Molecular Characterization and Expression of the Ecdysone Receptor and Ultraspiracle Genes in the Wheat Blossom Midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Insects
2.2. Cloning of S. mosellana EcR and USP Genes
2.3. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. 20E Treatment
2.5. Expression Analysis Using Reverse-Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
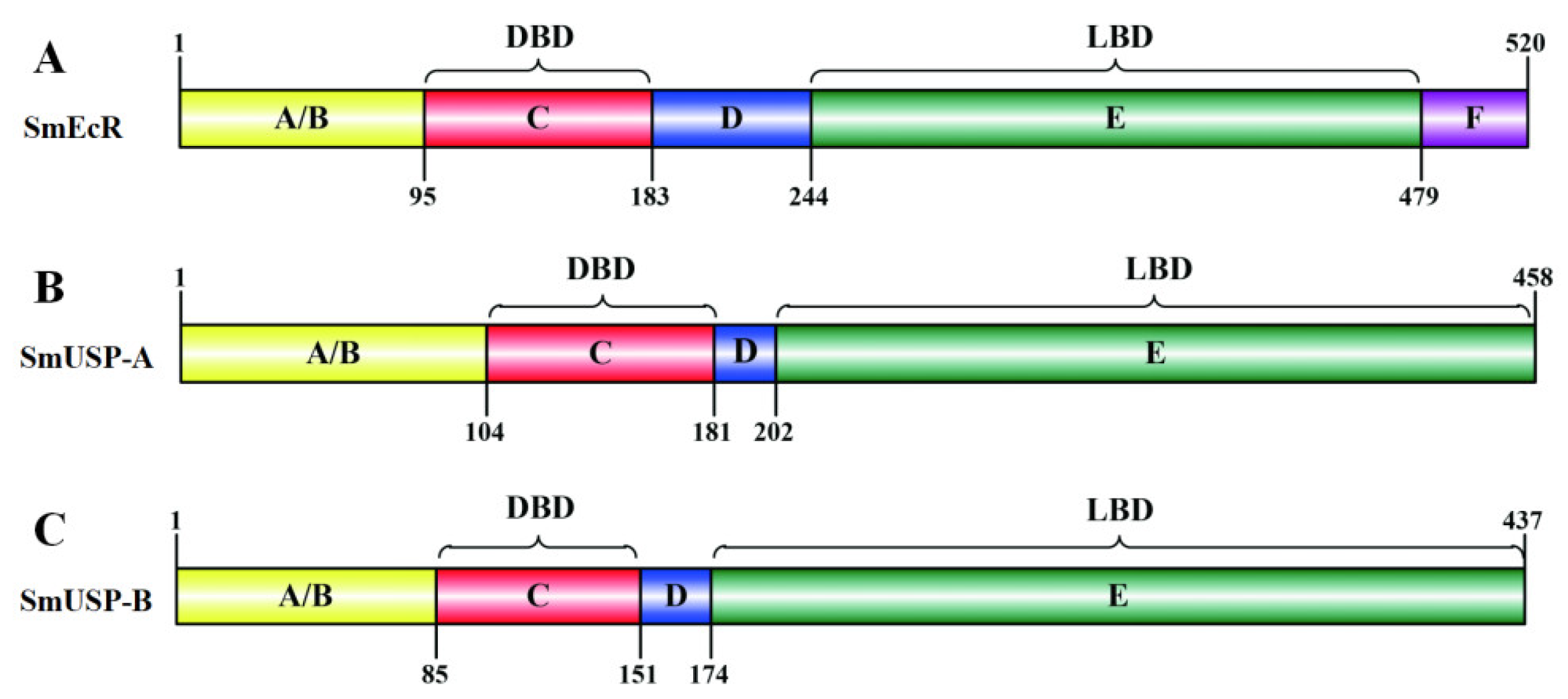
3.1. Characterization of SmEcR and SmUSP cDNAs
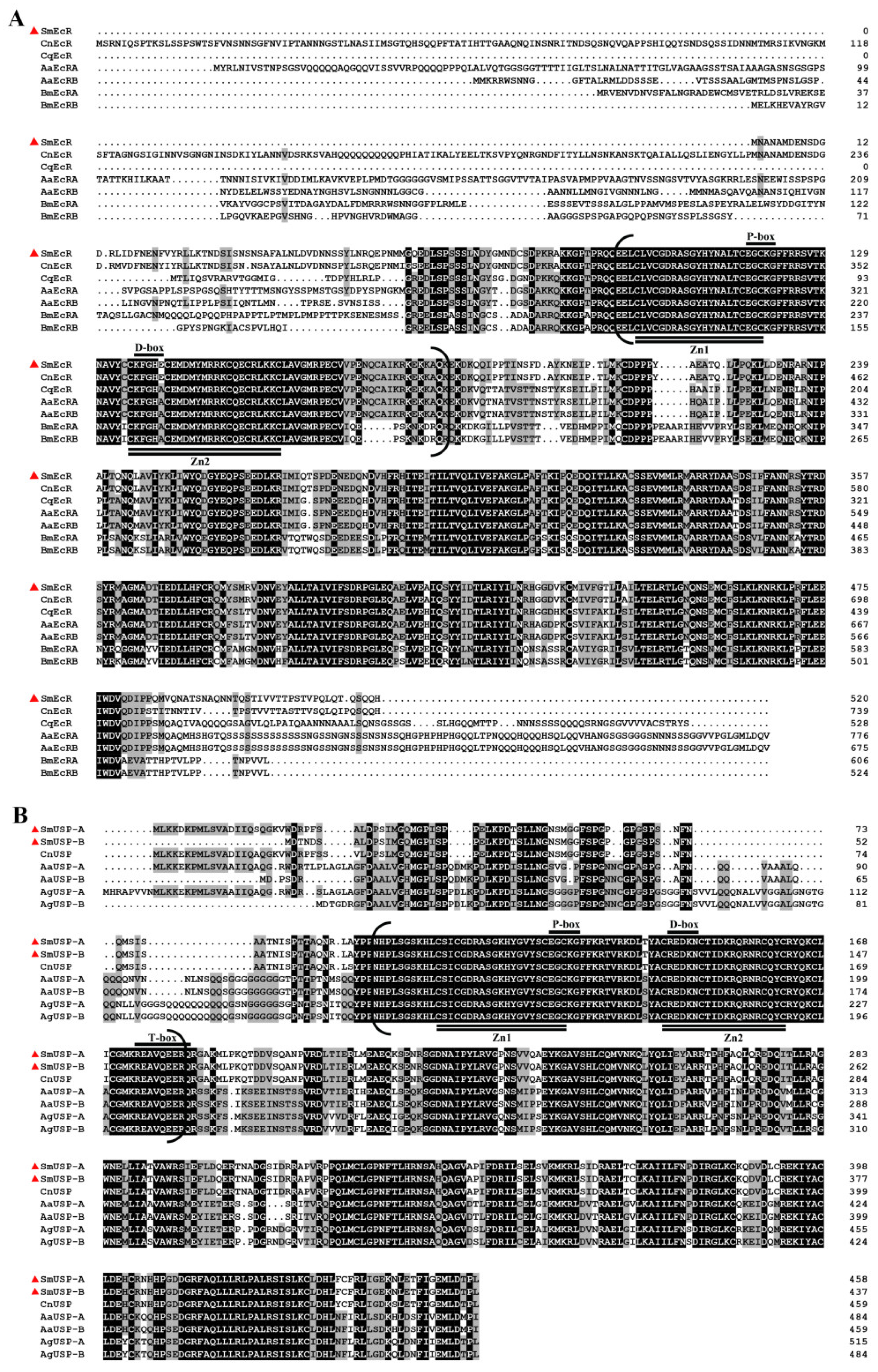
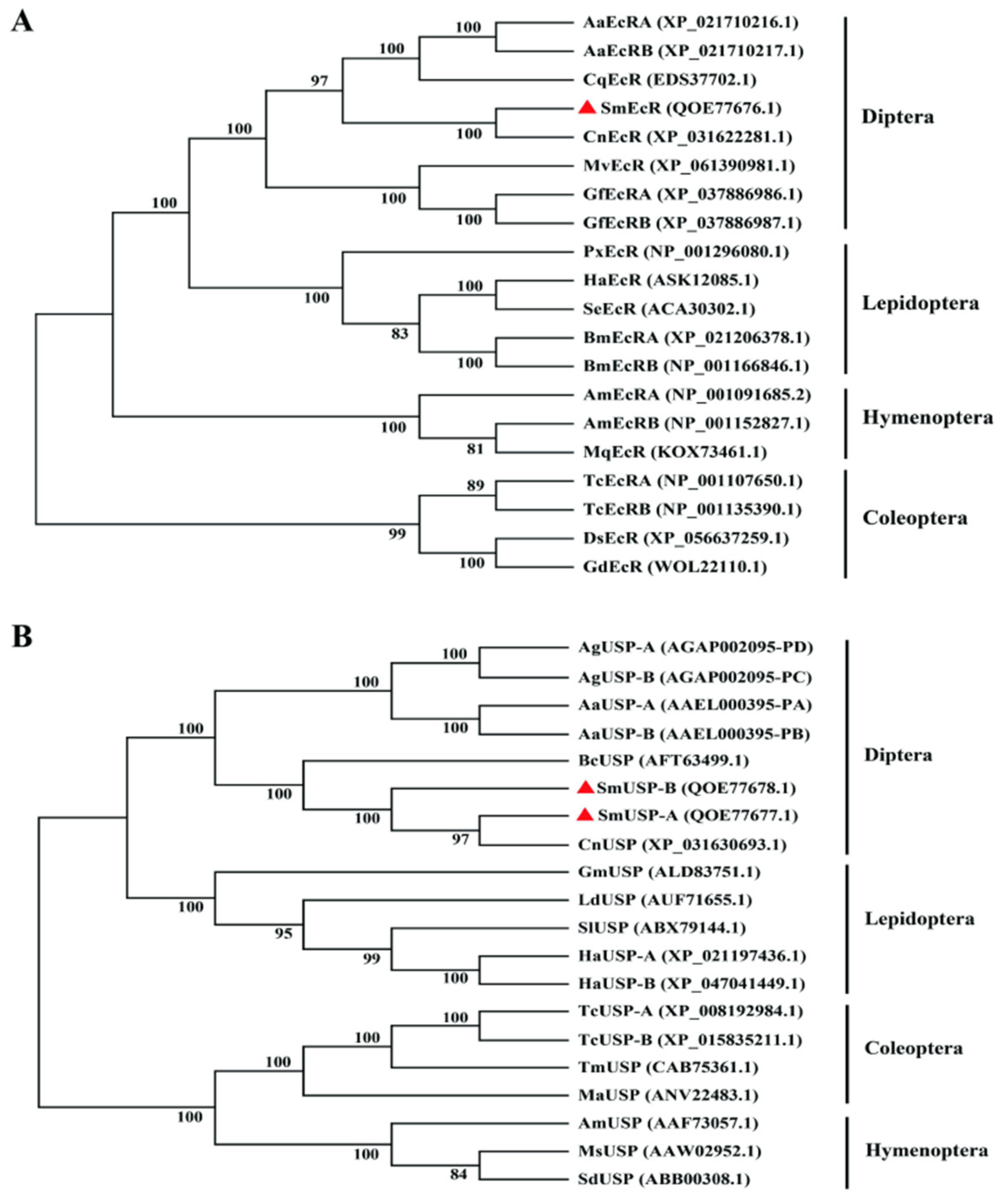
3.2. Sequence Comparison and Phylogenetic Analyses
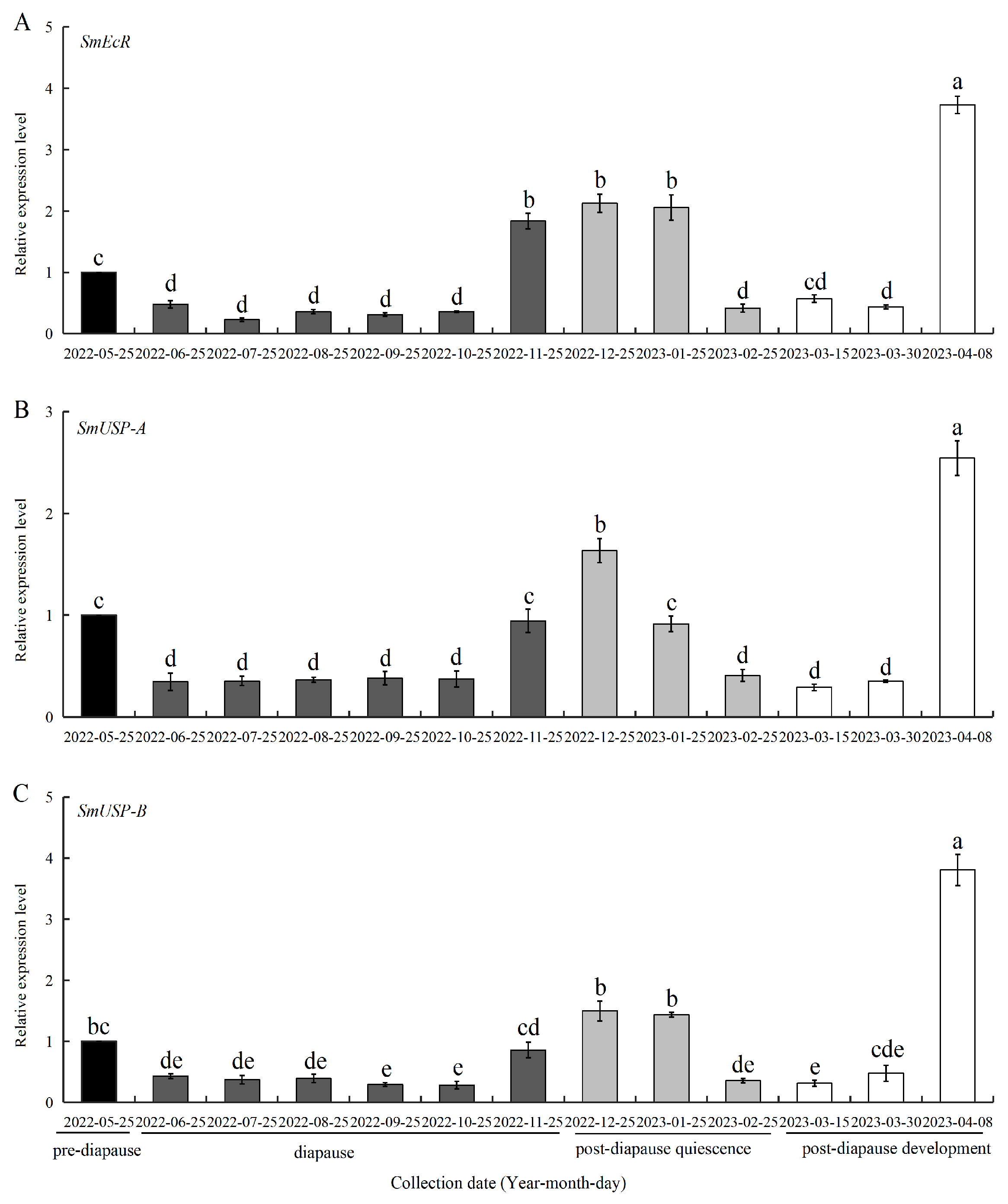
3.3. Expression of SmEcR and SmUSPs During Diapause
3.4. 20E Regulation of SmEcR and SmUSP Genes During Diapause
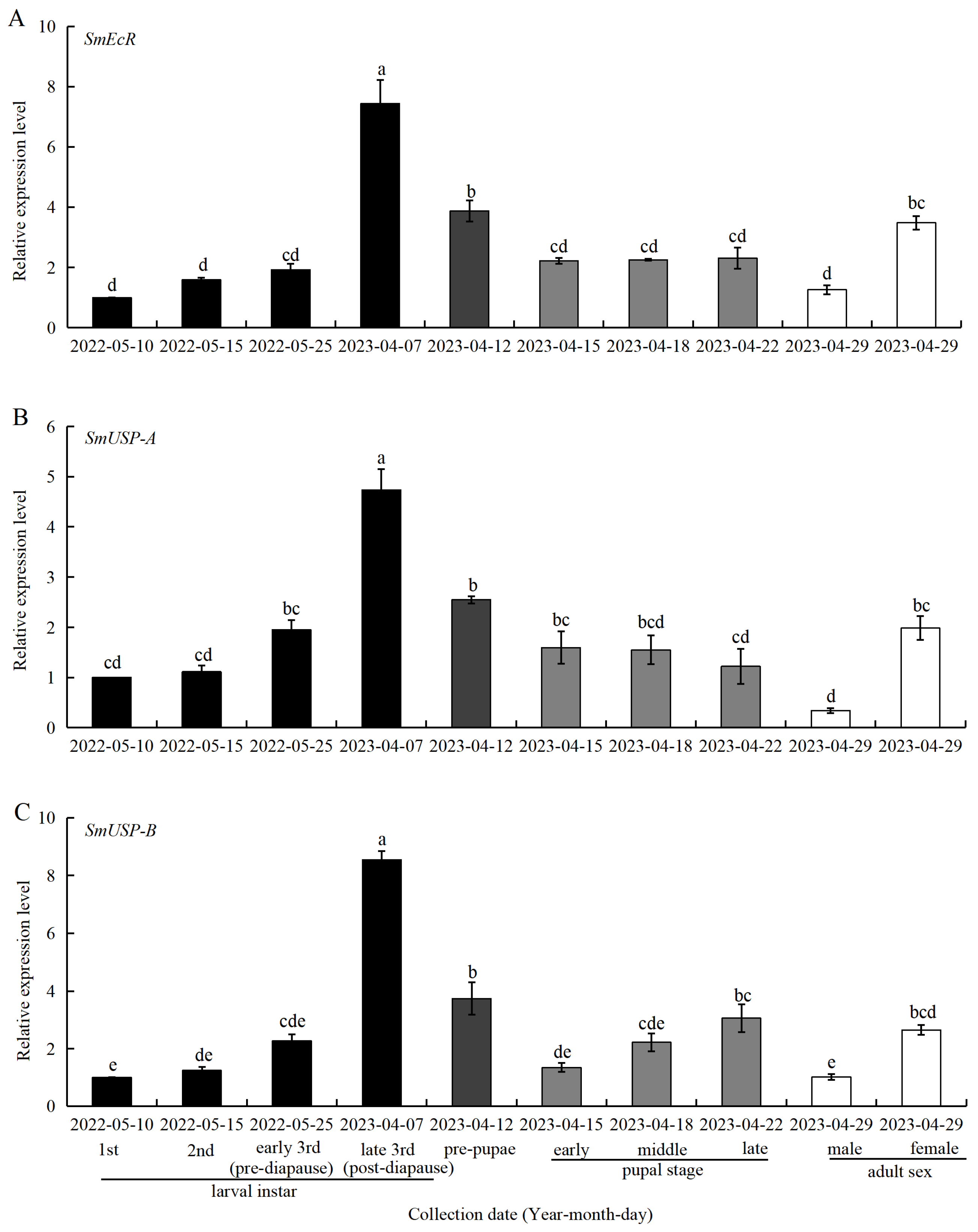
3.5. Expression of SmEcR and SmUSP Genes at Different Developmental Stages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hahn, D.A.; Denlinger, D.L. Meeting the energetic demands of insect diapause: Nutrient storage and utilization. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonato, V.; Collins, L.; Pegoraro, M.; Tauber, E.; Kyriacou, C.P. Is diapause an ancient adaptation in Drosophila? J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 98, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denlinger, D.L. Why study diapause? Entomol. Res. 2008, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddiford, L.M.; Hiruma, K.; Zhou, X.; Nelson, C.A. Insights into the molecular basis of the hormonal control of molting and metamorphosis from Manduca sexta and Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, N.; Rewitz, K.F.; O’Connor, M.B. Ecdysone control of developmental transitions: Lessons from Drosophila research. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Tian, Z.; Wu, Q.W.; King-Jones, K.; Liu, W.; Zhu, F.; Wang, X.P. Steroid hormone ecdysone deficiency stimulates preparation for photoperiodic reproductive diapause. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singtripop, T.W.; Wanichacheewa, S.; Tsuzuki, S.; Sakurai, S. Larval growth and diapause in a tropical moth, Omphisa fuscidentalis Hampson. Zool. Sci. 1999, 16, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singtripop, T.; Oda, Y.; Wanichacheewa, S.; Sakurai, S. Sensitivities to juvenile hormone and ecdysteroid in the diapause larvae of Omphisa fuscidentalis based on the hemolymph trehalose dynamics index. J. Insect Physiol. 