Ontogenetic Analysis of Chelonus formosanus and Diversity of Its Internal Microbiota
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Experimental Method
2.2.1. Determination of Individual Development of Chelonus formosanus
2.2.2. Samples Collection
2.2.3. DNA Extraction and 16S rDNA Sequencing
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Life Cycle of Chelonus formosanus
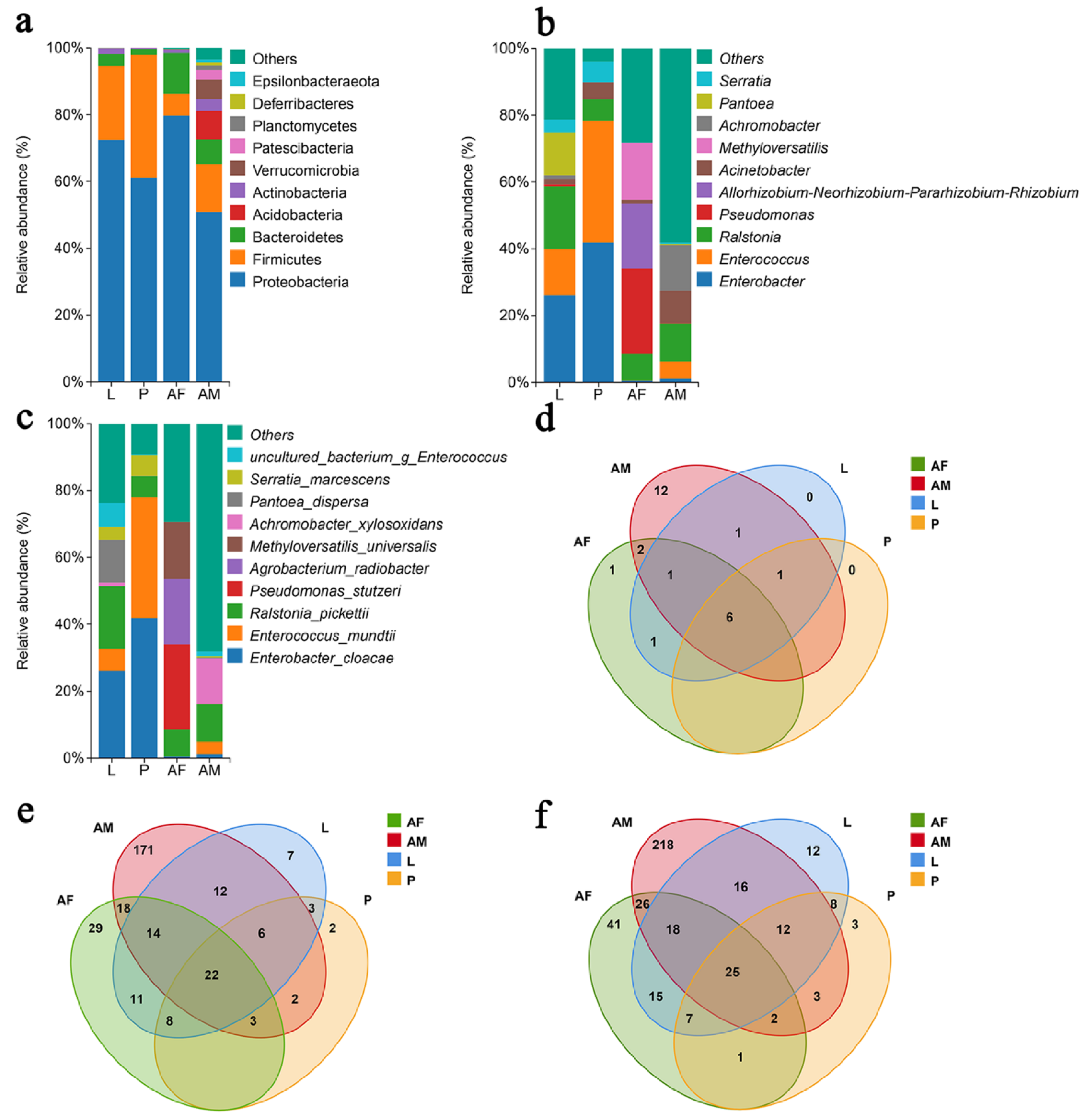
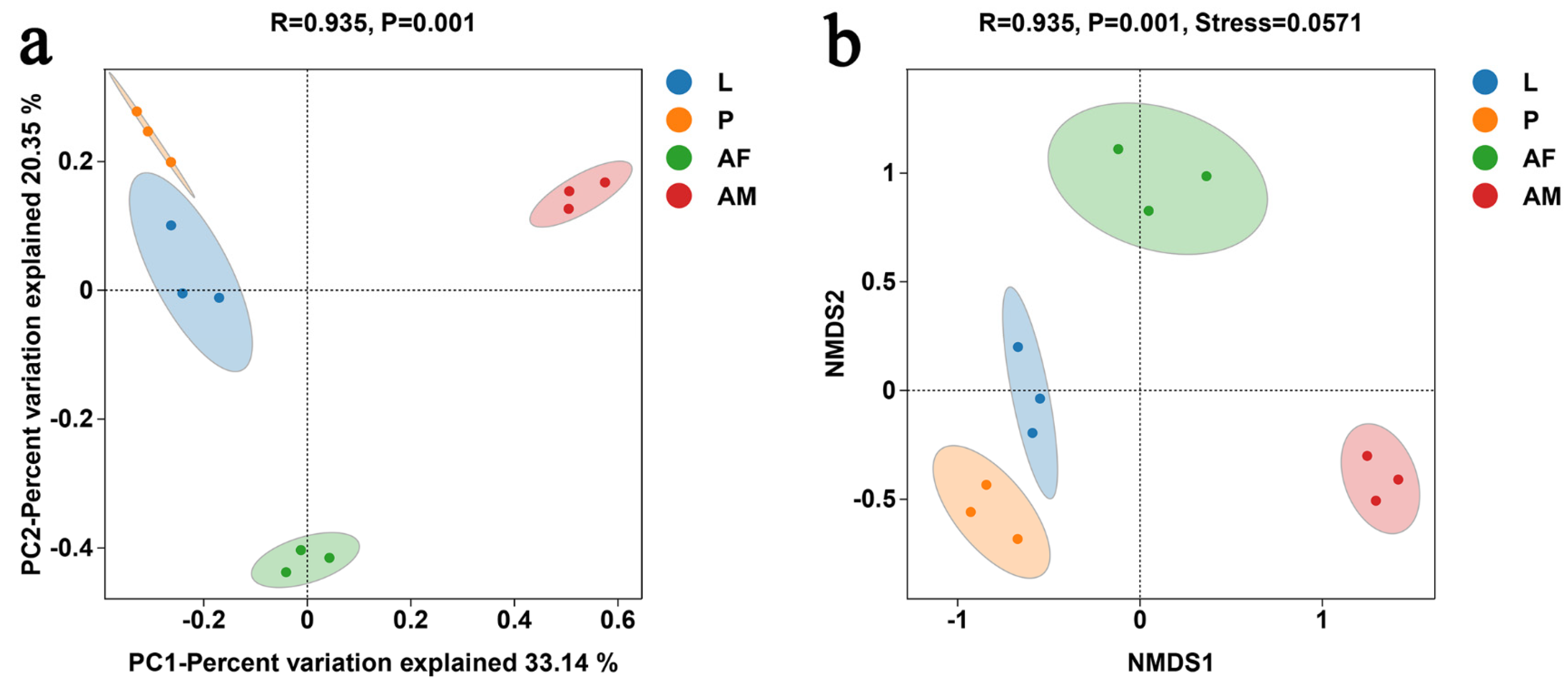
3.2. Bacterial Composition and Diversity in Chelonus formosanus
3.2.1. Overview of 16S rDNA Sequencing Associated with Taxonomic Annotation
3.2.2. Composition of Bacterial Communities at Different Developmental Stages of Chelonus formosanus
3.2.3. Functional Predictions of Bacterial Community of Chelonus formosanus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.Y. A Taxonomic Study on Genus Chelonus Panzer, 1806 (Hvmenoptera: Braconidae: Cheloninae) from China. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.H.; Lv, B.Q.; Lu, H.; Ji, X.C.; Yang, P.Y.; Su, H.; Cai, B. Investigation and preliminary study of biological characteristic of parasitic wasps of Spodoptera frugiperda in Hainan. Chin. J. Trop. Crops. 2020, 41, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Lalitha, Y.; Varshney, R.; Shylesha, A.; Van, C. Chelonus formosanus Sonan (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) an egg-larval parasitoid of the invasive pest Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) amenable to laboratory mass production in India. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Calcetas, O.A.; Joshi, R.C.; Gupta, A.; Ranjith, A.P.; Madrid, M.A.; Fameronag, J. New record of the egg-larval parasitoid, Chelonus Formosanus Sonan of Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) in the Philippines. JPT J. Prot. Tanam. (J. Plant Prot.) 2023, 7, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi, M.C.; Suroshe, S.S.; Doddachowdappa, S.; Shivakumara, K.T.; Mahesha, H.S.; Rana, V.S.; Gupta, A.; Murukesan, A.; Casini, R.; Elansary, H.O.; et al. Bio-Intensive tactics for the management of invasive Fall Armyworm for organic maize production. Plants 2023, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. Multiorganismal Insects: Diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Somani, J.; Roy, S.; Babu, A.; Pandey, A.K. Insect Microbial Symbionts: Ecology, Interactions, and Biological Significance. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, J.R.; Cavichiolli de Oliveira, N.; Medina, R.F.; Malacrinò, A.; Lindsey, A.R.I. Insect–Microbe Interactions and Their Influence on Organisms and Ecosystems. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.H. The Effects of Gut Microbiota on the Growth and the Repair of Irradiated Damage in Bactrocera dorsalis. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.Q.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.T.; Li, C.; Li, S.Q.; Sun, J.H.; Xu, L.T. Gut bacteria facilitate leaf beetles in adapting to dietary specialization by enhancing larval fitness. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akami, M.; Ren, X.M.; Qi, X.W.; Mansour, A.; Gao, B.L.; Cao, S.; Niu, C.Y. Symbiotic bacteria motivate the foraging decision and Promote fecundity and survival of Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, S.G.; Hunter, M.S. Manipulation of oviposition choice of the parasitoid wasp, Encarsia pergandiella, by the endosymbiotic bacterium Cardinium. J. Evol. Biol. 2007, 20, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, K.; Kooienga, E.; Sanders, M.; Pendarvis, K.; Yang, F.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Jordan, H.R. The effect of Rhodococcus rhodochrous supplementation on black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) development, nutrition, and waste conversion. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, W.Q.; Han, X.Z.; Hao, X.; Yao, Q.B.; Du, W.G. Gut microbiota modulation enhances the immune capacity of lizards under climate warming. Microbiome 2024, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Wang, L.N.; Gong, J.; Tang, Y.L.; Wei, K. Diversity analyses of bacterial symbionts in four Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) parasitic wasps, the dominant biological cntrol agents of wood-boring beetles in China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1439476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Dong, Y.L.; Yan, Z.Z.; Lv, D.B.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.P. Comparison of gut bacterial communities of Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) reared on different host plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P. Effects of Consumption of Different Types of Prey on Diversity and Composition of Gut Microbial Communities in Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.N.; Liu, L.Y.; Cai, X.M.; Yang, X.M.; Lin, J.T.; Shu, B.S. The bacterial and fungal communities of the larval midgut of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) varied by feeding on two cruciferous vegetables. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.T. Differences in Microbial Diversity and the Effects of Intracellular Symbiont on the Growth of Rhyzopertha dominica. Master’s Thesis, Henan of Technology University, Zhengzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, G.S. The Research on Composition of Symbiotie Microbial Communitiesof Diaphorina citri and the Factors Influencing Composition. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.L.; Su, X.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Yang, M.; Bai, J.H.; Zeng, J.Y.; Li, H.P. Similar gut bacteria composition in Apriona Germari on two preferred host plants. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 110, e21899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.W.; Xia, X.J.; Feng, Y.L.; Wu, W.; Li, H.J.; Sun, Z.T.; Li, J.M.; Chen, J.P. The Plant-sucking insect selects assembly of the gut microbiota from environment to enhance host reproduction. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laviad-Shitrit, S.; Sela, R.; Sharaby, Y.; Thorat, L.; Nath, B.B.; Halpern, M. Comparative microbiota composition across developmental stages of natural and laboratory-reared Chironomus circumdatus populations from India. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 746830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Huangfu, N.; Chen, L.L.; Zhang, K.X.; Li, D.Y.; Gao, X.K.; Li, B.B.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.Z.; Ji, J.C.; et al. Effects of developmental stages, sex difference, and diet types of the host marmalade hoverfly (Episyrphus balteatus) on symbiotic bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1433909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Serrano, F.; Pérez-Cobas, A.E.; Rosas, T.; Baixeras, J.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A. The gut microbiota composition of the moth Brithys crini reflects insect metamorphosis. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 79, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobles, S.; Jackson, C.R. Effects of life stage, site, and species on the dragonfly gut microbiome. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, R.; Laviad-Shitrit, S.; Halpern, M. Changes in microbiota composition along the metamorphosis developmental stages of Chironomus transvaalensis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 586678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, R.M.; Li, Y.; Dou, F.Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Huang, D.Y. Diversity and differences of gut bacterial communities in different instarlarvae and diapause prepupae of Colletes gigas (Hymenoptera:Colletidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2021, 64, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Effects of Developmental Stages, Diets and High Temperature Stress on Bacterial Diversity in Propylaea japonica. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Agricultural & Forestry University, Yang Ling, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Z.; Wang, G.P.; Ma, Y.X.; Lv, Z.Y.; You, Y.W.; Ma, P.T.; Yu, Y. Composition and diversity of gut bacterial community in different life stages of Osmia excavata Alfken (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yue, C.; Ma, N.; Yan, G.J. Effects of diet on the gut bacterial community of AldriChina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae) across developmental stages. Insects 2024, 15, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, P.C.A.; Trynka, G.; Franke, L.; Hunt, K.A.; Romanos, J.; Curtotti, A.; Zhernakova, A.; Heap, G.A.R.; Ádány, R.; Aromaa, A.; et al. Multiple common variants for celiac disease influencing immune gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looft, T.; Johnson, T.A.; Allen, H.K.; Bayles, D.O.; Alt, D.P.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Sul, W.J.; Stedtfeld, T.M.; Chai, B.; Cole, J.R.; et al. In-feed antibiotic effects on the swine intestinal microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, S.S. Effect of superparasitism on bionomics of Cotesia plutellae. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2001, 17, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.N. The Study on Molecular Mechanisms of Leptopilina Wasps Manipulating Host Behavior to Avoid Superparasitism. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tillman, P.G.; Powell, J.E. Intraspecific host discrimination and larval competition in Microplitis croceipes, Microplitis demolitor, Cotesia kazak (Hym.: Braconidae) and Hyposoter didymator (Hym.: Ichneumonidae), parasitoids of Heliothis virescens (Lep.: Noctuidae). Entomophaga 1992, 37, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.G.; Yang, J.Q.; Ji, Q.E.; Huang, J.C.; Cheng, J.H. Characteristics of individual development of Psyttalia incisi (Silvestri). J. Hunan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2007, 3, 321–323. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.Y.; Li, X.; Liu, T.X.; Zhang, S.Z. Ontogeny of Cotesia ruficrus, a Parasitoid of Spodoptera frugiperda. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2023, 39, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.C.; Yue, J.J.; Qing, S.; Chen, H.Y.; Liang, Y.P. A preliminary study on the biological characteristics of Chelonus formosanus Sonan. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2013, 29, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, Y.X.; Luo, L.Z.; Du, Q.; Jiang, X.F.; Zhang, L. Biology and bio-control potential of Zele chlorophthalmus (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasitoid of beet webworm, Loxostege sticticalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Chin. J. Biol. Control 2017, 33, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, Q.Q.; Wang, X.P. Parasitic efficacy and development performance of Cotesia marginiventris (Cresson) on Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith). J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2021, 50, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, M.; Cusumano, A.; Poelman, E.H. Microbial Symbionts of Parasitoids. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Yu, J.N.; Zhou, Y.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Ma, T.T.; Tan, X.M.; Wan, F.H.; Zhou, H.X. Differentiation of symbiotic bacteria is a new evidence for two genetic clades of Aphelinus mali (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) in China. Orient. Insects 2020, 54, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.Q. Preliminary Studies on the Compositions and Functions of Microbiota from Adult and Larval Gut of Two Leptopilina Wasps. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, N.N.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Chen, X.X. Characterization of larval gut microbiota of two endoparasitoid Wasps associated with their common host, Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e01208-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, T.Z.; Yu, X.P. Analysis of the bacterial community structure and diversity in the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) by16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2018, 61, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.K.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Lv, L.M.; Zhu, X.Z.; Wang, L.; Cui, J.J. Analysis of symbiotic bacteria of Propylea japonica larvae. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2018, 34, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.C.; Jiang, J.T.; Cheng, L.; Liu, J.S.; Li, T.; Peng, L.F. Bacterial composition and diversity in the litchi stink bug, Tessaratoma papillosa (Hemiptera: Tessaratomidae) from six provinces of China. J. Plant Prot. 2022, 49, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.L.; Huang, R.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.P.; Zhang, K.; Ma, L.; Li, T.T.; Wang, L.Z.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, B.B. Effects of insecticidal proteins of Enterobacter cloacae NK on cellular immunity of Galleria mellonella larvae. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1154811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Joop, G. Probiotic Enterococcus mundtii isolate rotects the model insect Tribolium castaneum against Bacillus thuringiensis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Ni, B.Q.; Wu, Y.N.; Yang, Y.Y.; Mu, D.L.; Wu, K.N.; Zhang, A.H.; Du, Y.L.; Li, Q. The cultivable gut bacteria Enterococcus mundtii promotes early-instar larval growth of Congethes punctiferalis via enhancing digestive enzyme activity. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 61796188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, M.C.; Furusawa, G.; Veera Singham, G. Multifaceted interactions between the pseudomonads and Insects: Mechanisms and prospects. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 1891–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceja-Navarro, J.A.; Vega, F.E.; Karaoz, U.; Hao, Z.; Jenkins, S.; Lim, H.C.; Kosina, P.; Infante, F.; Northen, T.R.; Brodie, E.L. Gut microbiota mediate caffeine detoxification in the primary insect pest of coffee. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, C.; Jiwal, S.; Rout, P.; Ramya, M. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by bacterial consortium isolated from agriculture soil. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.J.; Lowe-Power, T.M.; Rubert-Nason, K.F.; Lindroth, R.L.; Raffa, K.F. Interactions between bacteria and aspen defense chemicals at the phyllosphere–herbivore interface. J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; An, T.F.; Li, X.L.; Zou, J.; Lin, Z.; Gu, J.L.; Hu, R.X.; Fang, Z.Z. Genomic analysis of Ralstonia pickettii reveals the genetic features for potential pathogenicity and adaptive evolution in drinking water. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1272636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucker, R.M.; Bordenstein, S.R. The roles of host evolutionary relationships (Genus: Nasonia) and development in structuring microbial communities. Evolution 2012, 66, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.C.; Lu, Y.Q.; Chen, J.N.; Pan, Z.Q.; Pang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.C.; Strand, M.R.; Chen, X.X.; Huang, J.H. Parasite reliance on its host gut microbiota for ntrition and survival. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2574–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, A.Y.; Cui, J.J. Analysis of endophytic symbiotic bacterial composition in Chrysoperla sinica (Tjeder) Adults with 16S rDNA clone library. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2017, 33, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.H.; Peng, X.; Zheng, X.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, R.R.; Huang, Z.Y.; Yang, Z.D. Comparison of bacterial diversity and abundance between sexes of Leptocybe Invasa Fisher & La Salle (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) from China. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C. The Biodiversity of Helicoverpa armigera Symbiotic Bacteria and Its Regulatory Effects on the Defense Response in Contton. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, P. Diversity and Dynamic Changes of Symbiotic Bacteriain the Development of Ericerus pela. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
