Simple Summary
Animal groups differ in the primary sense (touch, taste, smell, vision, hearing) that they use to perceive the world around them. Discovering how evolution has shaped animal senses is essential to understanding how animals interact with their environments. Fireflies are a wonderful creature to study since they use bioluminescence to find mates at night, but there are some firefly species that use other means (e.g., pheromones) to find mates and fly during the day. We examined the genes that are expressed in the eye that support sight to see if there were patterns of evolution on specific genes and different patterns of selection between day-flying non-bioluminescent and nocturnal bioluminescent fireflies. Our research is unique among beetles and is complementary to work done in flies, butterflies, and moths and allows us to better understand the boundaries of evolution on the animal visual system.
Abstract
Most organisms are dependent on sensory cues from their environment for survival and reproduction. Fireflies (Coleoptera: Lampyridae) represent an ideal system for studying sensory niche adaptation due to many species relying on bioluminescent communication; as well as a diversity of ecologies. Here; using transcriptomics; we examine the phototransduction pathway in this non-model organism; and provide some of the first evidence for positive selection in the phototransduction pathway beyond opsins in beetles. Evidence for gene duplications within Lampyridae are found in inactivation no afterpotential C and inactivation no afterpotential D. We also find strong support for positive selection in arrestin-2; inactivation no afterpotential D; and transient receptor potential-like; with weak support for positive selection in guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha and neither inactivation nor afterpotential C. Taken with other recent work in flies; butterflies; and moths; this represents an exciting new avenue of study as we seek to further understand diversification and constraint on the phototransduction pathway in light of organism ecology.
1. Introduction
Organisms rely on sensory input from the environment to inform their basic ecology. Inputs occur across different channels, such as auditory (e.g., song), tactile (e.g., mechanosensory stimulation), gustatory (e.g., tastes), olfactory (e.g., pheromones, kairomones), and visual (e.g., bright colors, behavioral displays) channels, and are detected by different sensory structures and underlying molecular pathways. While many animals integrate input from several sensory channels depending on the circumstances, often a single channel dominates (e.g., vision in primates: [1], dragonflies and damselflies [2]), perhaps due to tradeoffs in investment in sensory structures [3,4] and the interplay of selection and constraint on the underlying molecular players (e.g., [5]). The extent to which selection and constraint play a role in adaptation to an organism’s specific sensory niche, particularly with respect to the underlying molecular mechanisms, remains a fascinating question that has been investigated mostly by work in model systems [6,7,8]. Modern sequencing technologies enable interrogation of these questions in non-model organisms, which present unique opportunities to study evolutionary forces in systems where evolutionary changes in primary sensory niche (i.e., nocturnal vs. diurnal) are known [9].
One of the best characterized signal pathways is the phototransduction (PT) pathway [8]. This is especially true in the model insect Drosophila melanogaster [6,10,11]. Bao and Friedrich expanded this knowledge to other model insects by examining conservation in PT genes in Drosophila as compared to Tribolium, Anopheles, and Apis [7]. This study found an increase in duplications within the higher flies (e.g., Drosophila) which would likely contribute to their higher photoresponse [7,12]. It has also been shown that duplication in Drosophila long-wavelength opsins enabled them to escape from ancestral pleiotropy [7,13,14,15,16]. However, opsins represent only one of many molecular players in the phototransduction (PT) pathway and examining the other components can help shed further light on this complex sensory system [17]. For example, recent studies in Heliconius butterflies have shown differences in PT gene expression beyond just the opsin genes, related to differences in visual light environment [8].
Fireflies (Coleoptera: Lampyridae) are an excellent system for studying sensory niche adaptation due to variation in their conspicuous bioluminescent mating displays. With over 2000 species distributed around the globe, variation in flash patterns across nocturnal taxa is widespread and serves in both species recognition and mate choice [18,19]. While the proximate and ultimate reasons for signal diversity in light-using species have been studied for centuries [20,21,22,23], several species have lost the ability to produce light as adults and are currently being studied. Instead of light, these day-active fireflies rely on pheromone signals to locate, recognize, and choose mates [24,25,26]. In contrast, pheromones may be relatively unimportant for nocturnal light-using species [24]. The change from nocturnal, primarily-visual, light signal use to diurnal, primarily-pheromone, signal use, makes fireflies an ideal system for testing hypotheses about the role of selection in these evolutionary transitions in sensory niches.
Previous studies in fireflies highlight the interplay of diversification and constraint in both morphological and molecular adaptations to sensory niche. Nocturnal, light-using fireflies that rely on bioluminescence for communication have larger eyes and smaller antennae than their diurnal, pheromone-using relatives [4]. This inverse relationship between eye and antenna size across sensory niches may indicate developmental constraints that limit investment in antennae at the expense of eyes, and vice versa [27]. At the molecular level, previous research has demonstrated that contrary to the insect eye bauplan, fireflies and their close relatives, along with most other beetles, have only two opsin paralogs: one which is ultraviolet sensitive and one which is long-wavelength sensitive. [28,29,30]. Sander and Hall found evidence for positive selection in both long-wavelength and ultraviolet opsin at evolutionary transitions from night to day activity [29]. Most positively selected amino acid sites in either opsin were concordant with substitutions observed in spectral shifts in other insect species. This suggests different selective pressures on the molecular level between nocturnal vs diurnal light environments. Additionally, certain fireflies have been shown to vary the expression levels of the long-wavelength opsin in correlation with peak bioluminescent signaling time [31].
