Mitogenomic Characterization and Comparative Analysis of Three Egg Parasitoid Wasps Parasitizing Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.2. Sanger Sequencing
2.3. High-Throughout Sequencing
2.4. Mt Genome Sequencing, Annotation and Bioinformatic Analyses
2.5. Gene Arrangement and Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Genome Structure, Organization and Composition
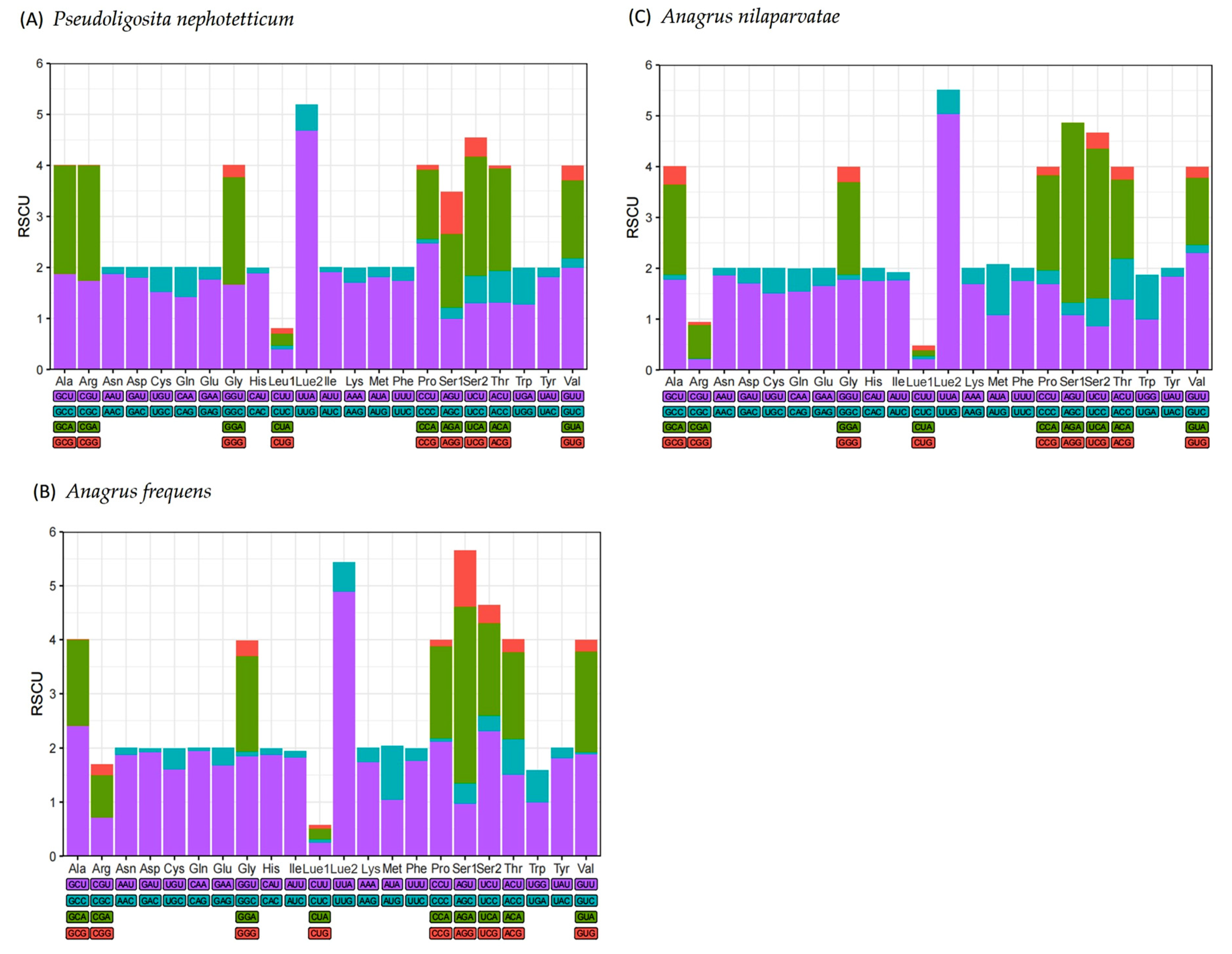
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes
3.3. The tRNAs and rRNAs
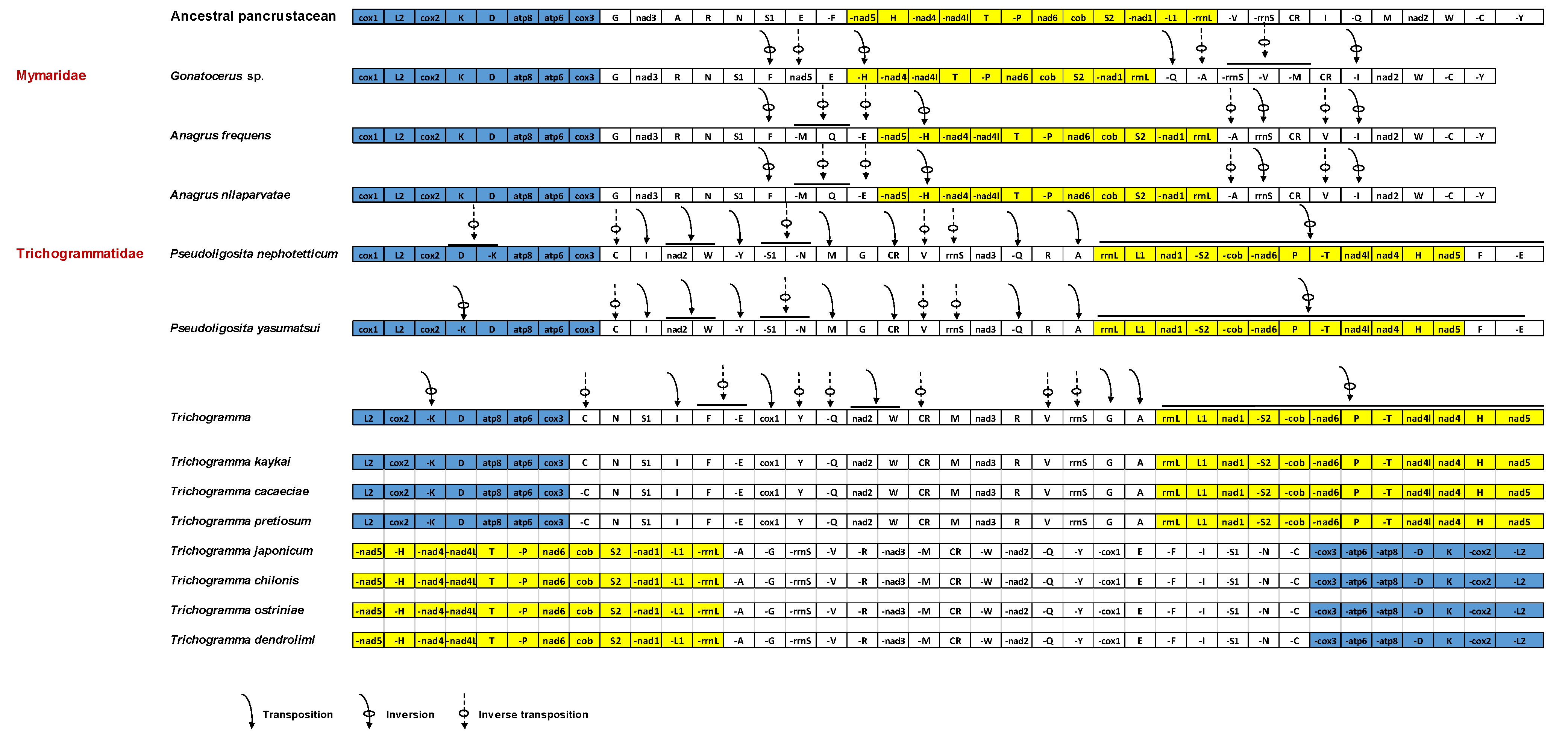
3.4. Gene Rearrangement
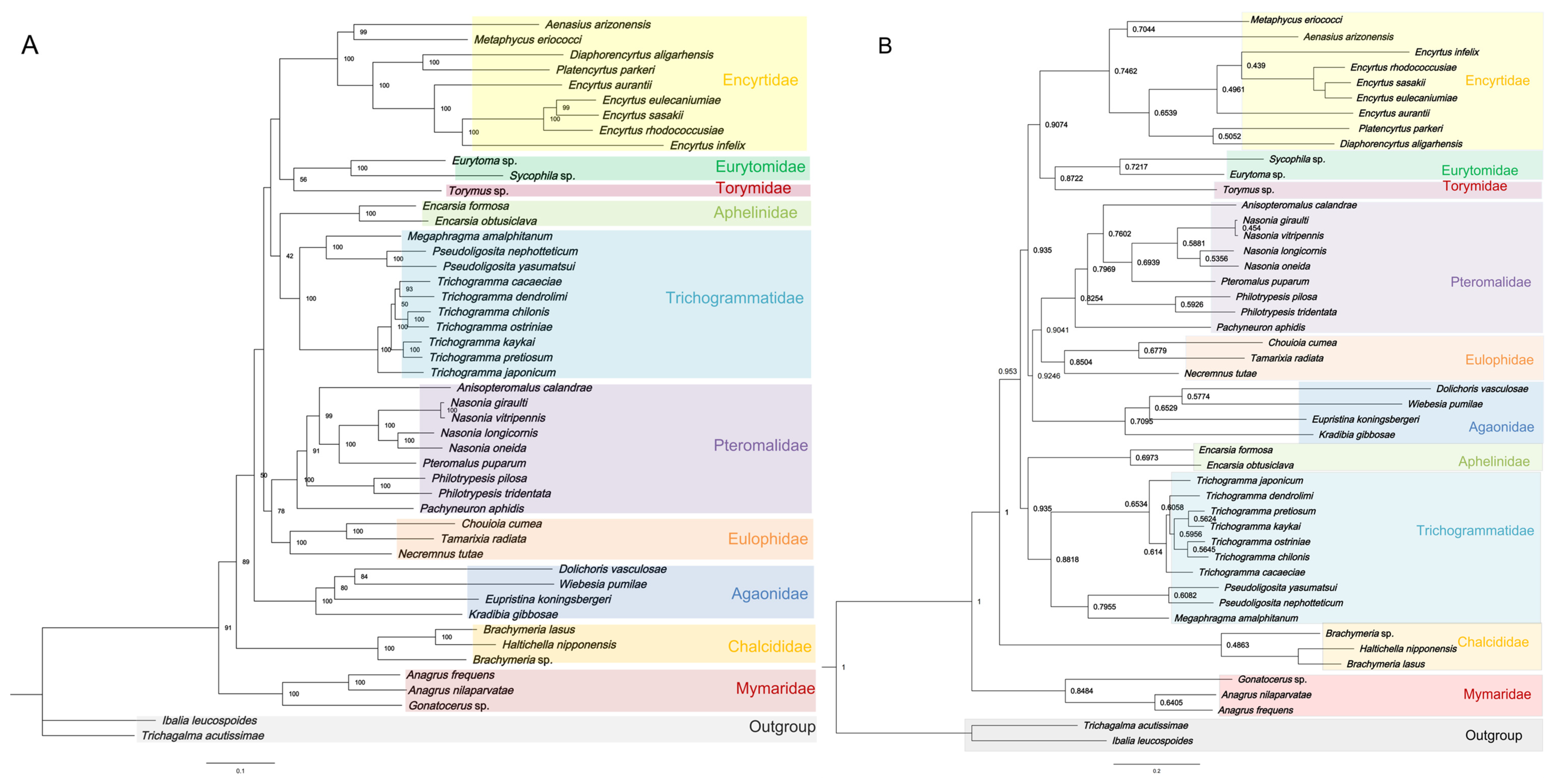
3.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bottrell, D.G.; Schoenly, K.G. Resurrecting the Ghost of Green Revolutions Past: The Brown Planthopper as a Recurring Threat to High-Yielding Rice Production in Tropical Asia. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenteren, J.C.; Bolckmans, K.; Köhl, J.; Ravensberg, W.J.; Urbaneja, A. Biological Control Using Invertebrates and Microorganisms: Plenty of New Opportunities. Biocontrol 2018, 63, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurr, G.M.; Liu, J.; Read, D.M.Y.; Catindig, J.L.A.; Cheng, J.A.; Lan, L.P.; Heong, K.L. Parasitoids of Asian Rice Planthopper (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) Pests and Prospects for Enhancing Biological Control by Ecological Engineering. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2011, 158, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heraty, J.M.; Burks, R.A.; Cruaud, A.; Gibson, G.A.P.; Liljeblad, J.; Munro, J.; Rasplus, J.; Delvare, G.; Janšta, P.; Gumovsky, A.; et al. A Phylogenetic Analysis of the Megadiverse C Halcidoidea (H Ymenoptera). Cladistics 2013, 29, 466–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.G.; Luft Albarracin, E.; Coll Araoz, M.V.; Virla, E.G. Effects of Host Species and Host Age on Biological Parameters of Anagrus virlai (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae), an Egg Parasitoid of Dalbulus maidis (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and Peregrinus maidis (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Biol. Control 2019, 131, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.-S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Desneux, N. Biological Control with Trichogramma in China: History, Present Status, and Perspectives. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Yang, Y.; Su, J.Y.; Shen, J.L.; Gao, C.F.; Zhu, Y.C. Assessment of the Impact of Insecticides on Anagrus nilaparvatae (Pang et Wang) (Hymenoptera: Mymanidae), an Egg Parasitoid of the Rice Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sann, C.; Wemheuer, F.; Beaurepaire, A.; Daniel, R.; Erler, S.; Vidal, S. Preliminary Investigation of Species Diversity of Rice Hopper Parasitoids in Southeast Asia. Insects 2018, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Sousa, J.; Meneses Carbonell, R. Some observations on the Habits and Biology of Paranagrusperforator Perkins (Hymenoptera, Mymaridae). Nat. Enemy Sogatodes Orizicola Muir 1978, 5, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Zheng, X.; Xu, H.; Johnson, A.C.; Heong, K.L.; Gurr, G.M.; Lu, Z. Nitrogen Fertilizer Promotes the Rice Pest Nilaparvata Lugens via Impaired Natural Enemy, Anagrus Flaveolus, Performance. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Liu, D.; Qiu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhan, Z. Evaluation of the Parasitism Capacity of a Thelytoky Egg Parasitoid on a Serious Rice Pest, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Animals 2022, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triapitsyn, S.V.; Shih, H.-T.; Huang, S.-H. Identification of Egg Parasitoids of Rice Leafhoppers and Planthoppers (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae and Delphacidae) of Economic Importance in Taiwan, Part 2: Trichogrammatidae (Hymenoptera). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2020, 23, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.S.; Niehuis, O.; Gunkel, S.; Bläser, M.; Mayer, C.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Kozlov, A.; Donath, A.; Van Noort, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Transcriptome Sequence-Based Phylogeny of Chalcidoid Wasps (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea) Reveals a History of Rapid Radiations, Convergence, and Evolutionary Success. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 120, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lindsey, A.R.I.; Peters, R.S.; Heraty, J.M.; Hopper, K.R.; Werren, J.H.; Martinson, E.O.; Woolley, J.B.; Yoder, M.J.; Krogmann, L. Conflicting Signal in Transcriptomic Markers Leads to a Poorly Resolved Backbone Phylogeny of Chalcidoid Wasps. Syst. Entomol. 