Cold Tolerance and Population Dynamics of Leptoglossus zonatus (Hemiptera: Coreidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Colony
2.2. Cold Tolerance
2.3. Oviposition Period
2.4. Population Demographics
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Cold Tolerance
3.2. Oviposition Period
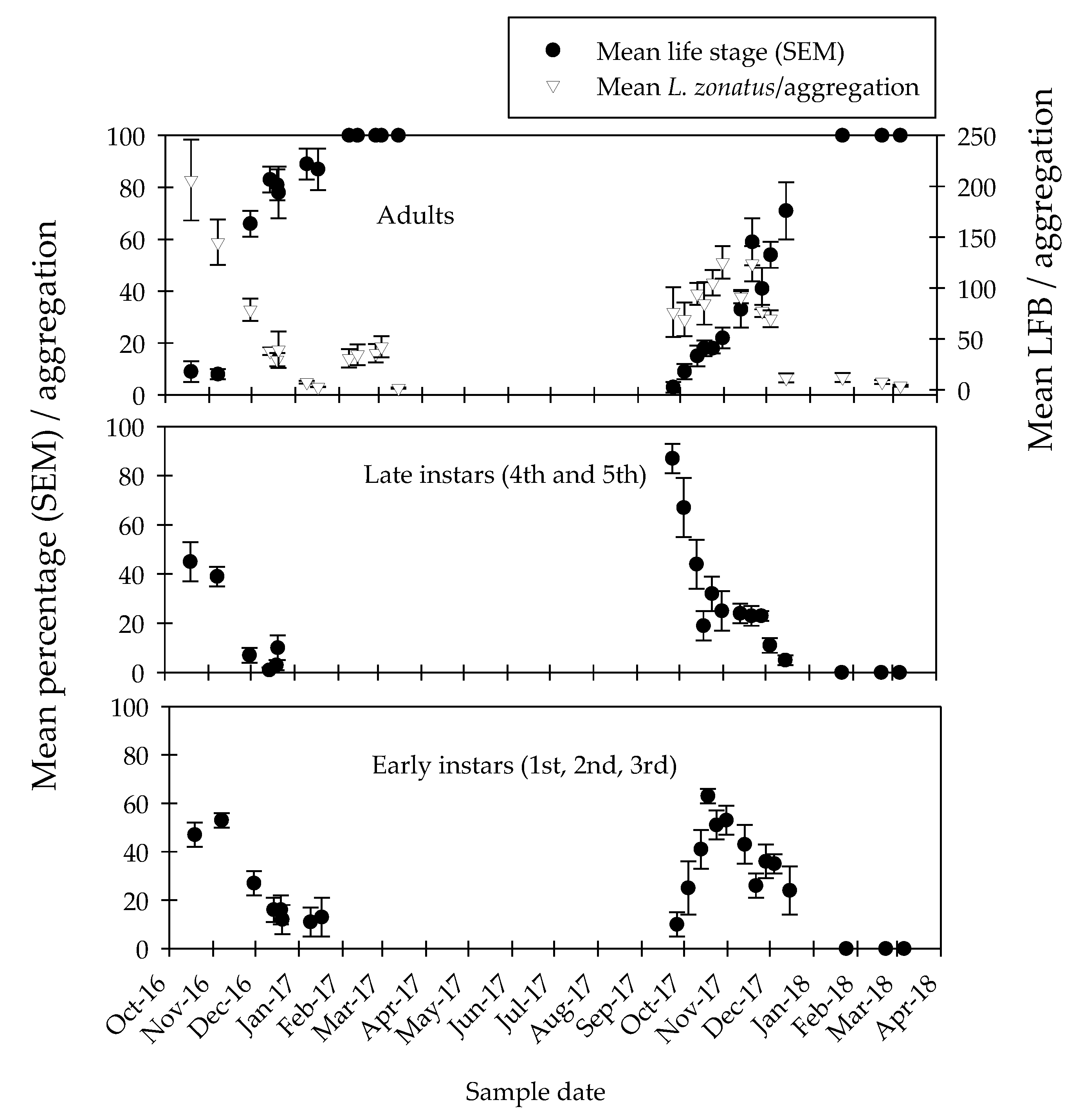
3.3. Population Dynamics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rice, R.E.; Bentley, W.J.; Beede, R.H. Insect and Mite Pests of Pistachio in California; Oakland, Calif.: Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of California: Oakland, CA, USA, 1989; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Zalom, F.G.; Haviland, D.R.; Symmes, E.J.; Tollerup, K.E. Almond: Insect and Mites. In University of California IPM Pest Management Guidelines, Publication 3431; University of California, Agriculture and Natural Resources: Oakland, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Daane, K.; Yokota, G.Y.; Krugner, R.; Steffan, S.; Da Silva, P.; Beede, B.; Bentley, W.; Weinberger, G. Large bugs damage pistachio nuts most severely during midseason. Calif. Agric. 2005, 59, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, F.M. Insect and mite pests of almond. In California Agricultural Experiment Station, Circular 513; University of California, Agriculture and Natural Resources: Oakland, CA, USA, 1962; pp. 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Albrigo, L.G.; Bullock, R.C. Injury to citrus fruit by leaf-footed and citrus plant bugs. Proc. Florida State Hortic. Soc. 1977, 90, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Panizzi, A.R. Desempeho de ninfas e adultos de Leptoglossus zonatus (Dallas, 1852) (Hemiperan: Coreidae) em diferentes alimentos. An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 1989, 18, 375–389. [Google Scholar]
- Essig, E.O. Insects of Western North America; Macmillan Press: New York, NY, USA, 1929; p. 1035. [Google Scholar]
- Bolkan, H.A.; Ogawa, J.M.; Rice, R.E.; Bostock, R.M.; Crane, J.C. Leaffooted bug (Hemipteran: Coreidae) and epicarp lesion of pistachio fruits. J. Econ. Entomol. 1984, 77, 1163–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, P.S.; Hawkins, R.S. 55th Annual Report; Arizona Agricultural Experiment Station, University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1945; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, C.W.; Panizzi, A.R. Heteroptera of Economic Importance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 369–856. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, A.L.; Higbee, B.S.; Haviland, D.; Brailovsky, H. Genetic variability of two leaffooted bug, Leptoglossus clypealis and Leptoglossus zonatus (Hemiptera: Coreidae) in the Central Valley of California. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 2576–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.C. A revision of the genus Leptoglossus Guerin (Hemiptera: Coreidae). Entomol. Am. 1969, 45, 35–140. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, C.; Somarriba, A. Suitability of physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.) as single host plant for the leaf-footed bug Leptoglossus zonatus Dallas (Het., Coreidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 1999, 123, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S.; Panizzi, A.R.; Niva, C.C. Alarm pheromone system of leaf-footed bug, Leptoglossus zonatus (Heteroptera: Coreidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 1994, 20, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Fadamiro, H.Y. Host preference and development of Leptoglossus zonatus (Hemiptera: Coreidae) on satsuma mandarin. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailides, T.J.; Morgan, D.P. Association of Botryosphaeria panicle and shoot blight of pistachio with injuries of fruit caused by Hemiptera insects and birds. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daane, K.; Yokota, G.Y.; Romero, D.; Haviland, D. California Pistachio Research Database, Predicting Leaffooted Bug Outbreaks to Improve Control. Available online: https://calpistachioresearch.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/9-10-08-13.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Daane, K.M.; Yokota, G.Y.; Wilson, H. Seasonal dynamics of the leaffooted bug Leptoglossus zonatus and its implications for control in almond and pistachios. Insects 2019, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daane, K.M.; Millar, J.G.; Rice, R.E.; da Silva, P.G.; Bentley, W.J.; Beede, R.H.; Weinberger, G. Stink bugs and leaffooted bugs. In Pistachio Production Manual; Ferguson, L., Haviland, D.R., Eds.; University of California, Agriculture and