Biochemical Mechanisms, Cross-resistance and Stability of Resistance to Metaflumizone in Plutella xylostella
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Bioassay
2.4. Enzyme Activity Assays
2.5. Cross-Resistance
2.6. Stability of Resistance
2.7. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Synergism of PBO, DEF, and DEM with Metaflumizone
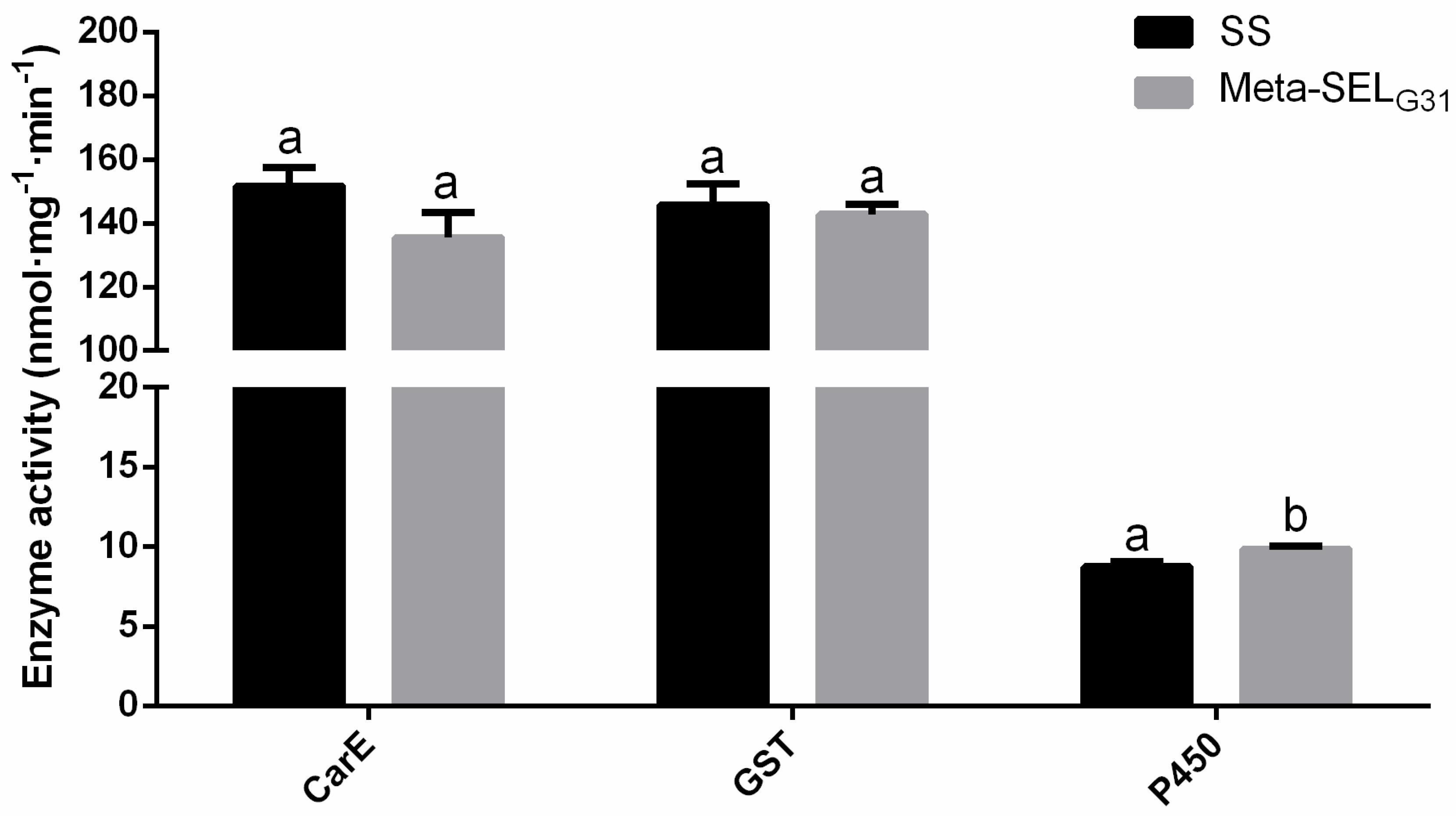
3.2. Activity of the Detoxification Enzymes in Susceptible and Metaflu-SEL Strains of P. xylostella
3.3. Cross-Resistance of Metaflumizone to Different Conventional and New Chemical Insecticides
3.4. Stability of Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zalucki, M.P.; Shabbir, A.; Silva, R.; Adamson, D.; Shu-Sheng, L.; Furlong, M.J. Estimating the Economic Cost of One of the World’s Major Insect Pests, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae): Just How Long Is a Piece of String? J. Econ. Èntomol. 2012, 105, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Feng, X.; Liu, S.-S.; You, M.; Furlong, M.J. Biology, Ecology, and Management of the Diamondback Moth in China. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 2016, 61, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, J.E.L.; Amaral, M.H.P.; Siqueira, H.A.A.; Barros, R.; Silva, P.A.F. Resistance monitoring of Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) to risk-reduced insecticides and cross resistance to spinetoram. Phytoparasitica 2016, 44, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Mao, K.; You, H.; Li, J. Susceptibility of field populations of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella, to a selection of insecticides in Central China. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 132, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APRD. Arthropod Pesticide Resistance Database. Available online: https://www.pesticideresistance.org/search.php (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- Takagi, K.; Hamaguchi, H.; Nishimatsu, T.; Konno, T. Discovery of metaflumizone, a novel semicarbazone insecticide. Veter Parasitol. 2007, 150, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, V.L.; Hayashi, J. Metaflumizone is a novel sodium channel blocker insecticide. Veter Parasitol. 2007, 150, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.S.; Gupta, S. Persistence of metaflumizone on cabbage (Brassica oleracea Linne) and soil, and its risk assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 185, 6201–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BASF. Agricultural Products: Metaflumizone Worldwide Technical Brochure; BASF: Ludwigshafen, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Metaflumizone. Pestic. Sci. Adm. 2009, 30, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Sun, X.; Su, J. Biochemical mechanisms for metaflumizone resistance in beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 113, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakame, S.K.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y. Baseline toxicity of metaflumizone and lack of cross resistance between indoxacarb and metaflumizone in diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J. Econ. Èntomol. 