2020, 45, 783–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Buckley, T.R.; Frati, F.; Stewart, J.B.; Beckenbach, A.T. Incorporating Molecular Evolution into Phylogenetic Analysis, and a New Compilation of Conserved Polymerase Chain Reaction Primers for Animal Mitochondrial DNA. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2006, 37, 545–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, K.; Chakraborty, R.; Cameron, S.L.; Sweet, A.D.; Chandra, K.; Kumar, V. Rearrangement and Evolution of Mitochondrial Genomes in Thysanoptera (Insecta). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.-C.; Qi, G.-Y.; Yao, T.-Y.; Li, Y.-X. Mitochondrial Genomes of Two Asexual Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) Strains and Comparison with Their Sexual Relatives. Insects 2022, 13, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.-P.; Qi, L.-Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-X.; Hu, H.-Y. Complete Mitochondrial Genome of a Parasitoid, Trichogramma Chilonis (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Trichogrammatidae) and Phylogenetic Analysis. Mitochondrial DNA B 2021, 6, 2466–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, P.-Y.; Xue, X.-F.; Hua, H.-Q.; Li, Y.-X.; Zhang, F.; Wei, S.-J. Extensive Gene Rearrangements in the Mitochondrial Genomes of Two Egg Parasitoids, Trichogramma japonicum and Trichogramma ostriniae (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Trichogrammatidae). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedoluzhko, A.V.; Sharko, F.S.; Boulygina, E.S.; Tsygankova, S.V.; Sokolov, A.S.; Mazur, A.M.; Polilov, A.A.; Prokhortchouk, E.B.; Skryabin, K.G. Mitochondrial Genome of Megaphragma Amalphitanum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Mitochondrial DNA A 2016, 27, 4526–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, H.; He, W.; Zhou, Q. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Parasitoid Wasp Pseudoligosita yasumatsui (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) and Its Phylogenetic Implications. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2023, 26, 102157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.-C.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.