Simple Summary
Sucking lice are blood-feeding, external parasites of mammals. To date, approximately 540 species have been discovered, occurring in 830 hosts. New species are discovered every year, and the total number is estimated at 1500. The discovery of a species is associated with a detailed description of morphological characteristics. Most descriptions concern only adult specimens. The present study adds to the knowledge by characterizing nymphs of Hoplopleura affinis, a species that parasites the striped field mouse Apodemus agrarius, a common rodent in Europe and Africa. In addition, a checklist of Hoplopleura species parasitizing members of the genus Apodemus was compiled.
Abstract
The genus Hoplopleura is the most speciose genus of sucking lice observed parasitizing rodents and lagomorphs (pikas). Despite the fact that the majority of Anoplura are believed to be monoxenic, many species within Hoplopleura may be oligoxenic. In addition, the occurrence of more than one parasite species per host species on individuals has been confirmed. As such, a precise species identification of the parasite, especially of the nymphs, is of high significance. The study is based on the material of 245 sucking louse specimens taken from 179 individuals of the striped field mouse Apodemus agrarius collected between 2008 and 2017. The study employs scanning microscopy to provide superior quality resolution of the studied traits. The study presents the first record of the characters of the nymphal stages of H. affinis, one of the common Eurasian species of the genus. Additional aspects of the biology and the host–parasite relationship of H. affinis are presented, e.g., female, male and nymphs of lice, showing different preferences in the choice of location (topography) on the host body. In addition, a global checklist has been made of all the species of Hoplopleura found parasitizing rodents of the genus Apodemus. Generally, the ranges of the occurrence of lice of this genus coincide with the geographic distribution of typical hosts, although this has not always been confirmed by local studies.
1. Introduction
Sucking lice (Psocodea: Anoplura) are hematophagous and wingless parasites of placental mammals (Mammalia: Eutheria) [1]. Most of the species have only one host throughout their life cycle, which represents the habitat for all developmental stages (eggs, three stages of nymphs, and adults). Thus far [2], 532 sucking lice species have been described, and these are known to be parasites of 830 mammal species. However, the total number of Anoplura species is estimated to be around 1500. It is believed that the majority of lice species are associated with only one host species (63%); the remaining taxa are parasites of two or more hosts; i.e., they are oligoxenic [3]. Currently, the largest genus within the Anoplura is Hoplopleura Enderlein, 1904 (Anoplura: Hoplopleuridae), including 176 species (136 recorded up to 1994 by Durden and Musser and 40 discovered later).
The five most common species of Hoplopleura in Europe are H. acanthopus (Burmeister, 1839), H. affinis (Burmeister, 1839), H. captiosa Johnson, 1960 (probably cosmopolitan), H. edentula Fahrenholz, 1916, and H. longula Neumann, 1909 [4]. The widest host range is shown by H. affinis, which is recorded from 8 species of the genus Apodemus, H. acanthopus in 5, H. captiosa in 2, H. edentula in 1, and H. longula was not found at all on the host of this genus [4,5,6,7,8].
Within Hoplopleura, 10 species parasitize the genus Apodemus Kaup, 1829 (Rodentia: Muridae). This is a Palearctic and Oriental (Eurasia, North Africa) genus, comprising 21 species. They are associated with various types of environments, from forests to open areas or arable fields, and some also enter buildings and human settlements. Some species are widespread and numerous, often recognized as crop and sanitary pests [9,10].
Hoplopleura species were usually identified only on the basis of adult characters (nymphs were not described for all); these characters are sometimes difficult to capture (especially when using a single identification method, e.g., only optical microscopy), which may cause identification errors, especially when studying a larger sample, where nymphal stages are also numerous. They could be assigned to the wrong species, identified on the basis of a higher probability of occurrence or alleged host specificity. This results in a misidentification of the host circle of different lice species and undermines the reliability of data on their distribution and biodiversity. Only three of the five species listed above currently have their full taxonomic characters on record, including descriptions of adult and nymphal stages (H. acanthopus [11], H. captiosa [12], H. longula [13]). To address this, the present study provides the first description of the nymphal stages of H. affinis from Apodemus agrarius.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lice and Host Material
The material, comprising 245 specimens of H. affinis (50 males, 174 females, 8 first instar nymphs, 9 second instar nymphs, 4 third instar nymphs) from 179 specimens of the striped field mouse Apodemus agrarius Pallas, 1771 was collected between 2008 and 2017. The origin of the host specimens is provided in Table 1 (two specimens—no data available). Additionally, small mammals (common European rodents and soricomorphs) from the scientific collections of the Department of Invertebrate Zoology and Parasitology, Gdańsk, Poland, were included; Myodes glareolus (n = 115), Microtus agrestis (n = 3), Mus musculus (n = 292), Apodemus flavicolis (n = 68), A. sylvaticus (n = 6), and Sorex araneus (n = 28) were examined for Hoplopleura lice (no specimens of H. affinis found).

Table 1.
Host and lice specimen data from Poland (physico-geographical regions follow [14]).
Where coparasitism of two sucking lice species of the genus Hoplopleura was observed, the individuals were not taken into account when creating nymphal stage characters due to risk of error. However, as the nymphs of Hoplopleura and Polyplax differ markedly, in cases where H. affinis and Polyplax serrata co-occurred, the nymphs were included in the identification.
The lice were collected with tweezers from ethanol-preserved rodent specimens (UGDIZP; Collection of Extant Invertebrates, University of Gdańsk, Department of Invertebrate Zoology and Parasitology, Gdańsk, Poland), by combing the coat. The lice present were kept in labeled individual vials (separately for each host) and preserved in 70% ethyl alcohol. Next, morphological structures and body surfaces of specimens were analyzed (measurements are given in mm), using two microscopic techniques:
- Specimens intended for analysis under a light microscope were prepared by slide-mounting in polyvinyl-lactophenol [15].
- Individuals intended for analysis with scanning electron microscopy were subjected to a series of alcohols (80–100%) and then dried in a mix of ethyl alcohol and hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) in 1:3, 1:1, and 3:1 proportions. Finally, the specimens were transferred to pure HMDS and placed in an incubator for 24 h (37 °C) [16]. The specimens were stuck to double-sided copper tape (by Mierzejewski Materiały Samoprzylepne) and fixed on the table of a scanning electron microscope. Observations and photographs were performed with the use of Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope JSM—7800F (manufacturer JEOL; stocked in Department of Materials Engineering and Bonding—Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Gdańsk University of Technology, Gdańsk, Poland).
