Trends and Emerging Hotspots in Toxicology of Chironomids: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategies
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Publication Patterns
3.2. Analysis of Journals
3.3. Countries’ and Authors’ Research Performances and Cooperation
3.4. The Most Cited Articles and High-Impact Articles in 1465 Publications
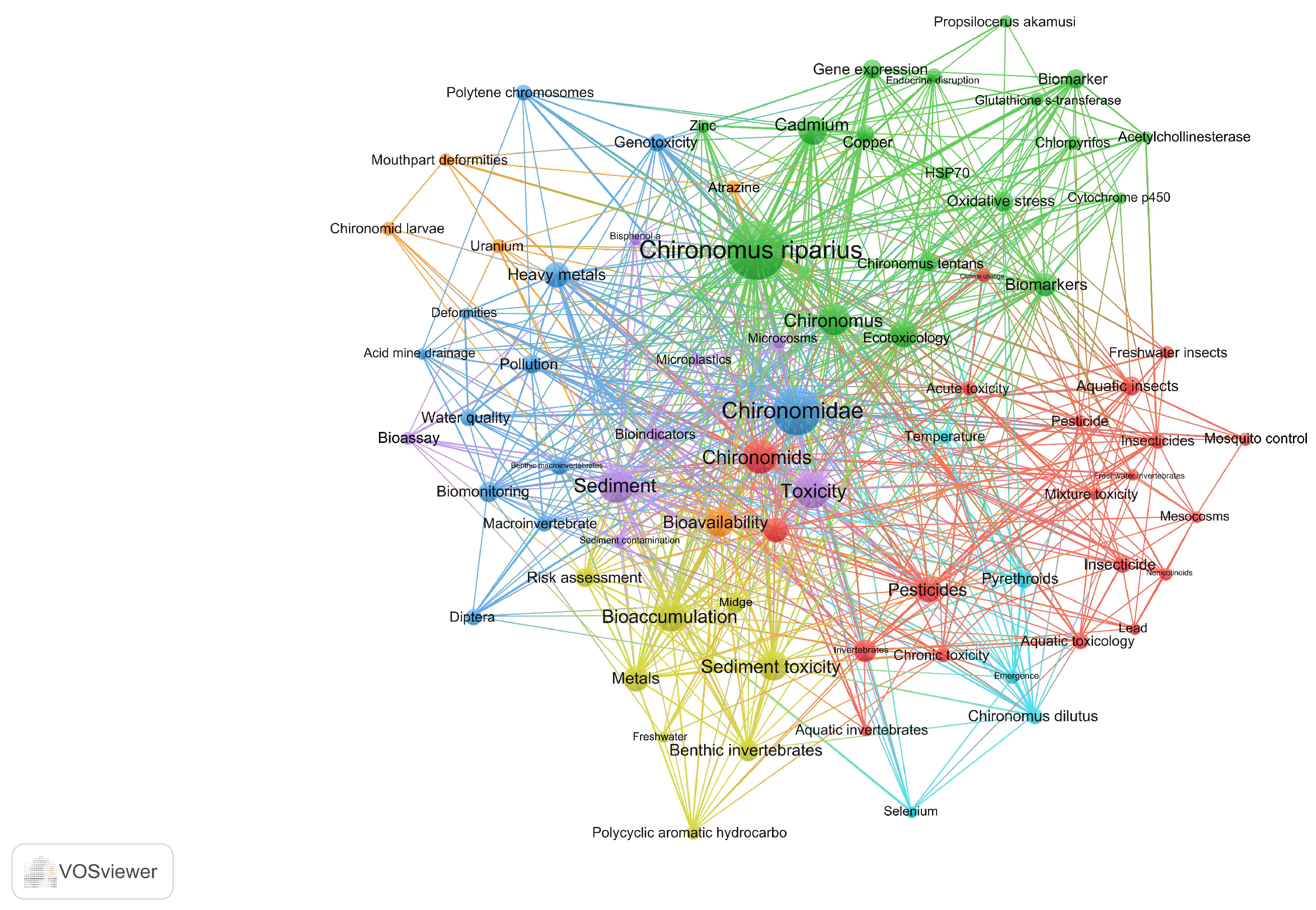
3.5. Analysis of Keywords Network
4. Discussion
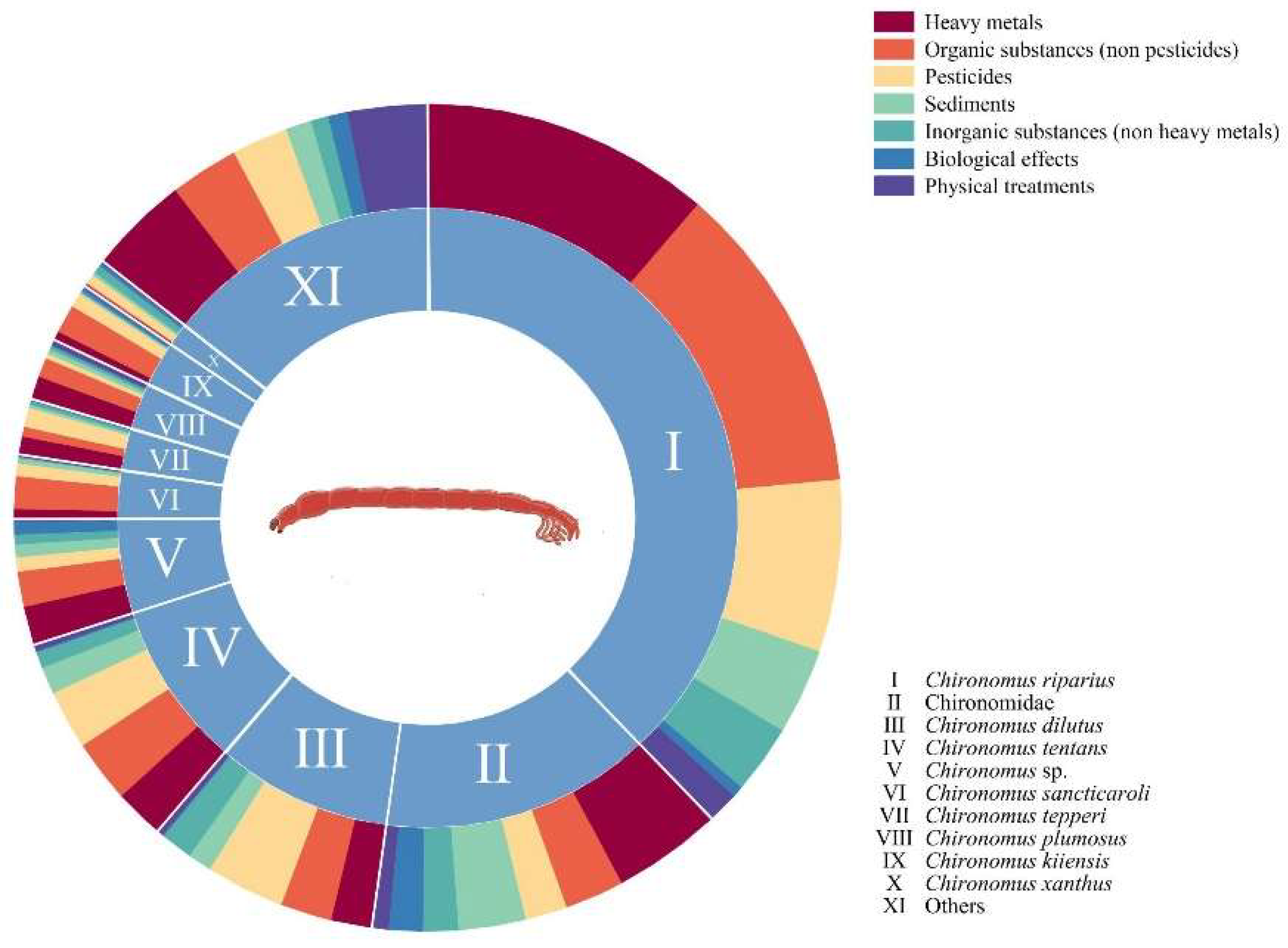
4.1. Analysis of Target Species and Environmental Stressors
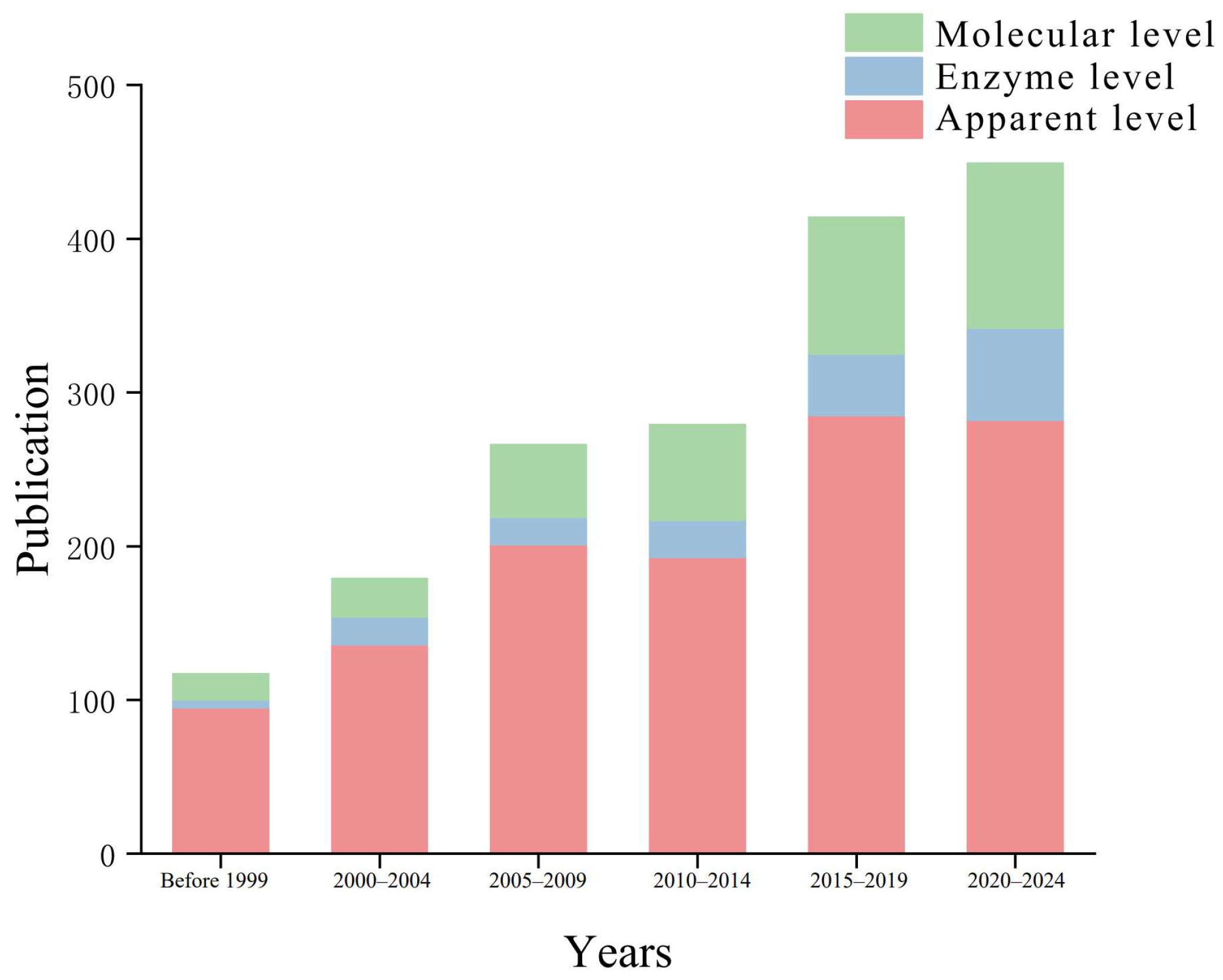
4.2. Species Response Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLachlan, A.; Armitage, P.D.; Cranston, P.S.; Pinder, L.C.V. The Chironomidae: The Biology and Ecology of Non-Biting Midges; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Volume 64, p. 667. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, T.; Ekrem, T.; Cranston, P. The larvae of the Holarctic Chironomidae (Diptera)-Introduction. Insect Syst. Evol. 2013, 66, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anderson, R.; Buikema, A., Jr.; Cairns, J., Jr. Chironomidae Toxicity Tests—Biological Background and Procedures. In Aquatic Invertebrate Bioassays; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1980; pp. 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama, S. Chronic effects of Cu on reproduction of Polypedilum nubifer (Chironomidae) through water and food. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1988, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.A.; Green, D.W.; Pascoe, D.; Gower, D.E. Effect of cadmium on oviposition and egg viability in Chironomus riparius (Diptera: Chironomidae). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1987, 38, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.A.; Moore, B.C.; Schaumloffel, J.; Dasgupta, N. Morphological abnormalities in Chironomus tentans exposed to cadmium—And copper-spiked sediments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 55, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailova, P.; Petrova, N.; Ilkova, J.; Bovero, S.; Brunetti, S.; White, K.; Sella, G. Genotoxic effect of copper on salivary gland polytene chromosomes of Chironomus riparius Meigen 1804 (Diptera, Chironomidae). Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafarifarsani, H.; Fazle Rohani, M.; Raeeszadeh, M.; Ahani, S.; Yousefi, M.; Talebi, M.; Sazzad Hossain, M. Pesticides and heavy metal toxicity in fish and possible remediation—A review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 1007–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ye, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, W. Essential and nonessential elements in the red-crowned crane Grus japonensis of Zhalong Wetland, northeastern China. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2014, 96, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, D.S.; Maurya, P.K. Heavy metal concentration in water, sediment, and tissues of fish species (Heteropneustis fossilis and Puntius ticto) from Kali River, India. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2014, 96, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Parvin, E.; Islam, M.M.; Akter, M.S.; Khan, S.; Al-Mamun, M.H. Lead- and cadmium-induced histopathological changes in gill, kidney and liver tissue of freshwater climbing perch Anabas testudineus (Bloch, 1792). Chem. Ecol. 2014, 30, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-H.; Tsunoda, H.; Tsunoda, M. Environmental Toxicology: Biological and Health Effects of Pollutants, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Masindi, V.; Muedi, K. Environmental Contamination by Heavy Metals. In Heavy Metals; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, C.H.; Sibly, R.M.; Sibly, R.M.; Peakall, D.B. Principles of Ecotoxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, P.K.; Gautam, R.; Banerjee, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.; Pandey, J. Heavy metals in the environment: Fate, transport, toxicity and remediation technologies. In Heavy Metals; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 101–130. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology: Volume 3: Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Shallari, S.; Schwartz, C.; Hasko, A.; Morel, J.L. Heavy metals in soils and plants of serpentine and industrial sites of Albania. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 209, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herawati, N.; Suzuki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Rivai, I.F.; Koyama, H. Cadmium, Copper, and Zinc Levels in Rice and Soil of Japan, Indonesia, and China by Soil Type. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 64, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E.; Stoffella, P.J. Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2005, 19, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P. Pesticides. Health, Safety and the Environment. By G. A. Matthews. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing (2006), pp. 235, £79.50. ISBN-13: 978-1-4051-3091-2. Exp. Agric. 2007, 43, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilden, R.C.; Huffling, K.; Sattler, B. Pesticides and Health Risks. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2010, 39, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarelli, A. Growing up with pesticides. Science 2013, 341, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Yang, L.; Tong, S.; Yu, Q.J.; Ruan, H.D.; Atabila, A.; et al. Exposure Routes and Health Risks Associated with Pesticide Application. Toxics 2022, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Mason, S.; Wilson, S.; Box, C.; Zellers, A.; Edwards, W.; Farley, H.; Amato, S. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estahbanati, S.; Fahrenfeld, N.L. Influence of wastewater treatment plant discharges on microplastic concentrations in surface water. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C. Airborne microplastics: Consequences to human health? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, M.S.-L.; Hii, L.-W.; Looi, C.K.; Lim, W.-M.; Wong, S.-F.; Kok, Y.-Y.; Tan, B.-K.; Wong, C.-Y.; Leong, C.-O. Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, D.K.; Kaw, J.L.; Srivastava, S.P.; Seth, P.K. Some biochemical and histopathological changes induced by polyvinyl chloride dust in rat lung. Environ. Res. 1978, 16, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atis, S.; Tutluoglu, B.; Levent, E.; Ozturk, C.; Tunaci, A.; Sahin, K.; Saral, A.; Oktay, I.; Kanik, A.; Nemery, B. The respiratory effects of occupational polypropylene flock exposure. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 25, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, J.C.; Avila, R.; Lourenço, A.G. Respiratory disease caused by synthetic fibres: A new occupational disease. Thorax 1975, 30, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Verbeken, E.; Vanhooren, H.M.; Nemery, B.; Hoet, P.H. Pulmonary toxicity of polyvinyl chloride particles after a single intratracheal instillation in rats. Time course and comparison with silica. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 194, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ravikumar, B.; Bai, G.; Li, X.Y. Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, Y.Y.; Mak, C.W.; Liebich, C.; Lam, S.W.; Sze, E.T.P.; Chan, K.M. Microplastic pollution in the marine waters and sediments of Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colborn, T.; Dumanoski, D.; Myers, J.P. Our Stolen Future: Are We Threatening Our Fertility, Intelligence, and Survival?: A Scientific Detective Story; Penguin Group: London, UK, 1998; Volume 29, p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus, T.; Blanck, H.; Faust, M. Hazard and Risk Assessment of Chemical Mixtures Under REACH—State of the Art, Gaps and Options for Improvement; Report PM/3 2010; Swedish Chemicals Inspectorate: Sundbyberg, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cedergreen, N. Quantifying Synergy: A Systematic Review of Mixture Toxicity Studies within Environmental Toxicology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcogliese, D.J. Implications of climate change for parasitism of animals in the aquatic environment. Can. J. Zool. 2001, 79, 1331–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kültz, D. Physiological mechanisms used by fish to cope with salinity stress. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.P.; Kumar, H.D.; Smith, R.C.; Worrest, R.C. Effects on aquatic ecosystems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biol. 1998, 46, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, R. “Oxidative stress” in fish by environmental pollutants. In Fish Ecotoxicology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, G.R.; Sloman, K.A. The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: Integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, A.; Salamanca, A. Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: A review with new data for freshwater invertebrates. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wu, D.L.; Chen, M.H.; Lv, W.W.; Zhao, Y.L. Accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in juvenile Eriocheir sinensis and oxidative stress effects in the liver. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kwak, I.S. Multi-Level Gene Expression in Response to Environmental Stress in Aquatic Invertebrate Chironomids: Potential Applications in Water Quality Monitoring. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, Vol 259; DeVoogt, P., Ed.; Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer International Publishing Ag: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 259, pp. 77–122. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.D.; Jin-Clark, Y.; Begum, K.; Starkey, S.R.; Zhu, K.Y. Gene expression profiling reveals decreased expression of two hemoglobin genes associated with increased consumption of oxygen in Chironomus tentans exposed to atrazine: A possible mechanism for adapting to oxygen deficiency. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 86, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilino, M.; Sánchez-Argüello, P.; Martínez-Guitarte, J.L. Vinclozolin alters the expression of hormonal and stress genes in the midge Chironomus riparius. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 174, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arambourou, H.; Llorente, L.; Moreno-Ocio, I.; Herrero, O.; Barata, C.; Fuertes, I.; Delorme, N.; Méndez-Fernández, L.; Planelló, R. Exposure to heavy metal-contaminated sediments disrupts gene expression, lipid profile, and life history traits in the midge Chironomus riparius. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arambourou, H.; Planelló, R.; Llorente, L.; Fuertes, I.; Barata, C.; Delorme, N.; Noury, P.; Herrero, O.; Villeneuve, A.; Bonnineau, C. Chironomus riparius exposure to field-collected contaminated sediments: From subcellular effect to whole-organism response. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingersoll, C.G.; Ankley, G.T.; Burton, G.A.; Dwyer, F.J.; Hoke, R.A.; Norberg-King, T.J.; Winger, P.V. Methods for Measuring the Toxicity and Bioaccumulation of Sediment-Associated Contaminants with Freshwater Invertebrates; EPA/600/R-94-024; Environmental Protection Agency: Duluth, MN, USA, 1994.
- OECD. Test No. 218: Sediment-Water Chironomid Toxicity Using Spiked Sediment, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pesta, B.; Fuerst, J.; Kirkegaard, E.O.W. Bibliometric Keyword Analysis across Seventeen Years (2000–2016) of Intelligence Articles. J. Intell. 2018, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejasen, C. Historical bibliometric analysis: A case of the journal of the siam society, 1972–1976. Proc. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigano, L.; Schmitz, M.; Hollert, H.; Linnemann, V.; Krauss, M.; Pfenninger, M. Mind your tyres: The ecotoxicological impact of urban sediments on an aquatic organism. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.J.; Martínez-Guitarte, J.L.; Dias, M.A.; Montagner, C.C.; Espindola, E.L.; Muñiz-González, A.B. New insights about the toxicity of 2,4-D: Gene expression analysis reveals modulation on several subcellular responses in Chironomus riparius. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 204, 106088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbenschlag, S.; Pietz, S.; Roder, N.; Schwenk, K.; Bundschuh, M. Phenotypic adaptation of Chironomus riparius to chronic Bti exposure: Effects on emergence time and nutrient content. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 273, 107013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria, H.B.; Wagner, V.; Foucault, Q.; Pfenninger, M. Unveiling population-specific outcomes: Examining life cycle traits of different strains of Chironomus riparius exposed to microplastics and cadmium questions generality of ecotoxicological results. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfrin, A.; Mazacotte, G.; Spaak, J.W.; Osakpolor, S.E.; Brühl, C.A.; Lencioni, V.; Kolbenschlag, S.; Schäfer, R.B.; Bundschuh, M.; Schulz, R. Modeling cumulative effects of acute exposure to toxicants on the life cycle of Chironomidae using Bti as a case study. Ecol. Model. 2024, 494, 110768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, D.N.; Pestana, J.L.T.; Silva, A.R.R.; Campos, D.; Soares, A.; Wrona, F.J.; Loureiro, S. Effects of naturally sourced bitumen samples from Alberta oil sands region (Canada) on aquatic benthic invertebrates: A case study with Chironomus riparius. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 942, 173496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.J.; Dong, W.Y.; Yu, X.H.; Zuo, Z.Q.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Z.L.; Jiang, J.H.; Zhang, X.Y. Enhanced multi-metals stabilization: Synergistic insights from hydroxyapatite and peroxide dosing strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.Y.; Zhu, P.F.; Wang, C.Q.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, M.; Pan, X.L. Nanoscale exopolymer reassembly-trap mechanism determines contrasting PFOS exposure patterns in aquatic animals with different feeding habitats: A nano-visualization study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohrabi, H.; Chamani, A.; Zamanpoore, M.; Tavabe, K.R. Exploring the interplay between water quality parameters and aquatic fauna in a human-dominated stream network in Iran. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, L.; Pirola, N.; Schiavon, A.; Rossaro, B. Response of Chironomidae (Diptera) to DDT, Mercury, and Arsenic Legacy Pollution in Sediments of the Toce River (Northern Italy). Insects 2024, 15, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, T.G.; Kim, J.W.; Cheon, S.P.; Kim, H.G.; Yu, T.S.; Kwak, I.S. Analysis of environmental factors in sediment based on benthic macroinvertebrates in streams, Korea. Entomol. Res. 2023, 53, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, I.; Moir, K.E.; Ridal, J.J.; Cumming, B.F. Subfossil Chironomid Assemblages as Indicators of Remedial Efficacy in the Historically Contaminated St. Lawrence River at Cornwall, Ontario. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 85, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayaturrahman, H.; Kwon, H.J.; Bao, Y.M.; Peera, S.G.; Lee, T.G. Assessing the Efficacy of Coagulation (Al3+) and Chlorination in Water Treatment Plant Processes: Inactivating Chironomid Larvae for Improved Tap Water Quality. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, F.F.; Melo, D.B.D.; Dolbeth, M.; Molozzi, J. Functional threshold responses of benthic macroinvertebrates to environmental stressors in reservoirs. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 116970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, H.Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Hu, H.; Yuan, B.Y.; You, J. Quantitative differentiation of toxicity contributions and predicted global risk of fipronil and its transformation products to aquatic invertebrates. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupe-Flores, B.; Mendes, M.; Phillips, I.; Panigrahi, B.; Liu, X.; Liber, K. Effects of diluted effluent on aquatic macroinvertebrate communities at the McClean Lake uranium operation in northern Saskatchewan. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, S.M.; Backe, W.J.; Erickson, R.J.; Hockett, J.R.; Howe, S.E.; Mundy, I.D.; Piasecki, E.; Sluka, H.; Votava, L.K.; Mount, D.R. Sublethal Toxicity of 17 Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances with Diverse Structures to Ceriodaphnia dubia, Hyalella azteca, and Chironomus dilutus. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, T.; Kabler, K.; Dreier, D.; Henry, K.; Jones, A.; McCoole, M.; Cafarella, M.; Collins, J.; Bradley, M.; Samel, A.; et al. Evaluating the Functional Equivalency of Test Organism Performance in Negative and Solvent Controls During Chronic Sediment Ecotoxicity Studies Based on US Environmental Protection Agency Guidance. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 43, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikins, D.M.; Mehler, W.T.; Veilleux, H.D.; Zhang, Y.F.; Goss, G.G. The Acute and Chronic Effects of a Sediment-Bound Synthetic Musk, Galaxolide, on Hyalella azteca, Chironomus dilutus, and Lumbriculus variegatus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 84, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wallace, S.M.; Kroll, K.J.; Denslow, N.D.; Gaillard, J.F.; Meyer, P.; Bonzongo, J.C.J. Acute and Chronic Toxicity Testing of Drinking Water Treatment Residuals in Freshwater Systems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, L.J.; Fan, D.L.; Wang, Z.; Gu, W.; Shi, L.L.; Liu, J.N.; Yang, J.X. Bisphenol P activates hormonal genes and introduces developmental outcomes in Chironomus tentans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.N.; Ji, G.X.; Shi, L.L.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.X. Deriving the freshwater quality criteria of BPA, BPF and BPAF for protecting aquatic life. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic-Zdravkovic, D.; Jovanovic, B.; Durdevic, A.; Stojkovie-Piperac, M.; Savic, A.; Vidmar, J.; Milosevic, D. An environmentally relevant concentration of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles induces morphological changes in the mouthparts of Chironomus tentans. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, K.; Merritt, R. An Introduction to The Aquatic Insects of North America. J. Anim. Ecol. 1996, 15, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietz, S.; Kainz, M.J.; Schröder, H.; Manfrin, A.; Schäfer, R.B.; Zubrod, J.P.; Bundschuh, M. Metal Exposure and Sex Shape the Fatty Acid Profile of Midges and Reduce the Aquatic Subsidy to Terrestrial Food Webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanders, J.R.; Long, G.; Reese, B.; Grosso, N.R.; Clements, W.; Stahl, R.G. Assessment of potential mercury toxicity to native invertebrates in a high-gradient stream. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2019, 15, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignati, D.A.L.; Bettinetti, R.; Boggero, A.; Valsecchi, S. Testing the Use of Standardized Laboratory Tests to Infer Hg Bioaccumulation in Indigenous Benthic Organisms of Lake Maggiore (NW Italy). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kwak, I.S. Cadmium-induced developmental alteration and upregulation of serine-type endopeptidase transcripts in wild freshwater populations of Chironomus plumosus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria, H.B.; Hannappel, P.; Pfenninger, M. Whole genome sequencing and RNA-seq evaluation allowed to detect Cd adaptation footprint in Chironomus riparius. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sprang, P.A.; Nys, C.; Blust, R.J.P.; Chowdhury, J.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Janssen, C.J.; De Schamphelaerez, K.A.C. The Derivation of Effects Threshold Concentrations of Lead for European Freshwater Ecosystems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailova, P.; Ilkova, J.; Petrova, N.; White, K. Rearrangements in the salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae) following exposure to lead. Caryologia 2001, 54, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.M.; Tull, D.L.; Jeppe, K.J.; De Souza, D.P.; Dayalan, S.; Pettigrove, V.J.; McConville, M.J.; Hoffmann, A.A. A multi-platform metabolomics approach demonstrates changes in energy metabolism and the transsulfuration pathway in Chironomus tepperi following exposure to zinc. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 162, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, V.; Pettigrove, V.J.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Golding, L.A. Effects of Lumbriculus variegatus (Annelida, Oligochaete) bioturbation on zinc sediment chemistry and toxicity to the epi-benthic invertebrate Chironomus tepperi (Diptera: Chironomidae). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byns, C.; Groffen, T.; Bervoets, L. Aquatic macroinvertebrate community responses to pollution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): Can we define threshold body burdens? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Courtene-Jones, W.; Boucher, J.; Pahl, S.; Raubenheimer, K.; Koelmans, A.A. Twenty years of microplastic pollution research-what have we learned? Science 2024, 386, eadl2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme(UNEP). Revised Draft Text of the International Legally Binding Instrument on Plastic Pollution, Including in the Marine Environment; United Nations Environment Programme(UNEP): Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, J.; Classen, S.; Gerth, D.; Dallmann, N.; Strauss, T.; Vaugeois, M.; Galic, N. Modeling temperature-dependent life-cycle toxicity of thiamethoxam in Chironomus riparius using a DEB-TKTD model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.S.; Ribeiro, F.; Rotili, E.A.; Venega, R.D.; Dornelas, A.S.P.; Soares, A.; Gravato, C.; Sarmento, R.A. Is Actara® a less toxic neonicotinoid formulation? A multigenerational study using the non-target organism Chironomus xanthus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 93779–93785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, R.S.; Ribeiro, F.; Dornelas, A.S.P.; Saraiva, A.D.; Soares, A.; Sarmento, R.A.; Gravato, C. What does not kill it makes it stronger! The tolerance of the F1 larvae of Chironomus xanthus to a neonicotinoid insecticide formulation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 250, 114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, T.J.D.; Martínez-Guitarte, J.L.; Dias, M.A.; Montagner, C.C.; Espindola, E.L.G.; Muñíz-González, A.B. Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of the Insecticide Fipronil Modulated Molecular Response in Chironomus riparius. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.M.; Burdett, A.S.; Mudford, E.M.; Helliwell, S.; Doran, G. The acute toxicity of fipronil to two non-target invertebrates associated with mosquito breeding sites in Australia. Acta Trop. 2011, 117, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Kwak, I.S. Biological and molecular responses of Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae) to herbicide 2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 151, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, I.B.F.; Duarte-Neto, P.J.; Sorigotto, L.R.; Yoshii, M.P.C.; Lopes, L.F.D.; Pereira, M.M.D.; Girotto, L.; Athayde, D.B.; Goulart, B.V.; Montagner, C.C.; et al. Effects of pasture intensification and sugarcane cultivation on non-target species: A realistic evaluation in pesticide-contaminated mesocosms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Cui, Z.X.; Yang, T.Y.; Sun, L.L.; Cao, C.W. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase is involved in susceptibility of Chironomus kiiensis Tokunaga, 1936 (Diptera: Chironomidae) to insecticides. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, W.; Josefsson, S.; Örberg, J.; Johansson, F. Combination effects of pyrethroids and neonicotinoids on development and survival of Chironomus riparius. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Liu, W.B.; Peng, Y.Y.; Meng, L.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Pan, Y.H.; Wang, D.Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yan, C.C. Genome-wide analyses of Glutathione S-transferase gene family and expression profiling under deltamethrin exposure in non-biting midge Propsilocerus akamusi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D-Genom. Proteom. 2023, 46, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.X.; Taylor, K.J.; Potito, A.P.; Molloy, K.; Beilman, D.W.; Tang, Y. Ecological impacts of N-deposition in a remote, high-elevation lake in the Three River Headwaters Region, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Paleolimnol. 2023, 69, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, S.D.; Liber, K.; Palace, V.; Hecker, M.; Doig, L.E.; Janz, D.M. Trophic dynamics of selenium in a boreal lake food web. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, S.D.; Liber, K.; Palace, V.; Hecker, M.; Doig, L.E.; Janz, D.M. Effects of selenium on benthic macroinvertebrates and fathead minnow (Pimephales promela) in a boreal lake ecosystem. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, S.D.; Liber, K.; Palace, V.; Hecker, M.; Doig, L.E.; Janz, D.M. Distribution of experimentally added selenium in a boreal lake ecosystem. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 1954–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.S.; Ali, A.; Zuck, C.; Uy, L.; Morris, J.G.M.; Wong, A.C.N. Vibrio cholerae Invasion Dynamics of the Chironomid Host Are Strongly Influenced by Aquatic Cell Density and Can Vary by Strain. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02652-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, N.M.; El-Shatoury, S.A.; Hanora, A.; Ahmed, R.S. Isolating non-O1/non-O39 Vibrio cholerae from Chironomus transvaalensis larvae and exuviae collected from polluted areas in Lake Manzala, Egypt. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, N.; Danin-Poleg, Y.; Broza, Y.Y.; Arakawa, E.; Ramakrishna, B.S.; Broza, M.; Kashi, Y. Environmental monitoring of Vibrio cholerae using chironomids in India. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broza, M.; Gancz, H.; Halpern, M.; Kashi, Y. Adult non-biting midges: Possible windborne carriers of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 non-O139. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röder, N.; Stoll, V.S.; Jupke, J.F.; Kolbenschlag, S.; Bundschuh, M.; Theissinger, K.; Schwenk, K. How non-target chironomid communities respond to mosquito control: Integrating DNA metabarcoding and joint species distribution modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstle, V.; Manfrin, A.; Kolbenschlag, S.; Gerken, M.; Ul Islam, A.; Entling, M.H.; Bundschuh, M.; Brühl, C.A. Benthic macroinvertebrate community shifts based on Bti-induced chironomid reduction also decrease Odonata emergence. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theissinger, K.; Roeder, N.; Allgeier, S.; Beermann, A.J.; Bruehl, C.A.; Friedrich, A.; Michiels, S.; Schwenk, K. Mosquito control actions affect chironomid diversity in temporary wetlands of the Upper Rhine Valley. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 4300–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-González, A.B.; Martínez-Guitarte, J.L.; Lencioni, V. Impact of Global Warming on Kryal Fauna: Thermal Tolerance Response of Diamesa steinboecki (Goetghebuer, 1933; Chironomidae). Diversity 2023, 15, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Folgar, R.; de la Fuente, M.; Morcillo, G.; Martínez-Guitarte, J.L. Characterization of six small HSP genes from Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae): Differential expression under conditions of normal growth and heat-induced stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A-Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 188, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, T.R.; Walker, I.R. Midge (Diptera: Chironomidae and Ceratopogonidae) emergence responses to temperature: Experiments to assess midges’ capacity as paleotemperature indicators. J. Paleolimnol. 2015, 53, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Goto, S.G. Thermal responses of the embryos and early instar larvae of the Antarctic midge Belgica antarctica (Insecta: Diptera). Polar Biol. 2023, 46, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, O.M.; Gantz, J.D.; Finch, G.; Lee, R.E.; Denlinger, D.L.; Benoit, J.B. Rapid stress hardening in the Antarctic midge improves male fertility by increasing courtship success and preventing decline of accessory gland proteins following cold exposure. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb242506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teets, N.M.; Kawarasaki, Y.; Lee, R.E.; Denlinger, D.L. Expression of genes involved in energy mobilization and osmoprotectant synthesis during thermal and dehydration stress in the Antarctic midge, Belgica antarctica. J. Comp. Physiol. B-Biochem. Syst. Environ. Physiol. 2013, 183, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabova, A.; Mukae, K.; Cherkasov, A.; Cornette, R.; Shagimardanova, E.; Sakashita, T.; Okuda, T.; Kikawada, T.; Gusev, O. Genetic background of enhanced radioresistance in an anhydrobiotic insect: Transcriptional response to ionizing radiations and desiccation. Extremophiles 2017, 21, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Gordillo, S.; González, A.L.; Kersch-Becker, M.F.; Moretti, M.S.; Moi, D.A.; Aidar, M.P.M.; Romero, G.Q. Warming and shifts in litter quality drive multiple responses in freshwater detritivore communities. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, O.; Nakahara, Y.; Vanyagina, V.; Malutina, L.; Cornette, R.; Sakashita, T.; Hamada, N.; Kikawada, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Okuda, T. Anhydrobiosis-Associated Nuclear DNA Damage and Repair in the Sleeping Chironomid: Linkage with Radioresistance. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Yi, X.Y.; Chen, F.; Tong, Y.J.; Mehler, W.T.; You, J. Identifying Organic Toxicants in Sediment Using Effect-Directed Analysis: A Combination of Bioaccessibility-Based Extraction and High-Throughput Midge Toxicity Testing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidian, A.H.; Zareh, M.; Poorbagher, H.; Vaziri, L.; Ashrafi, S. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in sediment, common reed, algae, and blood worm from the Shoor river, Iran. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.B.; Wallis, L.K.; Diamond, S.A.; Ma, H.B.; Hoff, D.J. Species Sensitivity and Dependenceon Exposure Conditions Impacting the Phototoxicity of Tio2 Nanoparticles to Benthic Organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, S.; Shannon, A.; Gruber, B.; Rackl, S.M.; Lucy, F.E. Ecotoxicological impact of Zequanox®, a novel biocide, on selected non-target Irish aquatic species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 107, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shami, S.A.; Salmah, M.R.C.; Hassan, A.A.; Azizah, M.N.S. Fluctuating Asymmetry of Chironomus spp. (Diptera: Chironomidae) Larvae in Association with Water Quality and Metal Pollution in Permatang Rawa River in the Juru River Basin, Penang, Malaysia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, J.C.; Lu, Y.C. Response of Propsilocerus akamusi (Diptera: Chironomidae) to the leachates from AMD-contaminated sediments: Implications for metal bioremediation of AMD-polluted areas. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 266, 106795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, V.; Grazioli, V.; Rossaro, B.; Bernabò, P. Transcriptional profiling induced by pesticides employed in organic agriculture in a wild population of Chironomus riparius under laboratory conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailova, P.; Sella, G.; Petrova, N. Chironomids (Diptera) and their salivary gland chromosomes as indicators of trace-metal genotoxicity. Ital. J. Zool. 2012, 79, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailova, P.; Warchalowska-Sliwa, E.; Szarek-Gwiazda, E.; Kownacki, A. Does biodiversity of macroinvertebrates and genome response of Chironomidae larvae (Diptera) reflect heavy metal pollution in a small pond? Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrankovic, J.; Bozanic, M.; Zivic, M.; Markovic, Z.; Marjanovic, S.; Golubovic, V.; Zivic, I. Antioxidant biomarker profile of chironomid larvae from carp ponds: Evaluation of the effects of different fish feeding patterns. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Herrero-Nogareda, L.; Cedergreen, N. A comparative study of acetylcholinesterase and general-esterase activity assays using different substrates, in vitro and in vivo exposures and model organisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebechi-Baggio, D.; Richardi, V.S.; Vicentini, M.; Guiloski, I.C.; de Assis, H.C.S.; Navarro-Silva, M.A. Factors that alter the biochemical biomarkers of environmental contamination in Chironomus sancticaroli (Diptera, Chironomidae). Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2016, 60, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.W.; Li, X.P.; Ge, S.L.; Sun, L.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Enzymatic activities as potential stress biomarkers of two substituted benzene compounds in Propsilocerus akamusi (Diptera: Chironomidae). Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 37, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J. Sinks and sources: Assessing microplastic abundance in river sediment and deposit feeders in an Austral temperate urban river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, S.B.; Park, C.H.; Choi, J. Expression of heat shock protein and hemoglobin genes in Chironomus tentans (Diptera, chironomidae) larvae exposed to various environmental pollutants: A potential biomarker of freshwater monitoring. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
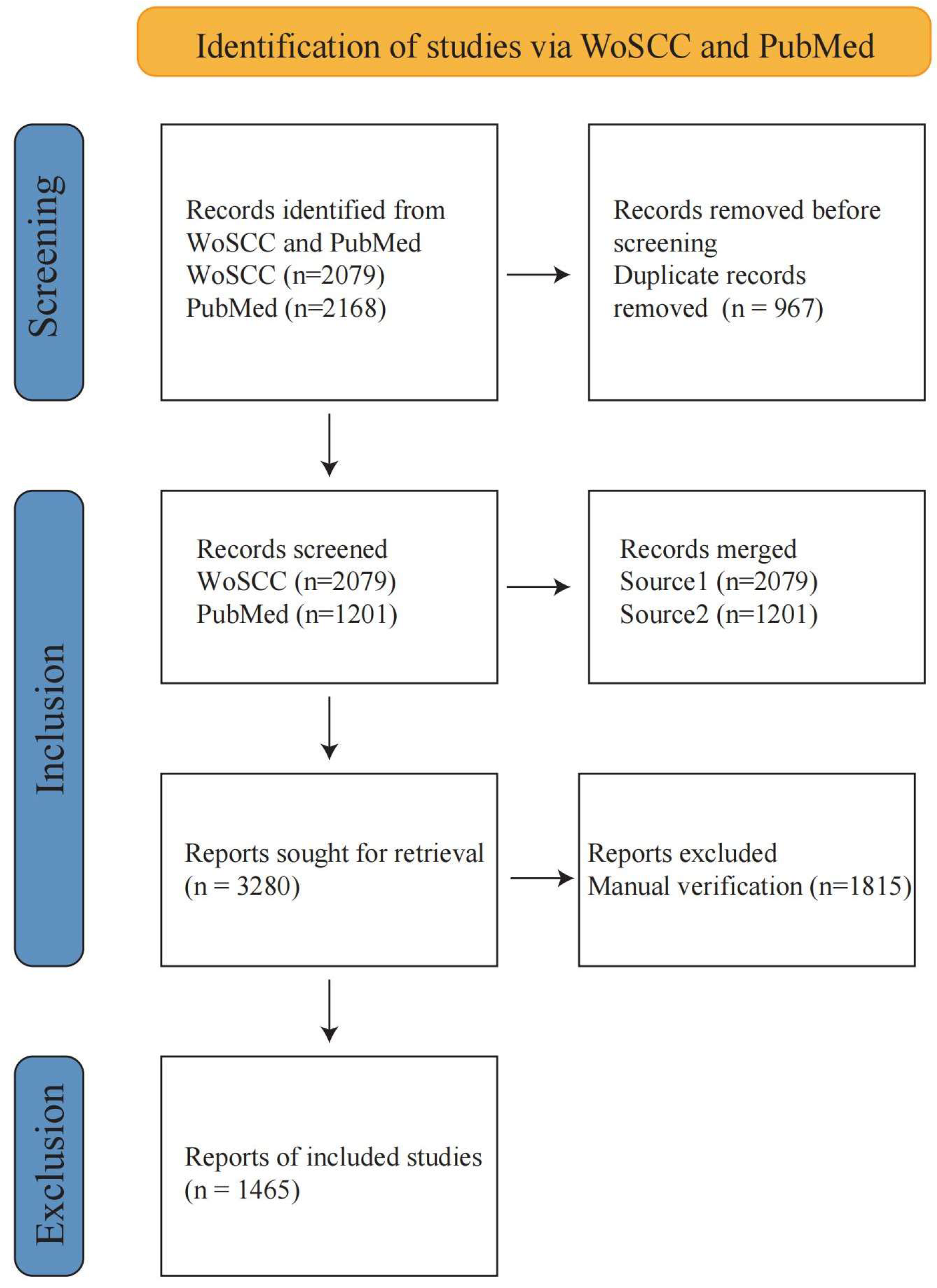
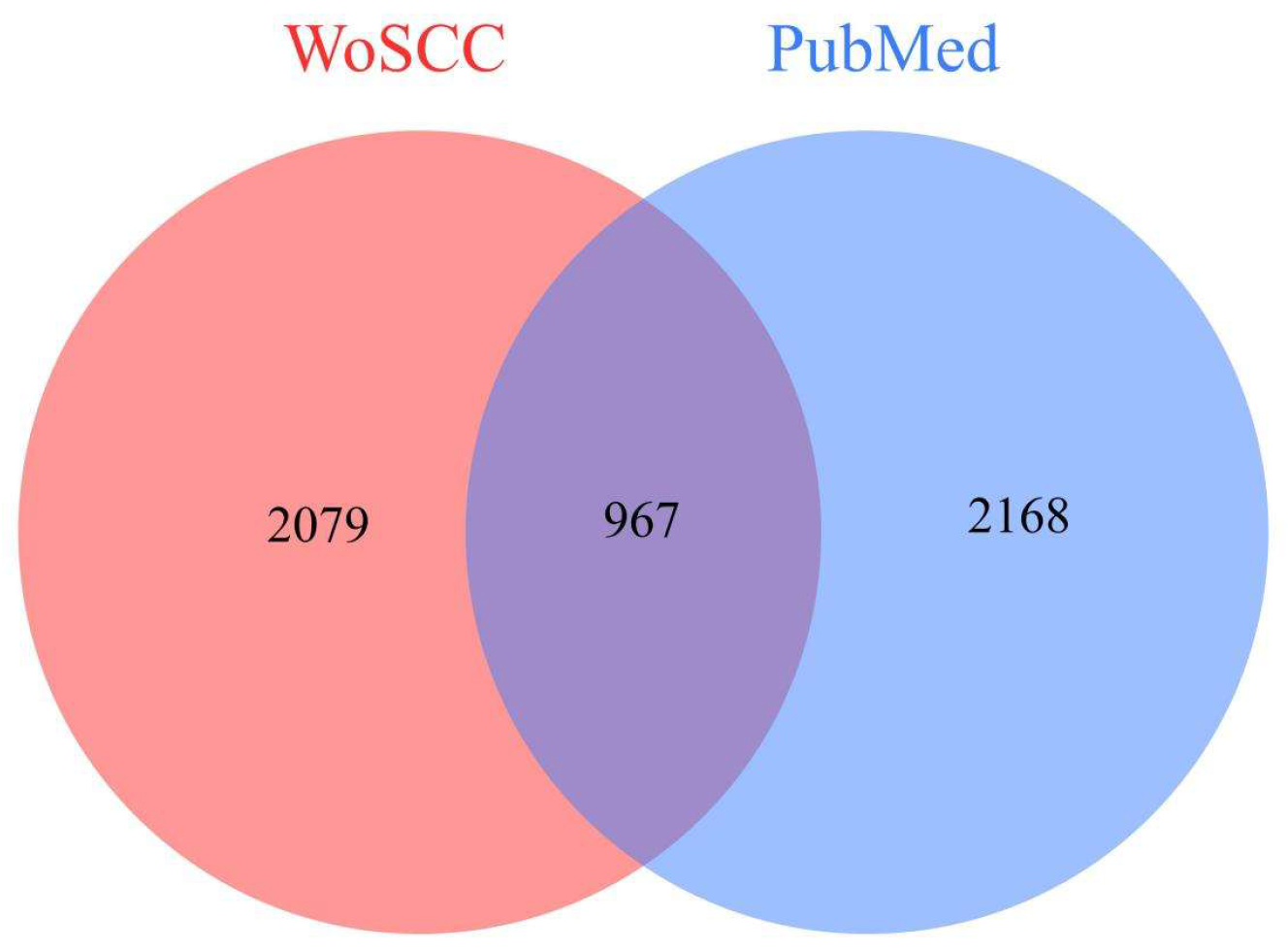

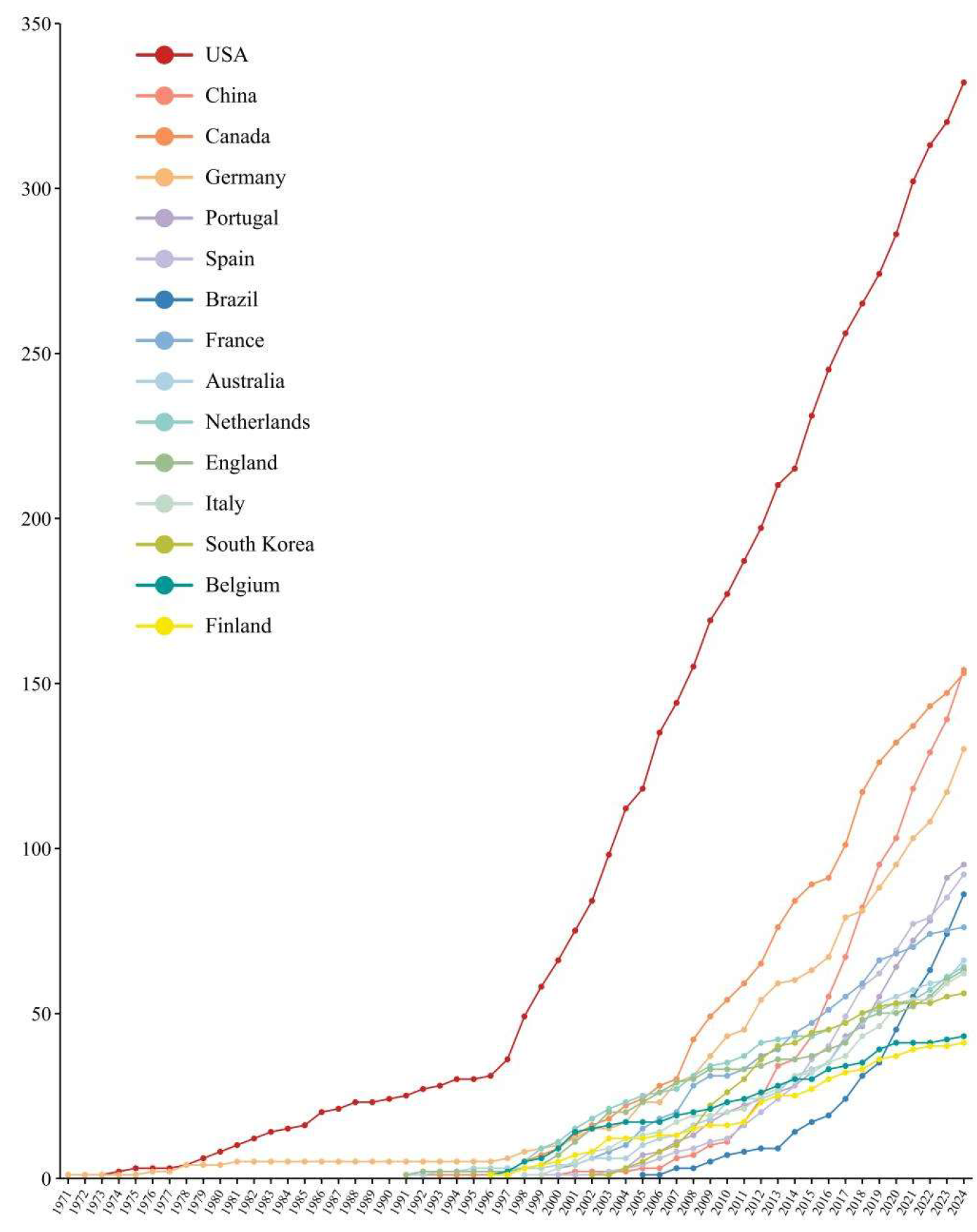

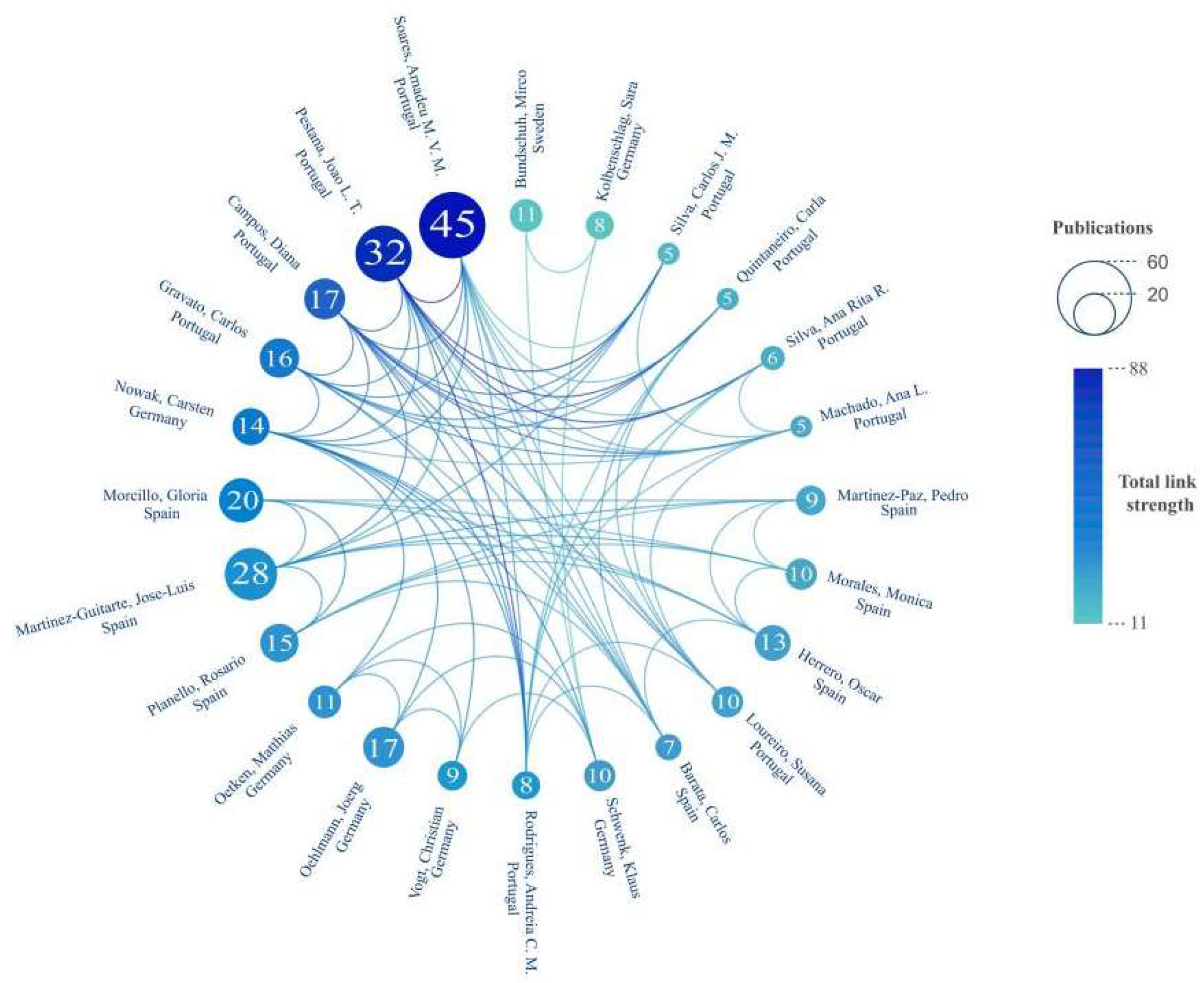
| Rank | Journal | Publisher | Publications | Citations | CPP | h-Index | IF | JIF Quartile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry | WILEY | 183 | 5558 | 30.37 | 41 | 3.6 | Q2 |
| 2 | Science of The Total Environment | ELSEVIER | 127 | 3379 | 26.61 | 33 | 8.2 | Q1 |
| 3 | Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety | ACADEMIC PRESS INC ELSEVIER SCIENCE | 111 | 2631 | 23.70 | 29 | 6.2 | Q1 |
| 4 | Environmental Pollution | ELSEVIER SCI LTD | 99 | 3142 | 31.74 | 33 | 7.6 | Q1 |
| 5 | Chemosphere | PERGAMON-ELSEVIER SCIENCE LTD | 79 | 2528 | 32.00 | 32 | 8.1 | Q1 |
| 6 | Archives of Environmental Contamination And Toxicology | SPRINGER | 68 | 1975 | 29.04 | 25 | 3.7 | Q2 |
| 7 | Aquatic Toxicology | ELSEVIER | 58 | 1632 | 28.14 | 25 | 4.1 | Q1 |
| 8 | Environmental Science & Technology | AMER CHEMICAL SOC | 51 | 1954 | 38.31 | 25 | 10.9 | Q1 |
| 9 | Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology | SPRINGER | 42 | 690 | 16.43 | 16 | 2.7 | Q3 |
| 10 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | SPRINGER HEIDELBERG | 35 | 520 | 14.86 | 14 | 5.8 | Q1 |
| 11 | Ecotoxicology | SPRINGER | 32 | 628 | 19.63 | 14 | 2.5 | Q3 |
| 12 | Environmental Monitoring and Assessment | SPRINGER | 21 | 279 | 13.29 | 12 | 2.9 | Q3 |
| 13 | Journal of Hazardous Materials | ELSEVIER | 19 | 333 | 17.53 | 10 | 12.2 | Q1 |
| 14 | Water Research | PERGAMON-ELSEVIER SCIENCE LTD | 18 | 464 | 25.78 | 13 | 11.5 | Q1 |
| 15 | Water Air and Soil Pollution | SPRINGER INT PUBL AG | 18 | 260 | 14.44 | 10 | 3.8 | Q3 |
| Rank | Country | Publications | Citations | CPP | H Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 331 | 9618 | 29.06 | 57 |
| 2 | China | 154 | 3009 | 19.54 | 31 |
| 3 | Canada | 153 | 4045 | 26.44 | 37 |
| 4 | Germany | 130 | 3463 | 26.64 | 37 |
| 5 | Portugal | 95 | 1875 | 19.74 | 27 |
| 6 | Spain | 92 | 2865 | 31.14 | 37 |
| 7 | Brazil | 86 | 1062 | 12.35 | 18 |
| 8 | France | 76 | 1815 | 23.88 | 28 |
| 9 | Australia | 66 | 1493 | 22.62 | 22 |
| 10 | Netherlands | 64 | 1811 | 28.30 | 27 |
| 11 | England | 63 | 1582 | 25.11 | 27 |
| 12 | Italy | 62 | 1331 | 21.47 | 26 |
| 13 | Republic of Korea | 56 | 1767 | 31.55 | 26 |
| 14 | Belgium | 43 | 1355 | 31.51 | 26 |
| 15 | Finland | 40 | 805 | 20.13 | 19 |