Natural Resources Publication 3545: Oakland, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, E.A.; Lisboa, L.C.O.; Araújo, V.A.; Serrão, J.E. Morphology of the spermathecae of Leptoglossus zonatus (Heteroptera: Coreidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2016, 109, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. SAS/STAT® 9.2 User’s Guide Second Edition. Available online: https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63033/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_introanova_a0000000088.htm (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Puntener, W. Manual for Field Trials in Plant Protection, 2nd ed.; Ciba-Geigy, Ltd.: Basle, Switzerland, 1981; p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- Salt, R.W. Principles of insect cold-hardiness. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1961, 6, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sømme, L. The physiology of cold hardiness in terrestrial arthropods. Eur. J. Entomol. 1999, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, J.D.; Horwarth, K.L.; Tomchaney, A.; Patterson, J.L. Antifreeze agents of terrestrial arthropods. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1982, 73, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.E.J. Principles of insect low temperature tolerance. In Insects at Low Temperature; Lee, R., Ed.; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 17–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cira, T.M.; Venette, R.C.; Aigner, J.; Kuhar, T.; Mullins, D.E.; Gabbert, S.E.; Hutchison, W.D. Cold tolerance of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) across geographic and temporal scales. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, A.; Davis, J.A. Cold tolerance and supercooling capacity of the redbanded stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, C.J.; Chown, S.L. Interactions between desiccation resistance, host-plant contact and the thermal biology of a leaf-dwelling sub-Antarctic caterpillar, Embryonopsis halticella (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). J. Insect Physiol. 1998, 44, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, H.V. Key themes in the study of seasonal adaptations in insects I. Patterns of cold hardiness. Appl. Entomol. Zoolog. 