The louse specimens were deposited in the Collection of Extant Invertebrates, University of Gdańsk, Department of Invertebrate Zoology and Parasitology, Gdańsk, Poland [17].
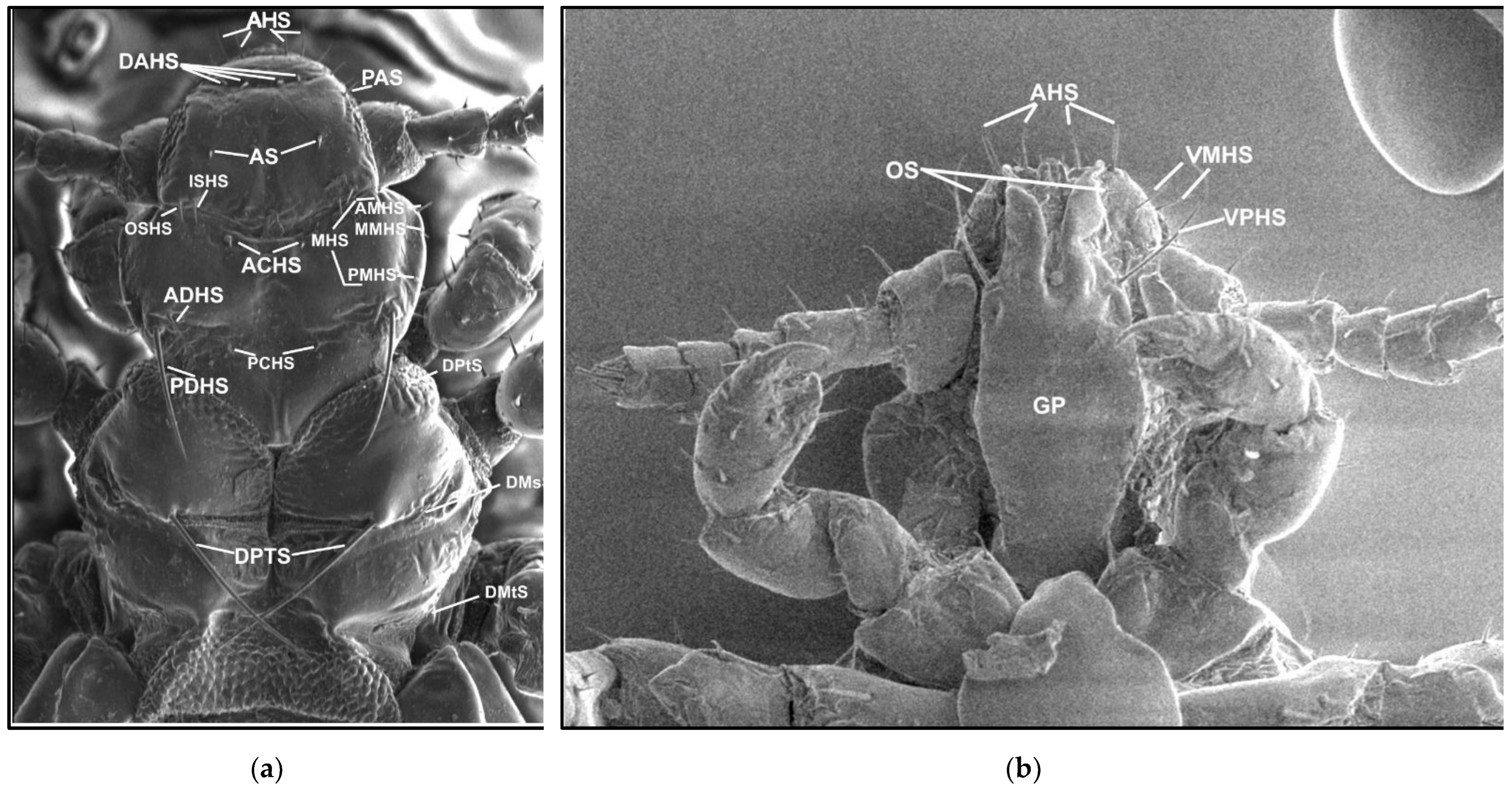
The names and abbreviations of individual setae or body parts are provided mostly following [1] (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
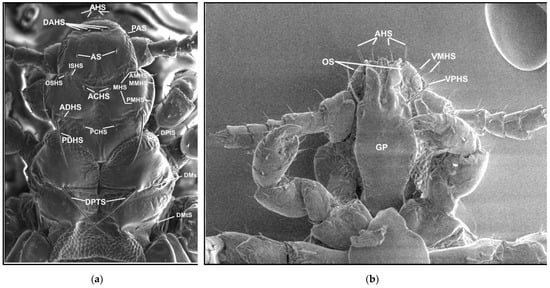
Figure 1.
Hoplopleura morphological characters: (a) dorsal head and thorax; (b) ventral head. Abbreviations of cephalic and thoracic setae: ACHS, anterior central head setae; ADHS, accessory dorsal head setae; AHS, apical head setae; AMHS, anterior marginal head setae; AS, antennal setae; DAHS, dorsal anterior head setae; DMsS, dorsal mesothoracic setae; DMtS, dorsal metathoracic setae; DPTS, dorsal principal thoracic setae; DPtS, dorsal prothoracic setae; ISHS, inner sutural head setae; MHS, marginal head setae; MMHS, middle marginal head setae; OS, oral setae; OSHS, outer sutural head setae; PAS, preantennal setae; PCHS, posterior central head setae; PDHS, posterior dorsal head setae; PMHS, posterior marginal head setae; VMHS, ventral marginal head setae; VPHS, ventral principal head setae.
