Comparative Assessment of Environmental DNA and Bulk-Sample Metabarcoding in Biosecurity Surveillance for Detecting Biting Midges (Ceratopogonidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Sample Collection
2.2. eDNA Capture and Extraction
2.3. PCR and Metabarcoding Sequencing
2.4. In-House Reference Database of Ceratopogonidae Species
2.5. OTU Analysis and Taxonomic Assignment
2.6. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Identification of Insect Trap Samples
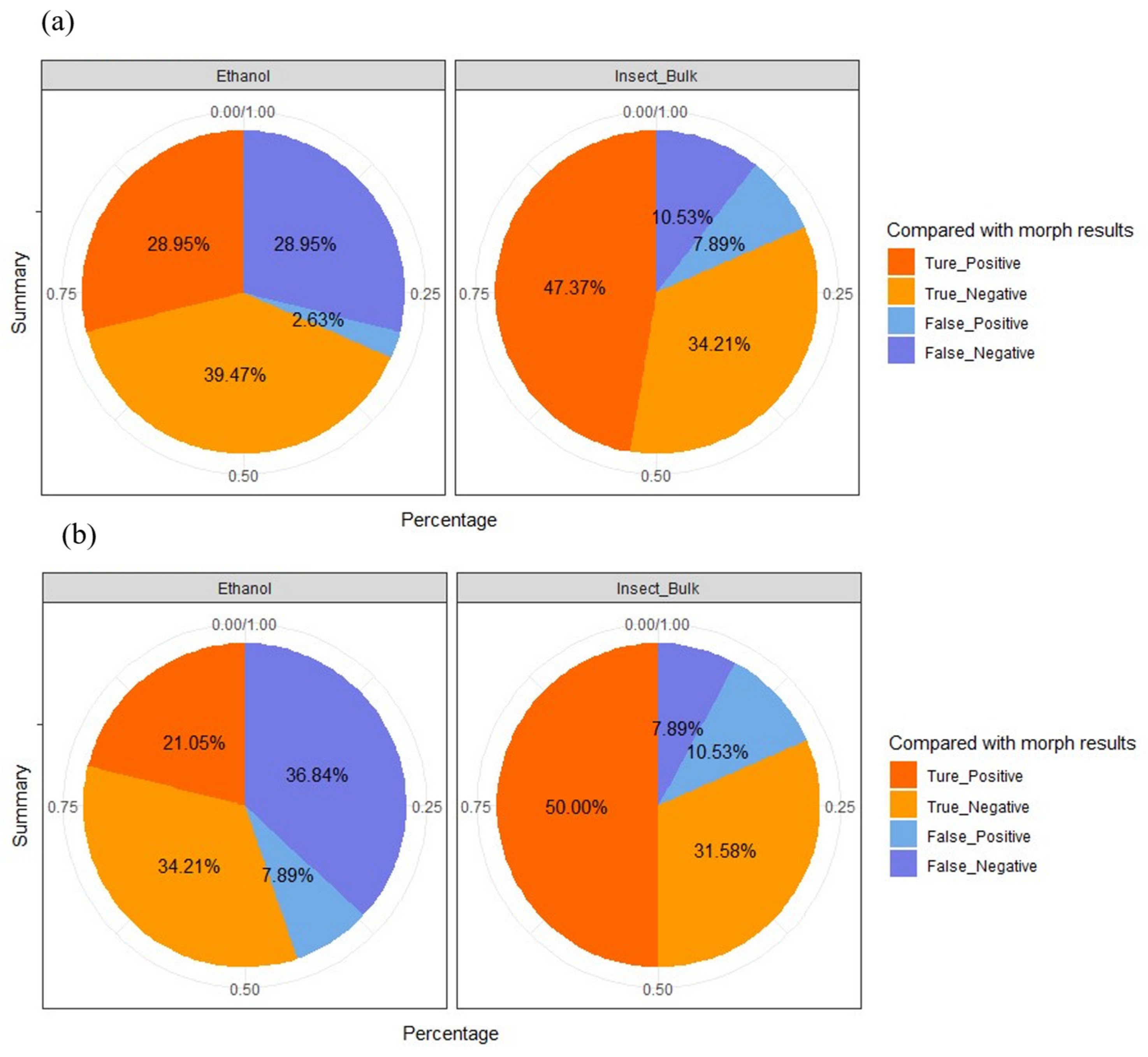
3.2. Detection Accuracy of eDNA Metabarcoding Approach
3.3. Effect of Target Species Abundance on eDNA Detection
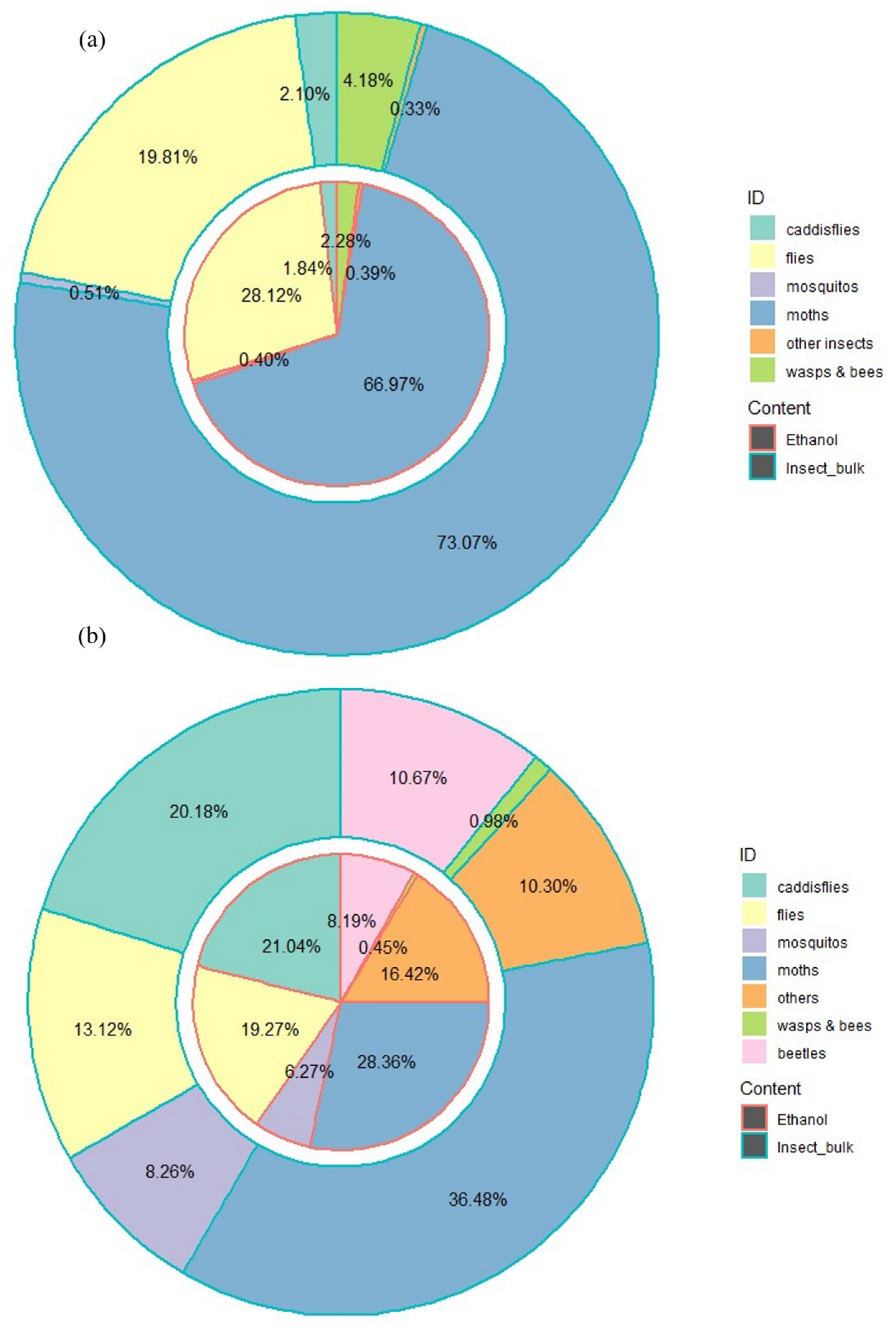
3.4. Impacts of Primer Choices and Sample Types on the Recovery of Overall Taxonomic Diversity
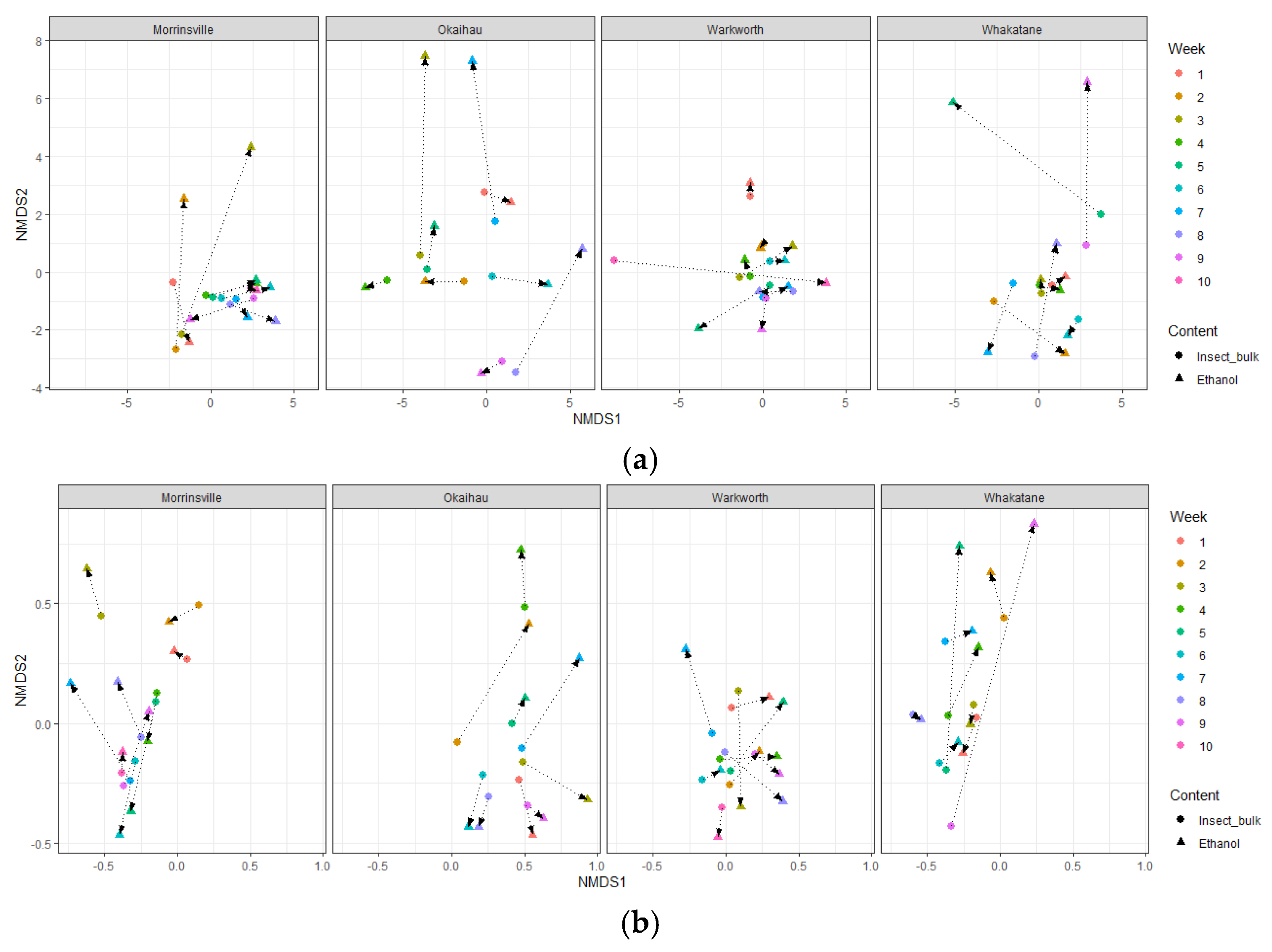
3.5. Similar Insect Community Composition Recovered by Ethanol Fluid and Insect Bulk Samples
4. Discussion
4.1. Detection of Target Species Is Greatly Impacted by Sample Types and Primer Selection
4.2. Consistent Insect Community Composition Data in Ethanol Versus Homogenized Samples
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| eDNA | Environmental DNA |
| COI | Cytochrome oxidase I |
| HTS | High-throughput sequencing |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| MPI | Ministry for Primary Industries |
| NCBI | National Centre for Biotechnology Information |
| NMDS | Non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| PHEL | Plant Health and Environment Laboratory |
| SRA | Sequence Read Archive |
References
- Mellor, P.S.; Boorman, J.; Baylis, M. Culicoides biting midges: Their role as arbovirus vectors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 307–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, P.S.; Carpenter, S.; Harrup, L.; Baylis, M.; Mertens, P.P. Bluetongue in Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: History of occurrence prior to 2006. Prev. Vet. Med. 2008, 87, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, H.; Werner, D. Biting Midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) as Vectors of Viruses. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, G.; Labuschagne, K.; Hermanides, K.; Boikanyo, S.; Majatladi, D.; Morey, L. Comparison of the efficiency of five suction light traps under field conditions in South Africa for the collection of Culicoides species. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 166, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, R.F.; Pedgley, D.E. Possible windborne spread to western Turkey of bluetongue virus in 1977 and of Akabane virus in 1979. Epidemiol. Infect. 1985, 95, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, R.F.; Maarouf, A.R. Possible introduction of epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer virus (serotype 2) and bluetongue virus (serotype 11) into British Columbia in 1987 and 1988 by infected Culicoides carried on the wind. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1991, 55, 367–370. [Google Scholar]
- Braverman, Y.; Chechik, F. Air streams and the introduction of animal diseases borne on Culicoides (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae) into Israel. Rev. Sci. Tech.-Off. Int. Epizoot. 1996, 15, 1037–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, R.F.; Pedgley, D.E.; Tucker, M.R. Possible spread of African horse sickness on the wind. Epidemiol. Infect. 1977, 79, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducheyne, E.; De Deken, R.; Bécu, S.; Codina, B.; Nomikou, K.; Mangana-Vougiaki, O.; Georgiev, G.; Purse, B.; Hendrickx, G. Quantifying the wind dispersal of Culicoides species in Greece and Bulgaria. Geospat. Health 2007, 1, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloster, J.; Mellor, P.; Manning, A.; Webster, H.; Hort, M. Assessing the risk of windborne spread of bluetongue in the 2006 outbreak of disease in northern Europe. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agren, E.C.; Burgin, L.; Lewerin, S.S.; Gloster, J.; Elvander, M. Possible means of introduction of bluetongue virus serotype 8 (BTV-8) to Sweden in August 2008: Comparison of results from two models for atmospheric transport of the Culicoides vector. Vet. Rec. 2010, 167, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Lastra, R.; Leginagoikoa, I.; Plazaola, J.M.; Ocabo, B.; Aduriz, G.; Nunes, T.; Juste, R.A. Bluetongue virus serotype 1 outbreak in the Basque Country (Northern Spain) 2007–2008. Data support a primary vector windborne transport. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, P.W.; Sendow, I.; Pritchard, L.I.; Sukarsih; Eaton, B.T. Regional overview of bluetongue viruses in South-East Asia: Viruses, vectors and surveillance. Vet. Ital. 2004, 40, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eagles, D.; Deveson, T.; Walker, P.; Zalucki, M.; Durr, P. Evaluation of long-distance dispersal of Culicoides midges into northern Australia using a migration model. