The Impact of Hydromorphological Alterations on Mayfly Assemblages of a Mid-Sized Lowland River in South-Eastern Europe
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
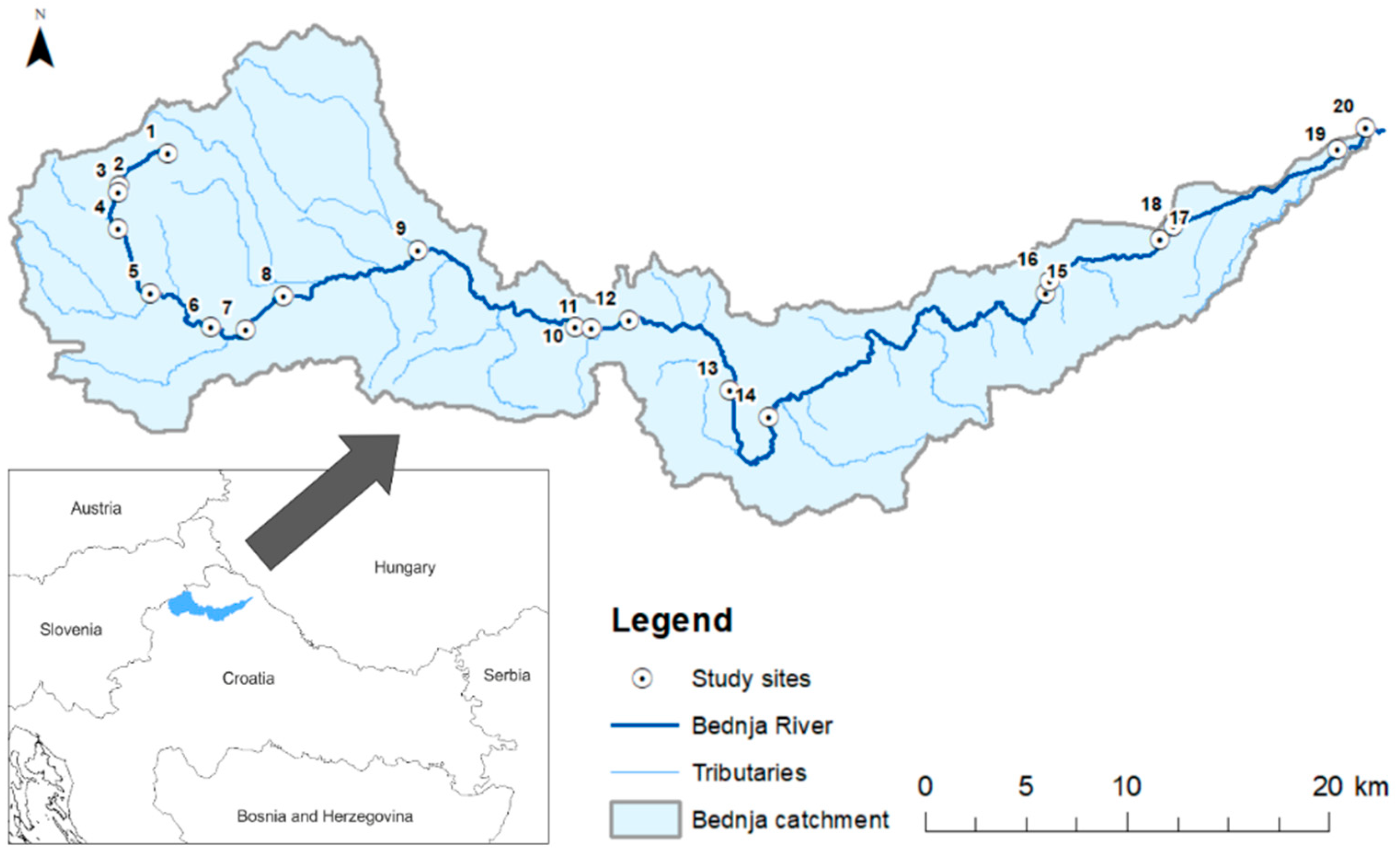
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Environmental Variables
2.3. Mayfly Sampling
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Variables
3.2. Water Velocity and Water Depth in Studied Microhabitats
3.3. Mayfly Assemblages
3.4. Mayflies and Environmental Variables
3.5. Mayfly Species and Microhabitats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brookes, A. Channelized Rivers: Perspectives for Environmental Management; Wiley: Chichester, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 1–326. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, P.J.; Fox, P.; Everard, M.; Holmes, N.T.H.; Dawson, F.H. River Habitat Survey: A New System for Classifying Rivers According to Their Habitat Quality. In Freshwater Quality: Defining the Indefinable; Boon, P.J., Howell, D.L., Eds.; HMSO: Edinburgh, UK, 1997; pp. 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, A.; Hering, D.; Feld, C.K.; Rolauffs, P. A New Method for Assessing the Impact of Hydromorphological Degradation on the Macroinvertebrate Fauna of Five German Stream Types. Hydrobiologia 2004, 516, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanič, G. Hydromorphological Degradation Impact on Benthic Invertebrates in Large Rivers in Slovenia. Hydrobiologia 2014, 729, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erba, S.; Buffagni, A.; Holmes, N.; O’Hare, M.; Scarlett, P.; Stenico, A. Preliminary Testing of River Habitat Survey Features for the Aims of the WFD Hydro-Morphological Assessment: An Overview from the STAR Project. Hydrobiologia 2006, 566, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, C.K.; Hering, D. Community Structure or Function: Effects of Environmental Stress on Benthic Macroinverte-Brates at Different Spatial Scales. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1380–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanič, G.; Mihaljević, Z.; Petkovska, V.; Pavlin Urbanič, M. Disentangling the Effects of Multiple Stressors on Large Rivers Using Benthic Invertebrates—A Study of Southeastern European Large Rivers with Implications for Management. Water 2020, 12, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinegger, R.; Trautwein, C.; Melcher, A.; Schmutz, S. Multiple Human Pressures and Their Spatial Patterns in European Running Waters. Water Environ. J. 2012, 26, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsák, M.; Bojková, J.; Zahrádková, S.; Omesová, M.; Helešic, J. Impact of Reservoirs and Channelization on Lowland River Macroinvertebrates: A Case Study from Central Europe. Limnologica 2009, 39, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, M.; Brittain, J.E. Order Ephemeroptera. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates: Ecology and General Biology, 4th ed.; Thorp, J., Rodgers, D.C., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 873–891. [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind, E.; Soldán, T. The Mayflies of Europe (Ephemeroptera); Apollo Books: Ollerup, Denmark, 2012; pp. 1–781. [Google Scholar]
