Pest Control Potential of Social Wasps in Small Farms and Urban Gardens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Foraging Activity in Social Wasps
3. Prey Captured by Social Wasps
4. The Management of Social Wasp Colonies for Exploitation as Pest Predators
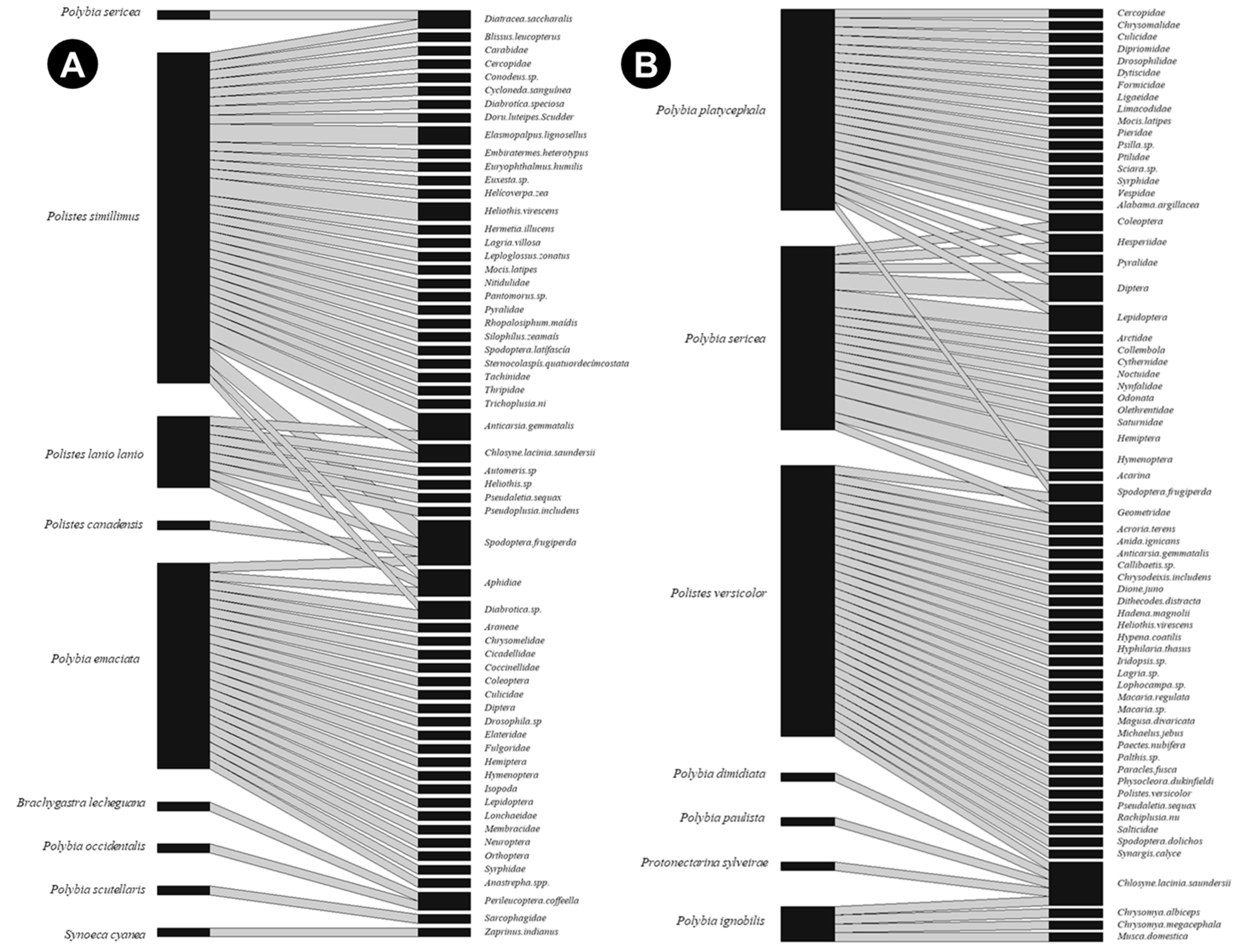
5. Prey Captured and Used by Social Wasps in Small Farms: A Study with Polistes simillimus
6. Prey Captured and Used by Social Wasps in Urban Gardens: A Study with Polybia platycephala
7. The Potential of Social Wasps as Biological Control Agents
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Botkin, D.; Keller, E. Ciência ambiental: Terra, um Planeta Vivo; LTC: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2011; 681p. [Google Scholar]
- Teodorovicz, T.; Alvarez, V.M.P.; Guimarães, T.A. Os mercados relevantes do ramo de agrotóxicos. Ensaios FEE 2016, 36, 869–892. [Google Scholar]
- Sanches-Bayo, F.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G. Worldwide decline of the entomofauna: A review of its drivers. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 232, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, B.A. Controle Biológico Conservativo e Produção Integrada do Morangueiro (PIMo). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Lavras, Lavras, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Parra, J.R.P.; Botelho, P.S.M.; Corrêa-Ferreira, S.; Bento, J.M.S. O Futuro do Controle Biológico. In Controle Biológico no Brasil, Parasitóides e Predadores; Parra, J.R., Botelho, P.S.M., Corrêa-Ferreira, S., Bento, J.M.S., Eds.; Manole: São Paulo, Brazil, 2002; pp. 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- DeBach, P. The necessity for an ecological approach to pest control on citrus in California. J. Econ. Entomol. 1951, 44, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabb, R.L.; Lawson, F.R. Some factors influencing the predation of Polistes wasps on tobacco hornworm. J. Econ. Entomol. 1957, 50, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences of Shang-Chiu. A preliminary study on the bionomics of hunting wasps and their utilization in cotton insect control. Acta Entomol. Sin. 1976, 19, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, O.W. The Social Wasps of the Americas Excluding the Vespinae; British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1978; 580p. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, J.M. The phylogenetic relationships and natural classification of the Vespoidea (Hymenoptera). Syst. Entomol. 1982, 7, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.G.; Matthews, R.W. The Social Biology of Wasps; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, R.M. Social Wasp (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) Foraging Behavior. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindo, M.; Dejean, A. Rhythm of activity and feeding behavior of Belonogaster juncea juncea (Hymenoptera:Vespidae). Sociobiology 1998, 32, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanne, R.L.; Taylor, B.J. Individual and Social Foraging in Social Wasps. In Food Exploitation by Social Insects: Ecological, Behavioral and Theoretical Approaches; Harau, S., Hrncir, M., Eds.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 53–79. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, B.C.; Paschoalini, M.F.; Prezoto, F. Temporal activity patterns and foraging behavior by social wasps (Hymenoptera, Polistinae) on fruits of Mangifera indica L. (Anacardiaceae). Sociobiology 2014, 61, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, M.A.; Lange, D.; Del-Claro, K.; Prezoto, F.; Campos, N.R.; Barbosa, B.C. Flower-visiting social wasps and plants interaction: Network pattern and environmental complexity. Psyche (Camb. Mass.) 2012, 2012, 478431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradbery, J.P. Wasps: An Account of the Biology and Natural History of Solitary and Social Wasps; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1973; 408p. [Google Scholar]