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2012, 26, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, R.C.; Moar, N.; Tomlinson, A.; Lowe, A. Aerial dispersal of biological material from Australia to New Zealand. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1978, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, K. The transoceanic migration of Lepidoptera to New Zealand—A history and a hypothesis on colonisation. N. Z. Entomol. 1978, 6, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, R.J. Adventive species of Lepidoptera recorded for the first time in New Zealand since 1988. N. Z. Entomol. 2001, 24, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, T. Colonization of eucalypts in New Zealand by Australian insects. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, T.; Frampton, E.; Motha, M.; Horner, G. Arbovirus and arbovirus vector surveillance in New Zealand. Surveillance 1991, 18, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, D.L.; Hagan, D.V.; Wood, J.R. Culicoides responses to 1-octen-3-ol and carbon dioxide in salt marshes near Sea Island, Georgia, USA. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1994, 8, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, L.; Boyd, B.; George, S.; Garcia, T.; Hannah, M.; Begg, D.; Pigott, C. Arbovirus surveillance programme. Surveillance 2019, 46, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Peacock, L.; Boyd, B.; George, S.; Garcia, T.; Hannah, M.; Thornton, D.; Pigott, C. Arbovirus surveillance programme. Surveillance 2020, 47, 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Darling, J.A.; Mahon, A.R. From molecules to management: Adopting DNA-based methods for monitoring biological invasions in aquatic environments. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Shokralla, S.; Zhou, X.; Singer, G.A.; Baird, D.J. Environmental barcoding: A next-generation sequencing approach for biomonitoring applications using river benthos. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Ashton, L.; Pedley, S.M.; Edwards, D.P.; Tang, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Kitching, R.; Dolman, P.M.; Woodcock, P.; Edwards, F.A. Reliable, verifiable and efficient monitoring of biodiversity via metabarcoding. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.F.; Shokralla, S.; Curry, C.; Baird, D.J.; Monk, W.A.; King, I.; Hajibabaei, M. Large-scale biomonitoring of remote and threatened ecosystems via high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milián-García, Y.; Janke, L.A.A.; Young, R.G.; Ambagala, A.; Hanner, R.H. Validation of an Effective Protocol for Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) Detection Using eDNA Metabarcoding. Insects 2021, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Coissac, E.; Zundel, S.; Riaz, T.; Shehzad, W.; Bessière, J.; Taberlet, P.; Pompanon, F. An in silico approach for the evaluation of DNA barcodes. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, M.M.; Specht, A.; Fonseca, V.G. Assessing insect biodiversity with automatic light traps in Brazil: Pearls and pitfalls of metabarcoding samples in preservative ethanol. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 2352–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Valentini, A.; Dejean, T.; Montarsi, F.; Taberlet, P.; Glaizot, O.; Fumagalli, L. Detection of invasive mosquito vectors using environmental DNA (eDNA) from water samples. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin, R.E.; Fonseca, D.M.; Nielsen, A.L.; Leskey, T.C.; Lockwood, J.L. Early detection of invasive exotic insect infestations using eDNA from crop surfaces. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2018, 16, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, K. The speciation of the genus Culicoides (Diptera, Heleidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1954, 47, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.Q.; Jiang, X.H.; Liu, G.P.; Li, X.F.; Hou, X.H. A species checklist of the subgenus Culicoides (Avaritia) in China, with a description of a new species (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae). ZooKeys 2017, 706, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, M.A.; Turner, C.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Renshaw, M.A.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. Environmental conditions influence eDNA persistence in aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Leray, M.; Yang, J.Y.; Meyer, C.P.; Mills, S.C.; Agudelo, N.; Ranwez, V.; Boehm, J.T.; Machida, R.J. A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: Application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina. 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation. 2013. Available online: http://support.illumina.com/downloads/16s_metagenomic_sequencing_library_preparation.ilmn (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (ggplot2); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Martoni, F.; Smith, R.L.; Piper, A.M.; Nancarrow, N.; Aftab, M.; Trebicki, P.; Kimber, R.B.E.; Rodoni, B.C.; Blacket, M.J. Non-destructive insect metabarcoding as a surveillance tool for the Australian grains industry: A first trial for the iMapPESTS smart trap. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2023, 7, e95650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, J.-N.; Vivancos, A.; Piggott, J.J.; Centeno, F.C.; Matthaei, C.D.; Leese, F. Comparison of environmental DNA and bulk-sample metabarcoding using highly degenerate cytochrome c oxidase I primers. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilson, C.E.; Thompson, D.G.; Venier, L.A.; Porter, T.M.; Swystun, T.; Chartrand, D.; Capell, S.; Hajibabaei, M. DNA metabarcoding and morphological macroinvertebrate metrics reveal the same changes in boreal watersheds across an environmental gradient. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocher, A.; Gantier, J.; Gaborit, P.; Zinger, L.; Holota, H.; Valiere, S.; Dusfour, I.; Girod, R.; Bañuls, A.; Murienne, J. Vector soup: High-throughput identification of Neotropical phlebotomine sand flies using metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackman, R.C.; Mächler, E.; Altermatt, F.; Arnold, A.; Beja, P.; Boets, P.; Egeter, B.; Elbrecht, V.; Filipe, A.F.; Jones, J.I. Advancing the use of molecular methods for routine freshwater macroinvertebrate biomonitoring—The need for calibration experiments. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2019, 3, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Spall, J.L.; Shokralla, S.; van Konynenburg, S. Assessing biodiversity of a freshwater benthic macroinvertebrate community through non-destructive environmental barcoding of DNA from preservative ethanol. BMC Ecol. 2012, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdozain, M.; Thompson, D.G.; Porter, T.M.; Kidd, K.A.; Kreutzweiser, D.P.; Sibley, P.K.; Swystun, T.; Chartrand, D.; Hajibabaei, M. Metabarcoding of storage ethanol vs. conventional morphometric identification in relation to the use of stream macroinvertebrates as ecological indicators in forest management. Ecol. Ind. 2019, 101, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizka, V.M.; Leese, F.; Peinert, B.; Geiger, M.F. DNA metabarcoding from sample fixative as a quick and voucher-preserving biodiversity assessment method. Genome 2019, 62, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krehenwinkel, H.; Wolf, M.; Lim, J.Y.; Rominger, A.J.; Simison, W.B.; Gillespie, R.G. Estimating and mitigating amplification bias in qualitative and quantitative arthropod metabarcoding. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linard, B.; Arribas, P.; Andújar, C.; Crampton-Platt, A.; Vogler, A.P. Lessons from genome skimming of arthropod-preserving ethanol. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquina, D.; Esparza-Salas, R.; Roslin, T.; Ronquist, F. Establishing arthropod community composition using metabarcoding: Surprising inconsistencies between soil samples and preservative ethanol and homogenate from Malaise trap catches. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1516–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, S.F.; Cottenie, K.; Gleason, J.E. Ethanol eDNA Reveals Unique Community Composition of Aquatic Macroinvertebrates Compared to Bulk Tissue Metabarcoding in a Biomonitoring Sampling Scheme. Diversity 2021, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, L.; Van der Hoorn, B.; Gorsich, E.E.; Trimbos, K.; Bodegom, P.V.; Schrama, M. How does eDNA compare to traditional trapping? Detecting mosquito communities in South-African freshwater ponds. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.N.; Larson, E.R. No evidence that crayfish carcasses produce detectable environmental DNA (eDNA) in a stream enclosure experiment. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, S.; Rodríguez, S.; Martínez, J.L.; Borrell, Y.J.; Ardura, A.; García-Vázquez, E. Evaluating freshwater macroinvertebrates from eDNA metabarcoding: A river Nalón case study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, L.M.; Simmons, M.; Wegleitner, B.J.; Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R. Quantifying environmental DNA signals for aquatic invasive species across multiple detection platforms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12800–12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunker, K.J.; Sepulveda, A.J.; Massengill, R.L.; Olsen, J.B.; Russ, O.L.; Wenburg, J.K.; Antonovich, A. Potential of environmental DNA to evaluate northern pike (Esox lucius) eradication efforts: An experimental test and case study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrecht, V.; Peinert, B.; Leese, F. Sorting things out: Assessing effects of unequal specimen biomass on DNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6918–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deagle, B.E.; Jarman, S.N.; Coissac, E.