Abstract
The friction coefficients of ionic liquids were evaluated by many investigations. Most investigations used fluorine-based ionic liquids as lubricants. However, these ionic liquids produce the corrosion wear. This investigation focuses on the use of cyano-based ionic liquids as lubricants. Compared to fluorine-based ionic liquids, cyano-based ionic liquids exhibit high friction coefficients against steel material. This work examines how the friction coefficients of cyano-based ionic liquids are influenced by the type of sliding material used (AISI 52100, TiO2, and tetrahedral amorphous carbon). TiO2 lubricated with 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tricyanomethanide, and ta-C lubricated with 1-butyl-1methylpyrrolidinium tetracyanoborate exhibited very low friction coefficients, smaller than fluorine-based ionic liquids. Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry analysis showed that anions adsorb onto the worn surface, suggesting that anion adsorption is a critical parameter influencing friction coefficients. Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry measurements revealed that cations decompose on the nascent surface, preventing adsorption on the worn surface. These results suggest that low friction coefficients require the decomposition of cations and adsorption of anions. The reactivity of nascent surface changes with the sliding material used due to varying catalytic activity of the nascent surfaces.
1. Introduction
Since the industrial revolution in the 18th century, the advance of science and technology has been astonishing. However, global warming resulting from CO2 emission has become a critical issue. Because of the problems associated with CO2 emission, the Conférence de Paris de 2015 sur le climat (COP21) established a target for the reduction of CO2 emissions for many countries. Achieving this goal requires an overall improvement in the energy efficiency of machines. From the perspective of tribology, one method of improving energy efficiency is to reduce energy loss due to friction. Recent works reported in the literature suggest ionic liquids can serve as an effective lubricant, reducing friction loss [1,2,3,4,5].
Ionic liquids are organic salts that exist in the liquid phase at temperatures less than 100 °C. They possess many attractive properties such as low melting points, high thermal stability, and low vapor pressure, in addition to refractory and lubricative properties [6,7,8,9]. The properties of ionic liquids can be controlled by altering their chemical structures, resulting in millions of potential combinations of cations and anions [10,11].
The mechanism of friction reduction in ionic liquids can be classified into two types, forming a reaction film and forming an adsorption film. In the former, an ionic liquid reacts with a sliding surface to form a reaction film, as opposed the latter, which forms an adsorption film. Most investigations use fluorine-based ionic liquids, which are of the forming reaction film type [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,12,13,14,15,16]. Fluorine-based ionic liquids react to form a metallic fluoride on the sliding surface and exhibit a low friction coefficient [17,18,19,20]. Unfortunately, despite its high performance, the hydrolysis of metallic fluorides can cause corrosion [20,21]. For example, when tetrafluoroborate and hexafluorophosphate, two commonly studied ionic liquids, undergo hydrolysis, they produce corrosive hydrogen fluoride as a product [22,23]. To avoid fluorine’s corrosion issues, this investigation focuses on cyano-based ionic liquids, which are of the forming adsorption film type. These ionic liquids consist of hydrogen, borate, carbon, and nitrogen [24,25,26,27,28,29]. Compared to fluorine-based ionic liquids, cyano-based ionic liquids show high friction coefficient against metallic materials [20,29,30]. A few investigations indicated the possibility that changing the sliding conditions, such as sliding materials, normal load, and temperature, can achieve low friction coefficients [20,25,26,29]. This investigation focused on the effect of the sliding materials on the friction coefficients and surface interactions of cyano-based ionic liquids.
