Phylogenetic Analysis of the Family Lepidostomatidae (Trichoptera: Integripalpia) Using Whole Mitochondrial Genomes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxon Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.2. Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
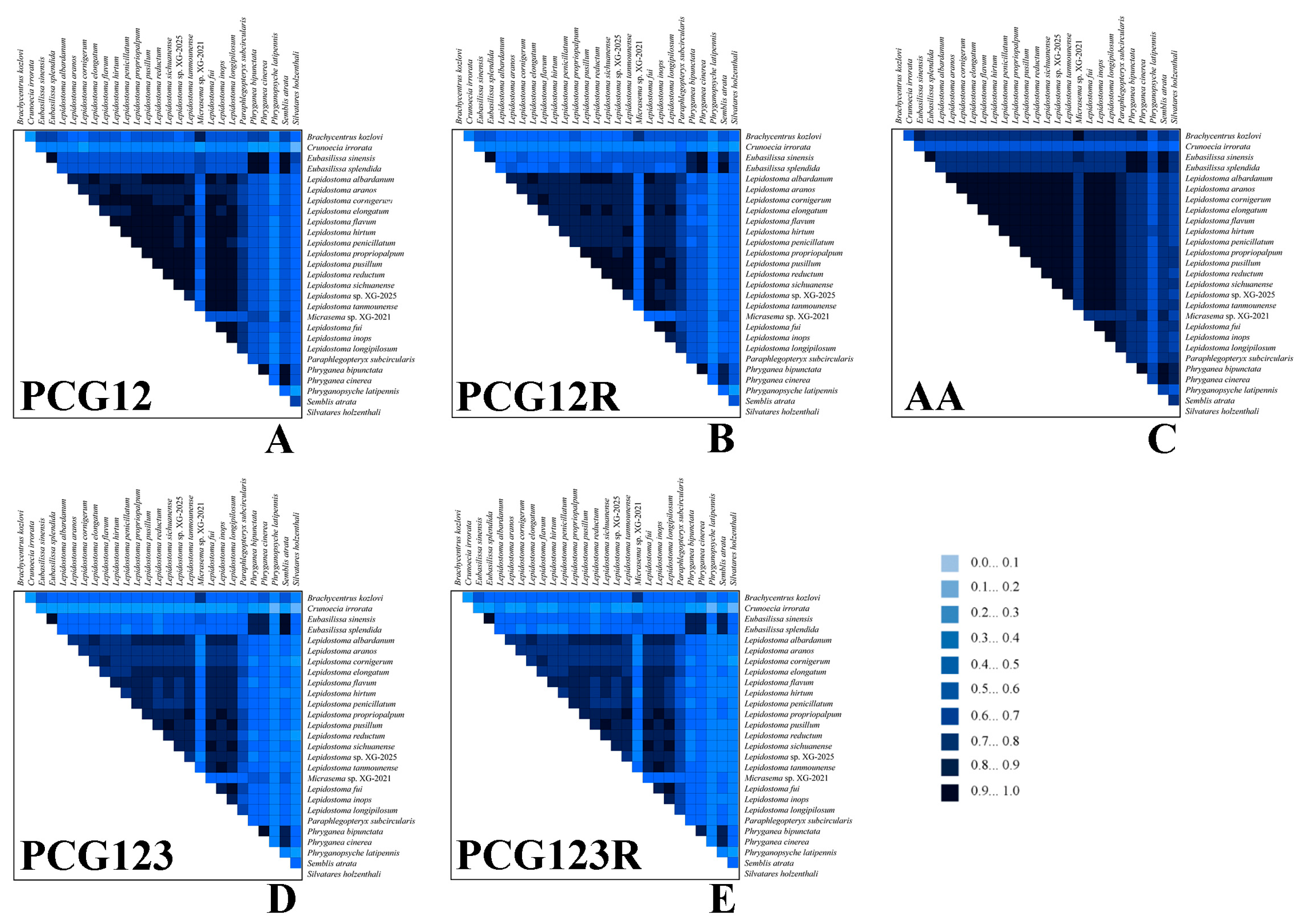
2.3. Comparative Mitogenomic Analyses
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mitogenome Features and Base Composition of Lepidostomatidae
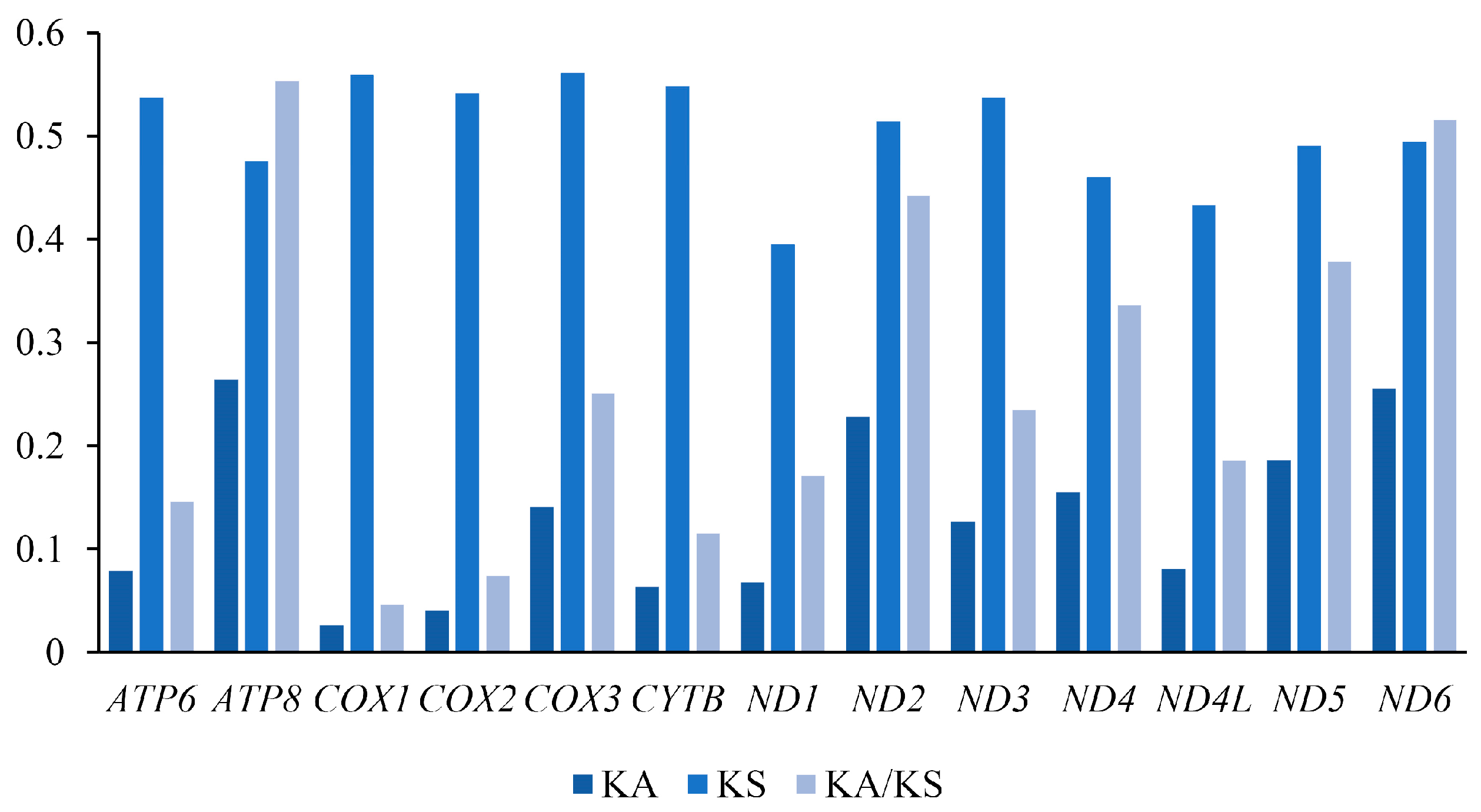
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes and Codon Usage
3.3. Transfer RNAs and Ribosomal RNAs and Control Regions
3.4. Phylogenetic Analyses of Lepidostomatidae
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morse, J.C.; Frandsen, P.B.; Graf, W.; Thomas, J.A. Diversity and Ecosystem Services of Trichoptera. Insects 2019, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Peng, L.; Vogler, A.P.; Morse, J.C.; Yang, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, B. Massive gene rearrangements of mitochondrial genomes and implications for the phylogeny of Trichoptera (Insecta). Syst. Entomol. 2023, 48, 278–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, G.F.F. Über die Metamorphose der Trichopteren; Hardpress Publishing: Miami, FL, USA, 1903; Volume 18, pp. 1–154. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, J.C. Trichoptera World Checklist. Available online: https://trichopt.app.clemson.edu/welcome.php (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Holzenthal, R.W.; Blahnik, R.J.; Prather, A.L.; Kjer, K.M. Order trichoptera kirby, 1813 (insecta), caddisflies. Zootaxa 2007, 1668, 639–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, R.J. Aquatic Insect Communities of a Small Stream on Mont St. Hilaire, Quebec. J. Fish. Board Can. 1969, 26, 1157–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T. Six new species of the genus Lepidostoma Rambur (Trichoptera, Lepidostomatidae) from Japan. Zoosymposia 2011, 5, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaouzas, I.; Waringer, J. The larva of Lepidostoma doehleri Malicky 1976 (Trichoptera: Lepidostomatidae) with notes on ecology and a key to larvae for species of the genus in Greece. Zootaxa 2016, 4189, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terefe, Y.; Vitecek, S.; Graf, W. Description of the larva of Oecetis mizrain Malicky & Graf, 2012 (Trichoptera, Leptoceridae) and Lepidostoma scotti (Ulmer, 1930) (Trichoptera, Lepidostomatidae) from Chilimo Forest, Central Ethiopia. Zookeys 2018, 766, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafius, E.J.; Anderson, N.H. Population dynamics and role of two species of Lepidostoma (Trichoptera: Lepidostomatidae) in an Orgeon coniferous forest stream [Lepidostoma cascadense, Lepidostoma unicolor; Oregon]. Ecology 1980, 61, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malicky, H. Phänologische Studien an tropischen Trichopteren: Chiangmai Zoo (Thailand). Braueria 2021, 48, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins, G.B. Larvae of the North American Caddisfly Genera (Trichoptera); University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dinakaran, S.; Sankarappan, A.; Balachandran, C. A new species of Caddisfly (Trichoptera: Lepidostomatidae: Lepidostoma) from Tamil Nadu, India. J. Threat. Taxa 2013, 5, 3531–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.H.; Grafius, E.J. Utilization and processing of allochthonous material by stream Trichoptera. Int. Ver. Theor. Und Angew. Limnol. Verhandlungen 1975, 19, 3083–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J. A synonymy of the caddisfly genus Lepidostoma Rambur (Trichoptera: Lepidostomatidae), including a species checklist. Tijdschr. Entomol. 2002, 145, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, R. A Monographic Revision and Synopsis of the Trichoptera of the European Fauna; John van Voorst: London, UK, 1876; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Weaver, J., III. The Chinese Lepidostomatidae (Trichoptera). Tijdschr. Entomol. 2002, 145, 267–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J. A synopsis of the North American Lepidostomatidae (Trichoptera). Contrib. Am. Entomol. Inst. 1988, 24, 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Suwannarat, N.; Laudee, P. Larval morphology, life cycle and nutritional values of Lepidostoma abruptum Banks 1931 (Trichoptera: Lepidostomatidae) from Lower-Hill Evergreen Forests of Southern Thailand. Zootaxa 2022, 5200, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.J.; Sperling, F.A. Preliminary evaluation of subgeneric designations within the caddisfly genus Lepidostoma (Rambur) (Trichoptera: Lepidostomatidae) based on mtDNA sequences. In Nova Supplementa Entomologica (Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Trichoptera); Antiquariat Geock & Evers: Pforzheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, S.L. Insect Mitochondrial Genomics: A Decade of Progress. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2025, 70, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L. Insect mitochondrial genomics: Implications for evolution and phylogeny. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Françoso, E.; Zuntini, A.R.; Ricardo, P.C.; Santos, P.K.F.; de Souza Araujo, N.; Silva, J.P.N.; Gonçalves, L.T.; Brito, R.; Gloag, R.; Taylor, B.A.; et al. Rapid evolution, rearrangements and whole mitogenome duplication in the Australian stingless bees Tetragonula (Hymenoptera: Apidae): A steppingstone towards understanding mitochondrial function and evolution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Ge, X.; Shi, F.; Wang, L.; Zang, H.; Sun, C.; Wang, B. New Mitogenome Features of Philopotamidae (Insecta: Trichoptera) with Two New Species of Gunungiella. Insects 2022, 13, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zang, H.; Ye, X.; Peng, L.; Wang, B.; Lian, G.; Sun, C. Comparative Mitogenomic Analyses of Hydropsychidae Revealing the Novel Rearrangement of Protein-Coding Gene and tRNA (Trichoptera: Annulipalpia). Insects 2022, 13, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wang, J.; Zang, H.; Chai, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C.; Wang, B. Mitogenomics Provide New Phylogenetic Insights of the Family Apataniidae (Trichoptera: Integripalpia). Insects 2024, 15, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.; Yiu, S.M.; Chin, F.Y. IDBA-UD: A de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Al-Arab, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Reinhardt, F.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M.; Bernt, M. Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10543–10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Le, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, F. SeqKit: A Cross-Platform and Ultrafast Toolkit for FASTA/Q File Manipulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kück, P.; Longo, G.C. FASconCAT-G: Extensive functions for multiple sequence alignment preparations concerning phylogenetic studies. Front. Zool. 2014, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kück, P.; Meid, S.; Christian, G.; Wägele, J.W.; Misof, B. AliGROOVE—Visualization of heterogeneous sequence divergence within multiple sequence alignments and detection of inflated branch support. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE7: New and Improved Tools for Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartillot, N.; Rodrigue, N.; Stubbs, D.; Richer, J. PhyloBayes MPI: Phylogenetic Reconstruction with Infinite Mixtures of Profiles in a Parallel Environment. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree Version 1.4.3. Computer Program Distributed by the Author. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 25 November 2018).
