A Revision of the Genus Argolis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae) from Asia †
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
| BMNH | The Natural History Museum, London, UK |
| BUCI | Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, India |
| CAU | Entomological Museum, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China |
| IZAS | Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China |
| MNHN | Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, France |
| NIAES | National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, Tsukuba, Japan |
| ZMUC | Natural History Museum of Denmark, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark |
3. Results
3.1. Argolis Stål, 1861
3.2. Key to the Asian Species of Argolis
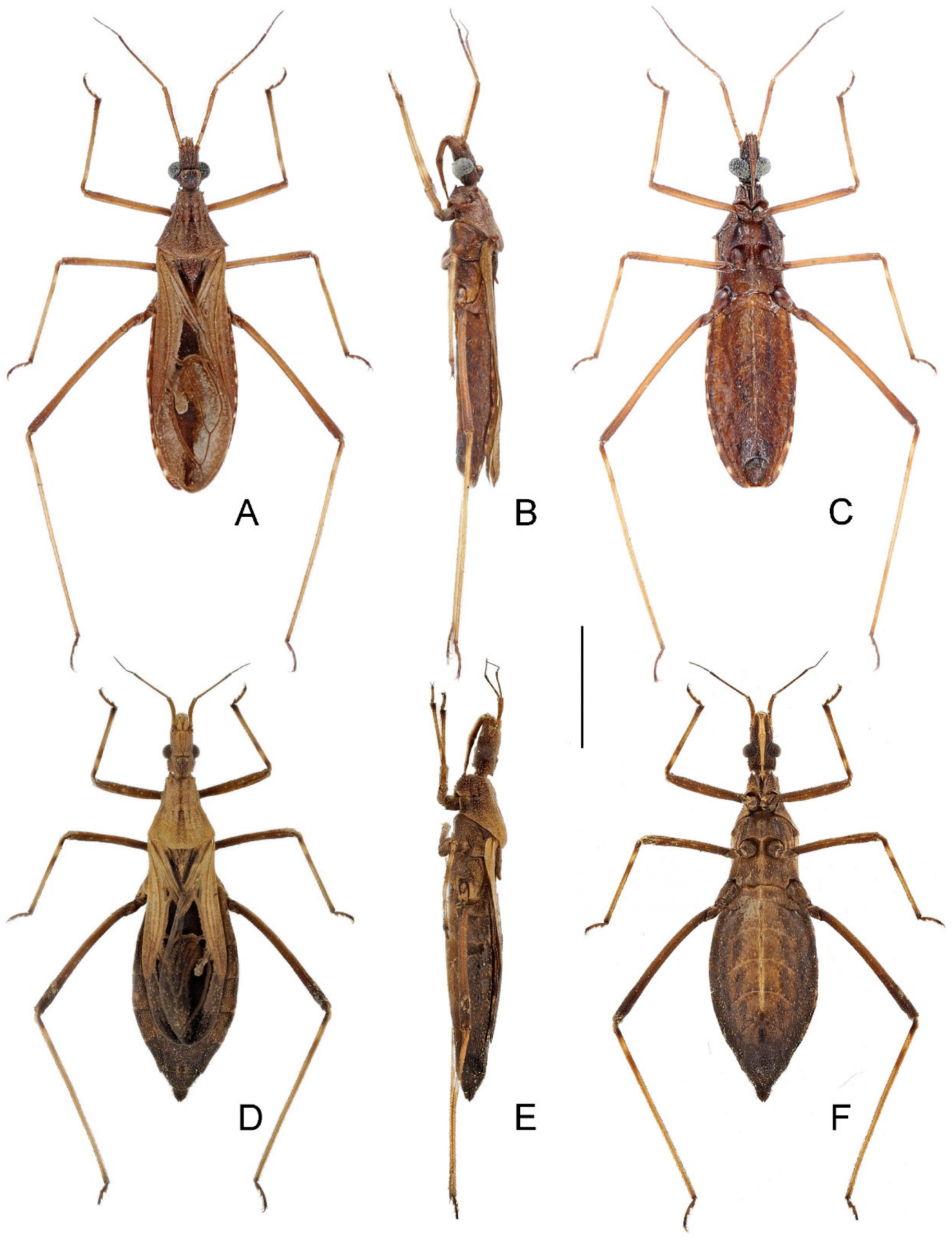