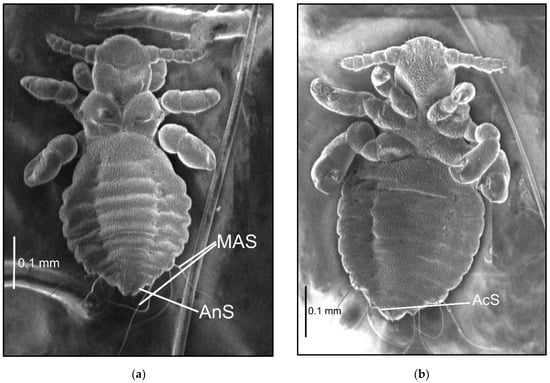
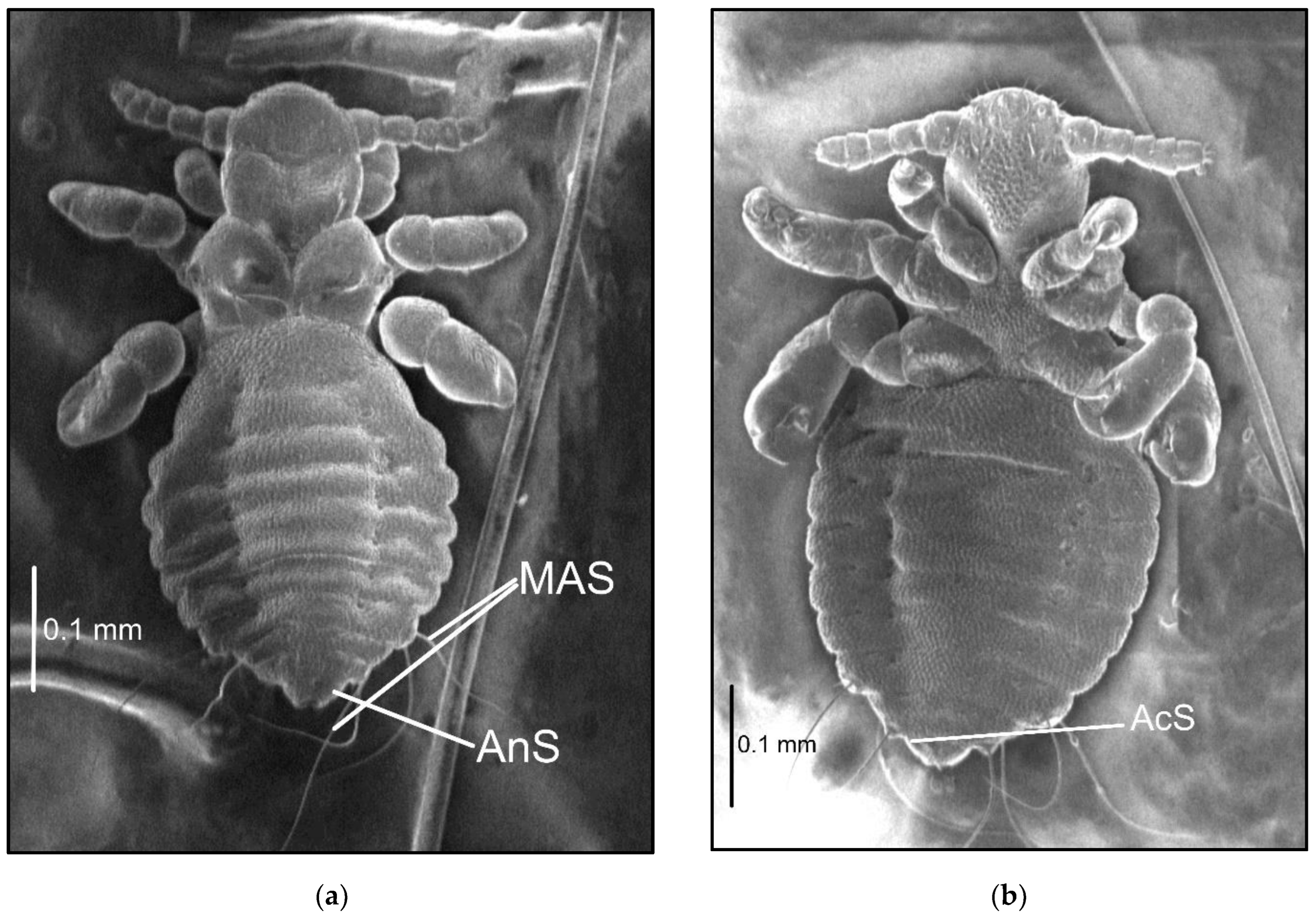
Figure 2.
Hoplopleura affinis nymph III: (a) dorsal; (b) ventral. Abbreviations of abdominal setae: AcS, accessory setae; AnS, anal setae; MAS, major abdominal setae; VCAS, ventral central abdominal setae (not visible on the photo).
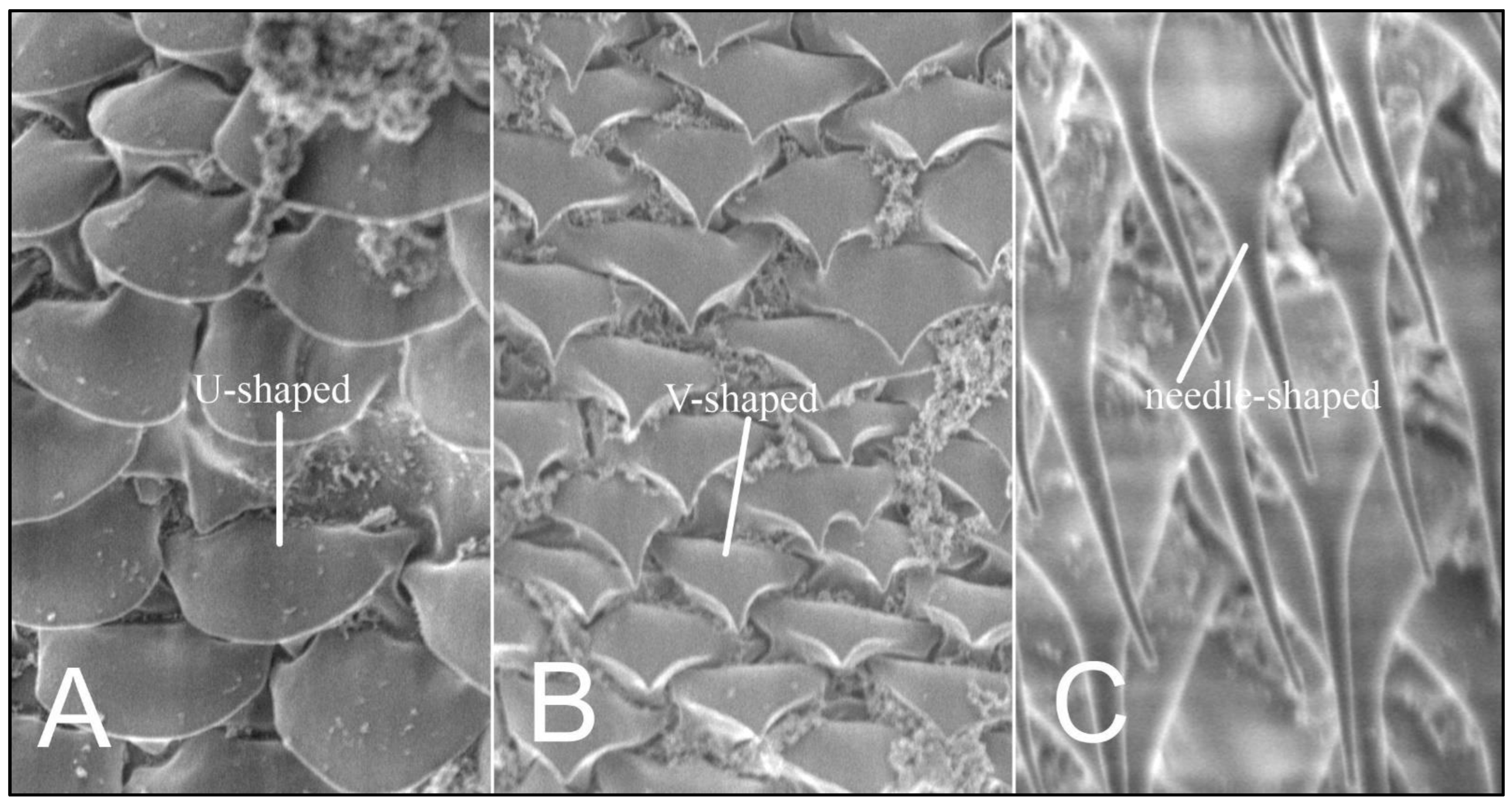
Using the scanning microscopy (SEM), three variants of ornamentation in the form of scales and setae shape are known to exist: smoothly-ended (U-shaped), sharp-ended (V-shaped), and needle-shaped setae (Figure 3).