- Prezoto, F.; Cortes, S.A.O.; Melo, A.C. Vespas: De vilãs a parceiras. Ciência Hoje 2008, 48, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Prezoto, F.; Ribeiro Júnior, C.; Cortes, S.A.O.; Elisei, T. Manejo de vespas e marimbondos em ambiente urbano. In Manejo de Pragas Urbanas, 1st ed.; Pinto, A.S., Rossi, M.M., Salmeron, E., Eds.; CP2: Piracicaba, Brazil, 2007; pp. 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva, N.B.; Prezoto, F.; Fonseca, M.G.; Blassioli-Morae, M.C.; Borges, M.; Laumann, R.A.; Auad, A.M. The social wasp Polybia fastidiosuscula Saussure (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) uses herbivore-induced maize plant volatiles to locate its prey. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejean, A.; Rodriguez-Perez, H.; Carpenter, J.M.; Azémar, F.; Corbara, B. The predatory behavior of the Neotropical social wasp Polybia rejecta. Behav. Process. 2017, 140, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.G.A.; Gonçalves, C.R.; Galvão, D.M.; Gonçalves, A.J.L.; Gomes, J.; Silva, M.N.; Simoni, L. Quarto Catálogo Dos Insetos Que Vivem Nas Plantas do Brasil: Seus Parasitos e Predadores; Ministério da Agricultura, Depto. de Defesa e Inspeção Agropecuária: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1968; 621p. [Google Scholar]
- Gravena, S. Táticas de manejo integrado do bicho mineiro do cafeeiro Perileucoptera coffeella (Guérin-Méneville, 1842): I—Dinâmica populacional e inimigos naturais. An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 1983, 12, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Gobbi, N. Contribuição Ao Estudo do Ciclo Básico de Espécies do Gênero Polybia, Com Especial Referencia A Polybia (Myrapetra) Paulista e P. Occidentalis. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 1984, 28, 451–457. [Google Scholar]
- Gobbi, N.; Machado, V.L.L. Material Capturado e Utilizado Na Alimentacao de Polybia (Myrapetra) Paulista (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 1985, 14, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Gobbi, N.; Machado, V.L.L. Material Capturado e Utilizado Na Alimentação de Polybia Ignobilis. An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 1986, 15, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Picanço, M.; Ribeiro, L.J.; Leite, G.L.D.; Gusmão, M.R. Seletividade de inseticidas a Polybia ignobilis (Halliday) (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) predador de Ascia monuste orseis (Godart) (Lepidoptera: Pieridae). An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 1988, 27, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, O.M. Vespas sociais (Hymenoptera, Vespidae): Características e importância em agrossistemas. Insecta 1996, 5, 13–39. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Farinha, A.E.C.; Pinto, N.P.O. Natural enemies of Chlosyne lacinia saundersii Doubl. & Hew. (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae) in the state of São Paulo. An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 1996, 25, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Prezoto, F.; Santos-Prezoto, H.H.; Machado, V.L.L.; Zanúncio, J.C. Prey Captured and Used in Polistes versicolor (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) Nourishment. Neotrop. Entomol. 2006, 35, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisei, T.; Nunes, J.V.E.; Ribeiro Junior, C.; Fernandes Junior, A.J.; Prezoto, F. Uso da vespa social Polistes versicolor no controle de desfolhadores de eucalipto. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2010, 45, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.M.; Marques, O.M. Contribuição ao Estudo dos Vespídeos do Brasil; Série Publicações Digitais; Universidade Federal da Bahia, Departamento de Fitotecnia: Salvador, Brazil, 2001; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Prezoto, F.; Machado, V.L.L. Ação de Polistes (Aphanilopterues) simillimus Zikán, 1951 (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) na produtividade de uma lavoura de milho infestada com Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Rev. Bras. Zoociênc 1999, 1, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Prezoto, F.; Braga, N. Predation of Zaprinus indianus (Diptera: Drosophilidae) by the social wasp Synoeca cyanea (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, F.E.; Cavalcante, R.D.; Cavalcante, M.L.S.; Melo, Q.M.S. Polybia sericea Olivier, 1791 (Hymenoptera, Vespidae), predador de Diatraea saccharalis Fabr. (Lepidoptera, Crambidae), no Ceará. Fitossanidade 1977, 2, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Herdina, A.; Bitencourt, G.; Di Mare, R.; Barbosa, B.C. Polybia (Myrapetra) scutellaris (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) foraging on flies at carcasses of Rattus norvegicus (Rodentia: Muridae). Sociobiology 2016, 63, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannotti, E.; Prezoto, F.; Machado, V.L.L. Foraging activity of Polistes lanio lanio (Fabr.) (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). An. Soc. Entomol. Brasil 1995, 24, 455–463. [Google Scholar]
- Prezoto, F.; Giannotti, E.; Machado, V.L.L. Atividade forrageadora e material coletado pela vespa social Polistes simillimus Zikán, 1951 (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Insecta 1994, 3, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.M.; Gomes, F.B.; Somavilla, A.; Krug, C. Polistes canadensis (Linnaeus, 1758) (Vespidae: Polistinae) in the Western Amazon: A Potential Biological Control Agent. Sociobiology 2017, 64, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, Y.; Hernández, J.; Caraballo, P. Actividad de forrajeo de la avispa social Polybia emaciata (Hymenoptera: Vespidae: Polistinae). Rev. Colomb. Entomol. 2013, 39, 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, V.L.L.; Gobbi, N.; Alves Junior, V.V. Material Capturado e Utilizado Na Alimentacao de Polybia (Trichothorax) Sericea (Hymenoptera-Vespidae). Rev. Bras. Zool. 1988, 5, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezoto, F.; Lima, M.A.P.; Machado, V.L.L. Survey of preys Captured and Used by Polybia platycephala (Richards) (Hymenoptera: Vespidae, Epiponini). Neotrop. Entomol. 2005, 34, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Gomes, G.; Oliveira, H.G.; Morlin Junior, J.J.; Desuó, I.C.; Silva, I.M.D.; Shima, S.N.; Von Zuben, C.J. Foraging by Polybia (Trichothorax) ignobilis (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) on flies at animal carcasses. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2007, 51, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichara-Filho, C.C.; Santos, G.M.D.M.; Resende, J.J.; Cruz, J.D.; Gobbi, N.; Machado, V.L.L. Foraging behavior of the swarm-founding wasp, Polybia (Trichothorax) sericea (Hymenoptera, Vespidae): Prey capture and load capacity. Sociobiology 2009, 53, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Dormann, C.F.; Fründ, J.; Blüthgen, N.; Gruber, B. Indices, graphs and null models: Analyzing bipartite ecological networks. Open Ecol. J. 2009, 2, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 April 2019).
