Abstract
The viscosity and tribological behavior of nanofluids formed by dispersed nano-diamond particles within Poly-Alpha-Olefin (PAO6) lubricant is studied at different concentrations. The variation of coefficient of friction with nanoparticle concentration is measured using pin-on-disc tribometry under boundary, mixed, and hydrodynamic regimes of lubrication. A multi-scale multi-physics thermo-mixed lubrication model is developed to provide fundamental understanding of the measured tribometric results. The analytical approach combines continuum contact mechanics, thermal-mixed lubrication comprising the interaction of rough surfaces, as well as a thermal network heat transfer model. In particular, Einstein’s viscosity model for dispersed hard particles together with Vogel’s viscosity-temperature dependence model for fluid viscosity containing nanoparticles represent new contributions to knowledge. This integrated numerical-experimental study of nanofluid thermal and tribological assessment has not hitherto been reported in literature. It is shown that improved heat transfer capability of nanofluids is particularly effective in the reduction of friction under a mixed regime of lubrication.
1. Introduction
Engine lubricants are generally poor heat transfer media. Various methods are used to improve their thermal conductivity (heat conduction) and heat transfer (heat convection), including the use of dispersant solid particles. Such two-phase solid–liquid media are known as nanofluids. The solid nanoparticles, typically 1–100 nm in size with high thermal conductivity, are suspended in a base fluid in order to primarily improve its thermal characteristics. The thermal conductivity of base fluids can be improved by as much as 20% using very low concentrations of nanoparticles (typically <5% by volume fraction) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. The heat transfer capability of nanofluids depends not only on particle concentration, but also on material type, size, shape and agglomeration of particles, and properties of the base fluid and any dispersant such as acidity regulators as well as operating temperature [9,10,11,12,13,14]. The size, shape, and agglomeration of nanoparticles are quantified using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) or Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) [15,16,17,18]. Nanoparticles are mainly made from any of: (a) metal dichalcogenides (e.g., Al2O3 and MoS2), (b) metals (e.g., Fe and Cu), or (c) carbon-based non-metallic particles (e.g., nano-diamonds, nanotubes and carbon onions) [19]. The thermal conductivity of diamond nanoparticles (−3200 W/mK) is approximately an order of magnitude greater than the metallic particles and four orders of magnitude greater than typical base fluids [8]. Diamond nanofluids are advantageous due to their superior thermal conductivity [4,8,20,21,22], better tribological behavior (reduced friction and wear) [16,17,23,24,25,26], and in some cases non-toxic and bio-compatible nature [27,28]. Additionally, the diminutive particle size is suitable for extremely narrow tribological load bearing conjunctions. They are also stable and efficient at various temperatures (tribo-chemical stability) [19,28]. Literature is recently quite prolific with reported experimental research around thermal conductivity and/or rheological properties of nanofluids [8,15,20]. These studies investigate the properties of base fluids in the presence of solid nanoparticles.
For viscosity of a suspension, the original model was proposed by Einstein [29]. A few studies have proposed modification to the conventional Maxwell’s thermal conductivity and Einstein’s viscosity model [15,30]. Other studies have focused on the tribological performance of nanofluids in sliding conjunctions. Anti-wear and friction reduction mechanisms for nanofluids are sought experimentally using tribometers such as block-on-ring and pin-on-disc [18,24,31,32,33]. A few studies have investigated the anti-wear and friction mechanisms under boundary and mixed regimes of lubrication using an experimental approach [34,35]. These studies have reported a more effective performance of nanofluids under the boundary-mixed regimes of lubrication. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) tools have been occasionally used to study the tribological properties of nanofluids [31,36]. Demas et al. [37] showed that MoS2:PAO10 nanolubricant reduces the coefficient of friction in piston-cylinder conjunction at high operating temperatures.
The current paper investigates the tribological properties of diamond nanoparticles, dispersed in PAO6 lubricant with various volumetric concentrations of 0.04, 0.1, and 1%. The viscosity of diamond nanofluids are compared with the base lubricant and various theories. A semi-empirical viscosity relationship is proposed using the Vogel’s viscosity model to include the effect of temperature and particle concentration. The variation of coefficient of friction with nanoparticle concentration is investigated under boundary, mixed, and hydrodynamic regimes of lubrication using pin-on-disc tribometry. A multi-scale, multi-physics theoretical model is developed to combine the viscosity properties of the nanofluids with the frictional and thermal properties of the contacting surfaces through application of fundamental continuum contact mechanics, nano-tribology, and heat transfer. The experimental and analytical results are combined in order to evaluate the thermal and tribological behavior of diamond nanofluids.
2. Experimental Measurements
2.1. Lubricants Viscosity
The thermophysical properties of Poly-Alpha-Olefin (PAO6) lubricant are provided in Table 1. The PAO6 lubricant was used as the base fluid for all the nanofluid variants in the current investigation. Blue nano-diamond particles form the additives in PAO6. These nanoparticles were blended to a uniformly dispersed and stable solution by the manufacturer. The nanofluid is stable under normal conditions, except when exposed to strong oxidizing agents. The stability of the fluid was confirmed after 6 months based on the visual investigation of color and absence of nano-diamond sediments in the container. A small percentage of molybdenum phosphorodithioate (less than 0.1 wt%) was present in the mixture. Physical and geometrical properties of diamond nanoparticles were extracted from the manufacturer’s datasheet (Table 2). Nanoparticles were dispersed in the PAO6 lubricant at three volumetric fractions (VF) of 0.04, 0.1, and 1.0%. The viscosity of PAO6 and the resulting nano-fluids were measured at four temperatures using a ViscoLite 700 series viscometer (Table 3). ViscoLite 700 viscometer is manufactured by Hydramotion Ltd. (York, UK) and the measurement uncertainty is 0.1 mPa·s within the temperature range −20 to 120 °C. Lubricants were heated in a water bath and measurements were taken when the temperature of lubricants was stabilized and reached the temperature of the bath. Viscosity of PAO6 is reported to be 0.0239 Pa·s at 40 °C in the manufacturer’s datasheet. The measured value using ViscoLite 700 equals 0.0237 Pa·s (−1% difference). All measurements were repeated three times (Table 3).

