Fine Structure and Optical Features of the Compound Eyes of Adult Female Ceratosolen gravelyi (Hymenoptera: Agaonidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
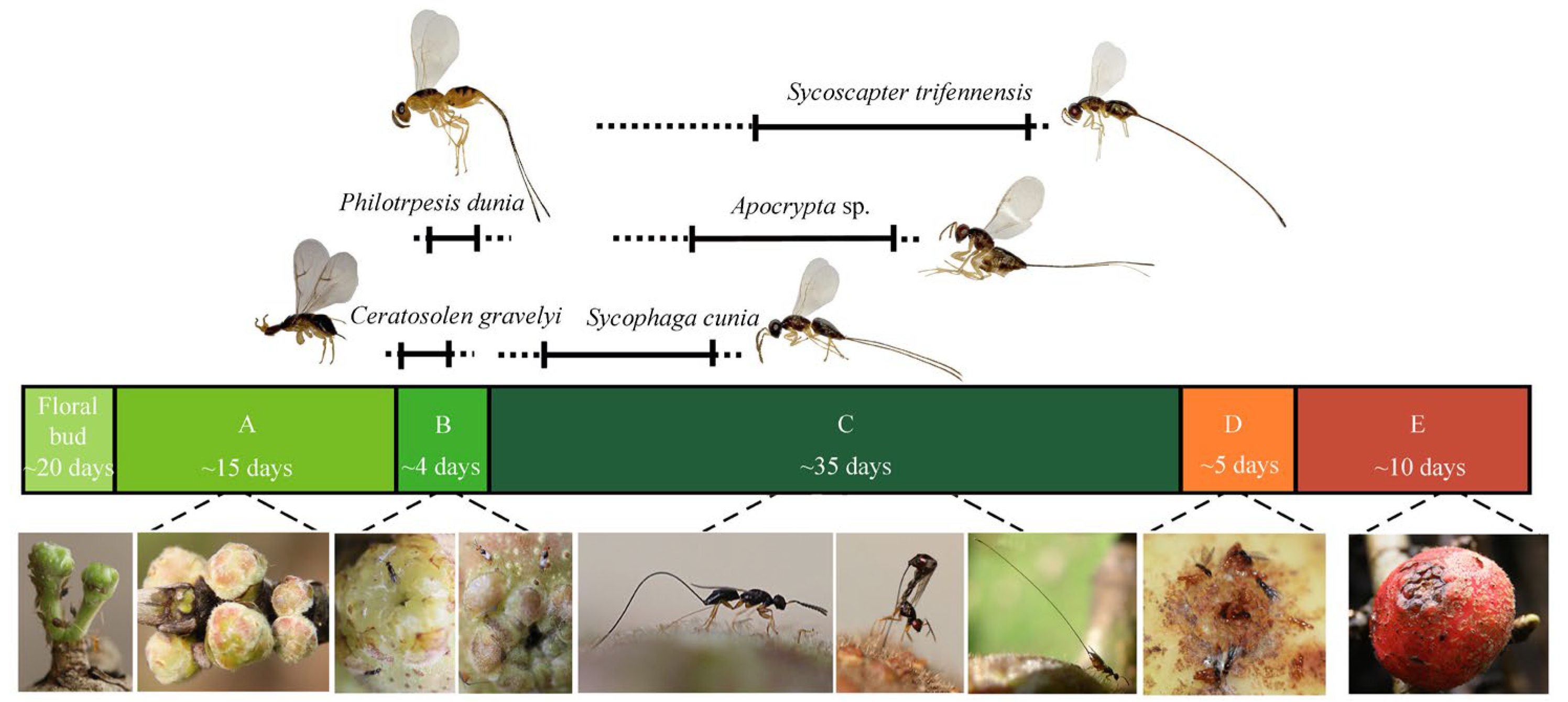
2.1. Wasp Community in Ficus Semicordata and Sample Preparations
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Optometric Measurements and Calculations
3. Results
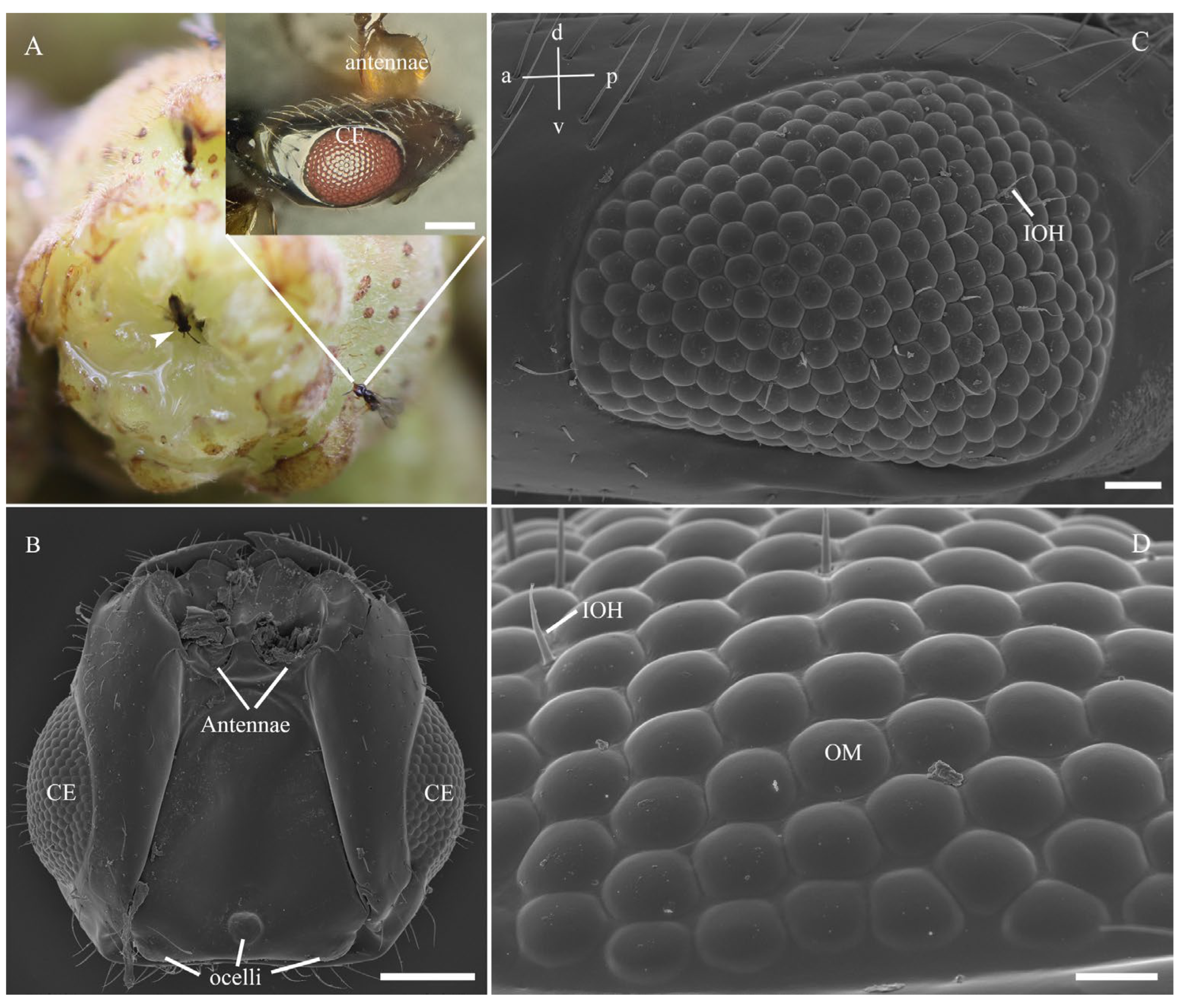
3.1. General Morphology of the Eye
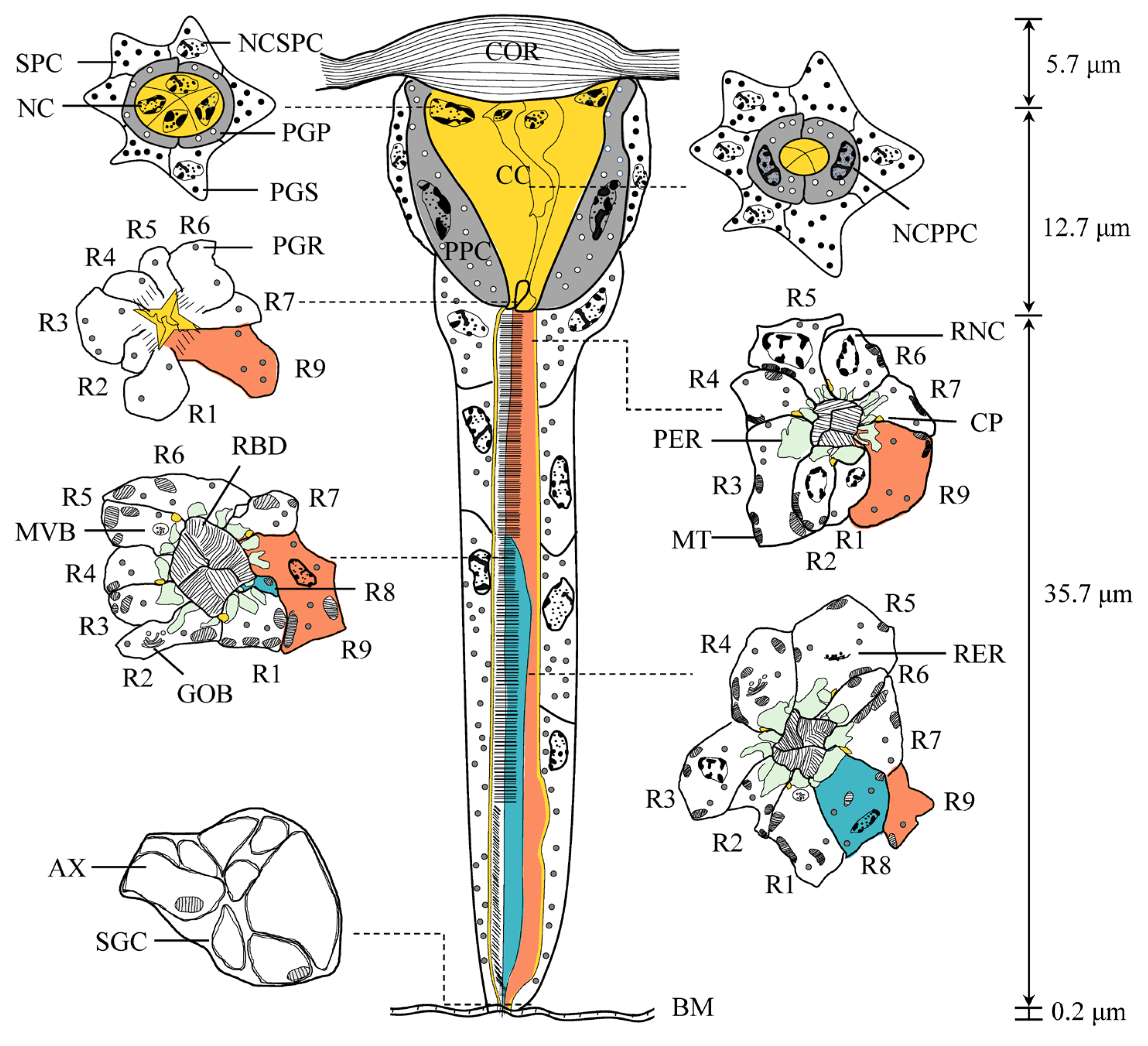
3.2. Fine Structural Organization of the Eye
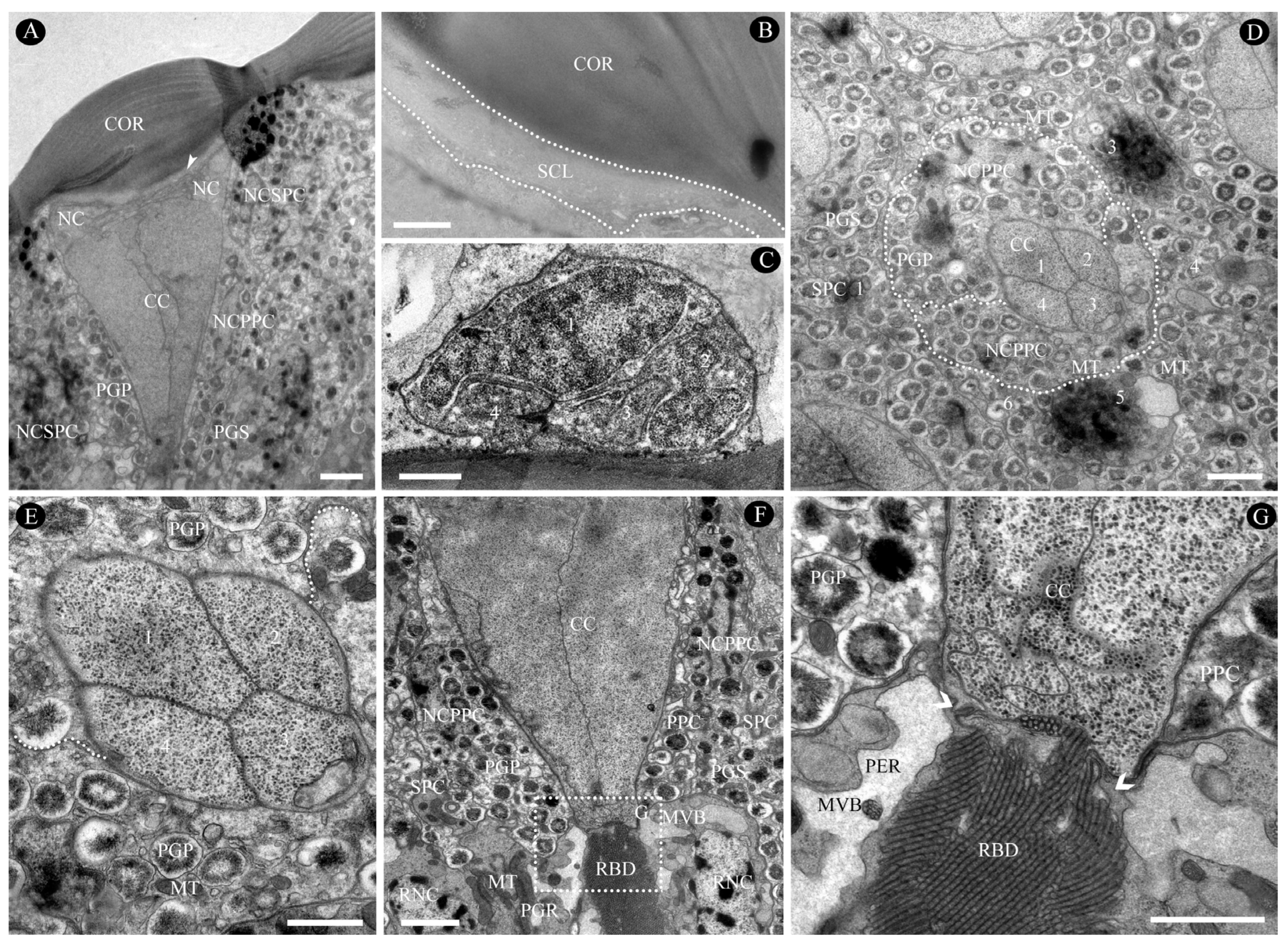
3.2.1. Dioptric Apparatus
3.2.2. Pigment Cells
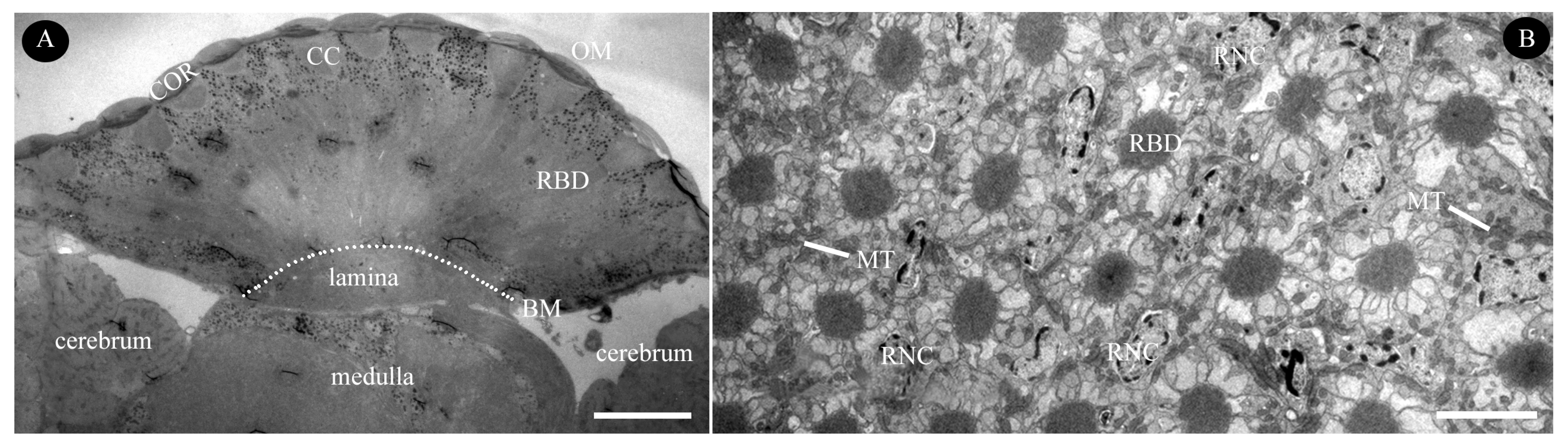
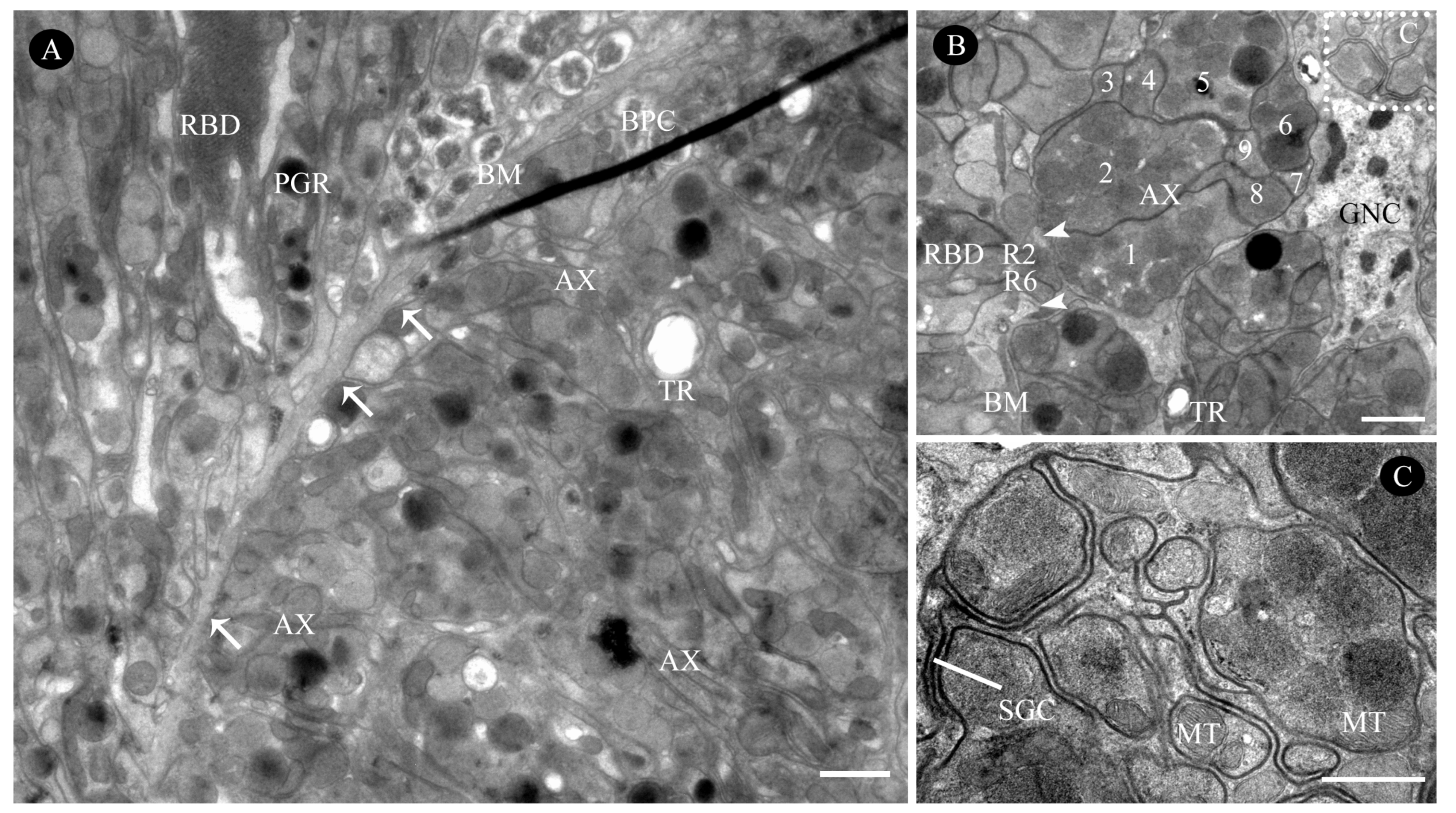
3.2.3. Retinula Cells and Rhabdom
3.2.4. Basal Matrix
3.3. Optical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Structural Features of the Eyes of C. gravelyi
4.1.1. External Morphology
4.1.2. Dioptric Apparatus
4.1.3. Pigment Cells and Pigment Granules
4.1.4. Retinula Cells and Rhabdom
4.2. Optical Features and Ecological Demand of the Eyes of C. gravelyi
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meyer-Rochow, V.B. Compound eyes of insects and crustaceans: Some examples that show there is still a lot of work left to be done. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.A.; Diakova, A.A.; Chaika, S.Y.; Polilov, A.A. Scaling of the sense organs of insects. 1. Introduction. Compound eyes. Entomol. Rev. 2022, 102, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelmann, M.; McGregor, A.P. Looking across the gap: Understanding the evolution of eyes and vision among insects. BioEssays 2024, 46, 2300240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherk, T.E. Development of the compound eyes of dragonflies (odonata). III. Adult compound eyes. J. Exp. Zool. 1978, 203, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jander, U.; Jander, R. Allometry and resolution of bee eyes (Apoidea). Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2002, 30, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, C.D.; Niven, J.E. Differential scaling within an insect compound eye. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20160042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.A.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B.; Polilov, A.A. Morphology and scaling of compound eyes in the smallest beetles (Coleoptera: Ptiliidae). Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2019, 48, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, N.J.; Makarova, A.A.; Gunn, P.; Villani, S.; Cohen, B.; Thasin, M.; Wu, J.; Shefter, D.; Pang, S.; Xu, C.S.; et al. A complete reconstruction of the early visual system of an adult insect. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 4611–4623.e4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.A.; Chua, N.J.; Diakova, A.V.; Desyatirkina, I.A.; Gunn, P.; Pang, S.; Xu, C.S.; Hess, H.; Chklovskii, D.B.; Polilov, A.A. The first complete 3D reconstruction and morphofunctional mapping of an insect eye. eLife 2025, 14, RP103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, F.G. Ecology of cave arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1983, 28, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffry, A.D.; Currea, J.P.; Franke-Gerth, F.A.; Palavalli-Nettimi, R.; Bodey, A.J.; Rau, C.; Samadi, N.; Gstöhl, S.J.; Schlepütz, C.M.; McGregor, A.P.; et al. Evolution of compound eye morphology underlies differences in vision between closely related Drosophila species. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvořáček, J.; Sehadová, H.; Weyda, F.; Tomčala, A.; Hejníková, M.; Kodrík, D. First comprehensive study of a giant among the insects, Titanus giganteus: Basic facts from its biochemistry, physiology, and anatomy. Insects 2020, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Müller, C.H.G.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B. How small can small be: The compound eye of the parasitoid wasp Trichogramma evanescens (Westwood, 1833) (Hymenoptera, Hexapoda), an insect of 0.3- to 0.4-mm total body size. Vis. Neurosci. 2011, 28, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrelet, A. The fine structure of the retina of the honey bee drone. Z. Zellforsch. 