Simple Summary
This biomolecular diagnostic test for the rapid identification of Philaenus italosignus Drosopoulos & Remane, 2000, is valuable in identifying one of the hemipteran species involved in the Italian invasion of Xylella fastidiosa Wells et al., 1987. The test utilizes a locked nucleic acid (LNA) probe, which increases the probe’s affinity with the target, thus ensuring higher specificity. The new qPCR test with LNA probe has proven to be a more reliable and reproducible method for identifying the different instars of P. italosignus, thereby improving territorial surveys for X. fastidiosa vector population management strategies and allowing discrimination between species collected in the field.
Abstract
To date, Philaenus spumarius (Linnaeus, 1758), Philaenus italosignus Drosopoulos & Remane, 2000, and Neophilaenus campestris (Fallén, 1805) are proven vectors of the phytopathogenic bacterium Xylella fastidiosa Wells et al., 1987 in Europe. Currently, the identification of these three species relies on the well-documented status of morphological and taxonomical characters, making the discrimination of vector adult males possible by genitalia comparison. This study updates the biomolecular diagnostic tests with a rapid identification tool for P. italosignus, using locked nucleic acid (LNA) probe technology. The test also overcomes the difficulties associated with the morphological identification of females and juveniles. The morphological α-taxonomic identification of the male, achieved through comparison with the type of the species, retains its primary role in specimen identification for probe building. Later, the proposed assay can contribute to the rapid identification of P. italosignus by the secondary (molecular) identification step. The new LNA qPCR test offers high reliability and reproducibility in the identification of P. italosignus instars, thus improving targeted surveys of X. fastidiosa vector populations and allowing discrimination between species collected in the field. The accurate identification and census of vector individuals, regardless of their gender and instar, enhances the efficacy of Xylella IPM-DSS (Integrated Pest Management Decision Support System) strategies.
Keywords:
biological invasion; alien; quarantine; invasive; plant pathogen; vector; spittlebug; Olive Quick Decline Syndrome; OQDS 1. Introduction
The vectors responsible for the spread of Xylella fastidiosa Wells et al., 1987 (Xf) [1] in Italy are indigenous xylem-sap-feeding Hemipterans. Despite all Aphrophoridae being potential vectors of X. fastidiosa [2], only Philaenus spumarius (L., 1758—the Meadow Spittlebug) has to date been found responsible for vectoring Xf in the field [3]. Neophilaenus campestris (Fallén, 1805) and Philaenus italosignus (Drosopoulos & Remane, 2000) are also considered vectors [4], although their role as vectors appears to be minimal [5,6] in the Italian pathosystems [7,8,9].
In the case of P. italosignus, molecular analyses using mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences confirm that the insect belongs to a clade comprising other species restricted to the Mediterranean. Philaenus spp. taxonomy and species descriptions use the male genitalia and anal tube segments [8]. Other Mediterranean Philaenus species are:
- -
- Philaenus arslani Abdul-Nour & Lahoud, 1996, present in Lebanon [10], associated with Echinops spp., Carduus spp., Cirsium spp. (Asteraceae), and Cistus spp. (Cistaceae) [11];
- -
- Philaenus loukasi Drosopoulos & Asche, 1991, is present in Greece [12] and is associated with Eryngium spp. (Asteraceae) [11];
- -
- Philaenus maghresignus Drosopoulos and Remane, 2000, present in Morocco, Algeria, Spain, and Tunisia [13,14], feeds on Asphodelus spp. (Asphodelaceae) [11];
- -
- Philaenus philopotamos Bückle & Guglielmino, 2025, recently described in north-east Italy [15], associated with Myricaria germanica (L.) Desv. (Tamaricaceae) and Calamagrostis pseudophragmites (Haller) Koeler (Poaceae) [15];
- -
- Philaenus signatus Melichar, 1896, present in Greece [14], feeds on Asphodelus spp. (Asphodelaceae) [11];
- -
- Philaenus tarifa Remane and Drosopoulos, 2001, which is present in the Iberian Peninsula [16], grows on Asphodelus spp. (Asphodelaceae) [11];
- -
- Philaenus tesselatus Melichar, 1889, is present in Tunisia [17] associated with various dicotyledonous plants [11].
Morphological and phylogenetic data divide the Mediterranean Philaenus species into two groups: P. italosignus, P. maghresignus, P. signatus, and P. tarifa into the signatus group; while P. arslani, P. loukasi, P. spumarius, and P. tesselatus are in the spumarius group [18].
Philaenus spumarius differs from P. italosignus due to its morphological traits and ecological preferences [19,20]. Philaenus spumarius is a widespread Palearctic species that also thrives in regions as far afield as New Zealand, Hawaii, the United States, Canada, and Japan [21,22,23]. Philaenus spumarius prefers dicotyledonous plants and winter-cold continental climates, as suggested by its reproductive parapause [8].
Philaenus italosignus is endemic to central and southern Italy, where it is zonal in Udvardy’s Palearctic Mediterranean province [24]. However, P. italosignus does not exhibit significant vector competence, mostly thriving on Asphodelus ramosus L. 1753 (Asphodelaceae) [14,25], and feeding on olive, primarily under restricted conditions.
The interest in the adults, male and female, and their morph identification arises from the need to avoid overestimating the field population of P. spumarius due to morphological similarities between the two sympatric species. Philaenus italosignus inhabits several areas and niches in Italy, closely associated with the presence of A. ramosus [14], its host plant species [25]. The choice of P. italosignus for its Mediterranean monocot, fire-resistant, and perennial host plant [26,27] represents an interesting shift to monophagia in comparison to P. spumarius’ vast polyphagia [28]. The choice allows P. italosignus to thrive in minute, diverse niches, permitting its presence in various Italian areas that are overgrazed or otherwise degraded [25,26,29]. However, P. italosignus is primarily associated with Italian regions [14]. In terms of phylogeography, the evidence suggests that P. italosignus differentiated in the Italian Mediterranean area, adapting to the climate and the availability of host plants during glacial periods. The genetic diversity observed within P. italosignus populations suggests that this species has adapted to niches different from those of P. spumarius, which may have facilitated its spread [30]. It is worth mentioning that, from the point of view of chromosome morphology recognition, P. italosignus exhibits significant heterochromatin C, with prominent bands on both autosomal and sex chromosomes. The variability in heterochromatin distribution suggests a significant evolutionary influence on the genetic diversity and adaptability of the species [31].
Adults of Philaenus spp. show dorsally a well-studied polymorphism on the head, prothorax, and tegmina [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. The polymorphism also complicates the discrimination among the Philaenus species, including spumarius and italosignus. Philaenus italosignus shares all six morphs available in Italy with the corresponding six of P. spumarius, but not the other seventeen [40].
