The Transition from Static to Dynamic Boundary Friction of a Lubricated Spreading and a Non-Spreading Adhesive Contact by Macroscopic Oscillatory Tribometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
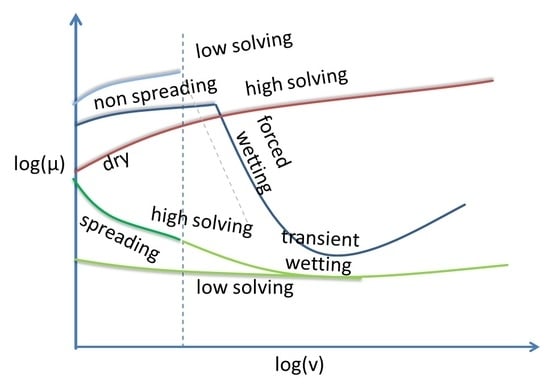
2. Motivation and Scientific Background
| slip rate of adhesive contact | (1) | |
| surface energy | (2) | |
| contact angle equation | (3) | |
| model for interfacial energy | (4) | |
| spreading energy of system | + | (5) |
| solving energy of lubricated thermoplastic | (6) | |
| interaction parameter | (7) | |
| velocity for forced wetting | (8) |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Tribological Experiments
3.3. Contact Angle Measurements
4. Results
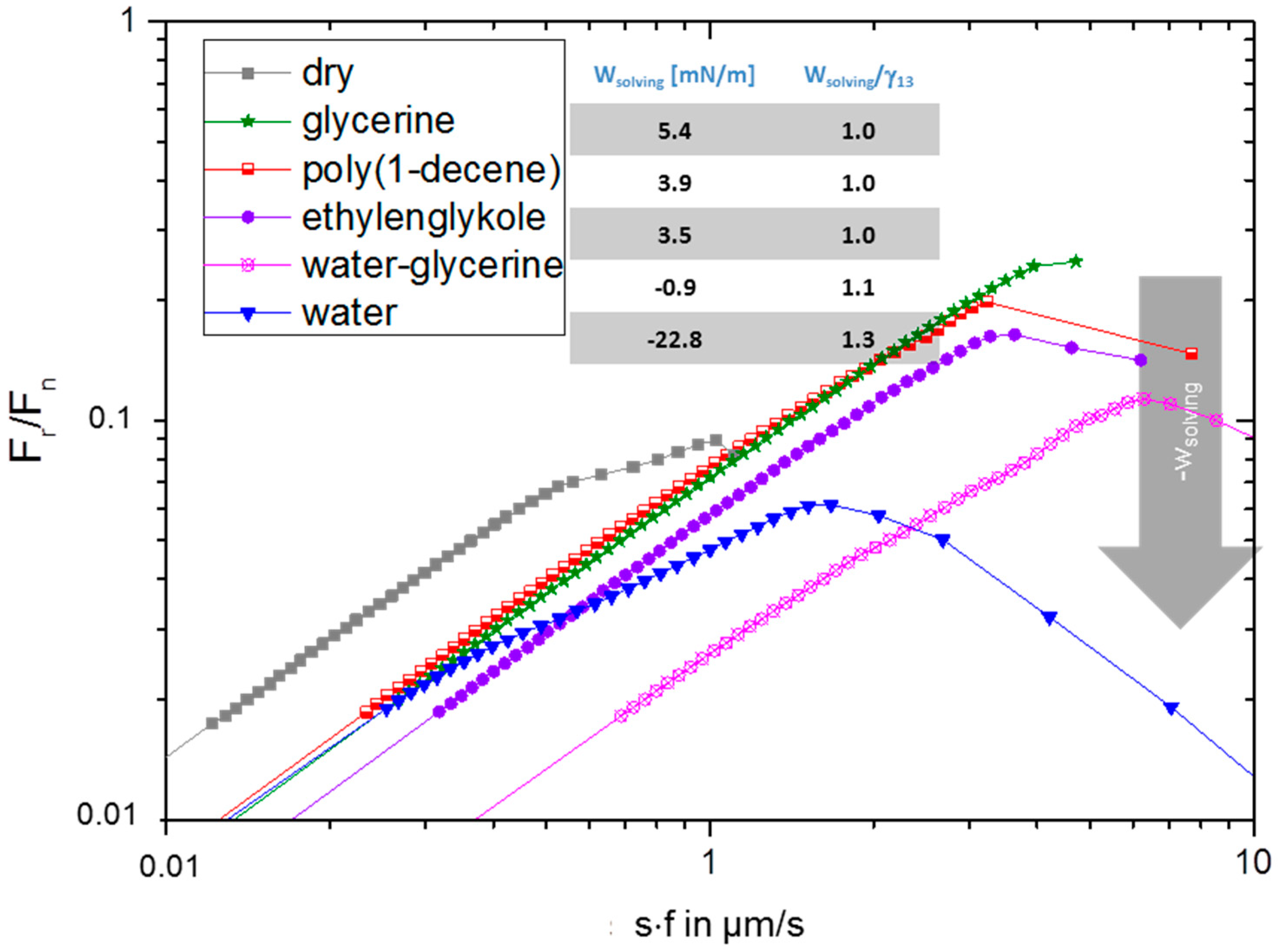
4.1. Contact Angle Measurements and Interaction Energies
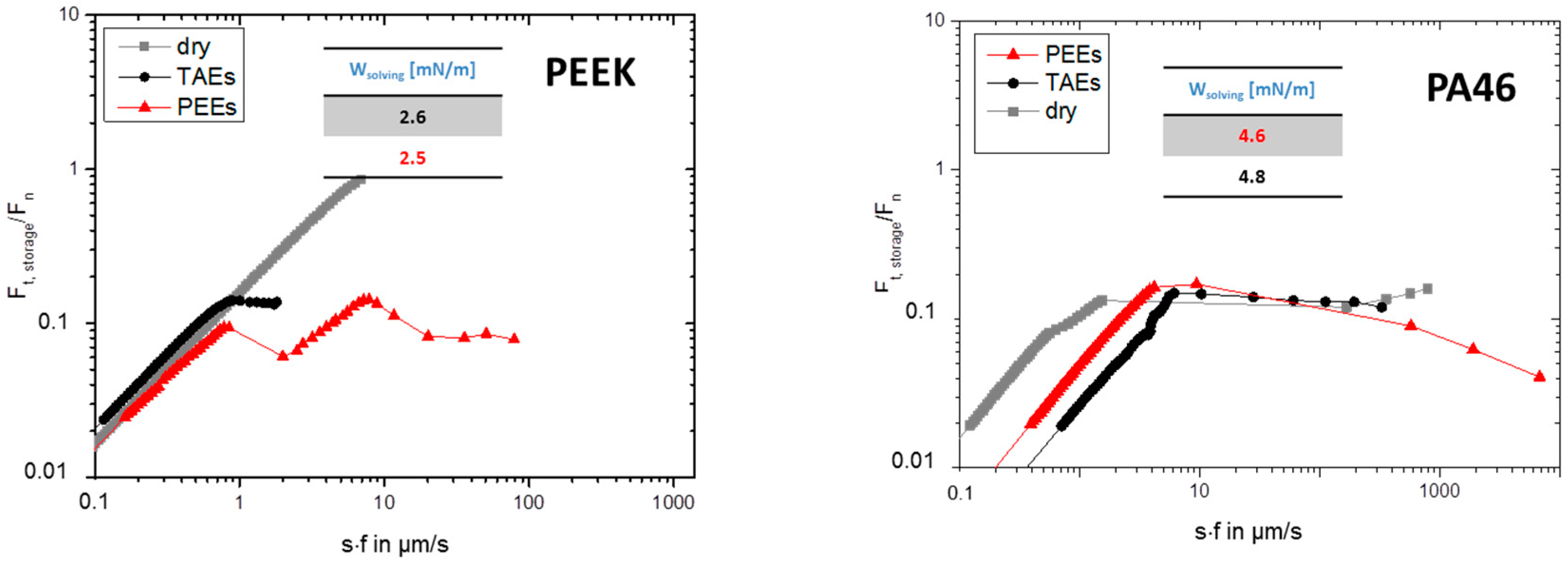
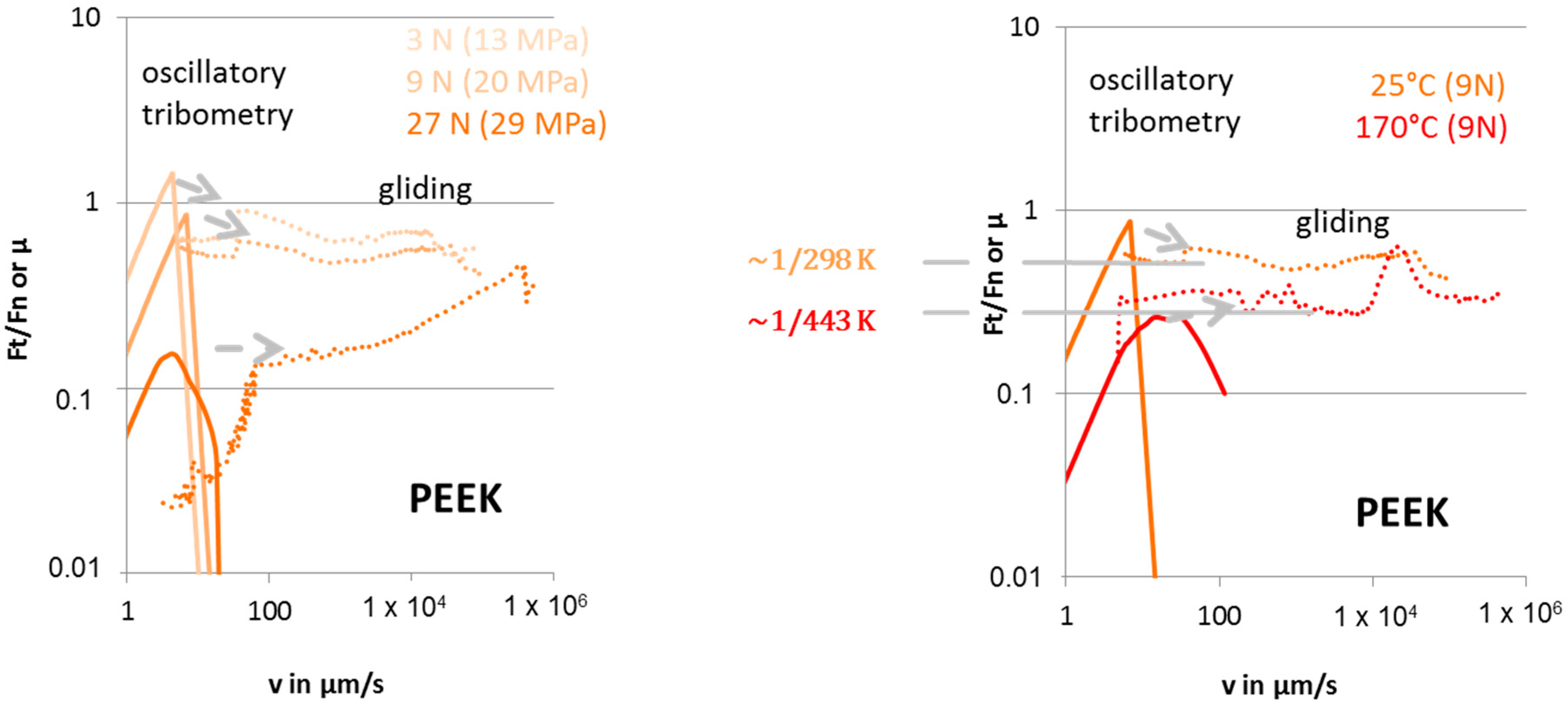
4.2. Static Friction and the Onset of Gliding
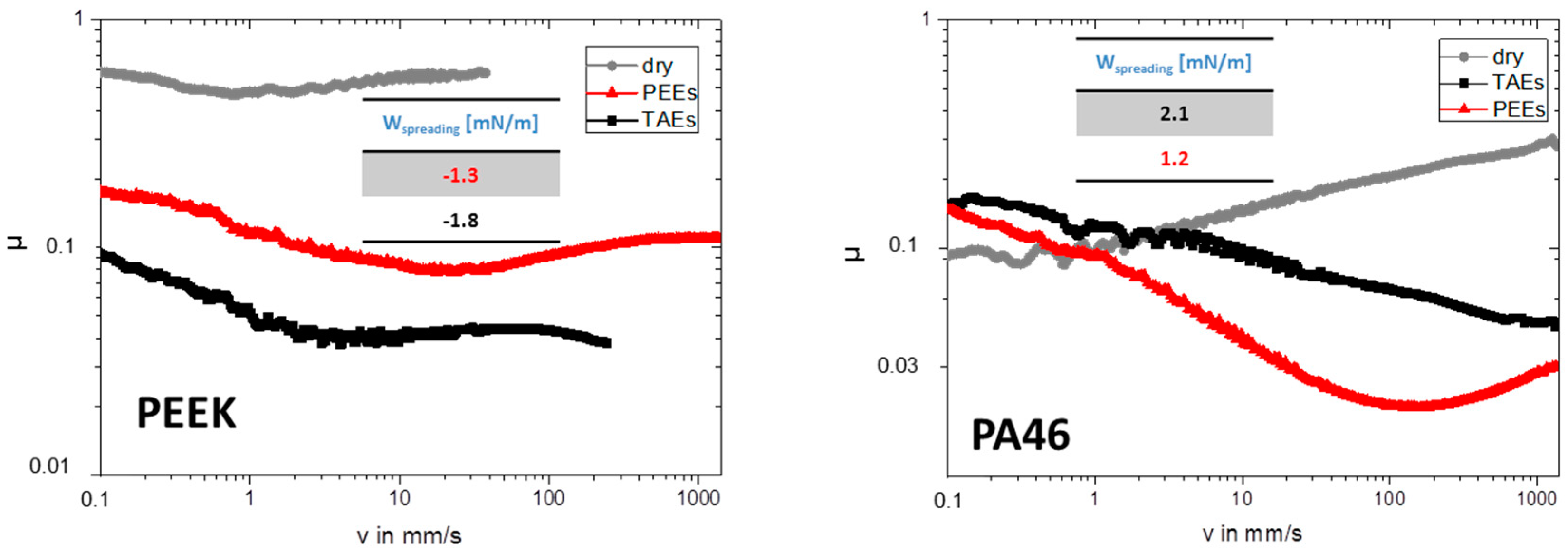
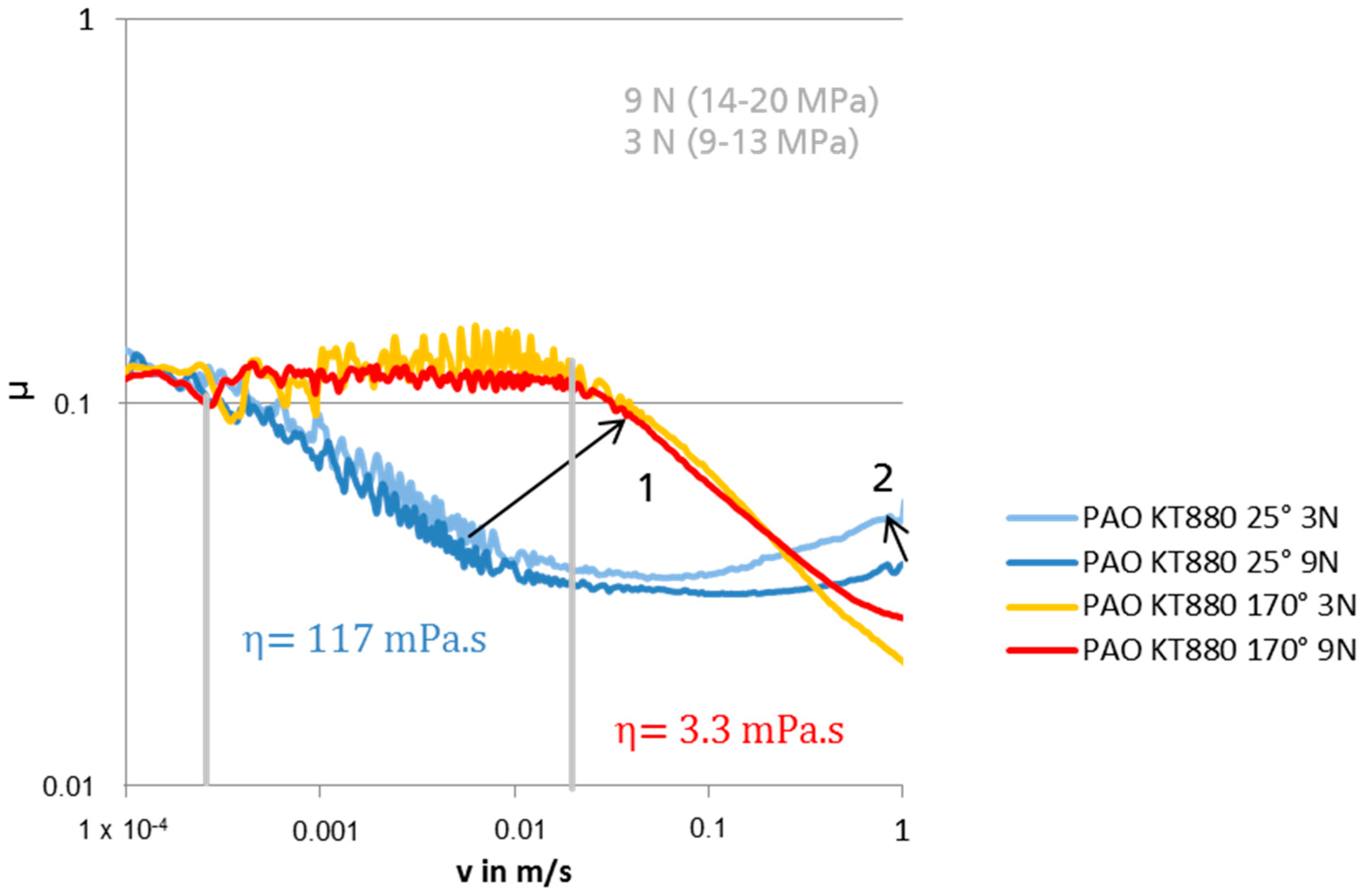
4.3. Dry Boundary Friction, Forced Wetting, Lubricated Boundary Friction and Mixed Lubrication
5. Discussion
5.1. Static Friction and the Onset of Gliding