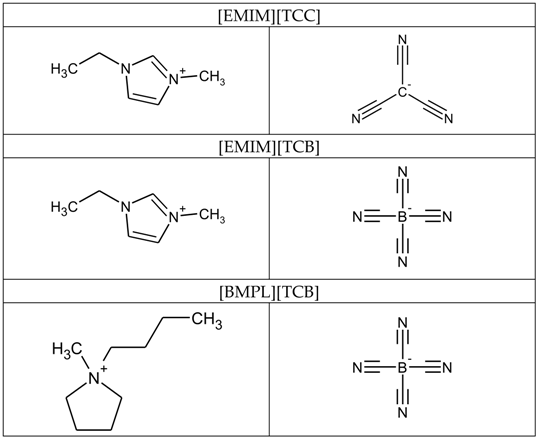
This work reports the friction coefficients of three types of cyano-based ionic liquids: 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tricyanomethanide [EMIM][TCC], 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetracyanoborate [EMIM][TCB], and 1-butyl-1methylpyrrolidinium tetracyanoborate [BMPL][TCB] against AISI 52100 steel, TiO2, and tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) surfaces. Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) was employed to investigate the byproducts that form on the surfaces when exposed to cyano-based ionic liquids. The reaction of cyano-based ionic liquids with sliding materials were analyzed via Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (Q-mass).
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
Three types of cyano-based ionic liquids were used as liquid lubricants to investigate the effects of cationic and anionic components on the friction coefficients. Table 1 shows the molecular structures of the cyano-based ionic liquids used. [EMIM][TCC] was purchased from IoLiTec, Heilbronn, Germany, at >98% purity. [EMIM][TCB] and [BMPL][TCB] were purchased from Merck Chemicals, Darmstadt, Germany, at >98% purity.

Table 1.
Molecular structures of cyano-based ionic liquids.
AISI 52100 was used as the ball specimen. AISI 52100, TiO2, and tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) were used as disk specimens to evaluate the effect of sliding materials on friction coefficients of cyano-based ionic liquids. The physical properties of the disk specimens are listed in Table 2. The surface roughness was measured by a surface profile meter (SURFCOM 1500SD3, ACCRETECH, Tokyo, Japan.) The hardness was measured using a tribo-indenter (Ti950, Hysitron, Minneapolis, MN, USA), and the ta-C film thickness was measured using a coating thickness analyzer (Calotest, Anton Paar Tritec SA, Graz, Austria). The ta-C film thickness was approximately 1 μm.

Table 2.
Physical properties of sliding materials.
2.2. Sliding Tests
The tribological properties of cyano-based ionic liquids under vacuum conditions were evaluated using a ball-on-disk friction tester (handmade) [30]. The specimens were ultrasonically cleaned (20 min) twice with a solution of petroleum benzine and acetone in a ratio of 1:1. Sliding tests were performed at a normal load of 3.5 N, with a sliding speed of 52.3 mm/s, for 2 h, under vacuum condition (2.0 × 10−5 Pa). Each experimental parameter was tested 10 times.
2.3. Analysis
The worn surfaces of the specimens were analyzed using ToF-SIMS (Billerica, MA, USA). After the sliding tests, each specimen was ultrasonically cleaned (10 min) with a solution of benzene and acetone in a ratio of 1:1. The primary ion source was Ga+, impact energy was 15 kV, ion irradiation time was 3 min, and measured area was 300 × 300 μm2. The mass resolution was 500 at Al (m/z = 27) and the lateral resolution was 2 μm.
The reactions of the cyano-based ionic liquids with sliding materials during the sliding tests were measured using Q-mass. The measurement principle of Q-mass is explained previously [25].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Friction Coefficients
Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the friction behavior of each ionic liquid against AISI 52100, TiO2, and ta-C, respectively. Figure 4 shows the mean friction coefficient calculated from the last 5 min of the sliding test lubricated with each cyano-based ionic liquid. [EMIM][TCC] exhibited low friction coefficients against all sliding materials. These friction coefficients showed a tendency to gradually decrease. The choice of sliding material impacted the friction coefficients of [EMIM][TCC]. The friction coefficient of TiO2 lubricated with [EMIM][TCC] was lower than that of AISI 52100, and lower than fluorine-based ionic liquids in the literature [30]. [EMIM][TCB] also showed sliding surface dependent friction coefficients, where TiO2 and ta-C display coefficients 0.1 higher than that of AISI 52100. Especially, in the initial sliding period, ta-C lubricated with [EMIM][TCB] exhibited a very high friction coefficient. It was considered that ta-C was removed by the sliding. In the case of [BMPL][TCB], TiO2 had the highest friction coefficient while ta-C exhibited a low friction coefficient. These values were lower than the values for fluorine-based ionic liquids in the literature [26]. From these results, it is shown that changing the cation or anion impacts the friction coefficient of cyano-based ionic liquids. In addition, the sliding materials impacts friction coefficients. The TiO2 lubricated with [EMIM][TCC] and the ta-C lubricated with [BMPL][TCB] showed lowest friction coefficients.