Table 1.
Thermophysical properties of PAO6 [31,38,39,40].

Table 2.
Properties of diamond nanoparticles.

Table 3.
Dynamic viscosity of PAO6 and diamond nanofluids (Standard deviations are shown in parentheses, ×10−5).
Vogel’s empirical viscosity model [41,42] accurately predicts the lubricant’s viscosity at different temperatures:
Parameters and are the dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) and temperature (K). The correlated Vogel values are reasonably accurate in comparison with the measured data when constants in Equation (1) are determined by fitting experimental viscosity values for a specific lubricant [42]. The constants , and are determined for the PAO6 lubricant and the formed nanofluids using the measured viscosities (Table 4). The measured viscosities are compared with Einstein’s theory for dispersed spherical particles in fluids [29], using

Table 4.
Constants for the Vogel equation for PAO6 and various nanofluids.
The parameters , and are dynamic viscosity of a nanofluid, that of the base lubricant (i.e., PAO6) and the volumetric concentration of nanoparticles [20].
Figure 1 shows the variation of viscosity ratio with the volumetric concentration of particles at different temperatures. Einstein’s model varies linearly with the concentration parameter and neglects the effect of thermal conductivity of the nanoparticles. At room temperature (20 °C), the measured (Vogel) viscosity ratio and the predictions by Einstein’s theory are quite similar, but the former has a non-linear behavior. Despite previous reports, and regarding the non-linear viscosity ratio [20], such non-linearity has not been investigated at higher temperatures, typical of tribological contact conjunctions. The results in Figure 1a suggest that the viscosity of the base lubricant (PAO6) decreases noticeably with temperature. Hence, the effect of the concentration of nanoparticles on the viscosity of PAO6 is generally small in a static fluid. Viscosity of the base lubricant is comparatively small at higher temperatures. Hence, a small variation in the viscosities due to thermal effects can potentially lead to a large viscosity ratio value (Figure 1b). Under dynamic conditions, such as when there is a flow through narrow tribological contact conjunctions subject to continuous frictional heat generation, nanoparticles are also more likely to interact with the solid surfaces in their proximity as opposed to the case for a static fluid, where the thermal interactions with the walls are negligible due to thermal equilibrium of bulk fluid. The effect of thermal conductivity of nanofluids on friction in tribological contact conjunctions is investigated in Section 3 and Section 4. Thermal conductivity and viscosity of nanofluids are related physically through specific surface area of nanoparticles. It is shown that an increase in the viscosity of nanofluids is related to the difficulty in the motion of nanoparticles in the base fluid due to Brownian motion, and a direct result of an increase in particles’ concentration [43,44]. The Brownian motion essentially varies with temperature. Hence, a greater thermal conductivity can promote dissipation of heat from a tribological conjunction through fluid convection and/or heat conduction due to the interaction of particles with the confining boundary solid surfaces.
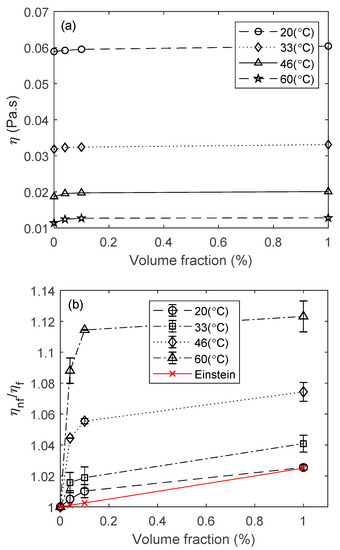
Figure 1.
Variation of dynamic viscosity with the volumetric concentration of diamond nanoparticles and temperature: (a) actual viscosity values, and (b) viscosity ratios (measured (Vogel correlations) viscosity vs. Einstein viscosity model [28]). The standard deviations are calculated for the measured viscosity at each temperature and presented using error bars.
At 20 °C, the difference in viscosities are solely due to the dispersion of nanoparticles when the bulk nanofluid is in thermal equilibrium with the ambient. The initial viscosity refers to the measured viscosities for all the lubricants at room temperature (20 °C). Hence, any difference in the viscosity at this temperature is merely due to the addition of nanoparticles to the base fluid, and not because of any thermal mechanism. As the temperature increases, the non-linearity in viscosity variations with the volume fraction increases (Figure 1a). However, these variations are not easily observable when using the actual viscosity values instead of the viscosity ratios as can be seen from Figure 1a. The dynamic viscosity ratio is utilized to highlight the significance of these variations with temperature as shown in Figure 1b. Thus, a small change in viscosity with temperature can lead to a significant increase in the viscosity ratio, especially at higher temperatures, where the viscosity of the base lubricant (PAO6) becomes quite small. Consequently, the viscosity ratio increases as much as 12% for the concentration of . Similar trends are also reported in the open literature for various nanofluids [8,9,45,46,47,48]. The viscosity ratios are reported using Vogel empirical model in Figure 1b. It should be noted that slight deviations might be observed between Vogel and measured results. Certain additives such as thioglycolic acid are utilized to prevent agglomeration of the nanoparticles. These additive agents can also affect the thermal conductivity of nanofluids [9]. Anti-agglomeration additives are not used in the current study. Thus, improvements in the thermal conductivity at higher temperatures are directly attributed to the action of diamond nanoparticles themselves.
