Evaluation of Red Palm Weevils (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus: Curculionidae) for Putative Oxidation of Ingested Polystyrene and Polyurethane and Their Gut Microbiota Response
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources of Red Palm Weevil (RPW) Larvae and Plastics
2.2. Diet Preparation
2.3. Growth Performance and Collection of Samples
2.4. Collection and Characterization of RPW, Residual Plastics, and Frass
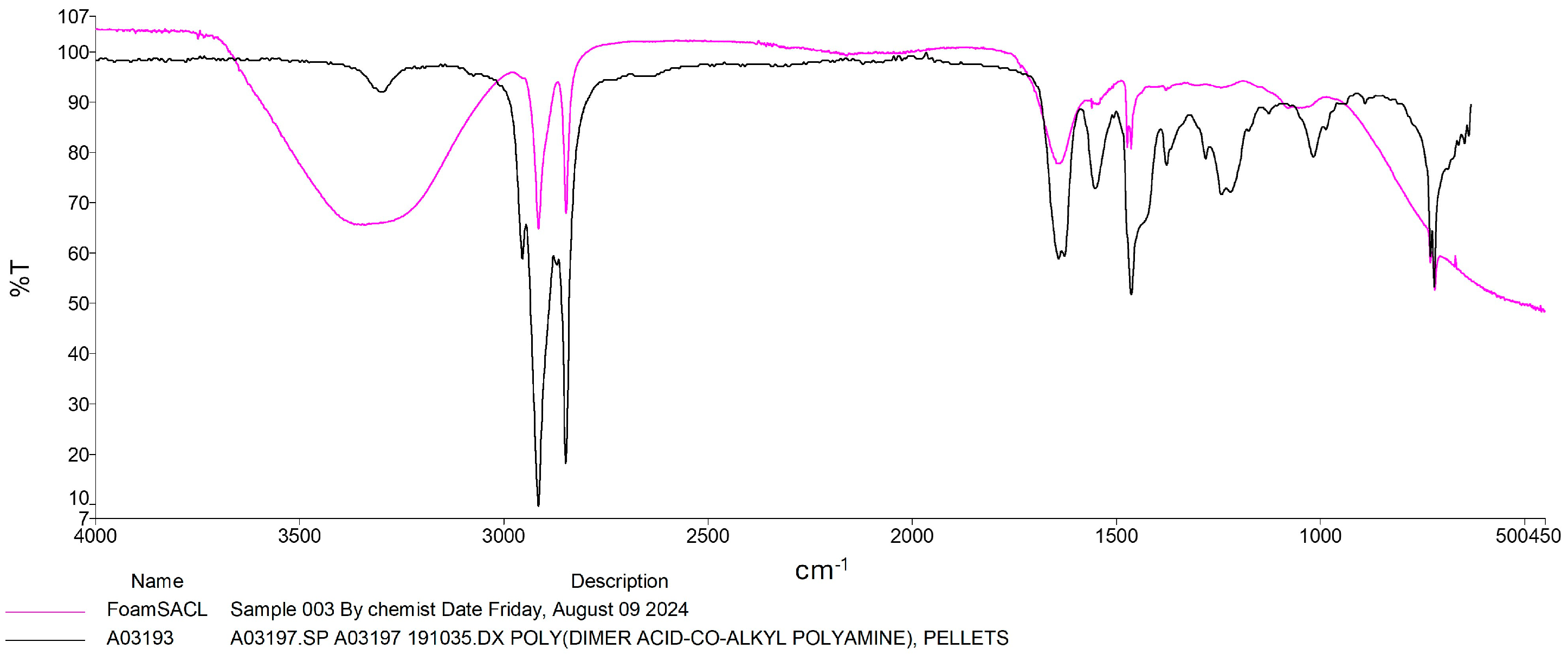
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
2.6. Diversity Gut Microbiome
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance and Survival Rate of RPW Larvae Reared on Plastic-Containing Diets
3.2. Plastic Transfomation by RPW Larvae
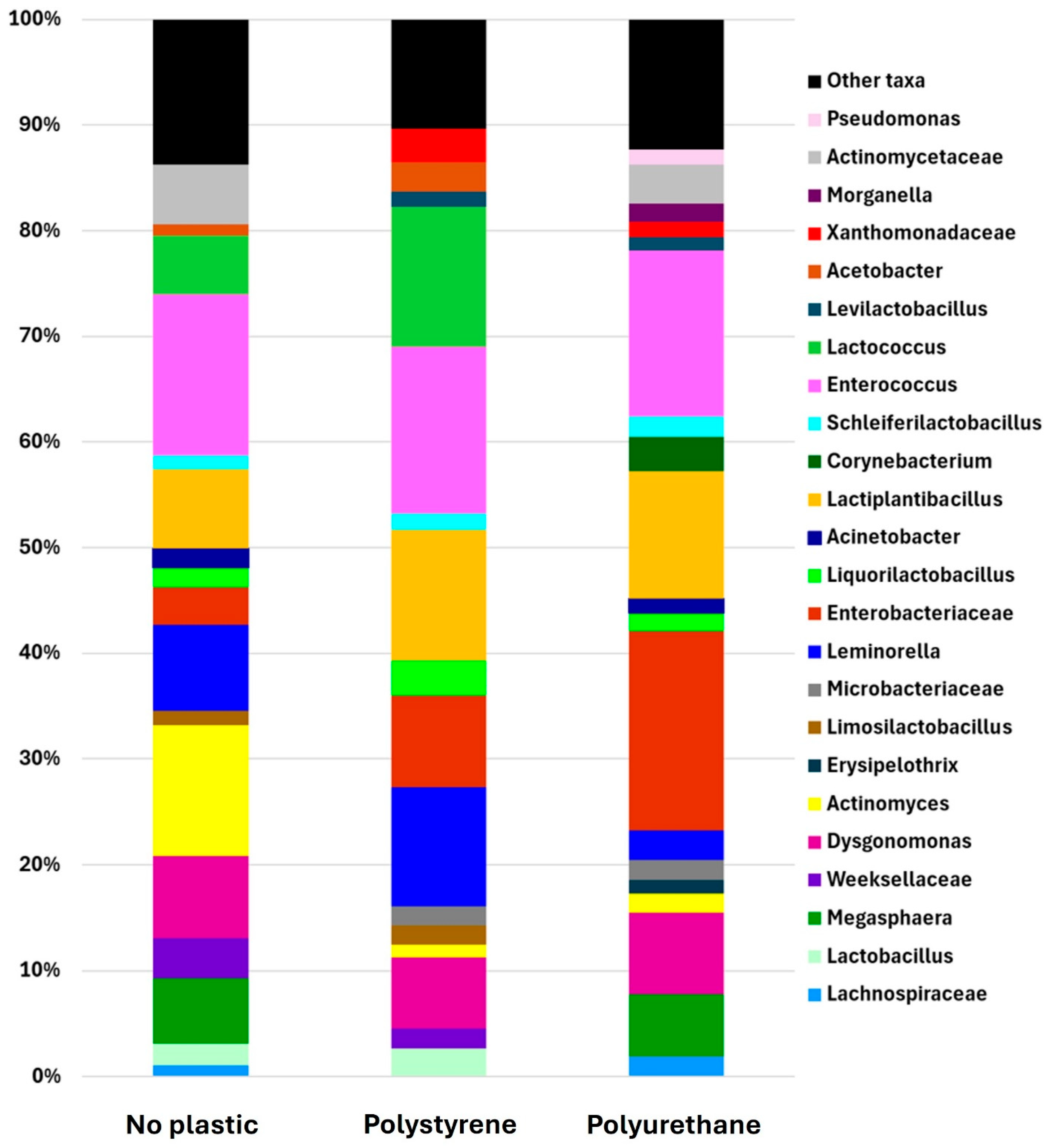
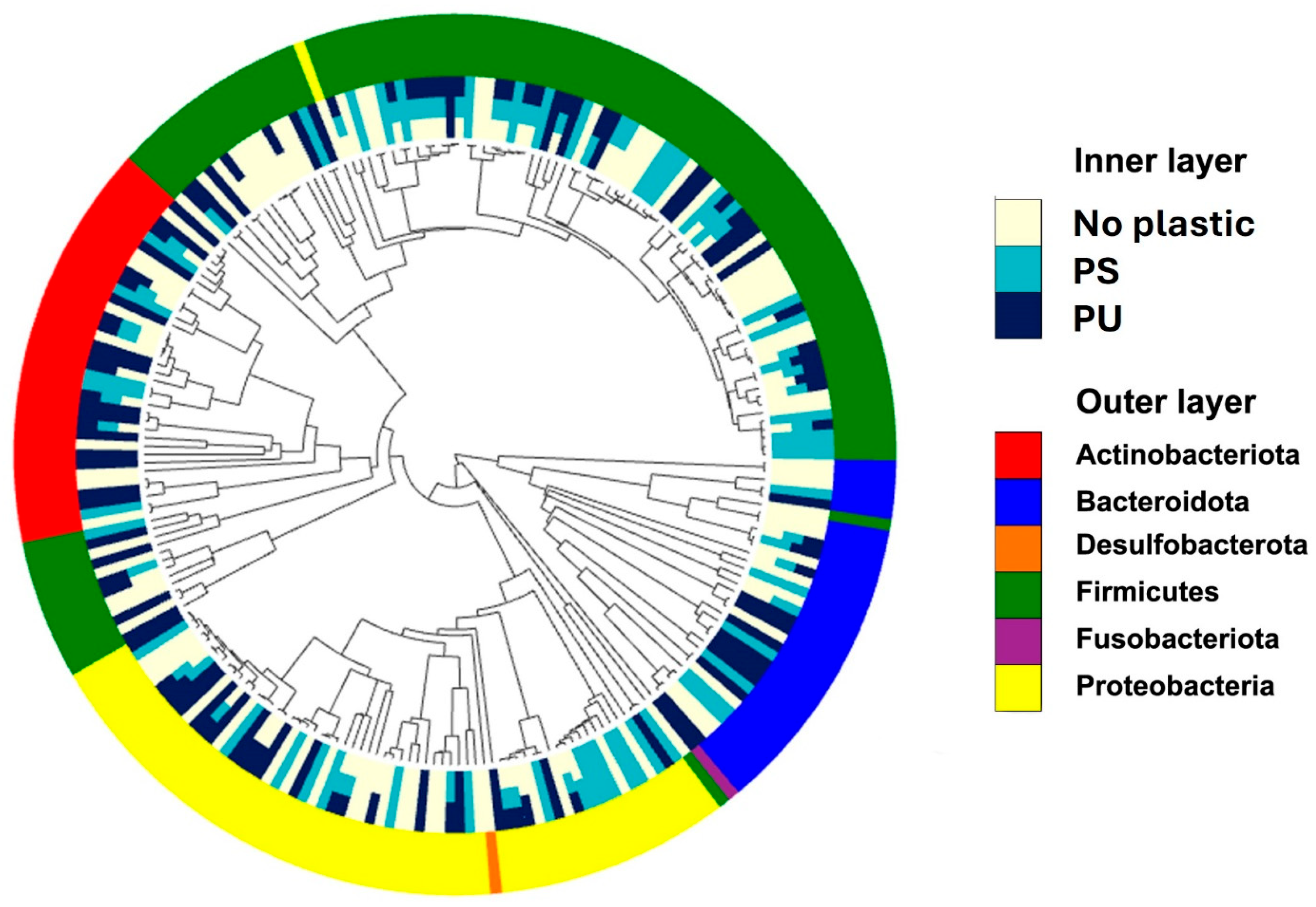
3.3. Gut Microbiota of RPW Larvae Reared on Plastic-Containing Diets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| PDB | Potato dextrose broth |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| RPW | Red palm weevil |
| YPDB | Yeast-enriched potato dextrose broth |
References
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics-The Facts. 2023. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2023/ (accessed on 22 March 2025).
