswanto Isolation and Characterization of Chitosan from Black Soldier Fly Exuviae. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1362, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprajukaew, K.; Nuntapong, N.; Pratumyot, K.; Chaiseeda, K.; Hahor, W.; Waeowannajit, S.; Meesin, S. Nutritive Value of Feed Substrate Waste from Black Soldier Fly Larvae Production, and Its Potential as an Aquafeed Ingredient. J. Insects Food Feed 2024, 10, 1811–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorilla, E.; Gariglio, M.; Gai, F.; Zambotto, V.; Bongiorno, V.; Cappone, E.E.; Biasato, I.; Bergagna, S.; Madrid, J.; Martinez-Miró, S. Dehydrated and Live Black Soldier Fly Larvae as Environmental Enrichment in Indigenous Slow-Growing Chickens: Performance, Gut Health, and Chitinolytic Enzyme Activity. Animal 2024, 18, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Xue, R.; Sun, J.; Ji, H. Assessment of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal as a Potential Substitute for Soybean Meal on Growth Performance and Flesh Quality of Grass Carp Ctenopharyngodon Idellus. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 14, 425–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Sun, G.; Wei, F.; Wu, Z.; Tian, H.; Meng, Y.; Ma, R. Replacing Fishmeal and Fish Oil with Complex Protein and Canola Oil: Effect on Organoleptic and Nutritional Quality of Triploid Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Foods 2024, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera Willora, F.; Farris, N.; Zatti, K.; Bisa, S.; Kiron, V.; Verlhac Trichet, V.; Danielsen, M.; Dalsgaard, T.; Sørensen, M. Full-Fat Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal and Yellow Mealworm Meal: Impact on Feed Protein Quality, Growth and Nutrient Utilization of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Post Smolts. Aquaculture 2024, 595, 741648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-T.; Bae, S.-W.; Park, H.-C.; Park, K.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Choi, Y.-C.; Han, S.-M.; Koh, Y. The Larval Age and Mouth Morphology of the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Int. J. Ind. Entomol. 2010, 21, 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, S. Creating Circular Economy of Waste Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) Technology BT. In Global Pathways for Efficient Waste Management and Inclusive Economic Development; Shahbaz, M., Sharma, G.D., Gedikli, A., Erdoğan, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 177–201. ISBN 978-981-96-5569-4. [Google Scholar]
- Facey, H.; Kithama, M.; Mohammadigheisar, M.; Huber, L.-A.; Shoveller, A.K.; Kiarie, E.G. Complete Replacement of Soybean Meal with Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal in Feeding Program for Broiler Chickens from Placement through to 49 Days of Age Reduced Growth Performance and Altered Organs Morphology. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Afzal, A.; Rashid, H.; Iqbal, S.; Zafar, R.; Khalid, K.; Rauf, A.; Majeed, M.; Malik, A.; Carter, C.G. Dietary Replacement of Soybean Meal with Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal in Juvenile Labeo Rohita and Catla Catla: Effects on Growth, Nutritional Quality, Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Disease Resistance. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketut Gede Wiryawan, I.; Hafiz Mandiling, I.; Kusuma Purnamasari, D.; Maslami, V.; Syamsuhaidi. Chemical Composition and Protein Quality of BSF Larvae Reared with Different Media in Lombok. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1360, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteri, M.; Di Rosa, A.R.; Lo Presti, V.; Giarratana, F.; Toscano, G.; Chiofalo, B. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal as Alternative to Fish Meal for Aquaculture Feed. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelomi, M. Nutrient Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). In African Edible Insects as Alternative Source of Food, Oil, Protein and Bioactive Components; Adam Mariod, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 195–212. ISBN 978-3-030-32952-5. [Google Scholar]