2.2. Surface Topography
Three-dimensional (3D) surface topography of the pin and disc samples are made using white light interferometry with 20× magnification (Figure 2). The surface roughness parameters were measured at several locations on each sample and their composite average is shown in Table 5. Skewness, , and Kurtosis, , are zero and 3 for a Gaussian distribution respectively. Therefore, the height distribution of surface asperities can be approximated with a Gaussian distribution for both the pin and the disc surfaces (Table 5).
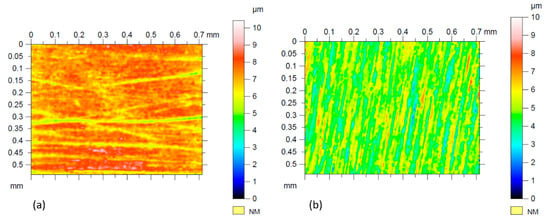
Figure 2.
Surface roughness contours using white light interferometry: (a) pin and (b) disc samples.

Table 5.
Surface properties of pin and disc.
2.3. Pin-On-Disc Tribometry
An in-house precision pin-on-disc tribometer was used to measure the coefficient of friction. Pin and disc samples are made of EN36C alloy steel with carburized surfaces for high hardness and wear resistance (Table 6). Friction was measured at the constant applied contact load of 5.1 N and with sliding velocity variation in the range: 0.1–1.6 ms−1 at room temperature (20 ± 2 °C). These conditions allow for a transition from boundary to mixed and through to hydrodynamic regimes of lubrication. During each measurement, a sliding velocity sweep was undertaken with a pause of 15 s for measurement of friction at all specified sliding velocities. At the end of the velocity sweep, the disc surface temperature was measured close to the contact outlet using an Infra-Red (IR) thermometer (PCE Instruments Ltd., Southampton, UK) and a 7–9 °C temperature rise was observed in all cases.

Table 6.
Geometrical and mechanical properties of pin and disc.
3. Analytical Method
A multi-scale multi-physics analytical model of the pin-disc conjunction is developed in order to study the tribological behavior of the nanofluids. A schematic representation of the contact conjunction and the corresponding control volume are shown in Figure 3.
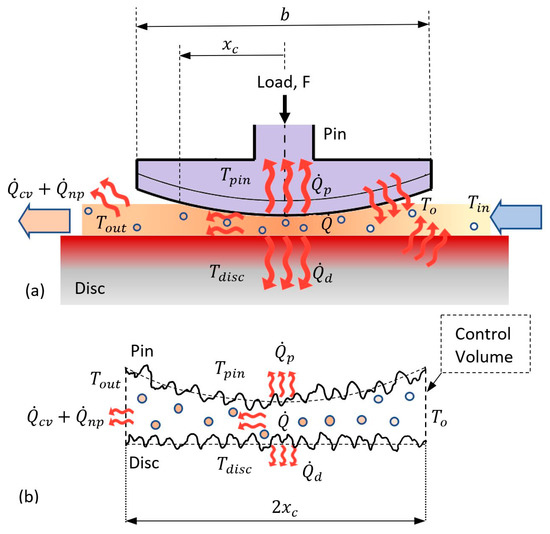
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic of contact conjunction and heat transfer mechanism in pin-on-disc tribometry; (b) Fluid control volume and its bounding surfaces in the presence of asperities. The generated/transferred heat flow rates are shown for contact friction, , contiguous surfaces, and , fluid flow convection, , and nanoparticles, . Temperatures are presented for fluid prior to contact, , fluid at the inlet of control volume, , fluid at the outlet, , and contiguous surface asperities, and .
The model includes prediction of viscous and boundary friction. A thermal model is incorporated to predict the average contact temperature for the determination of effective lubricant viscosity in the contact. The contact footprint is of finite line geometry. Using the classical Hertzian theory as an approximate approach to determine any localized contact deflection, , for an elastic line contact [49] leads to:
Parameters in this case are the following: load per unit length , the reduced (effective) Young’s modulus of elasticity: , contact width , and the reduced radius of curvature . Equation (3) yields a contact deflection of 2.17 × 10−8 m. This, together with the fact that surface asperities are an order of magnitude larger than the calculated contact deflection, means that the surfaces may be assumed to act as rigid bodies for the stated conditions. Therefore, conditions leading to fully lubricated contacts conform to a hydrodynamic regime of lubrication.