Vision in fireflies, like all insects, is regulated by the components of the phototransduction (PT) pathway (Figure 1). The phototransduction pathway consists of several key genes and is essentially a seven- to eight-step process that starts with light activating the insect rhodopsin and is terminated by arrestin-1 and/or -2 binding to the rhodopsin (for a more complete review see [8]). While most of what is known about the insect PT pathway comes from work in the dipteran fruit fly model organism, Drosophila melanogaster, and more recently the lepidopteran Heliconius melpomene [8], relatively little is known about the pathway in other insect groups, with the exception of opsins [32,33,34]. While opsin gene family expansion has been associated with selection on photoreceptor spectral sensitivity in butterflies [35], there is also evidence that opsin copy number does not correlate well with visual lifestyle in other insect groups such as dragonflies [36]. Opsins have also been well studied in fireflies [28,29]. Further, exploring the full phototransduction pathway in fireflies would provide one of the first studies of this pathway with respect to signal niche adaptation and especially potential for selection in beetles.
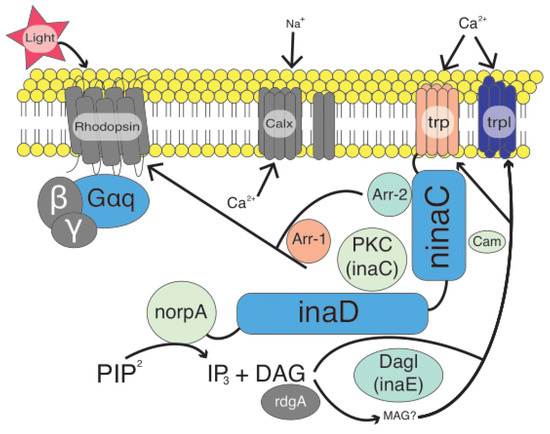
Figure 1.
Diagram of the basic insect phototransduction pathway (modified from [6]). Components in gray represent parts of the pathway not sampled. Components in orange were sampled but were recovered in too few taxa for selection analysis. All other components are colored to reflect relative omega values as reported via the PAML analysis. Dark blue indicates high relative omega values whereas lighter blue/green indicates low relative omega values.
With growing genomic tools for non-model organisms, including fireflies [29,37], it is possible to examine the entire PT pathway and test hypotheses regarding the visual evolution of these organisms. Here, we search a total of 32 both publicly available (10 transcriptomes) and novel unpublished (22 transcriptomes) firefly transcriptomes representing 20 species in total to address the following objectives: (1) Identify genes involved in phototransduction in firefly transcriptomes; (2) Test hypotheses of selection related to sensory niche adaptation (nocturnal vs diurnal); and (3) as a secondary focus, explore gene duplication and loss among fireflies and as compared to other, model, insects (i.e., Drosophila and Tribolium).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Sequencing
Because genome assemblies are available for only three firefly species (all lighted taxa), only one of which is closely related to a diurnal species with existing -omic data, PT genes were identified from previously published [29] and new [28] transcriptome assemblies (see Figure 2 for cladogram of generic relationships among sampled taxa) to capture taxonomic and ecological breadth. It should be noted that while [28] used transcriptome sequences to study opsin evolution, at the time only the opsin gene sequences were reported. Raw reads and transcriptome assemblies for the 22 libraries from [28] are reported here for the first time.
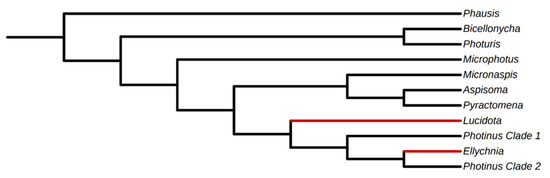
Figure 2.
Cladogram showing generic relationships of sampled taxa. Relationships modified from [29,38]. Taxa in red indicate diurnal lineages.
RNA was extracted from several body parts (i.e., head only, abdomen/light organ only, and whole body). As such, while there are 32 RNA-seq libraries in the study, these represent 20 taxa (Supplementary Table S1; https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.mkkwh70vq) (accessed on 8 June 2021). Both head and body tissue for transcriptome assembly was prepped separately for the following taxa: Micronaspis floridana Green, Pyractomena dispersa Green, P. pyralis Linnaeus (see [28]). Total RNA was extracted from each taxon using NucleoSpin columns (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA) and reverse-transcribed into cDNA libraries using the Illumina TruSeq RNA v2 sample preparation that both generates and amplifies full-length cDNAs. Prepped mRNA libraries were sequenced either on an GaIIX using 72 paired-end reads (RCO_011–RCO_025) by the DNA Sequencing Center at Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA or on an Illumina HiSeq 2000 utilizing 101-cycle paired-end reads (RCO_27–RCO_36) by the Microarray and Genomic Analysis Core Facility at the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA. Voucher specimens are deposited at BYU (for those with RCO numbers) or UGA (for those with KSH numbers). To aid in future identification, the COI sequences are also available on genbank (Supplementary Table S2). The transcriptomic data allows us to combine current data, as well as gain a knowledge of what parts of the phototransduction pathway are actually expressed in the firefly eye.