- Vilenica, M.; Previšić, A.; Ivković, M.; Popijač, A.; Vučković, I.; Kučinić, M.; Kerovec, M.; Gattolliat, J.-L.; Sartori, M.; Mihaljević, Z. Mayfly (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) Assemblages of a Regulated Perennial Mediterranean River System in the Western Balkans. Biologia 2016, 71, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Mičetić Stanković, V.; Sartori, M.; Kučinić, M.; Mihaljević, Z. Environmental Factors Affecting Mayfly Assemblages in Tufa-Depositing Habitats of the Dinaric Karst. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vilenica, M.; Brigić, A.; Sartori, M.; Mihaljević, Z. Microhabitat Selection and Distribution of Functional Feeding Groups of Mayfly Larvae (Ephemeroptera) In Lotic Karst Habitats. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2018, 419, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Vučković, N.; Mihaljević, Z. Littoral Mayfly Assemblages in South-East European Man-Made Lakes. J. Limnol. 2019, 78, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Kerovec, M.; Pozojević, I.; Mihaljević, Z. Mayfly Response to Different Stress Types in Small and Mid-Sized Lowland Rivers. ZooKeys 2020, 980, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauernfeind, E.; Moog, O. Mayflies (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) and the Assessment of Ecological Integrity: A Methodological Approach. Hydrobiologia 2000, 422, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, J.E.; Sartori, M. Ephemeroptera (Mayflies). In Encylopedia of Insects; Resh, V.H., Cardé, R.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lamp, W.O.; Britt, N.W. Resource Partitioning by Two Species of Stream Mayflies (Ephemeroptera: Heptageniidae). Great Lakes Entomol. 1981, 14, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Buffagni, A.; Crosa, G.; Marchetti, R. Size-Related Shift in the Physical Habitat in Two Mayfly Species (Ephemeroptera). Freshw. Biol. 1995, 34, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffagni, A.; Cazzola, M.; López-Rodríguez, M.J.; Alba-Tercedor, J.; Armanini, D.G. Volume 3—Ephemeroptera. In Distribution and Ecological Preferences of European Freshwater Organisms; Schmidt-Kloiber, A., Hering, D., Eds.; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria; Moscow, Russia, 2009; pp. 1–254. [Google Scholar]
- Buffagni, A.; Armanini, D.G.; Cazzola, M.; Alba-Tercedor, J.; López-Rodríguez, M.J.; Murphy, J.; Sandin, L.; Schmidt-Kloiber, A. Dataset “Ephemeroptera”. The Taxa and Autecology Database for Freshwater Organisms. Version 8.0. Available online: https://www.freshwaterecology.info/ (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Schmidt-Kloiber, A.; Hering, D. www.freshwaterecology.info—An Online Tool That Unifies, Standardises and Codifies More than 20,000 European Freshwater Organisms and Their Ecological Preferences. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 53, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.M.; Humpesch, U.H.; Macan, T. Larvae of the British Ephemeroptera: A Key with Ecological Notes; Scientific Publication No. 49; Freshwater Biological Association: Cumbria, UK, 1988; pp. 1–145. [Google Scholar]