3.1. Prediction of Friction
The minimum lubricant film thickness is evaluated under the hydrodynamic regime of lubrication with an assumed Reynolds’ contact exit boundary condition for a rigid line contact [49] as:
where, , , and are contact load, lubricant entrainment velocity, lubricant viscosity, and the minimum film thickness, respectively. Since the pin surface is not flat, friction due to viscous shear, , is obtained as:
For a fully flooded condition (i.e., hydrodynamic regime of lubrication), the wetted contact area is . For partially flooded contacts with a curved profile (i.e., mixed regime of lubrication), the real wetted area becomes: . The upper limit of the integral, (denoting the position of lubricant film rupture at the contact exit) is determined through solution of Equation (6) for the inlet/outlet boundary conditions (atmospheric pressure, ) [50]:
Thus, the wetted region of contact area is calculated as:
where denotes film thickness at any position across the contact. In mixed regime of lubrication, the contact load is partly carried by a lubricant film and partly by the contacting asperities on the counter face surfaces. The Hertzian theory of elastic contact between a pair of spherical surfaces is extended by considering several discrete spherical microcontacts at the scale of asperities. Asperity contact load, , and their area of contact, , vary with surface parameters and material properties as [51]:
and
where the surface parameters , and are extracted from Figure 2 and presented in Table 5. The statistical functions describe the probability of counter face asperity interactions for an assumed Gaussian distribution of asperity heights [49]. Greenwood and Tripp [51] show explicitly that contact load and area are proportional to the compliance of asperities, multiplied by the Gaussian exponential distribution of asperity heights Equation (10). The exponent is 5/2 and 2 for contact load and area respectively Equations (8) and (9). Since the pin profile is not flat, these functions are integrated over the contact area. The statistical functions are approximated using exponential curve fits in Equations (11) and (12). is the Stribeck’s oil film parameter [52], indicating the distance between the mean plane of counter face real rough surfaces, and so thus:
The generated frictional contribution due to direct asperity interactions (boundary friction), , becomes [51]:
It is assumed that a thin layer of lubricant is adsorbed into the asperity summits and the interspatial asperity valleys, acting with non-Newtonian Eyring shear stress, [53,54,55]. The boundary shear strength of the surfaces, , is taken as 0.22 as measured using lateral force microscopy for a range of similar contacting materials by Umer et al. [56]. Therefore, for a prevailing mixed regime of lubrication, the predicted contact friction, , becomes:
3.2. Thermal Analysis
A control volume thermal network model, similar to that proposed in [57,58], is used to develop an analytical thermal model for pin-disc conjunction. This model predicts the average contact temperature of the lubricant as well as the flash temperature of the contiguous contacting surfaces. Friction is regarded as the only source of heat generation, thus:
The generated heat is partly carried away from the contact by the flow of lubricant and nanoparticles (i.e., ) and partly conducted through the contacting surfaces; the pin; and the disc; . Hence
Convection cooling through lubricant flow is obtained from Equation (17), where the mass flow rate is approximated as: . Parameters and are lubricant density and cross-section of lubricant flow, respectively. The mass flow rates of the lubricant and nanoparticles are determined as and respectively, thus:
where , , and are the effective lubricant contact temperature, nanoparticles temperature, and heat capacities for lubricant and nanofluid, respectively.
The lubricant temperature initially rises to a temperature at the inlet conjunction due to the heat flux from the solid boundaries [57], thus
where the subscripts d and p refer to the disc and pin surfaces, respectively.
The variation of lubricant density, , with temperature is taken into account through theuse of Equation (19). The coefficient of thermal expansion is denoted as for the lubricant and is the fluid density at a reference temperature (). The density, , and specific heat capacity, , of nanofluids are calculated using the thermal properties of their constituent base lubricant and the diamond nanoparticles, as well as the volumetric concentration of nanoparticles, , [9]:
The generated heat at the center of the contact is transferred through a series of thermal-resistive barriers. These thermal resistors are: the lubricant film; , boundary layer convection; and surface flash thermal conduction; . The analogy of lubricant flow to a laminar flow through a tube is used to determine these resistances. The parameters , , and are the heat transfer coefficient of the boundary layer, thermal conductivity of lubricant film, thermal conductivity of solid surfaces and the characteristic length for flash temperature and are defined as follows:
Detailed calculation of these parameters is provided in [57,58,59]. The thermal conductivity of nanofluids, , is estimated using the modified Maxwell’s theory to include the effects of particle shape and size, as well as the contiguous nanolayer of fluid about the particle [58,60]:
Shape parameter, is considered to be equal to , where is the sphericity factor. It is the ratio of the surface area of a sphere, with its volume equal to that of the nanoparticle, to the actual surface area of the particle. The shape parameter, for perfectly spherical particles. A solid-like nanolayer of fluid molecules forms on the surface of particles due to Brownian motion and physisorption-chemisorption effects [61]. The thickness of this nanolayer is suggested to be up to 3 molecular layers of the base fluid [62]. Dolatabadi et al. [61] showed that the molecular stacking in the nanolayer is driven by the progressive adsorption-desorption process, utilizing Arrhenius and BET (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller) theories. The thickness of nanolayer, , can be determined using:
where is the reaction rate ratio of adsorption to desorption. and are the equilibrium pressure of adsorbates at the adsorption temperature and the pressure of the bulk lubricant above the last layer of adsorbate respectively. This method proposes that five molecular layers of PAO6 will form on the surface of diamond nanoparticles and the sixth layer will reach equilibrium with only 55% surface coverage. Parameter is the ratio of the thickness of nanolayer with respect to the nanoparticle’s radius (). This solid-like nanolayer has higher thermal conductivity than that of the base fluid. The equivalent thermal conductivity of the suspended nanoparticle, , equals the combined thermal conductivity of nanoparticle and its contiguous nanolayer:
where . and are the thermal conductivities of nanolayer and nanoparticle respectively. Yu and Choi [60] assumed that ; thus, . Using a similar approach to that of Morris et al. [57], the average contact temperature is predicted using Equation (26). The average contact temperature is not representative of the flash temperature of the asperities. The heat conduction through asperity pairs are neglected since the asperity area of contact is typically less than 1–5% of the total contact area [57]. The thermal resistance due to convection of lubricant is and the resistance due to the heat transfer of nanoparticles is: . Therefore, the effective average contact temperature becomes
where shows the product of thermal resistances of contacting surfaces and . Thus, the temperature rise of the counter face surfaces can also be predicted as
The tribological contact model is solved numerically. An initial guess for the film thickness is made, using Equation (4). The hydrodynamic and asperity contact loads are obtained iteratively (i.e., contact reaction: ). The following load convergence criterion is used:
where F is the applied pin load. If the criterion is not satisfied, then the film thickness is adjusted and the entire procedure is repeated; i.e.,
where is the under-relaxation factor in this case.