2002, 48, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.A.; Nachman, R.J.; Denlinger, D.L. Distinct microRNA and mRNA responses elicited by ecdysone, diapause hormone and a diapause hormone analog at diapause termination in pupae of the corn earworm, Helicoverpa zea. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 278, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Yan, Z.B.; Yin, X.M.; Lei, Z.S.; Zhou, Z. Dynamics of ecdysone titer and the interference of methoxyfenozide on diapause during the development of Carposina sasakii (Lepidoptera: Carposinidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2022, 65, 791–798. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Cai, D.X.; Geng, S.L.; Lyu, Z.P.; Wu, Y.L.; Guo, J.J.; Li, H.Y. Transcriptome-based analysis reveals a crucial role of the 20E/HR3 pathway in the diapause of Pieris rapae. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 199, 105787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.P.; Segraves, W.A.; Oro, A.E.; McKeown, M.; Evans, R.M. Drosophila ultraspiracle modulates ecdysone receptor function via heterodimer formation. Cell 1992, 71, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swevers, L.; Cherbas, L.; Cherbas, P.; Iatrou, K. Bombyx EcR (BmEcR) and Bombyx USP (BmCF1) combine to form a functional ecdysone receptor. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 26, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazina, M.Y.; Kocheryzhkina, E.V.; Nikolenko, J.V.; Krasnov, A.N.; Georgieva, S.G.; Vorobyeva, N.E. Nuclear receptors EcR, Usp, E75, DHR3, and ERR regulate transcription of ecdysone cascade genes. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 473, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Jones, K.; Charles, J.P.; Lam, G.; Thummel, C.S. The ecdysone-induced DHR4 orphan nuclear receptor coordinates growth and maturation in Drosophila. Cell 2005, 121, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, S.; Cao, Y. Transcriptional regulation by 20-hydroxyecydsone and its nuclear receptor EcR-USP. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2011, 54, 933–937. [Google Scholar]