-X. Information from the Mitochondrial Genomes of Two Egg Parasitoids, Gonatocerus sp. and Telenomus sp., Reveals a Controversial Phylogenetic Relationship between Mymaridae and Scelionidae. Genomics 2019, 111, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappini, E.; Lin, N.-Q. Anagrus (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) of China, with Descriptions of Nine New Species. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1998, 91, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taekul, C.; Valerio, A.A.; Austin, A.D.; Klompen, H.; Johnson, N.F. Molecular Phylogeny of Telenomine Egg Parasitoids (H Ymenoptera: P Latygastridae S.L.: T Elenominae): Evolution of Host Shifts and Implications for Classification. Syst. Entomol. 2014, 39, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA Primers for Amplification of Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I from Diverse Metazoan Invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotech. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentleman, R.; lhaka, R. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Computing 2011, 1, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of Nucleotide Composition at Fourfold Degenerate Sites of Animal Mitochondrial Genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boore, J.L. Animal Mitochondrial Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.-C.; Xiao, H.; Tang, P.; Li, X.-F.; Li, X.-K.; Zhu, C.-D.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, J.-H.; Van Achterberg, C.; Huang, D.-W.; et al. Evolutionary Timescale of Chalcidoid Wasps Inferred from over One Hundred Mitochondrial Genomes. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; An, Y. Novel Gene Rearrangement in the Mitochondrial Genome of Anastatus Fulloi (Hymenoptera Chalcidoidea) and Phylogenetic Implications for Chalcidoidea. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Qin, Y. Two Complete Mitogenomes of Chalcididae (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea): Genome Description and Phylogenetic Implications. Insects 2021, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castresana, J. Selection of Conserved Blocks from Multiple Alignments for Their Use in Phylogenetic Analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Sump. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X. DAMBE5: A Comprehensive Software Package for Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kück, P.; Meid, S.A.; Groß, C.; Wägele, J.W.; Misof, B. AliGROOVE—Visualization of Heterogeneous Sequence Divergence within Multiple Sequence Alignments and Detection of Inflated Branch Support. BMC Bioinf. 2014, 15, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. Figtree 1.4.0. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Wolstenholme, D.R. Animal Mitochondrial DNA: Structure and Evolution. In International Review of Cytology; 14-20k; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 141, pp. 173–216. ISBN 978-0-12-364544-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Han, Y.; Yuan, R.; Liu, J.; Van Achterberg, C.; Tang, P.; Chen, X. Comparative Mitochondrial Genomics of 104 Darwin Wasps (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) and Its Implication for Phylogeny. Insects 2022, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowton, M.; Austin, A.D. Evidence for AT-Transversion Bias in Wasp (Hymenoptera: Symphyta) Mitochondrial Genes and Its Implications for the Origin of Parasitism. J. Mol. Evol. 1997, 44, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-J.; Shi, M.; Chen, X.-X.; Sharkey, M.J.; Van Achterberg, C.; Ye, G.-Y.; He, J.-H. New Views on Strand Asymmetry in Insect Mitochondrial Genomes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jühling, F.; Pütz, J.; Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Middendorf, M.; Florentz, C.; Stadler, P.F. Improved Systematic tRNA Gene Annotation Allows New Insights into the Evolution of Mitochondrial tRNA Structures and into the Mechanisms of Mitochondrial Genome Rearrangements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 2833–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, R.H.; Crozier, Y.C. The Mitochondrial Genome of the Honeybee Apis Mellifera: Complete Sequence and Genome Organization. Genetics 1993, 133, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masta, S.E. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome Sequence of the Spider Habronattus Oregonensis Reveals Rearranged and Extremely Truncated tRNAs. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Hu, H. Adaptive Evidence of Mitochondrial Genes in Pteromalidae and Eulophidae (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea). PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, J. Mitochondrial Complex I. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L.; Brown, W.M. Big Trees from Little Genomes: Mitochondrial Gene Order as a Phylogenetic Tool. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowton, M.; Cameron, S.L.; Dowavic, J.I.; Austin, A.D.; Whiting, M.F. Characterization of 67 Mitochondrial tRNA Gene Rearrangements in the Hymenoptera Suggests That Mitochondrial tRNA Gene Position Is Selectively Neutral. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydemir, M.N.; Korkmaz, E.M. Comparative Mitogenomics of Hymenoptera Reveals Evolutionary Differences in Structure and Composition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-L.; Yang, F.; Yao, Z.-W.; Wu, Y.-K.; Liu, B.; Yuan, H.-B.; Lu, Y.-H. A Molecular Detection Approach for a Cotton Aphid-Parasitoid Complex in Northern China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Fang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Werren, J.H.; Ye, G. Mitochondrial DNA and Their Nuclear Copies in the Parasitic Wasp Pteromalus Puparum: A Comparative Analysis in Chalcidoidea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruaud, A.; Delvare, G.; Nidelet, S.; Sauné, L.; Ratnasingham, S.; Chartois, M.; Blaimer, B.B.; Gates, M.; Brady, S.G.; Faure, S.; et al. Ultra-conserved Elements and Morphology Reciprocally Illuminate Conflicting Phylogenetic Hypotheses in Chalcididae (Hymenoptera, Chalcidoidea). Cladistics 2021, 37, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Species | Feature | A % | T (U) % | C % | G % | AT % | GC % | AT Skew | GC Skew |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. nephotetticum | Whole genome | 38.7 | 47.9 | 5.3 | 8.0 | 86.6 | 13.4 | −0.11 | 0.20 |
| Protein-coding genes | 36.3 | 48.6 | 6.4 | 8.7 | 84.9 | 15.1 | −0.15 | 0.15 | |
| 1st condon site | 37.7 | 47.6 | 5.6 | 9.2 | 85.2 | 14.8 | −0.12 | 0.25 | |
| 2nd condon site | 31.6 | 50.1 | 8.3 | 10.0 | 81.7 | 18.3 | −0.23 | 0.09 | |
| 3rd condon site | 39.6 | 48.3 | 5.4 | 6.8 | 87.8 | 12.2 | −0.10 | 0.12 | |
| tRNA genes | 45.2 | 43.9 | 4.4 | 6.5 | 89.1 | 10.9 | 0.02 | 0.19 | |
| rRNA genes | 43.8 | 44.7 | 4.2 | 7.2 | 88.6 | 11.4 | −0.01 | 0.26 | |
| A. frequens | Whole genome | 42.1 | 44.8 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 86.9 | 13.1 | −0.03 | 0.06 |