- Elosegi, A.; Díez, J.; Mutz, M. Effects of Hydromorphological Integrity on Biodiversity and Functioning of River Ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 2019, 657, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertić Perić, M.; Matoničkin Kepčija, R.; Miliša, M.; Gottstein, S.; Lajtner, J.; Dragun, Z.; Filipović Marijić, V.; Krasnići, N.; Ivanković, D.; Erk, M. Benthos-Drift Relationships as Proxies for the Detection of the Most Suitable Bioindicator Taxa in Flowing Waters—A Pilot-Study within a Mediterranean Karst River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.; Church, M. Geomorphic and Ecological Consequences of Riprap Placement in River Systems. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, V.; Soldán, T. Mayflies as Bioindicators of Water Quality and Environmental Change on a Regional and Global Scale. In Current Directions in Research on Ephemeroptera; Corkum, L.D., Ciborowski, J.J.H., Eds.; Canadian Scholars’ Press Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1995; pp. 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, L.C.; Lamp, W.O. Mayfly Population Density, Persistence and Genetic Structure in Fragmented Headwaters Habitats. In International Advances in the Ccology, Zoogeography and Systematics of Mayflies and Stoneflies; Hauer, F.R., Stanford, J.A., Newell, R.L., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sowa, R. Jetki Ephemeroptera. In A Checklist of Rare and Endangered Animals in Poland; Glowacinski, Z., Ed.; Nature Protection Research Centre, PAS: Krakow, Poland, 1992; pp. 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Sartori, M.; Landolt, P.; Zurwerra, A. Liste rouge des éphémères de Suisse (Ephemeroptera). In Liste Rouge des Espèces Animales Menacées de Suisse; Duelli, P., Ed.; OFEFP: Berne, Switzerland, 1994; pp. 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Haybach, A.; Malzacher, P. Eintagsfliegen (Ephemeroptera). In Entomofauna Germanica. Band 6; Entomologische Nachrichten und Berichte, Beiheft 7: Dresden, Germany, 2006; pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.M.; Larsen, D.P.; Omemik, J.M. Regional Reference Sites: A Method for Assessing Stream Pollution. Environ. Manag. 1986, 10, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, J.L.; Herlihy, A.T.; Peck, D.V.; Hughes, R.M.; Whittier, T.R.; Tarquinio, E. A Process for Creating Multimetric Indices for Large-Scale Aquatic Surveys. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šegota, T.; Filipčić, A. Köppenova Podjela Klima i Hrvatsko Nazivlje. Geoadria 2003, 8, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čanjevac, I. Typology of Discharge Regimes of Rivers in Croatia. Hrvat. Geogr. Glas. 2013, 75, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- HAOP, Hrvatska Agencija za Okoliš u Prirodu. Pokrov i Namjena Korištenja Zemljišta; Corine Land Cover: Zagreb, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ESRI. ArcMap Version 10.0; ArcInfo License: Redlands, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- EN 15843 Water Quality. Guidance Standard on Determining the Degree of Modification of River Hydromorphology; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- AQEM Consortium. Manual for the Application of the AQEM Method. A Comprehensive Method to Assess European Streams Using Benthic Macroinvertebrates, Developed for the Purpose of the Water Framework Directive; Version 1.0; The AQEM Consortium: Duisburg-Essen, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Liebenau, I. Revision der Europäischen Arten der Gattung Baetis Leach, 1815. (Insecta, Ephemeroptera). Gewässer Abwässer 1969, 49, 1–214. [Google Scholar]