1970, 108, 530–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.; Polilov, A.; Fischer, S. Comparative morphological analysis of compound eye miniaturization in minute Hymenoptera. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2015, 44, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, M.F. Visual acuity in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 147–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.; Rigosi, E.; Nagloo, N.; O’Carroll, D.; Warrant, E.J. Spatial resolution and optical sensitivity in the compound eyes of two common European wasps, Vespula germanica and Vespula vulgaris. J. Exp. Biol. 2024, 227, jeb246670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freas, C.A.; Spetch, M.L. Varieties of visual navigation in insects. Anim. Cogn. 2023, 26, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrant, E.J.; Kelber, A.; Gislén, A.; Greiner, B.; Ribi, W.; Wcislo, W.T. Nocturnal vision and landmark orientation in a tropical halictid bee. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, A.; Greiner, B.; Ribi, W.A.; Zeil, J. Light and dark adaptation mechanisms in the compound eyes of Myrmecia ants that occupy discrete temporal niches. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, P.; de Almeida Caetano, C.; Schlindwein, C.; Alves-Dos-Santos, I.; Mota, T. Body size and the architecture of the visual system in crepuscular and diurnal bees. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2023, 138, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, B.; Cronin, T.W.; Ribi, W.A.; Wcislo, W.T.; Warrant, E.J. Anatomical and physiological evidence for polarisation vision in the nocturnal bee Megalopta genalis. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2007, 193, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B.; Müller, C.H.G. Compound eye miniaturization in Lepidoptera: A comparative morphological analysis. Acta Zool. 2014, 95, 438–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ran, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wei, G.; Li, J. Fine structure of the compound eyes of the crepuscular moth Grapholita molesta (Busck 1916) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1343702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, G.R.; Sharanowski, B.J. Parasitoid wasps. Curr. Biol. 2024, 34, R483–R488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Lu, Z.; Meinertzhagen, I.A. Three-dimensional ultrastructural organization of the ommatidium of the minute parasitoid wasp Trichogramma evanescens. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2019, 48, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichaud, F.; Casares, F. Shaping an optical dome: The size and shape of the insect compound eye. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 130, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.M.; Rasplus, J.-Y. Mutualists with attitude: Coevolving fig wasps and figs. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellberg, F.; Jousselin, E.; Hossaert-McKey, M.; Rasplus, J.Y. Biology, ecology, and evolution of fig-pollinating wasps (Chalcidoidea, Agaonidae). In Biology, Ecology and Evolution of Gall-Inducing Arthropods; Raman, A., Schaefer, C.W., Withers, T.M., Eds.; Science Publishers, Inc.: Enfield, NH, USA; Plymouth, UK, 2005; Volume 1–2, pp. 539–572. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, A.; Borges, R.M.; Chevallier, M.H.; Vignes, H.; Kobmoo, N.; Peng, Y.Q.; Cruaud, A.; Rasplus, J.Y.; Kjellberg, F.; Hossaert-Mckey, M. Geographic structuring into vicariant species-pairs in a wide-ranging, high-dispersal plant–insect mutualism: The case of Ficus racemosa and its pollinating wasps. Evol. Ecol. 2016, 30, 663–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.-H.; Sasaki, A.; Kusumi, J.; Chou, P.-A.; Tzeng, H.-Y.; Li, H.-Q.; Yu, H. Pollinator sharing, copollination, and speciation by host shifting among six closely related dioecious fig species. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Karpe, S.D.; Kumar, H.; Nongbri, L.B.; Venkateswaran, V.; Sowdhamini, R.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; Hansson, B.S.; Borges, R.M. Sensing volatiles throughout the body: Geographic- and tissue-specific olfactory receptor expression in the fig wasp. Insect Sci. 2025, 32, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, A.B.; Kaye, P.T.; Compton, S.G.; Noort, S. Fig volatiles: Their role in attracting pollinators and maintaining pollinator specificity. Plant Syst. Evol. 1993, 186, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grison-Pigé, L.; Hossaert-McKey, M.; Greeff, J.M.; Bessiere, J.