- Toomer, O.T.; Oviedo-Rondón, E.O.; Ali, M.; Joseph, M.; Vu, T.; Fallen, B.; Mian, R. Full-Fat Soybean Meals as an Alternative Poultry Feed Ingredient—Feed Processing Methods and Utilization—Review and Perspective. Animals 2024, 14, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgbechidinma, C.L.; Zheng, G.; Baguya, E.B.; Zhou, H.; Okon, S.U.; Zhang, C. Fatty Acid Composition and Nutritional Analysis of Waste Crude Fish Oil Obtained by Optimized Milder Extraction Methods. Environ. Eng. Res. 2023, 28, 220030–220034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilco-Romero, G.; Chisaguano-Tonato, A.M.; Herrera-Fontana, M.E.; Chimbo-Gándara, L.F.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M.; Vernaza, M.G.; Álvarez-Suárez, J.M. House Cricket (Acheta domesticus): A Review Based on Its Nutritional Composition, Quality, and Potential Uses in the Food Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 142, 104226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravzanaadii, N.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, W.-H.; Hong, S.-J.; Kim, N.-J. Nutritional Value of Mealworm, Tenebrio Molitor as Food Source. Int. J. Ind. Entomol. 2012, 25, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordiean, A.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Aljewicz, M.; Stolarski, M.J. Influence of Different Diets on Growth and Nutritional Composition of Yellow Mealworm. Foods 2022, 11, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröncke, N.; Benning, R. Influence of Dietary Protein Content on the Nutritional Composition of Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor L.). Insects 2023, 14, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, M.; Inada, M.; Horiguchi, S. Nutritional and Safety Evaluation of Locust (Caelifera) Powder as a Novel Food Material. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, K.; Incekara, U.; Turkez, H. Biomonitoring of the Genotoxic Effects and Oxidative Potentials of Commercial Edible Dung Beetles (Onitis sp.), Grasshopper (Caelifera sp.) and Mole Crickets (Gryllotalpa sp.) in Vitro. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2014, 30, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Ghisletta, M.; Yunusa, B.M.; Jiddum, F.A.; Saraswati, Y.R.; Fernando, I.; Nagdalian, A.A.; Gvozdenko, A.A.; Shah, M.A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Grasshoppers and Locusts as Human Foods–a Comprehensive Review. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 1247–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassoni, L.; Cappellozza, S.; Dalle Zotte, A.; Belluco, S.; Antonelli, P.; Marzoli, F.; Saviane, A. Nutritional Composition of Bombyx Mori Pupae: A Systematic Review. Insects 2022, 13, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Dey, S. Essential Amino Acids, Lipid Profile and Fat-Soluble Vitamins of the Edible Silkworm Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2014, 34, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hăbeanu, M.; Gheorghe, A.; Mihalcea, T. Nutritional Value of Silkworm Pupae (Bombyx mori) with Emphases on Fatty Acids Profile and Their Potential Applications for Humans and Animals. Insects 2023, 14, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravorty, J.; Ghosh, S.; Megu, K.; Jung, C.; Meyer-rochow, V.B. Nutritional and Anti-Nutritional Composition of Oecophylla smaragdina (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and Odontotermes sp. (Isoptera: Termitidae): Two Preferred Edible Insects of Arunach. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siulapwa, N.; Mwambungu, A.; Lungu, E.; Sichilima, W. Nutritional Value of Four Common Edible Insects in Zambia. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 876–884. [Google Scholar]
- Omotoso, O.T. Nutrient Composition, Mineral Analysis and Anti-Nutrient Factors of Oryctes rhinoceros L. (Scarabaeidae: Coleoptera) and Winged Termites, Marcrotermes nigeriensis Sjostedt.(Termitidae: Isoptera). Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negbenebor, H.E.; Tinuoye, O.O.; Nura, S. Evaluation of Essential Nutrients in Edible Locusts and Grasshoppers in Kano Metropolis. Sci. Afr. 2021, 20, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakeri, E.M.; Ogola, H.J.; Ayieko, M.A.; Amimo, F.A. An Open System for Farming Black Soldier Fly Larvae as a Source of Proteins for Smallscale Poultry and Fish Production. J. Insects Food Feed 2017, 3, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinasih, I.; Putra, R.E.; Permana, A.D.; Gusmara, F.F.; Nurhadi, M.Y.; Anitasari, R.A. Growth Performance of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Fed on Some Plant Based Organic Wastes. HAYATI J. Biosci. 2018, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kaiaty, A.M.; Atta, A.E.R.M.; Dawa, D.T.; El-sayed, T.R. The Impact of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia Illucens) as Feed Supplementation on Productive and Physiological Performance of Broiler Chickens. World’s Vet. J. 2022, 12, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotto Boccazzi, I.; Ottoboni, M.; Martin, E.; Comandatore, F.; Vallone, L.; Spranghers, T.; Eeckhout, M.; Mereghetti, V.; Pinotti, L.; Epis, S. A Survey of the Mycobiota Associated with Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Reared for Feed Production. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; İnal, F.; Riaz, R.; Ahsan, U.; Kuter, E.; Ali, U. A Review of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as a Potential Alternative Protein Source in Broiler Diets. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2023, 23, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, B.; Scheibelberger, R.; Axmann, S.; Adler, A.; Jäger, H. Impact of Substrate Contamination with Mycotoxins, Heavy Metals and Pesticides on the Growth Performance and Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) for Use in the Feed and Food Value Chain. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K. The Impact of Diet Protein and Carbohydrate on Select Life-History Traits of the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens (L.)(Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insects 2017, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsos, E.; Modica, B.; Freel, T. Immunomodulatory Potential of Black Soldier Fly Larvae: Applications beyond Nutrition in Animal Feeding Programs. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2022, 6, txac084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papuc, T.; Boaru, A.; Ladosi, D.; Struti, D.; Georgescu, B. Potential of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Alternative Protein Source in Salmonid Feeds—A Review. Indian J. Fish 2020, 67, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Park, Y.-K.; Yang, Y.-C.; Jung, B.-G.; Lee, B.-J. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Enhances Immune Activities and Increases Survivability of Broiler Chicks against Experimental Infection of Salmonella Gallinarum. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julita, U.; Suryani, Y.; Kinasih, I.; Yuliawati, A.; Cahyanto, T.; Maryeti, Y.; Permana, A.D.; Fitri, L.L. Growth Performance and Nutritional Composition of Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (L), (Diptera : Stratiomyidae) Reared on Horse and Sheep Manure. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 187, 12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, K.D.; Wickersham, T.A.; Drewery Merritt, L. Acceptance and Forage Utilization Responses of Steers Consuming Low-Quality Forage and Supplemented Black Soldier Fly Larvae as a Novel Feed. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Arana, G.; Vásquez-Bardales, J.; Maytahuari-Aricari, G.; Simirgiotis, M.J. Nutritional Analysis and Chemical Fingerprinting of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae MEAL Native to the Peruvian Amazon. Folia Amaz. 2024, 33, e33719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedalmoosavi, M.M.; Daş, G.; Mielenz, M.; Maak, S.; Wolf, P.; Metges, C.C. Growth, Nutrient Uptake, Blood Metabolites and Bone Properties in Broilers Consuming Feed with Mineral-Enriched Whole Black Soldier Fly Larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2024, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakti, W.; Shaw, C.; Müller, M.; Mewis, I.; Kloas, W.; Ulrichs, C. Tracing the Journey of Elements from Fish Feed to Nile tilapia Faeces to Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Comparative Approach. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1298885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.; Ayunda, K.; Dewi, S.H.; Sahara, R.M. Socialization of the Use of Cross-Sectional Area Variations Container for the Amount of Weight Reduction in Organic Waste by Using BSF Maggots (Black Soldier Fly). Sustain. Appl. Modif. Evid. Community 2024, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilo, H.; Nurmayulis, N.; Syahbana, M.A.; Sodiq, A.H. The Potential of Frass BSF as an Organic Fertilizer for Making Sustainable Agriculture a Reality. J. Biol. Trop. 2024, 24, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, A. Enhancing the Efficiency of Catalytic Conversion Processes for Biomass to Biofuels: Innovations in Catalyst Development and Pathways towards Sustainable Energy Solutions. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatundun, T.O.; Popoola, V.; Fakoyede, P.D.; Adebayo, D.O.; Kehinde, E.D.; Adetoro, Q.A.; Akhabue, O.B.; Ewemade, C.E.; Okpako, O.; Anyalebechi, P.E. Production of Biodiesel from Palm Kernel Oil through Base-Catalyzed Trans-Esterification Process. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 23, 2054–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärttling, D.; Schulz, H. Compilation of Black Soldier Fly Frass Analyses. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickerson, A.; Radley, R.; Marchant, B.; Kaulfuss, O.; Kabaluk, T. Hermetia illucens Frass Production and Use in Plant Nutrition and Pest Management 2017. Patent WO2015013826A1, 5 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Subramanian, S.; Tanga, C.M. Nutrient Quality and Maturity Status of Frass Fertilizer from Nine Edible Insects. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froonickx, L.; Berrens, S.; Broeckx, L.; Van Miert, S. The Potential of Black Soldier Fly to Recycle Nitrogen from Biowaste. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 44, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Magri, M.E.; Zurbrügg, C.; Lindström, A.; Vinnerås, B. Faecal Sludge Management with the Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens)—From a Hygiene Aspect. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancarosa, I.; Liland, N.S.; Biemans, D.; Araujo, P.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbø, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lock, E.; Amlund, H. Uptake of Heavy Metals and Arsenic in Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Grown on Seaweed-enriched Media. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Mathys, A. Decomposition of Biowaste Macronutrients, Microbes, and Chemicals in Black Soldier Fly Larval Treatment: A Review. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.; Ponton, F.; Than, A.; Taylor, P.W.; Chapman, T.; Morimoto, J. Interactions between Ecological Factors in the Developmental Environment Modulate Pupal and Adult Traits in a Polyphagous Fly. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 6342–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragan-Fonseca, K.B.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Nutritional Value of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) and Its Suitability as Animal Feed—A Review. J. Insects Food Feed 2017, 3, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Yao, H. Comprehensive Resource Utilization of Waste Using the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens (L.))(Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Animals 2019, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-B.; Wu, N.; Cai, R.-J.; Geng, W.-N.; Xu, X.-Y. Changes in Speciation, Mobility and Bioavailability of Cd, Cr and As during the Transformation Process of Pig Manure by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Moll, L.; De Smet, J.; Paas, A.; Tegtmeier, D.; Vilcinskas, A.; Cos, P.; Van Campenhout, L. In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) against a Selection of Human Pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0166421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvoli, D.; Montevecchi, G.; Lovato, F.; Masino, F.; Van Der Borght, M.; Messori, M.; Antonelli, A. Protein Films from Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens, Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Prepupae: Effect of Protein Solubility and Mild Crosslinking. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4506–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triunfo, M.; Tafi, E.; Guarnieri, A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Hahn, T.; Zibek, S.; Gagliardini, A.; Panariello, L.; Coltelli, M.B.; et al. Characterization of Chitin and Chitosan Derived from Hermetia illucens, a Further Step in a Circular Economy Process. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Greunen, L.; van Zeiri, A.; Yudhistira, B.; Ahmad, A.; Monnye, M. The Potential of Chitin and Chitosan from Dead Black Soldier Fly (BSF) (Hermetia illucens) for Biodegradable Packaging Material—A Critical Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 189, 1342–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianniciello, D.; Montosa, A.P.; de Melo Barbosa, R.; Villén, F.G.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Viseras, C.; Falabella, P. Development of Chitosan-Clay Nanocomposite Films from Hermetia illucens: Analysis of Chemical, Physical, and Mechanical Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 311, 143496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım-Aksoy, M.; Eljack, R.; Aksoy, J.; Beck, B.H. Frass from Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens, as a Possible Functional Dietary Ingredient in Channel Catfish Feed. Fishes 2023, 8, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.-Q.; Yu, T.-H.; Chen, S.-C.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Guo, Z.-K.; Huang, G.-X.; Xiao, J.; Huang, D.-W. Physical and Chemical Characterization of Chitin and Chitosan Extracted under Different Treatments from Black Soldier Fly. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, C.S.; Lock, S.S.M.; Mhd Yusof, S.M.; Rawindran, H.; Mong, G.R.; Lim, J.W.; Manogaran, M.D.; Suparmaniam, U. Chitin and Chitosan Production from Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermertia illucens) as Bioresource: Current Progress, Applications, Challenges and Way Forwards. Waste Biomass Valorization 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SKhayrova, A.; Lopatin, S. The Potential of Hermetia illucens as a Source of Chitin, Chitosan and Their Melanin Complexes. Polym. Sci. Peer Rev. J. 2022, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elouali, S.; Ait Hamdan, Y.; Benali, S.; Lhomme, P.; Gosselin, M.; Raquez, J.