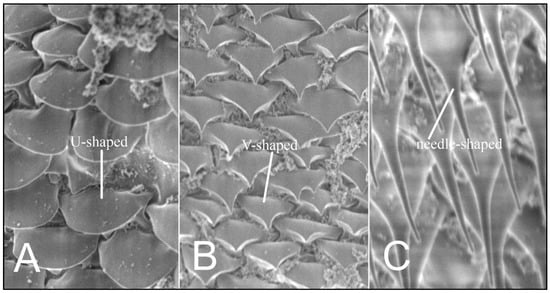
Figure 3.
Hoplopleura body scales (A) U-shaped; (B) V-shaped, and (C) setae.
2.2. The Checklist
The checklist of Hoplopleura species parasitizing the genus Apodemus has been compiled on the basis of data published during the period 1956–2019 (12 items: [4,5,6,7,10,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Apodemus species are ordered alphabetically. The scientific names, common names, and systematics of the hosts follow Wilson and Reeder [9] and the Taxonomic Information System [8].
3. Results
3.1. Description of Nymphal Stages
Nymph I (Figure 4; measurements n = 1), Body length: 0.44. Head: length 0.10, width 0.13.
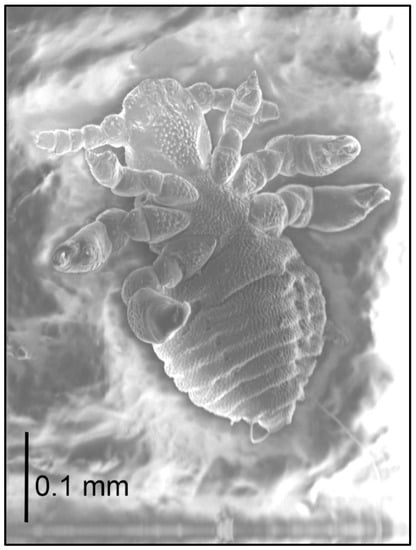

Figure 4.
Hoplopleura affinis nymph I, ventral.
Ventral: no GP; in its place, a large number of tubercles (they form an oval field), some reminiscent of small setae in shape; three tubercles (looking like a small setae) at the base of the antennae. Head posteriorly slightly concave on both ventral and dorsal surfaces. AHS 4 in number; OS almost as long as VMHS, but thinner; above OS, there are two short bristles with a tubercle between them; VMHS measuring approx. 1/3 VPHS. Tubercles (2–4) are also on the 2nd–4th segment of antennae.
Dorsal: DAHS, PCHS, AS present; OSHS and ISHS minor, at a considerable distance from one another; MHS present, but MMHS closer to the mid-portion of the body; PDHS reaches the first thoracic segment; ADHS above the preceding one; ACHS minute.
Thorax: length 0.10, width 0.21.
Dorsal: DPTS short, barely reaching the first thorax segment; DPtS, DMsS, and DMtS present; thorax very short and wide.
Abdomen: length 0.24, width 0.28.
Abdomen heart-shaped, heavily wrinkled. U and V-shaped scales covering the abdomen in a tile-like manner; spiracles visible on both ventral and dorsal surfaces, heavily depressed. VCAS one pair on segment 1 (difficult to detect); MAS 2; AcS 2.
Nymph II (Figure 5; measurements n = 9), Body length: 0.52 (0.37–0.72). Head: length 0.10 (0.07–0.14), width 0.14 (0.12–0.15).
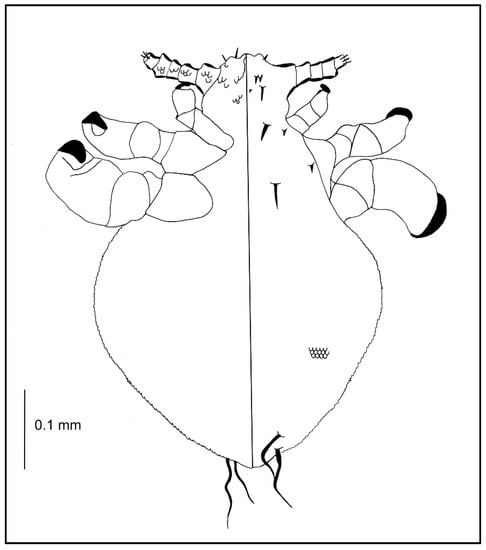
Figure 5.
Hoplopleura affinis nymph II: ventral (left) and dorsal (right) view.
Ventral: convex U-shaped scales covering almost the entire surface; tubercles more flat on head corners.
Dorsal: DAHS present; OSHS and ISHS at a minor distance from one another; MHS present; PDHS reaches the first thorax segment; ADHS equal to the previous setae; ACHS minute.