- Clary, D.O.; Wolstenholme, D.R. The mitochondrial DNA molecule of Drosophila yakuba: Nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.L.; Liu, Z.; Yan, L.P.; Duan, X.; Bu, W.J.; Wang, X.H.; Zheng, C.G. Mitogenomes provide new insights of evolutionary history of Boreheptagyiini and Diamesini (Diptera: Chironomidae: Diamesinae). Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.R.; Chen, M.H.; Li, S.Y.; Guo, B.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Qiao, Y.J.; Lin, X.L. Comparative Mitogenomic Analyses of Tanypodinae (Diptera: Chironomidae). Insects 2025, 16, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, T. Insights into the phylogeny of Hemiptera from increased mitogenomic taxon sampling. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 137, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, S.L.; Sullivan, J.; Song, H.; Miller, K.B.; Whiting, M.F. A mitochondrial genome phylogeny of the Neuropterida (lace-wings, alderflies and snakeflies) and their relationship to the other holometabolous insect orders. Zool. Scr. 2009, 38, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L.; Johnson, K.P.; Whiting, M.F. The Mitochondrial Genome of the Screamer Louse Bothriometopus (Phthiraptera: Ischnocera): Effects of Extensive Gene Rearrangements on the Evolution of the Genome. J. Mol. Evol. 2007, 65, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Valerio, A.; Austin, A.D.; Dowton, M.; Johnson, N.F. The first mitochondrial genome for the wasp superfamily Platygastroidea: The egg parasitoid Trissolcus basalis. Genome 2012, 55, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frandsen, P.B.; Holzenthal, R.W.; Espeland, M.; Breinholt, J.; Thomas Thorpe, J.A.; Simon, S.; Kawahara, A.Y.; Plotkin, D.; Hotaling, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Phylogenomics recovers multiple origins of portable case making in caddisflies (Insecta: Trichoptera), nature’s underwater architects. Roy. Soc. B—Biol. Sci. 2024, 291, 20240514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Peng, L.; Morse, J.C.; Wang, J.; Zang, H.; Yang, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, B. Phylogenomics resolves a 100-year-old debate regarding the evolutionary history of caddisflies (Insecta: Trichoptera). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2024, 201, 108196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | Length (bp) | A (%) | T (%) | C (%) | G (%) | A + T (%) | GC-Skew | AT-Skew |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lepidostoma albardanum | 15,053 | 38.82 | 39.40 | 14.34 | 7.43 | 78.22 | −0.317 | −0.007 |