The polymorphism also suggests the need for a molecular tool to aid in the identification of Philaenus by non-entomologists. However, a trained entomologist can identify Philaenus males in about 15 min using a medium-quality stereoscope, but not females [8].
Philaenus species identifications can significantly benefit from molecular techniques, particularly in cases involving a large number of identifications at the species level, as seen during Xf monitoring programs [41].
The presence of X. fastidiosa in southern Italy has led to intensive monitoring of P. italosignus in both olive and non-olive orchards to assess the presence and impact of the transmitted plant pathogen in the area [4,42]. Accurate identification of vectors, males, and females is therefore necessary to develop effective monitoring and vector control [43] or infection management [44]. We note that recent advances in molecular techniques have led to improvements in the specificity of identifying P. italosignus [44].
We propose a new species-specific biomolecular identification test based on a highly selective and diagnostic locked nucleic acid (LNA) probe. This technology leverages the enhanced sensitivity and specificity of LNA probes, which have shown significant potential in the qPCR detection of specific targets (diagnosis, identification of genes or gene fragments, etc.) due to their high binding affinity and stability [45,46]. The chemical structure of LNA probes confers excellent resistance to nucleases, thereby enabling more accurate and sensitive analysis than traditional probes [47,48,49,50,51,52]. Using LNA probes with real-time PCR techniques has significantly improved the sensitivity and specificity in detecting tobacco mosaic viruses, grapevine phytoplasmas, plant viruses [53], and insects [54,55]. Moreover, as reported in Rizzo et al. [55], qPCR assays with LNA probes enable the detection of Agrilus anxius Gory, 1841 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) from samples containing as few as 6,4 fg/µL of the target DNA. The LNA probe provides a practical opportunity to quickly mass-identify X. fastidiosa candidates or vectors, regardless of their gender or instar. The array of advantages was not previously available at this level of confidence. The LNA better assesses the vector census in field application of the Integrated Pest Management Decision Support System (IPM-DSS) [56] for routine life table and survivor analysis, in view of the Xf-induced disease surveillance. Finally, accessible tools such as the probe we propose can help improve invasive modelling.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Material
The specimens of P. italosignus (n = 81, adults) come from the collections of the UNIFI team [Department of Agriculture, Food, Environment, Forest Resources and Natural Resource Sciences (DAGRI), University of Florence] and UNIBA [Department of Soil, Plant and Food Sciences (DiSSPA), University of Bari Aldo Moro]. Some specimens from the same collections had undergone a previous SYBR Green qPCR test, as conducted by Rizzo et al. [44], which also involved numerous adult and juvenile specimens (n = 514) belonging to 24 different species, as reported in Table 1. The identification of Philaenus tesselatus (n = 12), Neophilaenus campestris (n = 194), and P. spumarius (n = 178), the latter two being vectors of Xf, deserves particular attention.

Table 1.
List of species in the molecular diagnostic assay. RPS: Regional Phytopathological Service Tuscany (Italy).
2.2. DNA Extraction
We performed nucleic acid extraction from target adult insects and non-target adult and juvenile insects according to the protocol described in Rizzo et al. [44]. Duplicate DNA extractions for each sample were eluted in 100 µL of sterile nuclease-free water. The extracted nucleic acids were either used immediately for qPCR or stored at −20 °C for future use. A QiaExpert spectrophotometer (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) estimated DNA quality and quantity by calculating the optical density ratios A260nm/230nm and A260nm/280nm for diluted and undiluted DNA extracts. The amplifiability check assessed the DNA suitability for qPCR testing using a qPCR probe reaction using the primers 18S uni-F/18S uni-R (5′-GCAAGGCTGAAACTTAAAGGAA-3′/5′-CCACCACCCATAGAATCAAGA-3′) and the probe 18S uni-P (HEX-ACGGAAGGGCACCAGGAGT-BHQ1), which amplifies a highly conserved region of the 18S ribosomal DNA of eukaryotes [57].
2.3. Analysis of Intra-Individual Variation in the qPCR Target Region of the Cytochrome B Gene
The cytochrome B (cytB) mitochondrial gene served as a candidate gene for discriminating P. italosignus from other Aphrophoridae using quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR). To verify the existence of multiple mitochondrial haplotypes (heteroplasmy) and NUMTs (nuclear pseudogenes) within a single individual, primers CB-N3665 5′–GTCCTACCATGAGGTCAAATATC–3′ [58] and the novel primer cytB-uni 5′–GGRATAAAATTATCAGGGTCYCC–3′ were used to amplify a fragment of 380 bp based on the cytB nucleotide sequence of P. italosignus, see GenBank: FJ664097.1, NCBI link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/FJ664097.1/ (accessed on 26 April 2023), and [11]. The reagent mix composition was 1 X GreenTaq PCR Buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 0.2 mM of each dNTP, 1.25 U of DreamTaq (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 0.2 µM of each primer (Eurofins Genomics, Ebersberg, Germany), and ca. 10 ng of DNA extracted as indicated above from adults of P. italosignus (specimen Pi P1), N. campestris (Nc C8 and Nc G6), N. lineatus (Nl 7/1), Neophilaenus sp. (N 1/2), P. spumarius (Ps D6 and Ps G2), and P. tesselatus (Pt 2/1) identified to genus or species level based on morphological traits. Nc C8, Nc G6, Ps D6, Ps G2, and Pi P1 were sampled in Italy [44]; meanwhile, N 1/2, Nl 7/1, and Pt 2/1 were from Tunisia. Thermal cycling consisted of 3 min at 95 °C for initial denaturation, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 56 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 30 s; a final extension of 30 min at 72 °C followed. PCR products obtained were purified using FastAP and Exonuclease I (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and subjected to direct Sanger sequencing in forward and reverse or purified from 1% agarose (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) gels using the ReliaPrep DNA Clean-Up and Concentration System (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA), and ligated, propagated, and PCR amplified as described in Marchi et al. [59]. Three clones/specimens underwent sequencing in both forward and reverse directions using T7 and SP6 plasmid primers. Chromas (Technelisyum) visualized the chromatograms. Sequences were aligned using Muscle, as implemented in the MEGA version 12 software package [60]. The BLAST software (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed 21 June 2023) analyzed three consensus sequences/specimens for their suitability as representatives of their respective genera. Then, BLAST translated the amino acid sequences to tentatively assign them to NUMTs [61] using the ExPASy Translate tool (https://web.expasy.org/translate/, accessed on 21 June 2023). To determine intra-individual variation in the cytB fragment sequence, the number of haplotypes and the number of segregating sites were calculated using DnaSP v6 software [62]. When the homologous sequences from two clones differed by one or more nucleotides, the sequences included different haplotypes [61].
