Insight into the Microbiota of Orthopteran in Relation to Gut Compartmentalisation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Survey Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Composition and Role of Gut Microbiome
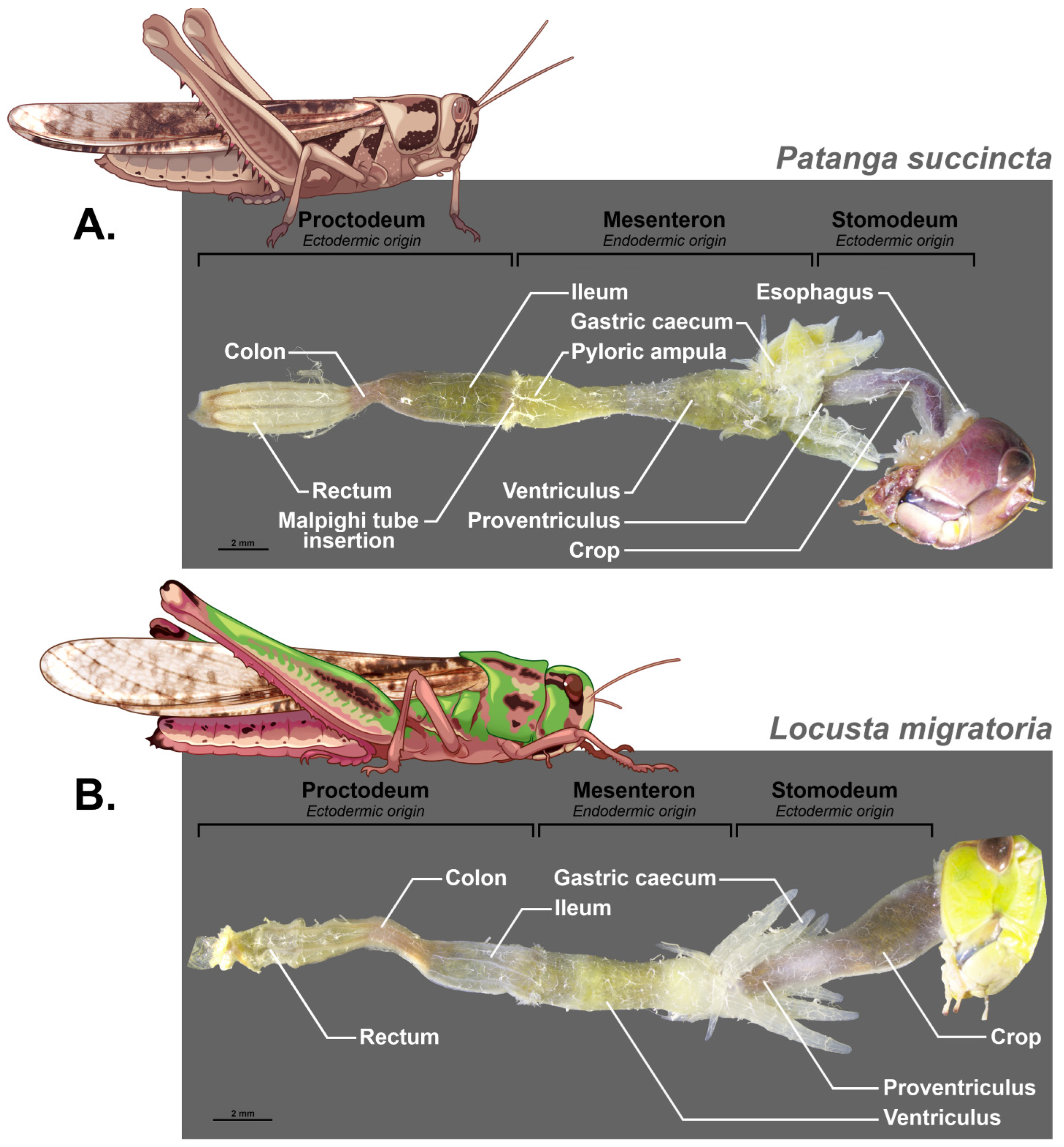
3.2. Compartmentalisation of the Digestive Tract
3.3. Digestive Tract Compartmentation and Microbiome Function
3.4. Microbiome and Food Safety
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monzenga Lokela, J.C.; Le Goff, G.; Bundo, K.; Hance, T. Influence of substrates on the rearing success of Rhynchophorus phoenicis (Fabricius). AJFST 2017, 81, 007–013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, F. La production de lépidoptères pour l’alimentation des populations d’Afrique: État de la question. Proc. R. Acad. Overseas Sci. 2020, 1, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- van Huis, A.; Rumpold, B.; Maya, C.; Roos, N. Nutritional Qualities and Enhancement of Edible Insects. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2021, 41, 551–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraporn, S.; Cansee, S.; Hupfauf, S.; Klammsteiner, T. Lactic Acid Bacteria from Bombyx mori Frass: Probiotic Properties and Antagonistic Activities. Agriculture 2024, 14, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhujaili, A.; Nocella, G.; Macready, A. Insects as food: Consumers’ acceptance and marketing. Foods 2023, 12, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongema, Y. World List of Edible Insects; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2015; Available online: https://tinyurl.com/yc55utv3 (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- van Huis, A. Insects as food and feed, a new emerging agricultural sector: A review. J. Insects Food Feed. 2020, 7, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, M.; Tougeron, K.; Hamidovic, A.; Tinkeu, L.S.N.; Hance, T.; Renoz, F. Deciphering the functional diversity of the gut microbiota of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens): Recent advances and future challenges. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordiean, A.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Stolarski, M.J.; Peni, D. Growth Potential of Yellow Mealworm Reared on Industrial Residues. Agriculture 2020, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magara, H.J.; Niassy, S.; Ayieko, M.A.; Mukundamago, M.; Egonyu, J.P.; Tanga, C.M.; Kimathi, E.K.; Ongere, J.O.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Hugel, S.; et al. Edible crickets (Orthoptera) around the world: Distribution, nutritional value, and other benefits, a review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7, 537915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krongdang, S.; Phokasem, P.; Venkatachalam, K.; Charoenphun, N. Edible insects in Thailand: An overview of status, properties, processing, and utilization in the food industry. Foods 2023, 12, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidau, C.J. Patterns in Orthoptera biodiversity. I. Adaptations in ecological and evolutionary contexts. JIB 2014, 2, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects–diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecoq, M.; Zhang, L. Encyclopedia of Pest Orthoptera of the World; Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lecoq, M.; Latchininsky, A.; Hunter, D. Locust and Grasshopper Management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 7, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; Frederich, M.; Uyttenbroeck, R.; Hatt, S.; Malik, P.; Lebecque, S.; Hamidia, M.; Maizek, K.; Goffin, D.; Willems, L.; et al. Grasshoppers as a food source? A review. BASE 2016, 20 (Suppl. 