Comparative Evaluation of Benchtop and Portable Near-Infrared Spectrometers for Predicting the Age and Blood Feeding History of Aedes aegypti
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito Rearing, Feeding and Sampling
2.2. Mosquito Scanning Using Labspec 4i
2.3. Mosquito Scanning Using NIRvascan
2.4. Data Analysis
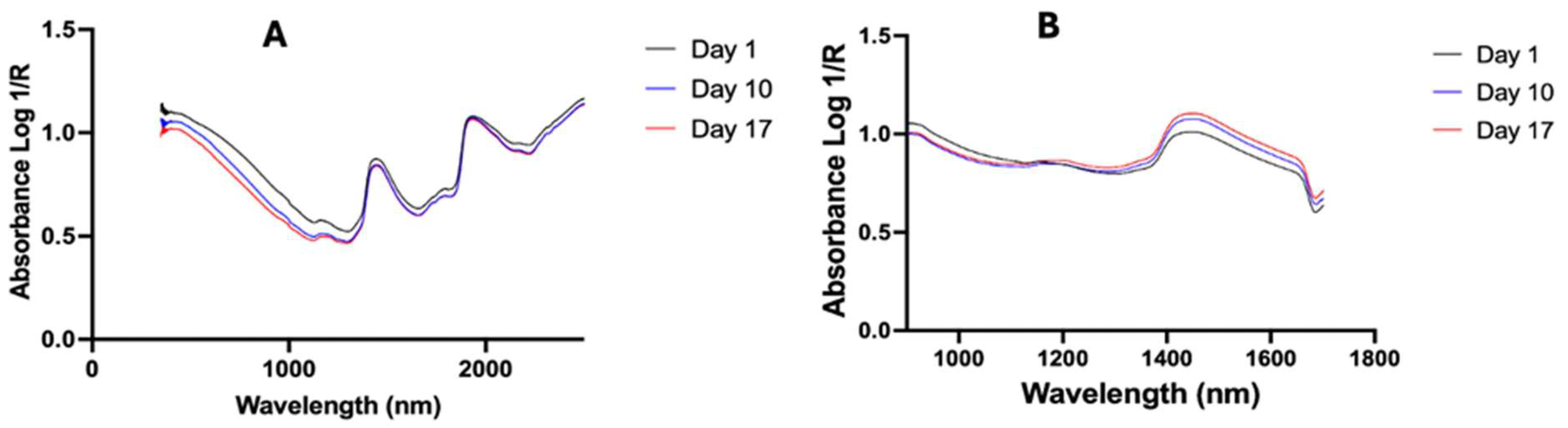
3. Results
3.1. Prediction Within the Training Set
3.2. Validation Set
3.2.1. Prediction of Age
3.2.2. Prediction of Blood-Meal History
3.3. Effect of Blood Meal on Age Prediction by Both Spectrometers
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Labspec 4i and NIRvascan in Terms of Time, Cost and Operational Complexity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M.G.; Halstead, S.B.; Artsob, H.; Buchy, P.; Farrar, J.; Gubler, D.J.; Hunsperger, E.; Kroeger, A.; Margolis, H.S.; Martínez, E.; et al. Dengue: A continuing global threat. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, S7–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Jamdar, S.F.; Alalowi, M.; Al Beaiji, S.M.A.A. Dengue virus: A global human threat: Review of literature. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, J.; Elankeswaran, B.; Erne, D.; Hedrich, N.; Lovey, T.; Marzetta, V.; Salvado, L.T.; Züger, C.; Schlagenhauf, P. Dengue “homegrown” in Europe (2022 to 2023). New Microbes New Infect. 2023, 56, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchs, A.; Conde, A.; Frank, A.; Gottet, C.; Hedrich, N.; Lovey, T.; Shindleman, H.; Schlagenhauf, P. The threat of dengue in Europe. New Microbes New Infect. 2022, 49–50, 101061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, G. The Epidemiology and Control of Malaria; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D.M.; Burke, D.S.; Harrison, B.A.; Whitmire, R.E.; Nisalak, A. Effect of Temperature on the Vector Efficiency of Aedes aegypti for Dengue 2 Virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1987, 36, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrulle, M.; Mousson, L.; Moutailler, S.; Vazeille, M.; Failloux, A.-B. Chikungunya virus and Aedes mosquitoes: Saliva is infectious as soon as two days after oral infection. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett Jones, C.; Shidrawi, G.R. Malaria Vectorial Capacity of a Population of Anopheles gambiae—An Exercise in Epidemiological Entomology. Bull. World Health Organ. 1969, 40, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Detinova, T. Age-grouping methods in Diptera of medical importance, with special reference to some vectors of malaria. Monogr. Ser. World Health Organ. 1962, 47, 13–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polovodova, V. Age changes in ovaries of Anopheles and methods of determination of age composition in mosquito population. Med. Parazit 1941, 10, 387. [Google Scholar]
- Polovodova, V.P. The determination of the physiological age of female Anopheles by number of gonotrophic cycles completed. Med. Parazitol. Parazitar Bolezn. 1949, 18, 352–355. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, B. Age structure of populations of Culex annulirostris (Diptera: Culicidae) at Kowanyama and Charleville, Queensland. J. Med. Entomol. 1979, 16, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellamy, R.E.; Corbet, P.S. Occurrence of ovariolar dilatations in nulliparous mosquitoes. Mosq. News 1974, 34, 334. [Google Scholar]
