Identification of Twenty-Two New Complete Genome Sequences of Honeybee Viruses Detected in Apis mellifera carnica Worker Bees from Slovenia
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. Quantitative RT-qPCR Assays
2.5. Selection of Samples for NGS
2.6. Library Preparation
2.7. Quality Control and Genome Assembly
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, J.D.; Schwarz, R.S. Bees brought to their knees: Microbes affecting honeybee health. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürst, M.A.; McMahon, D.P.; Osborne, J.L.; Paxton, R.J.; Brown, M.J.F. Disease associations between honeybees and bumblebees as a threat to wild pollinators. Nature 2014, 506, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley, R.; Boots, M.; Wilfert, L. Condition-dependent virulence of slow bee paralysis virus in Bombus terrestris: Are the impacts of honeybee viruses in wild pollinators underestimated? Oecologia 2017, 184, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toplak, I.; Šimenc, L.; Pislak Ocepek, M.; Bevk, D. Determination of Genetically Identical Strains of Four Honeybee Viruses in Bumblebee Positive Samples. Viruses 2020, 12, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pislak Ocepek, M.; Glavan, G.; Verovnik, R.; Šimenc, L.; Toplak, I. First Detection of Honeybee Pathogenic Viruses in Butterflies. Insects 2022, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Runckel, C.; Flenniken, M.L.; Engel, J.C.; Ruby, J.G.; Ganem, D.; Andino, R.; DeRisi, J.L. Temporal analysis of the honey bee microbiome reveals four novel viruses and seasonal prevalence of known viruses, Nosema, and Crithidia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remnant, E.J.; Shi, M.; Buchmann, G.; Blacquière, T.; Holmes, E.C.; Beekman, M.; Ashe, A. A Diverse Range of Novel RNA Viruses in Geographically Distinct Honey Bee Populations. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00158-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozinger, C.M.; Flenniken, M.L. Bee Viruses: Ecology, Pathogenicity, and Impacts. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, L.; Ball, B.V. Viruses. In Honey Bee Pathology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribière, M.; Triboulot, C.; Mathieu, L.; Aurières, C.; Faucon, J.P.; Pépin, M. Molecular diagnosis of chronic bee paralysis virus infection. Apidologie 2002, 33, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughenbaugh, K.F.; Martin, M.; Brutscher, L.M.; Cavigli, I.; Garcia, E.; Lavin, M.; Flenniken, M.L. Honey Bee Infecting Lake Sinai Viruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 3285–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacandritsos, N.; Granato, A.; Budge, G.; Papanastasiou, I.; Roinioti, E.; Caldon, M.; Falcaro, C.; Gallina, A.; Mutinelli, F. Sudden deaths and colony population decline in Greek honey bee colonies. J. Inverteb. Pathol. 2010, 105, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, P.; Regnault, J.; Schurr, F.; Dubois, E.; Ribière, M. Intra-laboratory validation of chronic bee paralysis virus quantitation using an accredited standardised real-time quantitative RT-PCR method. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 180, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toplak, I.; Rihtarič, D.; Jamnikar Ciglenečki, U.; Hostnik, P.; Jenčič, V.; Barlič-Maganja, D. Detection of six honeybee viruses in clinically affected colonies of Carniolan gray bee (Apis mellifera carnica). Slov. Vet. Res. 2012, 49, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Jamnikar Ciglenečki, U.; Toplak, I. Genetic diversity of acute bee paralysis virus in Slovenian honeybee samples. Acta Vet. Hung. 2013, 61, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnikar-Ciglenečki, U.; Pislak Ocepek, M.; Toplak, I. Genetic Diversity of Deformed Wing Virus from Apis mellifera carnica (Hymenoptera: Apidae) and Varroa Mite (Mesostigmata: Varroidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 112, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimenc, L.; Kuhar, U.; Jamnikar-Ciglenečki, U.; Toplak, I. First Complete Genome of Lake Sinai Virus Lineage 3 and Genetic Diversity of Lake Sinai Virus Strains from Honey Bees and Bumble Bees. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granberg, F.; Vicente-Rubiano, M.; Rubio-Guerri, C.; Karlsson, O.E.; Kukielka, D.; Belák, S.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Metagenomic detection of viral pathogens in Spanish honeybees: Co-infection by Aphid Lethal Paralysis, Israel Acute Paralysis and Lake Sinai Viruses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, S.; Galbraith, D.; Sela, N.; Erez, T.; Grozinger, C.M.; Chejanovsky, N. Presence of Apis rhabdovirus-1 in populations of pollinators and their parasites from two continents. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMenamin, A.J.; Flenniken, M.L. Recently identified bee viruses and their impact on bee pollinators. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnikar Ciglenečki, U.; Toplak, I.; Kuhar, U. Complete genome of chronic bee paralysis virus strain SLO/M92/2010, detected from Apis mellifera carnica. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00602-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimenc, L.; Knific, T.; Toplak, I. The comparison of honeybee viral loads for six honeybee viruses (ABPV, BQCV, CBPV, DWV, LSV3 and SBV) in healthy and clinically affected honeybees with TaqMan quantitative real-time RT-PCR assays. Viruses 2021, 13, e1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamnikar-Ciglenečki, U.; Toplak, I. Development of a real-time RT-PCR assay with TaqMan probe for specific detection of acute bee paralysis virus. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 184, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantawannakul, P.; Ward, L.; Boonham, N.; Brown, M. A scientific note on the detection of honeybee viruses using real-time PCR (TaqMan) in Varroa mites collected from a Thai honeybee (Apis mellifera) apiary. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2006, 91, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurr, F.; Tison, A.; Militano, L.; Cheviron, N.; Sircoulomb, F.; Rivière, M.P.; Ribière-Chabert, M.; Thiéry, R.; Dubois, E. Validation of quantitative real-time RT-PCR assays for the detection of six honeybee viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2019, 270, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequence from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurr, F.; Cougoule, N.; Rivière, M.P.; Ribière-Chabert, M.; Achour, H.; Ádám, D.; Castillo, C.; de