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics-The Facts. 2024. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2024/ (accessed on 22 March 2025).
- Chaudhary, A.K.; Vijayakumar, R. Studies on biological degradation of polystyrene by pure fungal cultures. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 4495–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, B.; Xu, A.; Cao, S.; Wei, R.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, M.; Dong, W. Biodegradation of polyether-polyurethane foam in yellow mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) and effects on the gut microbiome. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Qian, G.; Zhou, J. Feeding preference of insect larvae to waste electrical and electronic equipment plastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Deng, X.; Jiang, L.; Hao, L.; Shi, Y.; Lyu, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Current advances, challenges and strategies for enhancing the biodegradation of plastic waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Peng, X.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhuang, X. Biodegradation of expanded polystyrene and low-density polyethylene foams in larvae of Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae): Broad versus limited extent depolymerization and microbe-dependence versus independence. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-S.; Wu, W.-M.; Brandon, A.M.; Fan, H.-Q.; Receveur, J.P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Fan, R.; McClellan, R.L.; Gao, S.-H. Ubiquity of polystyrene digestion and biodegradation within yellow mealworms, larvae of Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Chemosphere 2018, 212, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Song, I.; Cha, H.J. Fast and facile biodegradation of polystyrene by the gut microbial flora of Plesiophthalmus davidis larvae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01361-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Fu, R.; Long, T.; Fan, B.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G. Biodegradation of polyethylene by Meyerozyma guilliermondii and Serratia marcescens isolated from the gut of waxworms (larvae of Plodia interpunctella). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.; Jiang, L. Biodegradation and mineralization of polystyrene by plastic-eating mealworms: Part 1. Chemical and physical characterization and isotopic tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12080–12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, A.M.; Gao, S.-H.; Tian, R.; Ning, D.; Yang, S.-S.; Zhou, J.; Wu, W.-M.; Criddle, C.S. Biodegradation of polyethylene and plastic mixtures in mealworms (larvae of Tenebrio molitor) and effects on the gut microbiome. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6526–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmberger, M.S.; Miesel, J.R.; Tiemann, L.K.; Grieshop, M.J. Soil invertebrates generate microplastics from polystyrene foam debris. J. Insect Sci. 2022, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhang, Y. Biodegradation of polystyrene and low-density polyethylene by Zophobas atratus larvae: Fragmentation into microplastics, gut microbiota shift, and microbial functional enzymes. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 132987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-S.; Wu, W.-M.; Bertocchini, F.; Benbow, M.E.; Devipriya, S.P.; Cha, H.J.; Peng, B.-Y.; Ding, M.-Q.; He, L.; Li, M.-X. Radical innovation breakthroughs of biodegradation of plastics by insects: History, present and future perspectives. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital-Vilchis, I.; Karunakaran, E. Using Insect Larvae and Their Microbiota for Plastic Degradation. Insects 2025, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkraly, O.A.; Elrahman, T.A.; Awad, M.; El-Saadany, H.M.; Atia, M.A.; Dosoky, N.S.; Ibrahim, E.-D.S.; Elnagdy, S.M. Exploring Gut Microbiota in Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus): Effects on Pest Management, Pesticide Resistance, and Thermal Stress Tolerance. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 1359–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promwee, A.; Chinarak, K.; Panpipat, W.; Panya, A.; Phonsatta, N.; Harcet, M.; Chaijan, M. Balancing the Growth Performance and Nutritional Value of Edible Farm-Raised Sago Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferregineus) Larvae by Feeding Various Plant Supplemented-Sago Palm Trunk Diets. Foods 2023, 12, 3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.-Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Benbow, M.E.; Criddle, C.S.