The Effects of Three Phenolic Substances on the Growth and Digestive Physiology of the Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Insects
2.2. Experimental Treatment
2.3. Determination of Larval Food Intake and Body Weight
2.4. Determination of Protein and Digestive Enzyme Activity of Larvae
2.5. Determination of Pupa Weight, Pupation Rate, Emergence Rate, and Adult Longevity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
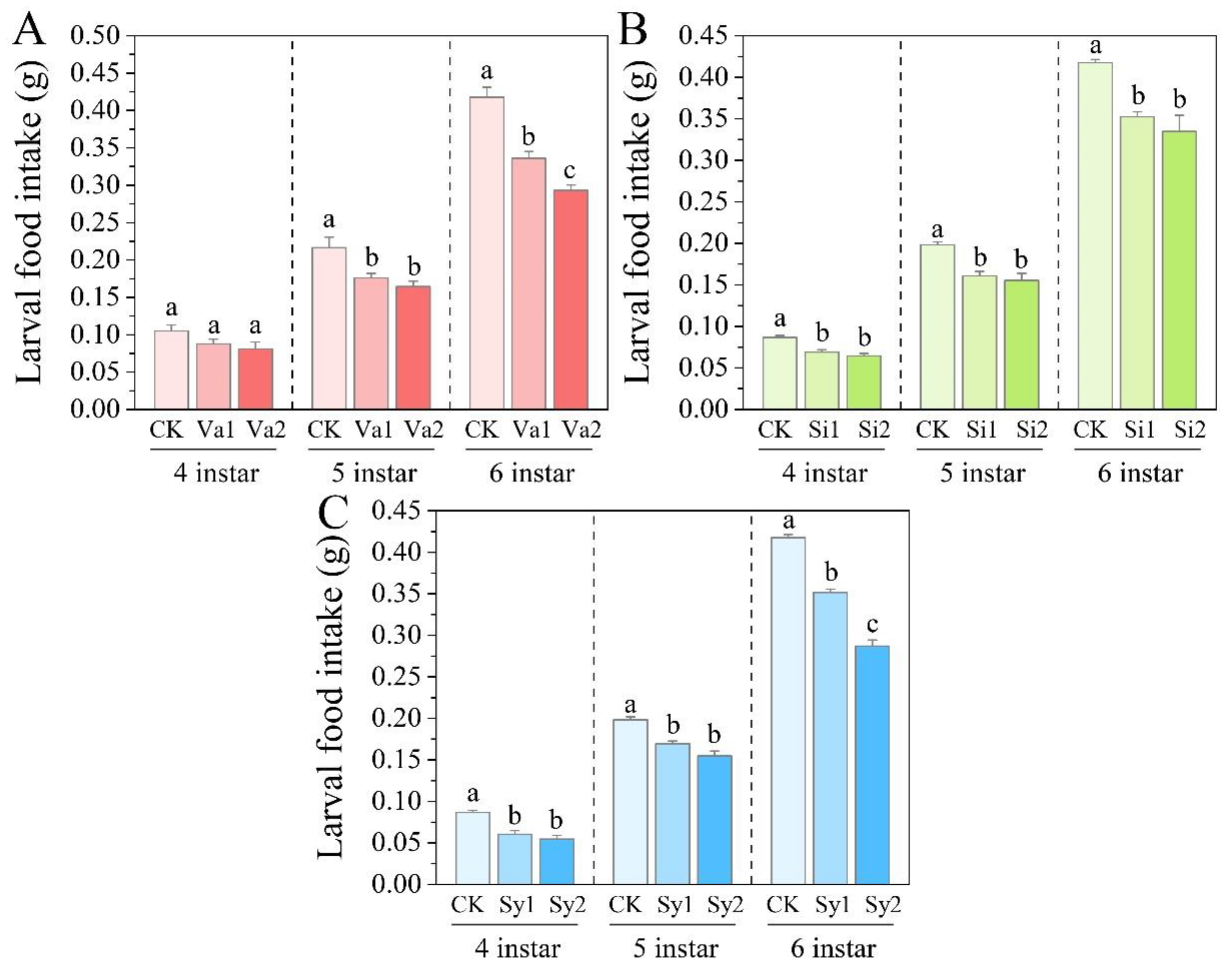
3.1. Changes in Larval Food Intake of S. frugiperda
3.2. Changes in Larval Body Weight of S. frugiperda
3.3. Changes in Protein Content of S. frugiperda Larvae
3.4. Changes in Pepsin Activity of S. frugiperda Larvae
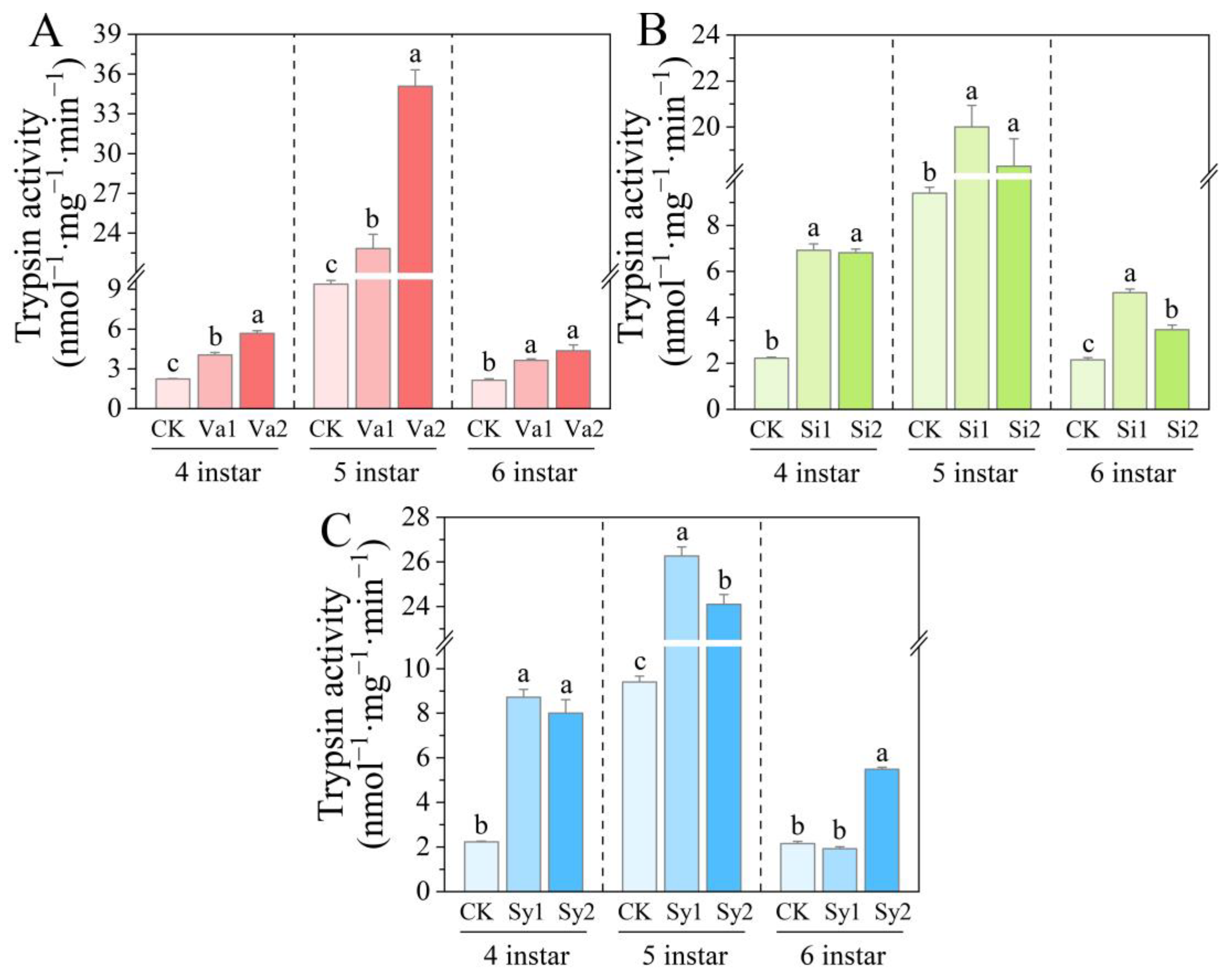
3.5. Changes in Trypsin Activity of S. frugiperda Larvae
3.6. Changes in α-Amylase Activity of S. frugiperda Larvae
3.7. Changes in Pupation Rate and Pupal Weight of S. frugiperda
3.8. Changes in the Emergence Rate and Adult Longevity of S. frugiperda
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, W.; Tayyab, M.; Khalil, F.; Hua, Z.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.Y.H. Silicon-mediated plant defense against pathogens and insect pests. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 168, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, T.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, D.; Yan, S. Silicon supplementation improves biomass and direct defense of ryegrass: A multi-omics study. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 204, 117357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.; Ullah, F.; Khan, M.M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shah, S.; Imran, M.; Assiri, M.A.; Fernandez-Grandon, G.M.; Desneux, N.; et al. Metabolic-based insecticide resistance mechanism and ecofriendly approaches for controlling of beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 1746–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.M.; Auad, A.M.; Mendes, S.M.; Frizzas, M.R. Economic impact of exotic insect pests in Brazilian agriculture. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 137, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, E.H.; Goodger, J.Q.D.; Woodrow, I.E.; Moller, B.L. Plant chemical defense: At what cost? Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisiriko, M.; Anastasiadi, M.; Terry, L.A.; Yasri, A.; Beale, M.H.; Ward, J.L. Phenolics from medicinal and aromatic plants: Characterisation and potential as biostimulants and bioprotectants. Molecules 2021, 26, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostkam, M.; Sohrabi, F.; Modarresi, M.; Kohanmoo, M.A.; Bayram, A. Genetic variation of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) cultivars to exogenously applied jasmonic acid to induce resistance to Liriomyza sativae. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2023, 17, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Ranjan, A.; Singh, A.K.; Sirhindi, G. Methyl jasmonate reduces cadmium toxicity by enhancing phenol and flavonoid metabolism and activating the antioxidant defense system in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan). Chemosphere 2024, 346, 140681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Mir, G.M.; Rouf, A.; War, A.R.; Hussain, B. Herbivore and phytohormone induced defensive response in kale against cabbage butterfly, Pieris brassicae Linn. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Dahuja, A.; Tiwari, S.; Punia, S.; Tak, Y.; Amarowicz, R.; Bhoite, A.G.; Singh, S.; Joshi, S.; Panesar, P.S.; et al. Recent trends in extraction of plant bioactives using green technologies: A review. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivira, A.; Sanabria, M.E.; Valera, N.; Vasquez, C. Toxicity of ethanolic extracts from Lippia origanoides and Gliricidia sepium to Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Boisduval) (Acari: Tetranychidae). Neotrop. Entomol. 2011, 40, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Su, H.; Zhang, S.; Jing, T.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y. Transcriptomic and metabolomic responses in cotton plant to Apolygus lucorum infestation. Insects 2022, 13, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.D.; Thierfelder, C.; Baudron, F.; Chinwada, P.; Midega, C.; Schaffner, U.; van den Berg, J. Agro-ecological options for fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda JE Smith) management: Providing low-cost, smallholder friendly solutions to an invasive pest. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, C.; Zhang, G.; Jin, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, C. Effect of plant secondary metabolites on common cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Entomol. Res. 2018, 48, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Tai, S.; Qi, L.; Yu, X.; Dai, W. Transcription factor CncC potentially regulates cytochrome P450 CYP321A1-mediated flavone tolerance in Helicoverpa armigera. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 191, 105360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Nur, F.A.; Ma, J.Y.; Wang, J.G.; Cao, C.W. Effects of poplar secondary metabolites on performance and detoxification enzyme activity of Lymantria dispar. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 225, 108587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Wu, H.; Yan, S.; Jiang, D. Evaluating the Toxic Effects of Tannic Acid Treatment on Hyphantria cunea Larvae. Insects 2022, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Ren, L.; Chen, F.; Feng, Y.; Luo, Y. Antifeedant Activity of Ginkgo biloba secondary metabolites against Hyphantria cunea larvae: Mechanisms and applications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topkara, E.F. Effects of selected plant secondary metabolites in mulberry, apple, plum, and walnut on the pupal parameters of Hyphantria cunea Drury, 1773 (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae) larvae infected by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. J. Entomol. Res. Soc. 2022, 24, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.