Graaf, D.C.; Forsgren, E.; Granato, A.; et al. Trueness and precision of the real-time RT-PCR method for quantifying the chronic bee paralysis virus genome in bee homogenates evaluated by a comparative inter-laboratory study. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 248, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravoet, J.; Maharramov, J.; Meeus, I.; De Smet, L.; Wenseleers, T.; Smagghe, G.; De Graaf, D.C. Comprehensive Bee Pathogen Screening in Belgium Reveals Crithidia mellificae as a New Contributory Factor to Winter Mortality. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurot-Daniels, C.; Glenny, W.; Daughenbaugh, K.F.; McMenamin, A.J.; Burkle, L.A.; Flenniken, M.L. Longitudinal monitoring of honey bee colonies reveals dynamic nature of virus abundance and indicates a negative impact of Lake Sinai virus 2 on colony health. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, J.R.; Cornman, R.S.; Evans, J.D.; Semberg, E.; Haddad, N.; Neumann, P.; Gauthier, L. Genome Characterization, Prevalence and Distribution of a Macula-Like Virus from Apis mellifera and Varroa destructor. Viruses 2015, 7, 3586–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhn, H.; Deboutte, W.; Schoonvaere, K.; Demaeght, P.; De Smet, L.; Amssalu, B.; Matthijnssens, J.; de Graaf, D.C. Metagenomic Approach with the NetoVIR Enrichment Protocol Reveals Virus Diversity within Ethiopian Honey Bees (Apis mellifera simensis). Viruses 2020, 12, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.-C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.