Ensemble Distribution Modeling of the Globally Invasive Asian Cycad Scale, Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi, 1977 (Hemiptera: Diaspididae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Occurrence Records
2.2. Data Sources and Processing of Environmental Data
2.3. Ensemble Algorithms, Pseudoabsences, and Covariate Selection
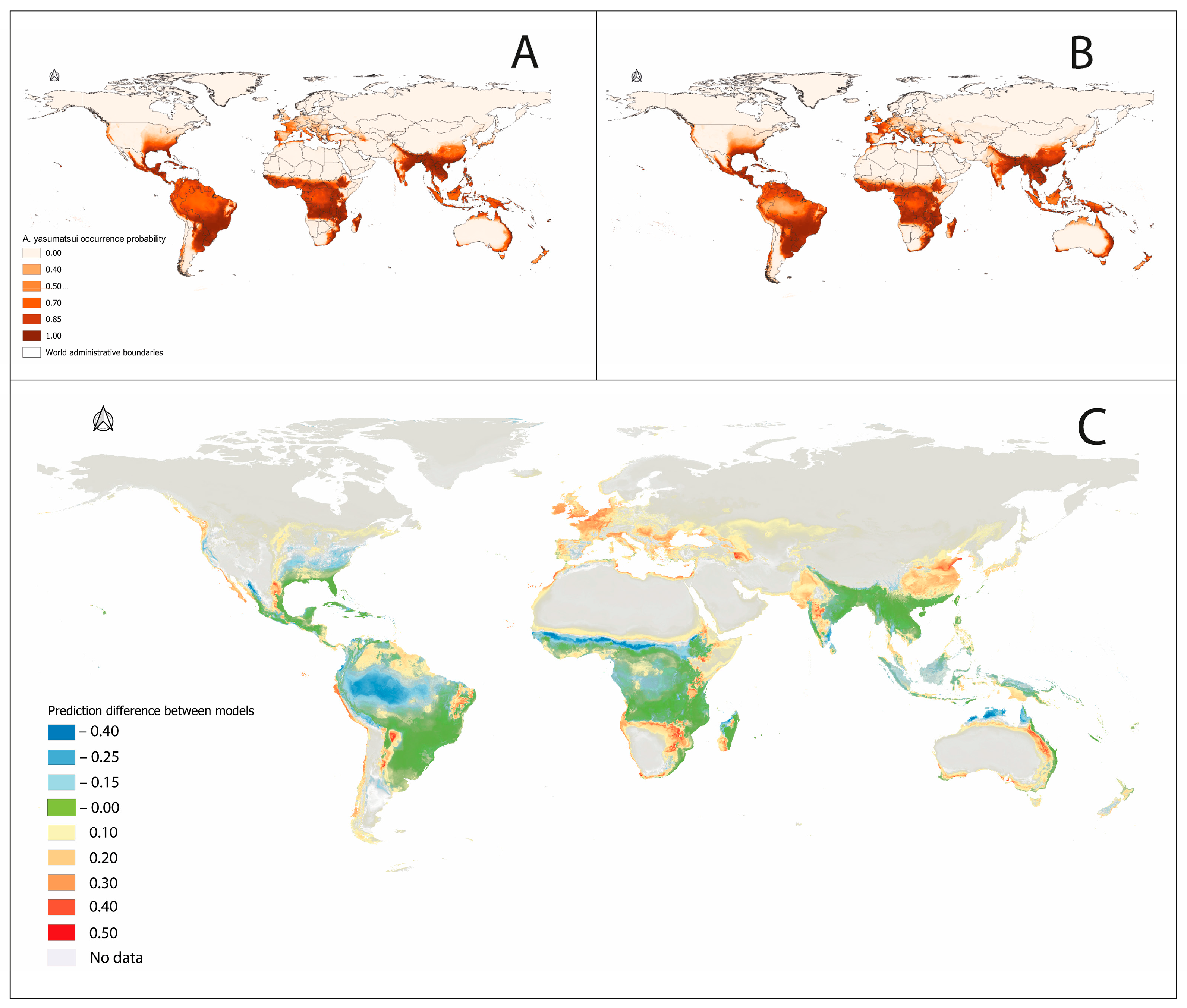
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruchin, A.B.; Esin, M.N.; Nikolaeva, A.M.; Aleksanov, V.V.; Tomkovich, K.P. Invading the North: Dispersal of Nearctic Treehopper Stictocephala bisonia (Hemiptera: Cicadomorpha: Membracidae) in European Russia. Period. Biol. 2024, 125, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venette, R.C.; Ragsdale, D.W. Assessing the Invasion by Soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae): Where Will It End? Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2004, 97, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissling, T.J.; Howard, F.W.; Hamon, A.B. Cycad Aulacaspis Scale, Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi (Insecta: Homoptera: Sternorrhyncha: Diaspididae); University of Florida Cooperative Extension Service, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, EDIS: Tampa, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S. A new species of Aulacaspis associated with a cycad in Thailand (Homoptera: Cocoidea). Insecta Matsumurana New Ser. 1977, 11, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Halbert, S.E. Entomology section. Triology 1998, 37, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, F.W.; Hamon, A.; Mclaughlin, M.; Weissling, T.; Yang, S.L. Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha: Diaspididae), a Scale Insect Pest of Cycads Recently Introduced into Florida. Fla. Entomol. 1999, 82, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, K.L.; Gullan, P.J.; Craven, P.; Wright, G.T.; Cook, L.G. Cycad Killer, Qu’est-Ce Que c’est? Dieback of Macrozamia Communis on the South Coast of New South Wales. Aust. J. Bot. 2021, 69, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marler, T.E.; Lindström, A.J.; Watson, G.W. Aulacaspis yasumatsui Delivers a Blow to International Cycad Horticulture. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normark, B.B.; Normark, R.D.; Vovides, A.; Solís-Montero, L.; González-Gómez, R.; Pulido-Silva, M.T.; Escobar-Castellanos, M.A.; Dominguez, M.; Perez-Farrera, M.A.; Janda, M.; et al. Cycad Aulacaspis Scale (Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi, 1977) in Mexico and Guatemala: A Threat to Native Cycads. Bioinvasions Rec. 2017, 6, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-gómez, M.; Chang-pérez, R.; Jiménez-puello, J.; Santos-mugas, A. Knowledge of Cycad Aulacaspis Scale (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) in Panama. BioInvasions Rec. 2021, 10, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gómez, R.; Riverón-Giró, F.B.; García-González, A.; Martínez-Rosas, R.; Solís-Montero, L. First Report of Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) in Mexico. Fla. Entomol. 2016, 99, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.A.; Dooley, J.W. Potential Invasive Species of Scale Insects for the USA and Caribbean Basin. In Potential Invasive Pests Agricultural Crops; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2013; pp. 320–341. [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenteren, J.C.; Colmenarez, Y.C. Biological Control in Barbados. In Biological Control in Latin America and the Caribbean: Its Rich History and Bright Future; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020; pp. 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CABI; EPPO. Aulacaspis yasumatsui. [Distribution Map]; Centre for Agricultural Bioscience International: Oxfordshire, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Metzler, H.; Zúñiga Orozco, A. Manejo de Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) Mediante El Uso de Jabones Comerciales En Costa Rica. Rev. Sedes Reg. 2012, 25, 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gelabert, D. The Invasive Armored Scale Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi (Hemiptera: Coccoidea: Diaspididae) in the Dominican Republic. Proc. Èntomol. Soc. Wash. 2019, 121, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.; Chang, N.T.; Lai, P.Y.; Hsu, T.C. Life Table of Cycad Scale, Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Hemiptera: Diaspididae), Reared on Cycas in Taiwan. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2010, 13, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniapan, R.; Shepard, M.; Carner, G.; Aun-Chuan Ooi, P. Arthropod Pests of Horticultural Crops in Tropical Asia; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Trencheva, K.; Trenchev, G.; Tomov, R.; Wu, S.