The oligos and LNA probe specific for P. italosignus were derived from the genomic region of cytochrome B (GenBank: accession number FJ664097.1, NCBI link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/FJ664097.1/, accessed on 21 July 2025), encompassing a 170 bp genomic region (Table 2).

Table 2.
List of the primers and probes used in the assay. LNA bases of probes are in capital letters, and standard DNA bases are in lowercase.
2.4. Design of P. italosignus Primers and LNA Probe
OligoArchitectTM Primers and Probe Design Online software (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, version 2014) facilitated the design of oligos and the LNA probe, taking into account primer melting temperatures, amplicon length, and the avoidance of secondary structures (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Sequence of a 650 bp fragment of the cytB gene from P. italosignus (GeneBank: FJ664097.1), indicating the Sense Primer (in blue), the Anti-Sense Primer (in green), and the LNA probe (in red).
The software accurately determined the position of the LNA probe, covering all insects included in the study. Eurofins Genomics (Ebersberg, Germany) synthesized the oligonucleotides. At the same time, BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) analyzed the primers and probe design, searching for homologous nucleotide sequences and aligning them with the MAFFT software package [63], in Geneious version 2025.1.3 (Biomatters Ltd, Auckland, New Zealand; http://www.geneious.com). The alignments performed within the cytB gene involved 269 sequences belonging to Philaenus arslani (Abdul-Nour & Lahoud, 1996), Philaenus maghresignus (Drosopoulos & Remane, 2000), P. italosignus, P. spumarius, P. tesselatus, P. tarifa, P. signatus, N. campestris, Aphrophora alni (Fallén, 1805), and Lepyronia coleoptrata (Linnaeus, 1758). In Figure 2, we have simplified the alignments because many of the aligned sequences were repetitive and exhibited identical variability for the target sequence. The extended version, which includes all sequences considered, is provided in Figure S1 (Supplementary Materials).
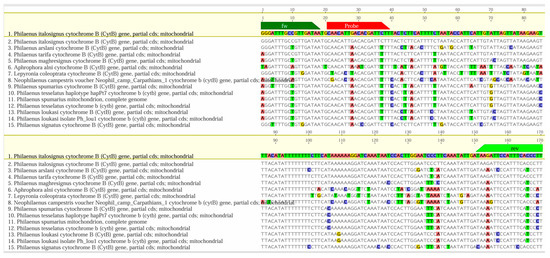
Figure 2.
Graphical alignments between the P. italosignus amplicon (including primers and the newly designed LNA probe) and 15 representative sequences from some genetically related species (Philaenus spp., Neophilaenus spp., etc.). The sequences of the primers and LNA probes are in green and red, respectively. We highlighted nucleotide alignment mismatches using the following colors: blue for C (cysteine), yellow for G (guanine), red for A (adenine), and green for T (thymine). See the complete picture in Figure S1, Supplementary Material.
2.5. qPCR Optimization
To optimize the qPCR run conditions, the optimal annealing conditions and concentrations of primers and LNA probes were determined. Primers and LNA probes were tested at concentrations of 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 µM for primers and 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 µM for LNA probes. A thermal gradient was established using 5 ng/µL of P. italosignus adult DNA, with an annealing temperature range of 52 °C to 60 °C.
Gene amplification reactions were performed in the CFX96 thermocycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), considering a final volume of 20 μL. The reactions were performed in a 96-well real-time PCR plate (Starlab, Milan, Italy) with 0.2 mL wells, and each reaction was run in duplicate. We performed duplicate analyses on all samples listed in Table 1. Each cycle included a no-template control (NTC), i.e., water, as well as positive and negative amplification controls for the target samples. We repeated the test in case of unclear or contradictory results. All data were analysed using CFX Maestro software, version 2.3 (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
2.6. Performance Characteristics
The EPPO standard PM7/98 (5) [64] suggests validating the test based on analytical specificity (inclusiveness and exclusivity), analytical sensitivity, repeatability, and reproducibility. Analytical specificity was tested by comparing qPCR amplification of target and non-target samples (Table 1), using genomic DNA extracted at a final concentration of 10 ng/µL for all insects listed in Table 1. Analytical sensitivity, which determined the limit of detection (LoD), was assessed using a 1:5 serial dilution in triplicate from the genomic DNA of single adults of P. italosignus. The assessment range was between 5 ng/µL and 12.8 fg/µL.
QIAxpert (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) performed all measurements using spectrophotometry technology to analyse the concentration and purity of DNA in the samples. These measurements obtained average Cq values and standard deviations (SDs) for the target species. We examined DNA extracted from eight adult P. italosignus in triplicate and diluted to 0.08 ng/µL. We performed the protocol at different times and by various operators to confirm reproducibility. CFX Maestro software 2.3 analysed the qPCR amplification data.
2.7. Blind Panel
An in-house blind test was performed for an evaluation of diagnostic specificity and accuracy on DNA extracted from 12 target and non-target insects (two P. italosignus, two P. spumarius, two P. tesselatus, two N. campestris, two N. lineatus, and two NTC) used at a final concentration of 5 ng/µL. The test utilized a qPCR assay with an LNA probe, and samples were received anonymously by the various operators. Two internal groups from the Phytopathology and Molecular Biology Laboratory of the Plant Protection Service in the Tuscany Region (Italy) conducted the blind panel, each consisting of two operators. DNA samples were numbered and processed in triplicate, including true positives, false positives, true negatives, and false negatives, based on the results of the blind panel. The evaluation followed the EPPO PM7/98 (5) [64] standard validation parameters.
3. Results
3.1. DNA Extraction
Nucleic acid extractions using the protocol described above [44] were all successful. The average concentrations (ng/µL) of extracted DNA and the absorbance ratios (A260/280) were within the ranges considered optimal for subsequent test validation operations (Table 3). Furthermore, the Cq values obtained in qPCR to test the amplifiability of the 18S ribosomal gene confirmed these data [57].

Table 3.
Average concentration, quality, and cycle number of crossing quantity (Cq) value of Philaenus italosignus adults. Values are means ± standard deviation.
3.2. Development and Optimization of P. italosignus-Specific qPCR
PCR amplification was performed using the cytB PCR primers set CB-N3665/cytB-uni to assess single-organism variability in the cytB regions of interest for qPCR primers and probes. A fragment of the expected size (approx. 400 bp) was obtained from all specimens used in the trial. Although chromatograms obtained by direct sequencing had to be discarded because of superimposed mixed traces, sequencing of cloned fragments was successful and provided reliable consensus sequences. The alignment of three clone sequences for each of eight specimens (24 clones in the final dataset) showed that no gaps were present and that the number of segregating sites varied from a minimum of 1, in the cases of Ps D6 and Nl 1/2, to a maximum of 19, in the case of Pt 2/1, over 334 bp (Figure 3). Specimens Ps D6 and Nl 1/2 provided two haplotypes. Meanwhile, Nc C8, Nc G6, Nl 7/1, Ps G2, Pi P1, and Pt 2/1 provided three haplotypes. Except for Pt 2/1 clone 12-2, in whose deduced amino acid sequence an in-frame stop codon was detected (Figure 3), no other reliable evidence of NUMTs could be found, which is meaningful given that all individuals tested here possess heteroplasmy cytB sequences in their mtDNA.