- Malzacher, P. Die Europäischen Arten der Gattung Caenis Stephens (Insecta: Ephemeroptera). The European Species of the Genus Caenis Stephens (Insecta: Ephemeroptera). Stuttg. Beitr. Naturkd. 1984, 373, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind, E.; Humpesch, U.H. Die Eintagsfliegen Zentraleuropas–Bestimmung und Ökologie; NMW: Vienna, Austria, 2010; pp. 1–250. [Google Scholar]
- StatSoft. Statistica 10.0 for Windows; StatSoft Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer V6: User Manual/Tutorial; Plymouth: New Zealand, Auckland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vilenica, M.; Ternjej, I.; Mihaljević, Z. What is New in Croatian Mayfly Fauna? Nat. Croat. 2021, 30, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedková, B.; Rádková, V.; Bojková, J.; Soldán, T.; Zahrádková, S. Mayflies (Ephemeroptera) as Indicators of Environmental Changes in the past Five Decades: A Case Study from the Morava and Odra River Basins (Czech Republic). Aquat. Conserv. 2015, 25, 622–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Brigić, A.; Kerovec, M.; Gottstein, S.; Ternjej, I. Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Changes of Mayflies (Insecta, Ephemeroptera) In a Western Balkan Peat Bog. ZooKeys 2016, 637, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Axelsson, E.P.; Hajalten, J.; Leroy, C.J.; Whitham, T.G.; Julkunen-Tiitto, R.; Wennstrom, A. Leaf Litter from Insect-Resistant Transgenic Trees Causes Changes in Aquatic Insect Community Composition. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligeiro, R.; Hughes, R.M.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Macedo, D.R.; Firmiano, K.R.; Ferreira, W.R.; Oliveira, D.; Melo, A.S.; Callisto, M. Defining Quantitative Stream Disturbance Gradients and the Additive Role of Habitat Variation to Explain Macroinvertebrate Taxa Richness. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 25, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayraud, S.; Philippe, M.; Maridet, L. The Response of Benthic Macroinvertebrates to Artificial Disturbance: Drift or Vertical Move-Ment in the Gravel Bed of Two Sub-Alpine Streams? Arch. Hydrobiol. 2000, 147, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biss, R.; Kübler, P.; Pinter, I.; Braukmann, U. Leitbildbezogenes Biozönotisches Bewertungsverfahren für Fließgewässer (aquatischer Bereich) in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Ein erster Beitrag zur integrierten ökologischen Fließgewässerbewertung. Umweltbundesamt Texte 62/02; Umweltbundesamt: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Schöll, F.; Haybach, A.; König, B. Das Erweiterte Potamontypieverfahren zur Ökologischen Bewertung von Bundeswasserstraßen (Fließgewässertypen 10 und 20: Kies-und Sandgeprägte Ströme, Qualitätskomponente Makrozoobenthos) nach Maßgabe der EU-Wasserrahmenrichtlinie. Hydrol. Wasserwirtsch. 2005, 49, 234–247. [Google Scholar]