-P.; Eden, J.-S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzoli, F.; Forzan, M.; Bortolotti, L.; Pacini, M.I.; Rodríguez-Flores, M.S.; Felicioli, A.; Mazzei, M. Next generation sequencing study on RNA viruses of Vespa velutina and Apis mellifera sharing the same foraging area. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govan, V.A.; Leat, N.; Allsopp, M.; Davison, S. Analysis of the complete genome sequence of acute bee paralysis virus shows that it belongs to the novel group of insect-infecting RNA viruses. Virology 2000, 277, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leat, N.; Ball, B.; Govan, V.; Davison, S. Analysis of the complete genome sequence of black queen-cell virus, a picorna-like virus of honey bees. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, V.; Blanchard, P.; Chaouch, S.; Lallemand, P.; Schurr, F.; Celle, O.; Dubois, E.; Tordo, N.; Thiery, R.; Houlgatte, R.; et al. Molecular characterisation and phylogenetic analysis of Chronic be paralysis virus, a honey bee virus. Virus Res. 2008, 132, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzi, G.; De Miranda, J.R.; Boniotti, M.B.; Cameron, C.E.; Lavazza, A.; Capucci, L.; Camazine, S.M.; Rossi, C. Molecular and biological characterization of deformed wing virus of honeybees (Apis mellifera L.). J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4998–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

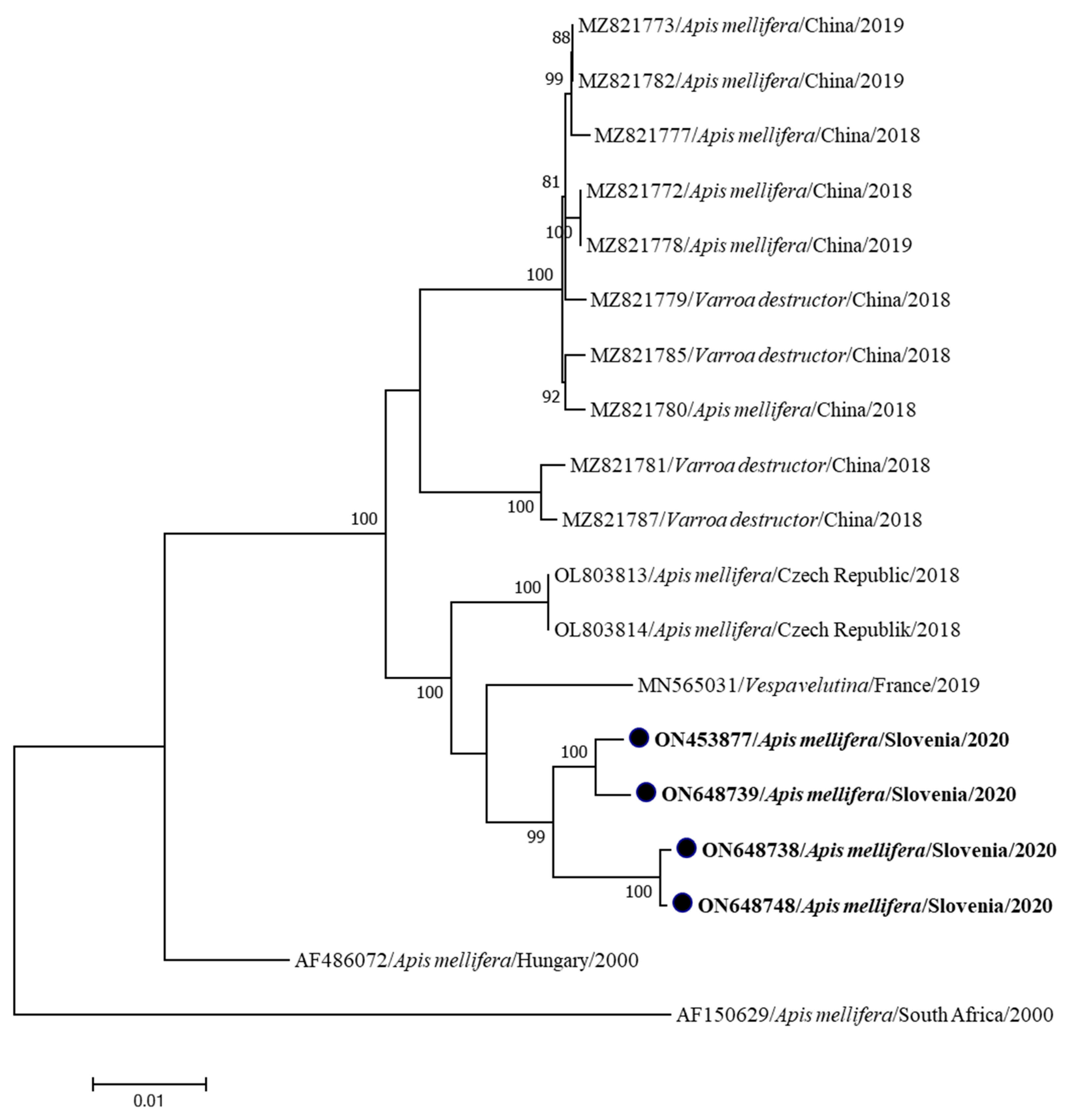
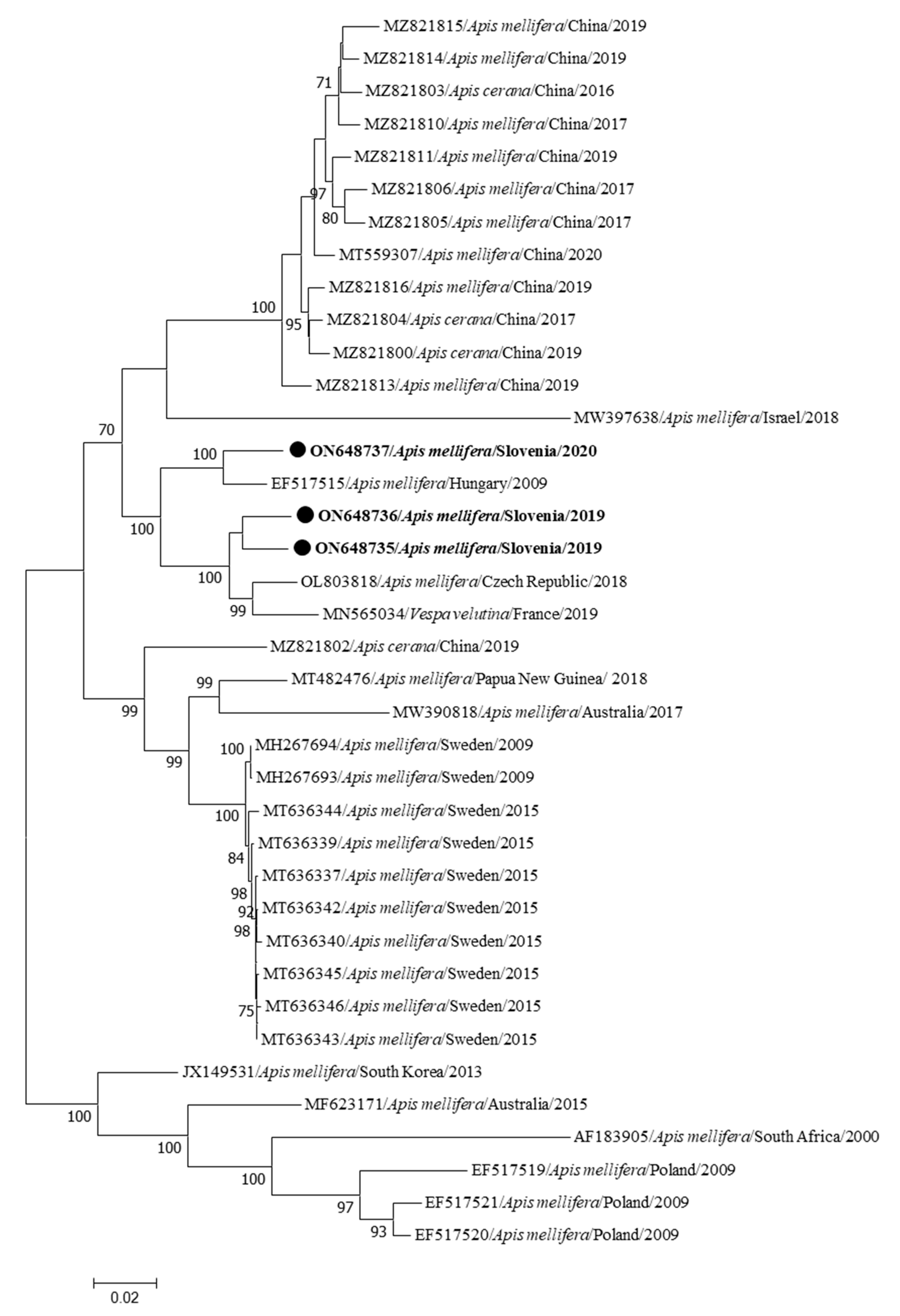
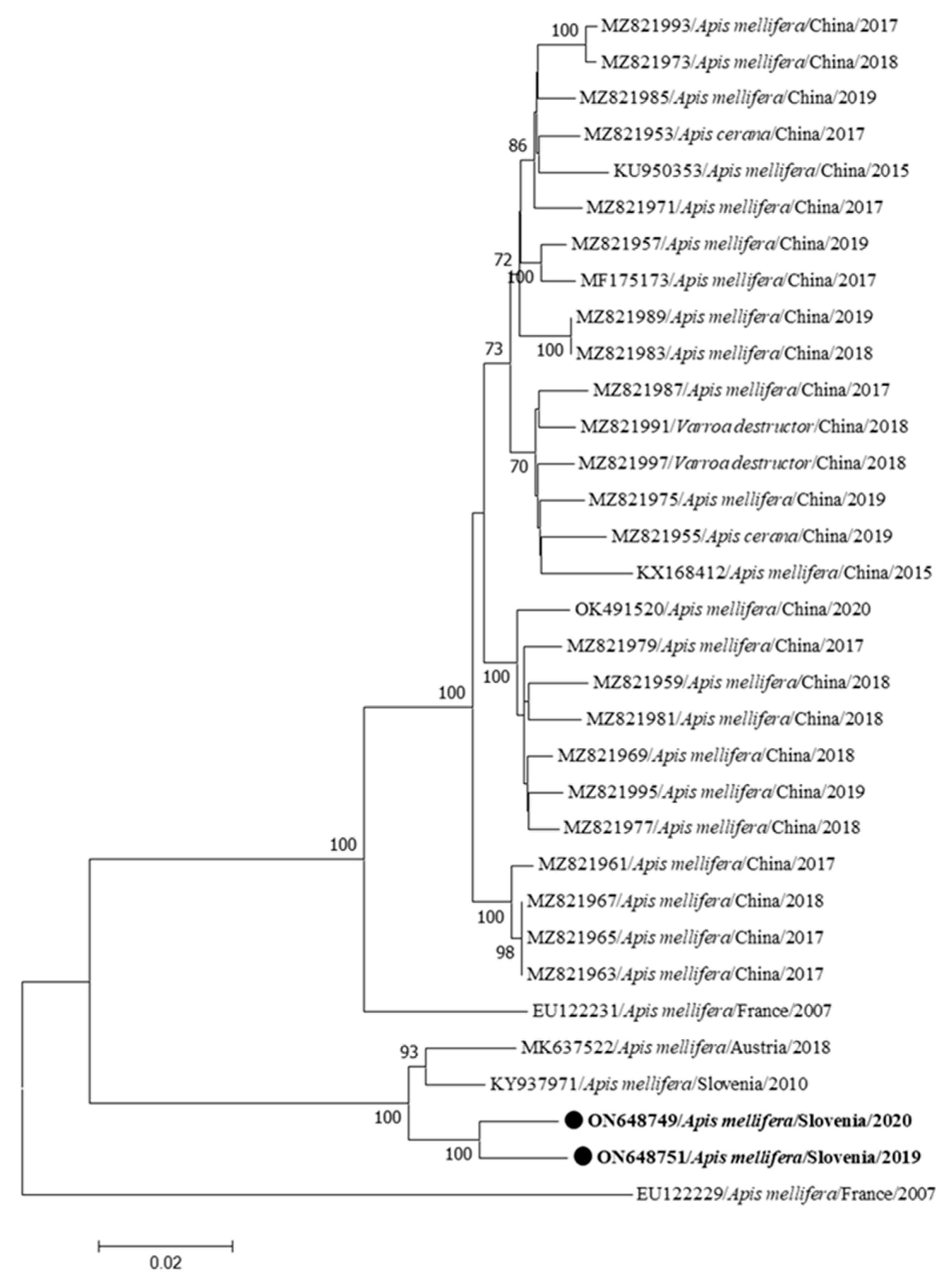

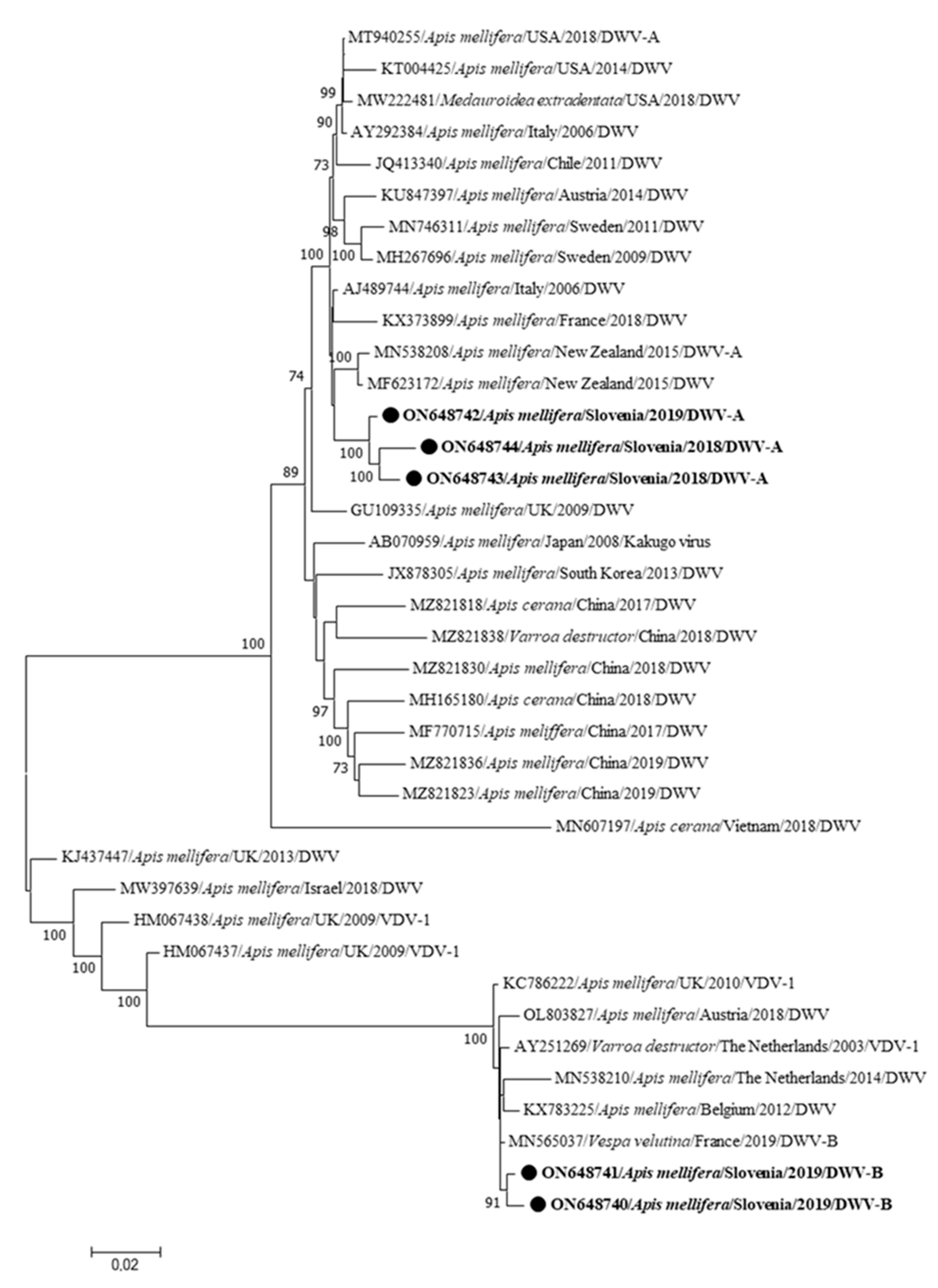
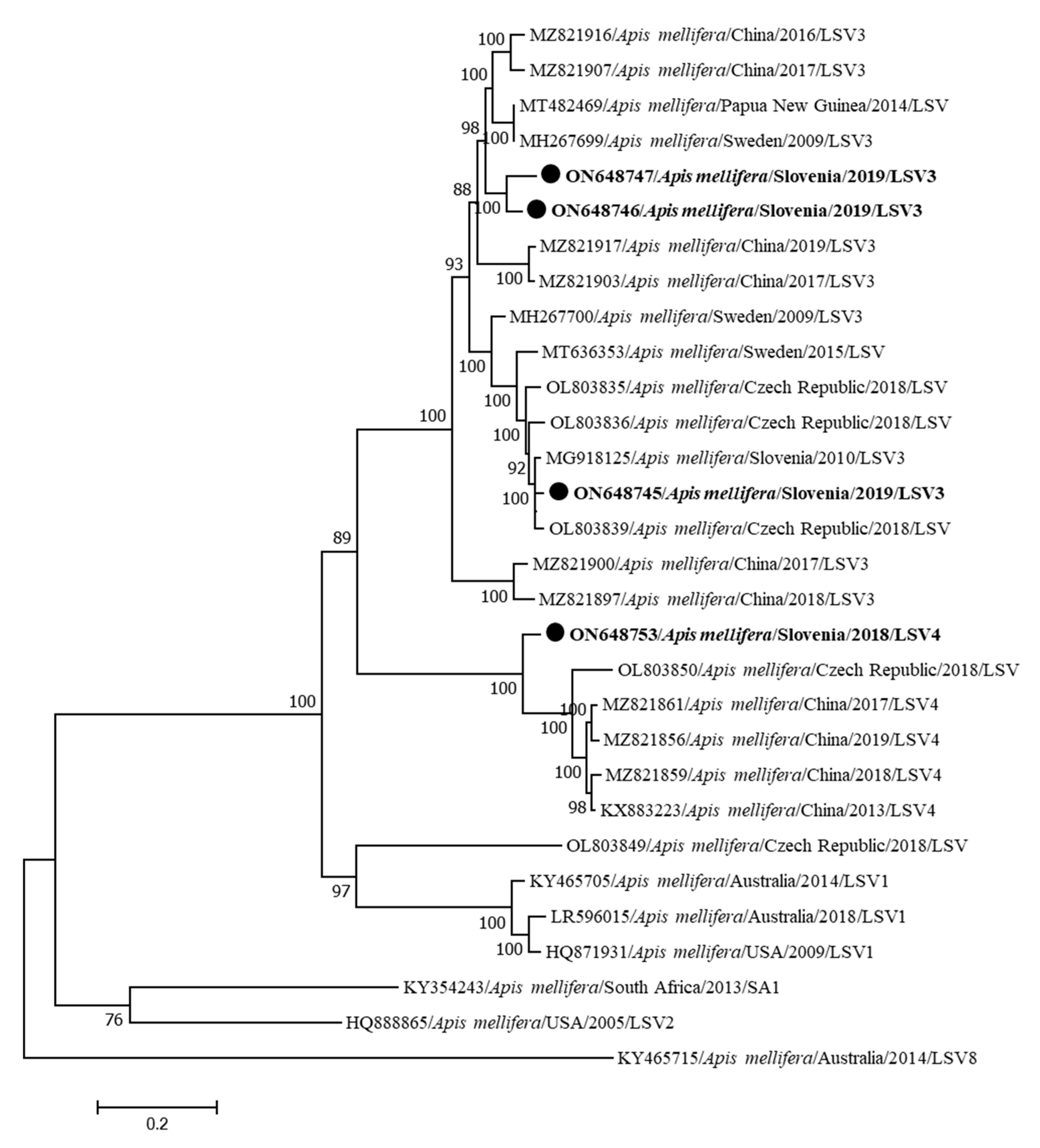
