Evaluation of Friction Behavior and Surface Interactions of Cyano-Based Ionic Liquids under Different Sliding Contacts and High Vacuum Condition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
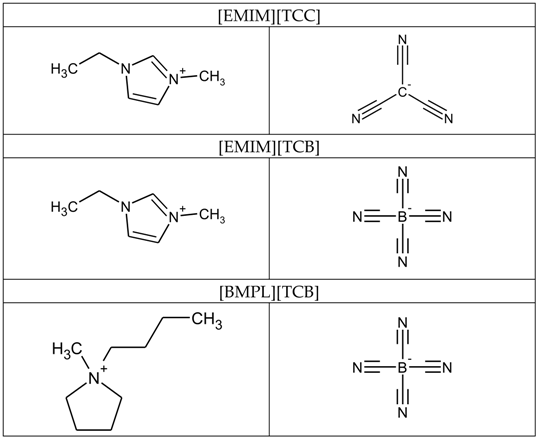
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sliding Tests
2.3. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
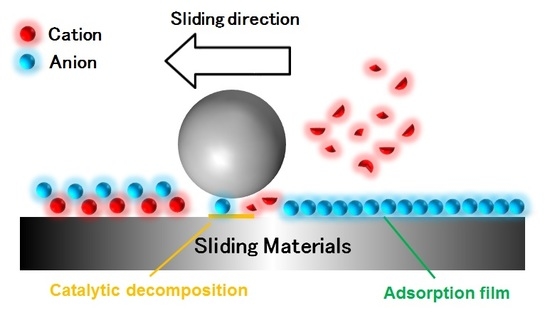
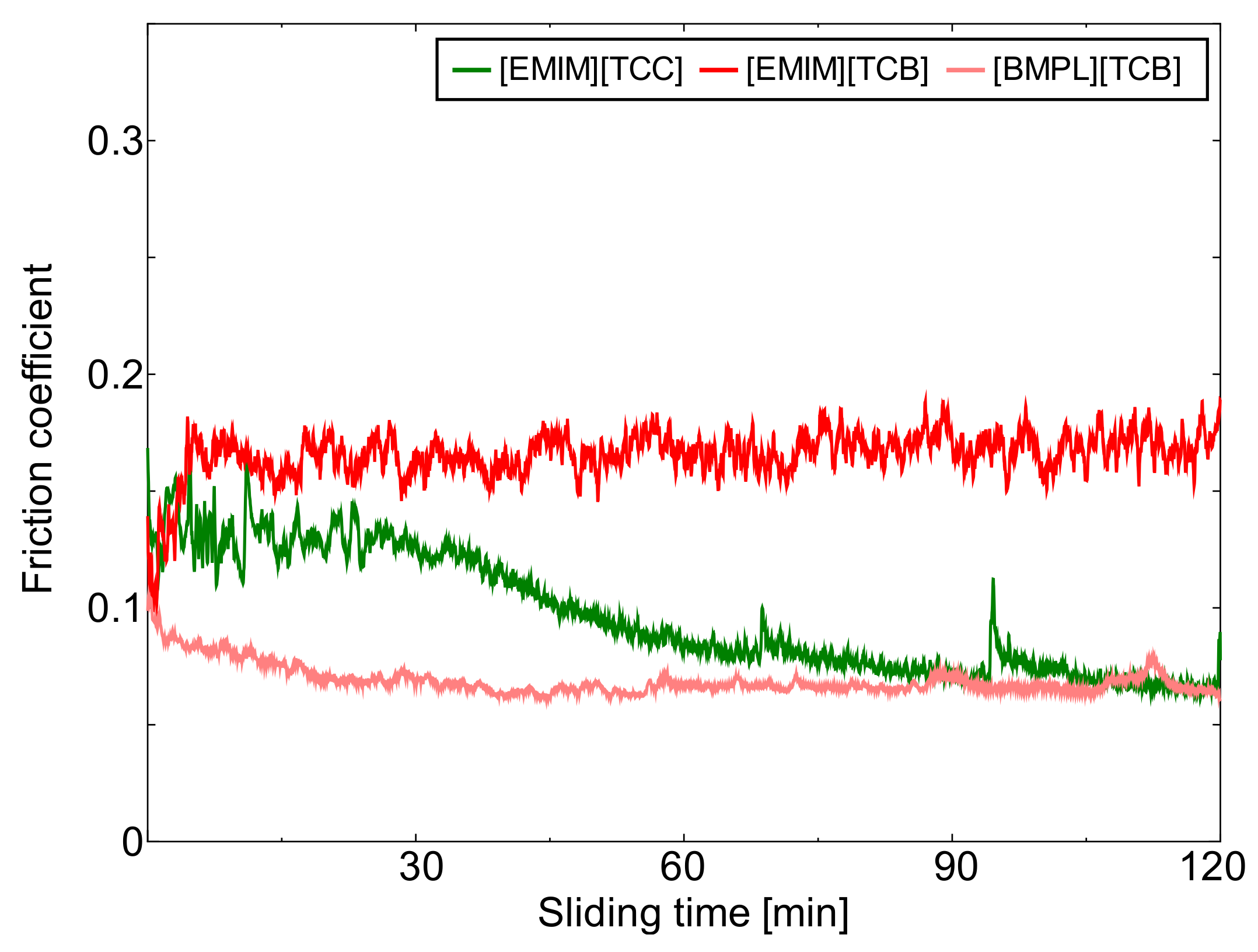
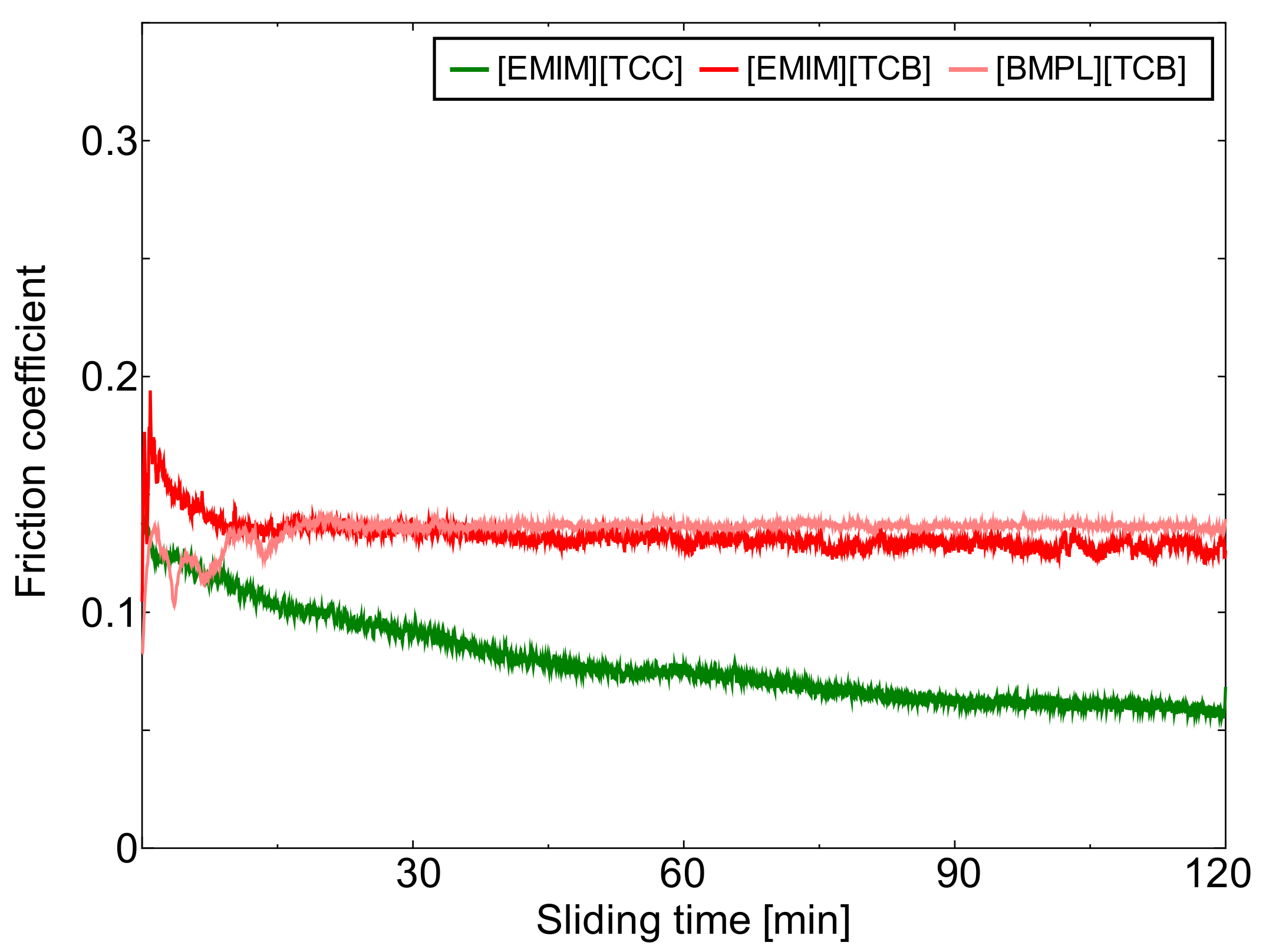
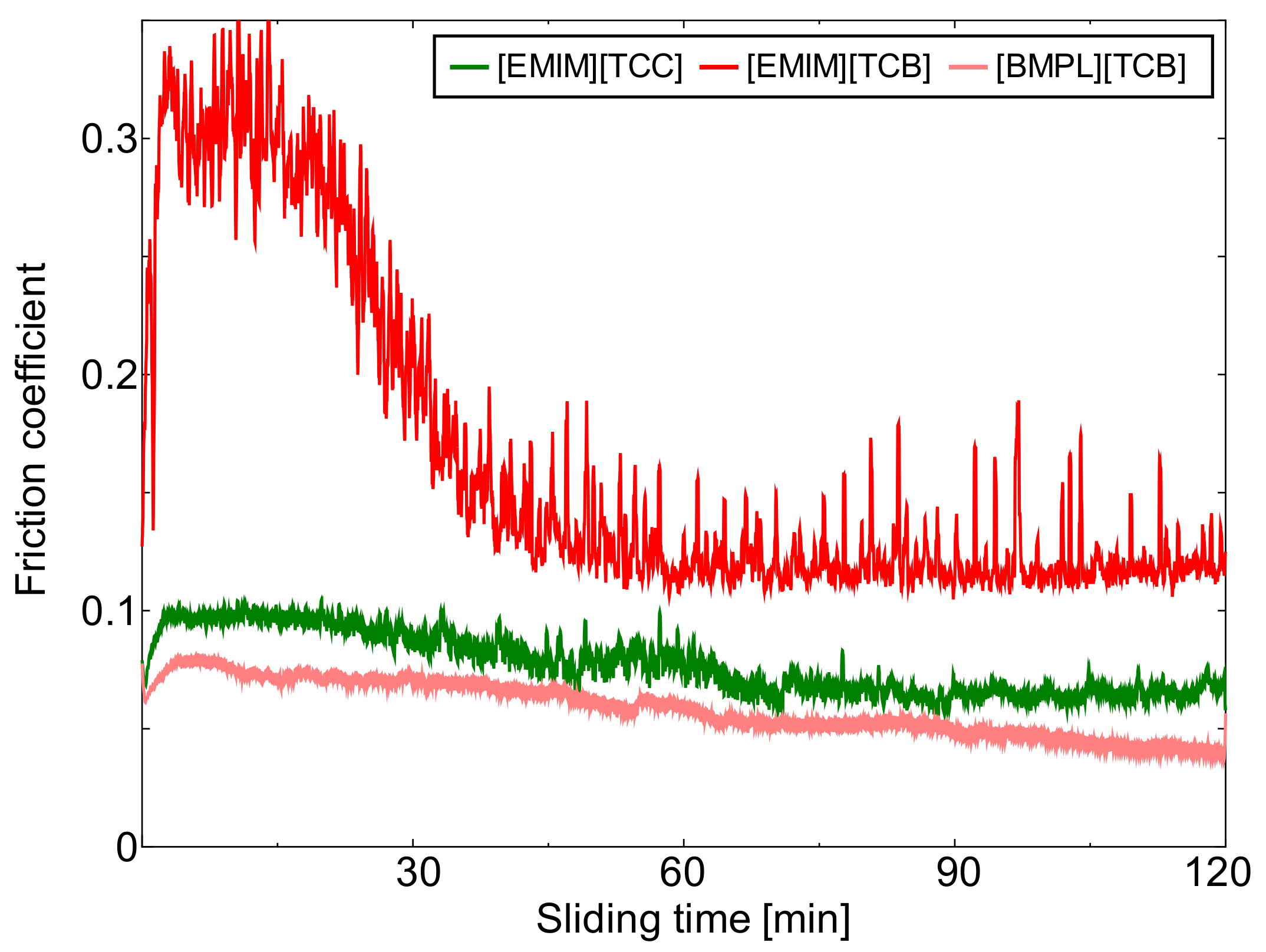
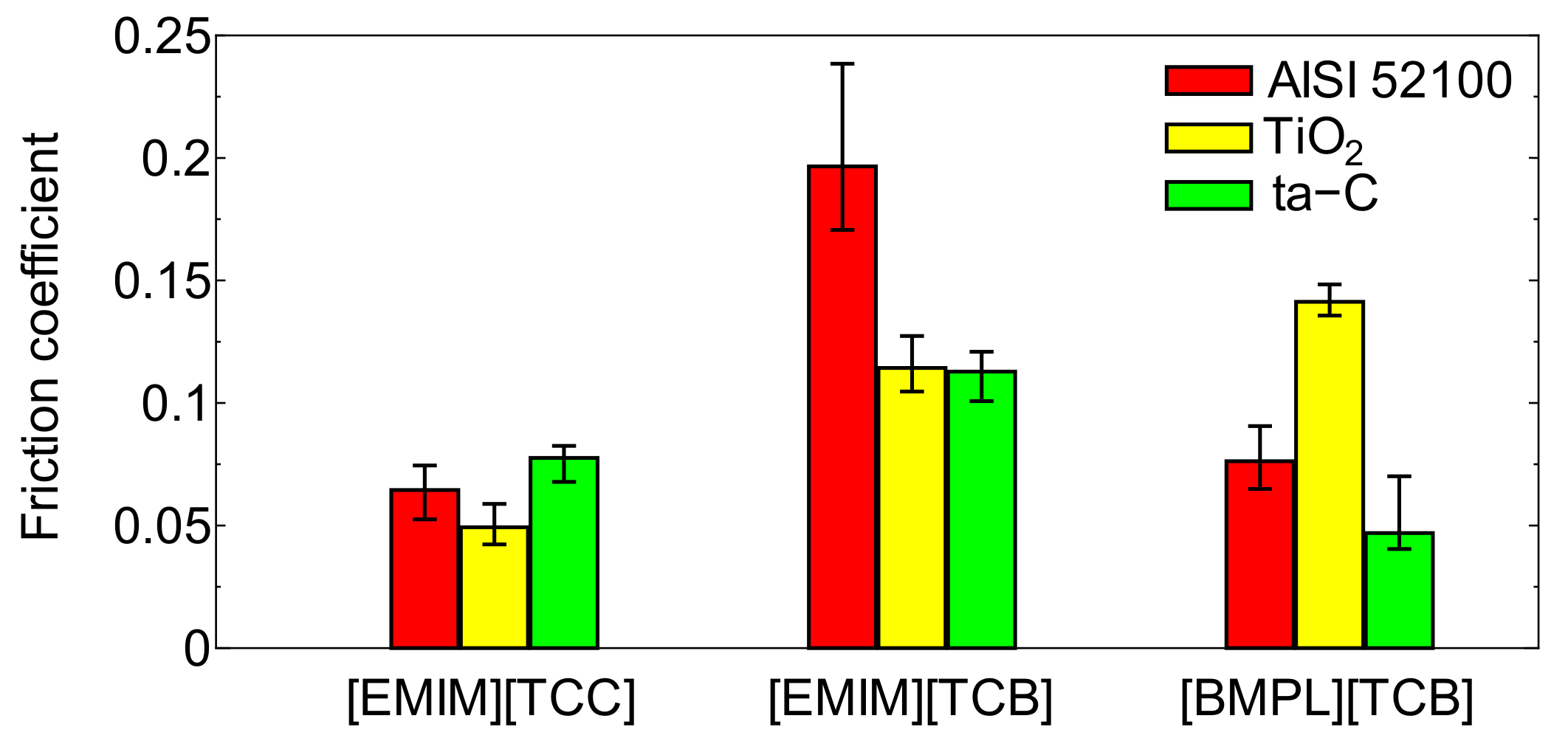
3.1. Friction Coefficients
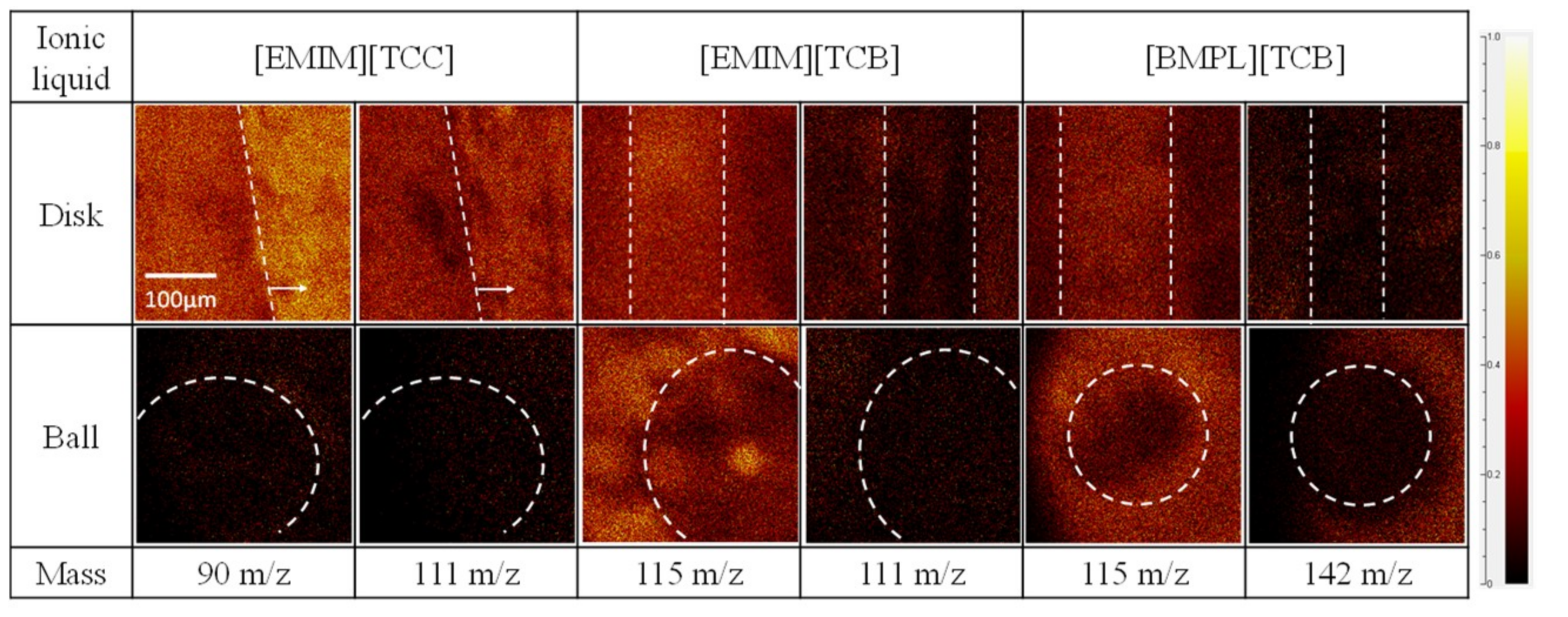
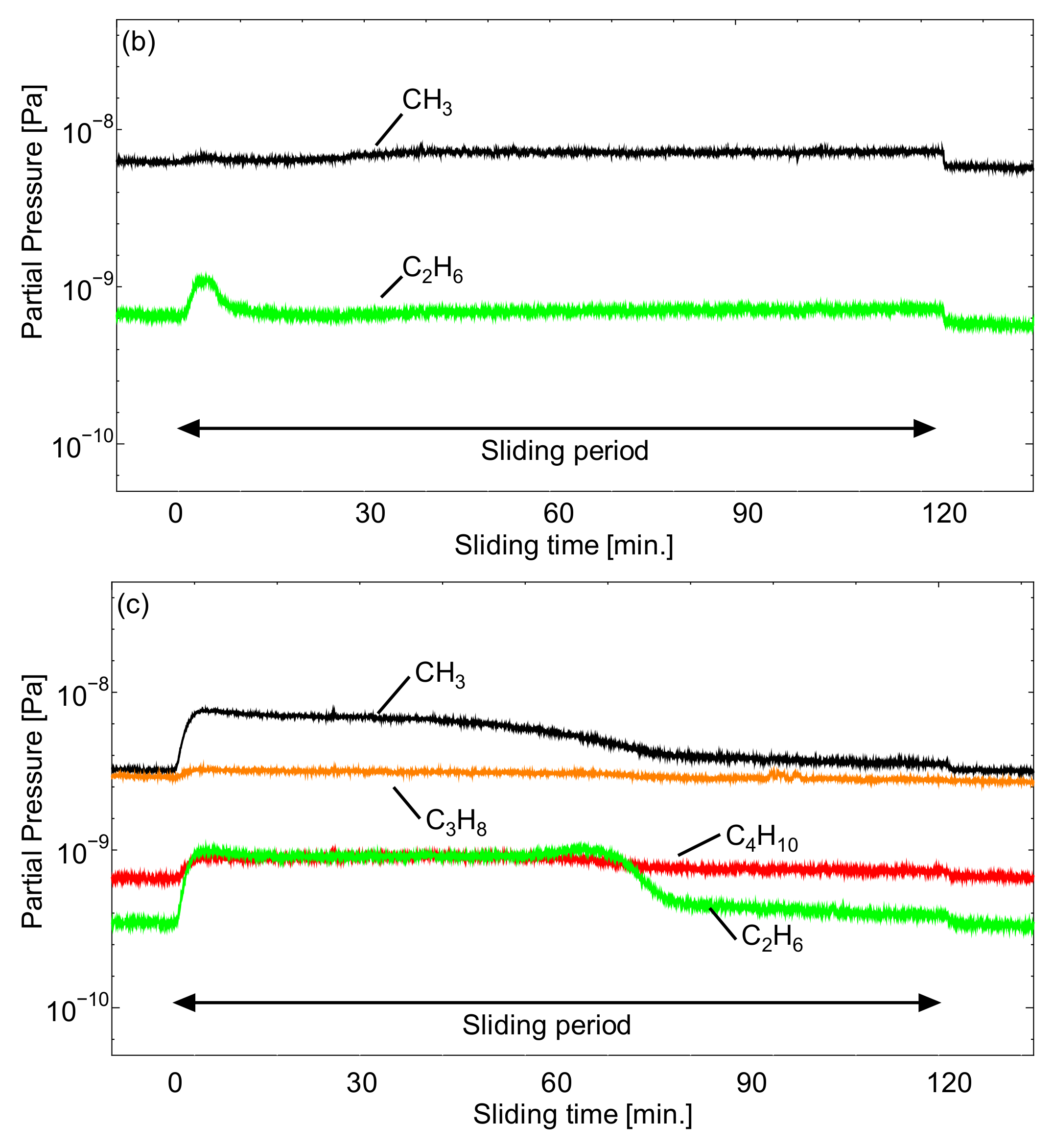
3.2. ToF-SIMS Analysis Results
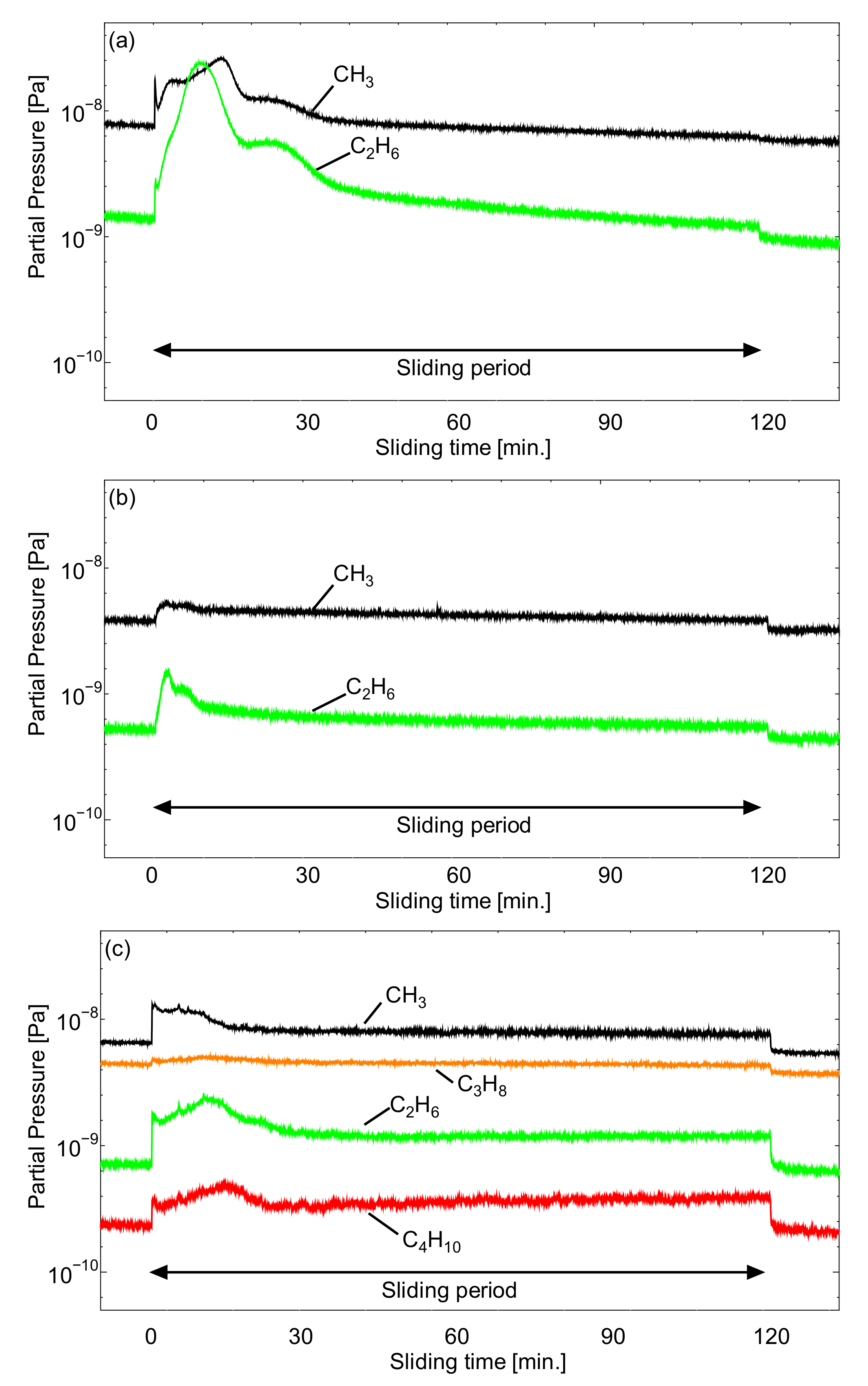
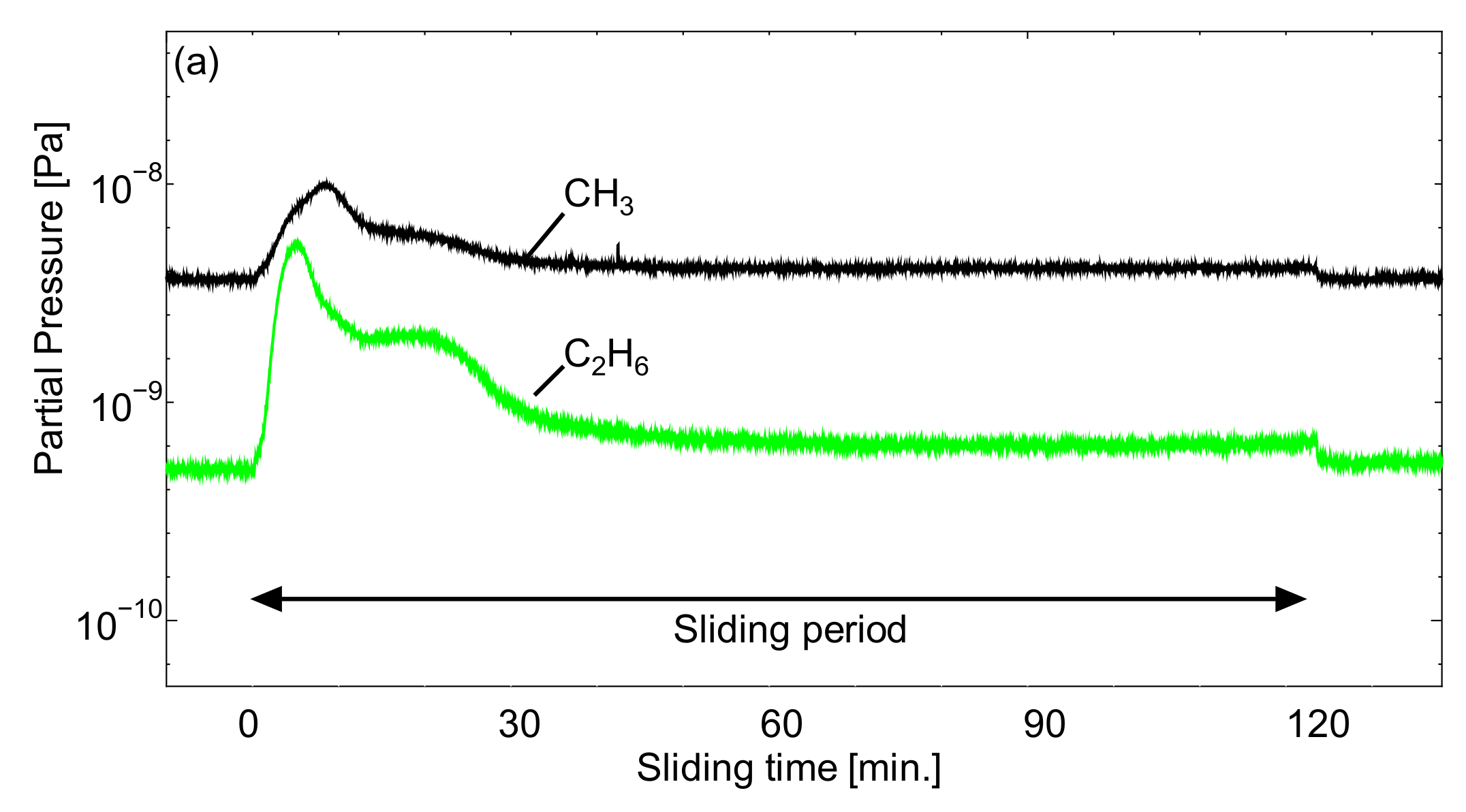
3.3. Q-Mass Analysis Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kondo, H.; Seto, J.; Ozawa, K.; Haga, S. Novel lubricants for magnetic thin film media. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 1989, 13, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricants. Chem. Commun. 