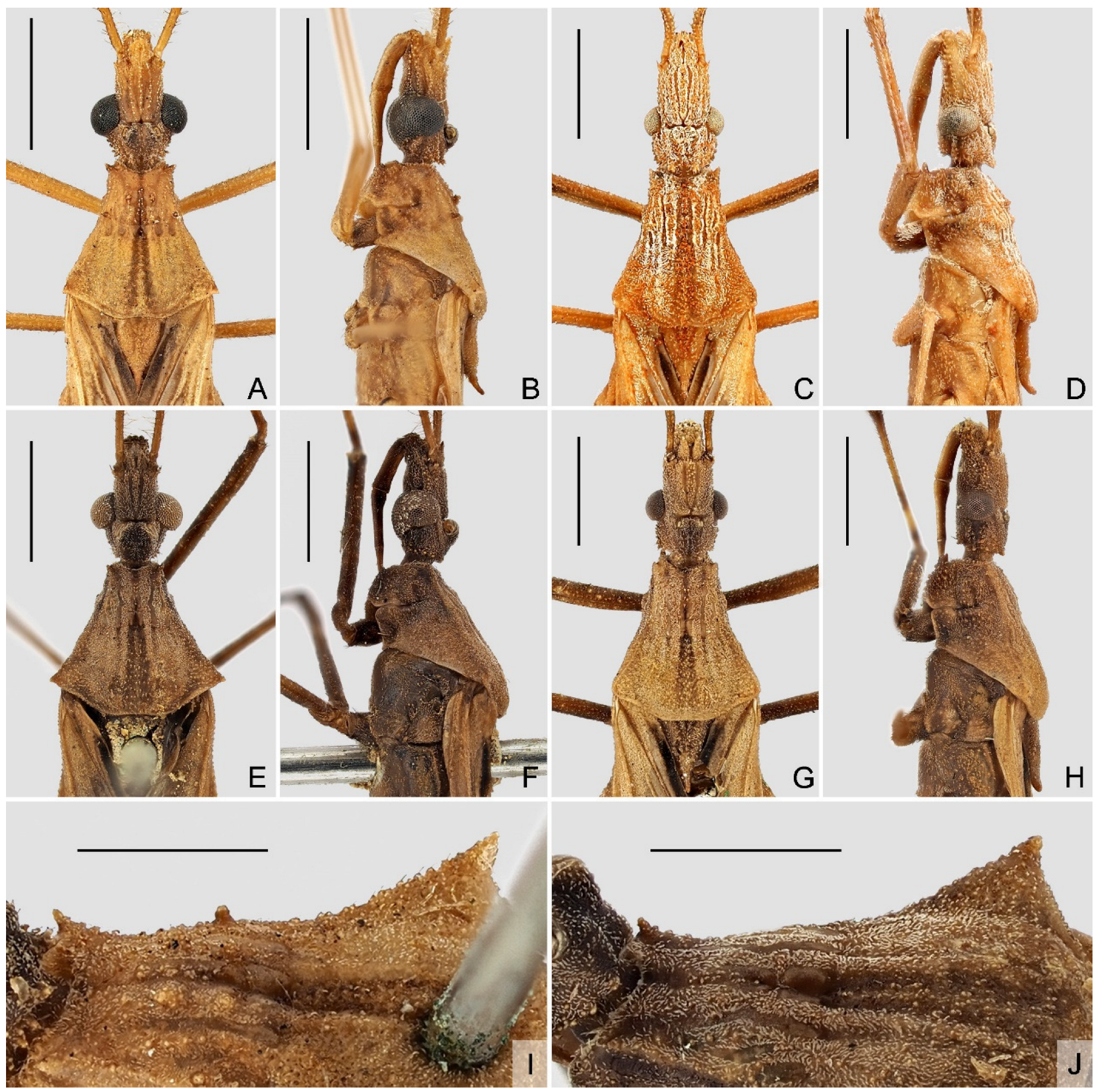
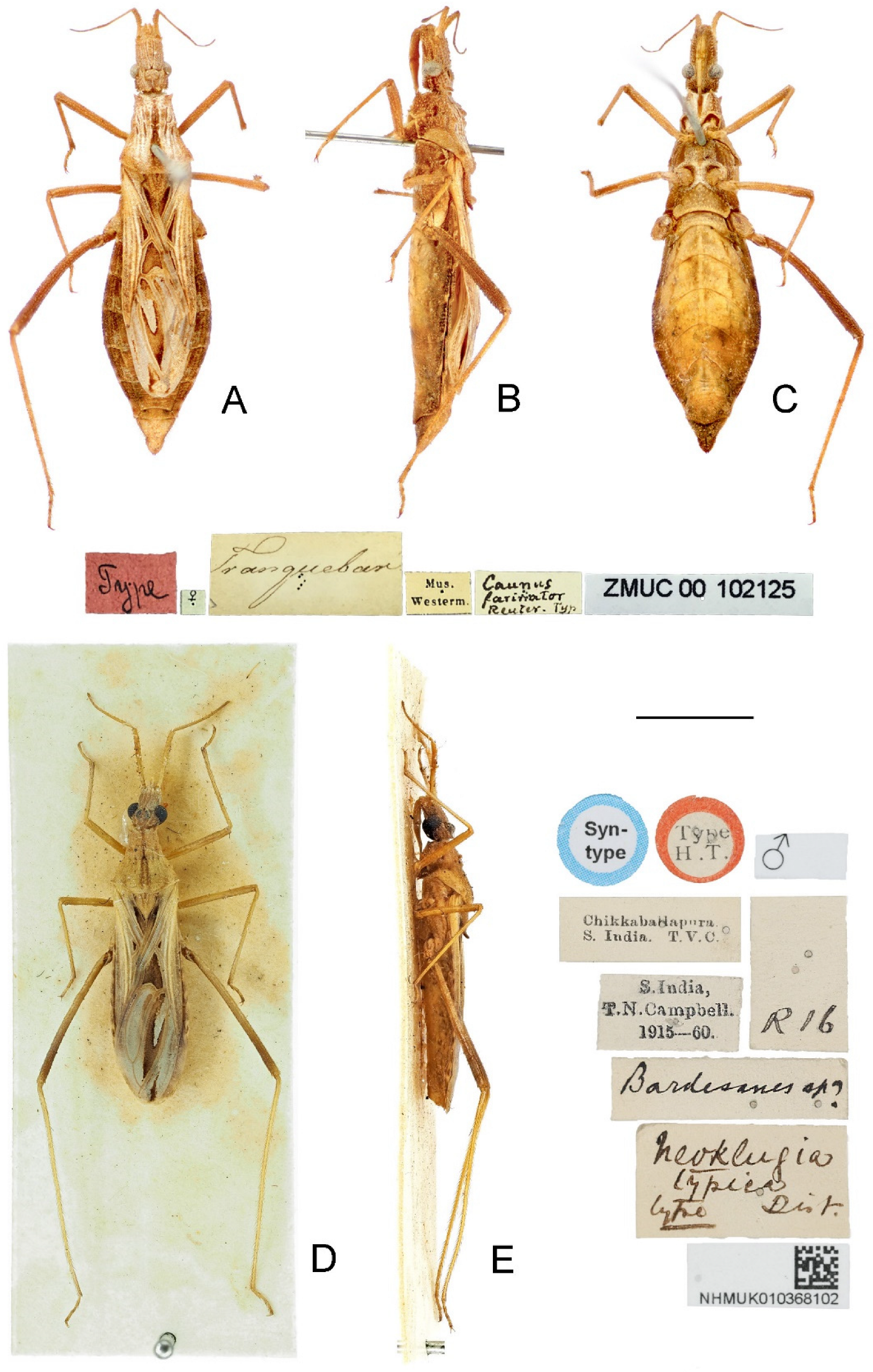
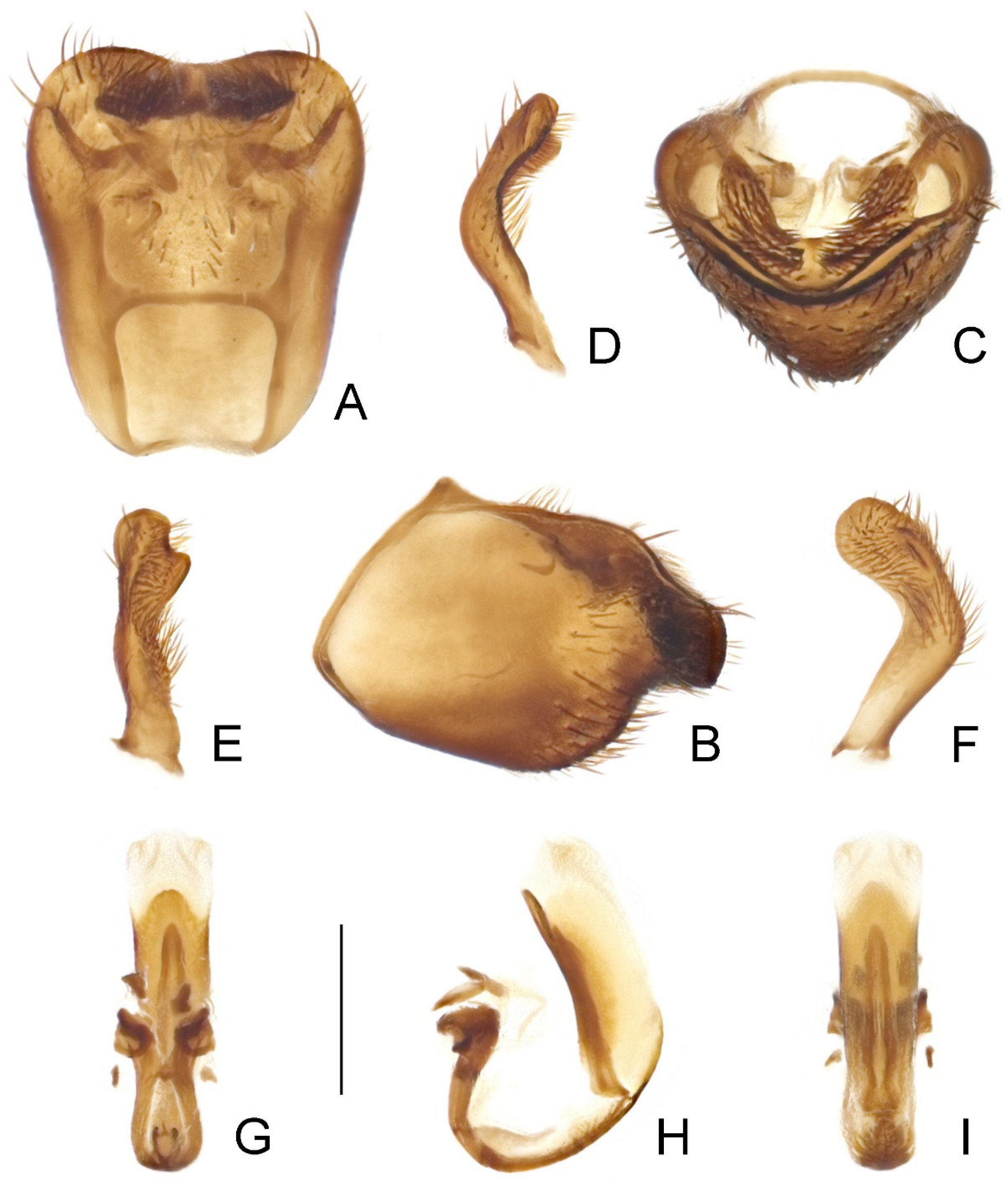
1 Body generally yellowish brown (Figure 1 and Figure 2); lateral margin of pronotum with one granulation at midpoint (Figure 5I); tibiae yellowish brown (Figure 2); ventral surface of pygophore not emarginate subapically in lateral view (Figure 7B).A. farinator (Reuter)