- Mayagaya, V.; Michel, K.; Benedict, M.; Killeen, G.; Wirtz, R.; Ferguson, H.; Dowell, F. Non-destructive determination of age and species of Anopheles gambiae s.l. using Near-infrared spectroscopy. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikulu, M.; Killeen, G.F.; Hugo, L.E.; Ryan, P.A.; Dowell, K.M.; Wirtz, R.A.; Moore, S.J.; Dowell, F.E. Near-infrared spectroscopy as a complementary age grading and species identification tool for African malaria vectors. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, B.; Sikulu-Lord, M.T.; Mayagaya, V.S.; Devine, G.; Dowell, F.; Churcher, T.S. Monitoring the Age of Mosquito Populations Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikulu-Lord, M.T.; Milali, M.P.; Henry, M.; Wirtz, R.A.; Hugo, L.E.; Dowell, F.E.; Devine, G.J. Near-infrared spectroscopy, a rapid method for predicting the age of male and female wild-type and Wolbachia infected Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikulu-Lord, M.T.; Devine, G.J.; Hugo, L.E.; Dowell, F.E. First report on the application of near-infrared spectroscopy to predict the age of Aedes albopictus Skuse. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikulu, M.T.; Majambere, S.; Khatib, B.O.; Ali, A.S.; Hugo, L.E.; Dowell, F.E. Using a near-infrared spectrometer to estimate the age of anopheles mosquitoes exposed to pyrethroids. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milali, M.P.; Kiware, S.S.; Govella, N.J.; Okumu, F.; Bansal, N.; Bozdag, S.; Charlwood, J.D.; Maia, M.F.; Ogoma, S.B.; Dowell, F.E.; et al. An autoencoder and artificial neural network-based method to estimate parity status of wild mosquitoes from near-infrared spectra. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djègbè, N.D.; Da, D.F.; Somé, B.M.; Paré, L.I.G.; Cissé, F.; Kaboré, J.; Churcher, T.S.; Dabiré, R.K. Exploring near-infrared spectroscopy ability to predict the age and species of Anopheles gambiae sensu lato mosquitoes from different environmental conditions in Burkina Faso. Malar. J. 2025, 24, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, T.; Chen, M.; Arnbrister, J.; Williamson, D.; Li, S.; Nair, S.; Brophy, M.; Garcia, V.M.; Walker, K.; Ernst, K.; et al. Assessing near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for evaluation of Aedes aegypti population age structure. Insects 2022, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, G.A.; Lord, A.R.; Santos, L.M.; Kariyawasam, T.N.; David, M.R.; Couto-Lima, D.; Tátila-Ferreira, A.; Pavan, M.G.; Sikulu-Lord, M.T.; Maciel-de-Freitas, R. Rapid and Non-Invasive Detection of Aedes aegypti Co-Infected with Zika and Dengue Viruses Using Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Viruses 2022, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.; Mutsaers, M.; Garcia, G.A.; David, M.R.; Pavan, M.G.; Petersen, M.T.; Corrêa-Antônio, J.; Couto-Lima, D.; Maes, L.; Dowell, F.; et al. High throughput estimates of Wolbachia, Zika and chikungunya infection in Aedes aegypti by near-infrared spectroscopy to improve arbovirus surveillance. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.N.; Dos Santos, L.M.B.; Chouin-Carneiro, T.; Pavan, M.G.; Garcia, G.A.; David, M.R.; Beier, J.C.; Dowell, F.E.; Maciel-de-Freitas, R.; Sikulu-Lord, M.T. Rapid, noninvasive detection of Zika virus in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes by near-infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat0496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikulu-Lord, M.T.; Maia, M.F.; Milali, M.P.; Henry, M.; Mkandawile, G.; Kho, E.A.; Wirtz, R.A.; Hugo, L.E.; Dowell, F.E.; Devine, G.J. Rapid and Non-destructive Detection and Identification of Two Strains of Wolbachia Aedes aegypti by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.F.; Kapulu, M.; Muthui, M.; Wagah, M.G.; Ferguson, H.M.; Dowell, F.E.; Baldini, F.; Ranford-Cartwright, L. Detection of Plasmodium falciparum infected Anopheles gambiae using near-infrared spectroscopy. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tátila-Ferreira, A.; Garcia, G.A.; dos Santos, L.; Pavan, M.G.; de C Moreira, C.J.; Victoriano, J.C.; da Silva-Junior, R.; dos Santos-Mallet, J.R.; Verly, T.; Britto, C.; et al. Near infrared spectroscopy accurately detects Trypanosoma cruzi non-destructively in midguts, rectum and excreta samples of Triatoma infestans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.E.; Hugo, L.E.; Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Williams, C.R.; Chenoweth, S.F.; Ritchie, S.A.; Ryan, P.A.; Kay, B.H.; Blows, M.W.; O’Neill, S.L. The use of transcriptional profiles to predict adult mosquito age under field conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18060–18065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, L.E.; Kay, B.H.; Eaglesham, G.K.; Holling, N.; Ryan, P.A. Investigation of cuticular hydrocarbons for determining the age and survivorship of Australian mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 74, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.K.; Peiris, K.H.S.; Scholte, E.J.; Wirtz, R.A.; Dowell, F.E. Age-grading the biting midge Culicoides sonorensis using near-infrared spectroscopy. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2010, 24, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Schmitt, J.M. Optimum wavelengths for measurement of blood hemoglobin content and tissue hydration by NIR spectrophotometry. In Optical Diagnostics of Living Cells and Biofluids; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 442–453. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Ostrander, L.E.; Lee, B.Y. In vivo reflectance of blood and tissue as a function of light wavelength. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1990, 37, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebman, K.; Swamidoss, I.; Vizcaino, L.; Lenhart, A.; Dowell, F.; Wirtz, R. The Influence of Diet on the Use of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Determine the Age of Female Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. of Mosquitoes Sampled | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | Unfed | Blood-Fed Once | Blood-Fed Twice | Total |
| 1 | 127 | 38 | 39 | 204 |
| 2 | 86 | 20 | 26 | 132 |
| 3 | 120 | 80 | 40 | 240 |
| Total | 333 | 138 | 105 | 576 |
| Labspec 4i | Region (nm) | NIRvascan | Region (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Cohort | Training | Validation | 1050–2350 | Training | Validation | 950–1650 |
| 1 | 100 | 104 | 14 | 190 | |||
| 2 | 50 | 82 | 82 | 50 | |||
| 3 | 60 | 180 | 190 | 50 | |||
| Blood meal | 1 | 80 | 124 | 500–2350 | 14 | 190 | 950–1650 |
| 2 | 68 | 64 | 82 | 50 | |||
| 3 | 120 | 120 | 220 * | 60 ** | |||
| Age in Days | Predictive Accuracy for Age [N] | Feeding Condition | Predictive Accuracy for Blood Feeding [N] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labspec 4i [N] | NIRvascan [N] | Labspec 4i [N] | NIRvascan [N] | ||
| 1 d (<10 d) | 100 [40] | 100 [62] | Unfed (0) | 96.3 [134] | 96.8 [158] |
| 10 d (≥10 d) | 81.3 [80] | 69.5 [82] | Fed Once * | 97.4 [77] | 98.2 [111] |
