Cryptic and Non-Cryptic Diversity in Cleptoparasitic Bees of the Genus Stelis Panzer, 1806, Subgenus Stelidomorpha Morawitz, 1875, with a Description of New Species from the Arabian Peninsula (Hymenoptera, Megachilidae) †
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Photography
2.2. DNA Analysis
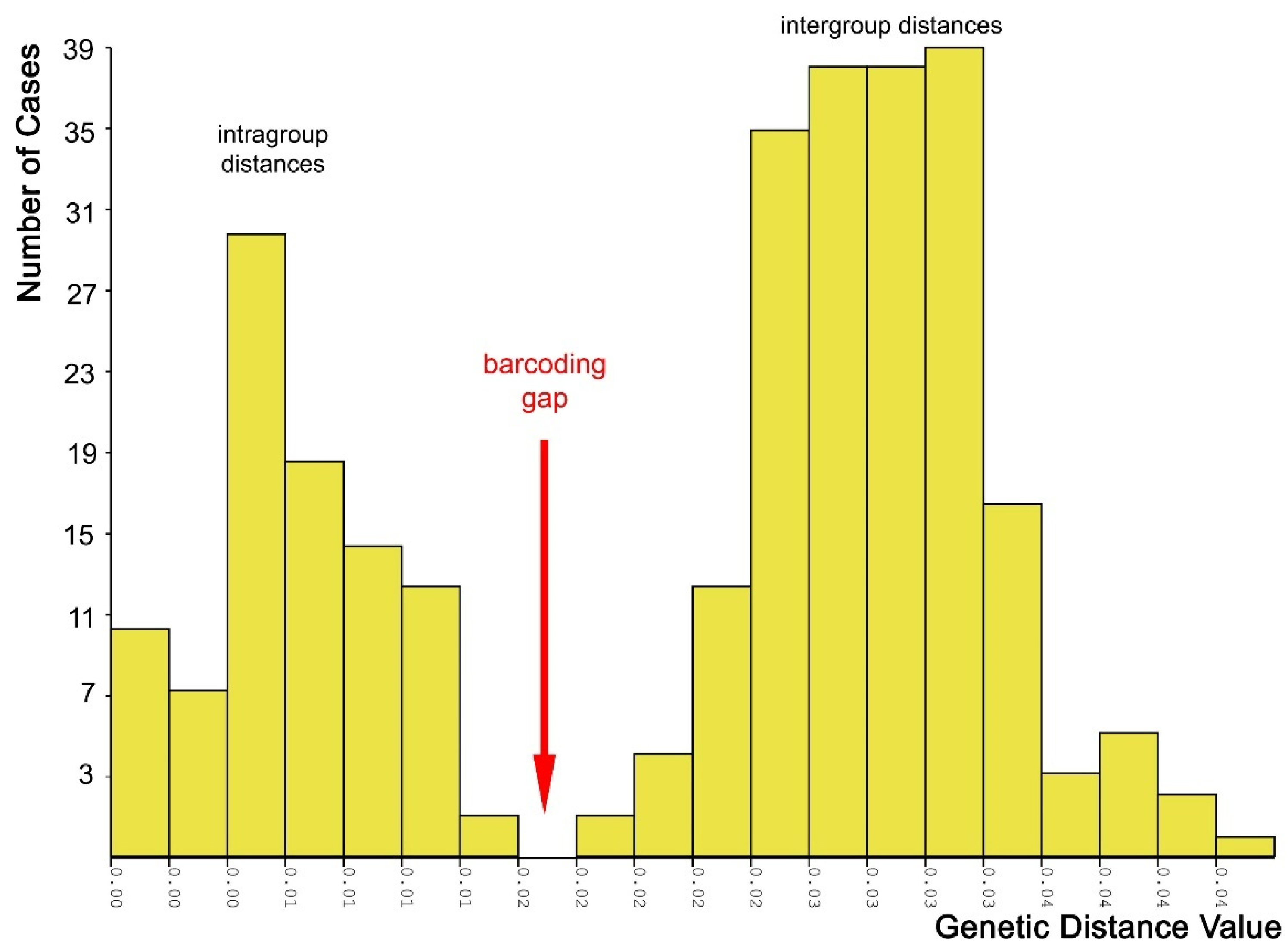
2.3. Molecular Species Delimitation
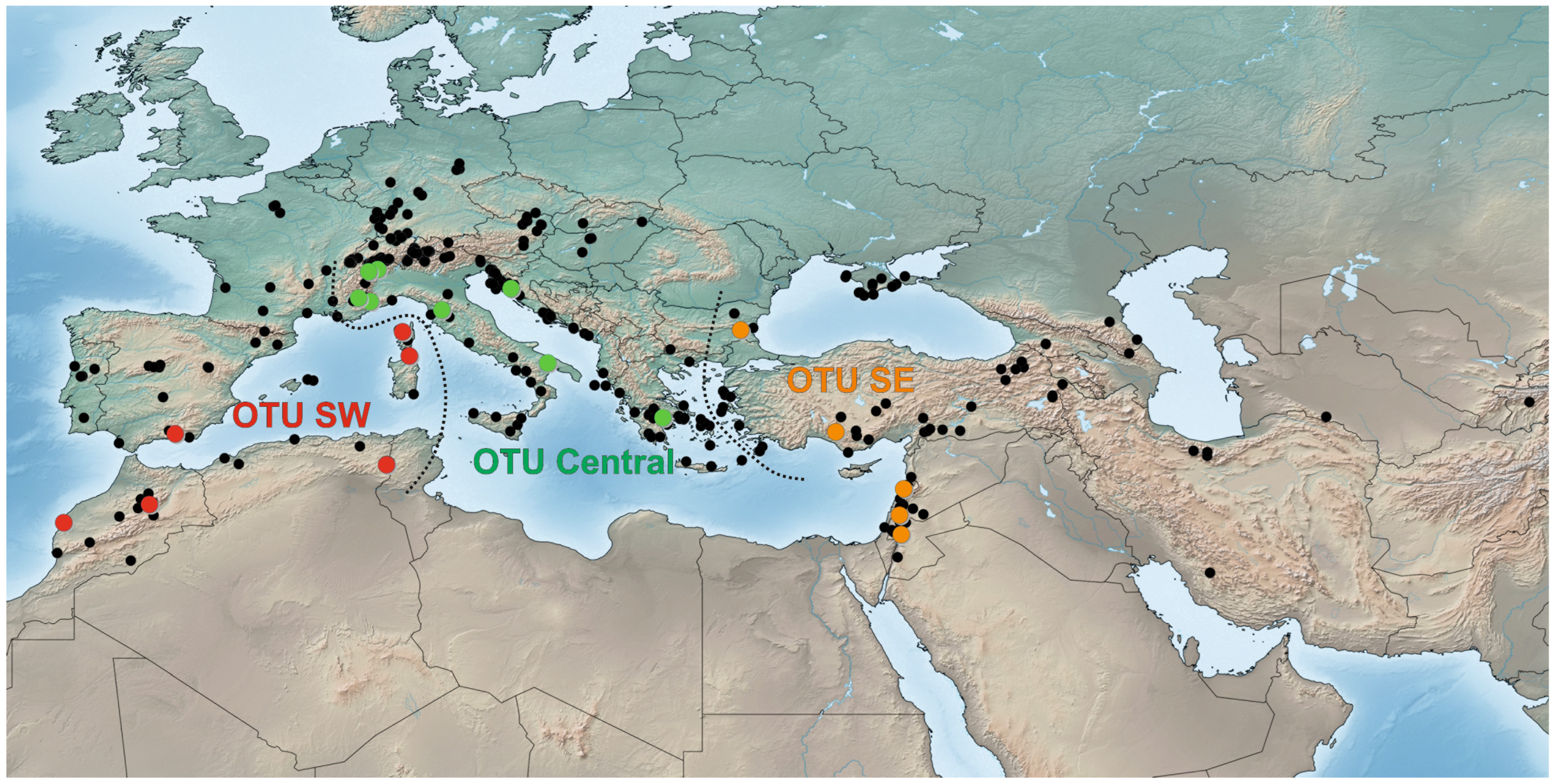