Figure 3.
Alignment of 24 cytB alleles cloned from Neophilaenus campestris (Nc C8 and Nc G6), N. lineatus (Nl 1/2 and Nl 7/1), Philaenus spumarius (Ps D6 and Ps G2), P. italosignus (Pi P1), and P. tesselatus (Pt 2/1) specimens used to evaluate the existence of variability due to heteroplasmy, in the nucleotide sequence targeted by the qPCR assay developed in this study. A homologous sequence (FJ664097.1) of P. italosignus was retrieved in the GenBank database and included for comparative purposes. The positions of the P.italosignus-specific qPCR assay primers (fw and rv) and probe are highlighted in blue, green, and red, respectively.
Optimization investigations of the qPCR assay revealed that the optimal reaction mixture (in a final volume of 20 µL) was obtained with 10 µL of 2× QuantiNova Probe PCR Master Mix (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), using primers at 0.2 and 0.4 µM, and the LNA probe at 0.2 µM. The optimal annealing temperature for the qPCR reaction was determined to be 55 °C, as determined by thermal gradient tests. Amplification curves showing a clear inflection point, or increasing kinetics, with a Cq value < 38 strongly suggest the sample positivity. Philaenus spumarius, P. tesselatus, N. lineatus, and N. campestris, Figure 4, as well as the other samples listed in Table 1, gave no amplification.
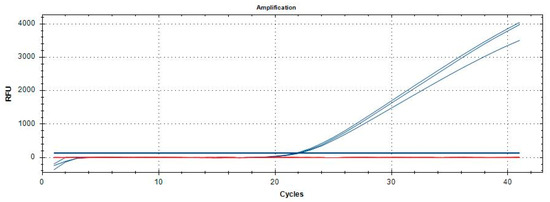
Figure 4.
Amplification curves of P. italosignus adults (blue) and adults of N. campestris, N. lineatus, P. tesselatus, and P. spumarius (red). The concentrations of each extract analysed were equal to 5 ng/µL.
3.3. Performance Characteristics
Analytical specificity tests against non-targets and targets (Table 4) yielded the expected results. The qPCR assay was inclusive for all P. italosignus specimens and exclusive for the non-target organisms tested. Non-target organisms had no false positives (within the reference cut-off value for the qPCR test). Therefore, both inclusivity and exclusivity resulted in an analytical specificity of 100% for the qPCR assay. Changing the analytical scenario, using different operators, extraction equipment, and volumetric dispensing equipment, etc., does not bias the qPCR assays, yielding the same qualitative results.

Table 4.
Philaenus italosignus analytical sensitivity (LoD) assays using 1:5 serial dilutions (from 5 ng/µL to 12.8 fg/µL) in triplicate (A, B, and C). The Cq values are the mean of the three threshold cycles of each dilution; Cq values above 38 were considered negative results.
The analytical sensitivity (LoD) assessed on P. italosignus adults (three in number for each reaction or test thereof) was 0.064 pg/µL (Table 4) with a corresponding limit value of 37.23. The R2 correlation values for the P. italosignus adults analysed were 0.99, with an efficiency of 100.2% (Figure 5). Abbreviation: n/a = not applicable.
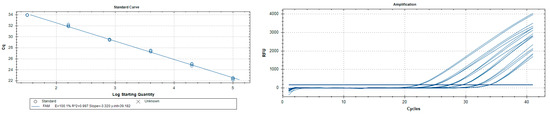
Figure 5.
Philaenus italosignus: serial dilutions 1:5 of adult DNA extracts. Amplification curves are shown on the right, and titration curves on the left.
The repeatability and reproducibility of the assay are shown in Table 5 and Table 6. Eight DNA extracts (replicates) were assayed in triplicate at a concentration of 0.08 ng/µL. The range of repeatability values found was from 31.6 ± 0.15 to 32.0 ± 0.30 (Table 5), while the range for reproducibility was from 31.2 ± 0.10 to 31.7 ± 0.23 (Table 6).

Table 5.
Philaenus italosignus: the assay’s repeatability values (average and SD) in triplicate (A, B, and C).

Table 6.
Philaenus italosignus: the assay’s reproducibility values (average and SD) in triplicate (F, G, and H).
3.4. Blind Panel
A blind test conducted in the laboratory of the Regional Phytosanitary Service of Tuscany (Italy) yielded results with 100% diagnostic specificity and accuracy, with no false positives or false negatives in the various analytical activities (Table 7). Furthermore, no non-specific reactions were found.

Table 7.
Blind panel for P. italosignus: results; NTC: no-template control.
4. Discussion
A census of vectors or candidates helps in understanding the transmission dynamics of X. fastidiosa and the plant pathogen’s crucial role in Syndrome induction. A proper IPM approach will contain the spread of the pathogen, as well as model the vector’s dispersion risk [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73]. IPM should focus more on infection management efficacy, mitigating the impact of X. fastidiosa [74]. Integrated Transmission Management (ITM) should prioritise the timing, triggering, and sorting of control actions [67], aiming for a more preventive and protective posture, rather than a too-late vector annihilation. ITM should combine genetic, chemical, biological, agronomical, and physical control means and actions [75,76,77,78,79,80] to minimise interactions between the quickly and LNA mass-scrutinized and identified vectors, the pathogen, and susceptible plants, thereby reducing the number of infections and the consequent acquisition opportunities for subsequent broods of the vectors. This LNA assay is significantly more sensitive than the previous SYBR Green assay, successfully detecting P. italosignus in larger vector or candidate mixed samples.
The morphological α-taxonomic primary identification must facilitate correct molecular identification for broader use and informed plant–pathogen findings in vector populations. It is also worth noting that a molecular test for identifying insect vectors will be used in multiple surveys to determine vector species and diagnose X. fastidiosa simultaneously. Finally, having a molecular identification tool can be helpful in all cases where entomological expertise for reliable and accurate recognition is lacking. It should be considered that cross-checking morphological, α-taxonomic, and molecular vector identification with X. fastidiosa molecular identification is a desirable strategy to follow in all cases of official activities at the territorial level by competent authorities, as it improves the reliability of the data and increases the robustness of the dataset.
