Transcriptome-Wide Identification of Neuropeptides and Neuropeptide Receptors in the Twenty-Eight-Spotted Ladybird Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing and Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Sequencing
2.3. Exploration of the Neuropeptides and Their Putative G Protein-Coupled Receptors
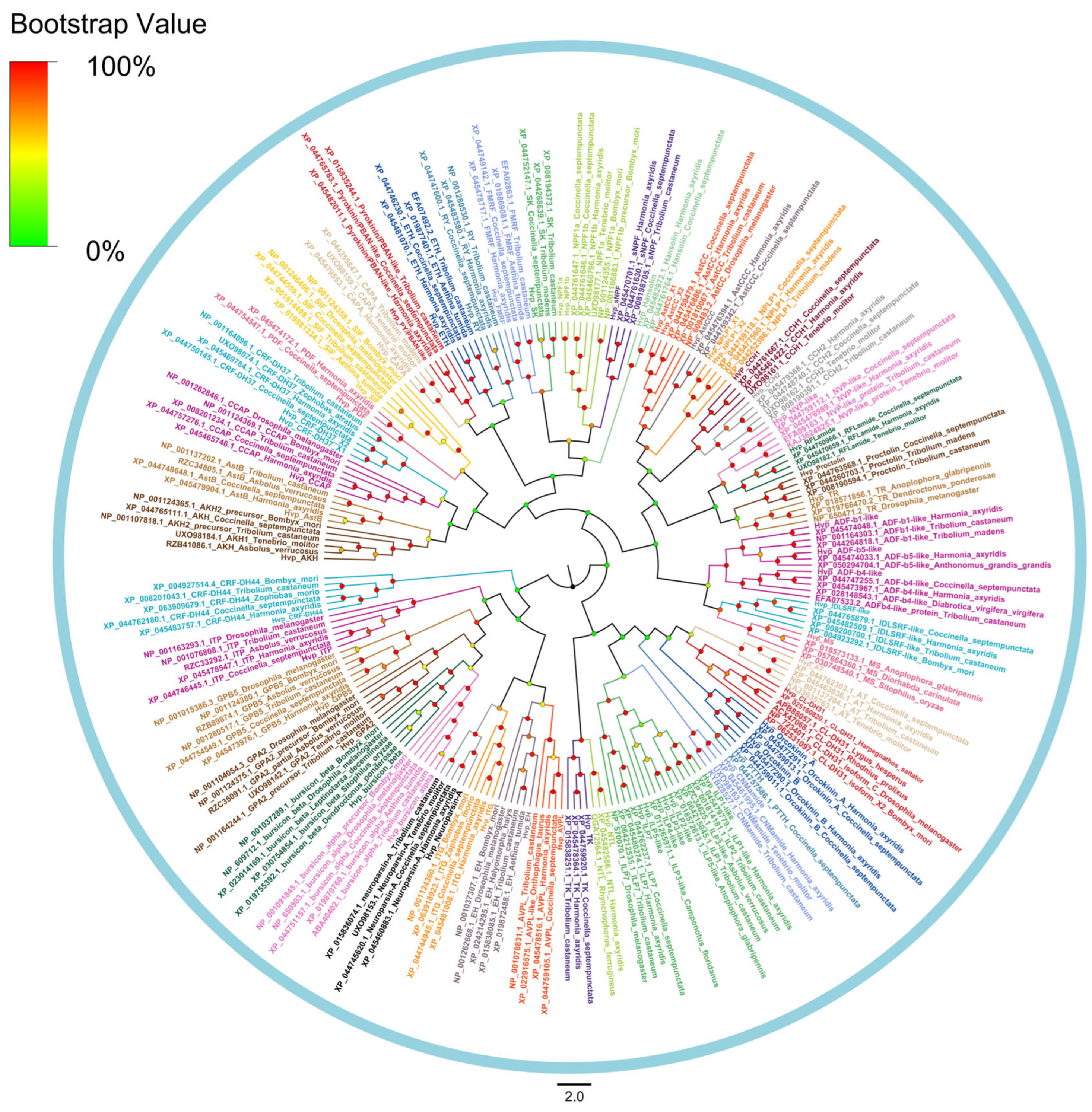
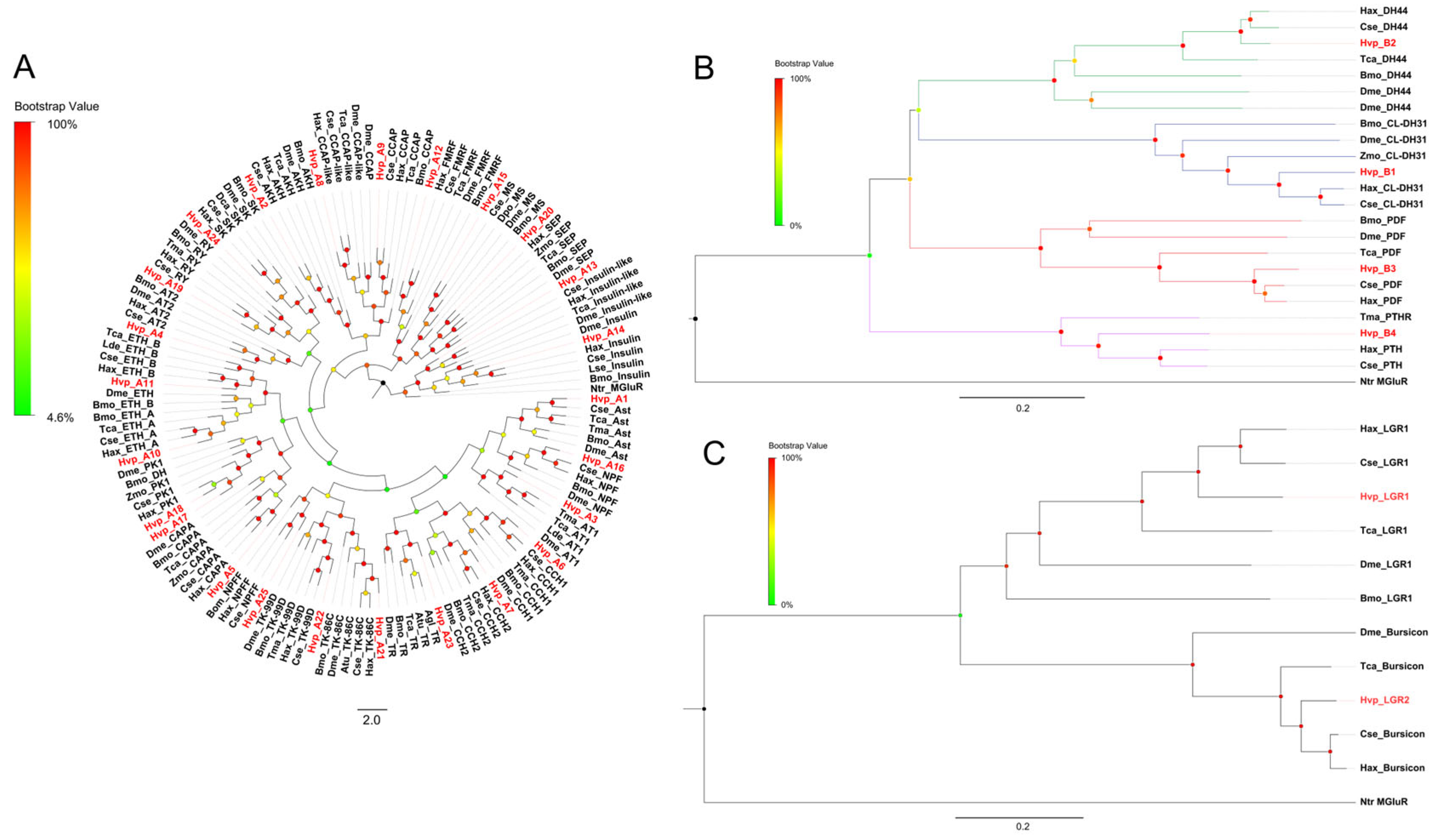
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Spatial Expression
2.6. Statistical Analysis
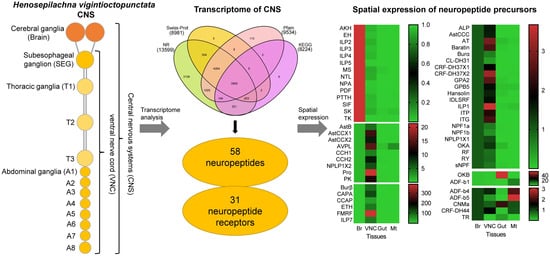
3. Results
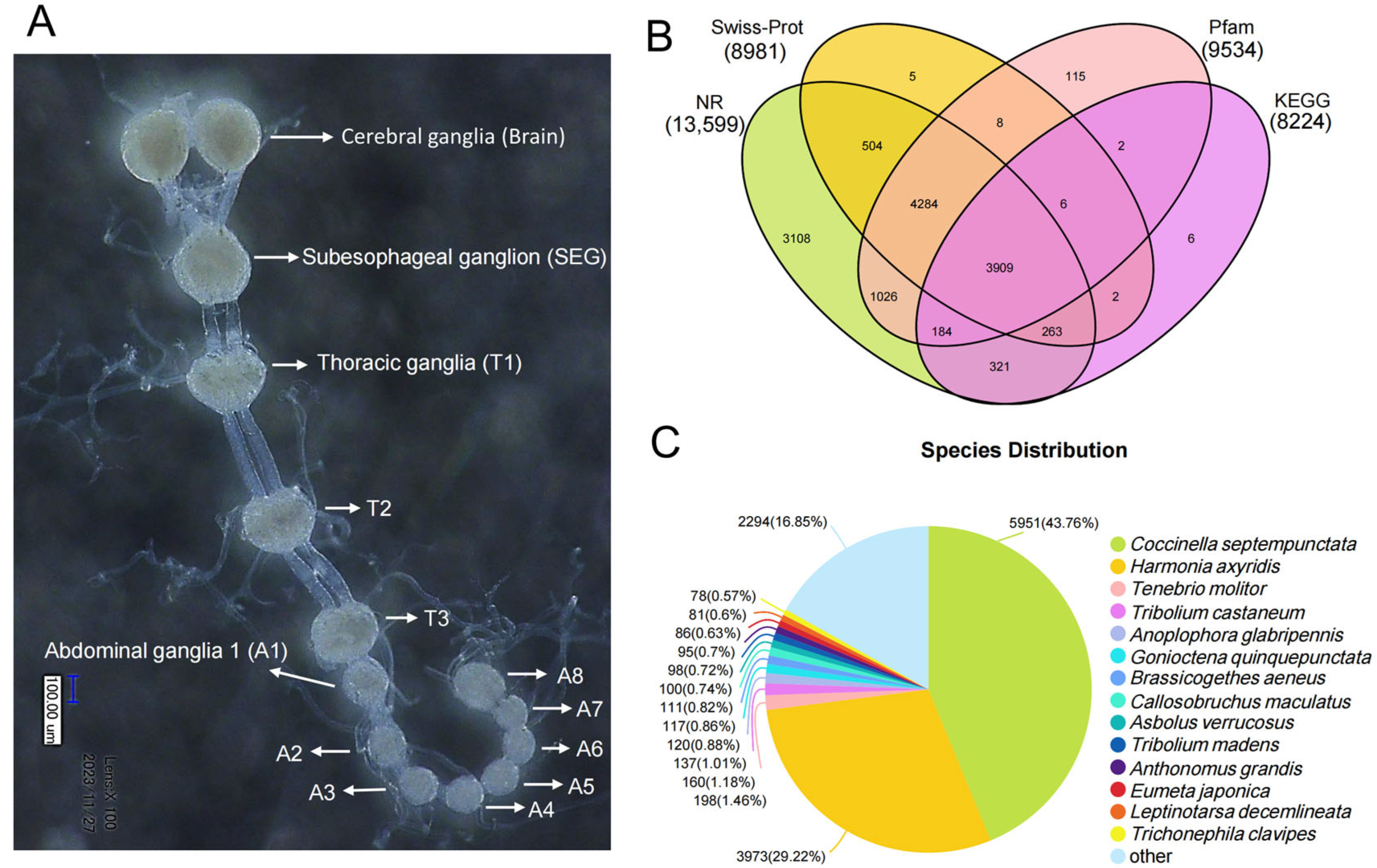
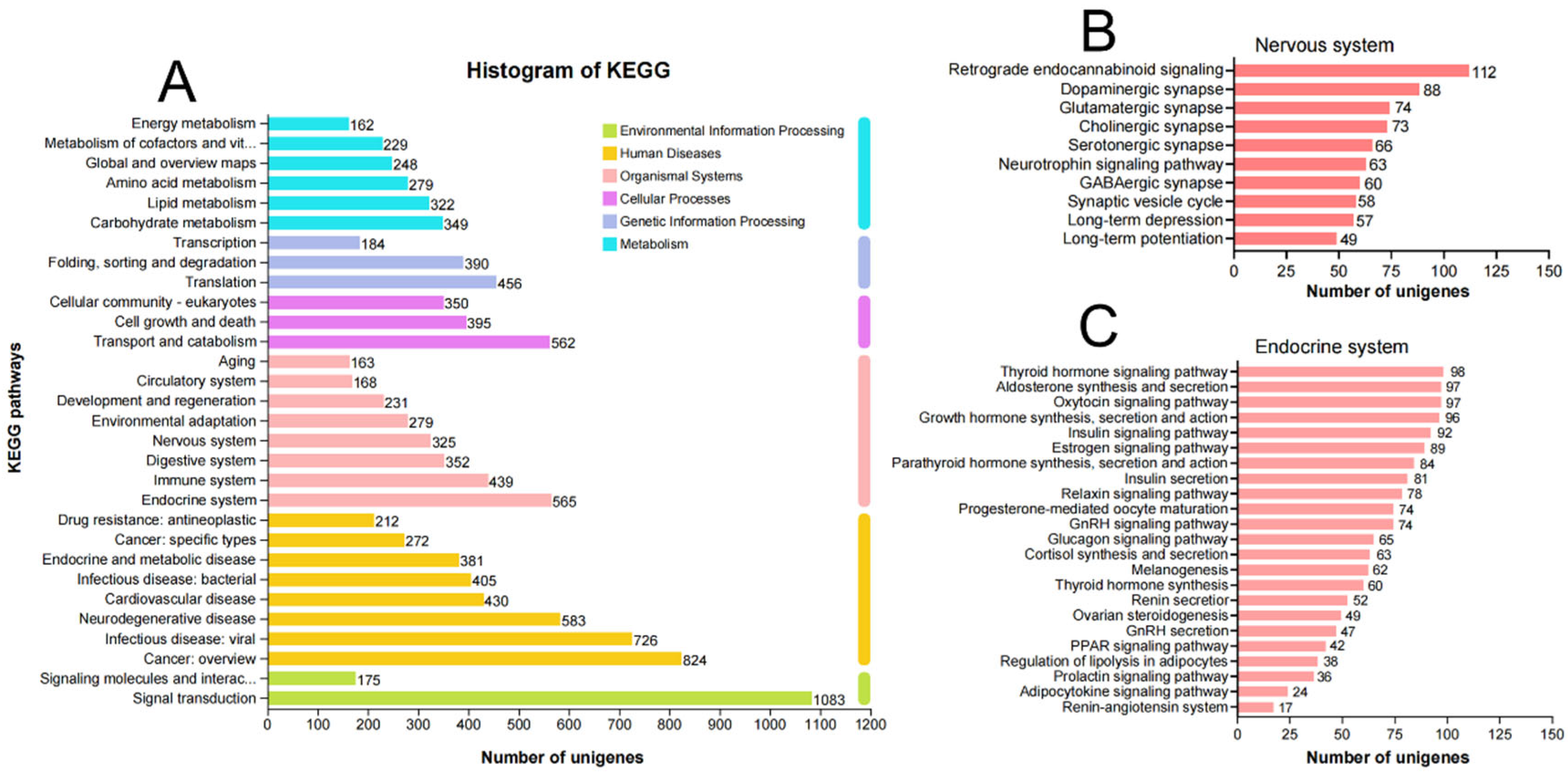
3.1. Summary of the Transcriptome Analyses
3.2. Analysis of Neuropeptides
3.3. Spatial Expression Patterns of Neuropeptide Precursors
3.4. G Protein-Coupled Receptors for Neuropeptides
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nässel, D.R. A brief history of insect neuropeptide and peptide hormone research. Cell Tissue Res. 2025, 399, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoofs, L.; De Loof, A.; Van Hiel, M.B. Neuropeptides as regulators of behavior in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El Asrar, R.; Cools, D.; Vanden Broeck, J. Role of peptide hormones in insect gut physiology. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 41, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caers, J.; Verlinden, H.; Zels, S.; Vandersmissen, H.P.; Vuerinckx, K.; Schoofs, L. More than two decades of research on insect neuropeptide GPCRs: An overview. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audsley, N.; Down, R.E. G protein coupled receptors as targets for next generation pesticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 67, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Bai, X.C. The activation mechanism of the insulin receptor: A structural perspective. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2023, 92, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altstein, M. Role of neuropeptides in sex pheromone production in moths. Peptides 2004, 25, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, X.; Ma, N.; Liu, X.; Wei, J.; Yin, X.; Zhou, S.; Rafaeli, A.; Song, Q.; An, S. Calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation of acetyl-coA carboxylase is required for pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide (PBAN)-induced sex pheromone biosynthesis in Helicoverpa armigera. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2017, 16, 2138–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadda, M.; Hasakiogullari, I.; Temmerman, L.; Beets, I.; Zels, S.; Schoofs, L. Regulation of feeding and metabolism by neuropeptide F and short neuropeptide F in invertebrates. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowański, S.; Walkowiak-Nowicka, K.; Winkiel, M.; Marciniak, P.; Urbański, A.; Pacholska-Bogalska, J. Insulin-like peptides and cross-talk with other factors in the regulation of insect metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 701203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Gulati, J.; Groβe-Wilde, E.; Vogel, H.; Hansson, B.S.; Knaden, M. The CCHamide 1 receptor modulates sensory perception and olfactory behavior in starved Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Tsuchimoto, M.; Nagata, S. CCHamide-2 Signaling Regulates Food Intake and Metabolism in Gryllus bimaculatus. Insects 2022, 13, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Stanley, D.; Yu, X.; Song, Q. The neuropeptide bursicon acts in cuticle metabolism. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 89, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S. Neuropeptide Bursicon and its receptor-mediated the transition from summer-form to winter-form of Cacopsylla chinensis. eLife 2024, 13, RP97298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Suetsugu, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Noda, H.; Shinoda, T. Transcriptome analysis of neuropeptides and G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) for neuropeptides in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Peptides 2014, 53, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Du, L.; Jiang, X.J.; Ju, Q.; Qu, C.J.; Qu, M.J.; Liu, T.X. Identification and characterization of neuropeptides and their G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in the cowpea aphid Aphis craccivora. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Hu, J.; Su, R.R.; Lu, W.; Zheng, X.L. Identification of neuropeptides and neuropeptide receptor genes in Phauda flammans (Walker). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Yang, X.; Tian, Z.; Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, X. Coordinated transcriptomics and peptidomics of central nervous system identify neuropeptides and their G protein-coupled receptors in the oriental fruit moth Grapholita molesta. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi Alamouti, M.; Majdi, M.; Talebi, R.; Dastranj, M.; Bandani, A.; Hossini Salekdeh, G.; Reza Ghaffari, M. Transcriptome wide identification of neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in Sunn pest, Eurygaster integriceps Puton. Gene 2024, 893, 147911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Predel, R.; Neupert, S.; Hauser, F.; Tanaka, Y.; Cazzamali, G.; Williamson, M.; Arakane, Y.; Verleyen, P.; Schoofs, L.; et al. Genomics, transcriptomics, and peptidomics of neuropeptides and protein hormones in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, P.; Pacholska-Bogalska, J.; Ragionieri, L. Neuropeptidomes of Tenebrio molitor L. and Zophobas atratus Fab. (Coleoptera, Polyphaga: Tenebrionidae). J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 2247–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Guo, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, L. Identification and expression profiling of neuropeptides and neuropeptide receptor genes in a natural enemy, Coccinella septempunctata. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1464989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, F.; Cazzamali, G.; Williamson, M.; Park, Y.; Li, B.; Tanaka, Y.; Predel, R.; Neupert, S.; Schachtner, J.; Verleyen, P.; et al. A genome-wide inventory of neurohormone GPCRs in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 142–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenstra, J.A. Coleoptera genome and transcriptome sequences reveal numerous differences in neuropeptide signaling between species. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nässel, D.R.; Zandawala, M. Recent advances in neuropeptide signaling in Drosophila, from genes to physiology and behavior. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 179, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, L.; Yamanaka, N.; Watanabe, K.; Daubnerová, I.; Zitnan, D.; Kataoka, H.; Tanaka, Y. The unique evolution of neuropeptide genes in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Zitnan, D.; Watanabe, K.; Kawada, T.; Satake, H.; Kaneko, Y.; Hiruma, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Shinoda, T.; et al. Neuropeptide receptor transcriptome reveals unidentified neuroendocrine pathways. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Deng, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, N. The G protein-coupled receptors in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yin, S.; Jang, R.; Wang, J.; Xue, Z.; Xu, T. NeuroPep: A comprehensive resource of neuropeptides. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2015, 2015, bav038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenstra, J.A. Mono- and dibasic proteolytic cleavage sites in insect neuroendocrine peptide precursors. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 43, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southey, B.R.; Amare, A.; Zimmerman, T.A.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Sweedler, J.V. NeuroPred: A tool to predict cleavage sites in neuropeptide precursors and provide the masses of the resulting peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W267–W272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1079, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bryant, S.H. CD-Search: Protein domain annotations on the fly. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W327–W331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, M.; Ye, C.; Qiu, B.; Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Pan, H. Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of the ladybird beetle Henosepilachna vigintioctomaculata. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, Research0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Li, X. Overexpression of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopa decarboxylase associated with pupal melanization in Spodoptera exigua. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummon, A.B.; Richmond, T.A.; Verleyen, P.; Baggerman, G.; Huybrechts, J.; Ewing, M.A.; Vierstraete, E.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Schoofs, L.; Robinson, G.E.; et al. From the genome to the proteome: Uncovering peptides in the Apis brain. Science 2006, 314, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetru, C.; Li, K.W.; Bulet, P.; Lagueux, M.; Hoffmann, J.A. Isolation and structural characterization of an insulin-related molecule, a predominant neuropeptide from Locusta migratoria. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 201, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, N.; Yamanaka, N. Nutrition-dependent control of insect development by insulin-like peptides. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 11, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defferrari, M.S.; Orchard, I.; Lange, A.B. An insulin-like growth factor in Rhodnius prolixus is involved in post-feeding nutrient balance and growth. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Fónagy, A.; Suzuki, A.; Mitsui, T. Multifunctionality of PBAN-related neuropeptides: Melanotropic activity of FXPRLamide peptides. In Insect Pheromone Research: New Directions; Cardé, R.T., Minks, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Oguchi, M.; Menjo, N.; Imai, K.; Saito, H.; Ikeda, M.; Isobe, M.; Yamashita, O. Precursor polyprotein for multiple neuropeptides secreted from the suboesophageal ganglion of the silkworm Bombyx mori: Characterization of the cDNA encoding the diapause hormone precursor and identification of additional peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3251–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Tanaka, M.; Kataoka, H.; Boo, K.S.; Tatsuki, S. Isolation and identification of the cDNA encoding the pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide and additional neuropeptides in the oriental tobacco budworm, Helicoverpa assulta (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 28, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomcala, A.; Bártů, I.; Simek, P.; Kodrík, D. Locust adipokinetic hormones mobilize diacylglycerols selectively. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 156, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gáliková, M.; Diesner, M.; Klepsatel, P.; Hehlert, P.; Xu, Y.; Bickmeyer, I.; Predel, R.; Kühnlein, R.P. Energy homeostasis control in Drosophila adipokinetic hormone mutants. Genetics 2015, 201, 665–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.M.; Saunders, C.J.; Johnson, E.C. The intrinsic nutrient sensing adipokinetic hormone producing cells function in modulation of metabolism, activity, and stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbakel, L.; Lenaerts, C.; Vranken, J.; Marchal, E.; Vanden Broeck, J. Essential role of eclosion hormone precursor and receptor genes in desert locust ecdysis. J. Insect Physiol. 2025, 161, 104736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, N. PTTH-Torso signaling system controls developmental timing, body size, and reproduction through regulating ecdysone homeostasis in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weger, A.A.; Rittschof, C.C. The diverse roles of insulin signaling in insect behavior. Front. Insect Sci. 2024, 4, 1360320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Predel, R.; Wegener, C. Biology of the CAPA peptides in insects. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2006, 63, 2477–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbakel, L.; Lenaerts, C.; Abou El Asrar, R.; Zandecki, C.; Bruyninckx, E.; Monjon, E.; Marchal, E.; Vanden Broeck, J. Prothoracicostatic activity of the ecdysis-regulating neuropeptide crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) in the desert locust. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asuncion-Uchi, M.; El Shawa, H.; Martin, T.; Fuse, M. Different actions of ecdysis-triggering hormone on the brain and ventral nerve cord of the hornworm, Manduca sexta. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 166, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Jang, H.; Oh, Y. The role of diuretic hormones (DHs) and their receptors in Drosophila. BMB Rep. 2023, 56, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenheer, R.A.; Nicolson, S.W.; Schegg, K.M.; Hull, J.J.; Schooley, D.A. Identification of a potent antidiuretic factor acting on beetle Malpighian tubules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachman, R.J.; Wang, X.J.; Etzkorn, F.A.; Kaczmarek, K.; Zabrocki, J.; Lopez, J.; Coast, G.M. Evaluation of insect CAP2b analogs with either an (E)-alkene, trans- or a (Z)-alkene, cis-Pro isostere identifies the Pro orientation for antidiuretic activity in the stink bug. Peptides 2013, 41, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Nachman, R.J.; Gui, S.H.; Piot, N.; Kaczmarek, K.; Zabrocki, J.; Dow, J.A.T.; Davies, S.A.; Smagghe, G. Efficacy and biosafety assessment of neuropeptide CAPA analogues against the peach-potato aphid (Myzus persicae). Insect Sci. 2022, 29, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachman, R.J.; Mahdian, K.; Nässel, D.R.; Isaac, R.E.; Pryor, N.; Smagghe, G. Biostable multi-Aib analogs of tachykinin-related peptides demonstrate potent oral aphicidal activity in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphidae). Peptides 2011, 32, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Nachman, R.J.; Kaczmarek, K.; Zabrocki, J.; Denlinger, D.L. Disruption of insect diapause using agonists and an antagonist of diapause hormone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16922–16926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.B.; Mishra, S.K.; Sridharan, K.; Barnes, E.R.; Alyokhin, A.; Tuttle, R.; Kokulapalan, W.; Garby, D.; Skizim, N.J.; Tang, Y.W.; et al. First sprayable double-stranded rna-based biopesticide product targets proteasome subunit beta type-5 in Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 728652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, L.L.; Li, W.Z.; Jin, L.; Li, G.Q. Rnai-based functional analysis of bursicon genes related to cuticle pigmentation in a ladybird beetle. J. Insect Physiol. 