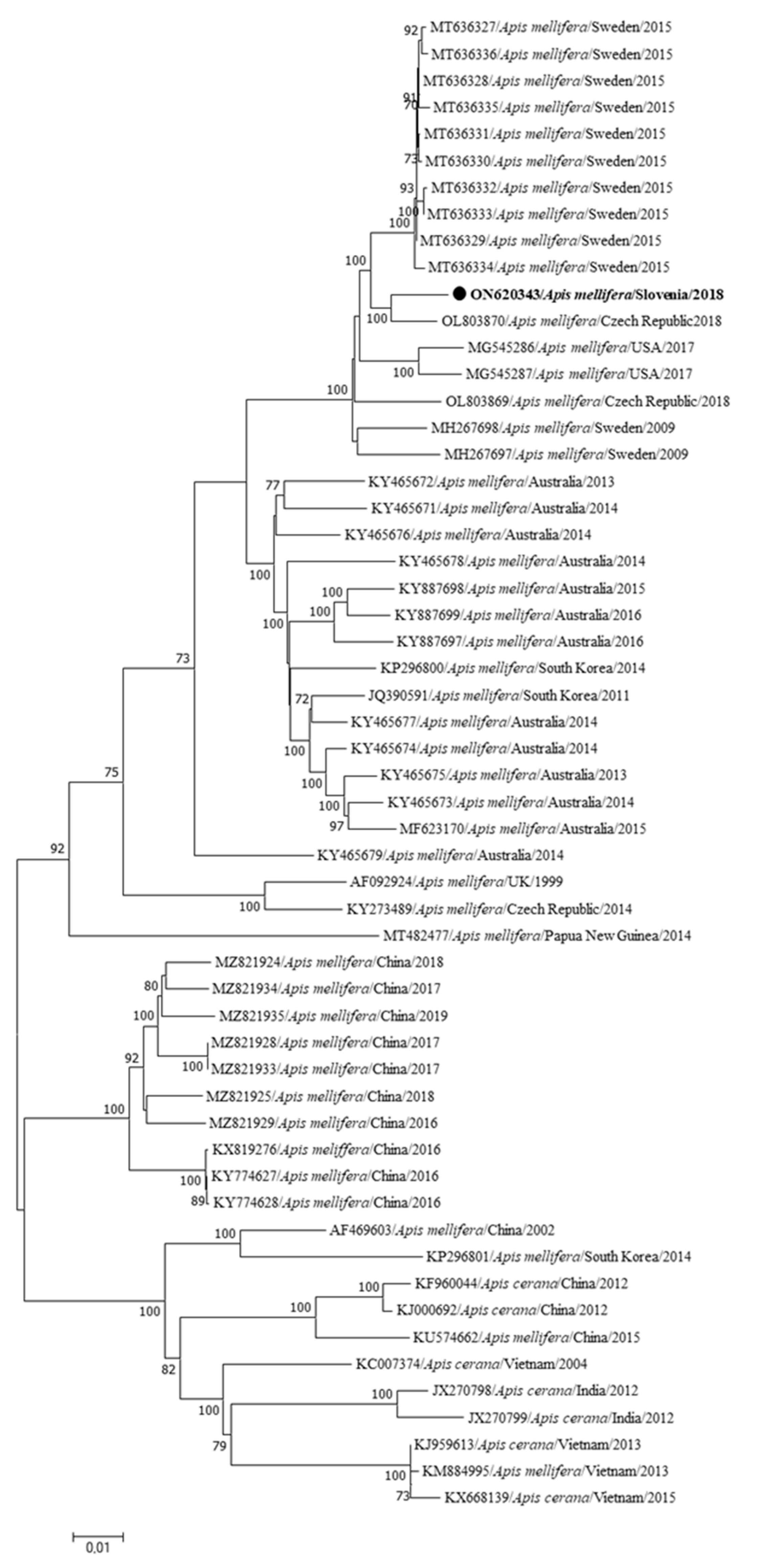


| Genome Name | Sample Name | Year/Month/Place of Collection | Clinical Status | Accession Number | Genome Length (bp) | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABPV 366/2020 | 366 | 2020/Jun/Mengeš | affected | ON453877 | 9457 | 100 |
| ABPV 377/2020 | 377 | 2020/Jul/Semič | affected | ON648739 | 9424 | 365 |
| ABPV 376/2020 | 376 | 2020/Jun/Žalec | affected | ON648748 | 9452 | 1787 |
| ABPV 386/2020 | 386 | 2020/Jul/Ljubljana | affected | ON648738 | 9440 | 57,446 |
| ARV-1 341/2019 | 341 | 2019/Feb/Videm | affected | ON620344 | 14,585 | 93 |
| BeeMLV LS13/2019 | LS13 | 2019/Nov/Ljubljana | healthy | ON648755 | 6411 | 6055 |
| BQCV 377/2020 | 377 | 2020/Jul/Semič | affected | ON648737 | 8451 | 35 |
| BQCV 336/2020 | 336 | 2020/Feb/Mirna Peč | affected | ON648735 | 8450 | 4676 |
| BQCV LS90/2019 | LS90 | 2019/Jul/Radovljica | affected | ON648736 | 8450 | 30 |
| CBPV RNA1 376/2020 | 376 | 2020/Jun/Žalec | affected | ON648749 | 3645 | 8964 |
| CBPV RNA2 376/2020 | 376 | 2020/Jun/Žalec | affected | ON648750 | 2272 | 8964 |
| CBPV RNA1 341/2019 | 341 | 2019/Feb/Videm | affected | ON648751 | 3617 | 8964 |
| CBPV RNA2 341/2019 | 341 | 2019/Feb/Videm | affected | ON648752 | 2272 | 8964 |
| DWV 341-2/2019 | 341 | 2019/Feb/Videm | affected | ON648742 | 10,145 | 5006 |
| DWV LS26/2018 | LS26 | 2018/Dec/Ljubljana | healthy | ON648744 | 9962 | 1575 |
| DWV LS13/2018 | LS13 | 2018/Nov/Ljubljana | healthy | ON648743 | 9647 | 7267 |
| DWV 341-1/2019 | 341 | 2019/Feb/Videm | affected | ON648741 | 10,126 | 31,035 |
| DWV 336/2019 | 336 | 2019/Feb/Mirna Peč | affected | ON648740 | 10,127 | 3342 |