Thus, the coefficient of friction is predicted as: . This depends on the nanofluids used. Therefore, for the base PAO6 lubricant the coefficient of friction is denoted by and for any nanofluid, comprising the PAO6 lubricant with a volume fraction of nanoparticles is denoted by . All coefficients of friction were also directly measured by the tribometer as well.
4. Results and Discussion
The ratio of coefficient of friction obtained for a nanofluid to that with the base lubricant only, provides a good measure of effectiveness of the nanoparticles in improving conjunctional efficiency. Figure 4 shows predicted variation of the coefficient of friction ratio, , with the Hersey’s service parameters, [63]. The predictions make use of the overall viscosity model for the nanofluids, making use of Equations (1) and (2). As the viscosity of the fluid changes with the Hersey parameter, the prevailing regime of lubrication alters according to the fluid viscosity (fluid viscosity determines its load carrying capacity). It is clear that the predicted coefficient of friction ratio conforms reasonably well to the measured tribometric data under identical conditions. This is a further indication of the validity of the viscosity model combined with viscous and boundary friction models. The values of the ratio below unity indicate reduced frictional losses as a result of introducing nanoparticles into the base lubricant. This is partially due to the initial higher viscosity of nanofluids at room temperature and partially due to enhanced nanofluid thermal characteristics (i.e., heat transfer) at contact temperatures above the ambient, as also noted through detailed numerical analysis by Shahmohamadi et al. [31]. The effect of heat transfer mechanism on the lubricant viscosity in a thin tribological contact conjunction is detailed in Figure 5 and distinguished from the initial viscosity variations due to concentration parameter. In effect, Figure 4 is a normalized form of the Stribeck’s curve [52]. The results obtained through measurements are shown by various VF concentrations, . These are compared with the results of analytical model predictions shown by the various line plots (for VF concentrations ) using the Einstein viscosity model (Figure 4a). As already stated, the Einstein’s model does not include the effect of thermal conductivity of nanoparticles. Thus, the predicted ratios are somewhat underestimated, particularly at lower nanoparticle concentrations. To improve the results from the predictive model, Einstein’s viscosity model is replaced with the Vogel’s empirical model based on measured viscosities. Analytical predictions together with the updated viscosity model are shown in Figure 4b. There is a −10% improvement in predictions vis-a-vis the measurements for conditions pertaining to mixed regime of lubrication. The improved predictions still show a level of deviation from measured ratios. More accurate predictions are anticipated after consideration of all possible friction and wear mechanisms in the models, as well as the rheological and thermal properties [64]. The demarcation line between mixed and hydrodynamic regimes of the lubrication is at the service parameter value of . Thereafter, under the hydrodynamic regime of lubrication, there are hardly any significant changes in the coefficient of friction ratio; regardless of any improvements in the nanofluid thermal conductivity.
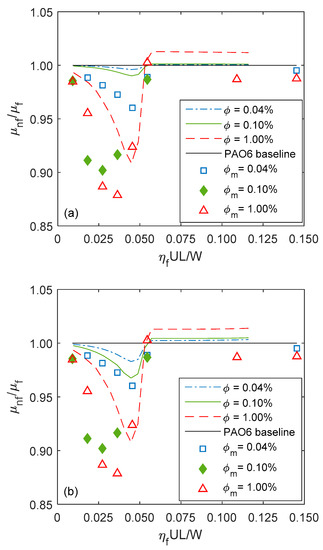
Figure 4.
The variation of coefficient of friction ratio with Hersey parameter and volumetric concentration of diamond nanoparticles at constant load of 5.1N based on: (a) Einstein’s viscosity model Equation (2) and (b) empirical Vogel’s viscosity-temperature dependence model Equation (1). Analytical results (lines) for various volumetric concentrations, , are compared with experimental measurements (markers) for the same volumetric concentrations, .
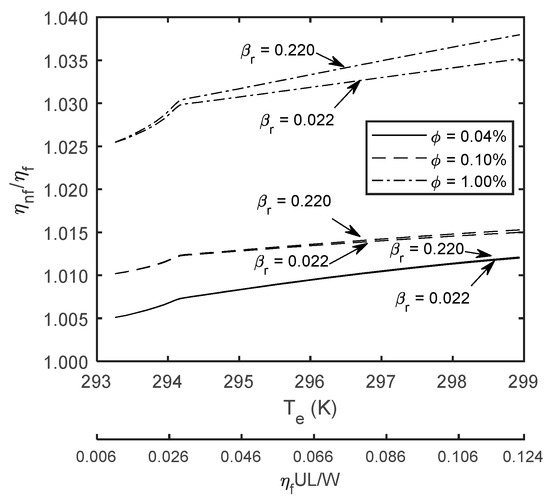
Figure 5.
Viscosity ratio variation with temperature in pin-disc conjunction and nanolayer ratio parameter.
All the measured and predicted results show an initial reduction in the coefficient of friction ratios, followed by a gradual deterioration to unity thereafter (indicating no further benefit after ). The initial improvement is due to rapid formation of a lubricant film resulting in reduced direct boundary interactions. The position of minimum indicates optimal mixed regime of lubrication for a given VF concentration of nanoparticles. Thereafter, there is increased viscous friction as the hydrodynamic regime of lubrication begins to dominate and the effect of nanoparticles is significantly diminished. Although there is some degree of scatter in the measured results, it is quite clear that reduced friction is achieved with increasing VF concentration of nanoparticles. However, the range of concentrations used is quite practical from the point of view of suspension stability. Clearly, as the VF of particles increases there is a chance of agglomeration. Zhang et al. [65] showed that nanoparticle concentrations of less than 1% led to effective improvements in friction. Battez et al. [66] used various nanoparticle types as anti-wear additives with up to 2% VF concentration in a PAO6 lubricant base. They showed that a VF concentration of 0.5% was optimal for the reduction of friction.