-A. Non-Indigenous Scale Insects on Ornamental Plants in Bulgaria and China: A Survey. Entomol. Hell. 2010, 19, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ülgentürk, S. Cycas Palmiyelerinin Kaçak Yolcusu; Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) An Unwanted Passenger on Cycas Palm; Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi Materyal ve Yöntem Sonuçlar ve Tartışma. Türk. Entomoloji Bül. 2015, 5, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozár, F.; Konczné Benedicty, Z.; Fetykó, K.; Kiss, B.; Szita, É. An Annotated Update of the Scale Insect Checklist of Hungary (Hemiptera, Coccoidea). Zookeys 2013, 309, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, J.F.; Hodges, G.S. First Report of Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) in Africa (Ivory Coast), and Update on Distribution. Fla. Entomol. 2007, 90, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, S.O.N.; Baraka, R.E.; Tobin-West, M.D.; Okwukwu, E. Cycad Aulacaspis Scale (Cas) Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi As A Major Pest of Sago Palm Cycas spp. in Nigeria. Int. J. Entomol. Nematol. Res. 2021, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Nesamari, R.; Millar, I.M.; Coutinho, T.A.; Roux, J. South African Cycads at Risk: Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Hemiptera: Coccoidea: Diaspididae) in South Africa. Afr. Entomol. 2015, 23, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.B.; Luoto, M. The Importance of Biotic Interactions for Modelling Species Distributions under Climate Change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Thuiller, W. Predicting Species Distribution: Offering More than Simple Habitat Models. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 993–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurado, P.; Araújo, M.B. An Evaluation of Methods for Modelling Species Distributions. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; White, M.; Newell, G. Measuring and Comparing the Accuracy of Species Distribution Models with Presence-Absence Data. Ecography 2011, 34, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Yaw, J.A.; McCune, J.L.; Pironon, S.; Sheth, S.N. Species Distribution Models Rarely Predict the Biology of Real Populations. Ecography 2022, 2022, e05877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagel, J.; Treurnicht, M.; Bond, W.J.; Kraaij, T.; Nottebrock, H.; Schutte-Vlok, A.L.; Tonnabel, J.; Esler, K.J.; Schurr, F.M. Mismatches between Demographic Niches and Geographic Distributions Are Strongest in Poorly Dispersed and Highly Persistent Plant Species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3663–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Gutiérrez, J.; Carvalheiro, L.G.; Polce, C.; van Loon, E.E.; Raes, N.; Reemer, M.; Biesmeijer, J.C. Fit-for-Purpose: Species Distribution Model Performance Depends on Evaluation Criteria—Dutch Hoverflies as a Case Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.P.; Lew, D.; Peterson, A.T. Evaluating Predictive Models of Species’ Distributions: Criteria for Selecting Optimal Models. Ecol. Modell. 