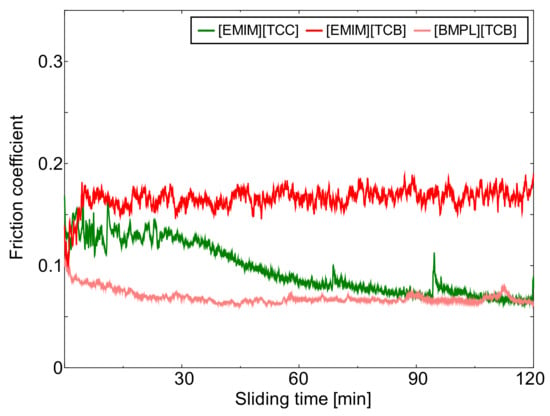
Figure 1.
Friction behavior of AISI 52100 lubricated with three cyano-based ionic liquids ([EMIM][TCC], [EMIM][TCB], and [BMPL][TCB]).
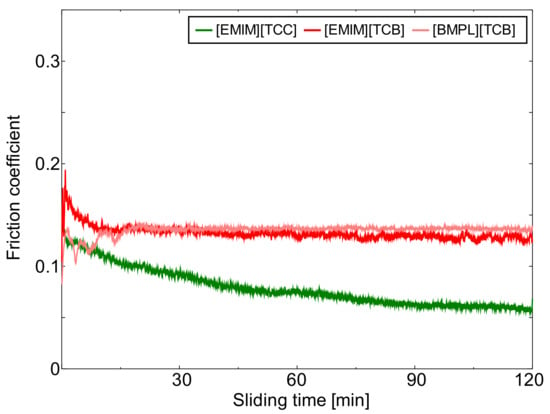
Figure 2.
Friction behavior of TiO2 lubricated with three cyano-based ionic liquids ([EMIM][TCC], [EMIM][TCB], and [BMPL][TCB]).
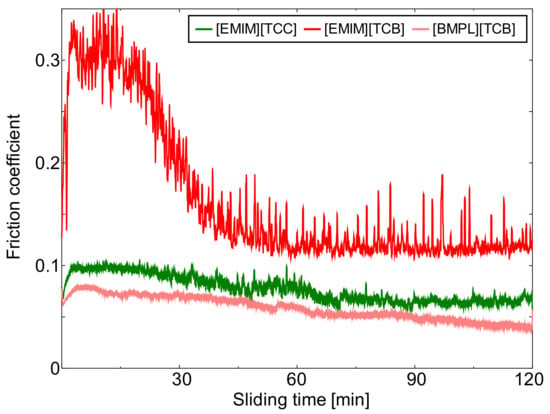
Figure 3.
Friction behavior of ta-C lubricated with three cyano-based ionic liquids ([EMIM][TCC], [EMIM][TCB], and [BMPL][TCB]).
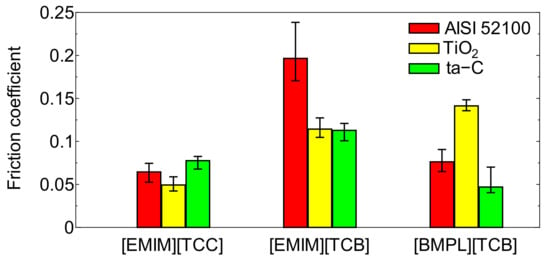
Figure 4.
The average of friction coefficients of three cyano-based ionic liquids ([EMIM][TCC], [EMIM][TCB], and [BMPL][TCB]) on three different surfaces (AISI 52100, TiO2, and ta-C) at last 5 min.