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhang, Y. Biodegradation of polystyrene by dark (Tenebrio obscurus) and yellow (Tenebrio molitor) mealworms (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5256–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpy, D.R.; Mattila, H.R.; Newton, I.L. Development of the honey bee gut microbiome throughout the queen-rearing process. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3182–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakumanu, M.L.; Reeves, A.M.; Anderson, T.D.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Williams, M.A. Honey bee gut microbiome is altered by in-hive pesticide exposures. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldert, C.; Abdo, Z.; Stewart, J.; HS, A. Dietary supplementation with phytochemicals improves diversity and abundance of honey bee gut microbiota. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1705–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Namin, S.M.; Jung, C. Differential bacterial Community of bee Bread and bee Pollen Revealed by 16s rRNA high-throughput sequencing. Insects 2022, 13, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-H.; Shih, Y.-h.; Lai, Y.-C.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Liu, Y.-T.; Lin, N.-C. Degradation of polyurethane by bacterium isolated from soil and assessment of polyurethanolytic activity of a Pseudomonas putida strain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9529–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, N.; Mikoryak, C.; Draper, R.K.; Balkus Jr, K.J. Electrospun linear polyethyleneimine scaffolds for cell growth. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Plastics and microplastics in the oceans: From emerging pollutants to emerged threat. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.; Siddiqui, S.; Nugraha, W.; Yudhistira, B.; Adli, D.; Nagdalian, A.; Blinov, A.; Mario, M. Overview of larvae of red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier)(Coleoptera: Curculionidae), as human food. J. Insects Food Feed. 2023, 9, 1265–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Dias-Pereira, P. Microplastics in terrestrial domestic animals and human health: Implications for food security and food safety and their role as sentinels. Animals 2023, 13, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombelli, P.; Howe, C.J.; Bertocchini, F. Polyethylene bio-degradation by caterpillars of the wax moth Galleria mellonella. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R292–R293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassone, B.J.; Grove, H.C.; Elebute, O.; Villanueva, S.M.; LeMoine, C.M. Role of the intestinal microbiome in low-density polyethylene degradation by caterpillar larvae of the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20200112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, L. Evidence of polyethylene biodegradation by bacterial strains from the guts of plastic-eating waxworms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13776–13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulak, P.; Proc, K.; Pytlak, A.; Puszka, A.; Gawdzik, B.; Bieganowski, A. Biodegradation of different types of plastics by Tenebrio molitor insect. Polymers 2021, 13, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Abd Manap, A.S.; Kolobe, S.D.; Monnye, M.; Yudhistira, B.; Fernando, I. Insects for plastic biodegradation–A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 186, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tao, H.; Wong, M.H. Feeding and metabolism effects of three common microplastics on Tenebrio molitor L. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upfold, J.; Rejasse, A.; Nielsen-Leroux, C.; Jensen, A.B.; Sanchis-Borja, V. The immunostimulatory role of an Enterococcus-dominated gut microbiota in host protection against bacterial and fungal pathogens in Galleria mellonella larvae. Front. Insect Sci. 2023, 3, 1260333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavia, M.; Messina, E.; Manachini, B.; Cappello, S.; Quatrini, P. The gut microbiota of larvae of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Oliver (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Fang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Shi, Z. The gut entomotype of red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Olivier (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae) and their effect on host nutrition metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofstad, T.; Olsen, I.; Eribe, E.R.; Falsen, E.; Collins, M.D.; Lawson, P.A. Dysgonomonas gen. nov. to accommodate Dysgonomonas gadei sp. nov., an organism isolated from a human gall bladder, and Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides (formerly CDC group DF-3). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annuk, H.; Shchepetova, J.; Kullisaar, T.; Songisepp, E.; Zilmer, M.; Mikelsaar, M. Characterization of intestinal lactobacilli as putative probiotic candidates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamtimin, T.; Han, H.; Khan, A.; Feng, P.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, X.; Fang, Y.; Liu, P.; Kulshrestha, S.; Shigaki, T. Gut microbiome of mealworms (Tenebrio molitor Larvae) show similar responses to polystyrene and corn straw diets. Microbiome 2023, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Su, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. Biodegradation of polystyrene by Tenebrio molitor, Galleria mellonella, and Zophobas atratus larvae and comparison of their degradation effects. Polymers 2021, 13, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Cho, H.w.; Jung, H.; Park, J.; Yun, S.; Ha, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, T.-J. Changes in intestinal microbiota due to the expanded polystyrene diet of mealworms (Tenebrio molitor). Indian J. Microbiol. 2021, 61, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucini, C.; Funari, R.; Mercati, D.; Nardi, F.; Carapelli, A.; Marri, L. Polystyrene shaping effect on the enriched bacterial community from the plastic-eating Alphitobius diaperinus (Insecta: Coleoptera). Symbiosis 2022, 86, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.R.; Magina, S.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Barros-Timmons, A. Lignin as a renewable building block for sustainable polyurethanes. Materials 2022, 15, 6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouteau, C.; Baumberger, S.; Cathala, B.; Dole, P. Lignin–polymer blends: Evaluation of compatibility by image analysis. Comptes Rendus. Biol. 2004, 327, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, J.; González-Tortuero, E.; Kuba, S.; Ferry, N. Bacterial community profiling and identification of bacteria with lignin-degrading potential in different gut segments of African palm weevil larvae (Rhynchophorus phoenicis). Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1401965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Treatments | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Polystyrene | Polyurethane | ||
| Head diameter (mm) | ||||
| Day 20 | 4.10 ± 0.53 b | 4.40 ± 0.52 b | 4.40 ± 0.32 c | 0.153 |
| Day 27 | 5.80 ± 0.63 a | 6.30 ± 0.67 a | 5.80 ± 0.42 b | 0.108 |
| Day 35 | 6.30 ± 0.48 a | 6.40 ± 0.70 a | 6.80 ± 0.42 a | 0.116 |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - |
| Live weight (g) | ||||
| Day 20 | 3.61 ± 0.56 | 3.96 ± 0.65 | 4.06 ± 0.60 | 0.224 |
| Day 27 | 3.50 ± 0.36 | 3.77 ± 0.61 | 3.83 ± 0.52 | 0.315 |
| Day 35 | 3.35 ± 0.28 | 3.74 ± 0.39 | 3.75 ± 0.55 | 0.066 |
| p-value | 0.387 | 0.639 | 0.442 | - |
| Survival rate (%) | ||||
| Day 20 | 100 ± 0.00 a | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | - |
| Day 27 | 78.89 ± 11.70 b | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | 0.013 |
| Day 35 | 41.11 ± 6.94 c | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | 0.000 |
| p-value | 0.000 | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Danmek, K.; Praphawilai, P.; Ghosh, S.; Jung, C.; Mohamadzade Namin, S.; Aedtem, P.; Chuttong, B. Evaluation of Red Palm Weevils (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus: Curculionidae) for Putative Oxidation of Ingested Polystyrene and Polyurethane and Their Gut Microbiota Response. Insects 2025, 16, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060587
Danmek K, Praphawilai P, Ghosh S, Jung C, Mohamadzade Namin S, Aedtem P, Chuttong B. Evaluation of Red Palm Weevils (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus: Curculionidae) for Putative Oxidation of Ingested Polystyrene and Polyurethane and Their Gut Microbiota Response. Insects. 2025; 16(6):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060587
Chicago/Turabian StyleDanmek, Khanchai, Pichet Praphawilai, Sampat Ghosh, Chuleui Jung, Saeed Mohamadzade Namin, Phattharawadee Aedtem, and Bajaree Chuttong. 2025. "Evaluation of Red Palm Weevils (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus: Curculionidae) for Putative Oxidation of Ingested Polystyrene and Polyurethane and Their Gut Microbiota Response" Insects 16, no. 6: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060587
APA StyleDanmek, K., Praphawilai, P., Ghosh, S., Jung, C., Mohamadzade Namin, S., Aedtem, P., & Chuttong, B. (2025). Evaluation of Red Palm Weevils (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus: Curculionidae) for Putative Oxidation of Ingested Polystyrene and Polyurethane and Their Gut Microbiota Response. Insects, 16(6), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060587