2024, 158, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.M.; Shang, F.; Ding, B.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.C.; Wang, J.J.; Dou, W. Characterization of two Bursicon genes and their association with wing development in the brown citrus aphid, Aphis citricidus. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 1684–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.H.; Pang, X.D.; Wen, S.Q.; Smagghe, G.; Liu, T.X.; Gui, S.H. Adipokinetic hormones and their receptor regulate the locomotor behavior in Tribolium castaneum. Insects 2025, 16, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Amir, M.B.; Ding, T.B.; Liu, T.X.; Smagghe, G.; Shi, Y. RNAi of neuropeptide CCHamide-1 and its receptor indicates role in feeding behavior in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Insects 2024, 15, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
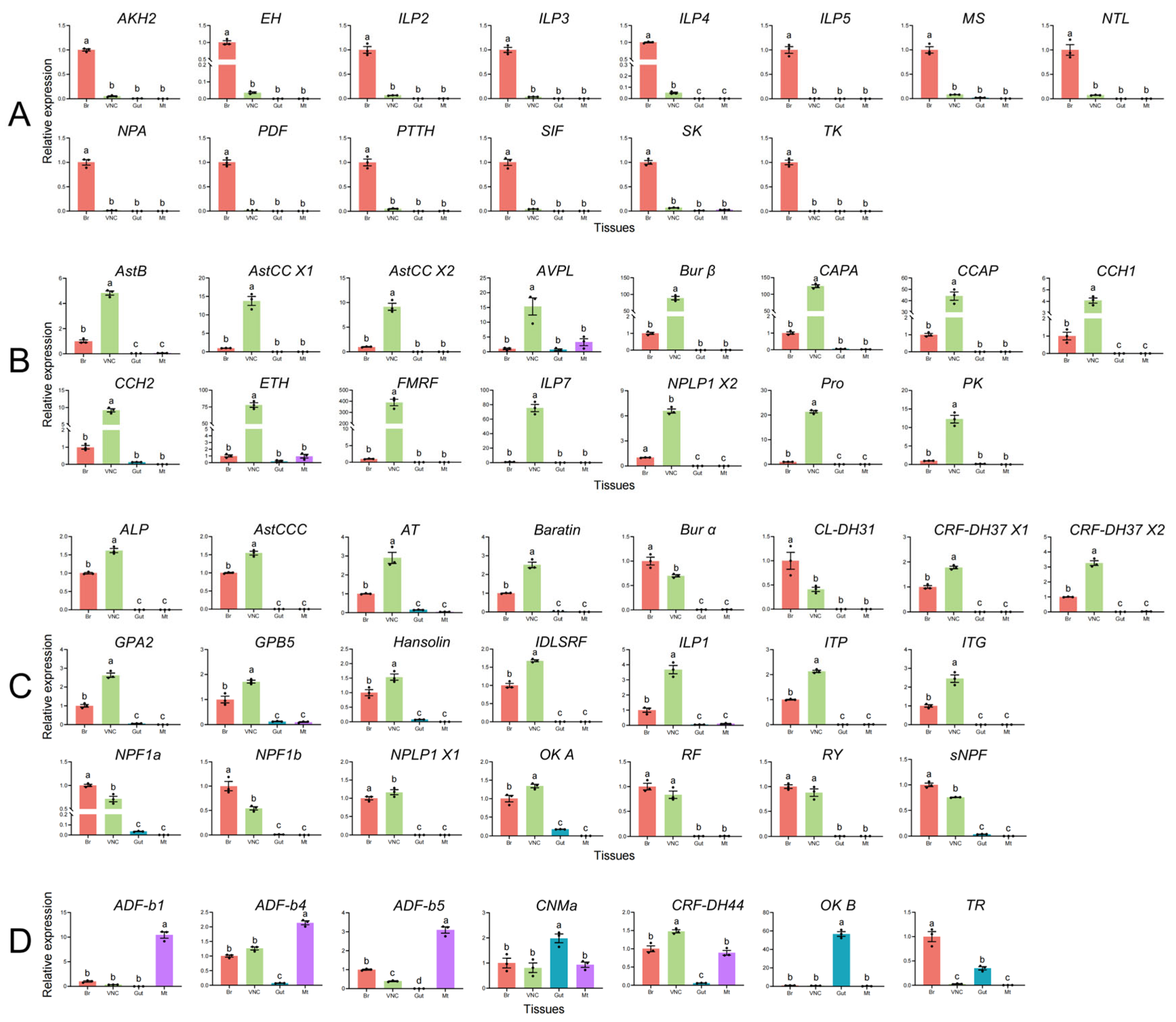
| Classification | Family | Neuropeptide Precursors | GenBank Accession No. | Transcripts Per Million (TPM) | Precursor size (aa) | Signal Peptide (aa) | Homology Search with Known Protein (Blastp) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | E-Value | Identity (%) | Accession No. | |||||||
| Neuropeptides | Adipokinetic hormone/ Hipertrehalosemic hormone/ Red pigment-concentrating | Adipokinetic hormone 2 (AKH2) | PV645140 | 116.45 | 72, complete | 20 | Tribolium castaneum | 8.00 × 1018 | 58.90% | NP_001107818.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Agatoxin-like peptide a | Agatoxin-like (ALP)/LQDVamide | PV645141 | 14.86 | 106, complete | 23 | Carabus violaceus | 1.00 × 1042 | 66.67% | XP_968442.2 |
| Neuropeptides | Allatostatin | Allatostatin B (AstB)/Prothoracicostatic peptide (PTSP)/myoinhibitory peptide (MIP) | PV645142 | 541.37 | 192, complete | 29 | Tribolium castaneum | 2.00 × 1050 | 48.45% | RZC34805.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Allatostatin | Allatostatin CC (AstCC) X1 | PV645143 | 188.64 | 137, complete | 23 | Zophobas atratus | 1.00 × 1053 | 67.72% | UXO98062.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Allatostatin | Allatostatin CC (AstCC) X2 | PV645144 | 4.2 | 140, complete | 26 | Zophobas atratus | 2.00 × 1053 | 67.72% | UXO98062.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Allatostatin | Allatostatin CCC (AstCCC) | PV645145 | 215.35 | 104, complete | 23 | Coccinella septempunctata | 9.00 × 1036 | 64% | XP_044759342 [26] |
| Neuropeptides | Allatotropin/Orexin | Allatotropin (AT) | PV645146 | 189.20 | 99, complete | 24 | Tribolium castaneum | 1.00 × 1013 | 40.95% | NP_001137204.1 |
| Osmoregulatory neuropeptides | Antidiuretic hormone | Antidiuretic factor b-1 (ADF-b1) | PV645147 | 14.64 | 129, complete | 22 | Tribolium castaneum | 1.00 × 1021 | 38.00% | EFA07530.1 [20] |
| Osmoregulatory neuropeptides | Antidiuretic hormone | Antidiuretic factor b-4 (ADF-b4) | PV645148 | 146.37 | 159, complete | 18 | Tribolium castaneum | 5.00 × 1033 | 57.00% | EFA07533.2 [20] |
| Osmoregulatory neuropeptides | Antidiuretic hormone | Antidiuretic factor b-5 (ADF-b5) | PV645149 | 197.04 | 138, complete | 18 | Tribolium castaneum | 2.00 × 1030 | 48.00% | EFA07534.1 [20] |
| Osmoregulatory neuropeptides | Vasopressin/oxytocin | Arginine-vasopressin-like (AVPL) | PV645150 | 388.95 | 152, complete | 21 | Tribolium castaneum | 1.00 × 1055 | 61.22% | NP_001078831.1 |
