Behavioral and Electrophysiological Effects of Ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi Sprague) (Apiales: Apiaceae) Essential Oil and Its Constituents on Nymphal and Adult Bean Bugs, Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Alydidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Essential Oils and Chemicals
2.2. Insects
2.3. Gas Chromatography (GC)
2.4. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
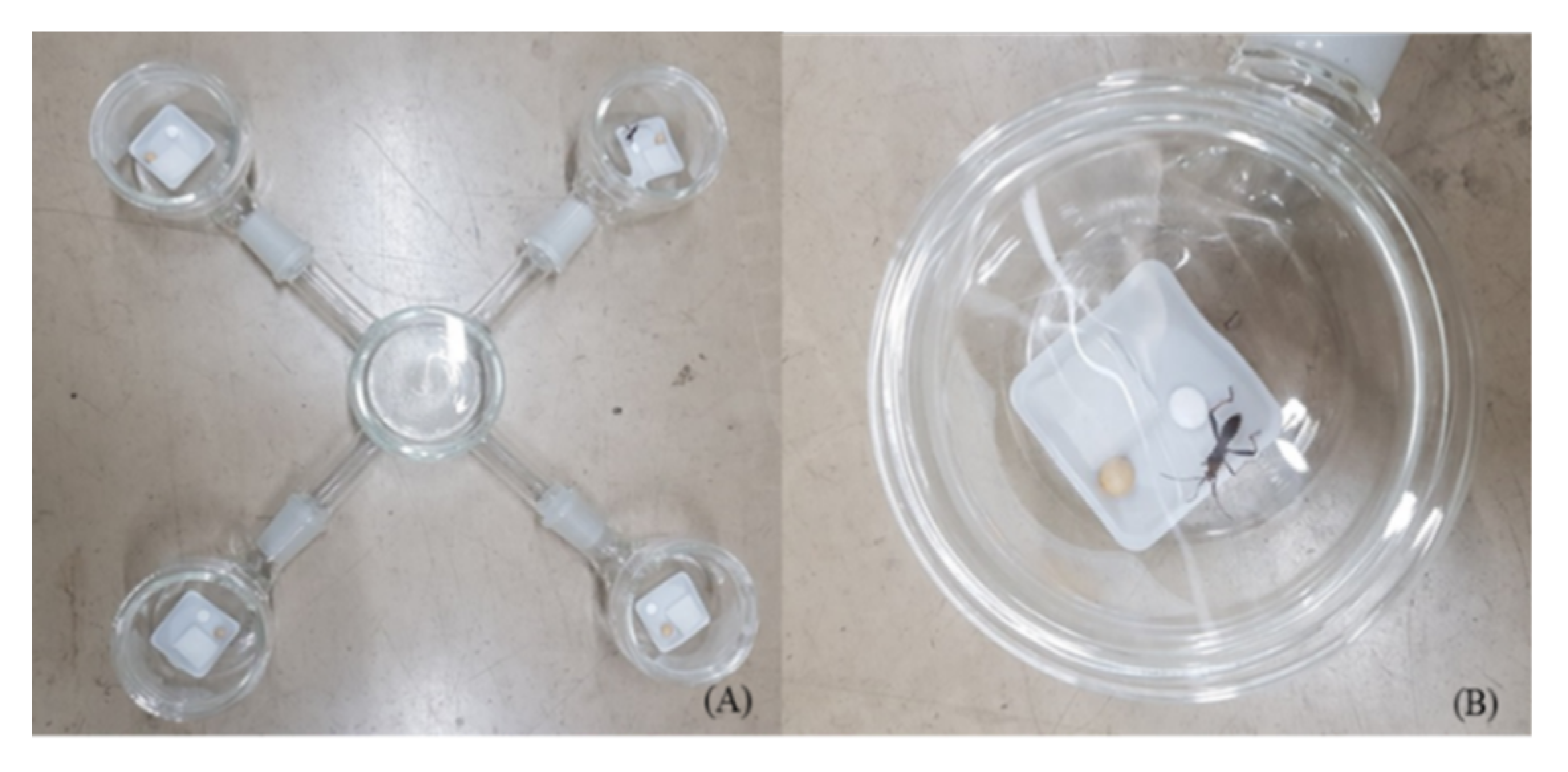
2.5. Repellent Activity Test
2.6. Electroantennogram (EAG)
3. Results and Discussion
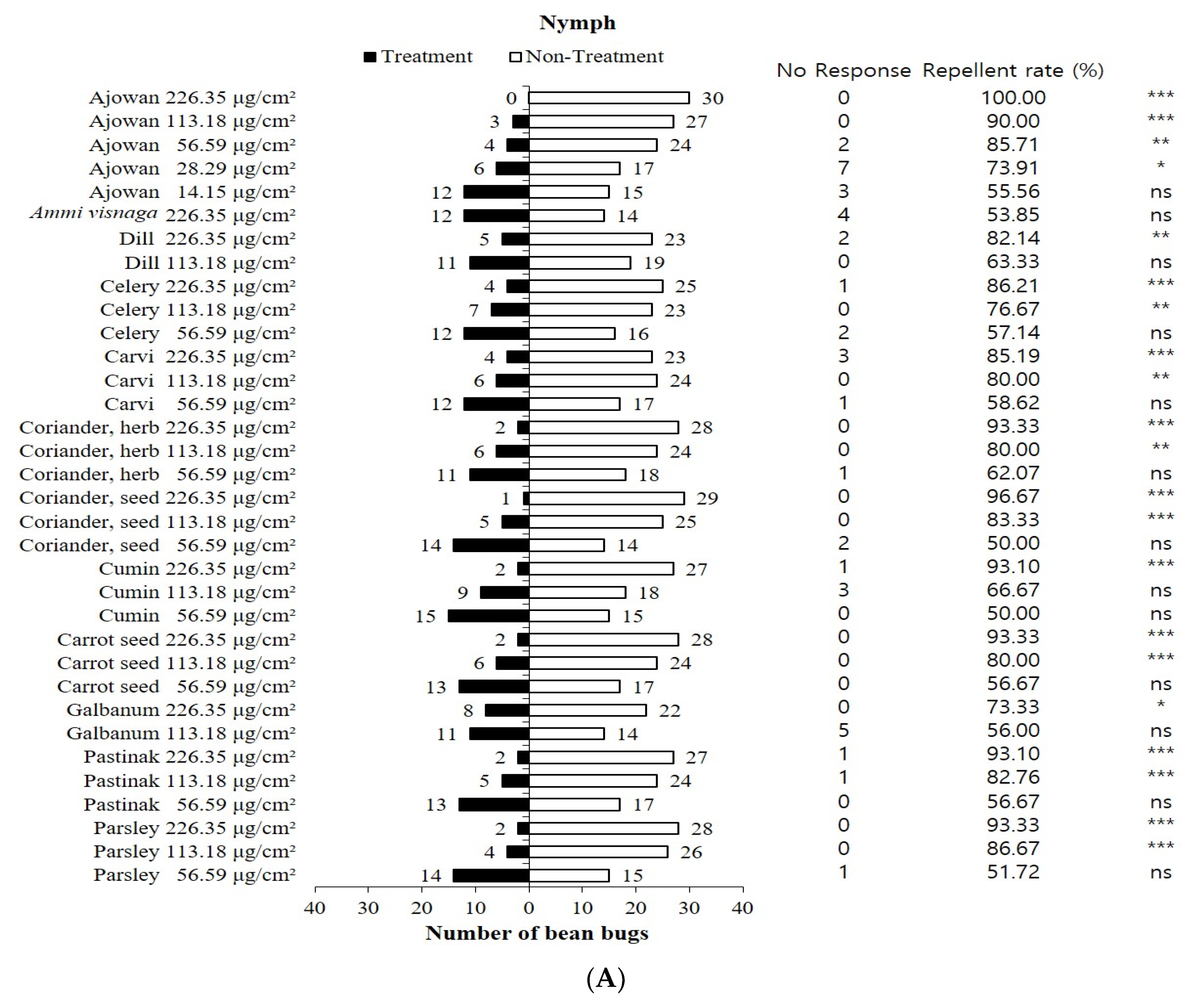
3.1. Repellent Activities of Apiaceae Plant Essential Oils
3.2. Repellent Activities of Constituents Identified from Ajowan Essential Oil
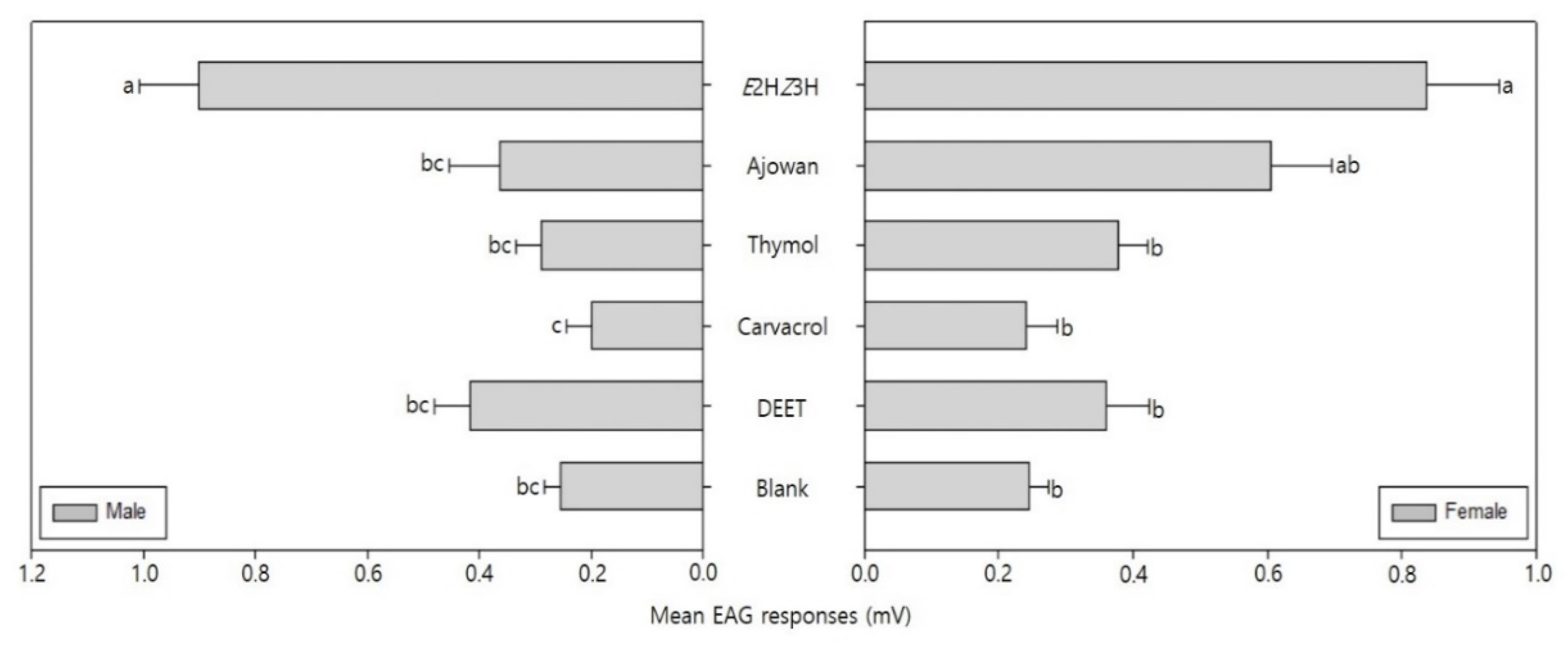
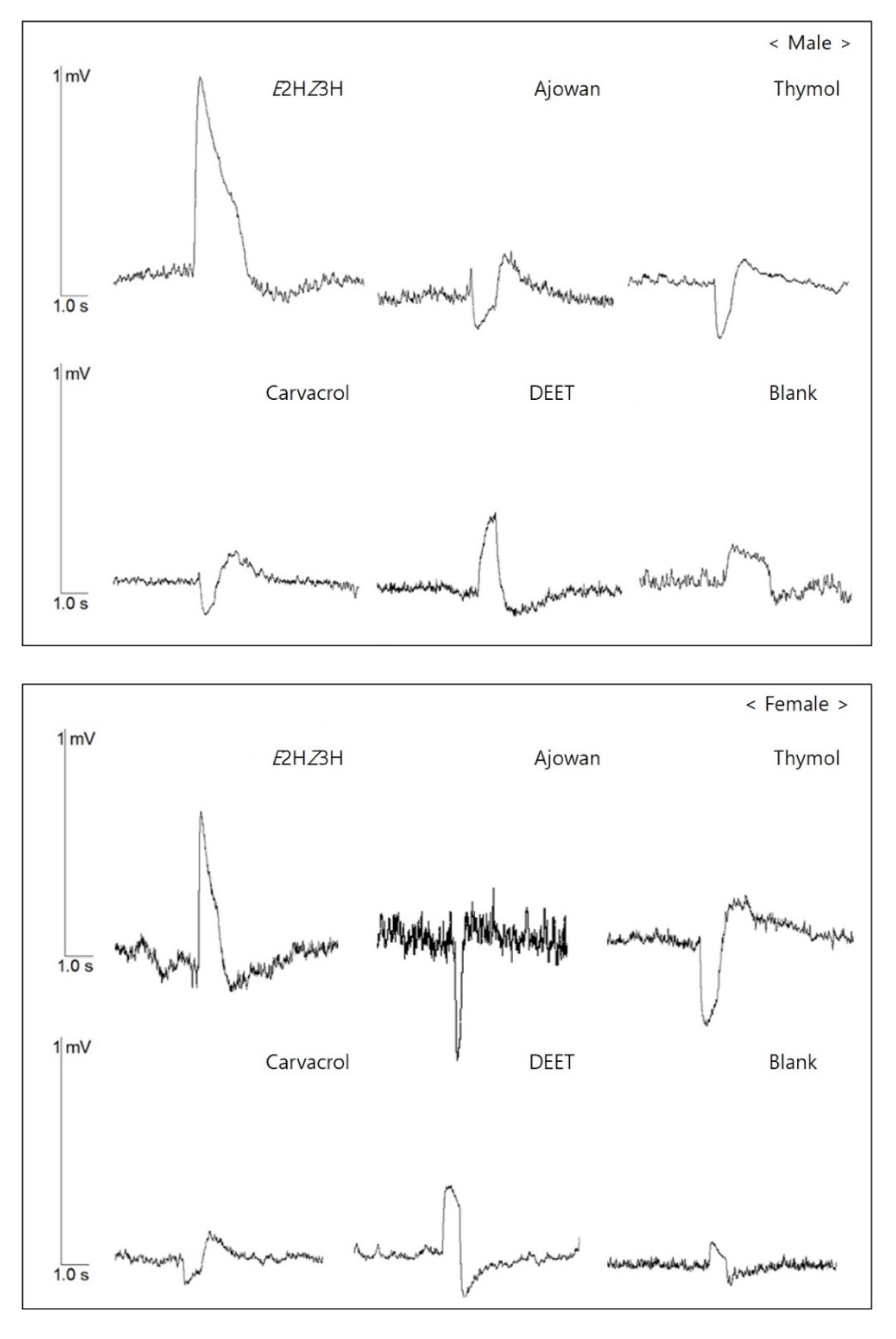
3.3. EAG Response of Bean Bugs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Son, C.K.; Park, S.G.; Hwang, Y.H.; Choi, B.S. Field occurrence of stink bug and its damage in soybean. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2000, 45, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.H.; Huh, H.S.; Park, C.G. Review on true bugs infesting tree fruits, upland crops, and weeds in Korea. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2003, 42, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Osakabe, M.; Honda, K. Influence of trap and barrier crops on occurrence of and damage by stink bugs and lepidopterous pod borers in soybean fields. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2002, 46, 233–241, (In Japanese with English Summary). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, U.T. Occurrence and control method of Riptortus pedestris (Hemiptera: Alydidae): Korean Perspectives. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 52, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Endo, N.; Takahashi, M. Reducing seed damage by soybean bugs by growing small-seeded soybeans and delaying sowing time. Crop Prot. 2006, 25, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Paik, C.H.; Choi, M.Y.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Na, S.Y. Seasonal occurrence, soybean damage and control efficacy of ban bug, Riptortus clavatus Thunberg (Hemiptera: Alydidae) at soybean in Honam province. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2004, 43, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, H. Population prevalence of occurrence and spatial distribution pattern of Piezodorus hybneri adults (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) on soybean. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1992, 27, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hayatsu, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Nagayama, A.; Tago, K.; Fukatsu, T. Symbiont-mediated insecticide resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo, N.; Wada, T.; Chiba, M. An attractant for Piezodorus hybneri (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) contained in the aggregation pheromone of Riptortus clavatus (Heteroptera: Alydidae). Kyushu Plant Prot. Res. 2003, 49, 88–91, (In Japanese with English summary). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, N.; Wada, T.; Mizutani, N.; Moriya, S.; Sasaki, R. Ambiguous response of Riptortus clavatus (Heteroptera: Alydidae) to different blends of its aggregation pheromone components. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2005, 40, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, H.S.; Park, K.H.; Seo, W.D.; Park, C.G. Interaction of aggregation pheromone components of the bean bug, Riptortus clavatus (Thnuberg) (Heteroptera: Alydidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2005, 40, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, H.S.; Yun, J.E.; Wada, T.; Mizutani, N.; Park, C.G. Composition of the aggregation pheromone components of Korean bean bug and attractiveness of different blends. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2008, 47, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S.; Higuchi, H.; Mizutani, N.; Nakamori, H.; Kadosawa, T.; Ono, M. Multifunctional communication in Riptortus clavatus (Heteroptera: Alydidae): Conspecific nymphs and egg parasitoid Ooencyrtus nezarae use the same adult attractant pheromones as chemical cue. J. Chem. Ecol. 1995, 21, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Mizutani, N.; Endo, N.; Fukuda, T.; Matsuyama, T.; Ito, K.; Moriya, S.; Sasaki, R. A new component of attractive aggregation pheromone in the bean bug, Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg) (Heteroptera: Alydidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2007, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Mizutani, N.; Honda, Y.; Endo, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Moriya, S.; Fukuda, T.; Sasaki, R. A supplemental component of aggregation attractant pheromone in the bean bug Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg), related to food exploitation. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2007, 42, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.M.; Kim, E.; Kim, D.; Bhuyain, M.M.H.; Lim, U.T. Use of aggregation pheromone traps increases infestation of adult Riptortus pedesris (Hemiptera: Alydidae) in soybean fields. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2578–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Tol, R.; van der Sommen, A.T.C.; Boff, M.I.C.; van Bezooijen, J.; Sabelis, M.W.; Smits, P.H. Plants protect their roots by alerting the enemies of grubs. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Paik, C.H.; Seo, H.Y.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.D. Feeding preference, nymphal development time, bodyweight increase, and survival rate of the ben bug, Riptortus clavatus (Thurnberg) (Hemiptera: Alydida), on soybean varieties. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2005, 44, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.K.; Lee, S.G.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, C.S.; Ahn, Y.J. Feeding and attraction of Agelastica coerulea (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) to Betulaceae plants. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 1978–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.C.; Zhu, J.; Harris, J.; Ochieng, S.A.; Baker, T.C. Electroantennogram responses of a parasitic wasp, Microplitis croceipes, to host-related volatile and anthropogenic compounds. Physiol. Entomol. 2001, 26, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, M.; Rajeswary, M.; Arivoli, S.; Tennyson, S.; Benelli, G. Larvicidal and repellent potential of Zingiber nimmonii (J. Graham) Dalzell (Zingiberaceae) essential oil: An eco-friendly tool against malaria, dengue, and lymphatic filariasis mosquito vectors? Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khater, H.F.; Ramadan, M.Y.; El-Madawy, R.S. ousicidal, ovicidal and repellent efficacy of some essential oils against lice and flies infesting water buffaloes in Egypt. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 164, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaenson, T.G.T.; Pålsson, K.; Borg-Karlson, A.K. Evaluation of extracts and oils of tick-repellent plants from Sweded. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2005, 19, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.R.; Finn, R.D.; Graham, K.M.; Sparagano, O.A. Present and future potential of plant-derived products to control arthropods of veterinary and medical significance. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z. Non-host plant essential oil volatiles with potential for a ‘push-pull’strategy to control the tea green leafhopper, Empoasca vitis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2015, 156, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.M.; Zeyaur, R.K.; Pickett, J.A. The use of push-pull strategies in integrated pest management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 375–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauchline, A.L.; Cook, S.M.; Powell, W.; Osborne, J.L. Effects of non-host plant odour on Meligethes aeneus during immigration to oilseed rape. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 146, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, H.J.; Kang, J.; Kim, G.H.; Park, I.K. Insecticidal and acetylcholine esterase inhibition activity of Apiaceae plant essential oils and their constituents against adults of German cockroach (Blattella germanica). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7194–7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.K.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.G.; Shin, S.C. Nematicidal activity of plant essential oils and components from ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi), allspice (Pimenta dioica) and litsea (Litsea cubeba) essential oils against pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). J. Nematol. 2007, 39, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.; Oh, C.S.; Koh, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, K.S.; Park, P.S.; Jang, M.J.; Lee, H.R.; Park, I.K. Antifungal activities after vaporization of ajowna (Trachyspermum ammi) and allspice (Pimenta dioica) essential oils and blends of their constituents against three Aspergillus species. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2016, 28, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.R.; Kim, G.H.; Choi, W.S.; Park, I.K. Repellent activity of Apiaceae plant essential oils and their constituents against adult German cockroaches. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, W.; Huh, H.S.; Park, C.G. Fish materials as potent attractants for the male of bean bug, Riptortus clavatus. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2005, 8, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, C.H.; Lee, G.H.; Oh, Y.J.; Park, C.G.; Hwang, C.Y.; Kim, S.S. Pheromone trap type and height for attracting of Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Alydidae) in soybean field. Korean J. App. Entomol. 2009, 48, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.D.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, G.H.; Oon, Y.N.; Nam, M.H. Attractiveness of stink bugs to color, height and location of aggregation pheromone trap. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 49, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, H.S.; Park, C.G. Increased attractiveness of the aggregation pheromone trap of bean bug, Riptortus clavatus. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2006, 45, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, D.F.; Lopes, E.A.; Fialho Moraes, A.R.; Soares, M.S.; Visôtto, L.E.; Oliveira, C.R.; Moreira Valente, V.M. Formulation of botanical for the control of plant-pathogens: A review. Crop Prot. 2018, 110, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.M.; Jung, C.S.; Kang, J.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, S.W.; Hyun, J.H.; Park, I.K. Larvicidal and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of Apiaceae plant essential oils and their constituents against Aedes albopictus and formulation development. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9977–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Yoon, J.S.; Jung, J.W.; Hong, K.B.; Ahn, Y.J.; Kwon, H.W. Toxicity and repellency of origanum essential oil and its components against Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) adults. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2010, 13, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.U.; Koo, H.N.; Kim, G.H. Chemical composition, larvicidal action, and adult repellency of Thymus magnus against Aedes albopictus. J. Am. Mosquito Control 2012, 28, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, F.; Youssefi, M.R.; Tabari, M.A. Combination of carvacrol and thymol against the poultry red mite (Dermanyssus gallinae). Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4239–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabari, M.A.; Youssefi, M.R.; Maggi, F.; Benelli, G. Toxic and repellent activity of selected monoterpnoids (thymol, carvacrol and linalool) against the castor bean tick, Ixodes ricinus (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet. Parsitol. 2017, 245, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabanca, N.; Bernier, U.R.; Ali, A.; Wang, M.; Demirci, B.; Blythe, E.K.; Khan, S.I.; Baser, K.H.C.; Khan, I.A. Bioassay-guided investigation of two Monarda essential oils as repellent of yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8573–8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moretti, A.N.; Zerba, E.N.; Alzogaray, R.A. Behavioral and toxicological responses of Rhodnius prolixus and Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) to 10 monoterpene alcohols. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terriquez, J.A.; Klotz, S.A.; Meister, E.A.; Klotz, J.H.; Schmidt, J.O. Repellency of DEET, picaridin and three essential oils to Triatoma rubida (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lihua, L.; Aijun, Z.; Liu, C. Repellency of selected chemicals against the bed bug (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 2522–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarda, A.; Rubilar, J.F.; Miltz, J.; Galotto, M.J. The antimicrobial activity of microencapsulated thymol and carvacrol. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 46, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, H.R.; Otis, G.W.; Daley, J.; Schulz, T. Trials of apiguard, a thymol-based miticide part 2. Non-target effects on honey bees. Am. Bee J. 2000, 140, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- George, D.R.; Sparagano, O.A.E.; Port, G.; Okello, E.; Shiei, R.S.; Guy, J.H. Repellence of plant essential oils to Dermanyssus gallinae and toxicity to the non-target invertebrate Tenebrio molitor. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 162, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlou, M. Potential of Origanum compactum as a cercaricide in Morocco. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2002, 96, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, K.; Perich, M.J.; Khan, I.A. Botanical derivatives in mosquito control: A review. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1991, 7, 210–237. [Google Scholar]
- Rhman, J.U.; Ali, A.; Khan, I.A. Plant based products: Use and development as repellents against mosquito: A review. Fitoterapia 2014, 95, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Cermak, S.C.; Kenar, J.A.; Brewer, G.; Haynes, K.F.; Boxier, D.; Baker, P.D.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Li, A.Y.; et al. Better than DEET repellent compounds derived from coconut oil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckh, J.; Kaissling, K.E.; Schneider, D. Insect olfactory receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1965, 30, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Sakurai, T.; Nishioka, T.; Touhara, K. Insect sex-pheromone signals mediated by specific combinations of olfactory receptors. Science 2005, 307, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M.L.; Perez, D.; Rozas, R. Empirical correlations between electroantennograms and bioassays for Periplaneta americana. J. Chem. Ecol. 1989, 15, 2539–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Khan, Z.R.; Caballero, P.; Juliano, B.O. Olfactory sensitivity of two sympatric species of rice leaf folders (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) to plant volatiles. J. Chem. Ecol. 1990, 16, 2647–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound | Retention Index | Composition Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DB-1MS | HP-INNOWAX | ||