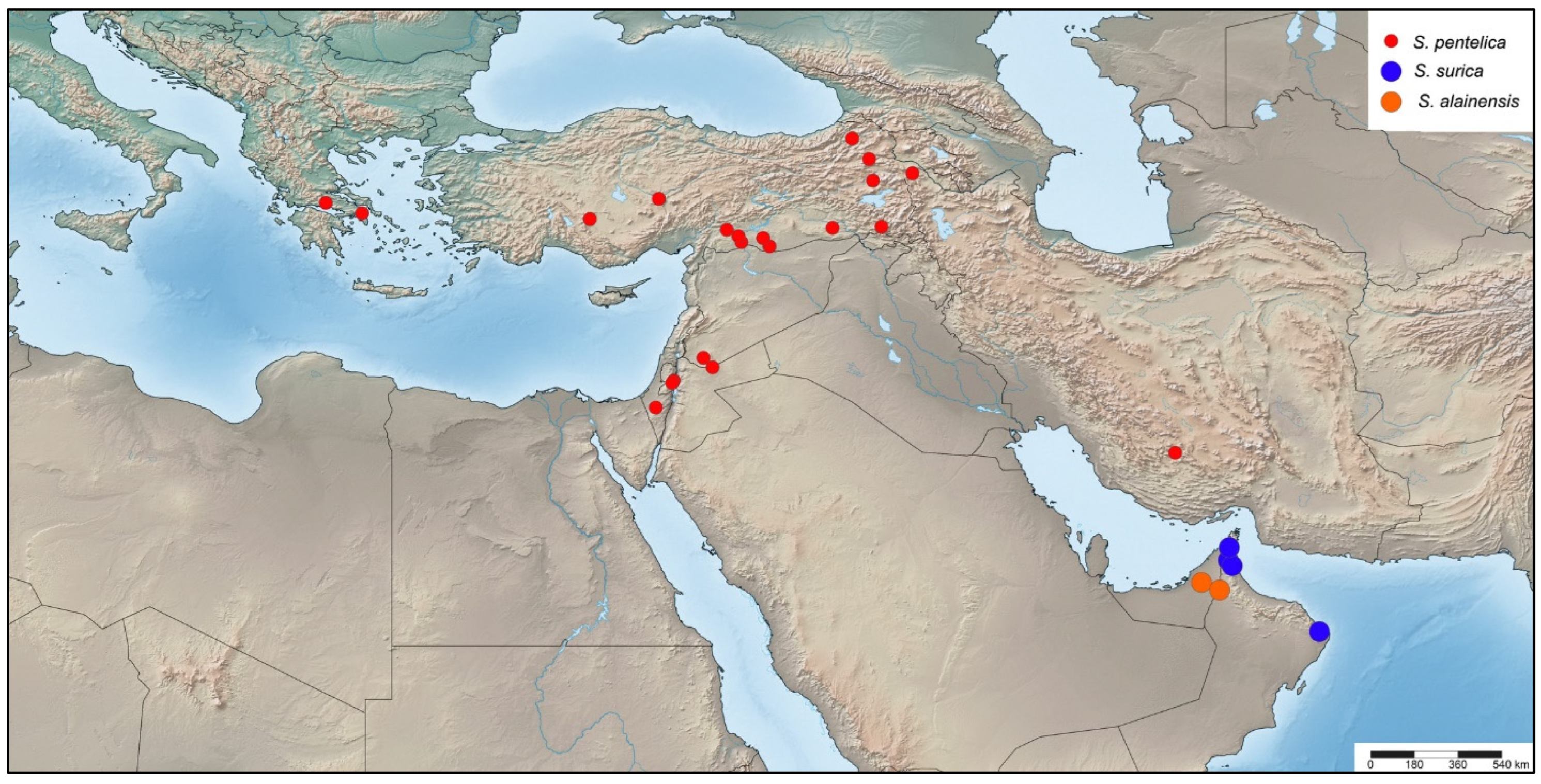
2.4. Distribution
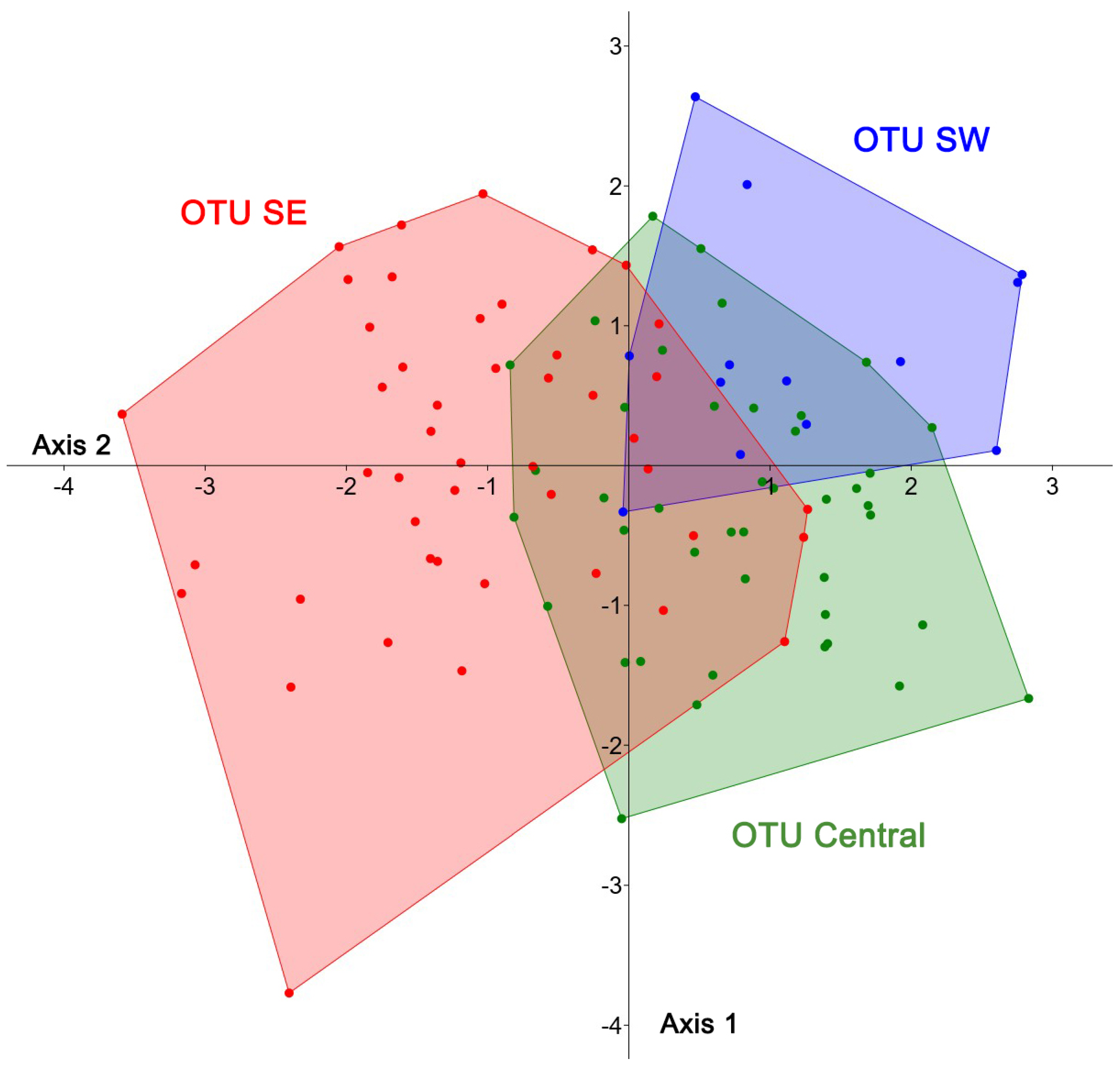
2.5. Morphometric Analysis
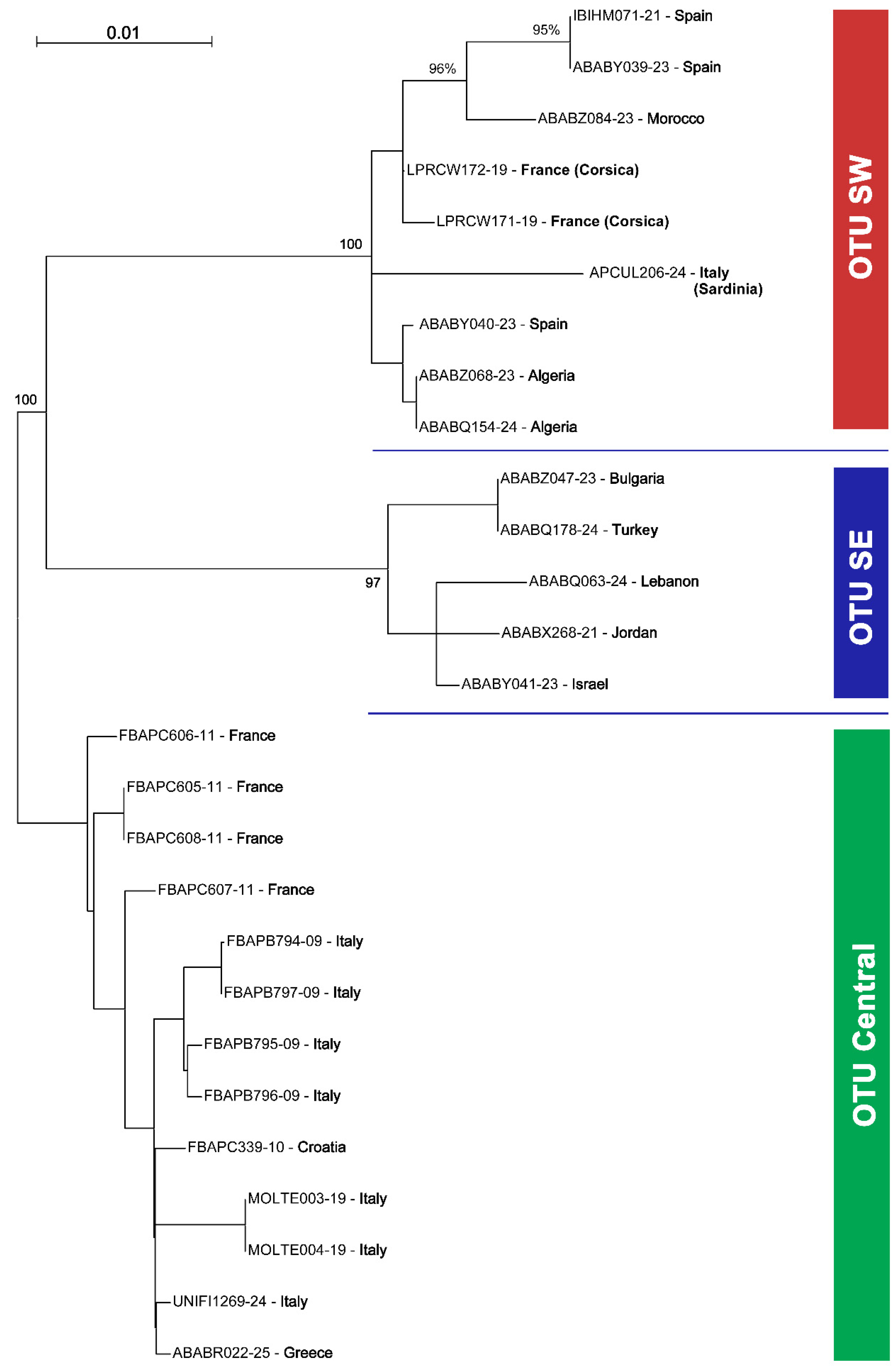