-M.; Rhazi, M. Extraction of Chitin and Chitosan from Hermetia illucens Breeding Waste: A Greener Approach for Industrial Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 285, 138302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, K.; Rajan, D.K.; Divya, D.; Rajarajeswaran, J.; Zhang, S.; Sathishkumar, P. New Insights into the Organic Waste-Derived Black Soldier Fly Chitin and Chitosan for Biomedical and Industrial Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, L.W.; Hoffman, L.C. Why for Feed and Not for Human Consumption? The Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2747–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syifa, F.T.; Hikmaturokhman, A.; Qisthani, N.N.; Fitriana, G.F.; Arifin, M. Implementation of Sensor Node and ESP8266-Based Network in Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Cultivation to Support Circular Economy. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Mechatronics Systems (AIMS), Bandung, Indonesia, 21–23 February 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, K.U.; Campbell, M.; Mauck, K.; Gebiola, M.; Karydis, K. Development and Testing of a Smart Bin toward Automated Rearing of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 18th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Mexico City, Mexico, 20–24 August 2022; pp. 1238–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Soontronprasatporn, K.; Arunrungrusmi, S.; Tunlasakun, K.; Mungkung, N.; Tamrongkunannun, T. Applying the Internet of Things (IoT) for Raising Black Soldier Fly (BSF) in Closed System to Minimize Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Edelweiss Appl. Sci. Technol. 2024, 8, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-fonseca, K.B.; Cortés-urquijo, J.; Pineda-mejía, J. Small-Scale Black Soldier Fly-Fish Farming: A Model with Socioeconomic Benefits. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, A.Z.; Akan, O.B. Sustainable and precision agriculture with the internet of everything (IoE). arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.06341. [Google Scholar]
- Purkayastha, D.; Khanal, P. Moving towards Fully Circular Insect Production: A Focus on Insect-Derived Biowastes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazmiño, M.F.; Del Hierro, A.G.; Flores, F.J. Genetic Diversity and Organic Waste Degrading Capacity of Hermetia illucens from the Evergreen Forest of the Equatorial Choco Lowland. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Deng, W.; Id, F.Z. Reference Gene Selection for Quantitative Gene Expression Analysis in Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazmiño-Palomino, A.; Reyes-Puig, C.; Del Hierro, A.G. Conociendo La Distribución Potencial Presente y Futura de La Mosca Soldado Negra, Hermetia illucens (Linnaeus) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/357183859 (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Kim, C.-H.; Ryu, J.; Lee, J.; Ko, K.; Lee, J.; Park, K.Y.; Chung, H. Use of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Food Waste Treatment and Energy Production in Asian Countries: A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutafela, R.N. High Value Organic Waste Treatment via Black Soldier Fly Bioconversion: Onsite Pilot Study. Master’s Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Gutiérrez, F.R.; Nguyen, D.H.; Morel, A.; Koottatep, T.; Tockner, K. Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Organic Waste Treatment-Prospects and Constraints. Proc. WasteSafe 2011, 2, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Diener, S.; Studt Solano, N.M.; Roa Gutiérrez, F.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Biological Treatment of Municipal Organic Waste Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Waste Biomass Valorization 2011, 2, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Tomberlin, J.; Vanlaerhoven, S.L. Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste. Environ. Èntomol. 2015, 44, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, T.; Khan, S.; Li, H.; Wen, T.; Yi, T.; Guo, J. Effects of black soldier fly larvae on biotransformation and residues of spent mushroom substrate and wet distiller’s grains. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frooninckx, L.; Broeckx, L.; Goossens, S.; Wuyts, A. Optimizing Substrate Moisture Content for Enhanced Larval Survival and Growth Performance in Hermetia illucens: Exploring Novel Approaches. Discov. Anim. 2024, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibonje, J.; Riungu, J.; James, K. Bioconversion of Faecal and Kitchen Waste Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens):. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Soc. Sci. 2024, 2, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Relationship of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) Gut Microbiota and Bioconversion Efficiency with Properties of Substrates. Waste Manag. 2024, 180, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyani, T.; Sivasubramanian, K.; Maheswari, M.; Chitra, N.; Saravanan, S.; Jothimani, P.; Karthika, S. The Efficiency of Black Soldier Fly Larvae with Vegetable, Fruit and Food Waste as Biological Tool for Sustainable Management of Organic Waste. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.Y. Black Soldier Fly Larvae as a Sustainable Animal Feed Ingredient in Kenya. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Menino, R.; Felizes, F.; Castelo-Branco, M.A.; Fareleira, P.; Moreira, O.; Nunes, R.; Murta, D. Agricultural Value of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Frass as Organic Fertilizer on Ryegrass. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msangi, J.W.; Mweresa, C.K.; Ndong’a, M.F.O. Using Organic Wastes as Feed Substrate for Black Soldier Fly Larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Vilela, J.; Andronicos, N.M.; Kolakshyapati, M.; Hilliar, M.; Sibanda, T.Z.; Andrew, N.R.; Swick, R.A.; Wilkinson, S.; Ruhnke, I. Black Soldier Fly Larvae in Broiler Diets Improve Broiler Performance and Modulate the Immune System. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Ortuño, J.; Stratakos, A.C.; Linton, M.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Elliott, T.; Koidis, A.; Theodoridou, K. Impact of Thermal and High-Pressure Treatments on the Microbiological Quality and in Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Animals 2020, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, M.; Zolotarev, K.; Nakhod, V.; Farafonova, T.; Mikhailov, A. Nutritional Value of Black Solder Fly (Hermetia illucens) Eggs and Larvae Reared on Fermented Milk Industry Waste as an Ingredient of Fish Feed. E3S Web Conf. 2022, 363, 03017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuel, M.; Sandrock, C.; Leiber, F.; Mathys, A.; Gold, M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Gangnat, I.D.M.; Kreuzer, M.; Terranova, M. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal and Fat Can Completely Replace Soybean Cake and Oil in Diets for Laying Hens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguara, A.; Deguara, S.; Buhagiar, J. A Multitrophic Culture System for the Production of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). Discov. Food 2024, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakuda, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Tanaka, A.; Sugimura, S.; Higashiura, Y.; Nakazato, T.; Bono, H.; Tabunoki, H. High Expression of Serine Protease, Brachyurin in the Posterior Midgut of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) during Horse Dropping Processing. BMC Res. Notes 2024, 17, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, L.; Generalovic, T.; Ali, Y.M.; Seilly, D.; Sivanesan, K.; Kalmar, L.; Pipan, M.; Christie, G.; Grant, A.J. A Novel Family of Defensin-like Peptides from Hermetia illucens with Antibacterial Properties. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stączek, S.; Cytryńska, M.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A. Unraveling the Role of Antimicrobial Peptides in Insects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Meng, G.; Zhu, L.; Ma, L.; Chen, K. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides as Guardians of Immunity and Beyond: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dho, M.; Candian, V.; Tedeschi, R. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides: Advancements, Enhancements and New Challenges. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Swain, S.S.; Behera, A.; Sahoo, G.; Mahapatra, P.K.; Panda, S.K. Antimicrobial Peptides Derived From Insects Offer a Novel Therapeutic Option to Combat Biofilm: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 661195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrä, J.; Berninghausen, O.; Leippe, M. Cecropins, Antibacterial Peptides from Insects and Mammals, Are Potently Fungicidal against Candida Albicans. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 189, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Mohamed, A.A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L. A Family of CSαβ Defensins and Defensin-Like Peptides from the Migratory Locust, Locusta Migratoria, and Their Expression Dynamics during Mycosis and Nosemosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guith, T.; Gourishetti, K.; Banerjee, P.; Ghosh, N.; Rana, M.; Chatterjee, G.; Biswas, S.; Bagchi, D.; Roy, S.; Das, A. Chapter 9—An Overview of Antimicrobial Peptides. In Downs Parasitic, Bacterial, and Fungal Infections; Bagchi, D., Das, A., Downs, B.