Based on the scientific literature, there appears to be only one molecular protocol for the molecular identification of P. italosignus [44], developed using SYBRGreen technology. The need for additional molecular tools for the identification of P. italosignus arose when considering an alternative technique with greater analytical sensitivity. The comparison between SYBRGreen and LNA suggests replacing the former with the latter just because of LNA’s better analytical sensitivity—see the validation data for the SYBR Green assay [44]. The use of different mechanisms of action and other target genes (cytB) strengthens the identification through cross-molecular confirmation. The method has a greater affinity and selectivity in comparison to standard TaqMan probes. This feature will be crucial in disease diagnosis and pest identification.
The nucleic acids extraction from adult P. italosignus yielded the expected results, highlighting optimal concentrations, quality, and purity values for gene amplification reactions, as was the case with the previous qPCR SYBR Green assay. Regarding analytical specificity, both in terms of inclusivity and exclusivity, a clear correspondence between the target and non-target was observed, with no evidence of non-specificity or erratic curves. The comparison involves close-level relationships very similar to P. italosignus, including P. spumarius, P. tesselatus, and N. campestris. At the genus level of Philaenus, we confirmed that there are no cross-reactions with the target P. italosignus. We found no interference with the specificity of the test when analysing 396 samples (12 of P. tesselatus, 12 of N. lineatus, 178 of P. spumarius, and 194 of N. campestris). These assessments were also carried out in silico by comparing 268 sequences belonging to different genera, including Philaenus. The analytical sensitivity found was 0.064 pg/µL, higher than that of the other test currently available for the specific identification of the species P. italosignus [44], which was 0.016 ng/µL. We note that the higher analytical sensitivity found does not appear to be essential in cases of molecular identification from adult individuals, given the amount of DNA present in each specimen (usually greater than 10 ng/μL).
It should be noted that the greater analytical sensitivity observed does not appear to be essential in cases of molecular identification from adult individuals, given the amount of DNA extracted from each specimen (usually greater than 10 fg/µL). Conversely, in cases of indirect diagnosis from genetic traces (e.g., frass, exuviae, etc.), the ability to detect very low amounts of nucleic acids is crucial. The blind panel also confirmed the validation data hypothesized regarding diagnostic specificity and accuracy (100%).
Concerning the validation data obtained, the new qPCR LNA protocol appears to be suitable for assessing the presence of P. italosignus in the field and for its census to estimate the size of the population and its role in the spread of X. fastidiosa, even in scenarios that are still unknown, assuming the homogeneous presence of Asphodelus host plants.
On the side of alpha-taxonomic morphological female identification, the challenge is to find several cuticular morpho-functionally specialized details in the genitalia of molecularly identified females. Female genitalia details require a different status for each species, and they have been reliably and clearly imaged using a compound microscope in bright field, serving as taxonomic characters for female-specific identification by a skilled entomologist. Reliable female identification will help assess the vector census and, consequently, facilitate the integration of the dataset for life table and survivor analysis in the next step, IPM DSS [56].
5. Conclusions
Philaenus italosignus can transmit X. fastidiosa, but few studies have investigated its role in the spread of the bacterium. The P. italosignus monophagia on A. ramosus suggests that it plays a marginal role in the transmission of X. fastidiosa. However, the recent report of new strains and sequence types of X. fastidiosa infecting different plants in southern Italy suggests that knowledge about Xylella vectors should be reviewed and updated. Morphological identification remains a primary method for identifying vectors. It is essential to propose robust results at the gene sequence level that can serve as a reference for biomolecular identification investigations (such as barcoding), especially in the design of specific molecular identification or indirect diagnosis (from genetic traces) molecular assays. The use of molecular assays capable of rapidly and accurately identifying insect vectors could help initiate sustainable phytosanitary measures against vectors and early infections promptly. The molecular assay we propose is characterized by high sensitivity and, above all, analytical specificity, thanks in part to LNA probe technology (with high binding affinity, thermal stability, and mismatch discrimination ability), which can offer more reliable and reproducible identification of male and female P. italosignus, even from pools, with results available in approximately two hours. Therefore, the ability to distinguish P. italosignus from other species with similar morphologies, particularly P. spumarius, is essential for evaluating and optimizing the efficacy of management strategies and plant health protection at the regional and national levels. Finally, we should consider that data on the distribution and population size of P. italosignus can contribute to improving predictive models of X. fastidiosa spread, facilitating timely containment or different measures. Alpha-taxonomic female vector or candidate identification remains challenging, but the option of new probes offers opportunities for IPM-DSS to refine the life table and analysis of survivors.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/insects16101014/s1. Figure S1: graphical alignments between the P. italosignus amplicon (including primers and newly designed LNA probe) and 15 representative sequences from some genetically related species (Philaenus spp., Neophilaenus spp., etc.). The sequences of the primers and LNA probes are in green and red, respectively. We highlighted nucleotide alignment mismatches using the following colors: blue for C (cysteine), yellow for G (guanine), red for A (adenine), and green for T (thymine).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.R., F.G., U.P., and F.P.; methodology, D.R., M.M., E.B., B.P., L.B., A.D., and S.C.; software, B.P.; validation, D.R., A.D., L.B., C.G.Z., V.P., B.P., M.M., U.P., and F.P.; formal analysis, D.R., C.R., U.P., and A.H.; investigation, D.R., V.P., A.D., C.R., L.B., and C.G.Z.; resources, D.R.; data curation, U.P., F.P., D.R., and F.G.; writing—original draft preparation, D.R., F.G., U.P., and F.P.; writing—review and editing, D.R., F.P., U.P., and F.G.; visualization, C.R., A.H., V.P., S.C., A.D., and D.R.; supervision, F.P. and D.R.; project administration, F.P., U.P., and D.R.; funding acquisition, D.R. and F.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Phytosanitary Service of the Tuscany Region provided funding for this research. Study partially granted by the projects GENFORAGRIS—Phenotyping of Olive Genotypes Resistant to Xylella fastidiosa and development of a highly sustainable AGRonomic management model financed by MASAF (D.M. n. 664538 of 28 December 2022) and RIGENERA—Approcci integRati per il mIglioramento GENEtico, la selezione e l’ottenimento di materiali vegetali Resistenti a Xylella fastidiosa financed by MASAF (D.M. n. 665024 of 29 December 2022).