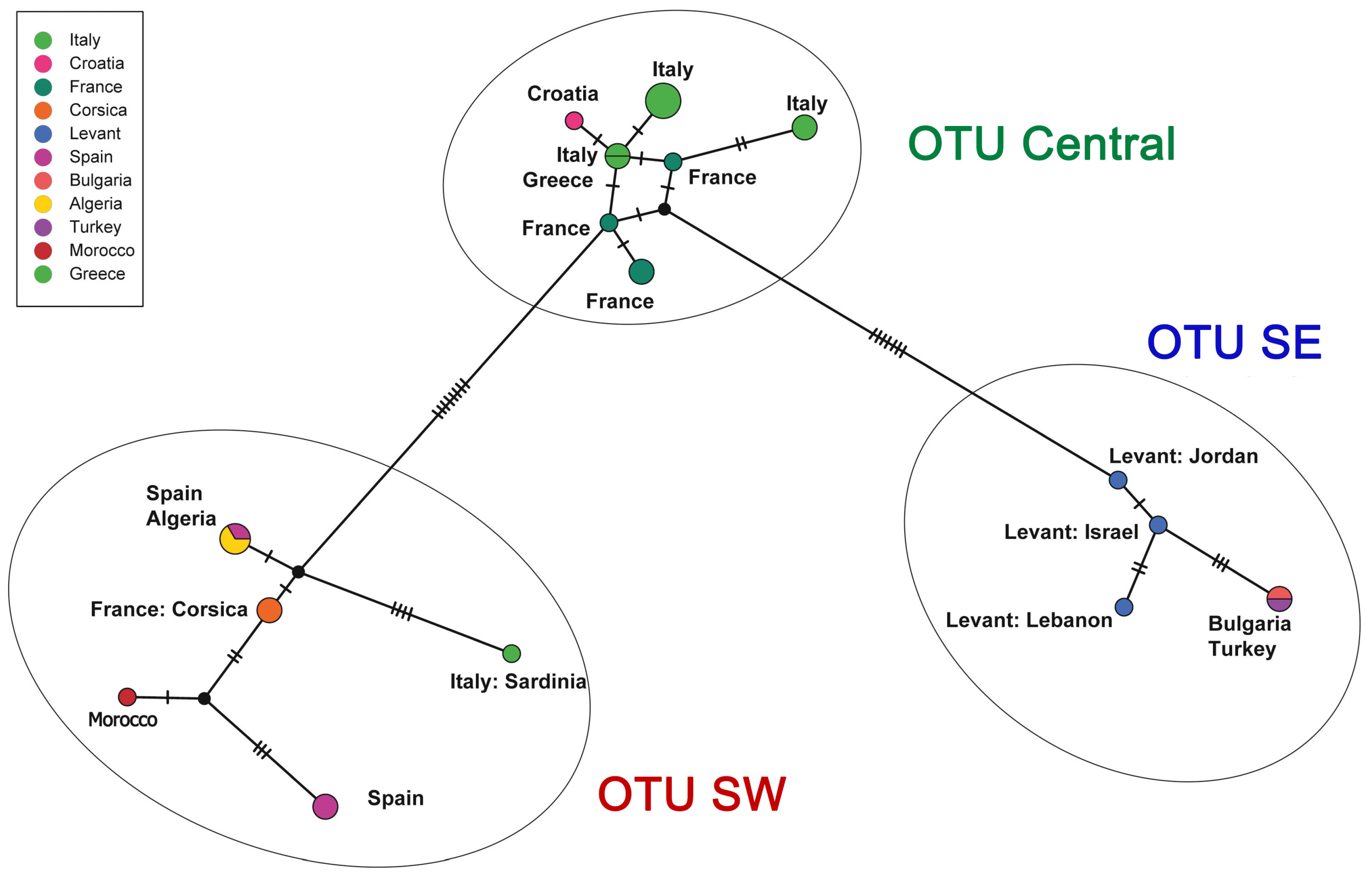
3. Results
- Stelis, Subgenus Stelidomorpha
- Stelis aegyptiaca (Radoszkowski, 1876)(Figure 1)
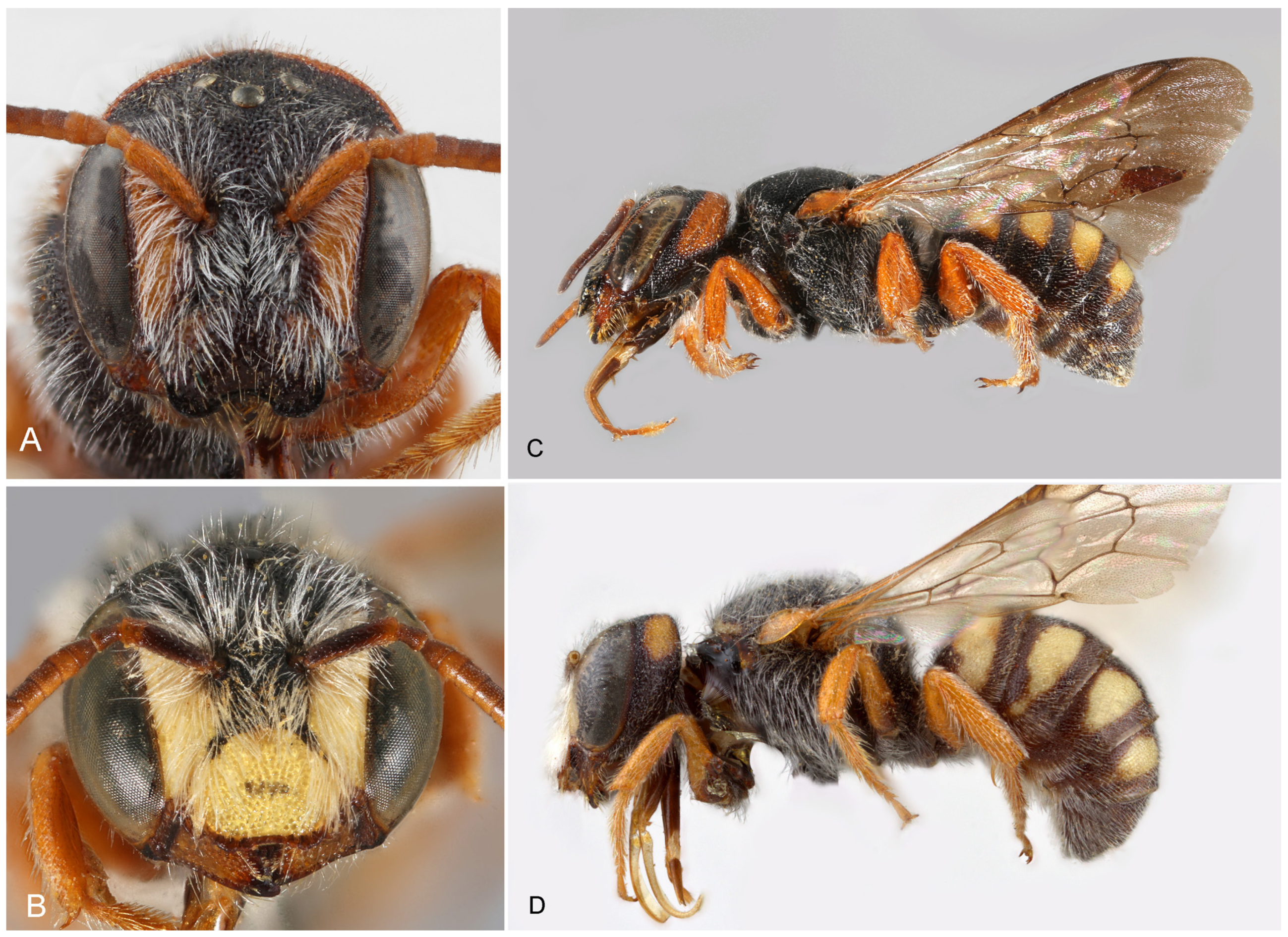



- Stelis alainensis Kasparek sp. nov.