2013, 106, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y. Long-term monitoring and characterization of resistance to chlorfenapyr in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) from China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 75, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Wan, H.; Li, J. Fitness and inheritance of metaflumizone resistance in Plutella xylostella. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 139, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IRAC, Insecticide Resistance Action Committee. IRAC Susceptibility Test Methods Series, Method No: 018, Version 3.4. Available online: www.irac-online.org (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Shao, Z.R.; Feng, X.; Li, S.; Li, Z.Y.; Huang, J.D.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.D. Guideline for Insecticide Resistance Monitoring of Plutella xylostella (L.) on Cruciferous Vegetables; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Asperen, K. A study of housefly esterases by means of a sensitive colorimetric method. J. Insect Physiol. 1962, 8, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, W.H.; Jakoby, W.B. Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-Transferases. In Detoxication and Drug Metabolism: Conjugation and Related Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981; Volume 77, pp. 398–405. [Google Scholar]
- Aitio, A. A simple and sensitive assay of 7-ethoxycoumarin deethylation. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 85, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E. Evolution of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1994, 39, 47–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. Probit-MS Chart: A Computer Program for Probit Analysis; National Chung Hsing University: Taichung, Taiwan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Denholm, I.; Rowland, M.W. Tactics for managing pesticide resistance in arthropods: Theory and practice. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shono, T.; Zhang, L.; Scott, J.G. Indoxacarb resistance in the house fly, Musca domestica. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2004, 80, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyed, A.H.; Ahmad, M.; Saleem, M.A. Cross-resistance and genetics of resistance to indoxacarb in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Hollingworth, R.M. Synergism of insecticides provides evidence of metabolic mechanisms of resistance in the obliquebanded leafroller Choristoneura rosaceana(Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2004, 60, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, L.J.; Bird, L. Genetics, cross-resistance and synergism of indoxacarb resistance in Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 73, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyed, A.H.; Wright, D.J. Genetics and evidence for an esterase-associated mechanism of resistance to indoxacarb in a field population of diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Sun, X.