-M. Fig volatile compounds--a first comparative study. Phytochemistry 2002, 61, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.M. On the air: Broadcasting and reception of volatile messages in brood-site pollination mutualisms. In Deciphering Chemical Language of Plant Communication; Blande, J.D., Glinwood, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 227–255. [Google Scholar]
- Hossaert-Mckey, M.; Soler, C.; Schatz, B.; Proffit, M. Floral scents: Their roles in nursery pollination mutualisms. Chemoecology 2010, 20, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.-H.; Yue, Z.; Jia, L.-Y.; Yang, X.-H.; Niu, L.-H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Sun, B.-F.; He, S.-M.; Li, Z.; et al. Obligate mutualism within a host drives the extreme specialization of a fig wasp genome. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, B. Research on the Species Divergence and Behavior of Pollinators Associated with Ficus hispida; University of Chinese Academy of Science: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooi, C.J.; Stavenga, D.G.; Arikawa, K.; Belušič, G.; Kelber, A. Evolution of insect color vision: From spectral sensitivity to visual ecology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohyama, T.; Schneider-Mizell, C.M.; Fetter, R.D.; Aleman, J.V.; Franconville, R.; Rivera-Alba, M.; Mensh, B.D.; Branson, K.M.; Simpson, J.H.; Truman, J.W.; et al. A multilevel multimodal circuit enhances action selection in Drosophila. Nature 2015, 520, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, Q.; Proffit, M.; Bessière, J.-M.; Li, Z.B.; Hossaert-McKey, M. Private channel: A single unusual compound assures specific pollinator attraction in Ficus semicordata. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, C.; Proffit, M.; Chen, C.; Hossaert-McKey, M. Private channels in plant-pollinator mutualisms. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aepli, F.; Labhart, T.; Meyer, E.P. Structural specializations of the cornea and retina at the dorsal rim of the compound eye in hymenopteran insects. Cell Tissue Res. 1985, 239, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M.; Seymoure, B.M.; Comi, T.J.; Loew, E.R. Species and sex differences in eye morphometry and visual responsivity of two crepuscular sweat bee species (Megalopta spp., Hymenoptera: Halictidae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 130, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, A.; Alkaladi, A.; Raderschall, C.A.; Robson, S.K.A.; Ribi, W.A. Compound eye adaptations for diurnal and nocturnal lifestyle in the intertidal ant, Polyrhachis sokolova. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.T.; Noyes, J. A new genus and species of fairyfly, Tinkerbella nana (Hymenoptera, Mymaridae), with comments on its sister genus Kikiki, and discussion on small size limits in arthropods. J. Hymenoptera Res. 2013, 32, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, H.B. The size of ommatidia in apposition eyes. J. Exp. Biol. 1952, 29, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yack, J.E.; Johnson, S.E.; Brown, S.G.; Warrant, E.J. The eyes of Macrosoma sp. (Lepidoptera: Hedyloidea): A nocturnal butterfly with superposition optics. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2007, 36, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.D.; Rasplus, J.-Y. Dispersal of fig pollinators in Asian tropical rain forests. J. Trop. Ecol. 2006, 22, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavenga, D.G. Angular and spectral sensitivity of fly photoreceptors. II. Dependence on facet lens F-number and rhabdomere type in Drosophila. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2003, 189, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Liang, B.; Chang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Agnarsson, I.; Li, D.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J. Eyeless cave-dwelling Leptonetela spiders still rely on light. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj0348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.W. Physics of vision in compound eyes. In Comparative Physiology and Evolution of Vision in Invertebrates: A: Invertebrate Photoreceptors; Autrum, H., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1979; pp. 225–313. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, S.; Narendra, A.; Zeil, J. The properties of the visual system in the Australian desert ant Melophorus bagoti. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2011, 40, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeman, M.A.; Pratt, S.C.; Franks, N.R. Navigation using visual landmarks by the ant Leptothorax albipennis. Insectes Soc. 2002, 49, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahake, A.; Stöckl, A.L.; Foster, J.J.; Sane, S.P.; Kelber, A. The roles of vision and antennal mechanoreception in hawkmoth flight control. eLife 2018, 7, e37606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Structural Elements | Parameters | Unit | N | Average | Range (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound eyes | eye height | µm | 20 | 147.6 ± 5.9 | 137.8–164.7 |
| eye width | µm | 20 | 201.3 ± 6.0 | 188.0–210.5 | |
| facet number | - | 11 | 247 ± 14 | 228–263 | |
| eye radius | µm | 3 | 90.4 ± 5.9 | 86.4–97.4 | |
| Ommatidia | facet diameter | µm | 150 | 11.8 ± 0.7 | 9.3–13.7 |
| length | µm | 30 | 54.3 ± 6.8 | 46.8–59.9 | |
| interommatidial angle | deg | 30 | 9.3 ± 0.9 | 7.7–12.5 | |
| Cornea | outer lens radius | µm | 20 | 7.1 ± 0.6 | 5.6–8.3 |
| inner lens radius | µm | 20 | 8.7 ± 0.9 | 7.7–10.8 | |
| maximum thickness | µm | 50 | 5.7 ± 0.8 | 4.1–7.9 | |
| number of chitin layers | - | 20 | 9.0 ± 1.0 | 8–10 | |
| Crystalline cone | length | µm | 50 | 12.7 ± 2.3 | 9.3–18.4 |
| distal diameter | µm | 50 | 8.9 ± 1.2 | 6.4–11.3 | |
| Pigment granule | PPC diameter * | µm | 150 | 0.62 ± 0.11 | 0.4–1.0 |
| SPC diameter * | µm | 150 | 0.57 ± 0.12 | 0.3–0.8 | |
| Rhabdom | length | µm | 20 | 35.7 ± 4.3 | 29.1–43.9 |
| distal diameter | µm | 20 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 2.0–2.8 | |
| proximal diameter | µm | 12 | 0.69 ± 0.1 | 0.5–0.9 | |
| microvillus diameter | nm | 150 | 57.2 ± 7.5 | 41.1–81.6 | |
