Insecticidal Activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Strains on the Nettle Caterpillar, Euprosterna elaeasa (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Concentration–Mortality Bioassay
2.3. Time–Mortality Bioassay
2.4. Anti–Feeding Effect
2.5. Mortality in Semi–Controlled Test
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Concentration–Mortality Bioassay
3.2. Time–Mortality Bioassay
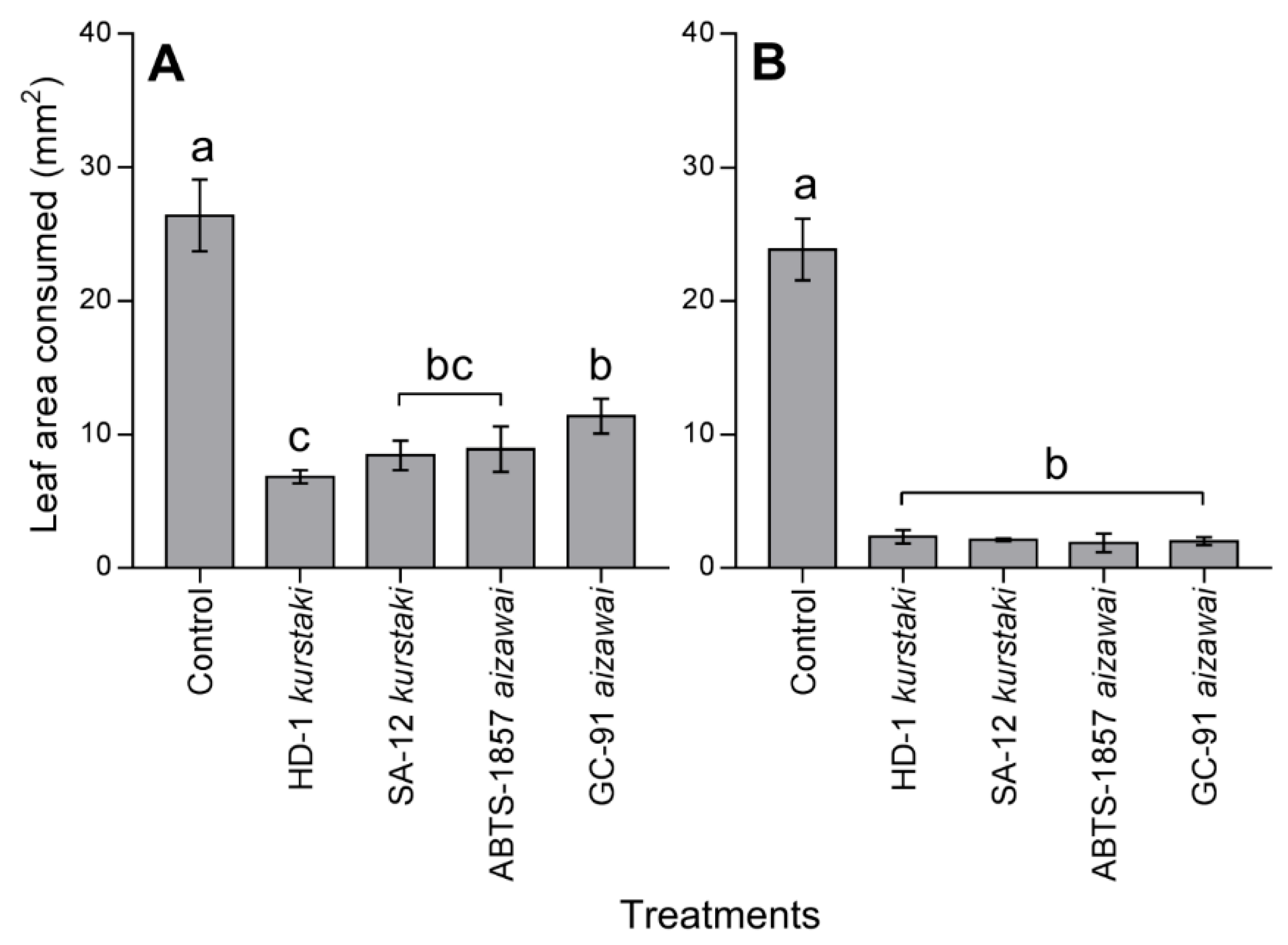
3.3. Anti–Feeding Effect
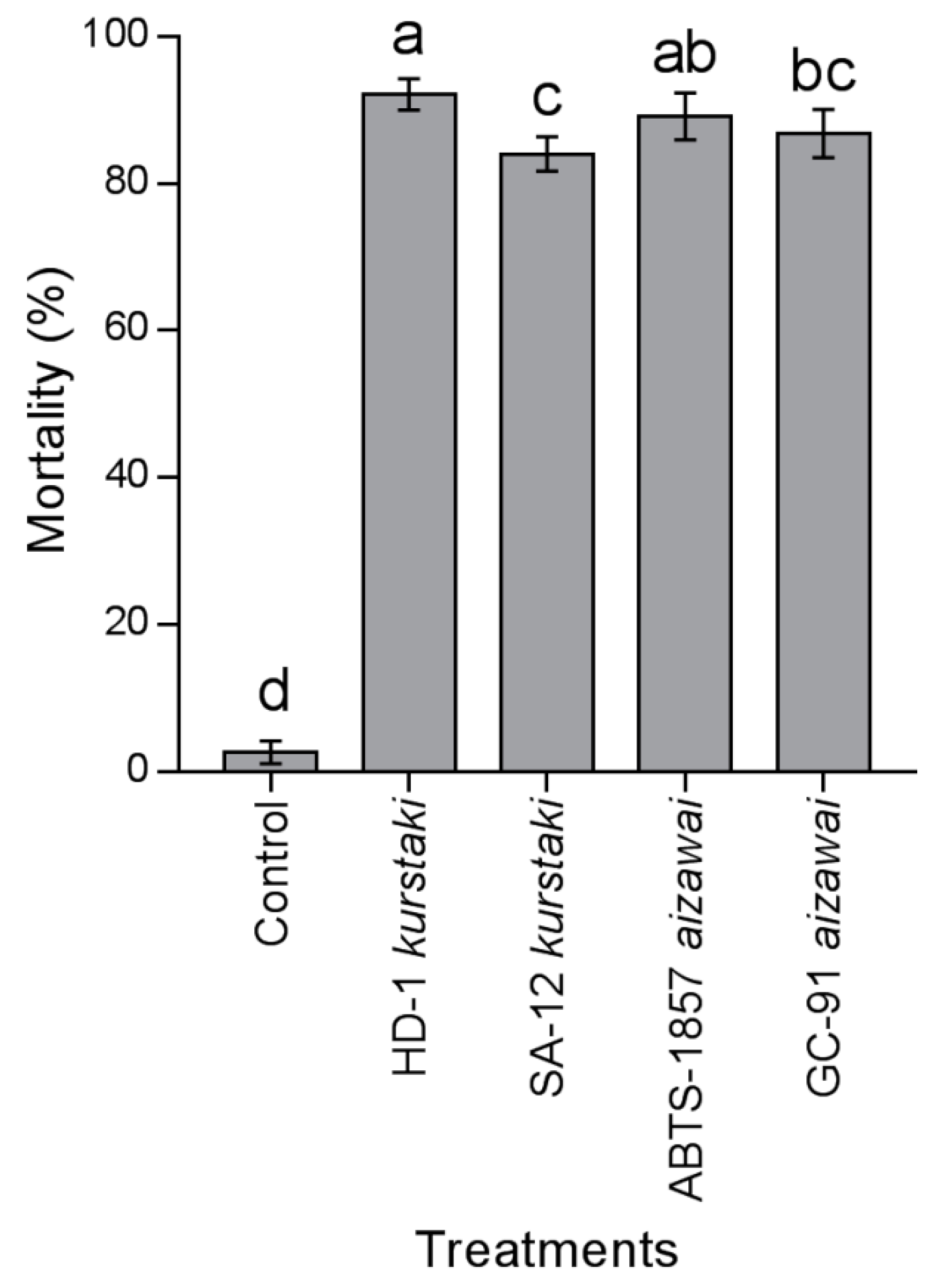
3.4. Mortality in Semi–Controlled Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Genty, P.; Desmier de Chenon, R.; Morin, J.P. Les ravageurs du palmier a huile en Amerique latine. Oléagineux 1978, 33, 325–419. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, L.C.; Plata-Rueda, A. Lepidoptera vectors of Pestalotiopsis fungal disease: First records in oil palm plantations from Colombia. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2013, 33, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, F.W.; Giblin-Davis, R.; Moore, D.; Abad, R. Insects on Palms; Cabi: London, UK, 2001; p. 400. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado, H.; de La Torre, R.A.; Barrera, E.; Martínez, L.; Bustillo, A. Ciclo de vida y tasa de consumo de Euprosterna elaeasa Dyar (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae) defoliador de la palma de aceite. Rev. Palmas 2014, 35, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, A.R.; Cruz, M.A.; Genty, P. The root absorption technique for controlling oil-palm pests. Oléagineux 1988, 43, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, O.L.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Martínez, L.C. Oil palm plantations as an agroecosystem: Impact on integrated pest management and pesticide use. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2013, 24, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Lambraño, R.; Caballero-Gallardo, K.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Toxicity and antifeedant activity of essential oils from three aromatic plants grown in Colombia against Euprosterna elaeasa and Acharia fusca (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, C.B.; Kuntom, A.; Dorasamy, S.; Omar, M.R.; Nor, M.Y.M.; Noh, M.R.M. 2006. Determination of acephate, methamidophos and monocrotophos in crude palm oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2006, 108, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, C.B.; Chong, C.L. Acephate, methamidophos and monocrotophos residues in a laboratory-scale oil refining process. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D. An overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Last, J.M. Global change: Ozone depletion, greenhouse warming, and public health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 1993, 14, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, J.L.; Wang, K.; Ferguson, G. Residual toxicity of avermectin b1 and pyridaben to eight commercially produced beneficial arthropod species used for control of greenhouse pests. Biol. Control 2000, 17, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantsidis, G.R.; O’Reilly, A.O.; Douris, V.; Vontas, J. Functional validation of target-site resistance mutations against sodium channel blocker insecticides (SCBIs) via molecular modeling and genome engineering in Drosophila. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 104, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeddam, J.L.; Cruzado, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Ravallec, M. A new nucleopolyhedrovirus from the oil-palm leaf-eater Euprosterna elaeasa (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae): Preliminary characterization and field assessment in Peruvian plantation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 96, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakeri, S.A.; Ali, S.R.A.; Tajuddin, N.S.; Kamaruzzaman, N.E. Efficacy of entomopathogenic fungi, Paecilomyces spp., in controlling the oil palm bagworm, Pteroma pendula (Joannis). J. Oil Palm Res. 2009, 21, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Kamarudin, N.; Ali, S.R.A.; Masri, M.M.M.; Ahmad, M.N.; Manan, C.A.H.C.; Kamarudin, N. Controlling Metisa plana Walker (Lepidoptera: Psychidae) outbreak using Bacillus thuringiensis at an oil palm plantation in Slim River, Perak, Malaysia. J. Oil Palm Res. 2017, 29, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnepf, E.; Crickmore, N.; Van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Feitelson, J.; Zeigler, D.R.; Dean, D.H. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.; Likitvivatanavong, S.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Bacillus thuringiensis: A story of a successful bioinsecticide. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.M.D.C.; Martinez, L.C.; Barbosa, S.G.; Serrão, J.E.; Wilcken, C.F.; Soares, M.A.; Silva, A.A.D.; Carvalho, A.G.D.; Zanuncio, J.C. Toxicity and cytopathology mediated by Bacillus thuringiensis in the midgut of Anticarsia gemmatalis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengol, G.; Escobar, M.C.; Maldonado, M.E.; Orduz, S. Diversity of Colombian strains of Bacillus thuringiensis with insecticidal activity against dipteran and lepidopteran insects. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Cowles, E.A.; Pietrantonio, P.V. The mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimov, S.; Weemen-Hendriks, M.; Dukiandjiev, S.; de Maagd, R.A. Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin Cry1 hybrid proteins with increased activity against the Colorado potato beetle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5328–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Ellar, D.J.; Bishop, A.; Johnson, C.; Lin, S.; Hart, E.R. Characterization of a Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin which is toxic to insects in three orders. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2000, 76, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Rolim, G.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Martínez, L.C.; Ribeiro, G.T.; Serrão, J.E.; Zanuncio, J.C. Side effects of Bacillus thuringiensis on the parasitoid Palmistichus elaeisis (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2020, 189, 109978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basri, W.M.; Ramlah, A.A.S.; Norman, K. Status report on the use of Bacillus thuringiensis in the control of some oil palm pests. Elaeis 1994, 6, 82–101. [Google Scholar]