Thorax: length 0.10 (0.07–0.14), width 0.14 (0.12–0.28).
Dorsal: DPTS reaches the first abdominal segment; DPtS, DMsS, and DMtS present.
Abdomen: length 0.32 (0.21–0.14), width 0.14 (0.21–0.52).
Abdomen very broadly heart-shaped; VCAS one pair on segment 1 (difficult to detect); MAS 4 in number; AcS 2.
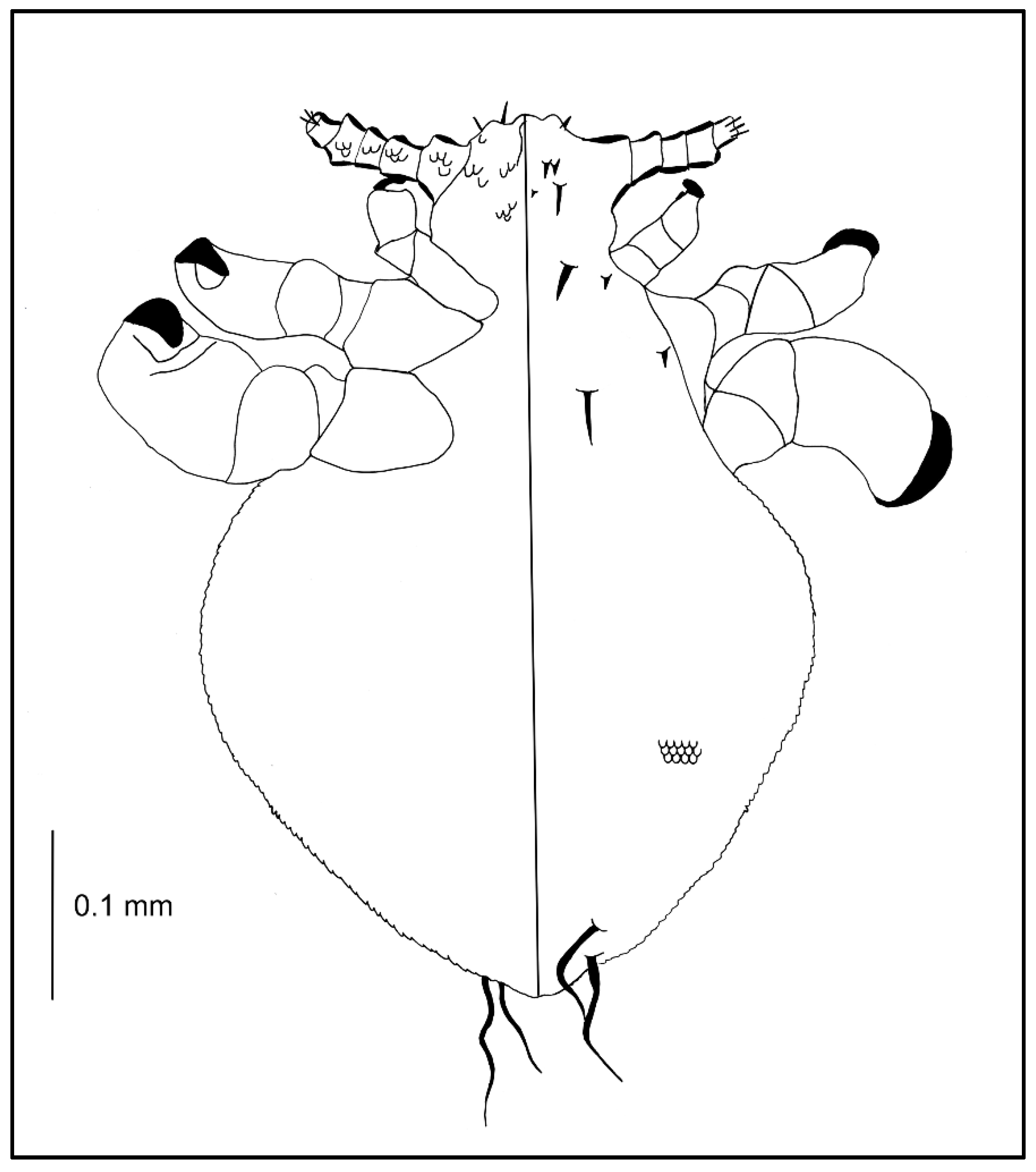
Nymph III (Figure 2; measurements n = 1), Body length: 0.65. Head: length 0.14, width 0.14.
Ventral: VPHS not as long; AHS, OS, and VPHS present; tubercles similar to first instar nymph; in place of GP heavily convex V-shaped tubercles present (they are arranged in the shape of a GP plate seen in adults); on the lateral corners the tubercles are flat, U-shaped.
Dorsal: DAHS, PAS, AS, and PCHS present; OSHS and ISHS not as close to one another, very short; MMHS closer to AMHS than PMHS; PDHS barely reaches the first segment of thorax; ADHS very short and thick; whole surface covered by wide U-shaped scales (apart from the occiput); ACHS minute.
Thorax: length 0.12, width 0.22.
Dorsal: DPTS reaches the first abdominal segment; DPtS, DMsS, and DMtS present; first part of the first segment covered thickly by scales as on the head; around the thoracic spiracle two horn-like processes, the upper larger.
Abdomen: length 0.39, width 0.34.
Abdomen heavily wrinkled, strongly covered with differently shaped scales, with well-visible spiracles (forming two lines separating the abdomen into three parts); anal area well marked, entrance heavily indented; VCAS one pair on segment 1 (difficult to detect); MAS 8 in number; AcS 2; AnS 2.
No morphological anomalies were observed in the study nymphs.
The parasite completes its entire life cycle on the host (eggs, nymphs, and adults), and feeds actively: most individuals were engorged with blood. This is confirmed by the prevalence of 36.3% and the mean intensity of 3.8 specimens (in 65 infested hosts) was recorded.
Co-occurrence of different louse species was found on one host (Apodemus agrarius). Hoplopleura affinis and H. acanthopus were observed in one case, and H. affinis and Polyplax serrata (Anoplura: Polyplacidae) in 16 cases.