2.2. Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation
Quality control, assembly, and transcriptome searches were performed using a pipeline constructed from existing computational tools after [36] to facilitate downstream evolutionary analyses. In short, RNA-seq reads were trimmed using the Mott algorithm implemented in PoPoolation version 1.2.2 [39], with a minimum read length = 40 and quality threshold = 20. The de novo assembly of the transcriptome contigs was carried out using Trinity version 2.0.6 [40] under the default parameters. Assembled transcriptomes were then annotated using the trinotate release 2013-08-26 pipeline. Detection and filtering for putative phototransduction genes were performed against a database comprised of insect visual phototransduction homologous groups taken from OrthoDB database [41]. Recovered insect sequences from the PT pathway were then aligned using MAFFT v. 7.407 [42] and converted into a profile hidden Markov model (pHMM) database using hmmbuild program of HMMER 3.1b1 [43]. Using this database, we screened TransDecoder-predicted proteomes for genes known from the PT pathway against pHMM database using hmmscan with an e-value cutoff of 10−5. Additionally, we used PIA [44] with default parameters to identify phototransduction genes that may be missed by the HMMER search using the raw Trinity transcriptome assemblies. This resulted in approximately 80 gene sequences. All redundant (identical) phototransduction gene sequences identified by both approaches were removed using CD-HIT [45,46]. After all putative hits were compiled, sequences were screened for any false positives, including sequences coding for other genes, or duplicate reads not the result of biology, but rather read coverage. Sequences were aligned via MAFFT with the outgroup beetle Tribolium castaneum to remove sequences with >98% similarity. Each unique sequence was then Blast searched using megablast against the NCBI database to confirm gene identity. Only those genes listed in the KEGG phototransduction pathway were included in downstream analysis (Table 1). Assemblies were assessed for quality and completeness using BUSCO v. 3 [47], comparing against the endopterygota_odb9 database.

Table 1.
Presence/absence data for genes sampled in the phototransduction pathway. Gray box indicates presence. * indicates presence of duplication in Photinus carolinus only.
2.3. Analyses of Positive Selection
Sequences for each gene were aligned independently in MAFFT using the outgroup taxon Tribolium castaneum and the default automatic alignment option (for alignments see dryad repository). Each subsequent alignment was used for Maximum Likelihood tree inference implemented within IQ-Tree v. 1.6.8 [48]. Tests for positive selection in each gene were performed in PAML v. 4.9 [49]. Using the branch-specific test, the free-ratios model (Ha; model = 2, nsites = 0) was tested against the branch model (Ho; model = 0, nsites = 0). The log likelihood of each model was compared with the likelihood ratio test (LRT) using X2 distributions (3.84 at p-value = 0.05) with appropriate degrees of freedom.
Inference of positive selection has been shown to be greatly influenced by the accuracy of MSA [50]. In particular the inference of selection obtained on MSAs produced by MAFFT shows overconfidence in identification of positive selection (i.e., increased rates of false positive results). In order to mitigate that problem, we implemented a Bayesian approach utilized in BAli-Phy version 3.4.1 [51], that essentially jointly estimates MSAs and positive selection (in our case branch-specific) and exhibits superior accuracy [50]. To run analyses of branch positive selection in BAli-Phy, for each gene we used the corresponding tree estimated by ML initializing 3 independent MCMC chains with 3000 iterations each as in [50]. MSA was sampled every 5th iteration. The seemingly low number of iterations is explained by the fact that at each MCMC draw, BAli-Phy updates multiple parameters compared to other MCMC software where only one parameter is updated per iteration. In order to improve our estimator of positive selection we used the Rao-Blackwellization technique, i.e., taking a conditional expectation of the current estimator [50].
The results of 3 runs were pulled together discarding 15% burn-in for each gene. Then Bayes factors (BF) were calculated to assess support for positive selection. We followed a scoring scheme proposed by [52], where BF > 20 exhibits strong support for positive selection, 20 < BF < 3 exhibits “positive” support and BF < 3 is “not worth more than a bare mention”.
To further explore positive selection in these diurnal lineages, we also ran branch-site tests to detect positive selection in specific amino acid sites (Ho: ⍵ = fixed at 1; Ha: ⍵ = variable) [53]. The models were tested as above using the LRT.
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Assemblies Recover Most Conserved Genes
To examine patterns of gene duplication and test for selection in the PT pathway across firefly species, we compiled transcriptome assemblies and gene trees from published [28,29] and new datasets. Transcriptomes varied in quality, generally according to input tissue type (Supplementary Table S1). Transcriptome assemblies captured the majority of conserved genes as full-length transcripts—mean BUSCO completeness across assemblies was 76% (range: 40–95%), the mean N50 was 2096 bp, and the mean maximum contig length was 17,138 bp. Total number of contigs varied from 19,676 to 77,811 (Supplementary Table S1).
3.2. Ortholog Search Strategy Identifies Phototransduction Genes
Ortholog search, followed by manual curation of results, identified twelve genes in the PT pathway across the transcriptomes in this dataset, including arrestin-1 (arr1), arrestin-2 (arr2), calmodulin (Cam), guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha (Gq), G protein-coupled receptor kinase 1 (Gprk1), inactivation no afterpotential C (inaC), inactivation no afterpotential D (inaD), inactivation no afterpotential E (inaE), neither inactivation nor afterpotential C (ninaC), no receptor potential A (norpA), transient receptor potential (trp), and transient receptor potential-like (trpl). Unfortunately, arr1, Cam, and trp were not recovered from any diurnal species. Therefore, we were unable to test these genes further. Because, to date, no sampled insect has been conclusively shown to be missing arr1, Cam, or trp, the absence of these genes in our data is likely due to low/no expression in the tissues sampled or insufficient sequencing depth. While not every gene was found in every species, putative duplications of various genes were found in several species: Photinus pyralis (inaC), Photinus macdermotti (inaC), Lucidota atra (inaC), Phausis reticulata (inaC), Bicellonycha wickershamorum (inaC), and Photinus carolinus (inaD; however, see below); see Table 1, Supplementary Table S3 and supplemental trees. The putative duplicate of inaC is present in the Photinus pyralis genome [37], the only species with a genome that overlaps with the taxa sampled in this study. The putative duplicate was on a different linkage group (inaC: LG1, LOC116181404, inaC copy: LG6, LOC116173989). However, the ortholog of the putative duplicate of inaD within Photinus carolinus does not seem to be present in the P. pyralis genome, and requires further confirmation.