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LNA | Locked Nucleic Acid |
| IPM | Integrated Pest Management |
| DSS | Decision Support System |
| qPCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| Xf | Xylella fastidiosa |
| UNIFI | University of Florence |
| UNIBA | University of Bari Aldo Moro |
| UNIPI | University of Pisa |
| LoD | Limit of Detection |
| NTC | No-Template Control |
| Nc | Neophilaenus campestris |
| Nl | Neophilaenus lineatus |
| Ps | Philaenus spumarius |
| Pt | Philaenus tesselatus |
| Pi | Philaenus italosignus |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| OQDS | Olive Quick Decline Syndrome |
| Cq | Cycle of quantification |
| dNTP | DeoxyNucleotide TriPhosphates |
| NUMTs | Nuclear Mitochondrial DNA Segments |
| ITM | Integrated Transmission Management |
References
- Wells, J.M.; Raju, B.C.; Hung, H.Y.; Weisburg, W.G.; Mandelco-Paul, L.; Brenner, D.J. Xylella fastidiosa gen. nov., sp. nov: Gram-Negative, Xylem-Limited, Fastidious Plant Bacteria Related to Xanthomonas spp. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1987, 37, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the Risk to Plant Health Posed by Xylella fastidiosa in the EU Territory, with the Identification and Evaluation of Risk Reduction Options. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponari, M.; Loconsole, G.; Cornara, D.; Yokomi, R.K.; Stradis, A.D.; Boscia, D.; Bosco, D.; Martelli, G.P.; Krugner, R.; Porcelli, F. Infectivity and Transmission of Xylella fastidiosa by Philaenus spumarius (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae) in Apulia, Italy. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalieri, V.; Altamura, G.; Fumarola, G.; Di Carolo, M.; Saponari, M.; Cornara, D.; Bosco, D.; Dongiovanni, C. Transmission of Xylella fastidiosa Subspecies Pauca Sequence Type 53 by Different Insect Species. Insects 2019, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Moussa, I.E.; Mazzoni, V.; Valentini, F.; Yaseen, T.; Lorusso, D.; Speranza, S.; Digiaro, M.; Varvaro, L.; Krugner, R.; D’Onghia, A.M. Seasonal Fluctuations of Sap-Feeding Insect Species Infected by Xylella fastidiosa in Apulian Olive Groves of Southern Italy. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornara, D.; Saponari, M.; Zeilinger, A.R.; De Stradis, A.; Boscia, D.; Loconsole, G.; Bosco, D.; Martelli, G.P.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Porcelli, F. Spittlebugs as Vectors of Xylella fastidiosa in Olive Orchards in Italy. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzavolta, T.; Bracalini, M.; Croci, F.; Ghelardini, L.; Luti, S.; Goti, E.; Marchi, R.; Tiberi, R.; Marchi, G. Philaenus Italosignus a Potential Vector of Xylella fastidiosa: Occurrence of the Spittlebug on Olive Trees in Tuscany (Italy). Bull. Insectol. 2019, 72, 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- EPPO. PM 7/141 (1) Philaenus Spumarius, Philaenus Italosignus and Neophilaenus Campestris. EPPO Bull. 2020, 50, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencioni, A.; Gargani, E.; Strangi, A.; Rizzo, D.; Iovinella, I.; Sacchetti, P.; Roversi, P.F.; Cutino, I. Transmission of Xylella fastidiosa Subspecies Multiplex from Naturally Infected to Healthy Rhamnus alaternus by Philaenus spumarius and Neophilaenus campestris. J. Pest Sci. 2024, 97, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Nour, H.; Lahoud, L. Revision du genre Philaenus Stål, 1964 au Liban avec la description d’une nouvelle espece: P. arslani, n. sp. (Homoptera, Auchenorrhyncha, Cercopidae). Nouv. Rev. Entomol. 1995, 12, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Maryańska-Nadachowska, A.; Drosopoulos, S.; Lachowska, D.; Kajtoch, Ł.; Kuznetsova, V.G. Molecular Phylogeny of the Mediterranean Species of Philaenus (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha: Aphrophoridae) Using Mitochondrial and Nuclear DNA Sequences. Syst. Entomol. 2010, 35, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosopoulos, S.; Asche, M. Biosystematic Studies on the Spittlebug Genus Philaenus with the Description of a New Species. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1991, 101, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosopoulos, S. New Data on the Nature and Origin of Colour Polymorphism in the Spittlebug Genus Philaenus (Hemiptera: Aphorophoridae). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2003, 39, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosopoulos, S.; Remane, R. Biogeographic Studies on the Spittlebug Philaenus Signatus Melichar, 1896 Species Group (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae) with the Description of Two New Allopatric Species. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2000, 36, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Bückle, C.; Guglielmino, A. Contribution to the Knowledge of the Genus Philaenus (Cercopoidea, Aphrophoridae) with Description of Two New Taxa. Zootaxa 2025, 5683, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remane, R.; Drosopoulos, S. Philaenus Tarifa sp. n.: An Additional Spittlebug Species from Southern Spain (Homoptera, Auchenorrhyncha Cercopidae). Dtsch. Entomol. Z. 2001, 48, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhris-Bouhachem, S.; Souissi, R.; Abou Kubaa, R.; El Moujabber, M.; Gnezdilov, V. Aphrophoridae as Potential Vectors of Xylella fastidiosa in Tunisia. Insects 2023, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosopoulos, S.; Maryańska-Nadachowska, A.; Kuznetsova, V.G. The Mediterranean: Area of Origin of Polymorphism and Speciation in the Spittlebug Philaenus (Hemiptera, Aphrophoridae). Zoosystemat. Evol. 2010, 86, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, V.; Aguin-Pombo, D. Comparative Cytogenetics of Auchenorrhyncha (Hemiptera, Homoptera): A Review. ZooKeys 2015, 538, 63–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarin, N.; Hasbroucq, S.; Carestia, G.; Glibert, A.; Bragard, C.; Grégoire, J.-C. Investigating Dispersal Abilities of Aphrophoridae in European Temperate Regions to Assess the Threat of Potential Xylella fastidiosa-Based Pathosystems. J. Pest Sci. 2023, 96, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandanayaka, M.R.M.; Nielsen, M.; Davis, V.A.; Butler, R.C. Do Spittlebugs Feed on Grape? Assessing Transmission Potential for Xylella fastidiosa. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2017, 70, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.J.; Mitchell, A.L. Host Records of Philaenus spumarius (Linn.) at Kilauea, Hawaii National Park (Homoptera: Cercopidae). Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 1946, 12, 515–516. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, Z.M.; Jones, P.L. The Effects of Host Plant Species and Plant Quality on Growth and Development in the Meadow Spittlebug (Philaenus spumarius) on Kent Island in the Bay of Fundy. Northeast. Nat. 2020, 27, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udvardy, M.D.F. A Classification of the Biogeographical Provinces of the World; IUCN Occasional Paper; International Union for Conservation of Natural Resources: Morges, Switzerland, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Albre, J.; Carrasco, J.M.G.; Gibernau, M. Ecology of the Meadow Spittlebug Philaenus spumarius in the Ajaccio Region (Corsica)—I: Spring. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2021, 111, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatti, S.; Guarino, R.; La Rosa, M. Flora d’Italia, 2nd ed.; Edagricole: Bologna, Italy, 2017; Volume 1, ISBN 88-506-5242-9. [Google Scholar]