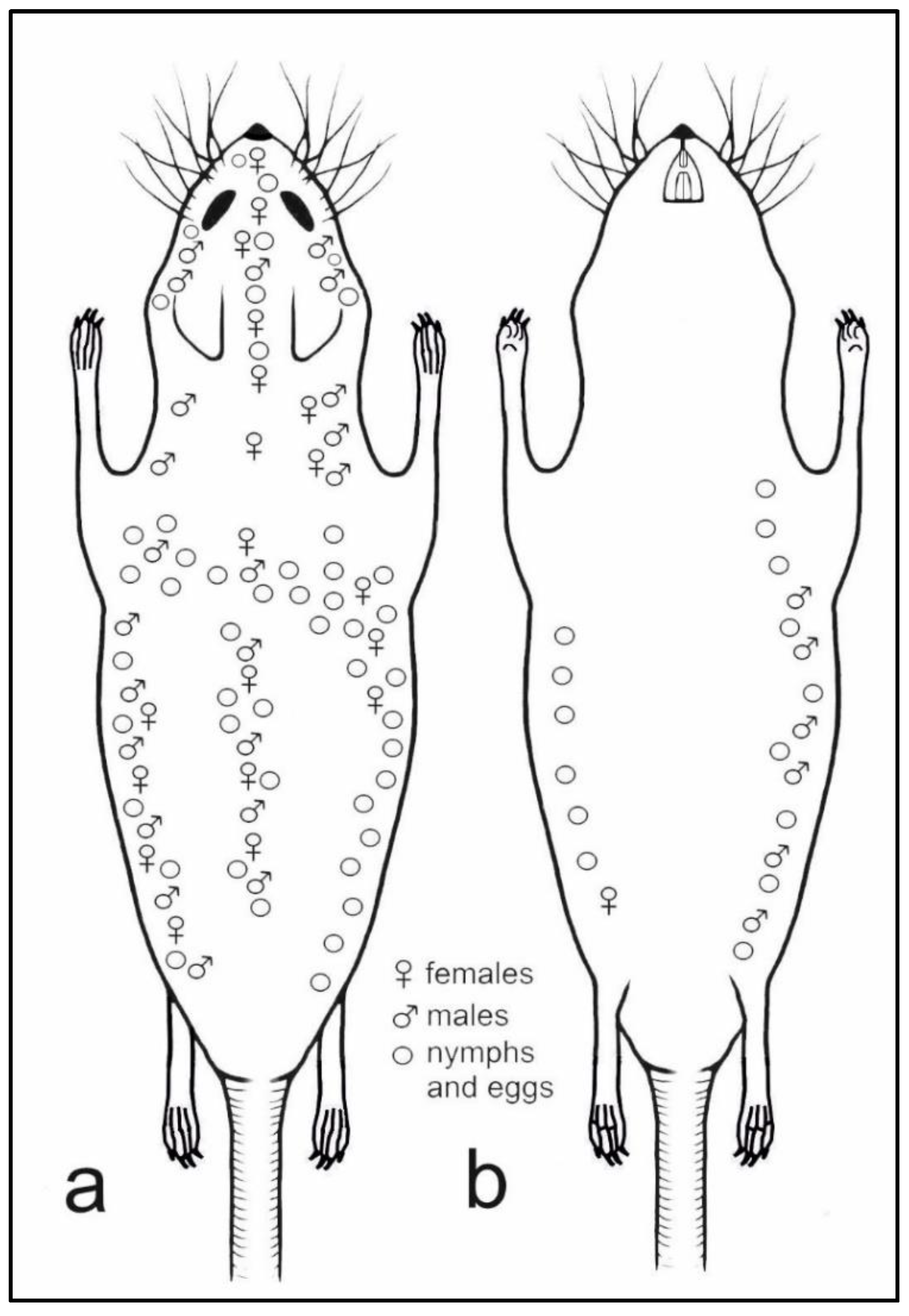
Topographic preferences have been observed for H. affinis (Figure 6). Females (n = 119) were observed on the abdominal surface, only near the right rear leg groin. On the dorsum, however, they formed three bands, i.e., along the spine and on the lateral parts of the body, which joined on the nape of the animal. In addition, the females were observed on the head of the host animal, forming a band from the nape, between the ears up to the nose. Males (n = 27) covered the entire right side of the host animal, from the dorsum to the venter. They were found along the dorsum; they formed two bands before the forelimbs and three bands on the head, i.e., on the mid-point and on the sides of the dorsal portion, as well as between the vibrissae (upper and lower labial and jugal). Nymphs and eggs were numerous on both sides of the animal (dorsal and ventral), forming two clear bands joining on the mid-point of the dorsum. In addition, they formed three bands on the head, joining between the eyes and ears. Nymphs and eggs were rarely observed on the dorsal surface of the neck.
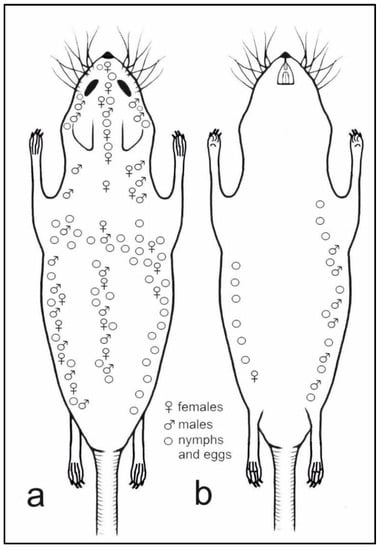
Figure 6.
Topographic preferences of all life stages of Hoplopleura affinis on host body: (a) dorsal view; (b) ventral view.
3.2. Checklist of Hoplopleura spp. on Murid Rodents of the Genus Apodemus
In 12 species of Apodemus mice (out of 20 known species), lice of the genus Hoplopleura (10 species) were recorded. Their distribution is consistent with the geographic ranges of the hosts, mainly in Eurasia and Africa (Table 2).

Table 2.
List of Hoplopleura species parasitizing members of the genus Apodemus. Geographic distributions of both Apodemus and Hoplopleura species are provided.
4. Discussion
The morphology of H. affinis nymphs considerably differs from other European species (H. acanthopus—Holarctic parasite on voles, H. captiosa—cosmopolitan on M. musculus, H. edentula—Eurasia, H. longula—Eurasia) (Table 2). No morphological characters of H. edentula nymphs exists. The characteristic, heart-shaped body, is a feature that distinguishes the nymphs of H. affinis from the other three mentioned above. H. affinis has a heart-shaped, more or less broad, corrugated abdomen, while H. acanthopus, H. captiosa, and H. longula have an elongated, egg-shaped or barrel-shaped abdomen with poorly or without corrugation [11,12,13].