| Other putative neuropeptide genes | NA | Baratin (NVP-like) | PV645151 | 684.9 | 314, complete | 21 | Tribolium castaneum | 1.00 × 1080 | 51.36% | EFA09163.1 [20] |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Cystine knot | Bursicon alpha (Bur α) | PP430623 | 544.05 | 169, complete | 29 | Tribolium castaneum | 4.00 × 1094 | 92.00% | NP_001107779.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Cystine knot | Bursicon beta (Bur β)/partner of bursicon | PP430624 | 385.62 | 142, complete | 26 | Tribolium castaneum | 3.00 × 1070 | 80.15% | NP_001107780.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Pyrokinin/Periviscerokinin/ Pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide | Capability (CAPA)/Periviscerokinin (PVK)/Cardioacceleratory peptide 2b (CAP2b) | PV645153 | 598.23 | 144, complete | 19 | Zophobas atratus | 3.00 × 1009 | 37.07% | UXO98070.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Crustacean cardioactive peptide | Crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) | PV645160 | 423.61 | 142, complete | 19 | Diorhabda sublineata | 3.00 × 1049 | 62.24% | XP_056637896.1 |
| Neuropeptides | CCHamide | CCHamide 1 (CCH1) | PV645154 | 173.87 | 161, complete | 33 | Tenebrio molitor | 6.00 × 1023 | 37.09% | UXO98161.1 |
| Neuropeptides | CCHamide | CCHamide 2 (CCH2) | PV645155 | 260.93 | 118, complete | 27 | Tenebrio molitor | 3.00 × 1027 | 41.23% | UXO98162.1 |
| Neuropeptides | CNMamide | CNMamide (CNMa) | PV645156 | 8.72 | 142, complete | 15 | Tenebrio molitor | 5.00 × 1012 | 34.04% | UXO98163.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Diuretic hormone | Calcitonin-like diuretic hormone 31 (CL-DH31) | PV645152 | 78.79 | 69, complete | 30 | Tribolium castaneum | 3.00 × 1007 | 61.54% | EEZ99367.2 |
| Osmoregulatory neuropeptides | Corticotropin-releasing hormone binding protein/Diuretic hormone-related | Corticotropin-releasing factor-like diuretic hormone 37 X1 (CRF-DH 37 X1) | PV645157 | 156.13 | 136, complete | 18 | Tribolium castaneum | 1.00 × 1012 | 34.31% | NP_001164096.1 [26] |
| Osmoregulatory neuropeptides | Corticotropin-releasing hormone binding protein/Diuretic hormone-related | Corticotropin-releasing factor-like diuretic hormone 37 X2 (CRF-DH 37 X2) | PV645158 | 92.62 | 155, complete | 18 | Tribolium castaneum | 2.00 × 1033 | 45.57% | XP_015835155.1 [26] |
| Osmoregulatory neuropeptides | Corticotropin-releasing hormone binding protein/Diuretic hormone-related | Corticotropin-releasing factor-like diuretic hormone 44 (CRF-DH 44) | PV645159 | 135.5 | 349, complete | 22 | Grapholitha molesta | 1.00 × 1070 | 46.00% | MN639889 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Eclosion hormone | Eclosion hormone (EH) | PV645162 | 16.63 | 81, complete | 25 | Halyomorpha halys | 6.00 × 1028 | 66.22% | XP_024214295.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Ecdysis-triggering hormone | Ecdysis-triggering hormone (ETH) | PV645161 | 26.51 | 155, complete | 22 | Colaphellus bowringi | 1.00 × 1014 | 43.44% | UDO48204.1 |
| Neuropeptides | FMRFamide-related peptide | FMRFamide (FMRF) | PV645163 | 469.43 | 207, complete | 17 | Harmonia axyridis | 1.00 × 1062 | 52.11% | XP_045478717.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Glycoprotein hormone | Glycoprotein hormone alpha 2 (GPA2) | PV645164 | 187.93 | 122, complete | 16 | Tribolium castaneum | 4.00 × 1067 | 77.87% | NP_001164244.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Glycoprotein hormone | Glycoprotein hormone beta 5 (GPB5) | PV645165 | 144.95 | 154, complete | 20 | Tribolium castaneum | 1.00 × 1065 | 64.47% | NP_001280517.1 |