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 101–106. ISBN 978-0-323-85730-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.-Y.; Chowdhury, M.; Huang, Y.-D.; Yu, X.-Q. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5807–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S. Sumoylation Modulates 20-Hydroxyecdysone Signaling by Maintaining USP Protein Levels in Drosophila. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 54, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect Fat Body: Energy, Metabolism, and Regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, U.; Juhasz, A.; Stockwell, S.; Escobar-Correas, S.; Marcora, A.; Paull, C.; Broadbent, J.A.; Wijffels, G. Unpacking the Proteome and Metaproteome of the Black Soldier Fly Larvae: Efficacy and Complementarity of Multiple Protein Extraction Protocols. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 7319–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, T.O.; Morici, M.; Berger, M.; Safdari, H.A.; Lele, D.S.; Beckert, B.; Kaur, K.J.; Wilson, D.N. Structural Basis for Translation Inhibition by the Glycosylated Drosocin Peptide. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, D.; Sarkar, S. Sustainable Waste Management Using Black Soldier Fly Larva: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 12701–12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratiomyidae, D.; Scieuzo, C.; Giglio, F.; Rinaldi, R.; Lekka, M.E.; Cozzolino, F.; Monti, M.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of the Peptide Fractions Extracted from the Hemolymph of Hermetia illucens. Insects 2023, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Gao, X.; Song, Q.; Zhang, H.; Elhag, O.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; et al. Structural and Functional Characterizations and Heterogenous Expression of the Antimicrobial Peptides, Hidefensins, from Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (L.). Protein Expr. Purif. 2022, 192, 106032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Ge, C.; Yao, H. Antimicrobial Peptides from Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Potential Antimicrobial Factors Representing An Alternative to Antibiotics in Livestock Farming. Animals 2021, 11, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józefiak, A.; Engberg, R.M. Insect Proteins as a Potential Source of Antimicrobial Peptides in Livestock Production. A Review. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2017, 26, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanik, K.; Świątkiewicz, M. Hermetia illucens as a Source of Antimicrobial Peptides—A Review of in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, A.; Kanost, M.R. Development of New Methods to Stimulate the Production of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Müller, A.; Heckel, D.G.; Gutzeit, H.; Vilcinskas, A. Nutritional Immunology: Diversification and Diet-Dependent Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 78, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Wolf, D.; Gutzeit, H.O. The Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens—A Promising Source for Sustainable Production of Proteins, Lipids and Bioactive Substances. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. C-A J. Biosci. 2017, 72, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHO, Y.; CHO, S. The Expression Pattern of Immunity-Related Genes in the Immunized Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Eur. J. Èntomol. 2024, 121, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Somma, A.; Moretta, A.; Cané, C.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P.; Duilio, A. Structural and Functional Characterization of a Novel Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptide from Hermetia illucens. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Id, Y.C.; Lin, H.; Chang, C.; Lin, S.; Han-, J.; Id, Y.L. Dynamic Expression of Cathepsin L in the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Gut during Escherichia Coli Challenge. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Jordan, H.R. Starvation Alters Gut Microbiome in Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Pucciarelli, V.; Borrelli, L.; Francesco, N.; Fulvia, A.; Ambrogio, B.; Eric, L.; Patrizia, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Lipids Extracted from Hermetia illucens Reared on Different Substrates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, F.; Fausto, A.M.; Della Pelle, G.; Roncevic, T.; Gerdol, M.; Picchietti, S. Attacins: A Promising Class of Insect Antimicrobial Peptides. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähteenmäki-Uutela, A.; Marimuthu, S.B.; Meijer, N. Regulations on Insects as Food and Feed: A Global Comparison. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, N.; Safitri, R.A.; Tao, W.; Hoek-Van den Hil, E.F. Review: European Union Legislation and Regulatory Framework for Edible Insect Production—Safety Issues. Animal 2025, 19, 101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, B.; Sancho, A.I.; Poulsen, M.; Lindholm Bøgh, K. Novel Foods: Allergenicity Assessment of Insect Proteins. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e200910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A. Review of US State-Level Entomophagy Regulation 2015. Available online: https://www.ifpti.org/cohort-5/lewis?srsltid=AfmBOooJbN87Z8h8KI4L4m2dm8-m2WQ39Ld3XDIf8L6QhythwflaeufJ (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Gaulkin, S. Calls for Regulatory Approval of Edible Insects. 2020. Available online: https://www.theregreview.org/2020/05/06/gaulkin-calls-regulatory-approval-edible-insects/ (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Larouche, J.; Campbell, B.; Hénault-Éthier, L.; Banks, I.J.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Preyer, C.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Vandenberg, G.W. The Edible Insect Sector in Canada and the United States. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C. Singapore to Approve 16 Species of Insects like Crickets and Grasshoppers to Be Sold as Food. 2023. Available online: https://www.straitstimes.com/singapore/16-species-of-insects-like-crickets-silkworms-will-receive-sfa-green-light-to-be-sold-as-food (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Xie, B.; Zhu, Y.; Chu, X.; Pokharel, S.S.; Qian, L.; Chen, F. Research Progress and Production Status of Edible Insects as Food in China. Foods 2024, 13, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, M.; He, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Ding, W.-F. Edible Insects in China: Utilization and Prospects. Insect Sci. 2017, 25, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safitri, R.A.; Vandeweyer, D.; Deruytter, D.; Meijer, N.; Coudron, C.L.; Banach, J.L.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Exploring Potential Uses of Insect Frass for Agricultural Production Considering Its Nutrients, and Chemical and Microbiological Safety. J. Insects Food Feed 2024, 11, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Sun, S.; Yin, Y.; Peng, C. Process Analysis and Parameters Optimization of Black Soldier Fly Sand Mixture with Two-Stage Sieve Surface Vibration Separating Machine. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, M.; Chia, S.Y.; Fischer, B.; Tomberlin, J.K. Welfare Considerations for Farming Black Soldier Flies, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae): A Model for the Insects as Food and Feed Industry. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 119–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perednia, D.; Anderson, J.; Rice, A. A Comparison of the Greenhouse Gas Production of Black Soldier Fly Larvae versus Aerobic Microbial Decomposition of an Organic Feed Material. Res. Rev. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 10–16. [Google Scholar]

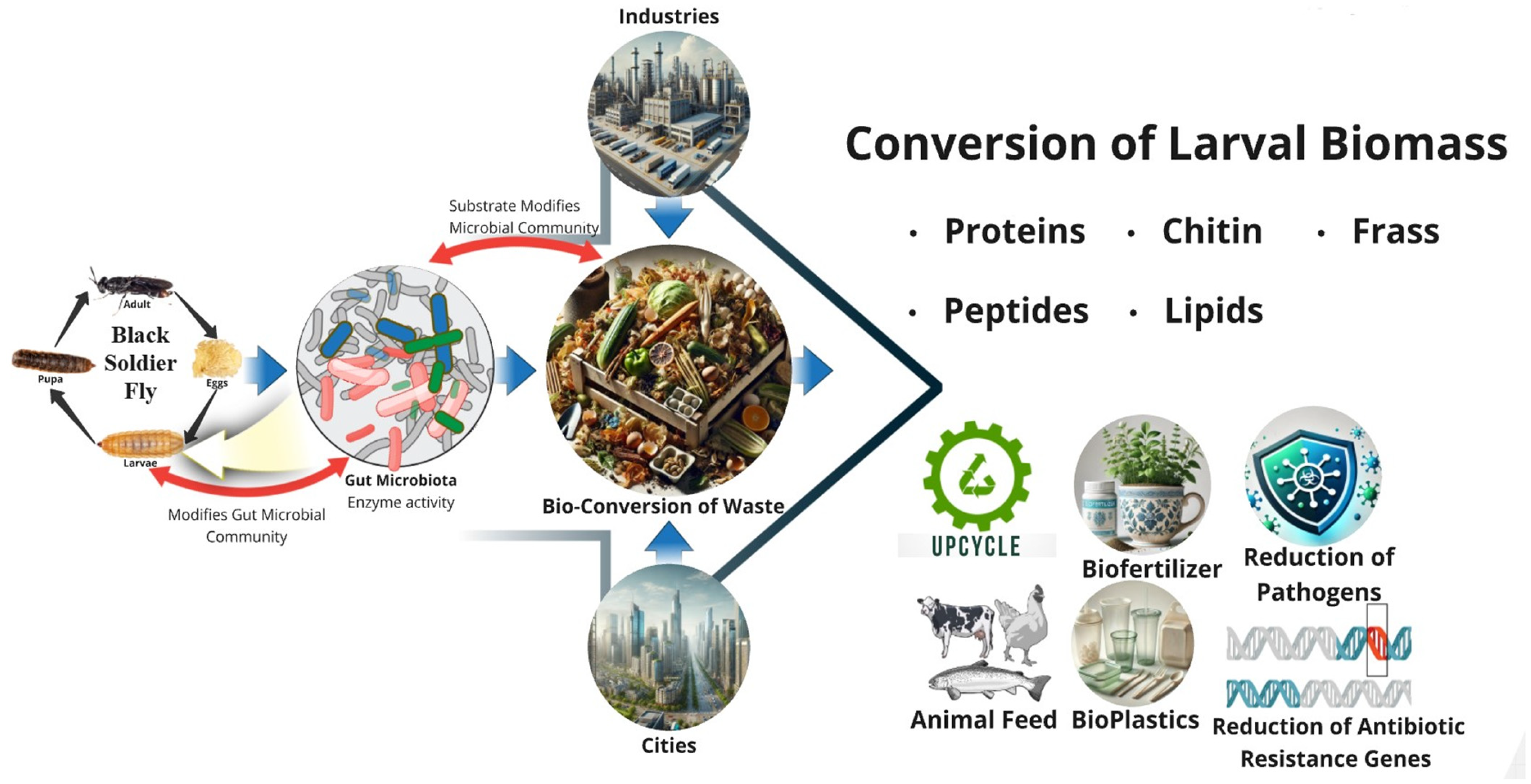
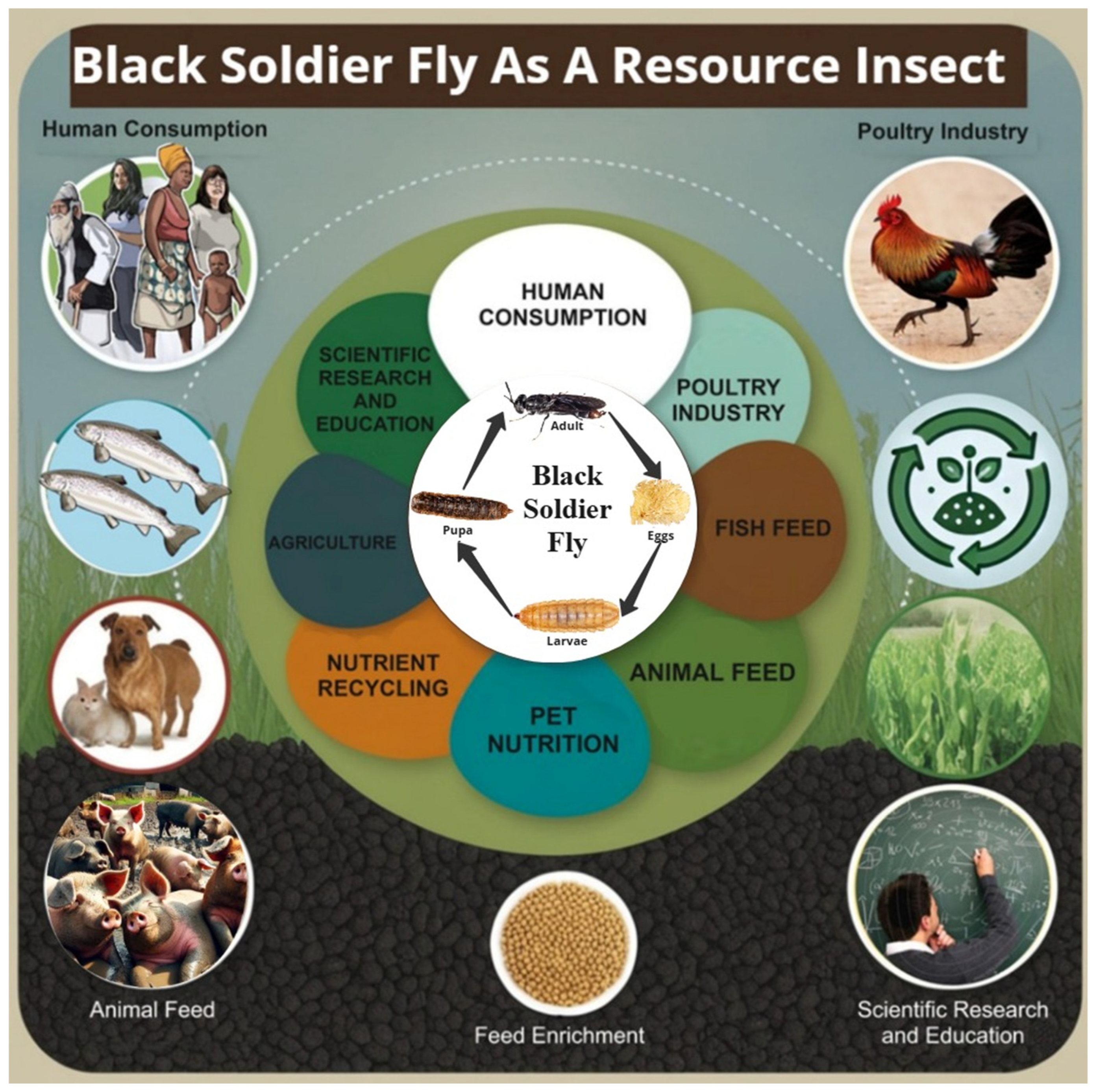

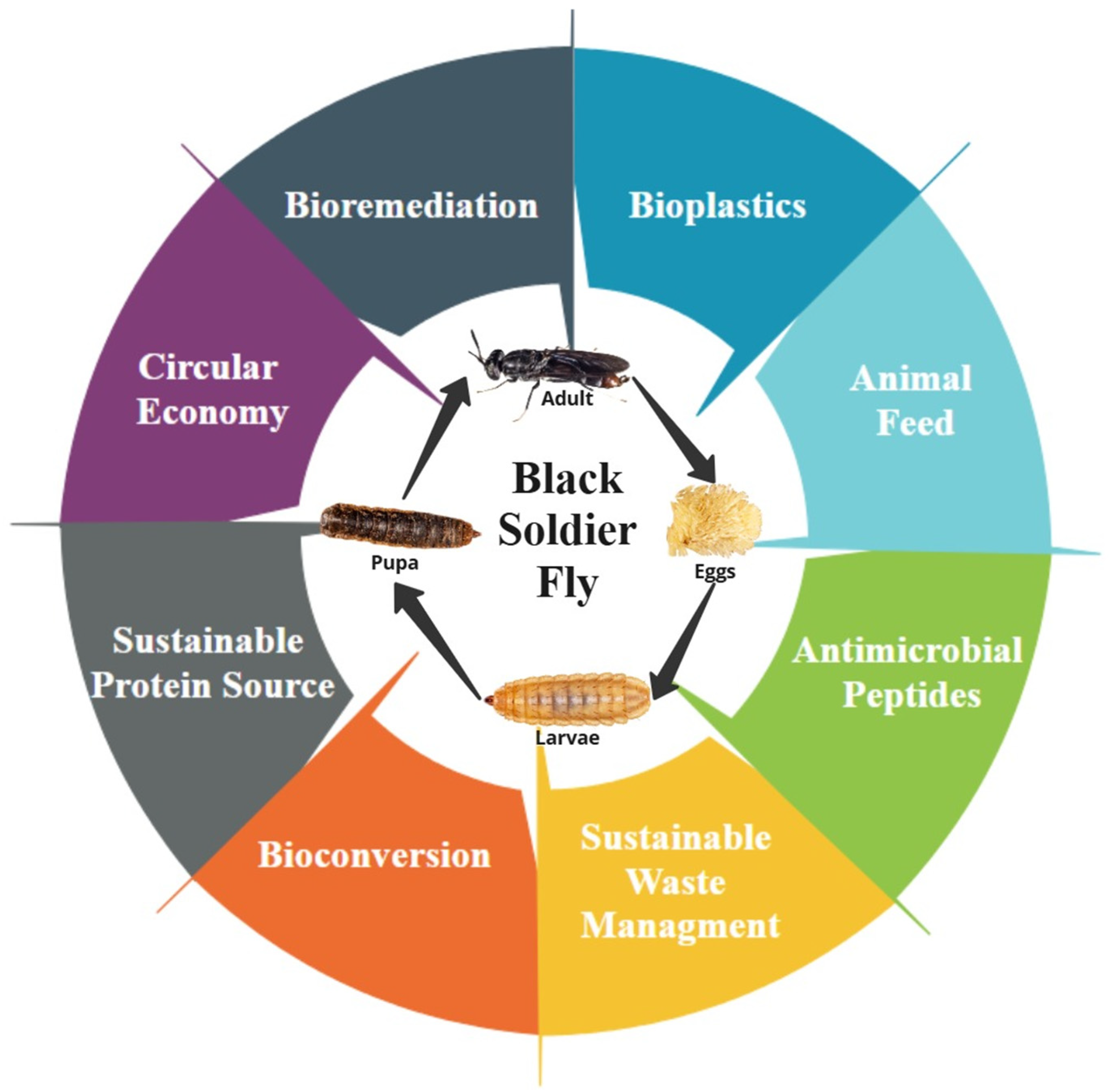
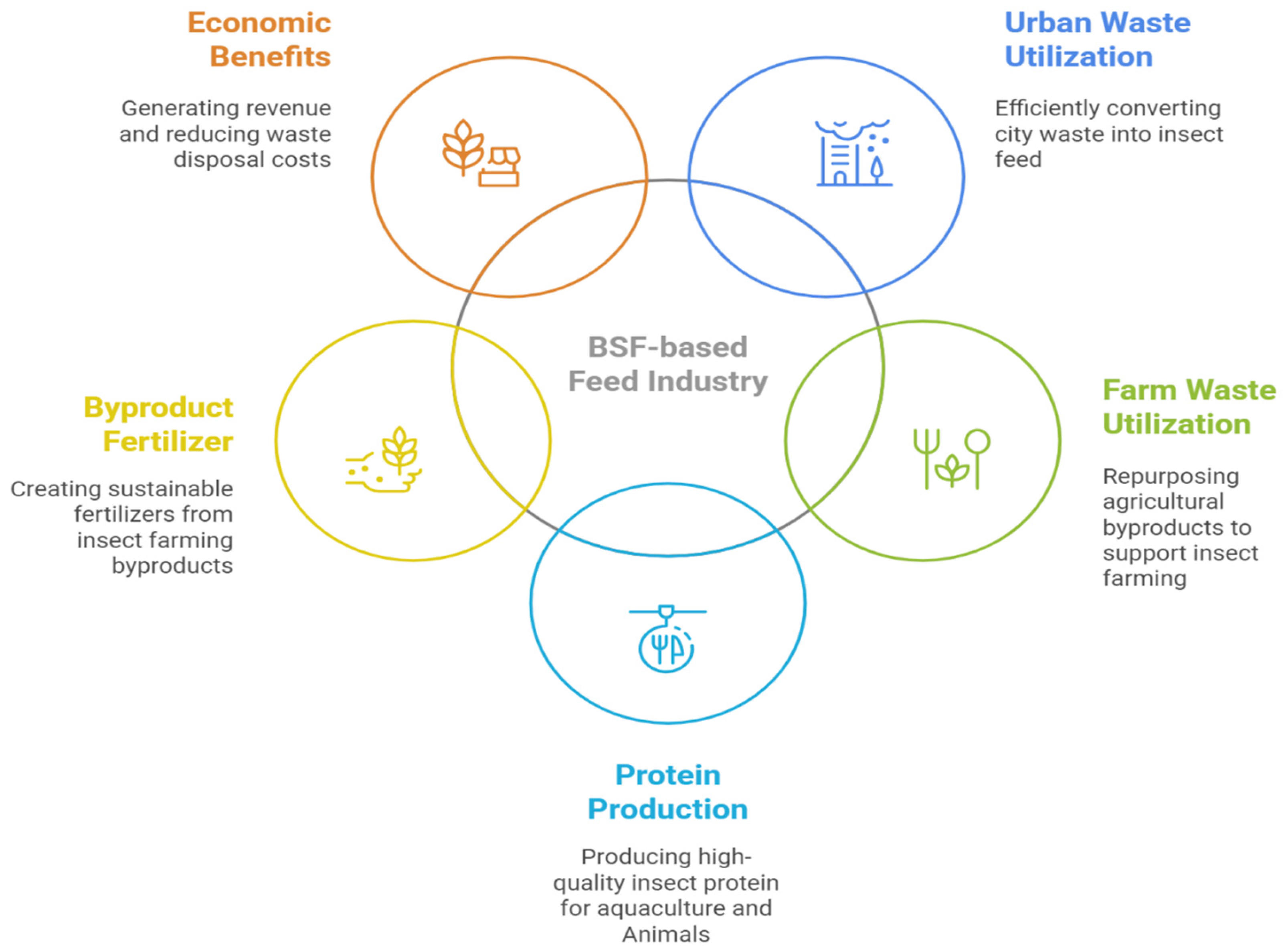
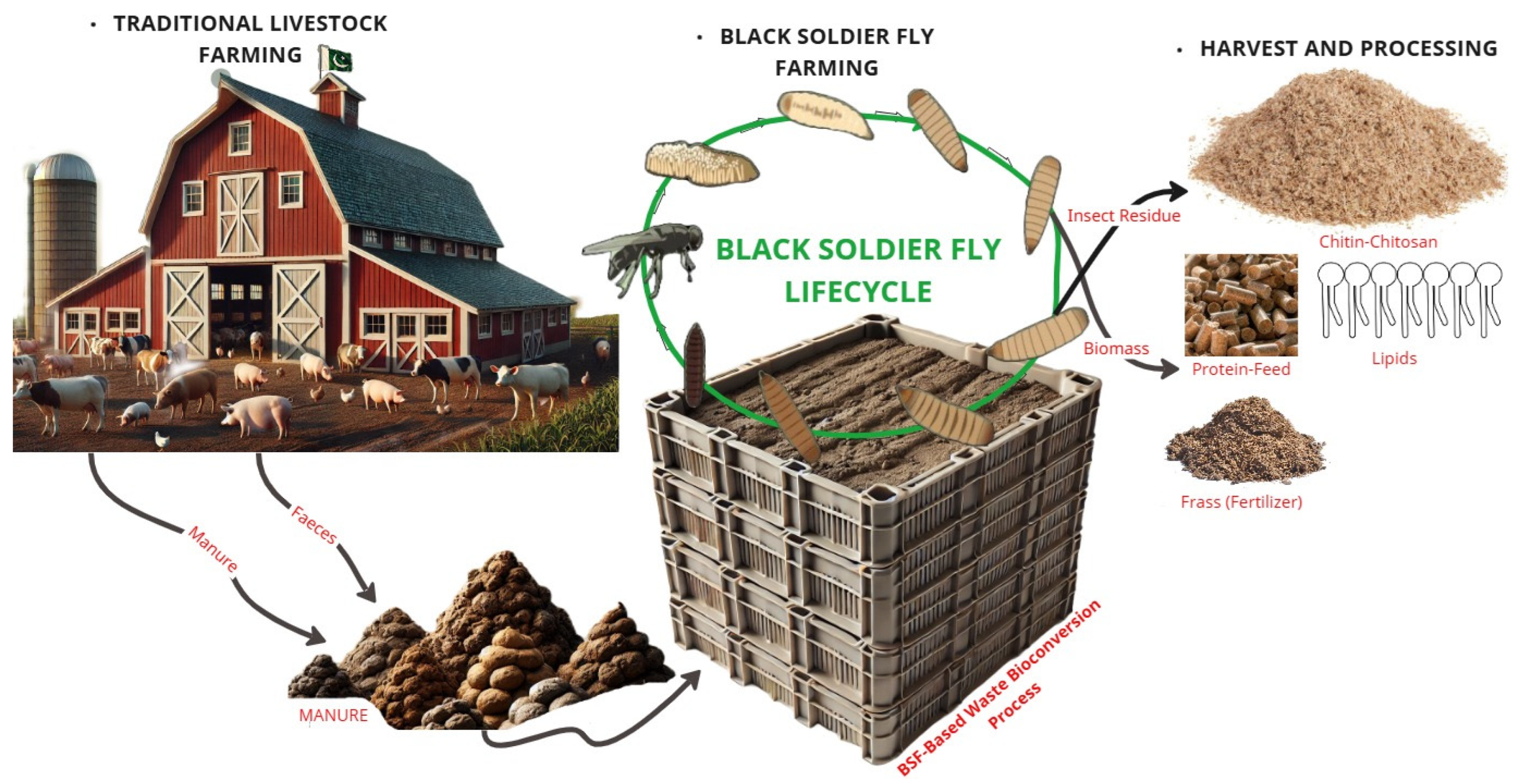
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tariq, M.R.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Mo, Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; ur Rehman, K.; et al. Black Soldier Fly: A Keystone Species for the Future of Sustainable Waste Management and Nutritional Resource Development: A Review. Insects 2025, 16, 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080750
Tariq MR, Liu S, Wang F, Wang H, Mo Q, Zhuang Z, Zheng C, Liang Y, Liu Y, ur Rehman K, et al. Black Soldier Fly: A Keystone Species for the Future of Sustainable Waste Management and Nutritional Resource Development: A Review. Insects. 2025; 16(8):750. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080750
Chicago/Turabian StyleTariq, Muhammad Raheel, Shaojuan Liu, Fei Wang, Hui Wang, Qianyuan Mo, Zhikai Zhuang, Chaozhong Zheng, Yanwen Liang, Youming Liu, Kashif ur Rehman, and et al. 2025. "Black Soldier Fly: A Keystone Species for the Future of Sustainable Waste Management and Nutritional Resource Development: A Review" Insects 16, no. 8: 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080750
APA StyleTariq, M. R., Liu, S., Wang, F., Wang, H., Mo, Q., Zhuang, Z., Zheng, C., Liang, Y., Liu, Y., ur Rehman, K., Helvaci, M., Qin, J., & Li, C. (2025). Black Soldier Fly: A Keystone Species for the Future of Sustainable Waste Management and Nutritional Resource Development: A Review. Insects, 16(8), 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080750