Analytical simulations carried out here commence at the room temperature of 20 °C. Therefore, the differences in the viscosity ratio at this temperature (Figure 5) are only due to the variation in concentration of the nanoparticles; lubricants are at thermal equilibrium with ambient at this temperature. During simulation, the concentration values are considered to remain unaltered, with any variation in the viscosity ratio attributed to improved thermal conductivity of the nanofluids and the interaction of nanoparticle dispersion with the walls of contiguous solids in the thin tribological conjunction. The thermal conductivity of nanofluids improves at higher contact temperatures [9] and the dispersed particles interact with the solid surfaces, thus leading to a rise in the viscosity ratio, , with increasing temperature and subsequently reduced asperity interactions in mixed regime of lubrication. For instance, viscosity of nanofluid for is 2.5% greater than the PAO6 at room temperature 293 K (Figure 5). This difference is approximately 3.5% at the end of simulation with a 6 °C rise in contact temperature. Thus, the reduction in coefficient of friction ratio can be partially due to the thermal characteristics of the nanofluids and partially due to an increase in viscosity by nanoparticle dispersion. The larger variations in the viscosity ratio occur between 293 and 295 K during the mixed regime of lubrication due to the direct interaction of surfaces and nanofluids in the narrow tribological conjunction (Figure 5).
The formation of nanolayer of fluid contiguous with particles affects the thermal characteristics of nanofluids [60,62]. The improved thermal characteristics, in turn, affect the viscosity ratio . The ratio varies in the range 0.022 to 0.22 for a known volume fraction . Viscosity ratio is relatively smaller for the smaller values of (Figure 5). The larger values of indicate smaller particle sizes for a constant nanolayer thickness ( nm). The thickness of nanolayer is assumed to be constant, since the average size of the fluid molecule is dictated by its constituent atoms [62]. Consequently, particles are dispersed with higher distribution density for a known volume fraction . The larger quantity of particles can intensely interact with fluid molecules and the contiguous solid surfaces during contact, leading to higher possibility of heat transfer from contact and relatively larger viscosity ratios.
The effectiveness of nanoparticles in mixed regime of lubrication is an important finding as the frictional losses mostly occur at low speed reversals in reciprocating contacts. Styles et al. [67] showed that a third of all piston ring-cylinder losses in IC engines occur at the piston reversal point at the top dead center in transition between the compression and the power strokes.
Figure 6 shows the variation of heat generation rate, , with the average contact temperature. The average contact temperature increases with sliding velocity. There is an initial rise because of direct asperity interactions (from 293 to 294 K), which reduces thereafter with gradual formation of a lubricant film during mixed regime of lubrication (from 294 to 295 K). After the transition to hydrodynamic regime of lubrication, the only mechanism of heat generation is viscous shear. Therefore, heat generation rate is directly proportional to the sliding velocity (from 295 to 299 K). The heat generation rate for nanofluids is slightly lower than the base lubricant during mixed regime of lubrication because of improved viscosity and thermal conductive properties of the nanofluids. The relatively more stable viscosity of nanofluids leads to marginally thicker lubricant films (Figure 7a) and viscous friction (Figure 4). Figure 7b shows the predicted minimum film thickness ratio in comparison to the ratio inferred from the measured coefficient of friction in the prevailing hydrodynamic regime of lubrication. The film ratios are only under-predicted by up to 3% compared with the experimentally inferred values.
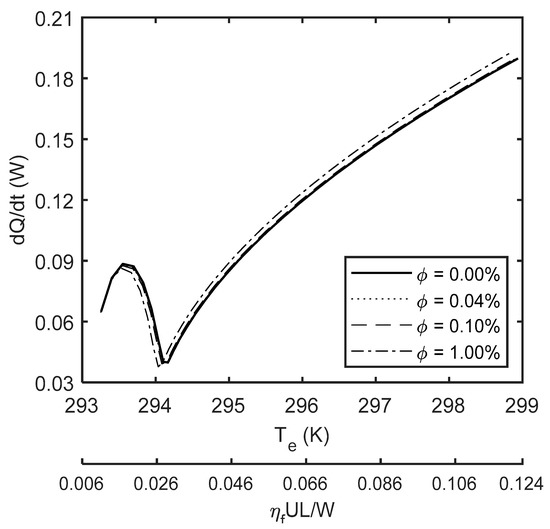
Figure 6.
Heat generation rate for PAO6 and nanofluids at different contact temperatures.
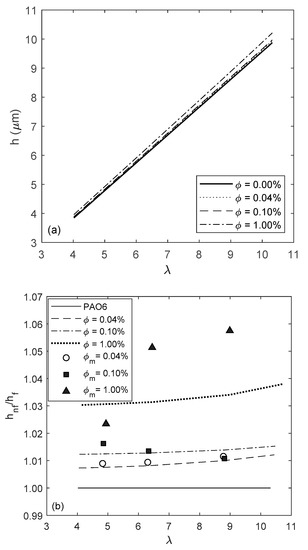
Figure 7.
(a) Minimum film thickness variation with the reduced film parameter , (b) minimum film thickness ratio: analytical prediction vs. evaluated from measured friction forces.