| Rank | Authors | Country | Institution | Publications | Citations | CPP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Soares, Amadeu M. V. M | Portugal | Universidade de Aveiro | 45 | 1076 | 23.91 |
| 2 | Pestana, Joao L. T. | Portugal | Universidade de Aveiro | 32 | 879 | 27.47 |
| 3 | You, Jing | China | Jinan University | 29 | 761 | 26.24 |
| 4 | Choi, Jinhee | Republic of Korea | University of Seoul | 28 | 1223 | 43.68 |
| 5 | Martinez-Guitarte, Jose-Luis | Spain | Universidad Nacional de Educacion a Distancia | 28 | 1001 | 35.75 |
| 6 | Liber, Karsten | Canada | University of Saskatchewan | 28 | 843 | 30.11 |
| 7 | Pettigrove, Vincent | Australia | University of Melbourne | 25 | 477 | 19.08 |
| 8 | Lydy, Michael J. | USA | Southern Illinois University | 22 | 1005 | 45.68 |
| 9 | Morcillo, Gloria | Spain | Universidad Nacional de Educacion a Distancia | 20 | 955 | 47.75 |
| 10 | Campos, Diana | Portugal | Universidade de Aveiro | 17 | 393 | 23.12 |
| 11 | Li, Huizhen | China | Jinan University | 17 | 320 | 18.82 |
| 12 | Oehlmann, Joerg | Germany | Goethe University Frankfurt | 17 | 499 | 29.35 |
| 13 | Gravato, Carlos | Portugal | Universidade de Aveiro | 16 | 526 | 32.88 |
| 14 | Planello, Rosario | Spain | Universidad Nacional de Educacion a Distancia | 15 | 549 | 36.60 |
| Rank | Publication | First Address Country | Other Participating Countries | First Address Participating Institutions | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sinks and sources: Assessing microplastic abundance in river sediment and deposit feeders in an Austral temperate urban river system | South Africa | Malaysia | Rhodes University | 343 |
| 2 | Feeding type and development drive the ingestion of microplastics by freshwater invertebrates | Germany | Norway | Goethe University Frankfurt | 300 |
| 3 | Distribution and toxicity of sediment-associated pesticides in agriculture-dominated water bodies of California’s Central Valley | USA | N/A | University of California System | 254 |
| 4 | Environmentally relevant concentrations of polyethylene microplastics negatively impact the survival, growth and emergence of sediment-dwelling invertebrates | Australia | N/A | Griffith University | 214 |
| 5 | Waterborne and sediment toxicity of fluoxetine to select organisms | USA | N/A | Baylor University | 188 |
| 6 | Fluctuating asymmetry of invertebrate populations as a biological indicator of environmental quality. | Australia | N/A | CSIRO Division of Entomology | 181 |
| 7 | Anthropogenic impacts on the distribution and biodiversity of benthic macroinvertebrates and water quality of the Langat River, Peninsular Malaysia | Malaysia | N/A | Universiti Putra Malaysia | 176 |
| 8 | Partitioning, bioavailability, and toxicity of the pyrethroid insecticide cypermethrin in sediments | England | N/A | Syngenta | 174 |
| 9 | Mechanism allowing an insect to survive complete dehydration and extreme temperatures | Japan | N/A | National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences-Japan | 167 |
| 10 | Impact of atrazine on organophosphate insecticide toxicity | USA | N/A | Wichita State University | 159 |
| 11 | Expression of heat shock protein and hemoglobin genes in Chironomus tentans (Diptera, Chironomidae) larvae exposed to various environmental pollutants: A potential biomarker of freshwater monitoring | Republic of Korea | N/A | University of Seoul | 152 |
| 12 | Effectiveness of a constructed wetland for retention of nonpoint-source pesticide pollution in the Lourens River catchment, South Africa | South Africa | N/A | Stellenbosch University | 145 |
| 13 | Temperature as a toxicity identification evaluation tool for pyrethroid | USA | China | Southern Illinois University System | 144 |
| 14 | Effects of mining activities on heavy metal concentrations in water, sediment, and macroinvertebrates in different reaches of the Pilcomayo River, South America | Netherlands | Bolivia | Radboud University Nijmegen | 143 |
| 15 | Bridging levels of pharmaceuticals in river water with biological community structure in the Llobregat river basin (Northeast Spain) | Spain | N/A | University of Barcelona | 143 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.-B.; Pei, W.-X.; Shao, Z.-M.; Nie, J.-X.; Cao, W.; Yan, C.-C. Trends and Emerging Hotspots in Toxicology of Chironomids: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Analysis. Insects 2025, 16, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060639
Liu W-B, Pei W-X, Shao Z-M, Nie J-X, Cao W, Yan C-C. Trends and Emerging Hotspots in Toxicology of Chironomids: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Analysis. Insects. 2025; 16(6):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wen-Bin, Wen-Xuan Pei, Zi-Ming Shao, Jia-Xin Nie, Wei Cao, and Chun-Cai Yan. 2025. "Trends and Emerging Hotspots in Toxicology of Chironomids: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Analysis" Insects 16, no. 6: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060639
APA StyleLiu, W.-B., Pei, W.-X., Shao, Z.-M., Nie, J.-X., Cao, W., & Yan, C.-C. (2025). Trends and Emerging Hotspots in Toxicology of Chironomids: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Analysis. Insects, 16(6), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060639