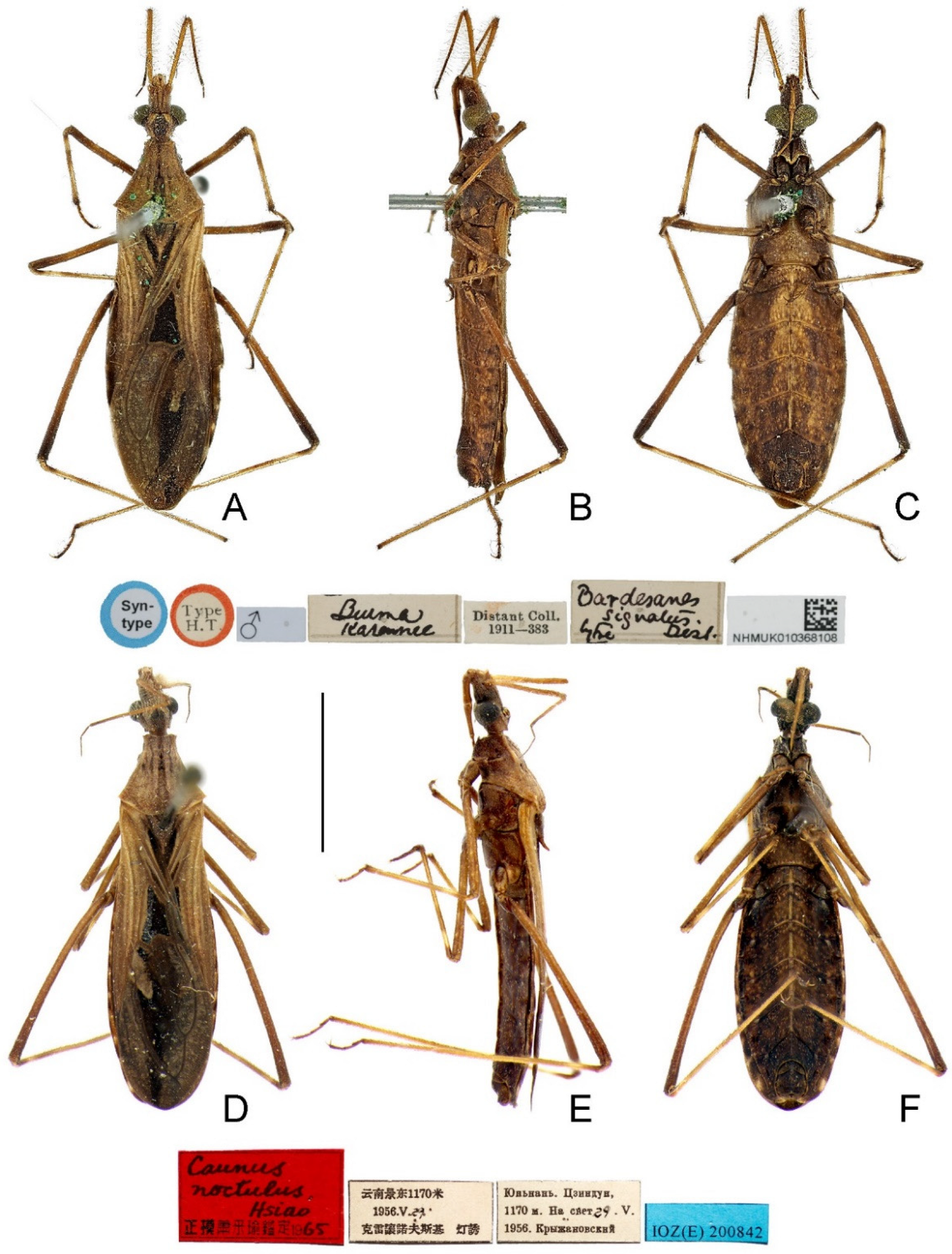
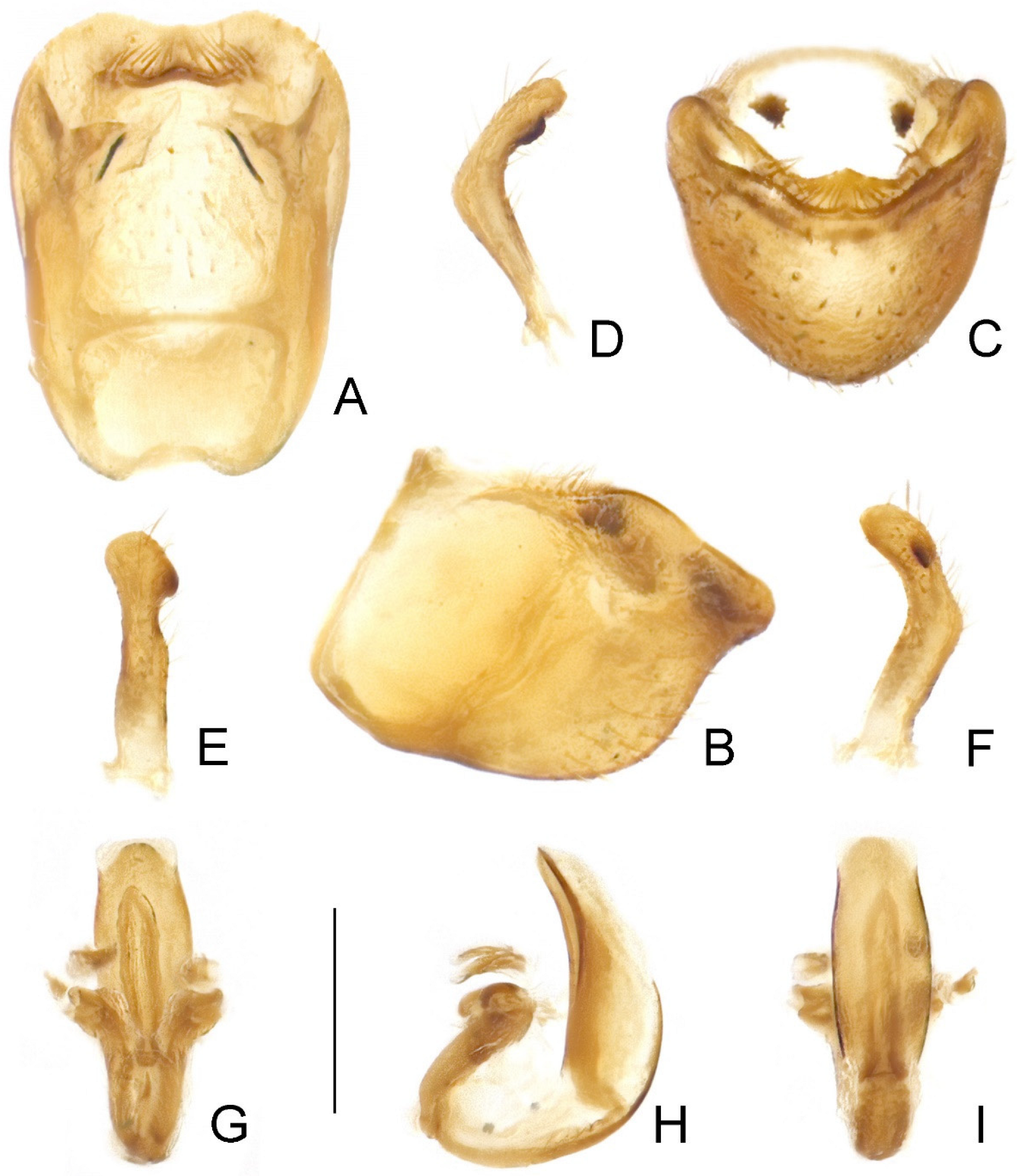
- Body generally dark brown (Figure 3 and Figure 4); lateral margin of pronotum simple, lacking granulation (Figure 5J); tibiae yellowish brown, each with one basal and one subbasal dark brown annuli (Figure 4); ventral surface of pygophore strongly emarginate subapically in lateral view (Figure 8B).A. signata (Distant), comb. nov.