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. DNA metabarcoding and the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I marker: Not a perfect match. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowart, D.A.; Pinheiro, M.; Mouchel, O.; Maguer, M.; Grall, J.; Miné, J.; Arnaud-Haond, S. Metabarcoding is powerful yet still blind: A comparative analysis of morphological and molecular surveys of seagrass communities. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UNCROSS2: Identification of cross-talk in 16S rRNA OTU tables. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, V.A.; Ferreira, S.; Campos, R.M.; da Silva, L.P.; Veríssimo, J.; Corley, M.F.; Beja, P. Efficient assessment of nocturnal flying insect communities by combining automatic light traps and DNA metabarcoding. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Múrria, C.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Somma, S.; Väisänen, L.; Fortuño, P.; Arnedo, M.A.; Prat, N. Taxonomic accuracy and complementarity between bulk and eDNA metabarcoding provides an alternative to morphology for biological assessment of freshwater macroinvertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doloiras-Laraño, A.D.; Yaegashi, S.; Serrana, J.M.; Ishitani, N.; Watanabe, K. Comparison of eDNA, bulk-sample metabarcoding, and morphological approaches: A case study of riverine benthic macroinvertebrate communities. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.M.; Galhardo, M.; Filipe, A.F.; Teixeira, A.; Pinheiro, P.; Paupério, J.; Alves, P.C.; Beja, P. Have the cake and eat it: Optimizing nondestructive DNA metabarcoding of macroinvertebrate samples for freshwater biomonitoring. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

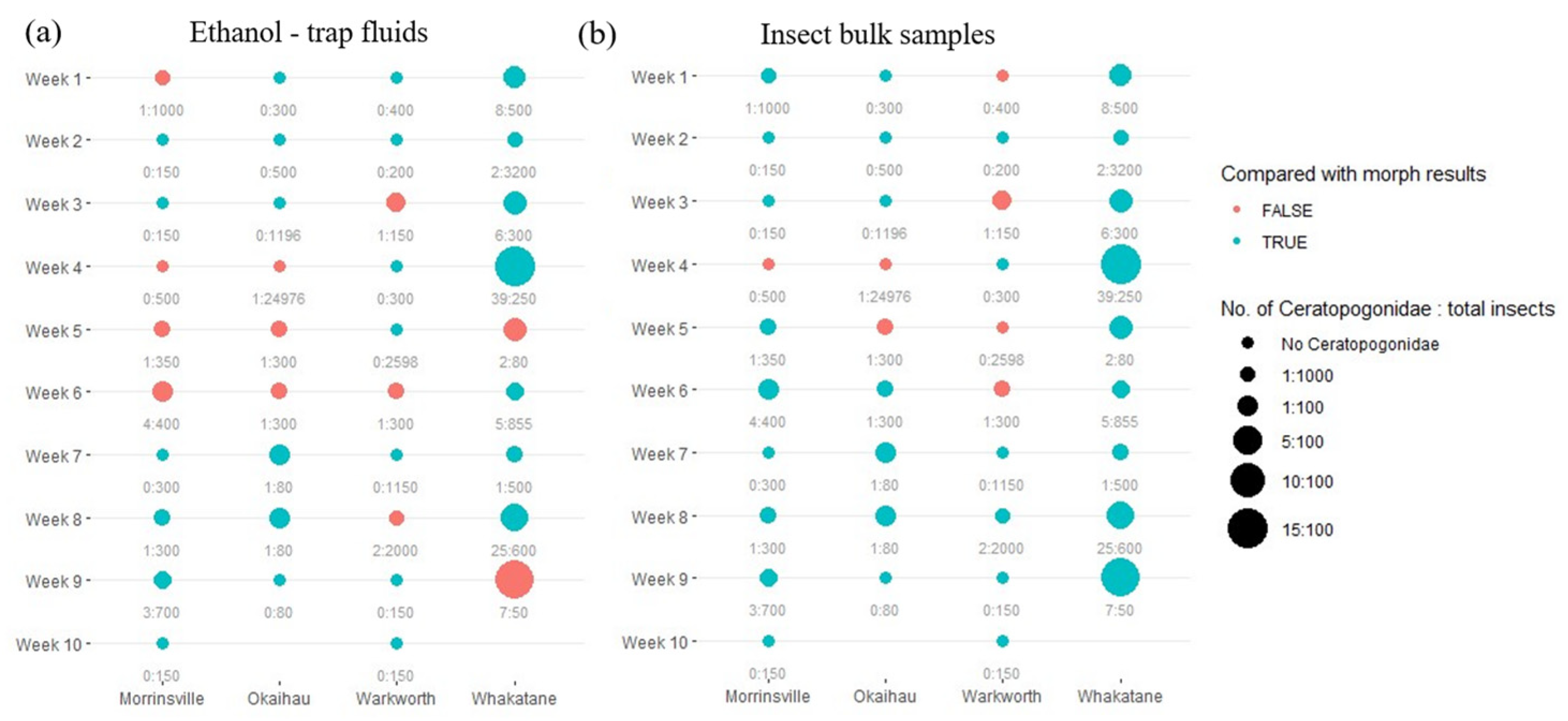

| Farm Location | Week Number | Collection Date | Total Number of Insects in the Trap | Number of Native Ceratopogonidae (% of Total Insects) | If Culicoides Present |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Okaihau | 1 | 7 February 2020 | 300 | 0 | No |
| 2 | 11 February 2020 | 500 | 0 | No | |
| 3 | 14 February 2020 | 1196 | 0 | No | |
| 4 | 24 February 2020 | 24,976 | 1 | No | |
| 5 | 4 March 2020 | 300 | 1 | No | |
| 6 | 9 March 2020 | 300 | 1 | No | |
| 7 | 18 March 2020 | 80 | 1 | No | |
| 8 | 23 March 2020 | 80 | 1 | No | |
| 9 | 31 March 2020 | 80 | 0 | No | |
| Total | 27,812 | 5 (0.02%) | |||
| Warkworth | 1 | 7 February 2020 | 600 | 0 | No |
| 2 | 12 February 2020 | 200 | 0 | No | |