2001, 21, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, T.; Dold, C.; Kailer, A. Complex fluids intribology to reduce friction: Mesogenic fluids, ionic liquids and ionic liquid crystals. Tribol. Int. 2013, 65, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, L. High-performance lubricant additives based on modified graphene oxide by ionic liquids. J. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 2015, 452, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Mu, L.; Shi, Y.; Dong, Y.; Feng, X.; Lu, X. High load capacity with ionic liquid-lubricated tribological system. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworokto, M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. 1992, 13, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvim, Y.; Mussmann, L.; Olivier, H. A novel class of versatile solvents for two phase catalysis: Hydrogenation, isomerization, and hydroformylation of alkenes catalyzed by rhodium complexed in liquid 1,3-dialkylimidazolium salts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 1996, 34, 2698–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Shinka, Y.; Masuko, M. Tribological characteristics of imidazolium-based room temperature ionic liquids under high vacuum. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 27, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, C.; Vos, N.D.; Stevens, C.V. Ionic liquid thermal stabilities: Decomposition mechanisms and analysis tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Yanagida, M.; Tanimoto, K.; Nomura, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Miyazaki, Y. Highly conductive room temperature molten salts based on small trimethylalkylammonium cations and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Chem. Lett. 2000, 8, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Ionic liquid lubricants: Designed chemistry for engineering applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jímenez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Carrion, F.J.; Martinez-Nicholas, G. Room temperature ionic liquids as lubricant additives in steel-aluminium contacts: Influence of sliding velocity, normal load and temperature. Wear 2006, 261, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Kamimura, H.; Mori, S. Thermo-oxidative stability of ionic liquids as lubricating fluid. J. Synth. Lubr. 2007, 24, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Howlett, P.C.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. A Review of Ionic Liquid Lubricants. Lubricants 2013, 1, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J. Tribological behavior of amorphous Cr coatings electrodeposited from Cr(III) baths under ionic liquid lubrication. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2007, 10, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viesca, J.-L.; Anand, M.; Blanco, D.; Fernández-González, A.; García, A.; Hadfield, M. Tribological Behaviour of PVD Coatings Lubricated with a FAP− Anion-Based Ionic Liquid Used as an Additive. Lubricants 2016, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Battez, A.; Ramos, D.; Blanco, D.; González, R.; Fernández-González, A.; Viesca, J.-L. Lubrication Properties of the Ionic Liquid Dodecyl-Methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viesca, J.-L.; Mallada, M.T.; Blanco, D.; Fernández-González, A.; Espina-Casado, J.; González, R.; Hernández Battez, A. Lubrication performance of an ammonium cation-based ionic liquid used as an additive in a polar oil. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yu, Q.; Meirong, C.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Investigation of the lubricity and antiwear behavior of guanidinium ionic liquids at high temperature. Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Yagi, S.; Koyama, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Lubricity and corrosiveness of ionic liquids for steel-on-steel sliding contacts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Kondo, Y.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Tribochemical reaction of ionic liquids under vacuum condition. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 54, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids are not always green: Hydrolysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Pardilla, J.; Espinosa, T.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ionic Liquids in Surface Protection. In Electrochemistry in Ionic Liquids; Torriero, A.A.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 533–561. ISBN 978-3-319-15131-1. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, I.; Inada, T.; Okada, Y. Tribological properties of halogen-free ionic liquids. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S.; Prakash, B. Lubrication mechanism of halogen-free ionic liquids. Tribol. Online 2017, 12, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okubo, H.; Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Sasaki, S. Tribological performance of halogen-free ionic liquids in steel-steel and DLC-DLC contacts. Tribol. Trans. 2018, 61, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Sato, K.; Watanabe, S.; Sasaki, S. Lubricating property of cyano-based ionic liquids against hard materials. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 5745–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Tadokoro, C.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Lubricating mechanism of cyano-based ionic liquids on nascent steel surface. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Sasaki, S. Tribological Properties of Cyano-Based Ionic Liquids under Different Environments. Tribol. Online 2018, 13, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Ichise, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Tadokoro, C.; Sasaki, S. Tribochemical reaction of ionic liquids as lubricants on steel sliding surfaces. In Surfactants in Tribology, 5th ed.; Biresaw, G., Mittal, K.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 1–18. ISBN 9781498734790. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, Y.; Koyama, T.; Sasaki, S. Tribological Properties of Ionic Liquids; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Siedlecka, E.M.; Czerwicka, M.; Stolte, S.; Stepnowski, P. Stability of ionic liquids in application conditions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2011, 12, 1974–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, H.; Ishimura, S.; Kumai, M. Thermal decomposition behaviors of imidazolium-type ionic liquids studied by pyrolysis-gas chromatography. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tim, J.W.; Katarina, M.J.; Kevin, J.F.; Douglas, R.M.; Janet, L.S. Thermal degradation of cyano containing ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 691–696. [Google Scholar]
- Kroon, M.C.; Buijs, W.; Peters, C.J.; Witkamp, G.-J. Quantum chemical aided prediction of the thermal decomposition mechanisms and temperatures of ionic liquids. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 465, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Tadokoro, C.; Sasaki, S. Effects of alkyl chain length of sulfate and phosphate anion-based ionic liquids on Tribochemical reactions. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Mori, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nanao, H. Study of tribochemical decomposition of ionic liquids on a nascent steel surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8965–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Method | Roughness, Ra (μm) | Hardness (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 52100 | Hardening | 0.05 | 7 |
| TiO2 | Sintering | 0.05 | 15 |
| ta-C | Arc Ion Plating | 0.01 | 73 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Sasaki, S.; Miyatake, M. Evaluation of Friction Behavior and Surface Interactions of Cyano-Based Ionic Liquids under Different Sliding Contacts and High Vacuum Condition. Lubricants 2018, 6, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030069
Kawada S, Watanabe S, Sasaki S, Miyatake M. Evaluation of Friction Behavior and Surface Interactions of Cyano-Based Ionic Liquids under Different Sliding Contacts and High Vacuum Condition. Lubricants. 2018; 6(3):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030069
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawada, Shouhei, Seiya Watanabe, Shinya Sasaki, and Masaaki Miyatake. 2018. "Evaluation of Friction Behavior and Surface Interactions of Cyano-Based Ionic Liquids under Different Sliding Contacts and High Vacuum Condition" Lubricants 6, no. 3: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030069
APA StyleKawada, S., Watanabe, S., Sasaki, S., & Miyatake, M. (2018). Evaluation of Friction Behavior and Surface Interactions of Cyano-Based Ionic Liquids under Different Sliding Contacts and High Vacuum Condition. Lubricants, 6(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030069