2003, 162, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konowalik, K.; Nosol, A. Evaluation Metrics and Validation of Presence-Only Species Distribution Models Based on Distributional Maps with Varying Coverage. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanle Satishchandra, N.; Geerts, S. Modeling the Distribution of the Invasive Alien Cycad Aulacaspis Scale in Africa under Current and Future Climate Scenarios. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, H. Predicting the Potential Distributions of the Invasive Cycad Scale Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) under Different Climate Change Scenarios and the Implications for Management. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, A.H.; Bell, J.F. A Review of Methods for the Assessment of Prediction Errors in Conservation Presence/Absence Models. Environ. Conserv. 1997, 24, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yackulic, C.B.; Chandler, R.; Zipkin, E.F.; Royle, J.A.; Nichols, J.D.; Campbell Grant, E.H.; Veran, S. Presence-Only Modelling Using MAXENT: When Can We Trust the Inferences? Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiner, F.T.; Guisan, A.; Bergamini, A.; Nobis, M.P. Overcoming Limitations of Modelling Rare Species by Using Ensembles of Small Models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y. Applying Various Algorithms for Species Distribution Modelling. Integr. Zool. 2013, 8, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampomah, E.K.; Qin, Z.; Nyame, G. Evaluation of Tree-Based Ensemble Machine Learning Models in Predicting Stock Price Direction of Movement. Information 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello-Lammens, M.E.; Boria, R.A.; Radosavljevic, A.; Vilela, B.; Anderson, R.P. SpThin: An R Package for Spatial Thinning of Species Occurrence Records for Use in Ecological Niche Models. Ecography 2015, 38, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Tokman, D.; Córdoba-Aguilar, A.; Dáttilo, W.; Lira-Noriega, A.; Sánchez-Guillén, R.A.; Villalobos, F. Insect Responses to Heat: Physiological Mechanisms, Evolution and Ecological Implications in a Warming World. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-Km Spatial Resolution Climate Surfaces for Global Land Areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.C. Google Earth as a (Not Just) Geography Education Tool. J. Geogr. 2007, 106, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Earth Engine Data Catalog. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Abatzoglou, J.T. Development of Gridded Surface Meteorological Data for Ecological Applications and Modelling. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Csiszar, I.; Eidenshink, J.; Myneni, R.; Baret, F.; Masuoka, E.; Wolfe, R.; Claverie, M. NOAA Climate Data Record (CDR) of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Version 4; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Hook, S.; Hulley, G. MOD11A1 MODIS/Terra Land Surface Temperature/Emissivity Daily L3 Global 1km SIN Grid V006. Distributed by NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC; 2015. Available online: https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/data/catalog/lpcloud-mod11a1-006 (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Miliaresis, G.C.; Argialas, D.P. Segmentation of Physiographic Features from the Global Digital Elevation Model/GTOPO30. Comput. Geosci. 1999, 25, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Itoh, T.; Motooka, T.; Watanabe, M.; Shiraishi, T.; Thapa, R.; Lucas, R. New Global Forest/Non-Forest Maps from ALOS PALSAR Data (2007–2010). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.A.; Kenyon, R.V.; Troxel, D.E. Comparison of Interpolating Methods for Image Resampling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1983, 2, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keys, R. Cubic Convolution Interpolation for Digital Image Processing. IEEE Trans. Acoust. 1981, 29, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Thuiller, W.; Zimmermann, N.E. Habitat Suitability and Distribution Models: With Applications in R; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 0521765137. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, C.G.; Loaiza, J.R.; Romero, L.M.; Alvarado, J.M.G.; Delgado, G.; Salas, O.R.; Rojas, M.R.; Aguilar-Avendaño, C.; Maynes, E.; Cordero, J.A.V.; et al. Anopheles albimanus (Diptera: Culicidae) Ensemble Distribution Modeling: Applications for Malaria Elimination. Insects 2022, 13, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Georges, D.; Gueguen, M.; Engler, R.; Breiner, F.; Lafourcade, B.; Patin, R.; Blancheteau, H. biomod2: Ensemble Platform for Species Distribution Modeling. R package version 4.2-1. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=biomod2 (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Elith, J.H.; Graham, C.P.H.; Anderson, R.P.; Dudík, M.; Ferrier, S.; Guisan, A.; Hijmans, R.J.; Huettmann, F.; Leathwick, J.R.; Lehmann, A.; et al. Novel Methods Improve Prediction of Species’ Distributions from Occurrence Data. Ecography 2006, 29, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbet-Massin, M.; Jiguet, F.; Albert, C.H.; Thuiller, W. Selecting Pseudo-Absences for Species Distribution Models: How, Where and How Many? Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, A.J.; Eisen, R.J.; Eisen, L.; McAllister, J.; Savage, H.M.; Mutebi, J.P.; Johansson, M.A. Consensus and Uncertainty in the Geographic Range of Aedes Aegypti and Aedes Albopictus in the Contiguous United States: Multi-Model Assessment and Synthesis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmke, B.; Greenwell, B.M. Hands-On Machine Learning with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Olden, J.D.; Lawler, J.J.; Poff, N.L. Machine Learning Methods Without Tears: A Primer for Ecologists. Q. Rev. Biol. 2008, 83, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Johnson, K. Applied Predictive Modeling; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, C.G.; Chaves, L.F.; Bergmann, L.R.; Hamer, G.L. Ensemble Species Distribution Modeling of Culex tarsalis (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Continental United States. J. Med. Entomol. 2023, 60, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Ferrier, S.; Huettmann, F.; Leathwick, J. The Evaluation Strip: A New and Robust Method for Plotting Predicted Responses from Species Distribution Models. Ecol. Modell. 2005, 186, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, O.; Tsoar, A.; Kadmon, R. Assessing the Accuracy of Species Distribution Models: Prevalence, Kappa and the True Skill Statistic (TSS). J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, D. Spaces of Global Capitalism; Verso: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 1844670651. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, R.G.; Bergmann, L.; Kock, R.; Gilbert, M.; Hogerwerf, L.; Wallace, R.; Holmberg, M. The Dawn of Structural One Health: A New Science Tracking Disease Emergence along Circuits of Capital. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 129, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.G. Dead Epidemiologists: On the Origins of COVID-19; Monthly Review Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, R.G.; Liebman, A.; Chaves, L.F.; Wallace, R. COVID-19 and Circuits of Capital. Mon. Rev. 2020, 72, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C. Guidelines for Assessing the Suitability of Spatial Climate Data Sets. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumwald, M.; Knüsel, B.; Baumberger, C.; Hirsch Hadorn, G.; Bresch, D.N.; Knutti, R. Understanding and Assessing Uncertainty of Observational Climate Datasets for Model Evaluation Using Ensembles. WIREs Clim. Change 2020, 11, e654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Peterson, T.C.; Karl, T.R. On the Development and Use of Homogenized Climate Datasets. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewontin, R.; Levins, R. Schmalhausen’s Law. Capital. Nat. Social. 2000, 11, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, L.F. Climate Change and the Biology of Insect Vectors of Human Pathogens; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781119070894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
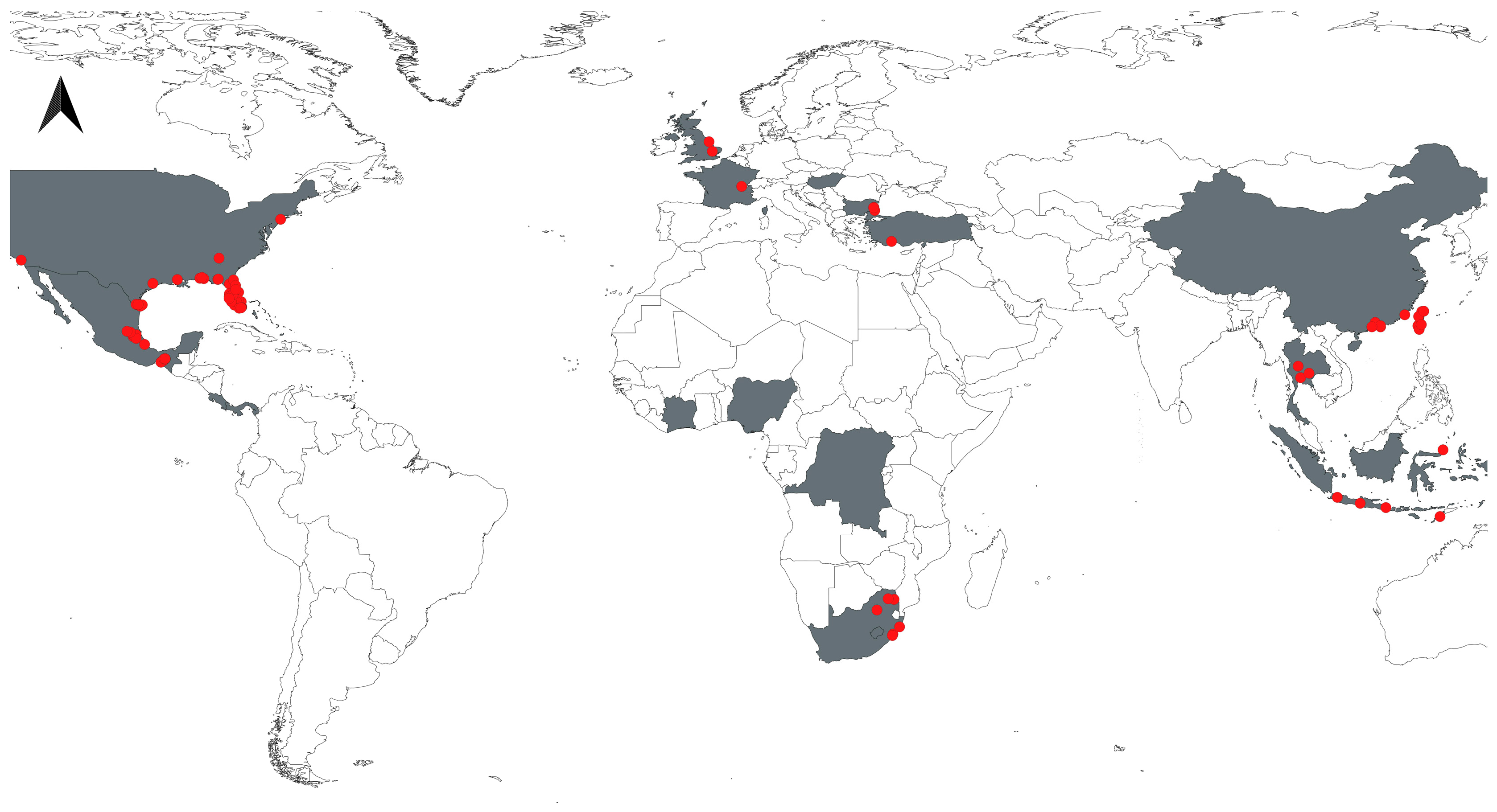
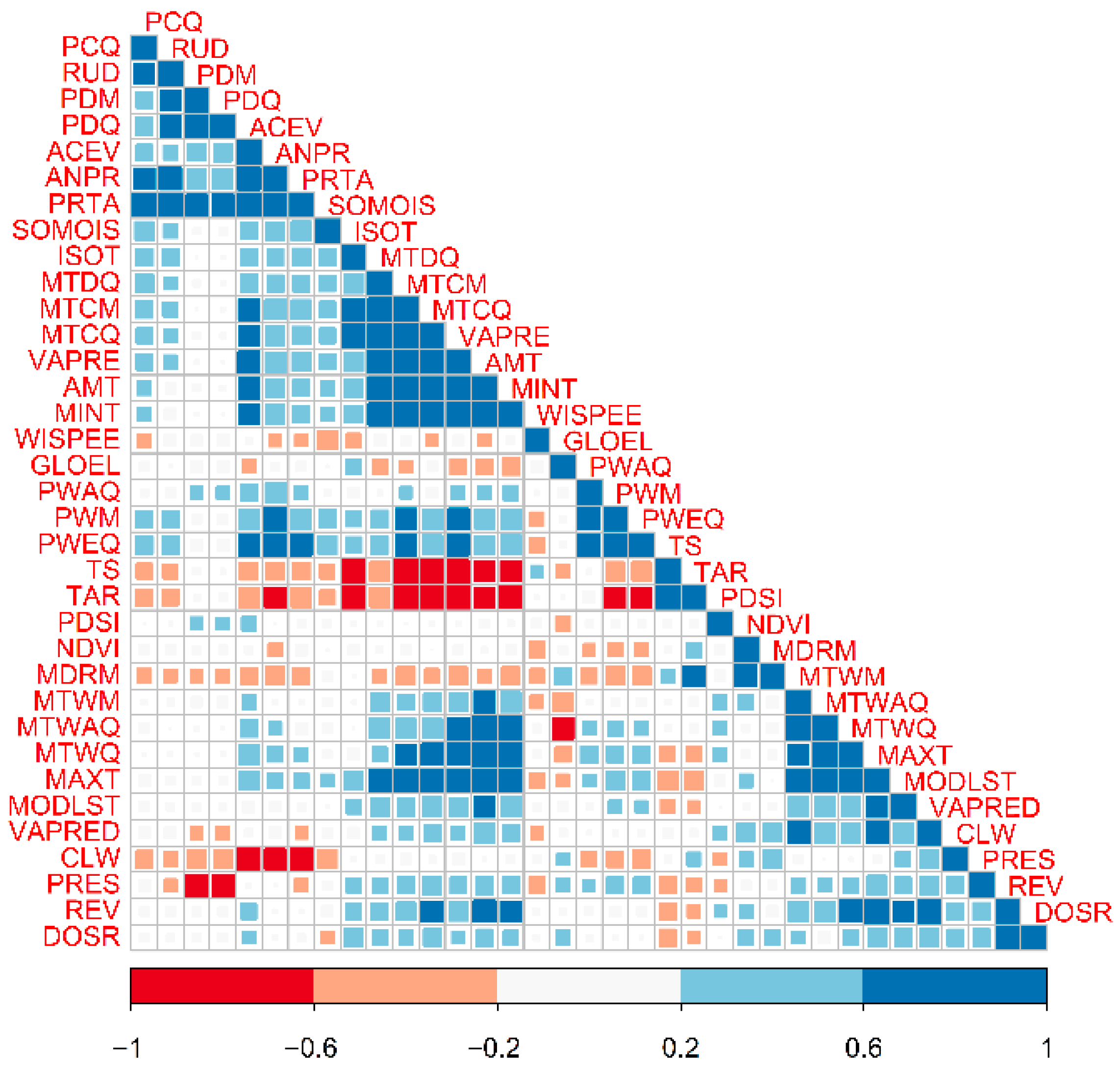
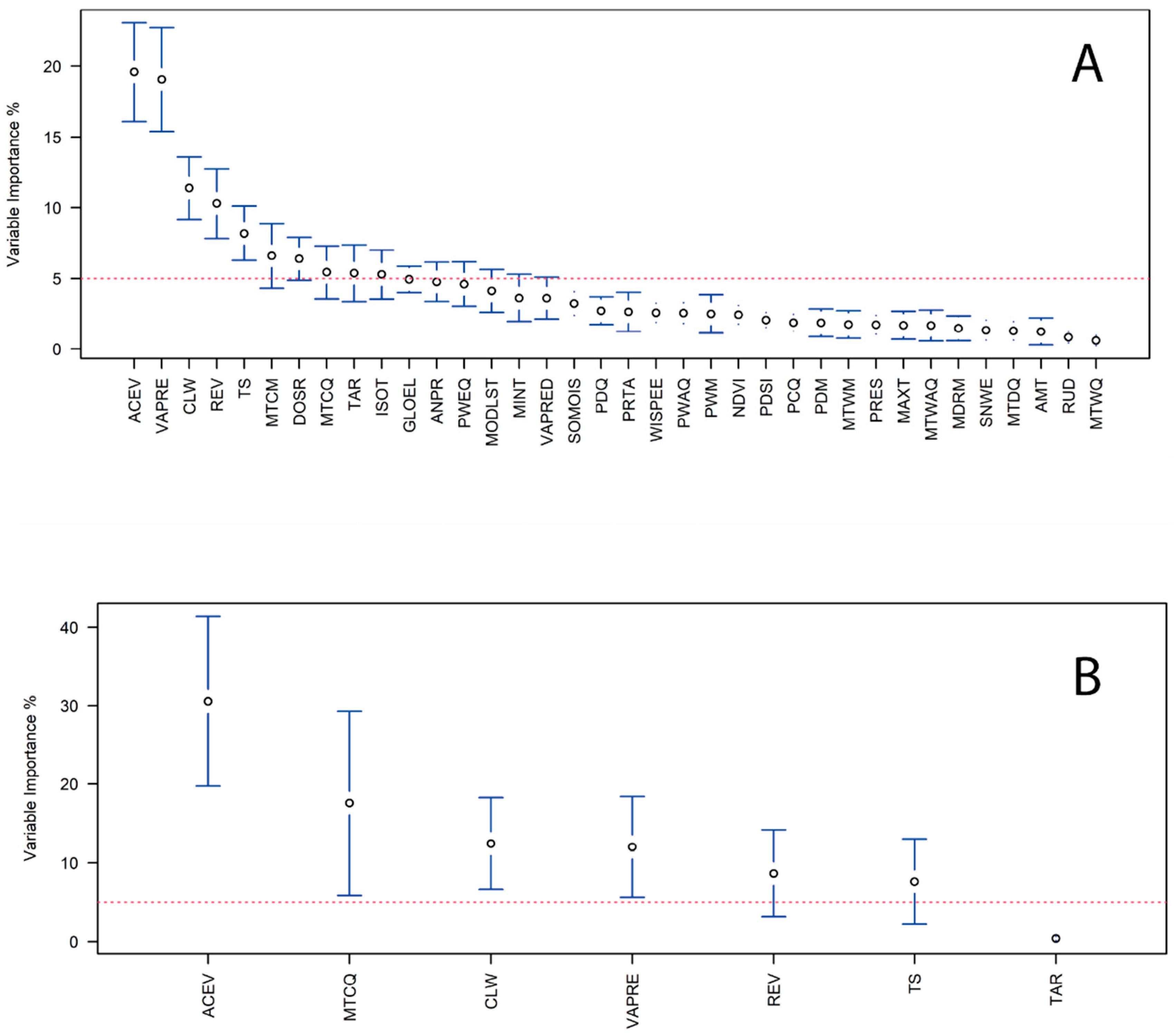
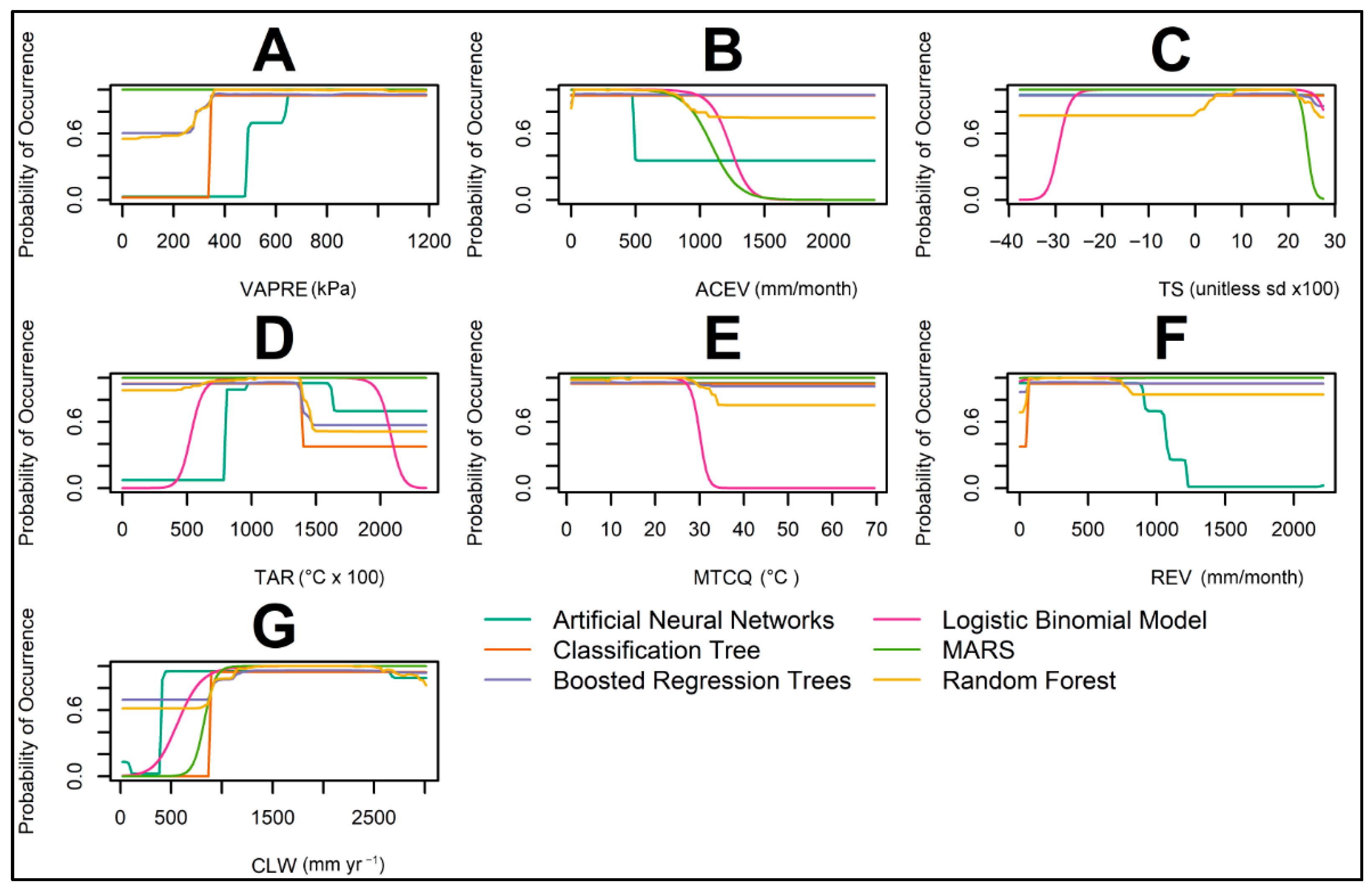
| Abbreviation | Covariate | Eco-Environmental Significance |
|---|---|---|
| ACEV | Actual Evapotranspiration (Derived) | Integrated energy–water flux; negative association; ever-wet per-humid climates correspond to lower suitability compared with sub-humid regimes |
| MTCQ | Mean Temp of Coldest Quarter | Winter constraint: suitability drops when MTCQ < ~3.5–4 °C, indicating cold-season limits on survival and establishment |
| CLW | Climate Water Deficit (Derived) | Unmet water demand; positive to a plateau; indicates tolerance of moderate moisture limitation, with saturation near the dry margin |
| VAPRE | Vapor Pressure | Atmospheric moisture (kPa); positive, saturating response that tracks the same moisture gradient as the deficit, peaking in sub-humid conditions and leveling toward the driest end |
| REV | Reference Evapotranspiration | Atmospheric evaporative demand (energy/temperature signal); helps distinguish sub-humid from per-humid settings |
| TS | Temperature Seasonality (sd × 100) | Captures thermal variability across the year; extreme seasonality reduces suitability |
| TAR | Temperature Annual Range | Annual amplitude of temperature; moderate ranges (~6–10 °C) align with higher suitability, whereas very low or very high ranges reduce establishment |
| Model | ROC | TSS |
|---|---|---|
| All (37 covariates) | 0.90 ± 0.08 | 0.76 ± 0.13 |