- Stelis canaria Warncke, 1992 stat. nov.(Figure 9)

- Stelis nasuta (Latreille, 1809)

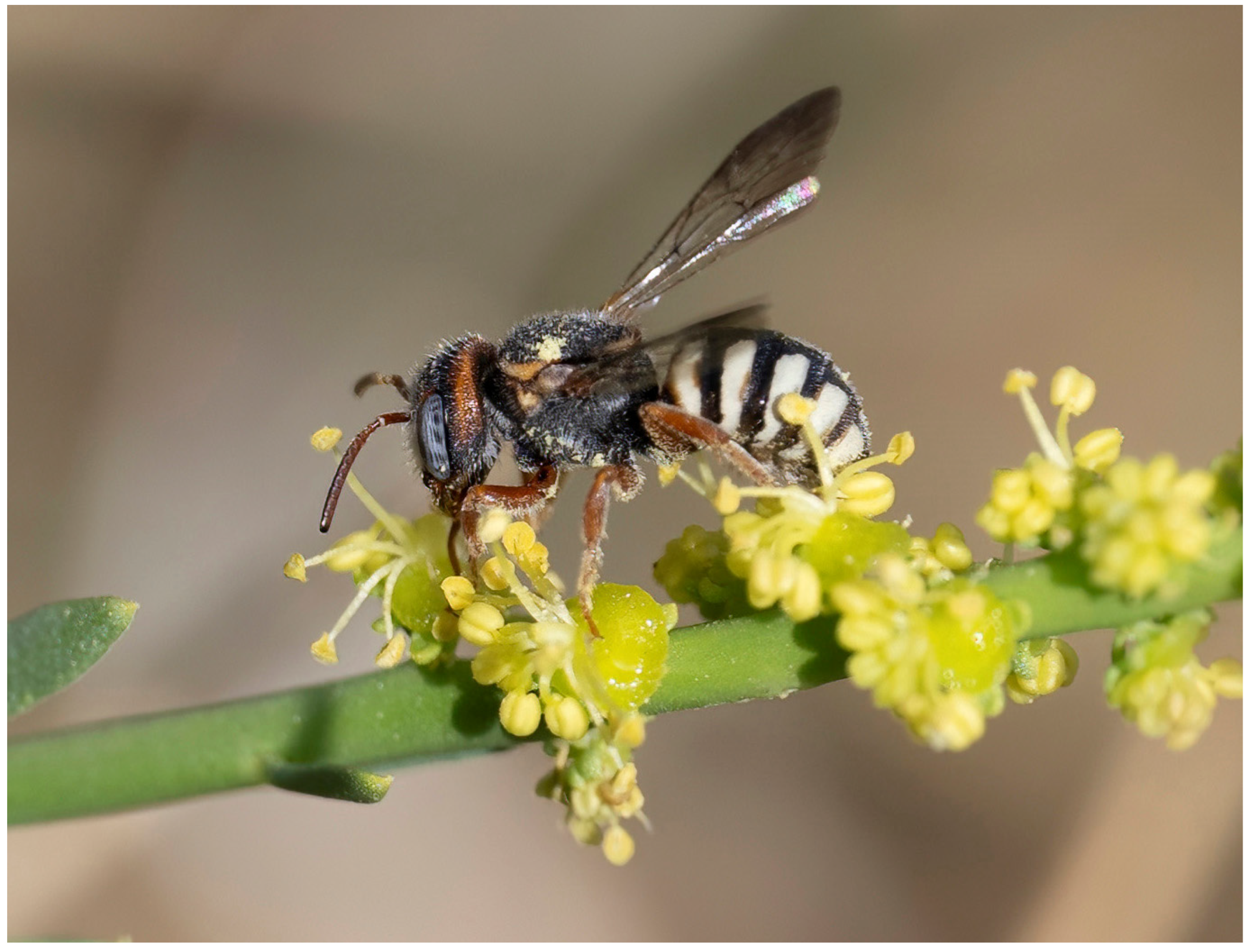
- Stelis pentelica Mavromoustakis, 1963
- Stelis pentelica Mavromoustakis, 1963.—Greece.
- Stelis bicornuta Pasteels, 1969.—Synonymy by Warncke (1992) [13].
- Stelis surica Kasparek sp. nov.


- Identification Key for the species of the subgenus Stelis (Stelidomorpha)
- Females
- 1
- Clypeus entirely black……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………2
- –
- Clypeus different.…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………4
- 2
- Antenna dark grey or black..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………S. nasuta
- –
- Antennal scape and underside of flagellomeres orange..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………3
- 3
- T1 with lateral bands not reaching the middle; tergal maculation yellow, occasionally bordered with reddish or brown tones at the edges.…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..S. aegyptiaca
- –
- T1 with uninterrupted tergal band; tergal maculation orange-red.……………………………………………………………………………S. canaria stat. nov.
- 4
- Clypeus dirty yellowish or orange-brown with black base and a broad black apical rim..……………………………………………………S. surica sp. nov.
- –
- Clypeus whitish or yellow with broad brown apical rim……………………………………………………………………………………………………………5
- 5
- Vertex short, 2.6–2.8x hind ocellus diameter……………………………………………………………………………………………………S. alainensis sp. nov.
- –
- Vertex long, 4.2–5.0x hind ocellus diameter..………………………………………………………………………………………………………………S. pentelica
- Males
- 1
- Antenna dark (dark grey, dark brown or black)..…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….2
- –
- Antenna predominantly orange or red-brown..………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………3
- 2
- Clypeus with fine, sometimes confluent punctures; pronotal lobe with anterior carina or low, indistinct lamella…………………………………S. nasuta
- –
- Clypeus with coarse punctation; pronotal lobe with high anterior lamella..……………………………………………………………………S. surica sp. nov.
- 3
- Scutellum and axillae in dorsal view V-shaped with emarginate apex…………………………………………………………………………………S. pentelica
- –
- Scutellum and axillae widely semicircular..…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..4
- 4
- T1 with uninterrupted orange-red band; metasomal terga with orange-red maculation..……………………………………………..…..S. canaria stat. nov.
- –
- T1 with lateral yellow or light orange bands; metasomal terga with yellow or whitish maculation..…………………………………………………………5
- 5
- Pale yellow lateral tergal bands on T1–T3 reaching the lateral margin at its contact with their corresponding sterna..………………S. alainensis sp. nov.
- –
- Pale yellow mediolateral bands on T1–T3 not reaching the lateral margin..……………………………………………………………………..…..S. aegyptiaca
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMK | Collection Max Kasparek, Heidelberg (Germany) |
| CSE | Collection Christian Schmid-Egger, Berlin (Germany) |
| DEI | Senckenberg Deutsches Entomologisches Institut, Müncheberg (Germany) |
References
- Michener, C.D. The Bees of the World, 2nd ed.; The John Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Litman, J.R.; Griswold, T.; Danforth, B.N. Phylogenetic systematics and a revised generic classification of anthidiine bees (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2016, 100, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, F.D.; Griswold, T. New species of the cleptoparasitic bee genus Stelis (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae, Anthidiini) from the Nearctic Region. Zootaxa 2013, 3646, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.B. On New Stelidine Bees from S.W. Asia and N.W. Africa, with a List of The Old-World Taxa Assigned to the Genus Stelis Panzer, 1806 (Hymenoptera, Apoidea, Megachilidae). Mitt. Mus. Naturkde. Berlin, Dtsch. Entomol. Z. 1999, 46, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasparek, M. The Cuckoo Bees of the Genus Stelis Panzer, 1806 in Europe, North Africa and the Middle East. A Review and Identification Guide. Entomofauna 2015, 18, 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Morawitz, F. Travel to Turkestan by the member-founder of the society A. P. Fedtschenko accomplished from the Imperial Society of Naturalists, Anthropologists, and Etnographists. Zoogeographical Investigations. Pt V., Division 7. Bees (Mellifera). Proc. Imp. Soc. Nat. Anthropol. Ethnogr. Moscow 1875, 1–160. [Google Scholar]
- Friese, H. Die Bienen Europa’s (Apidae Europaeae) Nach Ihren Gattungen, Arten und Varietäten auf Vergleichend Morphologisch-Biologischer Grundlage. Theil I. Schmarotzerbienen; Akad. Druck- und Verlagsanstalt: Innsbruck, Austria, 1895. [Google Scholar]
- Noskiewicz, J. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der paläarktischen Arten der Gattung Stelis Panz. (Hym., Apidae). Bull. Entomol. Pologne 1961, 31, 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- Radoszkowski, O. Compte-rendu des hyménopteres recueillis en Égypte et Abyssinie en 1873. [Fin]. Horae Soc. Entomol. Ross. 1876, 12, 117–150. [Google Scholar]
- Mavromoustakis, G.H. The Bees (Hymenoptera, Apoidea) of Attica (Greece). Part 3. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 13. Ser. 1962, 15, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Torre, C.G.d. Catalogus Hymenopterorum Hucusque Descriptorum Systematicus et Synonymicus. Volumen X. Apidae (Anthophila); Lipsiae: Leipzig, Germany, 1896. [Google Scholar]
- Pasteels, J.J. New Anthidiinae (Hymenoptera, Apoidea, Megachilidae) from the Mediterranean area and from the Near East. Isr. J. Entomol. 1969, 4, 409–434. [Google Scholar]
- Warncke, K. Die westpaläarktischen Arten der Bienengattung Stelis Panzer, 1806 (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Megachilinae). Entomofauna 1992, 13, 341–374. [Google Scholar]