5.2. Dry Boundary Friction, Forced Wetting, Lubricated Boundary Friction and Mixed Lubrication
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.W. State-of-the-art of polymer tribology. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherge, M.; Kramlich, J.; Böttcher, R.; Hoppe, T. Running-in due to material transfer of lubricated steel/PA46 (aliphatic polyamide) contacts. Wear 2013, 301, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samyn, P.; Schoukens, G. Calculation and Significance of the Maximum Polymer Surface Temperature T * in Reciprocating Cylinder-On-Plate Sliding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campen, S.; Green, J.; Lamb, G.; Atkinson, D.; Spikes, H. On the Increase in Boundary Friction with Sliding Speed. Tribol. Lett. 2012, 48, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahed, S.A.; Koplin, C.; Jaeger, R.; Scherge, M. On the Transition from Static to Dynamic Boundary Friction of Lubricated PEEK for a Spreading Adhesive Contact by Macroscopic Oscillatory Tribometry. Lubricants 2017, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallamach, A. A theory of dynamic rubber friction. Wear 1963, 6, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, M.K. Rate-Dependent Fracture at Adhesive Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 6562–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorvolakos, K.; Chaudhury, M.K. The Effects of Molecular Weight and Temperature on the Kinetic Friction of Silicone Rubbers. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6778–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosch, K.A. The Relation between the Friction and Visco-Elastic Properties of Rubber. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1963, 274, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Juvekar, V.A. Steady dynamic friction at elastomer–hard solid interface: A model based on population balance of bonds. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schertzer, M.; Iglesias, P. Meta-Analysis Comparing Wettability Parameters and the Effect of Wettability on Friction Coefficient in Lubrication. Lubricants 2018, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalin, M.; Polajnar, M. The Effect of Wetting and Surface Energy on the Friction and Slip in Oil-Lubricated Contacts. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 52, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, J.H. Modeling of rock friction: 1. Experimental results and constitutive equations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1979, 84, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruina, A.L. Friction Laws and Instabilities: A Quasistatic Analysis of Some Dry Frictional Behavior; Division of Engineering, Brown University: Providence, RI, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Putelat, T.; Dawes, J.H.P.; Willis, J.R. On the microphysical foundations of rate-and-state friction. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2011, 59, 1062–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, B. Wear of polymers: An essay on fundamental aspects. Tribol. Int. 1981, 14, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axén, N.; Jacobson, S. A model for the abrasive wear resistance of multiphase materials. Wear 1994, 174, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, B.J.; Sinha, S.K. Scratch Resistance and Localised Damage Characteristics of Polymer Surfaces—A Review. Materialwiss. Werkstofftech. 2003, 34, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipway, P.H.; Ngao, N.K. Microscale abrasive wear of polymeric materials. Wear 2003, 255, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellman, A.J.; Spencer, N.D. Surface Chemistry in Tribology. In Wear—Materials, Mechanisms and Practice; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: London, UK, 2005; pp. 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Mugele, F. Squeeze-out and wear: Fundamental principles and applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, R295–R355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu-Bavouzet, F.; Clain-Burckbuchler, J.; Buguin, A.; de Gennes, P.G.; Brochard-Wyart, F. Stick-Slip: Wet Versus Dry. J. Adhes. 2007, 83, 761–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Adhesion and stiction: Mechanisms, measurement techniques, and methods for reduction. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2003, 21, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diew, M.; Ernesto, A.; Cayer-Barrioz, J.; Mazuyer, D. Stribeck and Traction Curves Under Moderate Contact Pressure: From Friction to Interfacial Rheology. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 57, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.F. Grundlagen der Physikalischen Chemie von Grenzflächen und Methoden zur Bestimmung Grenzflächenenergetischer