Nymphs of H. longula have very long posterior dorsal head setae (PDHS), extending to the second abdominal segment. PDHS of H. affinis never reach the second abdominal segment [13].
The tubercles cover the upper part of the head of H. acanthopus, on H. affinis they additionally form a field along the middle part of the head (in place of the gular plate GP), while on the head of H. longula they form a cross-shape. The tubercles on ventral surface of head and antennae H. captiosa are blunt, H. affinis- line small setae in shape (V-shaped) [11,12,13].
Nymphs of H. affinis can be easily distinguished from one another: nymph I has two major abdominal setae (MAS) and two accessory setae (AcS); nymph II has four major abdominal setae and two accessory setae; nymph III—eight major abdominal setae, two accessory setae and two anal setae (AnS).
The nymphal stages of H. affinis demonstrate a similar heart-shaped body to H. malabarica and H. sicata, but these parasites were not found on Apodemus [26].
Anomalies in morphology (differences in the number and size of the setae on the sternal plates of the abdomen and irregularities in the structure of the plate itself) were observed for the adult examined individuals [27].
Hoplopleura affinis appears to be a typical parasite of A. agrarius in Europe; despite extensive research, it has not been found on Myodes glareolus, Microtus agrestis, Mus musculus, Apodemus sylvaticus, or Sorex araneus [4,25,28,29,30]. Other results indicate this as well: occurrence of all life stages on the host, observation of blood-filled individuals (this study).
Few studies provide the locations of the sucking lice on the host body. However, Dubinin [31] notes that for H. affinis parasitizing A. agrarius, the lice were located only on the dorsal head and a small neighboring part of the neck. The current study provides more extensive knowledge, with the louse being found to cover a larger preferred area, reaching the posterior limbs of the host. There are also no data on the occurrence of H. affinis nymphs and eggs present on A. agrarius in the available literature. The present study adds to the knowledge, with multiple occurrences on the dorsal and ventral parts of the animal. No differences were observed in topographic preferences for different life stages of H. affinis. One common feature is evident: none of the stages occurred on the ventral head. Perhaps this is due to the structure of the host’s coat, the hairs are sparser and shorter there [32] and specific behavior patterns, e.g., self-grooming or self-cleaning behaviors, when rodents self-groom by scratching to clean or groom the fur [33,34].
Analyzing the global checklist of Hoplopleura species of the genus Apodemus (Table 2), it can be seen that the absence of sucking lice findings in a given host is mainly due to its status: endemic, difficult to access or recently described species. This applies, for example, to A. alpicola, a poorly understood species discovered in the mid-twentieth century, endemic to the alpine region, and often inhabiting hard-to-reach protected areas. Similarly, poorly known is A. hyrcanicus, described only in 1992, limited in range to forest regions from the southern Caucasus to Central Asia, moreover, usually not sympatric with either Apodemus [9], which also limits the transmission of parasites. In contrast, in widely distributed and much better-studied species, such as A. agrarius, A. flavicollis, A. sylvaticus, and A. uralensis, there are usually several, also usually widespread, Hoplopleura species.
5. Conclusions
Research on sucking lice (Anoplura) has so far been carried out selectively, focusing mainly on their pathogenicity and related aspects. Descriptions of new species are usually based only on adults. The lack of knowledge of the juvenile stages generate false data on the host specificity of individual parasite species, their host circle, transfer possibilities between hosts, geographical distribution, or habitat preferences. Consequently, it leads to false conclusions regarding various aspects of the functioning of the parasite–host systems, the spread and transmission possibilities of parasites, and in the case of particularly pathogenic parasites or pathogens vectors, their health significance. The issue of the correct identification of the stages of juvenile parasites is currently one of the universal problems of parasitology. This especially applies to the phases of the life cycles, where juvenile stages are the dominant group in the structure of the parasite population, or mature stages, which are usually the basis for species identification, do not occur at all. An example is the parasitic nematodes of the Anisakidae family with complex life cycles where only larval stages are present in intermediate/paratenic hosts (fish). They are of zoonotic importance as they can be invasive and pathogenic to humans [35,36,37]. Problems with identifying the larval stages may also concern various ticks important as vectors of pathogens [38]. The lack of descriptions for nymphs causes them to be mistakenly assigned to species and consequently to host species. It also causes a lack of recognition the structure and dynamics of the population development of the lice species within the host, as well as the seasonal dynamics. Hence, it is important to describe the nymphal stages as well. The current study adds to the knowledge on this subject by providing descriptions for the nymphs of H. affinis. It should be kept in mind that assigning nymphs to a given species is extremely difficult and requires the consideration of a number of inter-related criteria, including the presence of adult stages and exclusion of coparasitism with similar species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.K. and J.N.I.; microscopy analysis, P.K. and J.N.I.; data analysis, P.K. and J.N.I.; sampling, P.K., J.N.I. and R.Ł.; writing—original draft preparation, P.K. and J.N.I.; writing—review and editing, P.K., J.N.I. and R.Ł.; funding acquisition, P.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by University of Gdańsk, grant number 538-L114-B928-15.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the editors and the reviewers for helpful comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Kim, K.C.; Ludwig, H.W. Phylogenetic relationships of parasitic Psocodea and taxonomic position of the Anoplura. Ann. Entomol. Soc. 1978, 71, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durden, L.A.; Musser, G.G. The mammalian hosts of the sucking lice (Anoplura) of the world: A host–parasite list. Bull. Soc. Vector Ecol. 1994, 19, 130–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.C. Blood-sucking lice (Anoplura) of small mammals: True parasites. In Micromammals and Microparasits from Evolutionary to Management; Morand, S., Krasnov, B.R., Poulin, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durden, L.A.; Musser, G.G. The sucking lice (Insecta, anoplura) of the world: A taxonomic checklist with records of mammalian hosts and geographical distributions. Bull. Am. Nat. Hist. 1994, 218, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S.J.; Hood, M.W.; Shaw, J.H.; Rayburn, J.D.; Kirby, M.D.; Hanfman, D.T.; Zidar, J.A. Index-Catalogue of Medical and Veterinary Zoology; Suppl. 21, Pt 5. Parasite-subject catalogue; Parasites: Arthropoda and miscellaneous phyla; United States Department of Agriculture. U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; p. 246.