1), 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Itterbeeck, J.; Rakotomalala Andrianavalona, I.N.; Rajemison, F.I.; Rakotondrasoa, J.F.; Ralantoarinaivo, V.R.; Hugel, S.; Fisher, B.L. Diversity and Use of Edible Grasshoppers, Locusts, Crickets, and Katydids (Orthoptera) in Madagascar. Foods 2019, 8, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Cruz-Monterroza, R.G.; Liceaca, M. Beyond human nutrition of edible insects: Health benefits and safetly aspects. Insects 2022, 13, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemsawasd, V.; Inthachat, W.; Suttisansanee, U.; Temviriyanukul, P. Road to The Red Carpet of Edible Crickets through Integration into the Human Food Chain with Biofunctions and Sustainability: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, M.D. Complete nutrient composition of commercially raised invertebrates used as food for insectivores. Zoo Biol. 2002, 21, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, M.; Songsermpong, S.; Kaewtapee, C.; Chanput, W. Effect of diet on the growth performance, feed conversion, and nutrient content of the house cricket. J. Insect Sci. 2020, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyen, G.; Ooms, T.; Vogels, L.; Vreysen, S.; Bovy, A.; Sabine, V.M.; Meesman, F. Insects as an Alternative Source for the Production of Fats for Cosmetics. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 69, 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Jino, T.; Surawang, S. Chemical Composition and Optimum Condition of Protein Concentrate Extraction from Commercial Crickets. TJST 2021, 10, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagio, F.P.; Tamaki, F.K.; Terra, W.R.; Ribeiro, A.F. Digestive morphophysiology of Gryllodes sigillatus (Orthoptera: Gryllidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffar, S.; Ahmad, S.; Lu, Y. Contribution of insect gut microbiota and their associated enzymes in insect physiology and biodegradation of pesticides. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 979383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraporn, S.; Liu, J.; Ren, F.; Wang, L.; Feng, M.; Terenius, O.; Swevers, L. Towards a Rational Basis for the Selection of Probiotics to Improve Silkworm Health and Performance. Insects 2025, 16, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandeweyer, D.; De Smet, J.; Van Looveren, N.; Van Campenhout, L. Biological contaminants in insects as food and feed. J. Insects Food Feed. 2021, 7, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.P. The normal bacterial flora of the alimentary canal of laboratory stocks of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria Forskål. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1966, 8, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, H.; Jia, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, Z. The Gut Bacteria of Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae) by Culturomics. Insects 2025, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, M.; Prather, C.; Sun, Y. The gut bacterial communities across six grasshopper species from a coastal tallgrass prairie. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ling, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Xue, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Li, X. Analysis of Intestinal Microbial Diversity of Four Species of Grasshoppers and Determination of Cellulose Digestibility. Insects 2022, 13, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, R.; Charnley, K. Mutualism between the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria and its gut microbiota. Res. Microbiol. 2002, 153, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.C.; Srygley, R.B.; Healy, F.; Swaminath, K.; Mueller, U.G. Spatial structure of the Mormon cricket gut microbiome and its predicted contribution to nutrition and immune function. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavy, O.; Lewin-Epstein, O.; Bendett, Y.; Gophna, U.; Gefen, E.; Hadany, L.; Ayali, A. Microbiome–related aspects of locust density-dependent phase transition. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, R.J.; Webster, G.; Weightman, A.J.; Charnley, A.K. Diversity of gut microbiota increases with aging and starvation in the desert locust. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2010, 97, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavy, O.; Gophna, U.; Gefen, E.; Ayali, A. The Effect of Density-Dependent Phase on the Locust Gut Bacterial Composition. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acoff, A.B. Investigating the Schistocerca Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Gregarious Behavior. Master’s Thesis, Southern Illinois University at Edwardsville, Edwardsville, IL, USA, 2023; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Idowu, A.B.; Edema, M.O. The microbial flora of the different gut regions of the variegated grasshopper Zonocerus variegatus (L.) (Orthoptera: Pyrgomorphidae). GJPAST 2002, 8, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, H.; Che, X. Bacterial Communities in the Feces of Laboratory Reared Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae) across Different Developmental Stages and Sexes. Insects 2022, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, W.; Liang, K.; Li, F.; Qin, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Gut microorganisms of Locusta migratoria in various life stages and its possible influence on cellulose digestibility. mSystems 2024, 9, e0060024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, E.; Sitinjak, I.V.; Nasution, A.F. Grasshopper (Oxya chinensis) Gut Bacteria and their Cellulolytic Activity. JPAM 2024, 18, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, D.W.; Dsouza, M.; Biswas, K.; Ward, D.F.; Deines, P.; Taylor, M.W. Microbial community structure in the gut of the New Zealand insect Auckland tree weta (Hemideina thoracica). Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleknavičius, D.; Lukša, J.; Strazdaitė-Žielienė, Ž.; Servienė, E. The Bacterial Microbiota of Edible Insects Acheta domesticus and Gryllus assimilis Revealed by High Content Analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, W.Q.; Xu, S.Q.; Guan, D.L. The comparison of gut bacteria communities and the functions among the sympatric grasshopper species from the Loess Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 806927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, Q.; Qin, M.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Shi, F. The Role of Feeding Characteristics in Shaping Gut Microbiota Composition and Function of Ensifera (Orthoptera). Insects 2022, 13, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mazel, F.; Pitteloud, C.; Guisan, A.; Pellissier, L. Contrasted host specificity of gut and endosymbiont bacterial communities in alpine grasshoppers and crickets. ISME Commun. 2024, 4, ycad013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoda, S.; Masui, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Sasaki, T. Wolbachia infection and cytoplasmic incompatibility in the cricket Teleogryllus taiwanemma. J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203, 2503–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, D. Determination of Wolbachia diversity in 23 cricket species (Gryllidae) from China. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2022, 115, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, Z.; Yuan, H. The gut microbiota diversity of five Orthoptera (Insecta, Polyneoptera) insects determined by DNA metabarcoding. Biodivers. Data J. 2023, 11, e98162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.H.; Stat, M.; Bunce, M.; Simmons, L.W. The influence of diet and environment on the gut microbial community of field crickets. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 4704–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, F.; Chen, L.; Cao, Q.; Shi, F. Gut bacterial communities across 12 Ensifera (Orthoptera) at different feeding habits and its prediction for the insect with contrasting feeding habits. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Douglas, A.E. The microbial dimension in insect nutritional ecology. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopania, E.; Wietecha, J.; Ciechańska, D. Studies on isolation of cellulose fibres from waste plant biomass. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2012, 96, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Y.; Li, W.; Li, F.; Xue, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, K.; Li, X. Microbial gut diversity in four grasshopper species and its correlation with cellulose digestibility. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1002532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.M. Cellulose digestion in insects. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1983, 75, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.J. Biodegradation of Cellulose: Enzymology and Biotechnology; Technomic Publishing Co. Inc.: Lancaster, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Oppert, C.; Klingeman, W.E.; Willis, J.D.; Oppert, B.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Prospecting for cellulolytic activity in insect digestive fluids. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 155, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.D.; Klingeman, W.E.; Oppert, C.; Oppert, B.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Characterization of cellulolytic activity from digestive fluids of Dissosteira carolina (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 157, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Gao, X.; Wang, F.; Song, A. Cellulolytic activity and structure of symbiotic bacteria in locust guts. GMR 2014, 13, 7926–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.; Muge, E.; Wamalwa, B. Cellulolytic Bacillus species isolated from the gut of the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria. Sci. Afr. 2021, 11, e00665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, S.; Raguvaran, K.; Nagarajan, K.; Chinnaperumal, K.; Maheswaran, R.; Chinnasamy, R. Isolation, molecular identification, and characterization of cellulolytic microbes from the gut of grasshopper Eyprepocnemis alacris alacris (Serv. 1838). Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 14, 21121–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhao, L.; Wu, F.; Zhou, H.; Shi, F. Screening and Identification of Protease-Producing Microorganisms in the Gut of Gryllotalpa orientalis (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae). Insects 2024, 15, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doidge, N.P.; Allen, J.L.; Bushell, R.; Lynch, M.; Browning, G.F.; Marenda, M.S. Development of a qPCR assay to identify and differentiate insect-associated strains of the Serratia marcescens complex. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2025, 37, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, M.G.; Klug, M.J. The contribution of hindgut bacteria to dietary carbohydrate utilization by crickets (Orthoptera: Gryllidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiology. A Comp. Physiol. 1991, 98, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, R.J.; Vennard, C.T.; Charnley, A.K. Exploitation of gut bacteria in the locust. Nature 2000, 403, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, R.J.; Vennard, C.T.; Charnley, A.K. A note: Gut bacteria produce components of a locust cohesion pheromone. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, R.J.; Vennard, C.T.; Buckling, A.; Charnley, A.K. Diversity of locust gut bacteria protects against pathogen invasion. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, C. The anatomy and histology of the alimentary tract of Locusta migratoria L. (Orthoptera: Acrididae). J. Morphol. 