- Omoto, C.; Diez-Rodríguez, G.I. Herança da resistência de Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) a lambda-cialotrina. Neotrop. Entomol. 2001, 30, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Matson, P.A.; Parton, W.J.; Power, A.G.; Swift, M.J. Agricultural Intensification and Ecosystem Properties. Science 1997, 277, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; Booij, C.J.H.; Tscharntke, T. Sustainable pest regulation in agricultural landscapes: A review on landscape composition, biodiversity and natural pest control. Proc. R. Soc. B 2006, 273, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, E. The World History of Beekeeping and Honey Hunting; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1999; 682p. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, D.; Hartley, S.; Suckling, D.M.; Lester, P. The stinging response of the common wasp (Vespula vulgaris): Plasticity and variation in individual aggressiveness. Insectes Soc. 2015, 62, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandt, J.M.; Thomson, J.; Geffre, A.C.; Toth, A.L. Lab rearing environment perturbs social traits: A case study with Polistes wasps. Behav. Ecol. 2015, 26, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, F.R.; Rabb, R.L.; Guthrie, F.E.; Bowery, T.G. Studies of an integrated control system forhornworms on tobaco. J. Econ. Entomol. 1961, 54, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, W.P.; Jeanne, R.L. Polistes Wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) as Control Agents for Lepidopterous Cabbage Pests. Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butignol, E.A. Observações sobre a bionomia da vespa predadora Polistes versicolor (Olivier, 1791) (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) em Florianópolis/SC. An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 1992, 19, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanne, R.L. The adaptiveness of social wasp nest architecture. Q. Rev. Biol. 1975, 50, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akre, R.D.; Hill, W.B.; MacDonald, J.F. Artificial housing for yellow jacket colonies. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1973, 66, 803–805. [Google Scholar]
- Jandt, J.M.; Jeanne, R.L. German yellowjacket (Vespula germanica) foragers use odors inside the nest to find carbohydrate food sources. Ethology 2005, 111, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akre, R.D.; Hill, W.B.; MacDonald, J.F.; Garnett, W.B. Foraging distances of Vespula pensylvanica workers. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1975, 48, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, B.J. Potential manageable exploitation of social wasps, Vespula spp. (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), as generalist predators of insect pests. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2003, 49, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, P.J.; Beggs, J.R. Invasive success and management strategies for social Vespula wasps. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.E.; Bourke, A.F. The influence of sociality on the conservation biology of social insects. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picanço, M.C.; Oliveira, I.R.; Rosado, J.F.; Silva, F.M.; Gontijo, P.C.; Silva, R.S. Natural Biological Control of Ascia monuste by the Social Wasp Polybia ignobilis (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Sociobiology 2010, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, V.E.M.; Bezerra, J.M.T.; Amâncio, F.F.; Passos, V.M.A.; Carneiro, M. Aumento da carga de dengue no Brasil e unidades federadas, 2000 e 2015: Análise do Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2017, 20, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, S.; Law, G.; Cini, A. Why we love bees and hate wasps. Ecol. Entomol. 2018, 43, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, P.A.; Gonring, A.H.R.; Picanço, M.C.; Ramos, R.S.; Martins, J.C.; Ferreira, D.D. Natural Biological Control of Diaphania spp. (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) by Social Wasps. Sociobiology 2012, 59, 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Picanço, M.C.; Bacci, L.; Queiroz, R.B.; Silva, G.A.; Miranda, M.M.M.; Leite, G.L.D.; Suinaga, F.A. Social wasp predators of Tuta absoluta. Sociobiology 2011, 58, 1–13. [Google Scholar]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prezoto, F.; Maciel, T.T.; Detoni, M.; Mayorquin, A.Z.; Barbosa, B.C. Pest Control Potential of Social Wasps in Small Farms and Urban Gardens. Insects 2019, 10, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10070192
Prezoto F, Maciel TT, Detoni M, Mayorquin AZ, Barbosa BC. Pest Control Potential of Social Wasps in Small Farms and Urban Gardens. Insects. 2019; 10(7):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10070192
Chicago/Turabian StylePrezoto, Fábio, Tatiane Tagliati Maciel, Mateus Detoni, Angie Zuleidi Mayorquin, and Bruno Corrêa Barbosa. 2019. "Pest Control Potential of Social Wasps in Small Farms and Urban Gardens" Insects 10, no. 7: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10070192
APA StylePrezoto, F., Maciel, T. T., Detoni, M., Mayorquin, A. Z., & Barbosa, B. C. (2019). Pest Control Potential of Social Wasps in Small Farms and Urban Gardens. Insects, 10(7), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10070192