| PG diameter * | µm | 150 | 0.47 ± 0.10 | 0.2–0.7 | |
| Interommatidial hairs | number | - | 20 | 15 ± 2 | 13–19 |
| length | µm | 30 | 13.0 ± 3.9 | 6.5–21.6 | |
| basal diameter | µm | 30 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 1.0–1.7 | |
| Basal matrix | thickness | nm | 20 | 198.9 ± 63.3 | 128–354 |
| Ocellus | diameter | µm | 15 | 35.0 and 33.2 | 25.5–42.8 |
| Parameters * | C. gravelyi | M. mymaripenne | T. evanescens | A. flavipes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body size (mm) | 2.74 | 0.2 | 0.3–0.4 | 0.45 |
| P1 | 0.064 | 0.133 | 0.098 | 0.076 |
| P2 | 0.012 | 0.037 | 0.016 | 0.021 |
| P3 | −0.003 | −0.009 | −0.002 | −0.004 |
| PI | 0.073 | 0.161 | 0.112 | 0.094 |
| f (µm) | 13.7 | 6.2 | 8.9 | 10.7 |
| f′ (µm) | 18.5 | 8.4 | 12.0 | 14.4 |
| F-number | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| Δρrh (°) | 10.0 | 22.2 | 8.1 | 4.8 |
| Δρ1 (°) | 2.4 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 3.5 |
| Sw (μm2/sr) | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Li, Z. Fine Structure and Optical Features of the Compound Eyes of Adult Female Ceratosolen gravelyi (Hymenoptera: Agaonidae). Insects 2025, 16, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070682
Xie H, Shi Y, Zhang S, Zhu Y, Shao S, Zhang Y, Yang P, Li Z. Fine Structure and Optical Features of the Compound Eyes of Adult Female Ceratosolen gravelyi (Hymenoptera: Agaonidae). Insects. 2025; 16(7):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070682
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Hua, Yan Shi, Shouxian Zhang, Yonghui Zhu, Subo Shao, Yuan Zhang, Pei Yang, and Zongbo Li. 2025. "Fine Structure and Optical Features of the Compound Eyes of Adult Female Ceratosolen gravelyi (Hymenoptera: Agaonidae)" Insects 16, no. 7: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070682
APA StyleXie, H., Shi, Y., Zhang, S., Zhu, Y., Shao, S., Zhang, Y., Yang, P., & Li, Z. (2025). Fine Structure and Optical Features of the Compound Eyes of Adult Female Ceratosolen gravelyi (Hymenoptera: Agaonidae). Insects, 16(7), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070682