- Friese, H. Neue Schmarotzerbienen (Palaearktisches Gebiet). Entomol. Nachr. 1899, 18, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Griswold, T.; Parker, F.D. Stelis rozeni, new species, the first record of the parasitic bee genus Stelis from southern Africa (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 2003, 76, 282–285. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Stoeckle, M.Y.; Zemlak, T.S.; Francis, C.M.M. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic barcode gap discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2021, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, A.; Ducasse, J.; Brouillet, S.; Flouri, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Kapli, P.; Knowles, L.L.; Kumari, S.; Stamatakis, A.; Sukumaran, J.; et al. SPART: A versatile and standardized data exchange format for species partition information. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2022, 22, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. A DNA-based registry for all animal species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility). GBIF Occurrence Download. Available online: https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.spswaw (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Shorthouse, D.P. SimpleMappr, an Online Tool to Produce Publication-Quality Point Maps; 2010. Available online: https://www.simplemappr.net (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Kasparek, M. Revision of the West Palaearctic Trachusa interrupta species complex (Apoidea: Anthidiini) with description of four new species. Zootaxa 2020, 4728, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasparek, M. Variation in Eoanthidium judaeense (Mavromoustakis, 1945) and E. clypeare (Morawitz, 1874) (Apoidea: Megachilidae: Anthidiini) in the Middle East: Semispecies or cases of geographic dimorphism? Zool. Middle East 2020, 66, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasparek, M. Taxonomic revision proves Trachusa pubescens (Morawitz, 1872) sensu lato to be a complex of allopatric and sympatric species in South-Eastern Europe and Western Asia (Hyme-noptera, Apoidea, Anthidiini). ZooKeys 2018, 764, 111–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Version 3.16. 2017. Palaeont. Electron. 2003, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tkalců, B. Sammelergebnisse der von RNDr. A. Hoffer geleiteten Algerien-Expeditionen in den Jahren 1971 u. 1972 (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). 1. Teil: Megachilidae. Acta Rerum Nat. Musei Natl. Slovaci Bratisl. 1975, 21, 165–190. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, E. Hymenoptera aculeata collected in Algeria by the Rev. A.E. Eaton, M.A., F.E.S., and the Rev. Francis David Morice, M.A., F.E.S. Trans. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1908, 56, 177–274. [Google Scholar]
- Aguib, S.; Louadi, K.; Schwarz, M. Le genre Stelis Panzer 1806 (Hymenoptera, Apoidea, Megachilidae) de l’Algérien avec une espèce nouvelle pour la fauna de ce pays. Entomofauna 2018, 35, 553–572. [Google Scholar]
- Grabener, S. Pollination Syndromes and Networks Along an Environmental Gradient in Southern Morocco. Master’s Thesis, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, J. Espèces Nouvelles de Mellifères de Barbarie (Diagnoses Préliminaires); G. Gounouihou: Bordeaux, France, 1895. [Google Scholar]
- Dathe, H.H. Order Hymenoptera, superfamily Apoidea. Families Colletidae, Andrenidae, Halictidae, Melittidae, Megachilidae and Apidae. Arthropod Fauna UAE 2009, 2, 335–432. [Google Scholar]
- Tkalců, B. Neue Taxa der Bienen von den Kanarischen Inseln. Mit Bemerkungen zu einigen bereits bekannten Arten (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Veröff. Übersee-Mus. Bremen (Naturwiss.) 1993, 12, 791–858. [Google Scholar]
- Latreille, P.A. Mémoire sur le genre l’Anthidie, Anthidium, de Fabricius classe des Insectes, ordre des Hyménoptères, famille des Apiaires. Ann. Mus. d’Hist. Nat. Paris 1809, 13, 24–53, 207–234. [Google Scholar]
- Proshchalykin, M.Y.; Fateryga, A.V. Annotated Catalogue of the Hymenoptera of Russia. Volume I. Symphyta and Apocrita: Aculeata. Proc. Zool. Inst. RAS 2017, 321 (Suppl. 6), 1–475. [Google Scholar]
- Maidl, F. Beiträge zur Hymenopterenfauna Dalmatiens, Montenegros und Albaniens. I. Teil: Aculeata und Chrysididae. Ann. Naturhistorischen Mus. Wien 1922, 35, 46–106. [Google Scholar]
- Scheuchl, E.; Willner, W. Taschenlexikon der Wildbienen Mitteleuropas. Alle Arten im Porträt; Quelle & Meyer: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Westrich, P. Die Wildbienen Deutschlands, 1st ed.; Ulmer: Stuttgart, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kasparek, M. The taxonomic identity of Anthidium fasciatellum Friese, 1917 (Hymenoptera: Apoidea: Anthidiini). J. Nat. History 2017, 51, 1743–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warncke, K. Beitrag zur Bienenfauna des Iran. 21. Die Gattung Stelis Pz. Boll. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Venezia 1985, 34, 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, S.; Schmid-Egger, C.; Morinière, J.; Haszprunar, G.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding largely supports 250 years of classical taxonomy: Identifications for Central European bees (Hymenoptera, Apoidea partim). Mol. Ecol. Res. 2015, 15, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecocq, T.; Brasero, N.; De Meulemeester, T.; Michez, D.; Dellicour, S.; Lhomme, P.; de Jonghe, R.; Valterová, I.; Urbanová, K.; Rasmont, P. An integrative taxonomic approach to assess the status of Corsican bumblebees: Implications for conservation. Anim. Conserv. 2015, 18, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, A.; Devallez, J.; Sonet, G.; Nagy, Z.T.; Boevé, J.-L. DNA barcoding and male genital morphology reveal five new cryptic species in the West Palearctic bee Seladonia smaragdula (Vachal, 1895) (Hymenoptera: Apoidea: Halictidae). Zootaxa 2015, 4034, 257–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praz, C.; Müller, A.; Genoud, D. Hidden diversity in European bees: Andrena amieti sp. n., a new Alpine bee species related to Andrena bicolor (Fabricius, 1775) (Hymenoptera, Apoidea, Andrenidae). Alp. Entomol. 