Probleme; IGB: Paris, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Busscher, H.J.; van Pelt, A.W.J.; de Boer, P.; de Jong, H.P.; Arends, J. The effect of surface roughening of polymers on measured contact angles of liquids. Colloids Surfaces 1984, 9, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
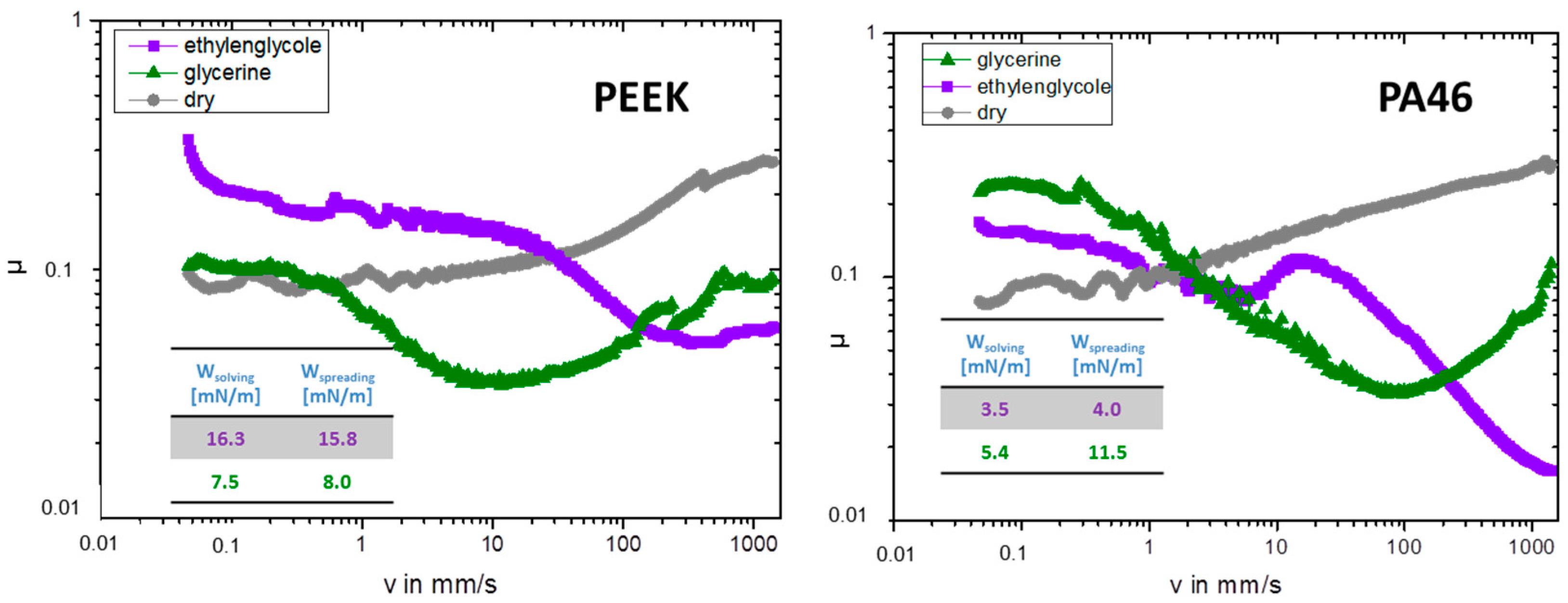

| Lubricant | Viscosity | Contact Angle on Steel [°] | PA46 | PEEK 450sf | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At 25 °C [mPa·s] | Wsolving [mN/m] | Wspreading [mN/m] | Wsolving/γ13 | Wsolving [mN/m] | Wspreading [mN/m] | ||
| pentaerythrite ester (PEEs) | 109 | 23.4 | 4.6 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 2.5 | −1.3 |
| trimellitic acid ester (TAEs) | 153 | 23.9 | 4.8 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 2.6 | −1.8 |
| ethylen glycol | 21 | 54.2 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 1.0 | 16.3 | 15.8 |
| water | 1 | 78.7 | −22.8 | 27.2 | 1.3 | 39.7 | 51.9 |
| glycerine | 1420 | 64.5 | 5.4 | 11.5 | 1.0 | 7.5 | 8.0 |
| 30% water, 70% glycerine | 20 | 72.2 | −0.9 | 11.6 | 1.1 | 12.2 | 13.5 |