- Leitner, P.; Lorenz, A. (Ephemeroptera): Additional Ecological Preferences and Biological Traits Classification for freshwaterecology.info. Version 8.0. Available online: https://www.freshwaterecology.info/fwe_referenceall.php?p=b2c9bXpiI3BhcmFtPTEzNg==#15 (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Vidaković Maoduš, I.; Pozojević, I.; Vilenica, M.; Mihaljević, Z. Longitudinal Dynamics of Odonata Assemblages in an Anthropogenically Impacted Lotic System. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Bilić, M.; Mičetić Stanković, V.; Kučinić, M. Mayfly Ecological Traits in a European Karst Spring: Species, Microhabitats and Life Histories. Community Ecol. 2018, 19, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmedtje, U.; Colling, M. Ökologische Typisierung der Aquatischen Makrofauna. Informationsberichte des Bayerischen Landesamtes für Wasserwirtschaft 4/96; Bayerisches Landesamt für Wasserwirtschaft (Herausgeber und Verlag): München, Germany, 1996; pp. 1–543. [Google Scholar]
- Boeykens, S.P.; Piol, M.N.; Samudio Legal, L.; Saralegui, A.B.; Vázquez, C. Eutrophication Decrease: Phosphate Adsorption Processes in Presence of Nitrates. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.C.; Housley, L.; Back, J.A.; King, R.S. Freshwater Eutrophication Drives Sharp Reductions in Temporal Beta Diversity. Ecology 2018, 99, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, P.; Hauer, C.; Ofenböck, T.; Pletterbauer, F.; Schmidt-Kloiber, A.; Graf, W. Fine Sediment Deposition Affects Biodiversity and Density of Benthic Macroinvertebrates: A Case Study in the Freshwater Pearl Mussel River Waldaist (Upper Austria). Limnologica 2015, 50, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, P.; Klecka, J.; Boukal, D.S. Spatial Heterogeneity and Habitat Permanence Affect Community Assembly but Not Phenology of Mayflies (Ephemeroptera) In Sandpit Pools. Zoosymposia 2016, 11, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.P. Substrate Associations and Longitudinal Distributions in Species of Ephemerellidae (Ephem-Eroptera: Insecta) from Western Oregon. Freshw. Invertebr. Biol. 1985, 4, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Dedieu, N.; Rhone, M.; Vigouroux, R.; Céréghino, R. Assessing the Impact of Gold Mining in Headwater Streams of Eastern Amazonia Using Ephemeroptera Assemblages and Biological Traits. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliša, M.; Habdija, I.; Primc-Habdija, B.; Radanović, I.; Matoničkin Kepčija, R. The Role of Flow Velocity in the Vertical Distribution of Particulate Organic Matter on Moss-Covered Travertine Barriers of the Plitvice Lakes (Croatia). Hydrobiologia 2006, 553, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čerba, D.; Koh, M.; Vlaičević, B.; Turković Čakalić, I.; Milošević, D.; Stojković Piperac, M. Diversity of Periphytic Chironomidae on Different Substrate Types in a Floodplain Aquatic Ecosystem. Diversity 2022, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
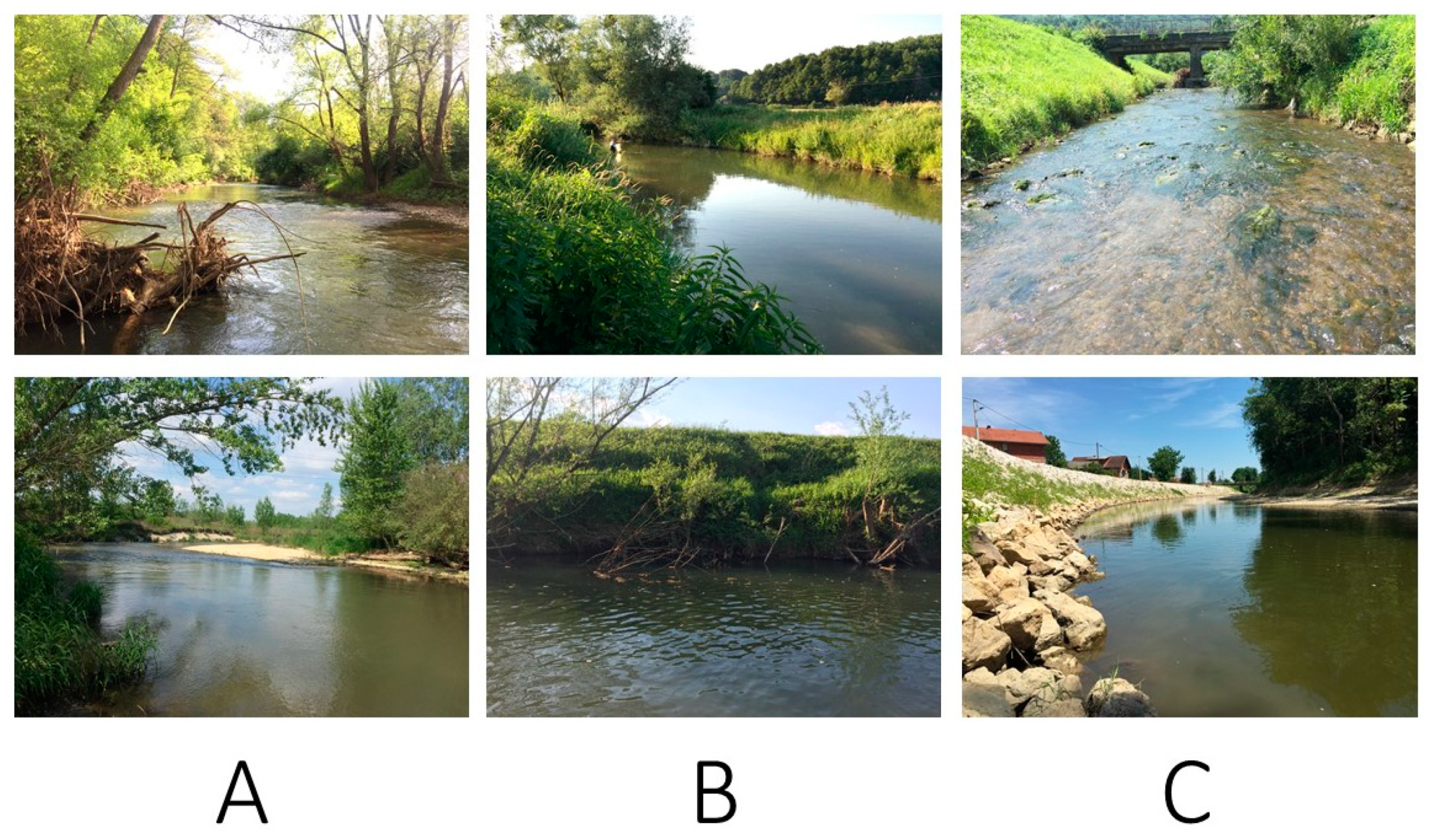









| Study Site | Morphological Modification Score | Habitat Group | Number of Microhabitats | Number of Mayfly Taxa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.78 | A | 6 | 4 |