3.2. ToF-SIMS Analysis Results
The worn surfaces of disk and ball specimens were analyzed using ToF-SIMS to identify substances present on the surface after the sliding tests. To get substance information on the worn surface, mapping images of each ion ([EMIM] cation = 111 m/e, [BMPL] cation = 142 m/e, [TCC] anion = 90 m/e, and [TCB] anion = 115 m/e) were obtained. Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 show mapping images for each sliding test. Inside the white showed frame was worn surface. The high-brightness region indicates high count value of each ion. [EMIM][TCB] against ta-C was not analyzed because of peeling of the ta-C. Figure 5 shows anions adsorbed on the worn surface of disk specimens when [EMIM][TCC] and [BMPL][TCB] were used as lubricants. On the other hand, no signs of cation or anion adsorption were observed for [EMIM][TCB], which exhibited a high friction coefficient. Figure 6 shows the same trend. When [EMIM][TCC], which exhibited a low friction coefficient, was used as the lubricant, the anion adsorbed onto the worn surfaces of the disk specimen but the cation showed no signs of adsorption. In the case of [EMIM][TCB] and [BMPL][TCB], both ions showed no signs of adsorption. Figure 7 shows anions adsorbed on the worn surface of disk specimen and cations showed no signs of adsorption. The results indicate that when anions are adsorbed on the sliding surface, ionic liquids are found to have a low friction coefficient. However, neither ion is adsorbed on the worn surfaces of ball specimens in all cases. Ball specimens constantly contact the disk specimen. Thus, the ball specimen became worn and the ions desorbed on the worn surface.
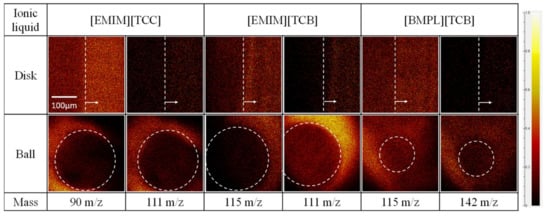
Figure 5.
Mapping images of each anion (90 m/z for [TCC] and 115 m/z for [TCB]) and cation (111 m/z for [EMIM] and 142 m/z for [BMPL]) against AISI 52100 disks and AISI 52100 balls.
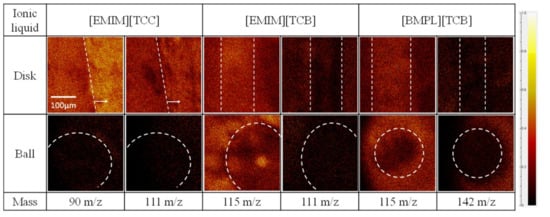
Figure 6.
Mapping images of each anion (90 m/z for [TCC] and 115 m/z for [TCB]) and cation (111 m/z for [EMIM] and 142 m/z for [BMPL]) against TiO2 disks and AISI 52100 balls.
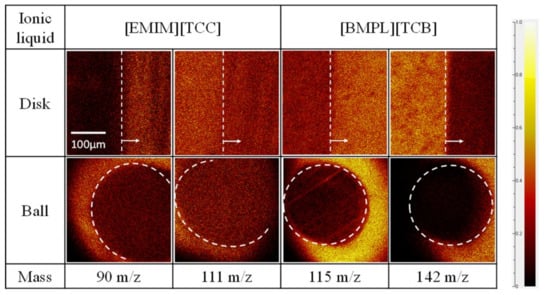
Figure 7.
Mapping images of each anion (90 m/z for [TCC] and 115 m/z for [TCB]) and cation (111 m/z for [EMIM] and 142 m/z for [BMPL]) against ta-C disks and AISI 52100 balls.
3.3. Q-Mass Analysis Results
The outgassing of the cyano-based ionic liquids during sliding was measured with Q-mass providing insight into the reactions that occur between ionic liquids with sliding materials. In Q-mass, the fragmentation of molecular structures occurs via primary ions. The fragmentation patterns of cyano-based ionic liquids have been reported in a previous study [9,28,31,32,33,34]. We found outgassing derived from anions could not be detected, indicating that the anions remained on the worn surfaces, which is consistent with trends shown in the ToF-SIMS results.