3.3. Analysis for Positive Selection Identifies Genes under Positive Selection
3.3.1. PAML
Tests for positive selection were performed in PAML [49] on two sets of trees, resulting from two different approaches to alignment. First, PAML was run on the original MAFFT alignment using Tribolium castaneum as the outgroup for each gene. The branch model test (model = 0, nsites = 0) for the null hypothesis showed elevated omega values (average ⍵ across all genes 0.081) for Gq (⍵ = 0.114), inaD (⍵ = 0.114), ninaC (⍵ = 0.110), and trpl (⍵ = 0.230). This analysis also supported the evidence for positive selection (likelihood ratio test statistic (LRT) > 3.84 at p-value cutoff 0.05) in arr2 (LRT = 43.59), inaC (LRT = 64.35), inaD (LRT = 28.04), ninaC (LRT = 43.76), and trpl (LRT = 16.07) when the alternative hypothesis (model = 2, nsites = 0) was selection in diurnal lineages.
In addition to branch model tests, branch-site tests were performed on the original MAFFT alignment. Only Gq and trpl passed the LRT statistic suggesting specific amino acid sites (sites 2, 37, 38, 39, 79, 80, 97, 98, 101; and 967, 1204, 1215, 1225 respectively) under positive selection in diurnal lineages (Supplementary Table S4).
3.3.2. BAli-Phy
Additionally, PAML was run on the alignment resulting from BAli-Phy [51,54] to account for potential overestimation of positive selection in the MAFFT alignment [50]. This analysis resulted in elevated omega values (average ⍵ across all genes 0.049), inaD (⍵ = 0.092), ninaC (⍵ = 0.109), and trpl (⍵ = 0.082). The PAML analysis of the BAli-Phy alignment also resulted in support for evidence of positive selection in arr2 (LRT = 56.28), Gq (LRT = 5.02), inaD (LRT = 22.30), ninaC (LRT = 45.10), and trpl (LRT = 114.44); (Table 2). Consistent between the two PAML results arr2, inaD, ninaC, and trpl were identified as possibly evolving under positive selection.

Table 2.
Summary of positive selection analyses carried out in PAML and BAli-Phy. P value for lrt significance is 0.05. Level of support for Bayes Factor is after [52].
To further explore genes identified by PAML to be under positive selection, we also tested them for selective-constraint using BAli-Phy by examining the Bayes Factor (BF). The genes arr2 (BF: 9.5), Gq (82.28), inaD (5.13), and trpl (8.59) were again identified as evolving under positive selection (Figure 3; Table 2).
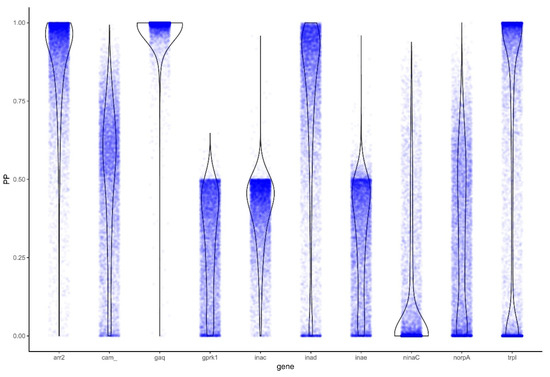
Figure 3.
Distributions of the posterior probability (PP) of positive selection across phototransduction genes. Violin plots represent estimated kernel density MCMC posterior probability of positive selection (blue dots).
Given these results, there is strong evidence in all three analyses for arr2, inaD, and trpl being under positive selection in diurnal lineages, with additional support in two analyses for positive selection in ninaC and Gq (Table 2).
4. Discussion
The insect phototransduction cascade is most well-known and studied in the model insects Drosophila and Heliconius (reviewed in [6,7,8]). Here we increase the knowledge of this cascade system by exploring the PT pathway in fireflies as examined in both novel unpublished and publicly available transcriptome data. We further explore these data by looking for patterns of selection that are potentially related to the signaling ecology of nocturnal vs diurnal fireflies.
Despite the notorious incompleteness of transcriptome data due to tissue-specific expression, we were able to find evidence for potential duplications of genes in the PT pathway in fireflies. Duplication rates of phototransduction genes have been shown to be higher in arthropods and related groups as opposed to other metazoan organisms [54]. These duplications have been demonstrated in several gene families such as TRP, r-opsin (rhabdomeric), and arrestin among others [8,54]. Here we add to the known duplication events in insects by showing evidence for duplications of inaC and inaD within fireflies. The low number of duplicates in the firefly PT pathway is in line with what has been reported in other insects (~15% in Drosophila compared to ~1.3% in Tribolium) [7].