| 2 | 3.00 | B | 3 | 7 |
| 3 | 2.22 | A | 6 | 10 |
| 4 | 1.44 | A | 3 | 5 |
| 5 | 3.89 | C | 3 | 7 |
| 6 | 4.56 | C | 4 | 11 |
| 7 | 4.22 | C | 4 | 8 |
| 8 | 2.78 | B | 3 | 7 |
| 9 | 2.78 | B | 3 | 5 |
| 10 | 3.22 | B | 2 | 8 |
| 11 | 4.11 | C | 3 | 12 |
| 12 | 2.89 | B | 4 | 13 |
| 13 | 2.89 | B | 4 | 8 |
| 14 | 2.11 | A | 3 | 10 |
| 15 | 2.89 | B | 3 | 11 |
| 16 | 1.67 | A | 5 | 12 |
| 17 | 5.00 | C | 2 | 11 |
| 18 | 2.44 | A | 4 | 10 |
| 19 | 3.67 | C | 2 | 10 |
| 20 | 1.22 | A | 4 | 10 |
| Mayfly Taxa/Habitat Group | Taxa Codes | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baetis sp. | B sp. | 200 | 100 | 159 |
| Baetis fuscatus (Linnaeus, 1761) | B fus | 610 | 105 | 266 |
| Baetis buceratus Eaton, 1870 | B buc | 148 | 28 | 114 |
| Baetis rhodani (Pictet, 1843) | B rho | 42 | 37 | 71 |
| Baetis vernus Curtis, 1834 | B ver | 34 | 16 | 19 |
| Baetis liebenauae Keffermüller, 1974 | B lie | 4 | 5 | |
| Baetis lutheri Müller-Liebenau, 1967 | B lut | 1 | 9 | |
| Centroptilum luteolum Müller, 1776 | C lut | 2 | 4 | |
| Cloeon dipterum (Linnaeus, 1761) | C dip | 1 | ||
| Procloeon bifidum (Bengtsson, 1912) | P bif | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| Procloeon pennulatum Bengtsson, 1915 | P penn | 1 | 1 | |
| Heptageniidae | Hept | 5 | 4 | 2 |
| Ecdyonurus macani Thomas & Sowa, 1970 | E mac | 3 | ||
| Electrogena ujhelyii (Sowa, 1981) | E ujh | 22 | 1 | |
| Heptagenia flava Rostock, 1878 | H fla | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| Heptagenia longicauda (Stephens, 1836) | H lon | 1 | 1 | |
| Leptophlebiidae | Lept | 8 | 1 | |
| Habrophlebia lauta McLachlan, 1884 | H lau | 29 | 2 | 2 |
| Paraleptophlebia submarginata (Stephens, 1836) | P sub | 2 | ||
| Ephemera danica Müller, 1764 | E dan | 2 | ||
| Ephemera lineata Eaton, 1870 | E lin | 1 | 1 | |
| Potamanthus luteus (Linnaeus, 1767) | P lut | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Serratella ignita (Poda, 1761) | S ign | 121 | 71 | 69 |
| Caenis sp. | C sp. | 2 | 1 | |
| Caenis luctuosa (Burmeister, 1839) | C luc | 9 | 39 | 6 |
| Caenis cf. pseudorivulorum Keffermüller, 1960 | C pse | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Abundance (individuals/m2) | 1247 | 415 | 739 | |
| Taxa richness | 22 | 17 | 22 |
| Mayfly Taxa/Abiotic Parameter | Water Temperature (°C) | O2 % | Conductivity (µS/cm) | pH | Water Depth (cm) | Water Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baetis fuscatus | R = 0.57, | R = 0.54, | R = −0.25, | R = 0.58, | R = 0.67, | |
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.03 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | ||
| Baetis buceratus | R = 0.33, | R = 0.25, | ||||
| p = 0.004 | p = 0.04 | |||||
| Baetis rhodani | R = −0.56, | |||||
| p = 0.01 | ||||||
| Baetis vernus | R = −0.28, | R = −0.26, | ||||
| p = 0.02 | p = 0.03 | |||||
| Baetis liebenauae | R = 0.31, | R = 0.25, | ||||
| p = 0.01 | p = 0.04 | |||||
| Baetis lutheri | R = 0.28, | R = 0.38, | R = −0.31, | R = 0.31, | ||
| p = 0.02 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.01 | |||
| Centroptilum luteolum | R = −0.24, | R = −0.25, | R = −0.25, | |||
| p = 0.04 | p = 0.03 | p = 0.03 | ||||