1939, 64, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarov, B.P. Grasshoppers and Locusts: A Handbook of General Acridology; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1966; Volume 1, p. 481. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Han, W.; Yin, H. Morphology and fine organization of the midgut of Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thomas, J.G. The sense organs on the mouth parts of the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria). J. Zool. 1966, 148, 420–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.D. The fine structure of the salivary glands of the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria Forskål. Z. Für Zellforsch. Und Mikrosk. Anat. 1969, 98, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Terra, W.R. Compartmentalization of the digestive process in Abracris flavolineata (Orthoptera: Acrididae) adults. Insect Biochem. 1990, 20, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochuli, D.F.; Roberts, B.; Sanson, G.D. Foregut Morphology of Locusta migratoria (L.) (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Aust. J. Entomol. 1994, 33, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanetti, C.S.; Zefa, E.; Passetti, F.; Mesa, A. Morphological characterization and comparative analysis of the proventriculus from three species of Endecous Saussure, 1878 (Orthoptera: Gryllidae: Phalangopsinae). Entomotropica 2002, 17, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Ren, B. A comparative study of the proventricular structure in twenty Chinese Tettigoniidae (Orthoptera) species. Entomol. Fenn. 2010, 23, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W. Peritrophic Membranes; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, R.O.; Cardoso, C.; Leal, C.S.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Ferreira, C.; Terra, W.R. Domain structure and expression along the midgut and carcass of peritrophins and cuticle proteins analogous to peritrophins in insects with and without peritrophic membrane. J. Insect Physiol. 2019, 114, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, J.L. Specialization in the alimentary canal of some mole crickets (Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1983, 12, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, W.R.; Ferreira, C.; Silva, C.P. Molecular Physiology and Evolution of Insect Digestive Systems. Entomology in Focus; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marana, S.R.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Terra, W.R.; Ferreira, C. Ultrastructure and secretory activity of Abracris flavolineata (Orthoptera: Acrididae) midguts. J. Insect Physiol. 1997, 43, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakici, Ö.; Ergen, G. Histologic description of midgut in Melanogryllus desertus (Pallas, 1771) (Orthoptera: Gryllidae). Biharean Biol. 2012, 6, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Karmakar, P. Symbionts associated with insect digestive system and their role in insect nutrition. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- Polat, I. The excretory system of Orthoptera. In Recent Advances in Biological Sciences; Iksad Publishing House: Ankara, Turkey, 2021; Volume 5, pp. 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, K.; Asahi, T.; Kataoka, K. Spatial and Sexual Divergence of Gut Bacterial Communities in Field Cricket Teleogryllus occipitalis (Orthoptera: Gryllidae). Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 2627–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.; Charnley, A.K. Abundance and distribution of the gut flora of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1981, 38, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, D.J.W.; Kaufman, M.G.; Klug, M.J.; Tiedje, J.M. Characterization of the cricket hindgut microbiota with fluorescently labeled rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Aquilanti, L.; Garofalo, C.; Roncolini, A.; Sabbatini, R.; Clementi, F.; Osimani, A. A glimpse into the microbiota of marketed ready-to-eat crickets (Acheta domesticus). Indian J. Microbiol. 