- Malmir, M.; Serrano, R.; Caniça, M.; Silva-Lima, B.; Silva, O. A Comprehensive Review on the Medicinal Plants from the Genus Asphodelus. Plants 2018, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, V.; Harkin, C.; Stewart, A.J.A. The Most Polyphagous Insect Herbivore? Host Plant Associations of the Meadow Spittlebug, Philaenus spumarius (L.). PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, E.; Pesaresi, S.; Galdenzi, D.; Gasparri, R.; Biscotti, N.; del Viscio, G.; Casavecchia, S. Post-Abandonment Dynamic on Mediterranean and Sub-Mediterranean Perennial Grasslands: The Edge Vegetation of the New Class Charybdido Pancratii-Asphodeletea Ramosi. Plant Sociol. 2016, 53, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryańska-Nadachowska, A.; Kajtoch, L.; Lachowska, D. Genetic Diversity of Philaenus spumarius and P. Tesselatus (Hemiptera, Aphrophoridae): Implications for Evolution and Taxonomy. Syst. Entomol. 2012, 37, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryańska-Nadachowska, A.; Kuznetsova, V.G.; Lachowska, D.; Drosopoulos, S. Mediterranean Species of the Spittlebug Genus Philaenus: Modes of Chromosome Evolution. J. Insect Sci. 2012, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, C.R.; King, D.R. Meadow Spittlebug; Research Bulletin; Ohio Agricultural Experiment Station: Wooster, OH, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, D.F.; Wiegert, R.G. Balanced Polymorphism in the Meadow Spittlebug, Philaenus spumarius. Am. Nat. 1962, 96, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkka, O. Geographical, Spatial and Temporal Variability in the Balanced Polymorphism of Philaenus spumarius. Heredity 1964, 19, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkka, O.; Raatikainen, M.; Vasaeainen, A.; Heinonen, L. Ecology and Ecological Genetics of Philaenus spumarius (L.) (Homoptera). Ann. Entomol. Fenn. 1967, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Farish, D.J.; Scudder, G.G.E. The Polymorphism in Philaenus spumarius (L.) (Hemiptera: Cercopidae) in British Columbia. J. Entomol. Soc. Br. Columbia 1967, 64, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Raatikainen, M. The Polymorphism of Philaenus spumarius (L.) (Homoptera) in Northern Italy. Ann. Entomol. Fenn. 1971, 37, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Yurtsever, S. Limited Polymorphism in Two Spittlebugs, Philaenus spumarius (Linnaeus) and P. signatus Melichar (Hemiptera: Cercopidae), in Island Populations from Western Turkey. Zool. Middle East 2018, 64, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapantaidaki, D.E.; Antonatos, S.; Evangelou, V.; Papachristos, D.P.; Milonas, P. Genetic and Endosymbiotic Diversity of Greek Populations of Philaenus spumarius, Philaenus signatus and Neophilaenus campestris, Vectors of Xylella fastidiosa. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahbib, N.; Picciotti, U.; Boukhris-Bouhachem, S.; Garganese, F.; Porcelli, F. Morphs of Philaenus Species, Candidate Xylella fastidiosa Vectors. Bull. Insectol. 2022, 75, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Bodino, N.; Cavalieri, V.; Dongiovanni, C.; Plazio, E.; Saladini, M.A.; Volani, S.; Simonetto, A.; Fumarola, G.; Di Carolo, M.; Porcelli, F.; et al. Phenology, Seasonal Abundance and Stage-Structure of Spittlebug (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae) Populations in Olive Groves in Italy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frem, M.; Chapman, D.; Fucilli, V.; Choueiri, E.; El Moujabber, M.; La Notte, P.; Nigro, F. Xylella fastidiosa Invasion of New Countries in Europe, the Middle East and North Africa: Ranking the Potential Exposure Scenarios. NeoBiota 2020, 59, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodino, N.; Cavalieri, V.; Dongiovanni, C.; Saladini, M.A.; Simonetto, A.; Volani, S.; Plazio, E.; Altamura, G.; Tauro, D.; Gilioli, G.; et al. Spittlebugs of Mediterranean Olive Groves: Host-Plant Exploitation throughout the Year. Insects 2020, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, D.; Bracalini, M.; Campigli, S.; Nencioni, A.; Porcelli, F.; Marchi, G.; Da Lio, D.; Bartolini, L.; Rossi, E.; Sacchetti, P.; et al. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Based on SYBR Green Technology for the Identification of Philaenus italosignus Drosopoulos & Remane (Hemiptera Aphrophoridae). Plants 2022, 11, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugozzoli, L.A.; Latorra, D.; Pucket, R.; Arar, K.; Hamby, K. Real-Time Genotyping with Oligonucleotide Probes Containing Locked Nucleic Acids. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 324, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmano, S.; Mulholland, V.; Kenyon, D.; Saddler, G.S.; Jeffries, C. Diagnosis of Phytoplasmas by Real-Time PCR Using Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) Probes. In Plant Pathology. Techniques and Protocols; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1302, pp. 113–122. ISBN 978-1-4939-2619-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, A.; Maryańska-Nadachowska, A.; Lachowska-Cierlik, D.; Kajtoch, L. The Secondary Contact Zone of Phylogenetic Lineages of the Philaenus spumarius (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae): An Example of Incomplete Allopatric Speciation. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, D.; Lee, K.M.; Park, K.W.; Suh, J.W.; Choi, S.M.; Park, K.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.H. Inhibition of miR-449a Promotes Cartilage Regeneration and Prevents Progression of Osteoarthritis in In Vivo Rat Models. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Regulating the On-Surface LNA Probe Density for the Highest Target Recognition Efficiency. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10389–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Lahiri, H.; Banerjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Molecularly Resolved Label-Free Sensing of Single Nucleobase Mismatches by Interfacial LNA Probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, G. LNA Real-Time PCR Probe Quantification of Hepatitis B Virus DNA. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, D.A.; Corey, D.R. Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA): Fine-Tuning the Recognition of DNA and RNA. Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.L.; Amorós, I.; Cuesta, G. LNA Probes in a Real-Time TaqMan PCR Assay for Genotyping of Giardia Duodenalis in Wastewaters. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yao, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Tan, L.; Yan, F.; et al. Unlocking Precision: Advancing Rapid Field Molecular Identification of Tuta Absoluta across Its Life Cycle Using Locked Nucleic Acid Strategies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 416, 136059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, D.; Pecori, F.; Moriconi, M.; Zubieta, C.G.; Palmigiano, B.; Bartolini, L.; Downes, A.; Ranaldi, C.; Papini, V.; Luchi, N.; et al. Molecular Identification of Agrilus anxius (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) Using a qPCR Assay with Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) Probe. J. Appl. Entomol. 2025, 149, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilioli, G.; De Francesco, A.; Simonetto, A. Ten Challenges for Plant Pest Modelling. In Proceedings of the Book of Abstract of XXVIII Congresso Nazionale Italiano di Entomologia, Siena, Italy, 16 June 2025; Volume 1, p. 138. [Google Scholar]