In insect phototransduction, inaD acts as a scaffold protein that is central to a group of proteins commonly known as the signalplex [55,56,57,58,59]. This signalplex is composed primarily of inaD, trp, norpA, and inaC, also found in one of our analyses to be under positive selection [6]. If inaD is lost or disrupted, it causes a downstream breakup of the signalplex [60]. Given the critical nature of inaD, duplications in this gene could provide redundancy or allow for differential expression. Additionally, inaD conservation has been shown to contribute to the remarkably fast photoresponse in the higher Diptera [61,62]. One hypothesis linking duplication to ecology is that duplicates in the signalplex could allow for amino acid changes to facilitate an increase in photoresponse [7]. Whether fireflies have an increased photoresponse compared to other beetles remains unknown. Further, inaD stability is dependent upon trp [6,63,64]. Further upstream in the cascade Gq plays a role in the portion of the cascade that leads to the production of DAG and MAG [65] which are hypothesized to play a critical role in activation of trp and trpl [8,66].
The interaction between trp and trpl in organisms which inhabit low-light vs. high-light environments has received much attention recently. It appears that one or the other can be up- or down-regulated depending on the dominant light environment. In Drosophila melanogaster (active primarily during the day) trp is not only the more abundant channel, but also flies act blindly with mutated trp [67]. In cockroaches (primarily nocturnal) the opposite was shown, trpl was the more abundant channel by far [68]. Recently, Macias-Munoz and colleagues [8] have shown an interesting relationship within the Lepidoptera. The day active Heliconius melpomene showed no differentiation in trp vs. trpl channels, however the night-active Manduca sexta showed lower relative expression of trp, showing a similar pattern to that of the cockroaches [8]. Here, we show strong support for the hypothesis that trpl is under more positive selection in the diurnal fireflies Ellychnia and Lucidota. Phrased another way, trpl is likely under purifying selection in the nocturnal firefly lineages, showing the consistent importance of trpl for nocturnal lineages.
InaD also forms a protein complex with ninaC (ninaC was also recovered in two of the three tests for positive selection), each of them binding Cam. This complex has been shown to mediate Ca2+ movement, thus greatly increasing the efficiency of arrestin [69,70]. In order for arrestin movement to take place, arrestins must bind to phosphoinositides, which is thought to be mediated via ninaC ([71], however see [72]).
There is also strong support for the detection of positive selection in arr2 in diurnal species of fireflies. The arrestin gene family is well known for mediation in many G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades [73]. In these systems, its purpose is to arrest or stop signaling [74,75]. While there are four known arrestin genes in mammalian systems [76], only two, arrestin-1 and arrestin-2, have been found in Drosophila and Heliconius [8,77,78,79,80]. Both arrestin genes were expressed in our Lampyridae taxa, however arrestin-1 was only found in a handful of taxa, and not recovered in either of the diurnal species included. In Lepidoptera, arr2 is more highly expressed than arr1. Arr2 does not reside in the rhabdomere (where phototransduction takes place) but is trafficked into the rhabdomere after phototransduction (see above).
Our results are compelling and demonstrate that fireflies, and likely bioluminescent beetles in general, are a strong system to study the relationship between ecology (e.g., signaling and activity times) and molecular evolution (e.g., selection and gene duplication). We provide the first significant steps in this direction and provide evidence for selection in the broader firefly visual system. In the future, using genomes from bioluminescent beetles to more deeply investigate the evolution of genes involved in the PT pathway by exploring synteny among these genes and more extensively exploring orthology among duplicates would provide deeper insight into how ecology may be driving and even maintaining genetic diversity at the genomic level. Here, our research was constrained as only one high-quality genome overlapped with the transcriptomes for the species we investigated.
We also identified several areas where functional analyses will further aid in the discussion of selection in the phototransduction pathway. For example in guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha multiple amino acid sites were found to have evidence for positive selection including a stretch from residue 37–39, which in Drosophila is the beginning of the G1 motif and extremely close to a nucleotide-binding region (AA40-47). Evidence for positive selection at specific sites in transient receptor potential like does not correspond with known functional regions in Drosophila (Supplementary Table S4).
Additionally, an in-depth quantification and qualification of PT genes across multiple firefly genomes, as well as expression data from throughout the diel changes period to compare potential differences of PT gene expression, is needed. Such experiments would also provide insight into dimorphic gene expression patterns as has been found in one species of firefly [31]. Firefly modes of communication have been described under various systems [81,82], however, most recently firefly communication modes were simplified into four groups: pheromone use only, continuous glow + pheromone, short or long flashes, and pheromone use + weak, daylight glow [83]. Sampling from these communication modes would allow for a finer scale look at the evolution of phototransduction genes.
Finally, tests for positive selection are subject to false positives [84] and functional follow-up studies are the necessary next step to further investigate the results presented here. While functional studies are currently infeasible or impossible for most firefly species because they have a long life cycle and cannot be reliably cultured in the lab, recent advances in applying CRISPR to Aquatica lateralis, a lab-culturable species from Japan, are promising [85]. Additionally, protein function can be further studied in vitro, in tissue culture, and in transgenic Drosophila. All of these offer exciting future avenues for further study. Understanding the protein function will help in the characterization of the inaC duplicate. While the duplicate was found mostly in bioluminescent species, it was also found in the non-bioluminescent Lucidota atra. Therefore it seems likely that the duplicate may serve more of a role in increasing overall visual acuity [86] as opposed to having a specific function in the transitions in sensory niche.