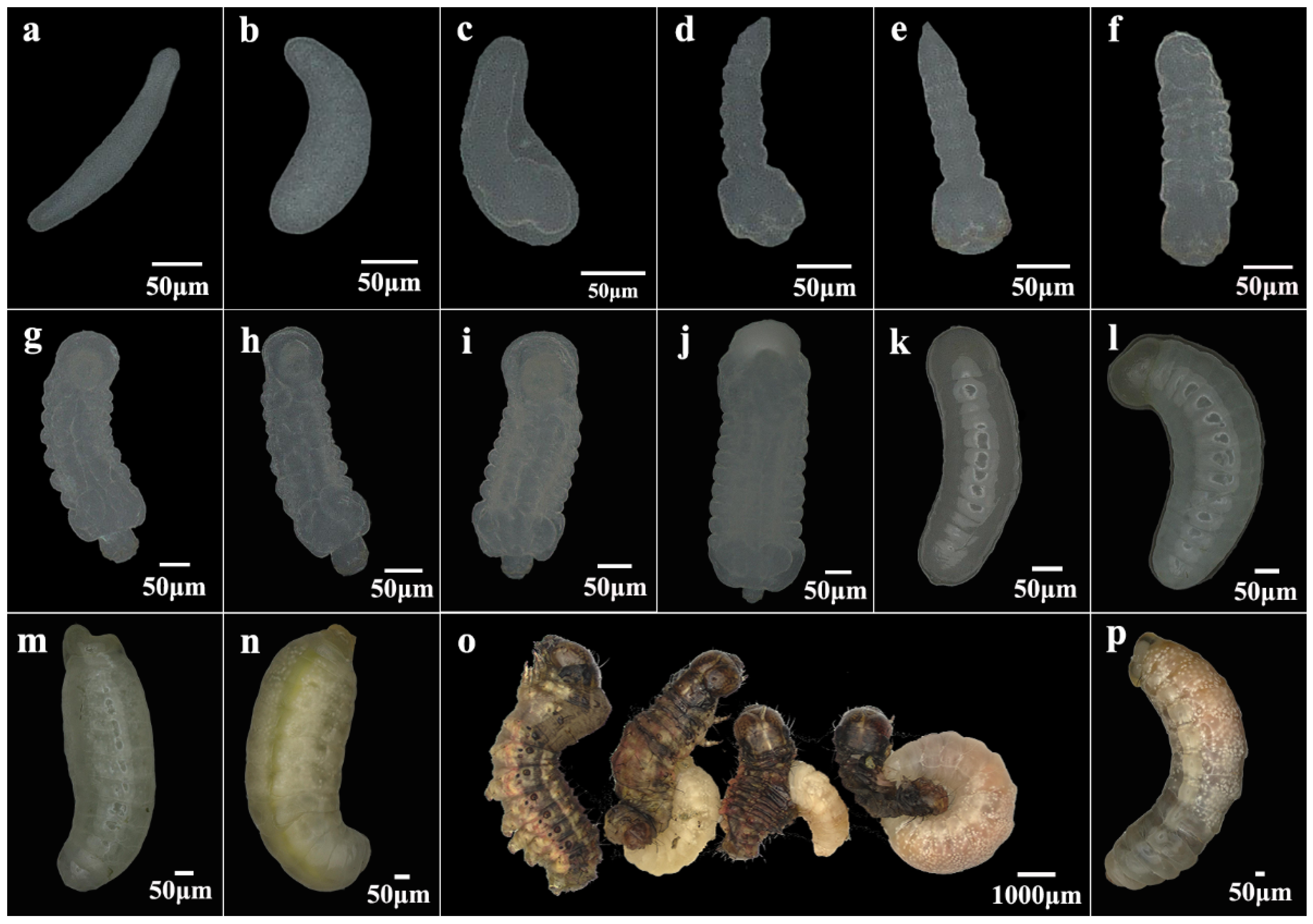





| Sample | Raw CCS | Clean CCS | Effective CCS | AvgLen (bp) | Effective (%) | OTU | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 10,954 | 9850 | 9691 | 1464 | 88.47 | 73 | 99.88 |
| L2 | 9174 | 7951 | 7853 | 1465 | 85.60 | 61 | 99.84 |
| L3 | 8280 | 7482 | 7429 | 1461 | 89.72 | 69 | 99.80 |
| P1 | 13,014 | 11,525 | 11,212 | 1468 | 86.15 | 38 | 99.93 |
| P2 | 11,513 | 10,309 | 10,093 | 1468 | 87.67 | 34 | 99.91 |
| P3 | 10,616 | 9601 | 9531 | 1476 | 89.78 | 37 | 99.95 |
| AF1 | 8012 | 7308 | 7270 | 1447 | 90.74 | 96 | 99.83 |
| AF2 | 13,033 | 11,529 | 11,286 | 1446 | 86.60 | 71 | 99.97 |
| AF3 | 10,667 | 9348 | 9094 | 1446 | 85.25 | 136 | 99.92 |
| AM1 | 10,000 | 8256 | 7832 | 1457 | 78.32 | 578 | 99.35 |
| AM2 | 12,753 | 9809 | 9236 | 1458 | 72.42 | 420 | 99.58 |
| AM3 | 8219 | 7216 | 6885 | 1457 | 83.77 | 405 | 99.73 |
| Sample | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 5.00 ± 0.58 b | 8.00 ± 0.00 b | 16.00 ± 1.15 b | 21.00 ± 1.53 b | 28.00 ± 1.00 c | 36.00 ± 1.15 b |
| P | 6.33 ± 0.33 b | 10.00 ± 0.57 b | 22.67 ± 0.88 b | 36.33 ± 3.06 b | 50.67 ± 0.88 bc | 66.33 ± 3.48 b |
| AF | 7.33 ± 1.20 b | 11.33 ± 0.88 b | 24.00 ± 1.00 b | 40.00 ± 2.65 b | 63.00 ± 6.03 b | 75.33 ± 7.67 b |
| AM | 21.33 ± 0.88 a | 51.00 ± 3.60 a | 95.00 ± 6.56 a | 140.00 ± 19.97 a | 210.00 ± 31.75 a | 266.67 ± 25.33 a |
| Total | 25 | 61 | 116 | 182 | 308 | 404 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, J.; Feng, Q.; Huang, W.; Lin, Z.; Ji, X. Ontogenetic Analysis of Chelonus formosanus and Diversity of Its Internal Microbiota. Insects 2025, 16, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020180
Jia J, Feng Q, Huang W, Lin Z, Ji X. Ontogenetic Analysis of Chelonus formosanus and Diversity of Its Internal Microbiota. Insects. 2025; 16(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020180
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Jingjing, Qing Feng, Weikang Huang, Zhufeng Lin, and Xuncong Ji. 2025. "Ontogenetic Analysis of Chelonus formosanus and Diversity of Its Internal Microbiota" Insects 16, no. 2: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020180
APA StyleJia, J., Feng, Q., Huang, W., Lin, Z., & Ji, X. (2025). Ontogenetic Analysis of Chelonus formosanus and Diversity of Its Internal Microbiota. Insects, 16(2), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020180