3.3. Argolis farinator (Reuter, 1882)
3.4. Argolis signata (Distant, 1909), comb. nov.
4. Discussion
4.1. Sexual Dimorphism in Argolis
4.2. Evaluation of Bardesanes and Neoklugia
4.3. Systematic Relationships of Argolis
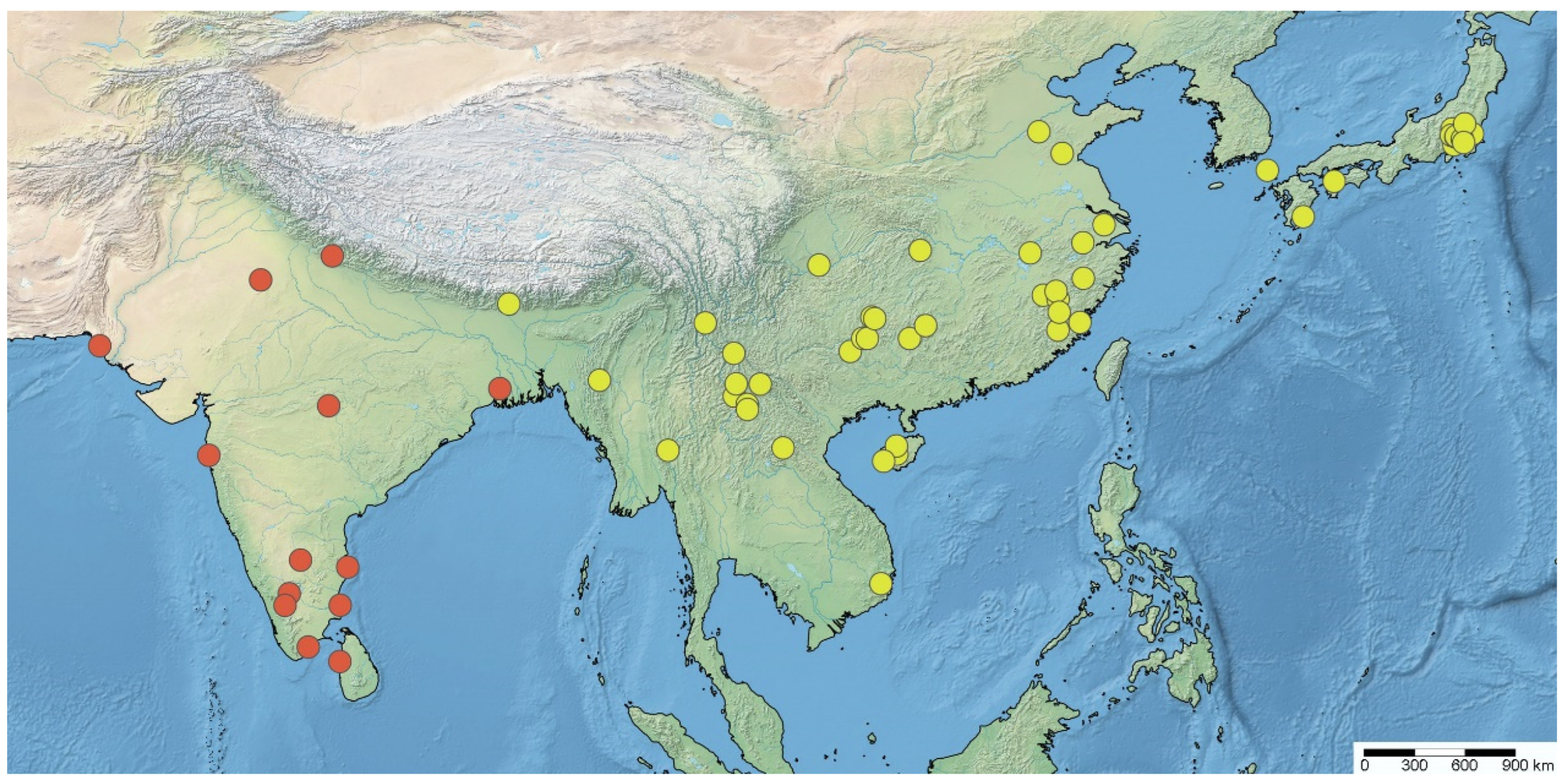
4.4. Distribution of Argolis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maldonado-Capriles, J. Systematic Catalogue of the Reduviidae of the World (Insecta: Heteroptera); A Special Edition of Caribbean Journal of Science: Mayagüez, Puerto Rico, 1990; pp. 1–694. [Google Scholar]
- Chłond, D. Planeocoris, a new genus of Stenopodainae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Reduviidae) from Madagascar. Zootaxa 2010, 2400, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Santana, H.R.; Oliveira, J.D. Pratigi aristeui, a new Neotropical genus and species of Stenopodainae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Reduviidae). Acta Entomol. Mus. Natl. Pragae 2016, 56, 491–506. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W. Notes on the genus Enoplocephala Miller (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae), with the description of a new species from Borneo. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2020, 68, 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W. Revision of the genus Dulitocoris Miller (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae), with the description of a new species from Borneo. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. (N.S.) 2020, 56, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhao, P.; Cai, W. Redescription of a little known assassin bug Caunus noctulus Hsiao (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae), with special reference to its sexual dimorphism. Zootaxa 2011, 2887, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiers, A. Faune de l’Empire Français. IX. Hémiptères Réduviidés de l’Afrique Noire; Éditions du Muséum: Paris, France, 1948; pp. 1–488. [Google Scholar]
- Villiers, A. Faune de Madagascar. XXVIII. Insects, Hémiptères, Reduviidae (1ère Partie); Office de la Recherche Scientifique et Technique Outre-Mer, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique: Paris, France, 1968; pp. 1–198. [Google Scholar]
- Stål, C. Miscellanea hemipterologica. Stettin. Entomol. Ztg. 1861, 22, 129–153. [Google Scholar]
- Stål, C. Hemiptera Africana. Tomus Tertius; Norstedtiana: Stockholm, Sweden, 1865; pp. 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Schouteden, H. Catalogues raisonnés de la faune entomologique du Congo Belge. Hémiptères—Réduviides. Fascicule 2. Ann. Mus. Congo Zool. 1931, 1, 89–162. [Google Scholar]
- Reuter, O.M. Monographia generis Oncocephalus Klug proximeque affinium. Acta Soc. Sci. Fenn. 1882, 12, 673–758. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, N.C.E. New Reduviidae in the collection of the British Museum (Natural History). II. J. Nat. Hist. 1950, 3, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, N.C.E. New Reduviidae in the collection of the British Museum (N.H.). VIII. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1952, 5, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiers, A. Mission zoologique de l’I.R.S.A.C. en Afrique orientale (P. Basilewsky et N. Leleup, 1957). LXXXIV. Hemiptera Reduviidae. Ann. Mus. Roy. Afr. Centr. 1962, 110, 454–477. [Google Scholar]
- Shorthouse, D.P. SimpleMappr, an Online Tool to Produce Publication-Quality Point Maps. Available online: https://www.simplemappr.net (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Weirauch, C. Cladistic analysis of Reduviidae (Heteroptera: Cimicomorpha) based on morphological characters. Syst. Entomol. 2008, 33, 229–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, F. Catalogue of the Specimens of Hemiptera Heteroptera in the Collection of the British Museum. Part VII; British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1873; pp. 1–213. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, F. Catalogue of the Specimens of Hemiptera Heteroptera in the Collection of the British Museum. Part VIII; British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1873; pp. 1–220. [Google Scholar]
- Stål, C. Enumeratio Hemipterorum. Bidrag till en förteckning ofver alla hittills kända Hemiptera, jemte systematiska meddelanden. 4. Kongliga Sven. Vetensk. Akad. Handl. (N.F.) 1874, 12, 1–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lethierry, L.; Severin, G. Catalogue Général des Hémiptères. Tome III. Hétéroptères, Tingidae, Phymatidae, Aradidae, Hebridae, Hydrometridae, Henicocephalidae, Reduviidae, Saldidae, Apophilidae, Ceratocombidae, Cimicidae, Anthocoridae; Friedländer & Fils: Berlin, Germany, 1896; pp. 1–275. [Google Scholar]
- Jeannel, R. Voyage de Ch. Alluaud et R. Jeannel en Afrique Orientale (1911–1912). Résultats Scientifiques. III. Henicocephalidae et Reduviidae; Lhomme: Paris, France, 1919; pp. 131–313. [Google Scholar]
- Putshkov, V.G. On the nomenclature of reduviid bugs (Heteroptera, Reduviidae). Vestn. Zool. 1985, 4, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, D.R. Status of the name Argolis in Insecta. Zootaxa 2018, 4471, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouteden, H. Pentatomidae et Reduviidae novae africanae. Wien. Entomol. Ztg. 1902, 21, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Distant, W.L. The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Rhynchota. Vol. II (Heteroptera); Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1903–1904; pp. 1–503. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, T.-Y. New and little known species of Stenopodainae (Heteroptera: Reduviidae) from China. Acta Entomol. Sin. 1977, 20, 68–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, T.-Y.; Ren, S.-Z. Reduviidae. In A Handbook for the Determination of the Chinese Hemiptera-Heteroptera. Vol. II; Hsiao, T.-Y., Ren, S.-Z., Zheng, L.-Y., Jing, H.-L., Zou, H.-G., Liu, S.