- González, G.R.; Acuña, R.S.; Moizant, R.C.; Maestre, R.B.; Quintana, A.D.; Marcano, J.F. Agricultural technology of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq,) and integrated management of its defoliator Opsiphanes cassina Felder (Lepidoptera: Brassolidae) in commercial plantations at Monagas State, Venezuela. Rev. Cient. UDO Agr. 2012, 12, 584–598. [Google Scholar]
- Prasetyo, A.E.; Lopez, J.A.; Eldridge, J.R.; Zommick, D.H.; Susanto, A. Long-term study of Bacillus thuringiensis application to control Tirathaba rufivena, along with the impact to Elaeidobius kamerunicus, insect biodiversity and oil palm productivity. J. Oil Palm Res. 2018, 30, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Wu, K. Recent progress on the interaction between insects and Bacillus thuringiensis crops. Philos. T. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.C.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Zanuncio, J.C.; Serrão, J.E. Leucothyreus femoratus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae): Feeding and behavioral activities as an oil palm defoliator. Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1964; p. 333. [Google Scholar]
- Berretta, M.F.; Pedarros, A.S.; Sauka, D.H.; Pérez, M.P.; Onco, M.I.; Benintende, G.B. Susceptibility of agricultural pests of regional importance in South America to a Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ia protein. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S.; Jin, M.; Wu, C.; Chakraborty, P.; Xiao, Y. Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein family Vip3A and mode of action against pest lepidopteran. Pest Manage. Sci. 2020, 76, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daquila, B.V.; Scudeler, E.L.; Dossi, F.C.A.; Moreira, D.R.; Pamphile, J.A.; Conte, H. Action of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bacillales: Bacillaceae) in the midgut of the sugarcane borer Diatraea saccharalis (Fabricius, 1794) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2019, 184, 109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.S.; Dias, N.P.; Costa, L.L.; De Bortoli, C.P.; Souza, E.H.; Santos, A.C.F.; De Bortoli, S.A.; Polanczyk, R.A. Interactions of Bacillus thuringiensis strains for Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) susceptibility. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 168, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle Loto, F.; Carrizo, A.E.; Romero, C.M.; Baigorí, M.D.; Pera, L.M. Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) strains from northern Argentina: Esterases, profiles, and susceptibility to Bacillus thuringiensis (Bacillales: Bacillaceae). Fla. Entomol. 