| Neuropeptides | NA | Hansolin | PV645166 | 5.20 | 121, complete | 20 | Tenebrio molitor | 4.00 × 1013 | 33.61% | UXO98170.1 |
| Neuropeptides | NA | IDLSRF-like peptide (IDLSRF) | PV645167 | 260.25 | 208, complete | 34 | Coccinella septempunctata | 4.00 × 10144 | 95.19% | XP_044765879.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor/Relaxin | Insulin-like peptide 1 (ILP1) | PV645168 | 16.26 | 123, complete | 21 | Harmonia axyridis | 1.00 × 1042 | 58.68% | XP_045479779.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor/Relaxin | Insulin-like peptide 2 (ILP2) | PV645169 | 122.58 | 124, complete | 21 | Harmonia axyridis | 1.00 × 1018 | 38.64% | XP_045479306.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor/Relaxin | Insulin-like peptide 3 (ILP3) | PV645170 | 13.66 | 131, complete | 20 | Coccinella septempunctata | 1.00 × 1013 | 36.36% | XP_044748903.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor/Relaxin | Insulin-like peptide 4 (ILP4) | PV645171 | 15.62 | 109, complete | 21 | Camponotus floridanus | 5.00 × 1008 | 34.62% | XP_025267327.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor/Relaxin | Insulin-like peptide 5 (ILP5) | PV645172 | 6.54 | 120, complete | 23 | Cryptolaemus montrouzieri | 3.00 × 1008 | 36.59% | KAL3266362.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor/Relaxin | Insulin-like peptide 7 (ILP7)/Relaxin | PV645173 | 79.70 | 144, complete | 24 | Coccinella septempunctata | 8.00 × 1081 | 79.86% | XP_044762237.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Crustacean hyperglycaemic hormone family | ion transport peptide (ITP) | PV645174 | 48.91 | 122, complete | 28 | Coccinella septempunctata | 3.00 × 1073 | 85.95% | XP_044746445.1 |
| Other putative neuropeptide genes | ITG-like | ITG-like (ITG) | PV645175 | 850.08 | 216, complete | 20 | Harmonia axyridis | 3.00 × 10131 | 89.30% | XP_045481008.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Myosuppressin | Myosuppressin (MS) | PV645178 | 2.04 | 86, complete | 24 | Anoplophora glabripennis | 1.00 × 1026 | 57.89% | XP_018573133.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Tachykinin-related peptides | Natalisin (NTL) | PV645179 | 11.50 | 150, complete | 19 | Rhynchophorus ferrugineus | 4.00 × 1020 | 38.78% | QGA72564.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | Neuroparsin/Ovary ecdysteroidogenic hormone | Neuroparsin A (NPA) | PV645180 | 129.02 | 101, complete | 25 | Harmonia axyridis | 7.00 × 1032 | 62.38% | XP_045460883.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Neuropeptide Y | Neuropeptide F 1a (NPF1a) | PV645211 | 6.25 | 88, complete | 26 | Tenebrio molitor | 8.00 × 1021 | 57.95% | UXO98177.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Neuropeptide Y | Neuropeptide F 1b (NPF1b) | PV645212 | 23.98 | 125, complete | 26 | Zophobas atratus | 4.00 × 1039 | 58.73% | UXO98088.1 |
| Other putative neuropeptide genes | Neuropeptide-like precursor | Neuropeptide-like precursor 1 X1 (NPLP1 X1) | PV645209 | 29.12 | 371, complete | 24 | Coccinella septempunctata | 5.00 × 10147 | 63.71% | XP_044759118.1 |
| Other putative neuropeptide genes | Neuropeptide-like precursor | Neuropeptide-like precursor 1 X2 (NPLP1 X2) | PV645210 | 4.74 | 371, complete | 24 | Coccinella septempunctata | 2.00 × 10143 | 64.36% | XP_044759118.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Orcokinin | Orcokinin A (OK A) | PV645213 | 17.87 | 151, complete | 19 | Harmonia axyridis | 7.00 × 1077 | 73.33% | XP_045477291.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Orcokinin | Orcokinin B (OK B) | PV645214 | 8.59 | 283, complete | 19 | Harmonia axyridis | 4.00 × 1075 | 52.63% | XP_045477290.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Pigment-dispersing hormone/Pigment- dispersing factor | Pigment-dispersing factor (PDF) | PV645215 | 207.47 | 105, complete | 27 | Photinus pyralis | 3.00 × 1007 | 37.50% | XP_031349268.1 |