2019, 3, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praz, C.; Genoud, D.; Vaucher, K.; Bénon, D.; Monks, J.; Wood, T.J. Unexpected levels of cryptic diversity in European bees of the genus Andrena subgenus Taeniandrena (Hymenoptera, Andrenidae): Implications for conservation. J. Hymen. Res. 2022, 91, 375–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.N.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4812–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struck, T.H.; Feder, J.L.; Bendiksby, M.; Birkeland, S.; Cerca, J.; Gusarov, V.I.; Kistenich, S.; Larsson, K.H.; Liow, L.H.; Nowak, M.D.; et al. Cryptic species—More than terminological chaos: A reply to Heethoff. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heethoff, M. Cryptic species—Conceptual or terminological chaos? A response to Struck et al. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jörger, K.M.; Schrödl, M. How to describe a cryptic species? Practical challenges of molecular taxonomy. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunova, T.; Picton, B.; Furfaro, G.; Mariottini, P.; Pontes, M.; Prkić, J.; Fletcher, K.; Malmberg, K.; Lundin, K.; Martynov, A. Multilevel fine-scale diversity challenges the ‘cryptic species’ concept. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.P.; Allmon, W.D. How we study cryptic species and their biological implications: A case study from marine shelled gastropods. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Hernández, N.; Oromí, P.; Arnedo, M.A. Integrative taxonomy uncovers hidden species diversity in woodlouse hunter spiders (Araneae, Dysderidae) endemic to the Macaronesian archipelagos. Syst. Biodivers. 2010, 8, 531–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Raso, J.E.; d’Udekem d’Acoz, C.; Moukrim, A.; Schubart, C.D.; Cuesta, J.A. A new cryptic species of Polybiidae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Portunoidea) from the East Atlantic, with considerations on the genus Polybius. Eur. J. Taxon. 2024, 930, 277–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagaja, M.; Staniec, B. Thiasophila szujeckii sp. n. (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae, Aleocharinae)—A cryptic species associated with Formica truncorum in Poland. Zootaxa 2015, 3955, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisbain, G.; Michez, D.; Rosa, P.; Ferreira, S.; Wood, T.J. Unexpected discovery of a near cryptic Dasypoda species in southern Spain (Hymenoptera: Melittidae). Osmia 2023, 11, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.G.; Evans, K.M. The species concept and cryptic diversity. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2008; Moestrup, Ø., Ed.; UNESCO: København, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Eldredge, N.; Cracraft, J. Phylogenetic Patterns and the Evolutionary Process; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, G.; Platnick, N.I. Systematics and Biogeography: Cladistics and Vicariance; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Emerson, B.C. Delimiting species–prospects and challenges for DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2025, 34, e17677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, M.J.; Baker, A.; McCluskey, K.; Smith, A.; Naik, S.; Ratnasingham, S.; Manjunath, R.; Perez, K.; Sones, J.; D’Souza, M.; et al. Addendum to a minimalist revision of Costa Rican Braconidae: 28 new species and 23 host records. ZooKeys 2021, 1075, 77–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brower, Z. Alleviating the taxonomic impediment of DNA barcoding and setting a bad precedent: Names for ten species of ‘Astraptes fulgerator’ (Lepidoptera: Hesperiidae: Eudaminae) with DNA-based diagnoses. Syst. Biodiv. 2010, 8, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Fric, Z.F.; Gante, H.F.; Hopkins, T.; Orfinger, A.B.; Scherz, M.D.; Scherz, M.D.; Sucháčková Bartŏnová, A.; Dal Pos, D. DNA barcodes on their own are not enough to describe a species. Syst. Entomol. 2022, 47, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Vaamonde, C.; Kirichenko, N.; Cama, A.; Doorenweerd, C.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Guiguet, A.; Gomboc, S.; Huemer, P.; Landry, J.-F.; Laštůvka, A.; et al. Evaluating DNA barcoding for species identification and discovery in European gracillariid moths. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 626752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, B.C.; Pellerier, T.A.; Reid, N.M.; Satler, J.D. How to fail at species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4369–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial, J.M.; Miralles, A.; De la Riva, I.; Vences, M. The integrative future of taxonomy. Front. Zool. 2010, 7, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbig, A.J.; Knox, A.G.; Parkin, D.T.; Sangster, G.; Collinson, M. Guidelines for assigning species rank. Ibis 2002, 144, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasparek, M. Discrepant results obtained from phenotypic classification and genetic barcoding: A case study of the anthidiine bee Anthidium dalmaticum (Megachilidae: Anthidiini). Zoosystema 2025, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasparek, M.; Boustani, M. DNA sequencing and multivariate morphometric analysis help unveil cryptic diversity in the Mediterranean wool carder bee identified as Anthidium undulatum Dours, 1873 (Apoidea: Megachilidae: Anthidiini). Arthropod Syst. Phylogeny 2025, 83, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.J.; Leclercq, V.; Schmid-Egger, C.; Praz, C. A contribution to the taxonomy of the genus Thyreus Panzer in the West and Central Palaearctic (Hymenoptera: Apidae), with two new species and key to European species. Zootaxa, 2025; in print. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, Y.; Oberprieler, R.G. An integrative taxonomic and phylogenetic approach reveals a new genus of Australasian Cycas-pollinating weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Cossoninae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2024, 202, zlad190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, U.G.S.L.; Eberle, J.; Thormann, J.; Bohacz, C.; Benjamin, S.P.; Ahrens, D. Multiple species delimitation approaches with COI barcodes poorly fit each other and morphospecies—An integrative taxonomy case of Sri Lankan Sericini chafers (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, e8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuataz, L.; Reding, J.-P.; Reding, A.; Roesti, C.; Stoffel, C.; Vinçon, G.; Gattolliat, J.-L. A comprehensive DNA barcoding reference database for Plecoptera of Switzerland. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, N.; Phillips, J.D.; Hanner, R.H. Delimiting species with single-locus DNA sequences. In DNA Barcoding. Methods in Molecular Biology; DeSalle, R., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellicour, S.; Flot, J.F. The hitchhiker’s guide to single-locus species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2018, 18, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, H.; Leuenberger, C. Analysis of ratios in multivariate morphometry. Syst. Biol. 2011, 60, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friese, H. Die Schmarotzerbienen und ihre Wirthe. Zool. Jahrb. Abt. Syst. Geogr. Biol. Tiere 1888, 3, 847–870. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, H. Die Hymenopteren des Nordostalpengebietes und seines Vorlandes. I. Teil. Denkschr. Österr. Akad. Wiss. Mathemat.-naturwiss. Kl. 1982, 124, 5–370. [Google Scholar]
- Amiet, F.; Herrmann, M.; Müller, A.; Neumeyer, R. Apidae 4: Anthidium, Chelostoma, Coelioxys, Dioxys, Heriades, Lithurgus, Megachile, Osmia, Stelis. In Fauna Helvetica; Centre Suisse de Cartographie de la Faune (CSCF) & Schweizerische Entomologische Gesellschaft (SEG): Neuchâtel, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]

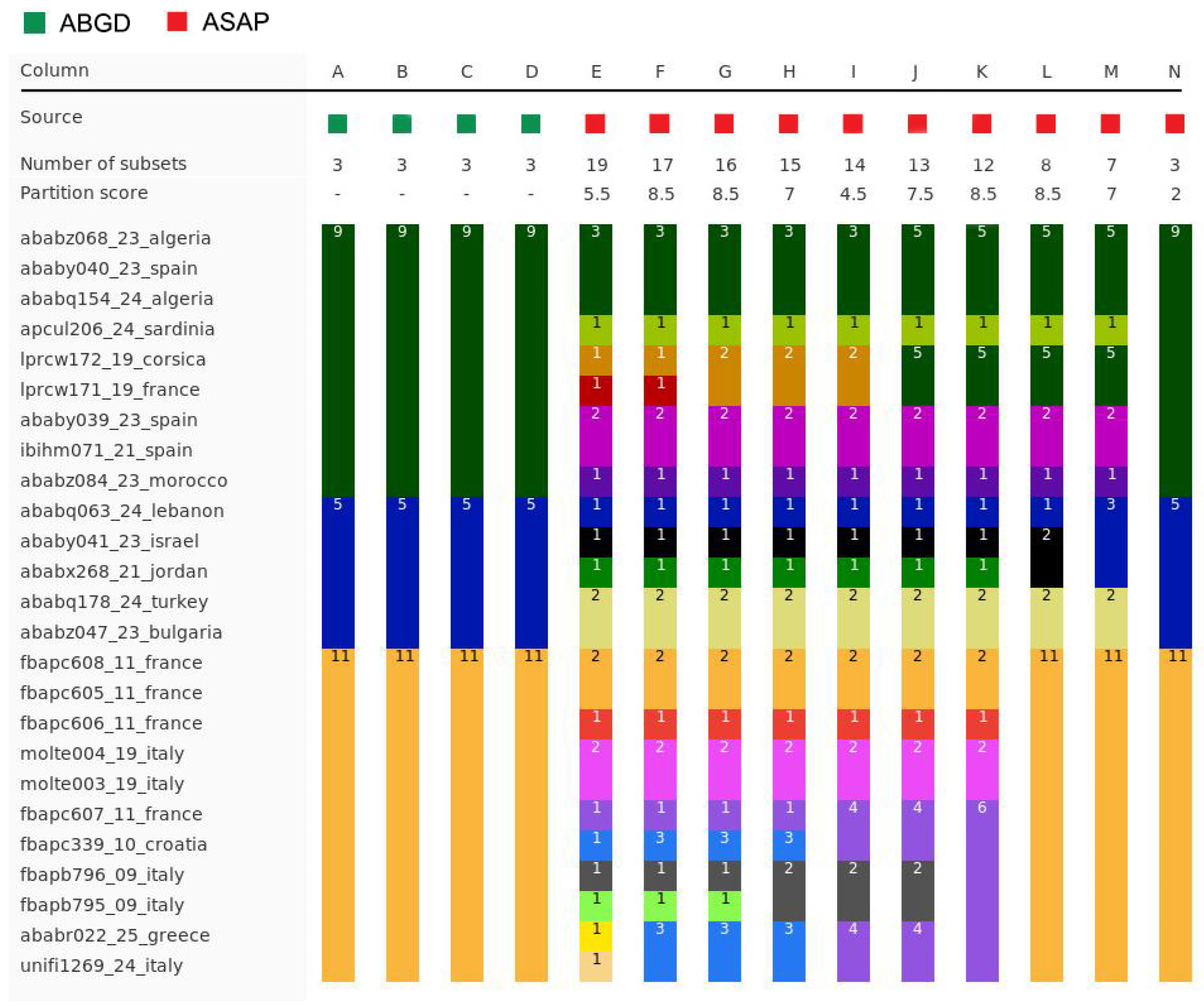
| Region | BIN | BOLD Specimen Page | Country | Year | Collector | bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 02269 | Italy | 1995 | C. Schmid-Egger | 426 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 02270 | Italy | 1995 | C. Schmid-Egger | 620 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 02271 | Italy | 1995 | C. Schmid-Egger | 620 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 02272 | Italy | 1995 | C. Schmid-Egger | 425 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 05944 | Croatia | 2004 | E. Scheuchl | 657 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 07065 | France | 2010 | C. Schmid-Egger | 658 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 07066 | France | 2010 | C. Schmid-Egger | 658 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 07067 | France | 2010 | C. Schmid-Egger | 658 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | BC ZSM HYM 07068 | France | 2010 | C. Schmid-Egger | 631 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | PAR_167 | Italy | 2019 | F. R. Dani | 658 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | PAR_168 | Italy | 2019 | F. R. Dani | 658 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | UNIFI1269-24 | Italy | 2024 | M. Bonifacino | 658 |
| Central | BOLD:AAO3679 | MK-seg421 | Greece | 2016 | C. Schmid-Egger | 658 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | BC-LPRCorse1976 | France: Corsica | 2019 | R. Le Divelec | 653 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | BC-LPRCorse1977 | France: Corsica | 2019 | R. Le Divelec | 653 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | INV12000 | Spain | 2021 | T. J. Wood | 659 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | MK-tjw226 | Spain | 2021 | T. J. Wood | 627 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | MK-tjw335 | Spain | 2022 | T. J. Wood | 632 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | MK-nou153 | Algeria | 2023 | N. Benarfa | 569 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | MK-nou190 | Algeria | 2023 | N. Benarfa | 610 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | MK-mons728 | Morocco | 2023 | A. Sentil | 633 |
| SW | BOLD:AEC4732 | GIU43_APCUL | Italy (Sardinia) | 2023 | M. Annessi/A. Di Giulio | 619 |
| SE | BOLD:ABW1388 | MK-whl007 | Jordan | 2016 | J. Gebert | 599 |
| SE | BOLD:ABW1388 | MK-oll0848 | Israel | 2019 | M. Halada | 631 |
| SE | BOLD:ABW1388 | MK-mk1237 | Bulgaria | 2022 | Z. Haladova | 634 |
| SE | BOLD:ABW1388 | MK-tuz041 | Lebanon | 2023 | V. Soon | 658 |
| SE | BOLD:ABW1388 | MK-mk1654 | Turkey | 2024 | M. Kasparek/O. Özgül | 627 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasparek, M.; Schmid-Egger, C.; Roberts, H. Cryptic and Non-Cryptic Diversity in Cleptoparasitic Bees of the Genus Stelis Panzer, 1806, Subgenus Stelidomorpha Morawitz, 1875, with a Description of New Species from the Arabian Peninsula (Hymenoptera, Megachilidae). Insects 2025, 16, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101030
Kasparek M, Schmid-Egger C, Roberts H. Cryptic and Non-Cryptic Diversity in Cleptoparasitic Bees of the Genus Stelis Panzer, 1806, Subgenus Stelidomorpha Morawitz, 1875, with a Description of New Species from the Arabian Peninsula (Hymenoptera, Megachilidae). Insects. 2025; 16(10):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101030
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasparek, Max, Christian Schmid-Egger, and Huw Roberts. 2025. "Cryptic and Non-Cryptic Diversity in Cleptoparasitic Bees of the Genus Stelis Panzer, 1806, Subgenus Stelidomorpha Morawitz, 1875, with a Description of New Species from the Arabian Peninsula (Hymenoptera, Megachilidae)" Insects 16, no. 10: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101030
APA StyleKasparek, M., Schmid-Egger, C., & Roberts, H. (2025). Cryptic and Non-Cryptic Diversity in Cleptoparasitic Bees of the Genus Stelis Panzer, 1806, Subgenus Stelidomorpha Morawitz, 1875, with a Description of New Species from the Arabian Peninsula (Hymenoptera, Megachilidae). Insects, 16(10), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101030