| Final (7 covariates) | 0.95 ±0.04 | 0.86 ± 0.08 |
| Algorithm | Updated Model Evaluation | Wei et al. [35] Data Model Evaluation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROC | TSS | ROC | TSS | |
| GLM | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.87 ± 0.01 | 0.83 ± 0.02 | 0.96 ± 0.05 |
| RF | 0.99 ± 0.13 | 0.91 ± 0.08 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.97 ± 0.10 |
| MARS | 0.97 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.10 | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 0.98 ± 0.03 |
| GBM | 0.98 ±0.01 | 0.89 ±0.08 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 0.97 ± 0.07 |
| ANN | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 0.82 ±0.12 | 0.80 ± 0.06 | 0.94 ± 0.15 |
| CTA | 0.91 ±0.04 | 0.81 ± 0.08 | 0.83 ± 0.05 | 0.92 ± 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valdés-Díaz, S.; Tuñón, R.; Castillo, D.; Sanchez, A.; Virola-Vasquez, B.; Corro, P.E.; Serrano-Peraza, F.; Zachrisson, B.; Loaiza, J.; Chang, R.; et al. Ensemble Distribution Modeling of the Globally Invasive Asian Cycad Scale, Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi, 1977 (Hemiptera: Diaspididae). Insects 2025, 16, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101016
Valdés-Díaz S, Tuñón R, Castillo D, Sanchez A, Virola-Vasquez B, Corro PE, Serrano-Peraza F, Zachrisson B, Loaiza J, Chang R, et al. Ensemble Distribution Modeling of the Globally Invasive Asian Cycad Scale, Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi, 1977 (Hemiptera: Diaspididae). Insects. 2025; 16(10):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101016
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdés-Díaz, Samuel, Reyna Tuñón, Dilma Castillo, Alieth Sanchez, Brenda Virola-Vasquez, Patricia Esther Corro, Francisco Serrano-Peraza, Bruno Zachrisson, Jose Loaiza, Rodrigo Chang, and et al. 2025. "Ensemble Distribution Modeling of the Globally Invasive Asian Cycad Scale, Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi, 1977 (Hemiptera: Diaspididae)" Insects 16, no. 10: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101016
APA StyleValdés-Díaz, S., Tuñón, R., Castillo, D., Sanchez, A., Virola-Vasquez, B., Corro, P. E., Serrano-Peraza, F., Zachrisson, B., Loaiza, J., Chang, R., & Chaves, L. F. (2025). Ensemble Distribution Modeling of the Globally Invasive Asian Cycad Scale, Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi, 1977 (Hemiptera: Diaspididae). Insects, 16(10), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101016