-X. High level of metaflumizone resistance and multiple insecticide resistance in field populations of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Guangdong Province, China. Crop. Prot. 2014, 61, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaağaç, S.U. Enzyme Activities and Analysis of Susceptibility Levels in Turkish Tuta Absoluta Populations to Chlorantraniliprole and Metaflumizone Insecticides. Phytoparasitica 2015, 43, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehare, S.; Ghodki, B.S.; Lande, G.K.; Pawade, V.; Thakare, A.S. Inheritance of resistance and cross resistance pattern in indoxacarb-resistant diamondback moth Plutella xylostella L. Èntomol. Res. 2010, 40, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Mu, W.; Wang, W.; Zhou, C.; Li, X. Resistance mechanisms and risk assessment regarding indoxacarb in the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Phytoparasitica 2014, 42, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-L.; Su, W.; Zhang, J.-H.; Yang, Y.-H.; Dong, K.; Wu, Y. Two novel sodium channel mutations associated with resistance to indoxacarb and metaflumizone in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Insect Sci. 2015, 23, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.B.S.; Shad, S.A. Genetic analysis, realized heritability and synergistic suppression of indoxacarb resistance in Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae). Crop. Prot. 2016, 84, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georghiou, G.P. The Evolution of Resistance to Pesticides. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1972, 3, 133–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Qin, S.; Yan, C.Y.; Ji, X.C.; Xie, S.H.; Chen, M.C. Monitoring on the resistance of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) to fifteen kinds of pesticides in Hainan region. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2014, 36, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Roditakis, E.; Mavridis, K.; Riga, M.; Vasakis, E.; Morou, E.; Rison, J.L.; Vontas, J. Identification and detection of indoxacarb resistance mutations in the para sodium channel of the tomato leafminer, Tuta absoluta. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Ijaz, M.; Shad, S.A.; Khan, H. Stability of Field-Selected Resistance to Conventional and Newer Chemistry Insecticides in the House Fly, Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Neotropical Èntomol. 2015, 44, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddiq, B.; Afzal, M.B.S.; Shad, S.A. Studies on genetics, stability and possible mechanism of deltamethrin resistance in Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae) from Pakistan. J. Genet. 2016, 95, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, M.B.S.; Shad, S.A.; Basoalto, E.; Ejaz, M.; Serrão, J.E. Characterization of indoxacarb resistance in Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae): Cross-resistance, stability and fitness cost. J. Asia Pacific Èntomol. 2015, 18, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Strain | Synergist | LC50(mg/L) 95%CL | Slope ± SE | SR a | N b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS | None | 1.47 (1.18~1.85) | 2.23 ± 0.27 | - | 240 |
| TPP | 1.44 (0.99~2.60) | 1.45 ± 0.23 | 1.02 | 193 | |
| DEM | 0.93 (0.63~1.33) | 1.49 ± 0.25 | 1.58 | 211 | |
| PBO | 1.36 (0.99~1.95) | 1.47 ± 0.22 | 1.08 | 185 | |
| Meta-SEL (G27) | None | 1968.31 (1544.16~2507.72) | 1.82 ± 0.25 | - | 232 |
| TPP | 1055.82 (696.59~1406.49) | 2.05 ± 0.34 | 1.86 | 186 | |
| DEM | 1387.59 (987.70~1827.14) | 2.22 ± 0.38 | 1.42 | 179 | |
| PBO | 1585.70 (1098.49~2205.19) | 1.73 ± 0.32 | 1.24 | 177 |
| Insecticide | Strain | LC50 (95% CL) mg·L−1 | Slope ± SE | χ2 | df | p | RR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| indoxacarb | SS | 1.69 (1.13~3.44) | 1.56 ± 0.38 | 0.42 | 2 | 0.81 | 11.63 |