- Lenaerts, C.; Van Wielendaele, P.; Peeters, P.; Vanden Broeck, J.; Marchal, E. Ecdysteroid signalling components in metamorphosis and development of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 75, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, W.S.; Swyryd, E.A.; Hogness, D.S. Drosophila tissues with different metamorphic responses to ecdysone express different ecdysone receptor isoforms. Cell 1993, 73, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakuchi, C.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kiuchi, M.; Tomita, S.; Kamimura, M. Molecular cloning, expression analysis and functional confirmation of two ecdysone receptor isoforms from the rice stem borer Chilo suppressalis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Minakuchi, C.; Nakagawa, Y.; Smagghe, G.; Miyagawa, H. Molecular cloning, expression analysis and functional confirmation of ecdysone receptor and ultraspiracle from the Colorado potato beetle Leptinotarsa decemlineata. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 4114–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.W.; Yang, D.T.; Wang, J.X.; Song, Q.S.; Gilbert, L.I.; Zhao, X.F. Hsc70 binds to ultraspiracle resulting in the upregulation of 20-hydroxyecdsone-responsive genes in Helicoverpa armigera. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 315, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.B.; Shen, W.F.; Liu, Y.; He, L.H.; Niu, B.L.; Meng, Z.Q.; Mu, J.J. Cloning and characterization of two EcR isoforms from Japanese pine sawyer, Monochamus alternates. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 84, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wan, B.; Jin, M.R.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.J.; Zhong, L.; Xia, B. Inhibition of ecdysone receptor (DcEcR) and ultraspiracle (DcUSP) expression in Diaphorina citri increased susceptibility to pesticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 194, 105518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapitskaya, M.; Wang, S.; Cress, D.E.; Dhadialla, T.S.; Raikhel, A.S. The mosquito ultraspiracle homologue, a partner of ecdysteroid receptor heterodimer: Cloning and characterization of isoforms expressed during vitellogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 121, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vögtli, M.; Imhof, M.O.; Brown, N.E.; Rauch, P.; Spindler-Barth, M.; Lezzi, M.; Henrich, V.C. Functional characterization of two Ultraspiracle forms (CtUSP-1 and CtUSP-2) from Chironomus tentans. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, C.; Minakuchi, C.; Yokoi, T.; Takimoto, S.; Hosoda, A.; Akama, Y. cDNA cloning of ecdysone receptor (EcR) and ultraspiracle (USP) from Harmonia axyridis and Epilachna vigintioctopunctata and the evaluation of the binding affinity of ecdysone agonists to the in vitro translated EcR/USP heterodimers. J. Pestic. Sci. 2014, 39, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Tan, A.J.; Palli, S.R. The function of nuclear receptors in regulation of female reproduction and embryogenesis in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Deng, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A.; Fu, K.Y.; Guo, W.C.; Li, G.Q. Ecdysone receptor isoforms play distinct roles in larval-pupal-adult transition in Leptinotarsa decemlineata. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Mu, L.L.; Kang, W.N.; Ze, L.J.; Shen, C.H.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G.Q. RNA interference targeting ecdysone receptor blocks the larval-pupal transition in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, M.O.; Rusconi, S.; Lezzi, M. Cloning of a Chironomus tentans cDNA encoding a protein (cEcRH) homologous to the Drosophila melanogaster ecdysteroid receptor (dEcR). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 23, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.C.; Palli, S.R.; Ladd, T.R.; Krell, P.J.; Retnakaran, A. The ultraspiracle gene of the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana: Cloning of cDNA and developmental expression of mRNA. Dev. Genet. 1998, 22, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, G.; Chavalle, S.; De Proft, M. Forecasting the emergence of the adult orange wheat blossom midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana (Géhin) (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in Belgium. Crop Prot. 2014, 58, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, G.; Reddy, G.V.P. Field efficacy of insect pathogen, botanical, and jasmonic acid for the management of wheat midge Sitodiplosis mosellana and the impact on adult parasitoid Macroglenes penetrans populations in spring wheat. Insect Sci. 2019, 26, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.B.; Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, Y.M.; Zhang, L.J.; Shi, W.P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.L. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of wheat kernels in response to the feeding of orange wheat blossom midges (Sitodiplosis mosellana) in the Field. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2022, 70, 1477–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Long, Z.R.; Feng, A.R.; Cheng, W.N. Effects of initial population number, wheat varieties and precipitation on infestation of Sitodiplosis mosellana (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). Acta Agri. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2015, 24, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.N.; Long, Z.R.; Zhang, Y.D.; Liang, T.T.; Zhu-Salzman, K.Y. Effects of temperature, soil moisture and photoperiod on diapause termination and post-diapause development of the wheat blossom midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana (Géhin) (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 103, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.N.; Li, J.J.; Li, Y.P.; Li, X.L.; Wu, J.X.; Wang, H.L. Quantitative analysis of ecdysteroid in adults and the pre-diapause, diapause and post-diapause larvae of wheat blossom midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana Gehin. Acta Phytophy. Sin. 2009, 36, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.N.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu-Salzman, K.Y. Cloning of heat shock protein genes (hsp70, hsc70 and hsp90) and their expression in response to larval diapause and thermal stress in the wheat blossom midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana. J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 95, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagne, R.J.; Doane, J.E. The larval instars of the wheat midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana (Gehin) (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 1999, 101, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.J.; Li, T.; Miao, J.; Duan, Y.; Jiang, Y.L.; Li, H.L.; Guo, P.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.Q. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the orange wheat blossom midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana Géhin (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) provides insights into the evolution of a detoxification system. G3 2022, 12, jkac161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.S.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, M.C.; Kyung, D.H.; Om, A.S.; Rhee, J.S.; Lee, J.S. Genome-wide identification of nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily genes in the copepod Tigriopus japonicus. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Henrich, V.C. Arthropod nuclear receptors and their role in molting. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6128–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Xu, S.; Dong, Y.Z.; Quan, L.F.; Chen, B.X. Ecdysone Receptor (EcR) and ultraspiracle protein (USP) genes from Conopomorpha sinensis Bradley eggs: Identification and expression in response to insecticides. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Chen, H.M.; Sun, Y.W.; Yu, X.D.; Xia, L.Q. RNA interference of the ecdysone receptor genes EcR and USP in Grain Aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) affects its survival and fecundity upon feeding on wheat plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah-Zawawi, M.R.; Afiqah-Aleng, N.; Ikhwanuddin, M.; Sung, Y.Y.; Tola, S.; Fazhan, H.; Waiho, K. Recent development in ecdysone receptor of crustaceans: Current knowledge and future applications in crustacean aquaculture. Rev. Aquacult. 2021, 13, 1938–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, P.; Staels, B.; Dacquet, C.; Spedding, M.; Laudet, V. Overview of nomenclature of nuclear receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, D.L.; Heneghan, A.F.; Connaghan-Jones, K.D.; Miura, M.T. Nuclear receptor structure: Implications for function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King-Jones, K.; Thummel, C.S. Nuclear receptors-a perspective from Drosophila. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarakonda, S.; Harp, J.M.; Kim, Y.; Ozyhar, A.; Rastinejad, F. Structure of the heterodimeric ecdysone receptor DNA-binding complex. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5827–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Z.; Dong, Y.