| 3 | 19 February 2020 | 150 | 1 | No | |
| 4 | 25 February 2020 | 300 | 0 | No | |
| 5 | 28 February 2020 | 2598 | 0 | No | |
| 6 | 10 March 2020 | 300 | 1 | No | |
| 7 | 19 March 2020 | 1150 | 0 | No | |
| 8 | 31 March 2020 | 2000 | 2 | No | |
| 9 | 3 April 2020 | 150 | 0 | No | |
| 10 | 9 April 2020 | 150 | 0 | No | |
| Total | 7598 | 4 (0.05%) | |||
| Morrinsville | 1 | 7 February 2020 | 1000 | 1 | No |
| 2 | 12 February 2020 | 150 | 0 | No | |
| 3 | 14 February 2020 | 150 | 0 | No | |
| 4 | 21 February 2020 | 500 | 0 | No | |
| 5 | 28 February 2020 | 350 | 1 | No | |
| 6 | 6 March 2020 | 400 | 4 | No | |
| 7 | 13 March 2020 | 300 | 0 | No | |
| 8 | 24 March 2020 | 300 | 1 | No | |
| 9 | 27 March 2020 | 700 | 3 | No | |
| 10 | 3 April 2020 | 150 | 0 | No | |
| Total | 4000 | 10 (0.25%) | |||
| Whakatane | 1 | 12 February 2020 | 500 | 8 | No |
| 2 | 14 February 2020 | 3200 | 2 | No | |
| 3 | 24 February 2020 | 300 | 6 | No | |
| 4 | 28 February 2020 | 250 | 39 | No | |
| 5 | 6 March 2020 | 80 | 2 | No | |
| 6 | 13 March 2020 | 855 | 5 | No | |
| 7 | 23 March 2020 | 500 | 1 | No | |
| 8 | 27 March 2020 | 600 | 25 | No | |
| 9 | 9 April 2020 | 50 | 7 | No | |
| Total | 6335 | 95 (1.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Li, D.; Balan, R.K.; George, S.; Peacock, L.; Pal, C. Comparative Assessment of Environmental DNA and Bulk-Sample Metabarcoding in Biosecurity Surveillance for Detecting Biting Midges (Ceratopogonidae). Insects 2025, 16, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060564
Wu J, Li D, Balan RK, George S, Peacock L, Pal C. Comparative Assessment of Environmental DNA and Bulk-Sample Metabarcoding in Biosecurity Surveillance for Detecting Biting Midges (Ceratopogonidae). Insects. 2025; 16(6):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060564
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jieyun, Dongmei Li, Rebijith K. Balan, Sherly George, Lora Peacock, and Chandan Pal. 2025. "Comparative Assessment of Environmental DNA and Bulk-Sample Metabarcoding in Biosecurity Surveillance for Detecting Biting Midges (Ceratopogonidae)" Insects 16, no. 6: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060564
APA StyleWu, J., Li, D., Balan, R. K., George, S., Peacock, L., & Pal, C. (2025). Comparative Assessment of Environmental DNA and Bulk-Sample Metabarcoding in Biosecurity Surveillance for Detecting Biting Midges (Ceratopogonidae). Insects, 16(6), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060564