Figure 8a–c shows the outgassing behavior of each cyano-based ionic liquid against AISI 52100. In cases of low friction coefficients ([EMIM][TCC] and [BMPL][TCB]), the amount of outgassing in the initial sliding period was large. This indicates that cyano-based ionic liquids with low friction coefficient reacted with the worn surface, resulting in cation decomposition. It has been suggested that this decomposition phenomenon occurs via catalytic decomposition on the nascent sliding surface where cations and anions interact with active sites causing the cation to undergo decomposition [28,35,36,37]. In cases of high friction coefficients ([EMIM][TCB]), where the amount of outgassing was smaller than other ionic liquids, there was lower reactivity on the worn surface. As a result, the anions left after cation decomposition adsorbed onto the worn surface. These results suggest that the decomposition of cations initiates the adsorption of anions. Figure 9a–c shows the outgassing behavior of each cyano-based ionic liquid against TiO2. Figure 10a–c shows the outgassing behavior of each cyano-based ionic liquid against ta-C. These results show the same trends as AISI 52100. In cases of low friction coefficients (TiO2 lubricated with [EMIM][TCC], ta-C lubricated with [EMIM][TCC] and [BMPL][TCB]), the amount of outgassing in the initial sliding period was large. In cases of high friction coefficients (TiO2 lubricated with [EMIM][TCB] and [BMPL][TCB], ta-C lubricated with [EMIM][TCB]), the amount of outgassing was small. These results suggest that the decomposition of cations encourages the adsorption of anions. [BMPL][TCB] shows the difference in behavior of TiO2 compared to the other sliding materials. We have shown that the catalytic activity of nascent surfaces varies with sliding material. The low activity of TiO2 compared with other sliding materials suggests that [BMPL][TCB] does not decompose because of sliding.
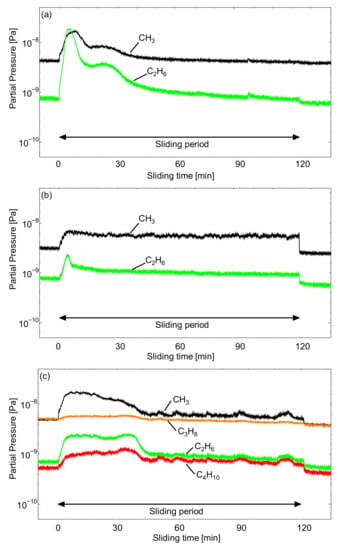
Figure 8.
Q-Mass analysis of the outgassing behavior at the surface of AISI 52100 of cyano-based ionic liquids (a) [EMIM][TCC], (b) [EMIM][[TCB], and (c) [BMPL][TCB].
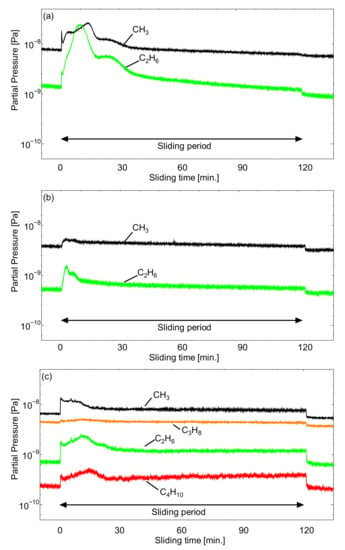
Figure 9.
Q-Mass analysis of the outgassing behavior at the surface of TiO2 of cyano-based ionic liquids (a) [EMIM][TCC], (b) [EMIM][[TCB], and (c) [BMPL][TCB].