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Andongma, A.A.; Rashid, M.A.; Krutmuang, P.; Niu, C.Y. Pupal diapause termination in Bactrocera minax: An insight on 20-hydroxyecdysone induced phenotypic and genotypic expressions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.M.; Wu, J.X.; Cheng, W.N.; Li, Y.P.; Hou, J.J. Determination of juvenile hormone in wheat blossom midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana (Gehin). Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2006, 15, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.N.; Li, X.J.; Zhao, J.J.; Zhu-Salzman, K. Cloning and characterization of Methoprene-tolerant (Met) and Krüppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) genes in the wheat blossom midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña, E.; Chafino, S.; Manjón, C.; Franch-Marro, X.; Martín, D. The occurrence of the holometabolous pupal stage requires the interaction between E93, Krüppel-Homolog 1 and Broad-Complex. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayukawa, T.; Jouraku, A.; Ito, Y.; Shinoda, T. Molecular mechanism underlying juvenile hormone-mediated repression of precocious larval-adult metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Y.; Connacher, R.P.; O’Connor, M.B. Control of the insect metamorphic transition by ecdysteroid production and secretion. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 43, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Jamil, M.; Jaworski, C.C.; Wu, Y.; Palma-Onetto, V.; Lyu, B.Q.; Luo, Y.P. Knockdown of the ecdysone receptor disrupts development and causes mortality in the melon fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2023, 32, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, Z.; Yang, Q.B.; Zhang, S.D.; Zhang, Q.W.; Liu, X.X. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of the ultraspiracle (USP) in the oriental fruit moth Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Olethreutidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 190, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchuk, A.R.; Figueiredo, V.L.; Simões, Z.L. Downregulation of ultraspiracle gene expression delays pupal development in honeybees. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, V.C.; Szekely, A.A.; Kim, S.J.; Brown, N.E.; Antoniewski, C.; Hayden, M.A.; Lepesant, J.A.; Gilbert, L.I. Expression and function of the ultraspiracle (usp) gene during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev. Biol. 1994, 165, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenaerts, C.; Marchal, E.; Peeters, P.; Vanden Broeck, J. The ecdysone receptor complex is essential for the reproductive success in the female desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| EcR sense | TCGTGGCTCCGATTTTAT | ORF cloning |
| EcR antisense | GCAACGAATCTTACGGAT | |
| USP-A sense | TGAACGAGCGACACTGAA | |
| USP-A antisense | CACCCCAATCACTGTCAA | |
| USP-B sense | CGAGCAGATAAACCTACG | |
| USP-B antisense | CTGGTGTGACTATCTGGC | |
| EcR sense | TGCGGCGTAAGTGTCAGGA | qPCR |
| EcR antisense | GCTTTCTTCTCTTTGCGTTTGA | |
| USP-A sense | AATGCTTTCCGTAGCCGATATA | |
| USP-A antisense | CTGGTTTGAGTTCAGGCGGT | |
| USP-B sense | ATGGATACAAATGATTCAGCTTTGG | |
| USP-B antisense | TGGTTGAAATTGCTGGGGC | |
| GAPDH sense | CCATCAAAGCAAGCAAGA | |
| GAPDH antisense | CAGCACGGAGCACAAGAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Meng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu-Salzman, K.; Cheng, W. Molecular Characterization and Expression of the Ecdysone Receptor and Ultraspiracle Genes in the Wheat Blossom Midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana. Insects 2025, 16, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050537
Huang Q, Meng L, Liu Y, Zhu-Salzman K, Cheng W. Molecular Characterization and Expression of the Ecdysone Receptor and Ultraspiracle Genes in the Wheat Blossom Midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana. Insects. 2025; 16(5):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050537
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qitong, Linqing Meng, Yuhan Liu, Keyan Zhu-Salzman, and Weining Cheng. 2025. "Molecular Characterization and Expression of the Ecdysone Receptor and Ultraspiracle Genes in the Wheat Blossom Midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana" Insects 16, no. 5: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050537
APA StyleHuang, Q., Meng, L., Liu, Y., Zhu-Salzman, K., & Cheng, W. (2025). Molecular Characterization and Expression of the Ecdysone Receptor and Ultraspiracle Genes in the Wheat Blossom Midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana. Insects, 16(5), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050537