-L., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1981; pp. 390–538. [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone, D.; Ravichandran, G. Keys to the sub-families and their genera of the non-tibiaroliate group of assassin bugs (Heteroptera: Reduviidae) of southern India. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1991, 88, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Putshkov, P.V.; Putshkov, V.G. Family Reduviidae Latreille, 1807—Assassin-bugs. In Catalogue of the Heteroptera of the Palaearctic Region. Vol. 2; Aukema, B., Rieger, C., Eds.; Netherlands Entomological Society: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 148–265. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, Y.C.; Kauntey, R.; Gupta, P. Catalogue of Stenopodinae species from India. Flora Fauna 2005, 11, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, D.P. A checklist of Indian assassin bugs (Insecta: Heteroptera: Reduviidae) with taxonomic status, distribution and diagnostic morphological characteristics. Zoos’ Print J. 2006, 21, 2388–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Miyamoto, S. Family Reduviidae Latreille, 1807. Assassin bugs. In A Field Guide to Japanese Bugs. Terrestrial Heteropterans. III; Ishikawa, T., Takai, M., Yasunaga, T., Eds.; Zenkoku Noson Kyoiku Kyokai, Publishing Company Limited: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; pp. 231–288. [Google Scholar]
- Aukema, B.; Rieger, C.; Rabitsch, W. Catalogue of the Heteroptera of the Palaearctic Region. Volume 6. Supplement; Netherlands Entomological Society: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. i–xxiv, 1–629. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T. Family Reduviidae. In Catalogue of the Insects of Japan. Vol. 4. Paraneoptera (Psocodea, Thysanoptera, Hemiptera); Hayashi, M., Tomokuni, M., Yoshizawa, K., Ishikawa, T., Eds.; Entomological Society of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 439–452. [Google Scholar]
- Distant, W.L. Rhynchota (Heteroptera) from British India. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Belg. 1909, 53, 360–376. [Google Scholar]
- Distant, W.L. The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Rhynchota. Vol. V (Heteroptera: Appendix); Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1910; pp. 1–362. [Google Scholar]
- Distant, W.L. Descriptions of new species and genera of the Heteropterous family Reduviidae from British India. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1919, 4, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boisduval, J.B.A.D. Histoire Naturelle des Insectes. Lépidoptères. Species Général des Lépidoptères. Explication des Planches Composant les Deux Livraisons Qui Accompagnent le 1er Vol; Librairie Encyclopédique de Roret: Paris, France, 1836; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone, D.; Murugan, C.; Ravichandran, G. Diversity in the functional organisation of the mandibular styles of assassin bugs (Heteroptera: Reduviidae). J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1998, 95, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, D.P. Chapter 4: Biodiversity of India assassin bugs (Insecta: Hemiptera: Reduviidae). In Conservation of Rainforests in India; Gupta, A.K., Kumar, A., Ramakantha, V., Eds.; WII-ENVIS Centre for Wildlife and Protected Areas: Dehradun, India, 2003; pp. 69–104. [Google Scholar]
- Thanasingh, P.D.; Ambrose, D.P. Biodiversity and distribution of entomofauna in three ecosystems in Thoothukudi District, Tamil Nadu. In Insect Pest Management: A Current Scenario; Ambrose, D.P., Ed.; Entomology Research Unit, St. Xavier’s College: Palayamkottai, India, 2011; pp. 38–57. [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone, D.; Ravichandran, G. Two new species of Stenopodinae Stal from Palghat Gap (Heteroptera: Reduviidae). Hexapoda 1989, 1, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran, G.; Livingstone, D.; Muthukrishnan, J. Functional aspect of the intromittent organs of non-tibiaroliate assassin bugs, Heteroptera: Reduviidae. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1998, 95, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, D.P. The status of biosystematics of Indian Reduviidae (Hemiptera: Heteroptera). In Perspectives on Biosystematics and Biodiversity: Prof. T.C. Narendran Commemoration Volume; Rajmohana, K., Sudheer, K., Girish Kumar, P., Santhosh, S., Eds.; University of Calicut: Kerala, India, 2004; pp. 441–459. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, H. Notes on Hemiptera from Tsushima. Gekkan-Mushi 1980, 117, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, K.; Kushwaha, S.; Biswas, B.; Mukherjee, P.; Bal, A. Redescription of Bardesanes signatus Distant (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) first record from India. Rec. Zool. Surv. India 2013, 113, 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shobharani, M.; Viraktamath, C.A.; Webb, M.D. Review of the leafhopper genus Penthimia Germar (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Deltocephalinae) from the Indian subcontinent with description of seven new species. Zootaxa 2018, 4369, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salini, S.; Gracy, R.G.; Akoijam, R.; Rabbani, M.K.; David, K.J.; Roca-Cusachs, M. Revision of Acesines Stål and Dunnius Distant, resurrection of Mycterizon Breddin (Hemiptera, Heteroptera, Pentatomidae, Pentatominae), and description of a new species from India. ZooKeys 2023, 1148, 79–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.R. Bursal glands of Reduviidae (Insecta—Heteroptera). Proc. Anim. Sci. 1988, 97, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Pu, T. Economic Insect Iconography of Guangxi. Predaceous Insects; Guangxi Press of Science and Technology: Nanning, China, 1990; pp. 1–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S. An Iconography of Hemiptera-Heteroptera Eggs in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 1–118. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S. Reduviidae. In Fauna of Shandong Forest Insect; Fauna of Shandong Forest Insect Edition Committee, Ed.; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Jin, G. A list of Hemiptera and their hosts from the forest regions in Lishui Prefecture, Zhejiang Province, China. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 1995, 17, 204–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; Lin, Q.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Hemiptera: Reduviidae. In Fauna of Insects, Fujian Province of China. Vol. 2; Huang, B., Ed.; Fujian Science & Technology Publishing House: Fuzhou, China, 1999; pp. 163–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D.; Shi, M.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, C. Appendices II. List of insects of Taohongling Nature Reserve. In Jiangxi Taohongling Seka Deer Reserve; Jiangxi Taohongling Seka Deer Reserve, Ed.; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 164–179. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, L.Z. List of Chinese Insects. Vol. I; Zhongshan University Press: Guangzhou, China, 2000; pp. 1–448. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Chen, R. Insect Resources. In Report of Comprehensive Scientific Investigation in Mangdangshan Nature Reserve, Fujian Province; Lin, P., Ed.; Xiamen University Press: Xiamen, China, 2003; pp. 193–266. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F. Insect Resources. In Report of Comprehensive Scientific Investigation in Daiyunshan Nature Reserve, Fujian Province; Lin, P., Ed.; Xiamen University Press: Xiamen, China, 2003; pp. 173–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T.; Cai, W.; Tomokuni, M. Assassin bugs (Heteroptera, Reduviidae) newly recorded from Japan. Jpn. J. Syst. Entomol. 2005, 11, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, P.; Cai, W. Investigation on insects of Reduviidae in Leigongshan National Nature Reserve. Guizhou For. Sci. Technol. 2006, 34, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.-Z.; Bai, M.; Wu, H.; Ji, L.-Q. Catalogue of the Insect Type Specimens Deposited in China. Vol. 1; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–792. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Cai, W. Reduviidae. In Insects from Leigongshan Landscape; Li, Z., Yang, M., Jin, D., Eds.; Guizhou Science and Technology Publishing House: Guiyang, China, 2007; pp. 189–203. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J. Notes on Hemiptera from Songyang County, Zhejiang Province, China. Jiangxi Plant Prot. 2009, 32, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. List of Wildlife in Guizhou; Guizhou Science and Technology Publishing House: Guiyang, China, 2011; pp. 1–678. [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa, M. Review of Reduviidae in Saitama Prefecture. Yosegaki 2012, 145, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Okuda, K. Caunus noctulus Hsiao, 1977, a latest discovery in about four decades in Japan, with the first record from Kyushu. Rostria 2012, 54, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Okuda, K.; Uchida, H. Collections records of Caunus noctulus in Saitama Prefecture. Yosegaki 2019, 172, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, M.; Okuda, K. A new record of Caunus noctulus (Heteroptera, Reduviidae, Stenopodainae) from Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. Rostria 2020, 65, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Okuda, K. Heteroptera (Insecta: Hemiptera) from Midori—Ku, Saitama City, Saitama Prefecture, Japan. Bull. Saitama Mus. Nat. Hist. (N.S.) 2020, 14, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Okuda, K. Assassin bug travels—The world of Reduviidae that you don’t know. Yosegaki 2020, 177, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa, M. Hemiptera of Saitama. In The Fauna of Saitama Prefecture; Saitama Prefecture Board of Education, Ed.; Saitama Prefecture Board of Education: Urawa, Japan, 1978; pp. 355–381. [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa, M. The reduviid-bugs (Reduviidae, Heteroptera) distributed in Saitama Prefecture. I. Emesinae, Stenopodainae and Peiratinae. Bull. Saitama Mus. Nat. Hist. 1990, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wygodzinsky, P.W. A Monograph of the Emesinae (Reduviidae, Hemiptera). Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1966, 133, 1–614. [Google Scholar]
- Forthman, M.; Weirauch, C. Millipede assassins and allies (Heteroptera: Reduviidae: Ectrichodiinae, Tribelocephalinae): Total evidence phylogeny, revised classification and evolution of sexual dimorphism. Syst. Entomol. 2017, 42, 575–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weirauch, C.; Forthman, M.; Grebennikov, V.; Baňař, P. From Eastern Arc Mountains to extreme sexual dimorphism: Systematics of the enigmatic assassin bug genus Xenocaucus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Tribelocephalinae). Org. Divers. Evol. 2017, 17, 421–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W. Taxonomic review of Xenorhyncocoris Miller (Heteroptera: Reduviidae: Ectrichodiinae), with description of X. attractivus sp. nov. and notes on sexual dimorphism of the genus. Eur. J. Taxon. 2021, 746, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacchi, J.C. Aportes a la morfologia y taxonomia de los stenopodainos americanos. (Heteroptera, Reduviidae). II. Consideraciones acerca de la subfamilia. Phys. (Secc. C) 1987, 45, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Blinn, R.L. Arenaeocoris evervatus (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae), a new genus and species from the southeastern United States. Zootaxa 2012, 3478, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouteden, H. Stenopodinae novae africanae (Hem. Reduv.). Rev. Zool. Bot. Afr. 1951, 45, 144–156. [Google Scholar]