| LSV3 LS74/2019 | LS74 | 2019/Mai/Ptuj | healthy | ON648746 | 5997 | 407 |
| LSV3 LS81/2019 | LS81 | 2019/Mai/Ljubljana | healthy | ON648747 | 6025 | 594 |
| LSV3 LS48/2019 | LS48 | 2019/Feb/Ljubljana | healthy | ON648745 | 5967 | 15,452 |
| LSV4 LS21/2018 | LS21 | 2018/Nov/M. Sobota | healthy | ON648753 | 5973 | 3375 |
| SBV LS20/2018 | LS20 | 2018/Nov/M.Sobota | healthy | ON620343 | 8787 | 30 |
| HPLV34 377/2020 | 377 | 2020/Jul/Semič | affected | ON648754 | 1460 | 6055 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šimenc Kramar, L.; Toplak, I. Identification of Twenty-Two New Complete Genome Sequences of Honeybee Viruses Detected in Apis mellifera carnica Worker Bees from Slovenia. Insects 2024, 15, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15110832
Šimenc Kramar L, Toplak I. Identification of Twenty-Two New Complete Genome Sequences of Honeybee Viruses Detected in Apis mellifera carnica Worker Bees from Slovenia. Insects. 2024; 15(11):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15110832
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠimenc Kramar, Laura, and Ivan Toplak. 2024. "Identification of Twenty-Two New Complete Genome Sequences of Honeybee Viruses Detected in Apis mellifera carnica Worker Bees from Slovenia" Insects 15, no. 11: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15110832
APA StyleŠimenc Kramar, L., & Toplak, I. (2024). Identification of Twenty-Two New Complete Genome Sequences of Honeybee Viruses Detected in Apis mellifera carnica Worker Bees from Slovenia. Insects, 15(11), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15110832