- Ioos, R.; Fourrier, C.; Iancu, G.; Gordon, T.R. Sensitive Detection of Fusarium circinatum in Pine Seed by Combining an Enrichment Procedure with a Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Using Dual-Labeled Probe Chemistry. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.S.B.; Silva, S.E.; Marabuto, E.; Silva, D.N.; Wilson, M.R.; Thompson, V.; Yurtsever, S.; Halkka, A.; Borges, P.A.V.; Quartau, J.A.; et al. New Mitochondrial and Nuclear Evidences Support Recent Demographic Expansion and an Atypical Phylogeographic Pattern in the Spittlebug Philaenus spumarius (Hemiptera, Aphrophoridae). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, G.; Cinello, T.; Rizzo, D.; Stefani, L.; Goti, E.; Della Bartola, M.; Luvisi, A.; Panattoni, A.; Materazzi, A. Occurrence of Different Phytoplasma Infections in Wild Herbaceous Dicots Growing in Vineyards Affected by Bois Noir in Tuscany (Italy). Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2015, 54, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis Version 12 for Adaptive and Green Computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, A.R.; Kim, M.J.; Park, I.A.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, I. Extent and Divergence of Heteroplasmy of the DNA Barcoding Region in Anapodisma miramae (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 3405–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPPO. PM 7/98 (5) Specific Requirements for Laboratories Preparing Accreditation for a Plant Pest Diagnostic Activity. EPPO Bull. 2021, 51, 468–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godefroid, M.; Morente, M.; Schartel, T.; Cornara, D.; Purcell, A.; Gallego, D.; Moreno, A.; Pereira, J.A.; Fereres, A. Climate Tolerances of Philaenus spumarius Should Be Considered in Risk Assessment of Disease Outbreaks Related to Xylella fastidiosa. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 95, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Amo, M.P.; Vicent, A.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Navas-Cortés, J.A.; Landa, B.B. Recent Research Accomplishments on Early Detection of Xylella fastidiosa Outbreaks in the Mediterranean Basin. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2023, 61, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, A.; Liccardo, A.; Porcelli, F. A Lattice Model to Manage the Vector and the Infection of the Xylella fastidiosa on Olive Trees. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liccardo, A.; Fierro, A.; Garganese, F.; Picciotti, U.; Porcelli, F. A Biological Control Model to Manage the Vector and the Infection of Xylella fastidiosa on Olive Trees. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onghia, A.M.; Santoro, F.; Minutillo, S.A.; Frasheri, D.; Gallo, M.; Gualano, S.; Cavallo, G.; Valentini, F. Optimisation of Sampling and Testing for Asymptomatic Olive Trees Infected by Xylella fastidiosa in Apulia Region, Italy. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2022, 61, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Serio, F.; Imbriani, G.; Girelli, C.R.; Miglietta, P.P.; Scortichini, M.; Fanizzi, F.P. A Decade after the Outbreak of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. Pauca in Apulia (Southern Italy): Methodical Literature Analysis of Research Strategies. Plants 2024, 13, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeger, M.; Caffier, D.; Candresse, T.; Chatzivassiliou, E.; Dehnen-Schmutz, K.; Gilioli, G.; Grégoire, J.C.; Miret, J.A.J.; MacLeod, A.; Navarro, M.N.; et al. Updated Pest Categorisation of Xylella fastidiosa. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Serio, F.; Bodino, N.; Cavalieri, V.; Demichelis, S.; Di Carolo, M.; Dongiovanni, C.; Fumarola, G.; Gilioli, G.; Guerrieri, E.; Picciotti, U.; et al. Collection of Data and Information on Biology and Control of Vectors of Xylella fastidiosa. EFSA J. 2019, 16, 1–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouhi, E.M.; Lachgar, M.; Hrimech, H.; Kartit, A. Optimizing Olive Disease Classification through Transfer Learning with Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2024, 14, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciotti, U.; Lahbib, N.; Sefa, V.; Porcelli, F.; Garganese, F. Aphrophoridae Role in Xylella fastidiosa subsp. Pauca ST53 Invasion in Southern Italy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddoud Debbabi, O.; Miazzi, M.M.; Elloumi, O.; Fendri, M.; Ben Amar, F.; Savoia, M.A.; Sion, S.; Souabni, H.; Mnasri, S.; Ben Abdelaali, S.; et al. Recovery, Assessment, and Molecular Characterization of Minor Olive Genotypes in Tunisia. Plants 2020, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoia, M.A.; Fanelli, V.; Miazzi, M.M.; Taranto, F.; Procino, S.; Susca, L.; Montilon, V.; Potere, O.; Nigro, F.; Montemurro, C. Apulian Autochthonous Olive Germplasm: A Promising Resource to Restore Cultivation in Xylella fastidiosa-Infected Areas. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugner, R.; Sisterson, M.S.; Backus, E.A.; Burbank, L.P.; Redak, R.A. Sharpshooters: A Review of What Moves Xylella fastidiosa. Austral Entomol. 2019, 58, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miazzi, M.M.; Pasqualone, A.; Zammitt-Mangion, M.; Savoia, M.A.; Fanelli, V.; Procino, S.; Gadaleta, S.; Aurelio, L.; Montemurro, C. A Glimpse into the Genetic Heritage of the Olive Tree in Malta. Agriculture 2024, 14, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, M.; Savoia, M.A.; Lucchese, P.G.; Fanelli, V.; Mascio, I.; Aurelio, F.L.; Miazzi, M.M.; Pacifico, A.; Montemurro, C.; Nigro, F. Behavior of Olive Genotypes Against Quick Decline Syndrome (QDS) Caused by Xylella fastidiosa subsp. Pauca in Apulia. Plants 2025, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dáder, B.; Viñuela, E.; Moreno, A.; Plaza, M.; Garzo, E.; Del Estal, P.; Fereres, A. Sulfoxaflor and Natural Pyrethrin with Piperonyl Butoxide Are Effective Alternatives to Neonicotinoids against Juveniles of Philaenus spumarius, the European Vector of Xylella fastidiosa. Insects 2019, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).