5. Conclusions
The viscosity and tribological behavior of diamond nanofluids are studied using PAO6 as the base lubricant. The effect of nanoparticle concentration, size, shape and contiguous fluid nanolayer is investigated. The sensitivity of viscosity ratio to temperature is explored in thin tribological contact conjunctions. Thermal conductivity and viscosity are related through structural properties and surface-to-area ratio of nanoparticles. Hence, the thermal and viscosity properties of diamond nanofluids are inseparable as one affects the other. Any potential improvement in the thermal conductivity of diamond nanofluids can promote greater interaction of particles with the contiguous solid surfaces in narrow tribological conjunctions, thus increasing the viscosity ratios with the rise in contact temperature and reducing the coefficient of friction in instances of a mixed regime of lubrication. A reduction of up to 10% in the coefficient of friction is measured relative to the PAO6 lubricant alone. A detailed new analytical model is presented which accurately predicts the tribological behavior of the nanofluids, which conform to the measurements. At a known volumetric concentration, smaller nanoparticles represent higher distribution density, consequently suggesting a higher rate of heat transfer through a larger quantity of particles.
Author Contributions
N.D. and R.R. developed the methodology and carried out the analytical modelling, experimental tests and data curation. C.B. prepared and provided the nanofluid samples. H.R. and C.P.G. were involved in the verification and discussion of methodology and results. All authors equally participated in preparation and correction of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support of Lloyd’s Registry Foundation under the International Cavitation Research Institute and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council for funding of the Encyclopaedic Program Grant (EP/G012334/1), under whose auspices some of the analytical methods used in this research were developed.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938, CONF-951135-29; Argonne National Lab.: IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, H.; Ebata, A.; Teramae, K. Alteration of thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles (dispersion of Al2O3, SiO2 and TiO2 ultra-fine particles). NETSU BUSSEI 1993, 7, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, S.U.S.; Li, S.; Eastman, J.A. Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles. J. Heat Transf. 1999, 121, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Li, Q. Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2000, 21, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Li, Q. Investigation on convective heat transfer and flow features of nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2003, 125, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Roetzi, W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 3701–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branson, B.T.; Beauchamp, P.S.; Beam, J.C.; Lukehart, C.M.; Davidson, J.L. Nanodiamond nanofluids for enhanced thermal conductivity. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3183–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xie, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q. Experimental investigation on the thermal transport properties of ethylene glycol based nanofluids containing low volume concentration diamond nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 380, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakac, S.; Pramuanjaroenkij, A. Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomascolo, M.; Colangelo, G.; Milanese, M.; de Risi, A. Review of heat transfer in nanofluids: Conductive, convective and radiative experimental results. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 1182–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.K.; Jung, W.H. Thermal conductivity and lubrication characteristics of nanofluids. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2006, 6, e67–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angayarkanni, S.A.; Philip, J. Review on thermal properties of nanofluids: Recent developments. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 225, 146–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.; Shima, P.D. Thermal properties of nanofluids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 183, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilkington, G.A.; Briscoe, W.H. Nanofluids mediating surface forces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 179, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeganeh, M.; Shahtahmasebi, N.; Kompany, A.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Youseffi, A.; Siller, L. Volume fraction and temperature variations of the effective thermal conductivity of nanodiamond fluids in deionized water. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 3186–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Tsui, W.C.; Liu, T.C. Experimental analysis of tribological properties of lubricating oils with nanoparticle additives. Wear 2006, 262, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, S.; Kolubaev, A.; Belyaev, S.; Lerner, M.; Tepper, F. Study of friction reduction by nanocopper additives to motor oil. Wear 2002, 252, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, V.; Ortega, J.A. Evaluating the Rheological and Tribological Behaviours of Coconut Oil Modified with Nanoparticles as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants 2019, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.M.; Ohmae, N. Nanolubricants; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Sussex, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sundar, L.S.; Singh, M.K.; Ramana, E.V.; Singh, B.; Gracio, J.; Sousa, A.C. Enhanced thermal conductivity and viscosity of nanodiamond-nickel nanocomposite nanofluids. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4039–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderova, O.; Taylor, T.; Cunningham, G.; Ray, M.; Walsh, J.; Casulli, M.; Hens, S.; McGuire, G.; Kuznetsov, V.; Lipa, S. Nanodiamond and onion-like carbon polymer nanocomposites. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.U.; Ali, H.M. Recent advances in application of nanofluids in heat transfer devices: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 556–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmud, B.; Pasalskiy, B. Nanomaterials in Lubricants: An Industrial Perspective on Current research. Lubricants 2013, 1, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.X.; Kang, Y.; Hwang, R.M.; Shyr, S.S.; Chang, Y.P. Tribological properties of diamond and SiO2 nanoparticles added in paraffin. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, A.M.; Veeregowda, D.H. Effects of two sliding motions on the superlubricity and wear of self-mated bearing steel lubricated by aqueous glycerol with and without nanodiamonds. Wear 2017, 386, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golchin, A.; Villain, A.; Emami, N. Tribological behaviour of nanodiamond reinforced UHMWPE in water-lubricated contacts. Tribol. Int. 2017, 110, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochalin, V.N.; Shenderova, O.; Ho, D.; Gogotsi, Y. The properties and applications of nanodiamonds. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, N.; Torelli, M.; McGuire, G.; Shenderova, O. Nanodiamond: A high impact nanomaterial. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. On the motion of small particles suspended in liquids at rest required by the molecular-kinetic theory of heat. Annalen der Physik 1905, 17, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, N.; Sohrabi, N.; Behzadmehr, A. A new model for calculating the effective viscosity of nanofluids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohamadi, H.