-Q.; Lin, H.-X. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant-environment interactions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of wheat kernels in response to the feeding of orange wheat blossom midges (Sitodiplosis mosellana) in the field. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1477–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-N.; Wang, H.; Yuan, L.-S.; Li, T.; Jiang, D.; Song, G.; Yan, S.-C. Silicon enhanced italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) production and induced defense responses against fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). Agronomy 2024, 14, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, T. Lignin modification in planta for valorization. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 1305–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivai, R.R.; Miyamoto, T.; Awano, T.; Yoshinaga, A.; Chen, S.; Sugiyama, J.; Tobimatsu, Y.; Umezawa, T.; Kobayashi, M. Limiting silicon supply alters lignin content and structures of sorghum seedling cell walls. Plant Sci. 2022, 321, 111325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, T.; Yuan, L.; Tan, M.; Jiang, D.; Yan, S. Digestive characteristics of Hyphantria cunea larvae on different host plants. Insects 2023, 14, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T.; Deng, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L. Salicylic acid improves the salt tolerance capacity of Saponaria officinalis by modulating its photosynthetic rate, osmoprotectants, antioxidant levels, and ion homeostasis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Lu, W.; Liu, F. Sublethal effects of four synthetic insecticides on the generalist predator Cyrtorhinus lividipennis. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, S.; Taggar, G.K.; Grewal, S.K. Alteration in the developmental physiology of Maruca vitrata (Fabricius) on jasmonic acid and salicylic acid treated pigeonpea. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2023, 17, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- War, A.R.; Paulraj, M.G.; Hussain, B.; Buhroo, A.A.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Sharma, H.C. Effect of plant secondary metabolites on legume pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera. J. Pest Sci. 2013, 86, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Yan, S.; Jiang, D. Identification and potential application of key insecticidal metabolites in Tilia amurensis, a low-preference host of Hyphantria cunea. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 199, 105796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.D.; Picanço, M.C.; Barbosa, L.C.d.A.; Guedes, R.N.C.; da Silva, É.M. Toxicity of leaf extracts of Ageratum conyzoidesto Lepidoptera pests of horticultural crops. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2004, 22, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basukriadi, A.; Wilkins, R.M. Oviposition deterrent activities of pachyrhizus erosus seed extract and other natural products on Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Tan, M.-t.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.-r.; Yan, S.-c. Evaluating the ecotoxicological effects of Pb contamination on the resistance against Lymantria dispar in forest plant, Larix olgensis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2490–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, G.; Praveen, A.; Tripathi, T.; Yadav, V.K.; Verma, P.C. Herbivore-responsive cotton phenolics and their impact on insect performance and biochemistry. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardke, J.T.; Lorenz, G.M., III; Leonard, B.R. Fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) ecology in southeastern cotton. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2015, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Huang, C.; Li, C.-y.; Zhou, H.-x.; Ren, Y.-l.; Li, Z.-y.; Xing, L.-s.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, X.; Liu, B.; et al. Biology, invasion and management of the agricultural invader: Fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 646–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Jia, X.; Nie, F.; Wu, K. Fall armyworm invasion heightens pesticide expenditure among Chinese smallholder farmers. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, J.-Y.; Deng, Y.-N.; Liu, X.-R.; Niu, D.; Zhang, W.-S. The Effects of Three Phenolic Substances on the Growth and Digestive Physiology of the Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insects 2025, 16, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070669
Lv J-Y, Deng Y-N, Liu X-R, Niu D, Zhang W-S. The Effects of Three Phenolic Substances on the Growth and Digestive Physiology of the Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insects. 2025; 16(7):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070669
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Jin-Yan, Ya-Nan Deng, Xiao-Rong Liu, Dan Niu, and Wan-Shu Zhang. 2025. "The Effects of Three Phenolic Substances on the Growth and Digestive Physiology of the Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)" Insects 16, no. 7: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070669
APA StyleLv, J.-Y., Deng, Y.-N., Liu, X.-R., Niu, D., & Zhang, W.-S. (2025). The Effects of Three Phenolic Substances on the Growth and Digestive Physiology of the Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insects, 16(7), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070669