2020, 60, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Camenzuli, L.; Belluco, S.; Meijer, N.; Ricci, A. Food safety issues related to uses of insects for feeds and foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klunder, H.C.; Wolkers-Rooijackers, J.; Korpela, J.M.; Nout, M.R. Microbiological aspects of processing and storage of edible insects. Food Control. 2012, 26, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoops, J.; Crauwels, S.; Waud, M.; Claes, J.; Lievens, B.; Van Campenhout, L. Microbial community assessment of mealworm larvae (Tenebrio molitor) and grasshoppers (Locusta migratoria migratorioides) sold for human consumption. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cassi, X.; Söderqvist, K.; Bakeeva, A.; Vaga, M.; Dicksved, J.; Vagsholm, I.; Jansson, A.; Boqvist, S. Microbial communities and food safety aspects of crickets (Acheta domesticus) reared under controlled conditions. J. Insects Food Feed. 2020, 6, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangena, D.N.; Mutungi, C.; Imathiu, S.; Kinyuru, J.; Affognon, H.; Ekesi, S.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Fiaboe, K.K. Effects of traditional processing techniques on the nutritional and microbiological quality of four edible insect species used for food and feed in East Africa. Foods 2020, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Origin | Tissue | Culture of Metabarcoding | Main Identified Phyla | Main Identified Families | Main Identified Genera/Species | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schistocerca gregaria (desert locust) | Laboratory reared | Foregut Midgut Hindgut | Culture | N/A | Bacilli Streptococci | Bacillus, Clostridium, Staphylococcus, Escherichia, Enterobacter, Klebsiella | [28] |
| Schistocerca gregaria | Laboratory reared | Whole gut | DGGE analysis | N/A | N/A | Enterococccus, Klebsiella, Serratia | [35] |
| Schistocerca gregaria | Laboratory-reared and field-collected | Hindgut | Illumina MiSeq | Proteobacteria Firmicutes | N/A | Enterobacter, Weissella, Spiroplasma, Enterococcus | [36] |
| Schistocerca gregaria (gregarious and solitary phase) | Laboratory reared | Feces and integument | Illumina MiSeq | Proteobacteria Firmicutes Actinobacteria Bacteriodetes | Enterobacteriaceae | Weissella, Klebsiella, Cronobacter, Enterobacter, Pantoea, Pediococcus, Enterobacillus, Pseudomonas, Pseudocitrobacter | [34] |
| Schistocerca cancellata | Laboratory-reared and field-collected | Whole gut | 16S Illumina sequencing | N/A | N/A | Weissella, Methylobacterium-Methylorubrum Lactococcus Pseudomonas Corynebacterium Serratia Curtobacterium Aureimonas Ammorrhizobium Enterococcus | [37] |
| Gampsocleis gratiosa | Bought on a market | Whole gut | Culturomics | Proteobacteria Firmicutes Actinobacteria | Enterobacterales Lactobacillales Bacillales | Klebsiella, Lactococcus, Enterococccus Kluyvera | [29] |
| Zonocerus variegatus | Field collected | Foregut Midgut Hindgut | Culture | Enterobacteriaceae | N/A | Proteus, Alcaligenes, Escherichia, Serratia, Sreptococcus, Lactobacillus, Staphylococcus | [38] |
| Anabrus simplex (cricket) | Laboratory-reared and field-collected | Foregut Midgut Hindgut | Illumina and Culture | N/A | Lactobacilliaceae Entorobacteriaceae Streptococcace | Pediococcus sp., P. acidicatici, Lactobacilus sp., Pantoae agglomerans, Klebsiella sp., Lactococcus garvieae | [33] |
| Gampsocleis gratiosa | Laboratory reared | Feces | Illumina MiSeq | Proteobacteria Firmicutes Thermotogae Bacteroidetes Acidobacteria Actinobacteria Chloroflexota Euryarchaeota Verrucomicrobia | Enterococcaceae Lactobacillaceae Streptococcaceae Burkholderiaceae Enterobacteriaceae Pseudomonadaceae Petrotogaceae | Kluyvera Obesumbacterium Buttiauxella Lactobacillus Hafnia Weissella Lactococcus Burkholderia Citrobacter Escherichia Serratia | [39] |