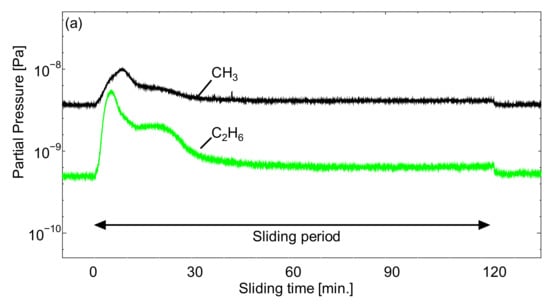
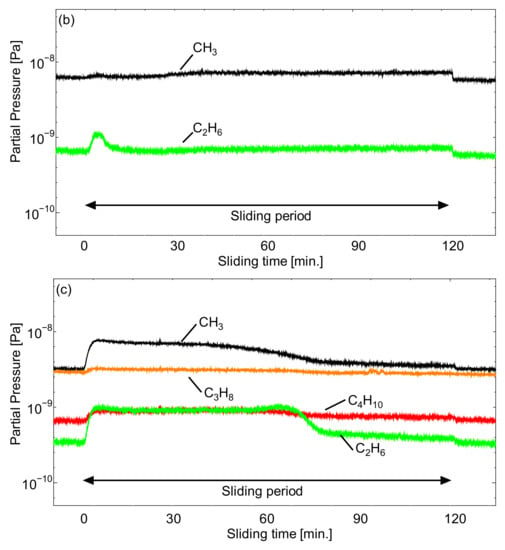
Figure 10.
Q-Mass analysis of the outgassing behavior at the surface of ta-C of cyano-based ionic liquids (a) [EMIM][TCC], (b) [EMIM][[TCB], and (c) [BMPL][TCB].
4. Conclusions
The friction coefficients of cyano-based ionic liquids against AISI 52100, TiO2, and ta-C were evaluated in vacuum condition. The substances present on the worn surface were identified using ToF-SIMS. The reactions that occur between the cyano-based ionic liquids with sliding materials were determined with Q-mass.
The friction coefficients of cyano-based ionic liquids was dependent on the composition of the sliding materials. TiO2 lubricated with [EMIM][TCC] and ta-C lubricated with [BMPL][TCB] exhibited low friction coefficients, smaller than that of fluorine-based ionic liquids. Through ToF-SIMS analysis, we have shown that in the case of low friction coefficients, anions adsorb onto the worn surface, suggesting that anion adsorption drives friction coefficients. Q-mass measurements show that in cases where there is high amount of anion adsorption, there is cation decomposition on the nascent surface. This suggests that low friction coefficients require decomposition of cations and adsorption of anions. The reactivity of nascent surface changes with the sliding material used due to variation in the catalytic activity of the nascent surfaces.
Author Contributions
S.K., S.W., S.S. and M.M. conceived the experiments and wrote this paper. S.K. performed the experiments.
Funding
This research was funded by JSPS fellows grant number 15J05958. And JSPS KAKENHI grant number JP16H02310 and JP26630041.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kondo, H.; Seto, J.; Ozawa, K.; Haga, S. Novel lubricants for magnetic thin film media. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 1989, 13, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricants. Chem. Commun. 2001, 21, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, T.; Dold, C.; Kailer, A. Complex fluids intribology to reduce friction: Mesogenic fluids, ionic liquids and ionic liquid crystals. Tribol. Int. 2013, 65, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, L. High-performance lubricant additives based on modified graphene oxide by ionic liquids. J. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 2015, 452, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Mu, L.; Shi, Y.; Dong, Y.; Feng, X.; Lu, X. High load capacity with ionic liquid-lubricated tribological system. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworokto, M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. 1992, 13, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvim, Y.; Mussmann, L.; Olivier, H. A novel class of versatile solvents for two phase catalysis: Hydrogenation, isomerization, and hydroformylation of alkenes catalyzed by rhodium complexed in liquid 1,3-dialkylimidazolium salts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 1996, 34, 2698–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Shinka, Y.; Masuko, M. Tribological characteristics of imidazolium-based room temperature ionic liquids under high vacuum. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 27, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, C.; Vos, N.D.; Stevens, C.V. Ionic liquid thermal stabilities: Decomposition mechanisms and analysis tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Yanagida, M.; Tanimoto, K.; Nomura, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Miyazaki, Y. Highly conductive room temperature molten salts based on small trimethylalkylammonium cations and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Chem. Lett. 2000, 8, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Ionic liquid lubricants: Designed chemistry for engineering applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jímenez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Carrion, F.J.; Martinez-Nicholas, G. Room temperature ionic liquids as lubricant additives in steel-aluminium contacts: Influence of sliding velocity, normal load and temperature. Wear 2006, 261, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Kamimura, H.; Mori, S. Thermo-oxidative stability of ionic liquids as lubricating fluid. J. Synth. Lubr. 2007, 24, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Howlett, P.C.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. A Review of Ionic Liquid Lubricants. Lubricants 2013, 1, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J. Tribological behavior of amorphous Cr coatings electrodeposited from Cr(III) baths under ionic liquid lubrication. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2007, 10, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viesca, J.