| Cloeon dipterum | R = 0.33, | R = 0.29, | R = −0.34, | |||
| p = 0.004 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.004 | ||||
| Procloeon bifidum | R = 0.25, | R = 0.39, | R = −0.33, | |||
| p = 0.04 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.01 | ||||
| Electrogena ujhelyii | R = −0.53, | R = 0.48, | R = −0.37, | R = −0.63, | R = −0.26, | |
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.002 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.03 | ||
| Heptagenia longicauda | R = 0.32, | |||||
| p = 0.01 | ||||||
| Habrophlebia lauta | R = −0.27, | R = −0.28, | R = −0.24, | R = −0.29, | ||
| p = 0.03 | p = 0.02 | p = 0.04 | p = 0.02 | |||
| Ephemera lineata | R = 0.34, | |||||
| p = 0.003 | ||||||
| Potamanthus luteus | R = 0.48, | R = 0.33, | R = 0.29, | R = 0.29, | ||
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.02 | |||
| Serratella ignita | R = 0.60, | R = 0.51, | R = 0.43, | R = 0.31, | R = 0.28, | |
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.0001 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.02 | ||
| Caenis luctuosa | R = 0.44, | R = 0.25, | R = 0.27, | R = 0.26, | ||
| p = 0.0001 | p = 0.03 | p = 0.02 | p = 0.03 | |||
| Caenis cf. pseudorivulorum | R = 0.25, | R = 0.43, | ||||
| p = 0.03 | p = 0.0002 |
| Mayfly Taxa/Abiotic Parameter | BOD | COD | NH4+ | NO2− | NO3− | Kjeldahl N | Org N | Total N | PO43− | Total P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baetis fuscatus | R = 0.24, | R = 0.41, | R = 0.39, | R = 0.46, | ||||||
| p = 0.05 | p = 0.0003 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.0001 | |||||||
| Baetis buceratus | R = 0.29, | R = 0.27, | R = 0.40, | R = 0.51, | R = 0.38, | R = 0.45, | ||||
| p = 0.02 | p = 0.03 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.000 | |||||
| Baetis rhodani | R = −0.46, | R = −0.28, | R = −0.48, | R = −0.30, | R = −0.32, | |||||
| p = 0.0001 | p = 0.02 | p = 0.0002 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.01 | ||||||
| Baetis vernus | R = −0.26, | R = −0.24, | R = −0.33, | |||||||
| p = 0.03 | p = 0.04 | p = 0.01 | ||||||||
| Baetis liebenauae | R = 0.25, | |||||||||
| p = 0.03 | ||||||||||
| Baetis lutheri | R = −0.25, | |||||||||
| p = 0.04 | ||||||||||
| Cloeon dipterum | R = 0.25, | |||||||||
| p = 0.03 | ||||||||||
| Procloeon bifidum | R = 0.23, | |||||||||
| p = 0.05 | ||||||||||
| Procloeon pennulatum | R = −0.30, | R = −0.27, | ||||||||
| p = 0.01 | p = 0.02 | |||||||||
| Electrogena ujhelyii | R = −0.50, | R = −0.37, | R = −0.52, | R = −0.54, | R = −0.61, | |||||
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | ||||||
| Heptagenia longicauda | R = 0.30, | R = 0.28, | R = 0.28, | R = 0.24, | ||||||
| p = 0.01 | p = 0.02 | p = 0.02 | p = 0.04 | |||||||
| Habrophlebia lauta | R = −0.32, | R = −0.29, | R = −0.30, | R = −0.25, | R = −0.36, | |||||
| p = 0.01 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.03 | p = 0.002 | ||||||
| Ephemera lineata | R = 0.25, | |||||||||
| p = 0.03 | ||||||||||
| Potamanthus luteus | R = 0.25, | R = 0.40, | R = 0.32, | R = 0.26, | ||||||
| p = 0.04 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.03 | |||||||
| Serratella ignita | R = 0.38, | R = 0.40, | R = 0.29, | |||||||