| Locusta migratoria | Laboratory reared | Whole gut | 16S rRNA, Sanger sequencing | Proteobacteria Firmicutes Bacteroidetes Actinobacteria | N/A | Enterobacter Weissella Lactococcus Pseudocitro bacter Kluyvera Providentia Serratia | [40] |
| Oxya chinensis | Field collected | Whole gut | 16S rRNA | Firmicutes | N/A | Bacillus wiedmannii, Bacillus marcorestinctum, Bacillus halotolerans, Paenibacillus zanthoxyli, Bacillus hominis | [41] |
| Hemideina thoracica | Field collected | Foregut Midgut Hindgut | 16S rRNA | Actinobacteria Bacteroidetes Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria Verrucomicrobia | Coriobacteriaceae Bacteroidaceae Porphyromonadaceae Rikenellaceae Deferribacteraceae Lactobacillaceae Leuconostocaceae Christensenellaceae Clostridiaceae Defluviitaleaceae Lachnospiraceae Ruminococcaceae Erysipelotrichaceae Desulfovibrionaceae Unclassified Verrucomicrobiaceae | N/A | [42] |
| Conocephalus fasciatus, Conocephalus strictus, Orchelimum concinnum, Orchelimum vulgare, Paroxya atlantica, Scudderia texensis | Field collected | Whole gut | Illumina MiSeq | Proteobacteria Actinobacteria Firmicutes Tenericutes | Listeriaceae Lactobacillaceae Methylobacteriaceae Rhizobiaceae Sphingomonadaceae Enterobacteriaceae Pseudomonadaceae | N/A | [30] |
| Acheta domesticus, Gryllus assimilis | Laboratory-reared and field-collected | Surface and whole body | Next-generation sequencing and Illumina MiSeq | Parabacteroides Bacteroides Firmicutes | Porphyromonadaceae Bacteriodaceae Rikenellaceae Enterobacteriaceae Verrucommicrobiaceae Pseudomonadaceae | Lactococcus, Candidatus, Azobacteroides, Coprococcus, Enterococcus, Akkermansia, Acinetobacter | [43] |
| Acrida cinerea, Trilophilia annulata, Atractomorpha sinensis, Synergus mongolicus | Field collected | Whole gut | Illumina HiSeq | Proteobacteria Firmicutes Cyanobacteria Actinobacteria Bacteroidetes Tenericutes Fusobacteria | Enterobacteriaceae Streptococcaceae Enterococcaceae Moraxellaceae Anaplasmataceae Staphylococcaceae Microbacteriaceae Clostridiaceae Xanthomonadaceae Brevibacteriaceae | Klebsiella Staphylococcus Wolbachia Acinetobacter Pantoea, Enterococcus Stenotrophomonas Microbacterium Brevibacterium Corynebacterium Lactococcus | [31] |
| Oxya chinensis, Paratettix meridionalis, Gastrimargus marmoratus, Calliptamus abbreviatus | Field collected | Whole gut | Illumina MiSeq | Firmicutes Proteobacteria | N/A | Bacillus Enterobacter Enterococcus Pantoea Halomonas | [44] |
| Mecopoda niponensis, Ocellarnaca emeiensis, Gryllotalpa orientalis | Field collected | Midgut Hindgut | Illumina MiSeq | Proteobacteria Mucoromycota Basidiomycota Firmicutes | N/A | Intestinimonas massiliensis, Leclercia adecarboxylata, Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniea, Kluyveria criocrescens, Lactococcus lactis | [45] |
| 24 Species | Field collected | Whole gut | 16S rRNA | N/A | Enterobacteriaceae Erwiniaceae Sphingomonadaceae Streptococcaceae | Wolbachia (super group A, B and F) Spiroplasma Pantoea | [46] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hance, T.; Hamidovic, A.; Suraporn, S. Insight into the Microbiota of Orthopteran in Relation to Gut Compartmentalisation. Insects 2025, 16, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060555
Hance T, Hamidovic A, Suraporn S. Insight into the Microbiota of Orthopteran in Relation to Gut Compartmentalisation. Insects. 2025; 16(6):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060555
Chicago/Turabian StyleHance, Thierry, Alisa Hamidovic, and Siripuk Suraporn. 2025. "Insight into the Microbiota of Orthopteran in Relation to Gut Compartmentalisation" Insects 16, no. 6: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060555
APA StyleHance, T., Hamidovic, A., & Suraporn, S. (2025). Insight into the Microbiota of Orthopteran in Relation to Gut Compartmentalisation. Insects, 16(6), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060555