2019, 102, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venette, R.C.; Luhman, J.C.; Hutchison, W.D. Survivorship of field-collected European corn borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) larvae and its impact on estimates of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner. J. Entomol. Sci. 2000, 35, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommireddy, P.L.; Leonard, B.R. Survivorship of Helicoverpa zea and Heliothis virescens on cotton plant structures expressing a Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashtoly, T.A.; Abolmaaty, A.; El-Said El-Zemaity, M.; Hussien, M.I.; Alm, S.R. Enhanced toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies kurstaki and aizawai to black cutworm larvae (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) with Bacillus sp. NFD2 and Pseudomonas sp. FNFD1. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liao, C.; Brooks, L.; Trowell, S.C.; Akhurst, R.J. Binding of Cry δ-endotoxins to brush border membrane vesicles of Helicoverpa armigera and Helicoverpa punctigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insect Sci. 2005, 12, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Roberts, H.L.; Schmidt, O. Tolerance to Bacillus thuringiensis endotoxin in immune-suppressed larvae of the flour moth Ephestia kuehniella. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2007, 96, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Han, J.K.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, J.I.; Kim, K.S. Various enterotoxin and other virulence factor genes widespread among Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis strains. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodhan, M.; Haider, Z.; Shirale, D.K.; Islam, M.; Hossain, M.; Paranjape, V.; Shelton, A.M. Susceptibility of field populations of eggplant fruit and shoot borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenée) to Cry1Ac, the protein expressed in Bt eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) in Bangladesh. Insects 2019, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Rup, P.J.; Koul, O. Acute, sublethal and combination effects of azadirachtin and Bacillus thuringiensis toxins on Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2007, 97, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri-BeSheli, B. Efficacy of Bacillus thuringiensis, mineral oil, insecticidal emulsion and insecticidal gel against Phyllocnistis citrella Stainton (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae). Plant Prot. Sci. 2008, 44, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amizadeh, M.; Hejazi, M.J.; Niknam, G.; Arzanlou, M. Compatibility and interaction between Bacillus thuringiensis and certain insecticides: Perspective in management of Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbeck, A.; Otto, M. Specificity and combinatorial effects of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxins in the context of GMO environmental risk assessment. Frontiers Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, A.S.; Gringorten, J.L. Degradation of Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin in host insect gut juice. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 167, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, N.A.; Robinson, C.J.; McMahon, M.D.; Holt, J.; Handelsman, J.; Raffa, K.F. Contributions of gut bacteria to Bacillus thuringiensis-induced mortality vary across a range of Lepidoptera. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Bravo, A. Processing of Cry1Ab δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis by Manduca sexta and Spodoptera frugiperda midgut proteases: Role in protoxin activation and toxin inactivation. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Celis, R.; Jiménez-Lacharme, F.; Hidalgo-Salvatierra, O. Susceptibility of the larvae of Sibine apicalis (Dyar) to Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki. Turrialba 1974, 24, 106–107. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, L.C.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Serrao, J.E.; Zanuncio, J.C. Life history traits and damage potential of an invasive pest Acharia fusca (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae) on oil palm. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, G.; Karuppiah, H.; Sreeramulu, B.; Paulchamy, R.; Sundaram, J. Occurrence of natural lectin with bacterial agglutination property in the serum of lepidopteran pest, Parasa lepida. Entomol. Sci. 2019, 22, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Strain | No. Insects | Lethal Concentration | Estimated Concentration (mg mL−1) | 95% Confidence Interval (mg mL−1) | Slope ± SE | χ2 (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD-1 var. kurstaki | 150 | LC50 | 1.133 | 0.845–1.561 | 2.22 ± 0.25 | 1.23 (0.36) |
| 150 | LC90 | 4.268 | 2.802–8.512 | |||
| SA-12 var. kurstaki | 150 | LC50 | 1.258 | 0.805–2.136 | 2.40 ± 0.41 | 1.89 (0.16) |
| 150 | LC90 | 4.299 | 2.442–10.92 | |||
| ABTS-1857 var. aizawai | 150 | LC50 | 0.840 | 0.664–1.075 | 1.73 ± 0.35 | 1.34 (0.22) |
| 150 | LC90 | 4.623 | 3.172–7.875 | |||
| GC-91 var. aizawai | 150 | LC50 | 1.097 | 0.742–1.724 | 2.40 ± 0.41 | 1.38 (0.22) |
| 150 | LC90 | 4.579 | 2.647–8.894 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plata-Rueda, A.; Quintero, H.A.; Serrão, J.E.; Martínez, L.C. Insecticidal Activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Strains on the Nettle Caterpillar, Euprosterna elaeasa (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae). Insects 2020, 11, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050310
Plata-Rueda A, Quintero HA, Serrão JE, Martínez LC. Insecticidal Activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Strains on the Nettle Caterpillar, Euprosterna elaeasa (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae). Insects. 2020; 11(5):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050310
Chicago/Turabian StylePlata-Rueda, Angelica, Hughes Antonio Quintero, José Eduardo Serrão, and Luis Carlos Martínez. 2020. "Insecticidal Activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Strains on the Nettle Caterpillar, Euprosterna elaeasa (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae)" Insects 11, no. 5: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050310
APA StylePlata-Rueda, A., Quintero, H. A., Serrão, J. E., & Martínez, L. C. (2020). Insecticidal Activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Strains on the Nettle Caterpillar, Euprosterna elaeasa (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae). Insects, 11(5), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050310