- Stål, C. Hemiptera från Kafferlandet. Öfvers. Kongl. Vetensk. Akad. Förh. 1855, 12, 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Villiers, A. Hémiptères Réduviidés, Phymatidés et Hénicocéphalidés de Côte d’Ivoire. Bull. Inst. Fond. Afr. Noire (Sér. A) 1965, 27, 1151–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Villiers, A. La Réserve Naturelle Intégrale du Mont Nimba. XXV. Hemiptera Reduviidae. Mém. Inst. Franç. Afr. Noire 1963, 66, 479–565. [Google Scholar]
- Forthman, M.; Weirauch, C. Phylogenetics and biogeography of the endemic Madagascan millipede assassin bugs (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Ectrichodiinae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 100, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.S.; Weirauch, C. Uncovering hidden diversity: Phylogeny and taxonomy of Physoderinae (Reduviidae, Heteroptera), with emphasis on Physoderes Westwood in the Oriental and Australasian regions. Eur. J. Taxon. 2017, 341, 1–118. [Google Scholar]





| Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|
| General habitus | Elongate oval | Subfusiform |
| Postocular region of head | Gradually converging posteriorly | Nearly parallel-sided or only weakly converging posteriorly |
| Eye | Large, nearly touching each other in ventral view | Small, far removed from each other in ventral view |
| Ocellus | Distinctly elevated | Slightly elevated |
| Antennal scape | Longer than head, straight, strongly hairy | Shorter than head, curve, finely hairy |
| Antennal pedicel | Strongly hairy | Finely hairy |
| Pronotum | Wider than long, anterior lobe distinctly shorter than posterior lobe | Longer than wide, anterior lobe slightly shorter than posterior lobe |
| Humeral angles of pronotum | Acute, slightly to distinctly protruding laterally | Blunt, angulated or acute, weakly protruding laterally |
| Hind femur | Reaching apex of abdomen | Not reaching apex of abdomen |
| Hemelytron | Reaching or slightly surpassing apex of abdomen | Far removed from apex of abdomen |
| Abdomen | Elongate oval | Subfusiform |
| Intersegment suture between abdominal sternites VI and VII | Widely curved anteriorly | Sharply incised anteriorly at midpoint |
| Argolis farinator | Argolis signata, comb. nov. | |
|---|---|---|
| General body color | Yellowish brown | Dark brown |
| Setigerous tubercles on head and prothorax | Prominent | Minute |
| Ratio of anteocular and postocular regions of head | More than 2.7 times | Less than 2.2 times |
| Tubercles on posterior head margin | Prominent | Blunt |
| Granulations on disc of pronotum | Two distinct pairs | Two indistinct pairs |
| Granulations on lateral margin of pronotum | Present | Absent |
| Coloration of femur | Fore and mid femora yellowish brown, hind femur dark brown | Brown to dark brown |
| Coloration of tibia | Uniformly yellowish brown | Yellowish brown with basal and subbasal annuli |
| Coloration of hemelytron | Coriaceous portion yellowish brown, membrane pale greyish brown | Coriaceous portion brown, membrane dark greyish brown |
| Cubital cell of hemelytron | Shorter than half of length of apical external cell | Longer than half of length of apical external cell |
| Pygophore | Finely expanded in dorsal view, ventral surface not emarginate subapically in lateral view | Distinctly expanded in dorsal view, ventral surface strongly emarginate subapically in lateral view |
| Paramere | Relatively slender, with a short subapical keel | Relatively stout, with a wide subapical keel enclosing an arc with apex of paramere |
| Phallus | Basal plate arms gradually divergent apically, struts simply curved at bases | Basal plate arms widely separated at base and slightly convergent apically, struts bisinuate at bases |
| Abdominal tergite IX in female | Apical half relatively broad | Apical half relatively narrow |
| Valvula II | Apically acute | Apically blunt |
| Species | Distribution | References |
|---|---|---|
| Argolis acuta Schouteden, 1951 | AF: DR Congo | [80] |
| Argolis bergrothi Schouteden, 1902 | AF: DR Congo | [11] |
| Argolis calabarensis (Stål, 1858) | AF: Benin, DR Congo, Guinea, Nigeria, Togo | [7] |
| Argolis capensis (Stål, 1855) | AF: South Africa | [81] |
| Argolis dolichomera (Reuter, 1882) | AF: South Africa | [12] |
| Argolis farinator (Reuter, 1882) | OR: India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka | Present study |
| Argolis lamtoensis Villiers, 1965 | AF: Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea | [82] |
| Argolis meloui Villiers, 1948 | AF: DR Congo, Niger, Senegal, Tchad | [7] |
| Argolis moniliata Miller, 1950 | AF: Uganda | [13] |
| Argolis nigrofasciata Villiers, 1963 | AF: Guinea | [83] |
| Argolis pedestris Miller, 1952 | AF: South Africa | [14] |
| Argolis proxima Schouteden, 1902 | AF: Congo, DR Congo | [7,11] |
| Argolis seyrigi (Villiers, 1951) | AF: Madagascar | [8] |
| Argolis signata (Distant, 1909), comb. nov. | OR: China, India, Laos, Myanmar, Vietnam; PA: Japan | Present study |
| Argolis ugandensis Villiers, 1962 | AF: Uganda | [15] |
| Argolis villiersi Schouteden, 1951 | AF: Angola, DR Congo | [1,80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Webb, M.D.; Cai, W. A Revision of the Genus Argolis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae) from Asia. Insects 2023, 14, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14080680
Chen Z, Webb MD, Cai W. A Revision of the Genus Argolis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae) from Asia. Insects. 2023; 14(8):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14080680
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhuo, Michael D. Webb, and Wanzhi Cai. 2023. "A Revision of the Genus Argolis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae) from Asia" Insects 14, no. 8: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14080680
APA StyleChen, Z., Webb, M. D., & Cai, W. (2023). A Revision of the Genus Argolis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Stenopodainae) from Asia. Insects, 14(8), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14080680