| Protein-coding genes | 36.9 | 48.4 | 6.6 | 8.2 | 85.2 | 14.8 | −0.13 | 0.11 | |
| 1st condon site | 38.7 | 46.0 | 9.4 | 6.2 | 84.7 | 15.6 | −0.09 | 0.21 | |
| 2nd condon site | 34.0 | 48.0 | 9.4 | 8.6 | 82.0 | 18.0 | −0.17 | 0.04 | |
| 3rd condon site | 37.9 | 51.0 | 6.0 | 5.1 | 88.9 | 11.1 | −0.15 | 0.08 | |
| tRNA genes | 46.1 | 44.9 | 3.4 | 5.6 | 91.0 | 9.0 | 0.01 | 0.24 | |
| rRNA genes | 45.3 | 46.0 | 3.7 | 5.0 | 91.3 | 8.7 | −0.01 | 0.15 | |
| A. nilaparvatae | Whole genome | 40.8 | 46.1 | 6.2 | 6.9 | 86.9 | 13.1 | −0.06 | 0.05 |
| Protein-coding genes | 36.8 | 47.8 | 6.8 | 8.6 | 84.6 | 15.4 | −0.13 | 0.12 | |
| 1st condon site | 39.5 | 46.5 | 5.0 | 9.0 | 86.0 | 14.0 | −0.08 | 0.29 | |
| 2nd condon site | 33.0 | 47.7 | 9.1 | 10.2 | 80.7 | 19.3 | −0.18 | 0.06 | |
| 3rd condon site | 37.9 | 49.3 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 87.2 | 12.8 | −0.13 | 0.03 | |
| tRNA genes | 46.3 | 44.8 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 91.1 | 8.9 | 0.02 | 0.22 | |
| rRNA genes | 50.0 | 41.7 | 3.5 | 4.8 | 91.7 | 8.3 | 0.09 | 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, W.; Li, T.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q. Mitogenomic Characterization and Comparative Analysis of Three Egg Parasitoid Wasps Parasitizing Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Insects 2025, 16, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050543
He W, Li T, Wang L, Wu H, Wang J, Zhou Q. Mitogenomic Characterization and Comparative Analysis of Three Egg Parasitoid Wasps Parasitizing Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Insects. 2025; 16(5):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050543
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Wei, Tingting Li, Liyang Wang, Hongxuan Wu, Jie Wang, and Qiang Zhou. 2025. "Mitogenomic Characterization and Comparative Analysis of Three Egg Parasitoid Wasps Parasitizing Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)" Insects 16, no. 5: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050543
APA StyleHe, W., Li, T., Wang, L., Wu, H., Wang, J., & Zhou, Q. (2025). Mitogenomic Characterization and Comparative Analysis of Three Egg Parasitoid Wasps Parasitizing Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Insects, 16(5), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050543