| poly(1-decene) | 25 | 16.7 | 3.9 | 2.3 | 1.0 | 3.9 | −0.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koplin, C.; Abdel-Wahed, S.A.; Jaeger, R.; Scherge, M. The Transition from Static to Dynamic Boundary Friction of a Lubricated Spreading and a Non-Spreading Adhesive Contact by Macroscopic Oscillatory Tribometry. Lubricants 2019, 7, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7010006
Koplin C, Abdel-Wahed SA, Jaeger R, Scherge M. The Transition from Static to Dynamic Boundary Friction of a Lubricated Spreading and a Non-Spreading Adhesive Contact by Macroscopic Oscillatory Tribometry. Lubricants. 2019; 7(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoplin, Christof, Sherif Ahmed Abdel-Wahed, Raimund Jaeger, and Matthias Scherge. 2019. "The Transition from Static to Dynamic Boundary Friction of a Lubricated Spreading and a Non-Spreading Adhesive Contact by Macroscopic Oscillatory Tribometry" Lubricants 7, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7010006
APA StyleKoplin, C., Abdel-Wahed, S. A., Jaeger, R., & Scherge, M. (2019). The Transition from Static to Dynamic Boundary Friction of a Lubricated Spreading and a Non-Spreading Adhesive Contact by Macroscopic Oscillatory Tribometry. Lubricants, 7(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7010006