- Krištofík, J.; Lysy, J. Seasonal dynamics of sucking lice (Anoplura) in small mammals (Insectivora, Rodentia) in the natural foci of infections in South West Slovakia. Biológia 1992, 47, 605–617. [Google Scholar]
- Dik, B.; Selçuk, A.Y.; Kefelioğlu, H.; Keskin, A. A preliminary report of the sucking lice (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Anoplura) of some small mammals of Turkey with four new records. Trans. Am. Entomol. Soc. 2019, 145, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). Available online: http://www.itis.gov (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammals Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd ed.; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 1–2142. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, D.; Feijó, A.; Cheng, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, R.; Abramov, A.V.; Xia, L.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Shi, L.; et al. Evolutionary history of field mice (Murinae: Apodemus), with emphasis on morphological variation among species in China and description of a new species. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2019, 187, 518–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, E.F.; Beer, J.R. The immature stages of the genus Hoplopleura (Anoplura: Hoplopleuridae) in North America, with description of two new species. J. Parasitol. 1959, 45, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C. A new species of Hoplopleura from Thailand, with notes and description of nymphal stages of Hoplopleura captiosa Johnson (Anoplura). Parasitology 1966, 56, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozina, P.; Izdebska, J.N.; Kowalczyk, R. The first description of the nymphal stages of Hoplopleura longula (Psocodea: Anoplura: Hoplopleuridae) from the harvest mouse Micromys minutus (Rodentia: Muridae). Biodivers. Data J. 2021, 9, e63747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solon, J.; Borzyszkowski, J.; Bidłasik, M.; Richling, A.; Badora, K.; Balon, J.; Brzezińska-Wójcik, T.; Chabudziński, Ł.; Dobrowolski, R.; Grzegorczyk, I.; et al. Physico-geographical mesoregions of Poland: Verification and adjustment of boundaries on the basis of contemporary spatial data. Geogr. Pol. 2018, 91, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadulski, S.; Izdebska, J.N. Methods used in studies of parasitic arthropods in mammals. In Arthropods. Epidemiological Importance; Buczek, A., Błaszak, C., Eds.; Koliber: Lublin, Poland, 2006; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Murtey, M.D.; Ramasamy, P. Sample preparations for scanning electron microscopy–life sciences. In Modern Electron Microscopy in Physical and Life Sciences; Janecek, M., Kral, R., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.Q. Repositories for mite and tick specimens: Acronyms and their nomenclature. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 2432–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K. Studies on the Murine Lice in Japan (Part 2). Description of Hoplopleura himenezumi n. sp. (Hoplopleuridae, Anoplura) collected from Apodemus argenteus argenteus. Bull. Tokyo Med. Dent. Univ. 1956, 3, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Zwolski, W. Badania nad ektoparazytofauną drobnych ssaków w ogniskach naturalnych gorączki błotnej. Wiad. Parazytol. 1960, 6, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.C.; Kulkarni, S.M.; Bhat, H.R. Hoplopleura himalayana, sp. nov. (Anoplura: Hoplopleuridae), parasitizing Apodemus flavicollis in the Himalayan Region of India. Orient. Insects 1973, 7, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.M. Accounts of Nepalese mammals and analysis of the host-ectoparasite data by computer techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Kadulski, S.; Izdebska, J.N. Anoplura u gryzoni (Rodentia) z terenów Polski Północnej. Wiad. Parazytol. 2004, 50, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stanko, M.; Fričová, J.; Miklisová, D.; Mošanský, L. Host-parasite relationships among parasitic arthropods and common vole (Microtus arvalis, Rodentia) in lowland ecosystems of Slovakia. In Arthropods: Epidemiological Importance; Buczek, A., Błaszak, C., Eds.; Koliber: Lublin, Poland, 2006; pp. 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Stanko, M.; Fričová, J.; Miklisová, D.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Krasnov, B.R. Environment-related and host-related factors affecting the occurrence of lice on rodents in Central Europe. Parasitology 2015, 142, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegner, Z. Klucze do oznaczania owadów Polski. Część XVI. In Wszy-Anoplura; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1972; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P. Some Anoplura of the Oriental region. A study of Hoplopleura pacifica Ewing and allies. J. Med. Entomol. 1972, 9, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozina, P.; Izdebska, J.N. Morphological anomalies in the body structure of Hoplopleura spp. (Anoplura: Hoplopleuridae). Ann. Parasitol. 2021, 67, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Haitlinger, R. Parasitological investigation of small mammals of Góry Sowie (Middle Sudetes). Pol. Pismo. Entomol. 1976, 46, 207–239. [Google Scholar]
- Grinbergs, A. Review of the animal lice fauna of Latvia. Latvijas Entomol. 1980, 23, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Haitlinger, R. Arthropods (Acari, Anoplura, Siphonaptera) of small mammals of Świętokrzyskie Provinence. Zesz. Nauk. Uniw. Przyr. Wroc. 2010, 577, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dubinin, V.B. Parazitofauna mysevidnykh gryzunov i eyo izmeneiya v delt Volgi. Parazitologieeskij Zbornik 1953, 15, 252–301. [Google Scholar]
- Marinis, A.M.D.; Agnelli, P. Guide to the microscope analysis of Italian mammals hairs: Insectivora, Rodentia and Lagomorpha. Ital. J. Zool. 1993, 60, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Song, C.; Berridge, K.C.; Graybiel, A.M.; Fentress, J.C. Neurobiology of rodent self-grooming and its value for translational neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Hao, J.; Yao, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, T.; Jin, Z.; Meng, F. Observations of the foraging behavior and activity patterns of the Korean wood mouse, Apodemus peninsulae, in China, using infra-red cameras. Zookeys 2020, 992, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggi, L.; Mattiucci, S.; Gibson, D.I.; Berland, B.; Nascetti, G.; Cianchi, R.; Cianchi, R.; Bullini, L. Pseudoterranova decipiens species A and B (Nematoda, Ascaridoidea): Nomenclatural designation, morphological diagnostic characters and genetic markers. Syst. Parasitol. 2000, 45, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, S.; Norman, R.; Gasser, R.; Beveridge, I. Redescription and genetic characterization of selected Contracaecum spp. (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from various hosts in Australia. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 1507–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiucci, S.; Cipriani, P.; Levsen, A.; Paoletti, M.; Nascetti, G. Molecular epidemiology of Anisakis and anisakiasis: An ecological and evolutionary road map. Adv. Parasitol. 2018, 99, 93–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lah, E.F.C.; Yaakop, S.; Ahamad, M.; George, E.; Nor, S.M. Precise identification of different stages of a tick, Ixodes granulatus Supino, 1897 (Acari: Ixodidae). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).