| p = 0.001 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.02 | ||||||||
| Caenis luctuosa | R = 0.25, | R = 0.25, | R = 0.33, | R = 0.34, | R = 0.33, | |||||
| p = 0.04 | p = 0.04 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.004 | p = 0.01 | ||||||
| Caenis cf. pseudorivulorum | R = 0.24, | R = 0.38, | R = 0.45, | R = 0.31, | ||||||
| p = 0.04 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.0001 | p = 0.01 |
| Mayfly Taxa/Environmental Variables | Distance from Source | Land-Use Category Share (%) | Morphological Modification | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Near Natural | Intensive Agriculture | Extensive Agriculture | Urban | |||
| Baetis fuscatus | R = 0.65, | R = −0.37, | R = 0.59, | R = 0.44, | ||
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.0001 | |||
| Baetis buceratus | R = 0.27, | R = −0.31, p = 0.001 | R = 0.30, | |||
| p = 0.01 | p = 0.01 | |||||
| Baetis rhodani | R = −0.41, | R = 0.27, | R = −0.36, | R = 0.27, | ||
| p = 0.0004 | p = 0.02 | p = 0.002 | p = 0.02 | |||
| Baetis vernus | R = −0.23, | |||||
| p = 0.05 | ||||||
| Centroptilum luteolum | R = −0.27, | |||||
| p = 0.02 | ||||||
| Cloeon dipterum | R = 0.29, | |||||
| p = 0.01 | ||||||
| Procloeon pennulatum | R = −0.25, | |||||
| p = 0.04 | ||||||
| Electrogena ujhelyii | R = −0.66, | R = 0.52, | R = −0.51, | R = −0.70, | ||
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.000 | |||
| Heptagenia longicauda | R = 0.36, | |||||
| p = 0.002 | ||||||
| Habrophlebia lauta | R = −0.34, | R = −0.32, | ||||
| p = 0.003 | p = 0.01 | |||||
| Ephemera danica | R = −0.24, | |||||
| p = 0.04 | ||||||
| Ephemera lineata | R = 0.26, | |||||
| p = 0.03 | ||||||
| Potamanthus luteus | R = 0.37, | |||||
| p = 0.001 | ||||||
| Serratella ignita | R = 0.54, | R = −0.24, | R = 0.52, | |||
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.04 | p = 0.000 | ||||
| Caenis luctuosa | R = 0.44, | R = 0.24, | R = 0.37, | |||
| p = 0.0001 | p = 0.05 | p = 0.001 | ||||
| Caenis cf. pseudorivulorum | R = 0.50, | R = −0.39, | R = 0.37, | |||
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.002 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vilenica, M.; Vidaković Maoduš, I.; Mihaljević, Z. The Impact of Hydromorphological Alterations on Mayfly Assemblages of a Mid-Sized Lowland River in South-Eastern Europe. Insects 2022, 13, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050436
Vilenica M, Vidaković Maoduš I, Mihaljević Z. The Impact of Hydromorphological Alterations on Mayfly Assemblages of a Mid-Sized Lowland River in South-Eastern Europe. Insects. 2022; 13(5):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050436
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilenica, Marina, Iva Vidaković Maoduš, and Zlatko Mihaljević. 2022. "The Impact of Hydromorphological Alterations on Mayfly Assemblages of a Mid-Sized Lowland River in South-Eastern Europe" Insects 13, no. 5: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050436
APA StyleVilenica, M., Vidaković Maoduš, I., & Mihaljević, Z. (2022). The Impact of Hydromorphological Alterations on Mayfly Assemblages of a Mid-Sized Lowland River in South-Eastern Europe. Insects, 13(5), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050436