| Lepidostoma elongatum | 15,234 | 39.13 | 40.47 | 13.13 | 7.26 | 79.60 | −0.288 | −0.017 |
| Lepidostoma aranos | 15,870 | 38.49 | 39.19 | 15.00 | 7.30 | 77.67 | −0.345 | −0.009 |
| Lepidostoma cornigerum | 15,325 | 38.04 | 39.11 | 15.37 | 7.48 | 77.15 | −0.346 | −0.014 |
| Lepidostoma flavum | 15,816 | 38.12 | 40.05 | 14.53 | 7.23 | 78.17 | −0.335 | −0.025 |
| Lepidostoma hirtum | 15,663 | 38.75 | 39.45 | 14.45 | 7.35 | 78.20 | −0.325 | −0.009 |
| Lepidostoma penicillatum | 15,875 | 39.04 | 40.34 | 13.44 | 7.15 | 79.38 | −0.305 | −0.016 |
| Lepidostoma propriopalpum | 15,158 | 39.12 | 40.32 | 13.28 | 7.27 | 79.44 | −0.293 | −0.015 |
| Lepidostoma pusillum | 16,036 | 38.83 | 39.92 | 13.81 | 7.39 | 78.74 | −0.303 | −0.014 |
| Lepidostoma reductum | 15,077 | 38.56 | 38.03 | 15.24 | 8.17 | 76.59 | −0.302 | 0.007 |
| Lepidostoma sichuanense | 16,165 | 38.47 | 39.65 | 14.24 | 7.52 | 78.11 | −0.309 | −0.015 |
| Lepidostoma sp. XG-2025 | 15,115 | 38.86 | 39.05 | 14.49 | 7.61 | 77.90 | −0.311 | −0.002 |
| Lepidostoma tanmounense | 15,065 | 38.58 | 40.07 | 13.88 | 7.47 | 78.65 | −0.300 | −0.019 |
| Paraphlegopteryx subcircularis | 16,495 | 38.87 | 41.53 | 12.57 | 6.80 | 80.40 | −0.298 | −0.033 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, Z.; Chai, L.; Cao, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Family Lepidostomatidae (Trichoptera: Integripalpia) Using Whole Mitochondrial Genomes. Insects 2025, 16, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050536
Ge X, Wang J, Deng Z, Chai L, Cao W, Liu W, Zhang J, Yan C. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Family Lepidostomatidae (Trichoptera: Integripalpia) Using Whole Mitochondrial Genomes. Insects. 2025; 16(5):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050536
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Xinyu, Jingyuan Wang, Zhen Deng, Lu Chai, Wei Cao, Wenbin Liu, Jiwei Zhang, and Chuncai Yan. 2025. "Phylogenetic Analysis of the Family Lepidostomatidae (Trichoptera: Integripalpia) Using Whole Mitochondrial Genomes" Insects 16, no. 5: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050536
APA StyleGe, X., Wang, J., Deng, Z., Chai, L., Cao, W., Liu, W., Zhang, J., & Yan, C. (2025). Phylogenetic Analysis of the Family Lepidostomatidae (Trichoptera: Integripalpia) Using Whole Mitochondrial Genomes. Insects, 16(5), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050536