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; Garner, C.P.; Balodimos, N. Thermohydrodynamics of lubricant flow with carbon nanoparticles in tribological contacts. Tribol. Int. 2016, 113, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, L.; Leshchinsky, V.; Lapsker, I.; Volovik, Y.; Nepomnyashchy, O.; Lvovsky, M.; Popovitz-Biro, R.; Feldman, Y.; Tenne, R. Tribological properties of WS2 nanoparticles under mixed lubrication. Wear 2003, 255, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of Nickel-Based Nanolubricants via a facile in situ one-step route and investigation of their tribologial properties. Trib. Lett. 2013, 51, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinstreuer, C.; Xu, Z. Mathematical modelling and computer simulations of nanofluid flow with applications to cooling and lubrication. Fluids 2016, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannous, J.; Dassenoy, F.; Lahouij, I.; Le Mogne, T.; Vacher, B.; Bruhacs, A.; Tremel, W. Understanding the tribochemical mechanisms of IF-MoS2 nanoparticles under boundary lubrication. Trib. Lett. 2011, 41, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahian, O.; Kolsi, L.; Amani, M.; Estelle, P.; Ahmadi, G.; Kleinstreuer, C.; Marshall, J.S.; Taylor, R.A.; Abu-Nada, E.; Rashidi, S.; et al. Recent advances in modelling and simulation of nanofluid flows—Part II: Applications. Phys. Rep. 2019, 791, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demas, N.G.; Timofeeva, E.V.; Routbort, J.L.; Fenske, G.R. Tribological effects of BN and MoS2 Nanoparticles added to Polyalphaolefin oil in piston skirt/cylinder liner tests. Trib. Lett. 2012, 47, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echavarri Otero, J.; Lafont Morgado, P.; Chacon Tanarro, E.; de la Guerra Ochoa, E.; Diaz Lantada, A.; Munoz-Guijosa, J.M.; Munoz Sanz, J.L. Analytical model for predicting the friction coefficient in point contacts with thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Proc. IMechE Part. J. J. Eng. Trib. 2011, 225, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totten, G.E.; Westbrook, S.R.; Shah, R.J. Fuels and Lubricants Handbook: Technology, Properties, Performance and Testing; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarey, M.J.G.; Comunas, M.J.P.; Lopez, E.R.; Amigo, A.; Fernandez, J. Volumetric behaviour of some motor and gear-boxes oils at high pressure: Compressibility estimation at EHL conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 58, 10877–10885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H. Das temperaturabhaengigkeitsgesetz der viskositaet von fluessigkeiten. Phys. Z. 1921, 22, 645–646. [Google Scholar]
- Stachowiak, G.W.; Batchelor, A.W. Engineering Tribology; Elsevier: Amesterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Suganthai, K.S.; Rajan, K.S. Metal oxide nanofluids: Review of formulation, thermophysical properties, mechanisms and heat transfer performance. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 226–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani Esfahani, M.; Mohseni Languri, E.; Rao Nunna, M. Effect of particle size and viscosity on thermal conductivity enhancement of graphese oxide nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 76, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Putra, N.; Thiesen, P.; Roetzel, W. Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. ASME 2003, 125, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Peterson, G.P. Experimental investigation of temperature and volume fraction variations on the effective thermal conductivity of nanoparticle suspensions (nanofluids). J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 084314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Desgranges, F.; Roy, G.; Galanis, N.; Mare, T.; Boucher, S.; Angue Minsta, H. Temperature and particle-size dependent viscosity data for water-based nanofluids—Hysteresis phenomenon. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2007, 28, 1492–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbubul, I.M.; Saidur, R.; Amalina, M.A. Latest developments on the viscosity of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, R.; Rahnejat, H. Fundamentals of Tribology; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gohar, R. Elastohydrodynamics; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Tripp, J.H. The contact of two nominally flat rough surfaces. Proc. IMechE 1970, 185, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stribeck, R. Die wesentliechenichen eigenschaften gleit und rollen lager (Ball bearings for various loads). Trans. ASME 1907, 29, 420–463. [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe, B.J.; Evans, D.C. The shear properties of Langmuir—Blodgett layers. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1982, 380, 389–407. [Google Scholar]
- Eyring, H. Viscosity, plasticity, and diffusion as examples of absolute reaction rates. J. Chem. Phys. 1936, 4, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.W.F.; Rahnejat, H. Nanoscale friction as a function of activation energies. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 3, 044002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, J.; Morris, N.; Leighton, M.; Rahmani, R.; Howell-Smith, S.; Wild, R.; Rahnejat, H. Asperity level tribological investigation of automotive bore material and coatings. Tribol. Int. 2018, 117, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; King, P.D.; Fitzsimons, B. Tribology of piston compression ring conjunction under transient thermal mixed regime of lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2014, 59, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Choi, S.U.S.; Yu, W.; Pradeep, T. Nanofluids: Science and Technology; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids; Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Choi, S.U.S. The role of interfacial layers in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids: A renovated Hamilton-Crosser model. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2004, 6, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatabadi, N.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; Garner, C.P. Thermal conductivity and molecular heat transport of nanofluids. R. Soc. Chem. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2516–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.P.; Choi, S.U.S. Role of Brownian motion in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 4316–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersey, M.D. The Laws of Lubrication of Horizontal Journal Bearings. J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 1914, 4, 542–552. [Google Scholar]
- Saurin, N.; Espinosa, T.; Sanes, J.; Carrion, F.J.; Bermudez, M.D. Ionic nanofluids in tribology. Lubricants 2015, 3, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, J. Synthesis, structure and lubricating properties of dialkyldithiophosphate-modified Mo-S compound nanoclusters. Wear 1997, 209, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battez, A.H.; Gonzalez, R.; Viesca, J.L.; Fernandez, J.E.; Diaz Fernandez, J.M.; Machado, A.; Chou, R.; Riba, J. CuO, ZrO2 and ZnO nanoparticles as antiwear additive in oil lubricants. Wear 2008, 265, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styles, G.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; Fitzsimons, B. In-cycle and life-time friction transience in piston ring-liner conjunction under mixed regime of lubrication. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2014, 15, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).