| 17 d (≥10 d) | 100 [90] | 100 [142] | Fed Twice * | 86 [57] | 97.8 [47] |
| Average | 92.9 [210] | 91.3 [286] | Average | 94.4 [268] | 97.4 [316] |
| Labspec | NIRvascan | |
|---|---|---|
| < or ≥10 Days Age Group | < or ≥10 Days Age Group | |
| 1 d | 96.3 [81] | 100 [58] |
| 10 d | 87.3 [118] | 83.6 [116] |
| 17 d | 97.6 [167] | 91.8 [116] |
| Average | 94.0 [366] | 90.0 [290] |
| Fed Condition | Predictive Accuracy [N] | |
|---|---|---|
| Labspec 4i | NIRvascan | |
| Unfed (0) | 77.9 [199] | 72.4 [174] |
| Fed Once (1) * | 88.5 [61] | 70.5 [68] |
| Fed Twice (2) * | 95.8 [48] | 68.9 [58] |
| Total Average | 82.8 [308] | 71.3 [300] |
| Blood Feeding Status | Age | Labspec 4i | NIRvascan | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Predicted Age | p-Value | Mean Predicted Age | p-Value | ||
| Unfed | 10 | 14.3 | 0.001 | 14.5 | 0.049 |
| Fed | 10 | 12.3 | 13.2 | ||
| Unfed | 17 | 15.2 | 0.005 | 14.5 | 0.678 |
| Fed | 17 | 14.1 | 14.8 | ||
| Feature | NIRvascan | Labspec 4i |
|---|---|---|
| General configuration |  |  |
| Size | 82.2 × 66 × 45 mm, highly portable, lightweight (136 g) | 127 × 356 × 292 mm, portable but larger than NIRvascan (5600 g) |
| Spectral range | 900–1700 nm | 350–2500 nm |
| Resolution | 10 nm | - 3 @ 700 nm (Visible) - 10 @ 1400 nm (SWIR1) - 10 @ 2100 nm (SWIR2) |
| Current applications | - Agricultural monitoring - Food quality inspection - Pharmaceutical analysis - Recycling and material identification | - Mineral identification - Environmental analysis - Biological and agricultural research - Mosquito analysis |
| Average sampling time | 30–45 s/sample | 5–10 s/per sample |
| Average training time | 10 min | 30 min |
| Cost | USD 2695 | USD 60,000 |
| Advantages | - Easy to use - Portable - Ideal for in-field, rapid analysis - More affordable - Can be operated with a smartphone | - Broad spectral range - High signal-to-noise ratio - Versatile analysis modes - Sample scanning and prediction can be automated |
| Limitations | - Limited spectral range - Low signal-to-noise ratio - Scanning and prediction cannot be automated | - Less portable - Costly - Requires a laptop computer to operate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, A.; Flores, E.A.; Maciel-de-Freitas, R.; Kariyawasam, T.; Sikulu-Lord, M.T. Comparative Evaluation of Benchtop and Portable Near-Infrared Spectrometers for Predicting the Age and Blood Feeding History of Aedes aegypti. Insects 2025, 16, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111143
Takahashi A, Flores EA, Maciel-de-Freitas R, Kariyawasam T, Sikulu-Lord MT. Comparative Evaluation of Benchtop and Portable Near-Infrared Spectrometers for Predicting the Age and Blood Feeding History of Aedes aegypti. Insects. 2025; 16(11):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111143
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Ayako, Elvis Aquino Flores, Rafael Maciel-de-Freitas, Tharanga Kariyawasam, and Maggy T. Sikulu-Lord. 2025. "Comparative Evaluation of Benchtop and Portable Near-Infrared Spectrometers for Predicting the Age and Blood Feeding History of Aedes aegypti" Insects 16, no. 11: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111143
APA StyleTakahashi, A., Flores, E. A., Maciel-de-Freitas, R., Kariyawasam, T., & Sikulu-Lord, M. T. (2025). Comparative Evaluation of Benchtop and Portable Near-Infrared Spectrometers for Predicting the Age and Blood Feeding History of Aedes aegypti. Insects, 16(11), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111143