2005, 40, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.G.; Tveten, M.S.; Figuli, P.J. Development, longevity and fecundity of Leptoglossus zonatus on meridic diet. Southwestern Entomol. 1995, 20, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Barta, M. Biology and temperature requirements of the invasive seed bug Leptoglossus occidentalis (Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Europe. J. Pest Sci. 2016, 89, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, J.E.; Packauskas, R.J.; Taylor, S.J.; O’Brien, M.F. Eastern range extension of Leptoglossus occidentalis with a key to Leptoglossus species of America north of Mexico (Heteroptera: Coreidae). Great Lakes entomol. 1990, 23, 99–104. [Google Scholar]

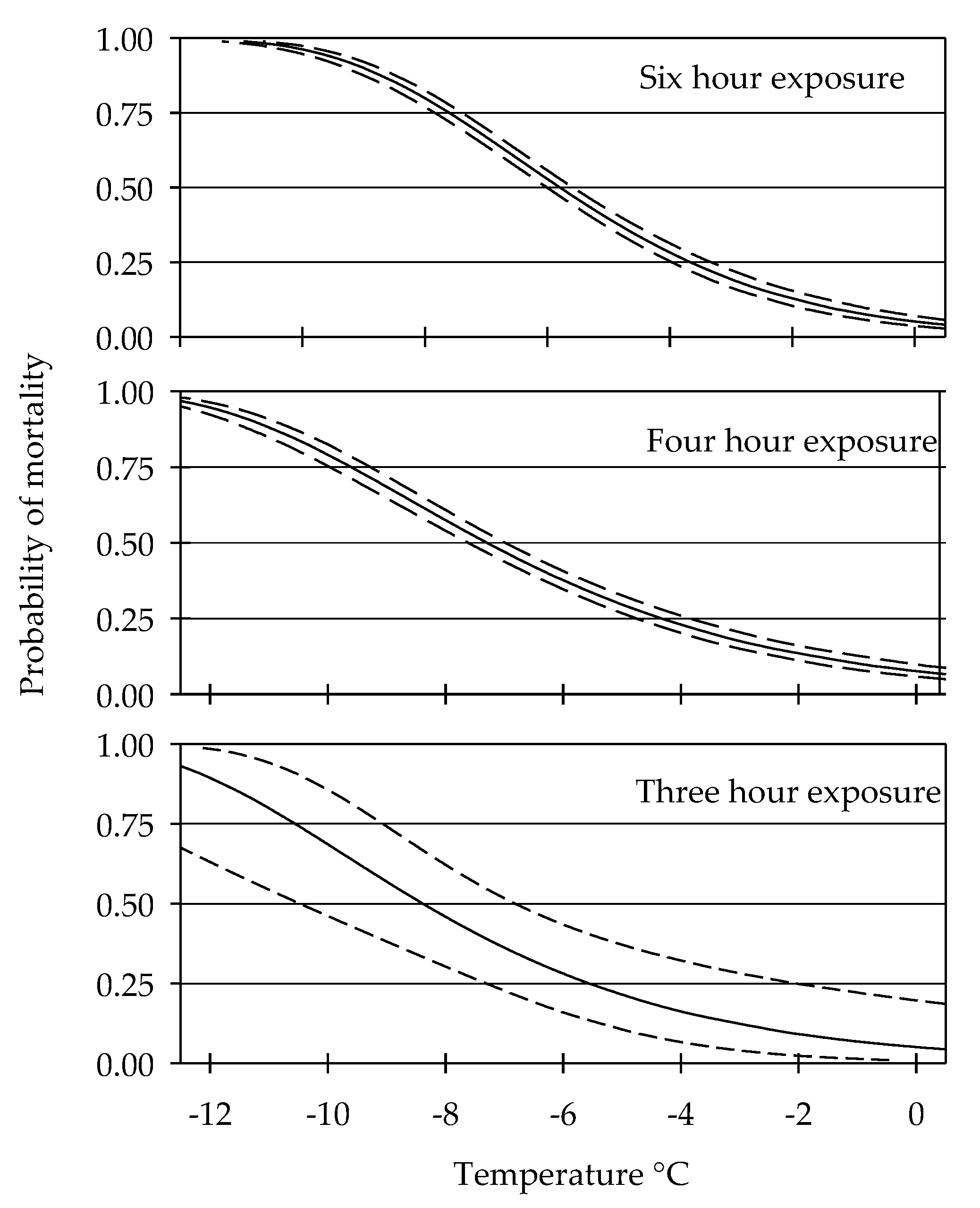
| Hours of Exposure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 3 | 4 | 6 | |||
| °C | n | mean ± (SE) | n | mean ± (SE) | n | mean ± (SE) |
| −10 | 180 | * 65 ± 5 a | 260 | 70 ± 4 a | 240 | 93 ± 2 a |
| −9 | 120 | 58 ± 4 a | 120 | 67 ± 4 a | 120 | 80 ± 4 b |
| −6 | 480 | 24 ± 3 b | 480 | 48 ± 4 b | 480 | 76 ± 2 b |
| −5 | 540 | 16 ± 3 c | 660 | 13 ± 3 c | 840 | 23 ± 3 c |
| −2 | 120 | 11 ± 3 cd | 60 | 23 ± 4 c | 60 | 25 ± 3 c |
| 0 | 780 | 2.6 ± 0.7 d | 850 | 3.1 ± 0.7 d | 1020 | 2.6 ± 0.6 d |
| Date | Number of Samples | Total Dissected | Mean Percentage w/Eggs | Mean Eggs/Female |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 Oct–19 Dec 2016 | 10 | 71 | 0 | 0 |
| 22 Feb–3 Mar 2017 | 8 | 45 | 26 ± 1.3 | 5.6 ± 7.0 |
| 17–Mar 2017 | 11 | 53 | 42 ± 0.8 | 16 ± 2.0 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tollerup, K.E. Cold Tolerance and Population Dynamics of Leptoglossus zonatus (Hemiptera: Coreidae). Insects 2019, 10, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100351
Tollerup KE. Cold Tolerance and Population Dynamics of Leptoglossus zonatus (Hemiptera: Coreidae). Insects. 2019; 10(10):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100351
Chicago/Turabian StyleTollerup, Kristen E. 2019. "Cold Tolerance and Population Dynamics of Leptoglossus zonatus (Hemiptera: Coreidae)" Insects 10, no. 10: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100351
APA StyleTollerup, K. E. (2019). Cold Tolerance and Population Dynamics of Leptoglossus zonatus (Hemiptera: Coreidae). Insects, 10(10), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100351