-L.; Anand, M.; Blanco, D.; Fernández-González, A.; García, A.; Hadfield, M. Tribological Behaviour of PVD Coatings Lubricated with a FAP− Anion-Based Ionic Liquid Used as an Additive. Lubricants 2016, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Battez, A.; Ramos, D.; Blanco, D.; González, R.; Fernández-González, A.; Viesca, J.-L. Lubrication Properties of the Ionic Liquid Dodecyl-Methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viesca, J.-L.; Mallada, M.T.; Blanco, D.; Fernández-González, A.; Espina-Casado, J.; González, R.; Hernández Battez, A. Lubrication performance of an ammonium cation-based ionic liquid used as an additive in a polar oil. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yu, Q.; Meirong, C.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Investigation of the lubricity and antiwear behavior of guanidinium ionic liquids at high temperature. Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Yagi, S.; Koyama, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Lubricity and corrosiveness of ionic liquids for steel-on-steel sliding contacts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Kondo, Y.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Tribochemical reaction of ionic liquids under vacuum condition. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 54, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids are not always green: Hydrolysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Pardilla, J.; Espinosa, T.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ionic Liquids in Surface Protection. In Electrochemistry in Ionic Liquids; Torriero, A.A.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 533–561. ISBN 978-3-319-15131-1. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, I.; Inada, T.; Okada, Y. Tribological properties of halogen-free ionic liquids. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S.; Prakash, B. Lubrication mechanism of halogen-free ionic liquids. Tribol. Online 2017, 12, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okubo, H.; Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Sasaki, S. Tribological performance of halogen-free ionic liquids in steel-steel and DLC-DLC contacts. Tribol. Trans. 2018, 61, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Sato, K.; Watanabe, S.; Sasaki, S. Lubricating property of cyano-based ionic liquids against hard materials. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 5745–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Tadokoro, C.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Lubricating mechanism of cyano-based ionic liquids on nascent steel surface. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Sasaki, S. Tribological Properties of Cyano-Based Ionic Liquids under Different Environments. Tribol. Online 2018, 13, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Ichise, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Tadokoro, C.; Sasaki, S. Tribochemical reaction of ionic liquids as lubricants on steel sliding surfaces. In Surfactants in Tribology, 5th ed.; Biresaw, G., Mittal, K.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 1–18. ISBN 9781498734790. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, Y.; Koyama, T.; Sasaki, S. Tribological Properties of Ionic Liquids; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Siedlecka, E.M.; Czerwicka, M.; Stolte, S.; Stepnowski, P. Stability of ionic liquids in application conditions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2011, 12, 1974–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, H.; Ishimura, S.; Kumai, M. Thermal decomposition behaviors of imidazolium-type ionic liquids studied by pyrolysis-gas chromatography. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tim, J.W.; Katarina, M.J.; Kevin, J.F.; Douglas, R.M.; Janet, L.S. Thermal degradation of cyano containing ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 691–696. [Google Scholar]
- Kroon, M.C.; Buijs, W.; Peters, C.J.; Witkamp, G.-J. Quantum chemical aided prediction of the thermal decomposition mechanisms and temperatures of ionic liquids. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 465, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Tadokoro, C.; Sasaki, S. Effects of alkyl chain length of sulfate and phosphate anion-based ionic liquids on Tribochemical reactions. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Mori, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nanao, H. Study of tribochemical decomposition of ionic liquids on a nascent steel surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8965–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).