| α-Pinene | 928 | 1021 | 0.87 |
| Camphene | 940 | 1064 | 0.10 |
| β-Pinene | 967 | 1108 | 1.26 |
| Myrcene | 981 | 1165 | 0.48 |
| α-Terpinene | 1007 | 1181 | 0.13 |
| p-Cymene | 1012 | 1275 | 24.40 |
| 1,8-Cineole | 1018 | 1209 | 0.32 |
| Limonene | 1020 | 1200 | 0.44 |
| γ-Terpinene | 1050 | 1248 | 27.77 |
| Terpine-4-ol | 1159 | 1610 | 0.32 |
| Thymol | 1273 | 2207 | 41.77 |
| Carvacrol | 1278 | 2235 | 0.55 |
| Sum | - | - | 98.41 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-C.; Seo, S.-M.; Huh, M.-J.; Kwon, J.-H.; Nam, I.; Park, J.-H.; Park, I.-K. Behavioral and Electrophysiological Effects of Ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi Sprague) (Apiales: Apiaceae) Essential Oil and Its Constituents on Nymphal and Adult Bean Bugs, Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Alydidae). Insects 2020, 11, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020104
Lee S-C, Seo S-M, Huh M-J, Kwon J-H, Nam I, Park J-H, Park I-K. Behavioral and Electrophysiological Effects of Ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi Sprague) (Apiales: Apiaceae) Essential Oil and Its Constituents on Nymphal and Adult Bean Bugs, Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Alydidae). Insects. 2020; 11(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sung-Chan, Seon-Mi Seo, Min-Jung Huh, Jun-Hyeong Kwon, Il Nam, Ji-Hong Park, and Il-Kwon Park. 2020. "Behavioral and Electrophysiological Effects of Ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi Sprague) (Apiales: Apiaceae) Essential Oil and Its Constituents on Nymphal and Adult Bean Bugs, Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Alydidae)" Insects 11, no. 2: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020104
APA StyleLee, S.-C., Seo, S.-M., Huh, M.-J., Kwon, J.-H., Nam, I., Park, J.-H., & Park, I.-K. (2020). Behavioral and Electrophysiological Effects of Ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi Sprague) (Apiales: Apiaceae) Essential Oil and Its Constituents on Nymphal and Adult Bean Bugs, Riptortus clavatus (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Alydidae). Insects, 11(2), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020104