5. Conclusions
This study represents one of the first attempts to assess positive selection in the phototransduction genes in a non-model insect beyond the r-opsin gene family. Arr2, inaD, and trpl represent critical components of the insect phototransduction pathway. All three are associated with light-dependent interactions within the eye. While sexual communication in many fireflies is critically dependent on vision, bioluminescent communication tends to take place beginning in the dusk hours and continuing into the night. In this dark environment, regardless of sexual activity, there are simply fewer photons reaching the firefly eye, meaning the PT pathway is not as active. For those lineages (Ellychnia and Lucidota) active during the day, and therefore more dependent on light for survival and reproduction, it is intriguing that these light-activated genes have support for evolving under positive selection, and are therefore diverging from those in the conserved, nocturnal sensory niche. As we investigate the variation in this system, both with a larger taxon sampling, and with more complete genomic resources, our understanding of insect vision will come into sharper focus. While this study adds an important component in insect visual research of non-model organisms, more remains to be addressed. As it stands, we have successfully identified several genes that are strong candidates for further positive selection studies. In the case of inaC, we have also identified a tantalizing area of study into the loss of certain phototransduction genes across the beetle tree of life. Further study will surely help our understanding of positive selection in terms of adaptation to differing sensory niches.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/insects12060561/s1, Table S1, Assembly summary statistics for transcriptomes, Table S2, SRA and NCBI accession numbers for new data, Table S3, Presence/absence data for genes sampled in the PT pathway, & Table S4, Summary of branch-site analyses.
Author Contributions
G.J.M. coordinated the study, generated the data, performed analyses, and drafted the manuscript. S.E.L. conceived the study, performed analyses, participated in data interpretation, and revised the manuscript. A.S. performed transcriptome assemblies and positive selection analyses, participated in data interpretation, and revised the manuscript. S.M.B. conceived the study and helped in design and coordination, assisted in data interpretation, and assisted in drafting and revising the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
G.J.M. was supported in part by the BYU Graduate Student Fellowship. G.J.M., A.S., and S.M.B. were supported by grants from the National Science Foundation (S.M.B.; DEB-1655981) and the American Philosophical Society (S.M.B.).
Data Availability Statement
The data sets and trees supporting the results of this article are available in the datadryad repository, https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.mkkwh70vq (accessed on 7 June 2021). Raw reads generated in this study are available through BioProject PRJNA737479. COX1 sequences from as-yet-unidentified species are available on NCBI (accessions: MZ394513–MZ394519).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the members of the Bybee Lab at BYU as well as Jim Lloyd and Marc Branham for access to specimens. We further thank members of the Bybee lab for assistance with Illumina library preparation We thank the BYU DNA Sequencing Center and the Microarray and Genomic Analysis Core Facility at the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah for transcriptome sequencing as well as Perry Ridge, David Morris, Ryan Hillary, and Perry Wood for assistance with transcriptome assembly and analyses. We also are appreciative to BYU for access to the Fulton Supercomputer, as well as the Oakley lab for access to and assistance with the PIA pipeline.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gilad, Y.; Przeworski, M.; Lancet, D. Loss of olfactory receptor genes coincides with the acquisition of full trichromatic vision in primates. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bybee, S.; Córdoba-Aguilar, A.; Duryea, M.C.; Futahashi, R.; Hansson, B.; Lorenzo-Carballa, M.O.; Schilder, R.; Stoks, R.; Suvorov, A.; Svensson, E.I.; et al. Odonata (dragonflies and damselflies) as a bridge between ecology and evolutionary genomics. Front Zool. 2016, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keesey, I.W.; Grabe, V.; Gruber, L.; Koerte, S.; Obiero, G.F.; Bolton, G.; Khallaf, M.A.; Kunert, G.; Lavista-Llanos, S.; Valenzano, D.R.; et al. Inverse resource allocation between vision and olfaction across the genus Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanger-Hall, K.F.; Sander Lower, S.E.; Lindberg, L.; Hopkins, A.; Pallansch, J.; Hall, D.W. The evolution of sexual signal modes and associated sensor morphology in fireflies (Lampyridae, Coleoptera). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, G.M.; Boston, E.S.M.; Finarelli, J.A.; Murphy, W.J.; Higgins, D.G.; Teeling, E.C. The Birth and Death of Olfactory Receptor Gene Families in Mammalian Niche Adaptation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1390–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montell, C. Drosophila visual transduction. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Friedrich, M. Molecular evolution of the Drosophila retinome: Exceptional gene gain in the higher Diptera. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias-Muñoz, A.; Rangel Olguin, A.G.; Briscoe, A.D. Evolution of Phototransduction Genes in Lepidoptera. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 2107–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, S.M.; Friedrich, M.; Humphreys, W.F.; Jones, T.M.; Warrant, E.J.; Wcislo, W.T. Consequences of evolutionary transitions in changing photic environments. Austral Ento. 2017, 56, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, R.C. Phototransduction in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204 Pt 20, 3403–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.; Minke, B. Drosophila photoreceptors and signaling mechanisms. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2009, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, R.C.; Raghu, P. Visual transduction in Drosophila. Nature 2001, 413, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.H.; Xu, H.; Munch, T.A.; Bennett, R.R.; Grable, E.A. The retina of Manduca sexta: Rhodopsin expression, the mosaic of green-, blue- and UV-sensitive photoreceptors, and regional specialization. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.L. Gene duplication and the origin of novel proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8791–8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakakuwa, M.; Kurasawa, M.; Giurfa, M.; Arikawa, K. Spectral heterogeneity of honeybee ommatidia. Naturwissenschaften 2005, 92, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, G.C.; Wolfe, K.H. Turning a hobby into a job: How duplicated genes find new functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plachetzki, D.C.; Fong, C.R.; Oakley, T.H. The evolution of phototransduction from an ancestral cyclic nucleotide gated pathway. Proc. R. Soc. B 2010, 277, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- South, A.; Lewis, S.M. Determinants of reproductive success across sequential episodes of sexual selection in a firefly. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.E. Studies on the Flash Communication System in Photinus Fireflies. Misc. Publ. Mus. Zool. 1966, 130, 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bethune, C.J.S. A Luminous Larva. Can. Èntomol. 1868, 1, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branner, J.C. The luminosity of termites. Science 1910, 32, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, H.A. The synchronal flashing of fireflies. Science 1916, 44, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B. A luminous spider. Science 1925, 62, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, A.; LeVan, K.; Leombruni, L.; Orians, C.M.; Lewis, S.M. Examining the Role of Cuticular Hydrocarbons in Firefly Species Recognition. Ethology 2008, 114, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, R.D.; De Cock, R.; Matthysen, E. Sexual communication by pheromones in a firefly, Phosphaenus hemipterus (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Anim. Behav. 2005, 70, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Q.-L.; Lewis, S.M. Mate Recognition and Sex Differences in Cuticular Hydrocarbons of the Diurnal Firefly Ellychnia corrusca (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Ann. Èntomol. Soc. Am. 2010, 103, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhout, H.F.; Emlen, D.J. Competition among body parts in the development and evolution of insect morphology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3685–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.J.; Lord, N.P.; Branham, M.A.; Bybee, S.M. Review of the firefly visual system (Coleoptera: Lampyridae) and evolution of the opsin genes underlying color vision. Org. Divers. Evol. 2015, 15, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, S.E.; Hall, D.W. Variation in opsin genes correlates with signalling ecology in North American fireflies. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 4679–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, C.R.; Fujimoto, M.S.; Lord, N.P.; Shin, S.; McKenna, D.D.; Suvorov, A.; Martin, G.J.; Bybee, S.M. Overcoming the loss of blue sensitivity through opsin duplication in the largest animal group, beetles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, Y.; Kainuma, T. Diel changes in the expression of long wavelength-sensitive and ultraviolet-sensitive opsin genes in the Japanese firefly, Luciola cruciata. Gene 2009, 436, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.C.; Ayers, D.M.; Popp, M.P.; Hargrave, P.A. Short wavelength-sensitive opsins from the Saharan silver and carpenter ants. Invert. Neurosci. 1997, 3, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, A.D.; Chittka, L. The evolution of color vision in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 471–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuda, R.; Marlétaz, F.; Bentley, M.A.; Holland, P.W.H. Conservation, Duplication, and Divergence of Five Opsin Genes in Insect Evolution. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briscoe, A.D.; Bybee, S.M.; Bernard, G.D.; Yuan, F.; Sison-Mangus, M.P.; Reed, R.D.; Warren, A.D.; Llorente-Bousquets, J.; Chiao, C.-C. Positive selection of a duplicated UV-sensitive visual pigment coincides with wing pigment evolution in Heliconius butterflies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3628–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvorov, A.; Jensen, N.O.; Sharkey, C.R.; Fujimoto, M.S.; Bodily, P.; Wightman, H.M.C.; Ogden, T.H.; Clement, M.J.; Bybee, S.M. Opsins have evolved under the permanent heterozygote model: Insights from phylotranscriptomics of Odonata. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 26, 1306–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, T.R.; Lower, S.E.; Chang, C.-H.; Bessho-Uehara, M.; Martin, G.J.; Bewick, A.J.; Behringer, M.; Debat, H.J.; Wong, I.; Day, J.C.; et al. Firefly genomes illuminate parallel origins of bioluminescence in beetles. Elife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.J.; Stanger-Hall, K.F.; Branham, M.A.; Da Silveira, L.F.L.; Lower, S.E.; Hall, D.W.; Li, X.-Y.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Bybee, S.M. Higher-level phylogeny and reclassification of Lampyridae (Coleoptera: Elateroidea). Insect Syst. Divers. 2019, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofler, R.; Orozco-Terwengel, P.; De Maio, N.; Pandey, R.V.; Nolte, V.; Futschik, A.; Kosiol, C.; Schlötterer, C. PoPoolation: A toolbox for population genetic analysis of next generation sequencing data from pooled individuals. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, R.M.; Tegenfeldt, F.; Li, J.; Zdobnov, E.M.; Kriventseva, E.V. OrthoDB: A hierarchical catalog of animal, fungal and bacterial orthologs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D358–D365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7, improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, S.R. Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, D.I.; Pankey, M.S.; Zaharoff, A.K.; Battelle, B.A.; Bracken-Grissom, H.D.; Breinholt, J.W.; Bybee, S.M.; Cronin, T.W.; Garm, A.; Lindgren, A.R.; et al. Using phylogenetically-informed annotation (PIA) to search for light-interacting genes in transcriptomes from non-model organisms. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4, Phylogenetic Analysis by Maximum Likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redelings, B. Erasing Errors due to Alignment Ambiguity When Estimating Positive Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchard, M.A.; Redelings, B.D. BAli-Phy: Simultaneous Bayesian inference of alignment and phylogeny. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2047–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayes Factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R. Codon-substitution models for detecting molecular adaptation at individual sites along specific lineages. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, A.S.; Pankey, M.S.; Plachetzki, D.C.; Villacorta, C.; Syme, A.E.; Serb, J.M.; Omilian, A.R.; Oakley, T.H. Gene duplication and the origins of morphological complexity in pancrustacean eyes, a genomic approach. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevesich, J.; Kreuz, A.J.; Montell, C. Requirement for the PDZ domain protein, INAD, for localization of the TRP store-operated channel to a signaling complex. Neuron 1997, 18, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, B.H.; Zhu, M.Y. Regulation of the TRP Ca2+ channel by INAD in Drosophila photoreceptors. Neuron 1996, 16, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wes, P.D.; Xu, X.Z.; Li, H.S.; Chien, F.; Doberstein, S.K.; Montell, C. Termination of phototransduction requires binding of the NINAC myosin III and the PDZ protein INAD. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-Z.S.; Wes, P.; Chen, H.; Li, H.-S.; Yu, M.; Morgan, S.; Liu, Y.; Montell, C. Retinal targets for calmodulin include proteins implicated in synaptic transmission. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31297–31307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.; Sander, P.; Gobert, A.; Bähner, M.; Hermann, R.; Paulsen, R. The transient receptor potential protein (Trp), a putative store-operated Ca2+ channel essential for phosphoinositide-mediated photoreception, forms a signaling complex with NorpA, InaC and InaD. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 7036–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, S.; Sierralta, J.; Sun, Y.; Bodner, R.; Suzuki, E.; Becker, A.; Socolich, M.; Zuker, C.S. A multivalent PDZ-domain protein assembles signalling complexes in a G-protein-coupled cascade. Nature 1997, 388, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, S.B.; Weckstrom, M. Fast and slow photoreceptors—a comparative-study of the functional diversity of coding and conductances in the Diptera. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1993, 172, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Socolich, M.; Wall, M.A.; Graves, J.; Wang, Z.; Ranganathan, R. Dynamic scaffolding in a G protein-coupled signaling system. Cell 2007, 131, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Montell, C. TRP and the PDZ protein, INAD, form the core complex required for retention of the signalplex in Drosophila photoreceptor cells. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, S.; Sun, Y.; Suzuki, E.; Zuker, C. Independent anchoring and assembly mechanisms of INAD signaling complexes in Drosophila photoreceptors. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Shah, S.; Suzuki, E.; Zars, T.; O’Day, P.M.; Hyde, D.R. The drosophila dgq gene encodes a Gα protein that mediates phototransduction. Neuron 1994, 13, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.-T.; Tseng-Crank, J.; Kim, E.; Mahapatra, C.; Shino, S.; Zhou, Y.; An, L.; Doerge, R.W.; Pak, W.L. DAG lipase activity is necessary for TRP channel regulation in Drosophila photoreceptors. Neuron 2008, 58, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montell, C.; Rubin, G.M. Molecular characterization of the Drosophila trp locus: A putative integral membrane protein required for phototransduction. Neuron 1989, 2, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.S.; Meisner, S.; Liu, H.; Weckström, M.; Torkkeli, P.H. Transcriptome analysis and RNA interference of cockroach phototransduction indicate three opsins and suggest a major role for TRPL channels. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Satoh, A.K.; Postma, M.; Huang, J.; Ready, D.F.; Hardie, R.C. Ca2+-dependent metarhodopsin inactivation mediated by calmodulin and NINAC myosin III. Neuron 2008, 59, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, K.; Wasserman, D.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Mills, E.; Elsaesser, R.; Li, H.-S.; Montell, C. Dependence on a retinophilin/myosin complex for stability of PKC and INAD and termination of phototransduction. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11337–11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Montell, C. Light-dependent translocation of visual arrestin regulated by the NINAC myosin III. Neuron 2004, 43, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.K.; Ready, D.F. Arrestin1 mediates light-dependent rhodopsin endocytosis and cell survival. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolph, P.J.; Ranganathan, R.; Colley, N.J.; Hardy, R.W.; Socolich, M.; Zuker, C.S. Arrestin function in inactivation of G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin in vivo. Science 1993, 260, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, H. Light-regulated binding of rhodopsin kinase and other proteins to cattle photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 4389–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, C.; Chabre, M.; Plouet, J.; Tuyen, V.V.; De Kozak, Y.; Faure, J.P.; Kuhn, H. Retinal S antigen identified as the 48K protein regulating light-dependent phosphodiesterase in rods. Science 1985, 228, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. The structural basis of arrestin-mediated regulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 110, 465–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.P.; Shieh, B.H.; Zuker, C.S. Isolation and structure of an arrestin gene from Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, D.R.; Mecklenburg, K.L.; Pollock, J.A.; Vihtelic, T.S.; Benzer, S. Twenty Drosophila visual system cDNA clones: One is a homolog of human arrestin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVine, H.; Smith, D.P.; Whitney, M.; Malicki, D.M.; Dolph, P.J.; Smith, G.F.; Burkhart, W.; Zuker, C.S. Isolation of a novel visual-system-specific arrestin: An in vivo substrate for light-dependent phosphorylation. Mech. Dev. 1990, 33, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Komori, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Sakai, Y.; Hotta, Y.; Matsumoto, H. A 49-kilodalton phosphoprotein in the Drosophila photoreceptor is an arrestin homolog. Science 1990, 248, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.E. Bioluminescent Communication in Insects. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 1971, 16, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, N. Flash Communication Systems of Japanese Fireflies. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2004, 44, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanger-Hall, K.F.; Lloyd, J.E.; Hillis, D.M. Phylogeny of North American fireflies (Coleoptera: Lampyridae): Implications for the evolution of light signals. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2007, 45, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y. False-positive results obtained from the branch-site test of positive selection. Genes Genet. Syst. 2008, 83, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; He, J.; Dong, Z.; Liu, G.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Ren, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Genomic and experimental data provide new insights into luciferin biosynthesis and bioluminescence evolution in fireflies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, M. Evolution of visual performance-associated genes in Drosophila. eLS 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).