| G23 | 19.66 (13.65~34.01) | 1.54 ± 0.32 | 3.98 | 3 | 0.26 | ||
| spinosad | SS | 0.55 (0.37~1.03) | 1.51 ± 0.27 | 2.23 | 4 | 0.69 | 1.75 |
| G23 | 0.95 (0.65~1.52) | 1.07 ± 0.16 | 3.98 | 5 | 0.55 | ||
| spinetoram | SS | 0.08 (0.03~0.14) | 1.33 ± 0.32 | 0.81 | 3 | 0.85 | 3.52 |
| G23 | 0.20 (0.15~0.28) | 1.64 ± 0.22 | 4.41 | 5 | 0.49 | ||
| abamectin | SS | 0.07 (0.05~0.08) | 1.83 ± 0.21 | 2.50 | 4 | 0.65 | 2.81 |
| G23 | 0.18 (0.08~0.29) | 1.44 ± 0.30 | 2.12 | 2 | 0.35 | ||
| beta-cypermethrin | SS | 6.51 (4.35~16.71) | 1.71 ± 0.48 | 2.82 | 2 | 0.24 | 0.71 |
| G23 | 4.67 (3.01~10.15) | 1.18 ± 0.28 | 0.33 | 3 | 0.95 | ||
| chlorfenapyr | SS | 0.41 (0.29~0.81) | 1.92 ± 0.40 | 2.49 | 2 | 0.29 | 0.49 |
| G22 | 0.32 (0.16~0.57) | 0.81 ± 0.20 | 1.16 | 4 | 0.88 | ||
| diafenthiuron | SS | 21.44 (16.45~28.96) | 2.09 ± 0.31 | 2.89 | 4 | 0.58 | 0.79 |
| G23 | 16.96 (11.64~24.48) | 1.30 ± 0.21 | 1.51 | 4 | 0.83 | ||
| chlorantraniliprole | SS | 0.07 (0.03~0.11) | 1.27 ± 0.23 | 0.17 | 3 | 0.98 | 2.16 |
| G23 | 0.15 (0.08~0.22) | 1.39 ± 0.24 | 5.07 | 4 | 0.28 | ||
| BT (WG-001) | SS | 0.89 (0.49~5.17) | 1.43 ± 0.41 | 0.05 | 3 | 1.00 | 3.34 |
| G22 | 2.98 (1.49~12.60) | 0.89 ± 0.19 | 3.51 | 5 | 0.62 | ||
| chlorfluazuron | SS | 1.34 (0.86~1.94) | 1.39 ± 0.24 | 2.24 | 4 | 0.69 | 0.97 |
| G22 | 1.29 (0.95~1.91) | 1.71 ± 0.32 | 1.58 | 3 | 0.66 |
| G a | N | LC50 (mg/L) (95%CL) | Slope ± SE | χ2 | p | df | RR b | DR c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G28 | 210 | 1599.13 (1289.07~1983.45) | 2.14 ± 0.27 | 1.58 | 0.81 | 4 | 1087.85 | - |
| G31 | 210 | 668.42 (420.28~1355.04) | 0.97 ± 0.20 | 1.12 | 0.89 | 4 | 454.71 | 58.20 |
| G32 | 179 | 795.37 (475.42~2600.78) | 1.36 ± 0.33 | 0.49 | 0.92 | 3 | 541.07 | 50.26 |
| G34 | 187 | 329.15 (234.62~509.16) | 1.68 ± 0.33 | 0.98 | 0.81 | 3 | 223.91 | 79.42 |
| G35 | 214 | 127.07 (76.55~255.38) | 1.03 ± 0.24 | 1.85 | 0.76 | 4 | 86.44 | 92.05 |
| G36 | 209 | 33.81 (20.57~51.23) | 1.08 ± 0.20 | 4.00 | 0.41 | 4 | 23.00 | 97.89 |
| G39 | 219 | 1.82 (0.46~3.17) | 1.04 ± 0.28 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 3 | 1.23 | 99.89 |
| G40 | 183 | 3.71 (2.34~11.10) | 1.84 ± 0.45 | 1.63 | 0.65 | 3 | 2.53 | 99.77 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; You, H.; Li, J. Biochemical Mechanisms, Cross-resistance and Stability of Resistance to Metaflumizone in Plutella xylostella. Insects 2020, 11, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050311
Shen J, Li Z, Li D, Wang R, Zhang S, You H, Li J. Biochemical Mechanisms, Cross-resistance and Stability of Resistance to Metaflumizone in Plutella xylostella. Insects. 2020; 11(5):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050311
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jun, Zhao Li, Dongyang Li, Rumeng Wang, Shuzhen Zhang, Hong You, and Jianhong Li. 2020. "Biochemical Mechanisms, Cross-resistance and Stability of Resistance to Metaflumizone in Plutella xylostella" Insects 11, no. 5: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050311
APA StyleShen, J., Li, Z., Li, D., Wang, R., Zhang, S., You, H., & Li, J. (2020). Biochemical Mechanisms, Cross-resistance and Stability of Resistance to Metaflumizone in Plutella xylostella. Insects, 11(5), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11050311