| Protein hormones (polypeptides) | NA | Prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) | PV645217 | 15.86 | 176, complete | 18 | Tribolium madens | 2.00 × 1019 | 31.25% | XP_044258306.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Proctolin | Proctolin (Pro) | PV645216 | 3543.72 | 86, complete | 30 | Rhynchophorus ferrugineus | 4.00 × 1016 | 53.25% | QGA72571.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Pyrokinin/Periviscerokinin/ Pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide | Pyrokinin (PK)/phermone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide like (PBAN-like) | PV645218 | 467.84 | 142, complete | 23 | Tribolium castaneum | 7.00 × 1013 | 38.32% | XP_015835244.1 |
| Neuropeptides | RFamide neuropeptide | RFLamide (RF) | PV645219 | 59.54 | 182, complete | 27 | Tenebrio molitor | 1.00 × 1042 | 43.46% | UXO98182.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Luqin/Ryamide | Ryamide (RY) | PV645220 | 32.54 | 120, complete | 23 | Coccinella septempunctata | 1.00 × 1038 | 63.64% | XP_044747600.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Neuropeptide Y | short neuropeptide F (sNPF) | PV645221 | 217.92 | 99, complete | 26 | Harmonia axyridis | 5.00 × 1041 | 68.82% | XP_045470701.1 |
| Neuropeptides | FMRFamide related peptide | SIFamide (SIF) | PV645222 | 130.03 | 74, complete | 25 | Coccinella septempunctata | 1.00 × 1025 | 67.12% | XP_044744559.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Gastrin/cholecystokinin | Sulfakinin (SK) | PV645223 | 10.41 | 104, complete | 27 | Coccinella septempunctata | 8.00 × 1025 | 49.51% | XP_044752147.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Tachykinin-related peptides | Tachykinin (TK) | PV645224 | 81.99 | 276, complete | 22 | Coccinella septempunctata | 5.00 × 1097 | 61.25% | XP_044759920.1 |
| Neuropeptides | Trissin | Trissin (TR) | PV645225 | 10.24 | 86, complete | 21 | Anoplophora glabripennis | 2.00 × 1014 | 50.00% | XP_018571856.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yao, S.; Lin, A.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Liu, X.; Du, M.; Liu, X.; An, S. Transcriptome-Wide Identification of Neuropeptides and Neuropeptide Receptors in the Twenty-Eight-Spotted Ladybird Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insects 2025, 16, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060624
Lei Q, Wang Z, Yao S, Lin A, Zhang Y, Sun C, Liu X, Du M, Liu X, An S. Transcriptome-Wide Identification of Neuropeptides and Neuropeptide Receptors in the Twenty-Eight-Spotted Ladybird Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insects. 2025; 16(6):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060624
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Quanxing, Ziming Wang, Shuangyan Yao, Aili Lin, Yunhui Zhang, Chengxian Sun, Xiaoguang Liu, Mengfang Du, Xiaoming Liu, and Shiheng An. 2025. "Transcriptome-Wide Identification of Neuropeptides and Neuropeptide Receptors in the Twenty-Eight-Spotted Ladybird Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata" Insects 16, no. 6: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060624
APA StyleLei, Q., Wang, Z., Yao, S., Lin, A., Zhang, Y., Sun, C., Liu, X., Du, M., Liu, X., & An, S. (2025). Transcriptome-Wide Identification of Neuropeptides and Neuropeptide Receptors in the Twenty-Eight-Spotted Ladybird Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insects, 16(6), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060624