On the Growth Rate of Tribomaterial in Bovine Serum Lubricated Sliding Contacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
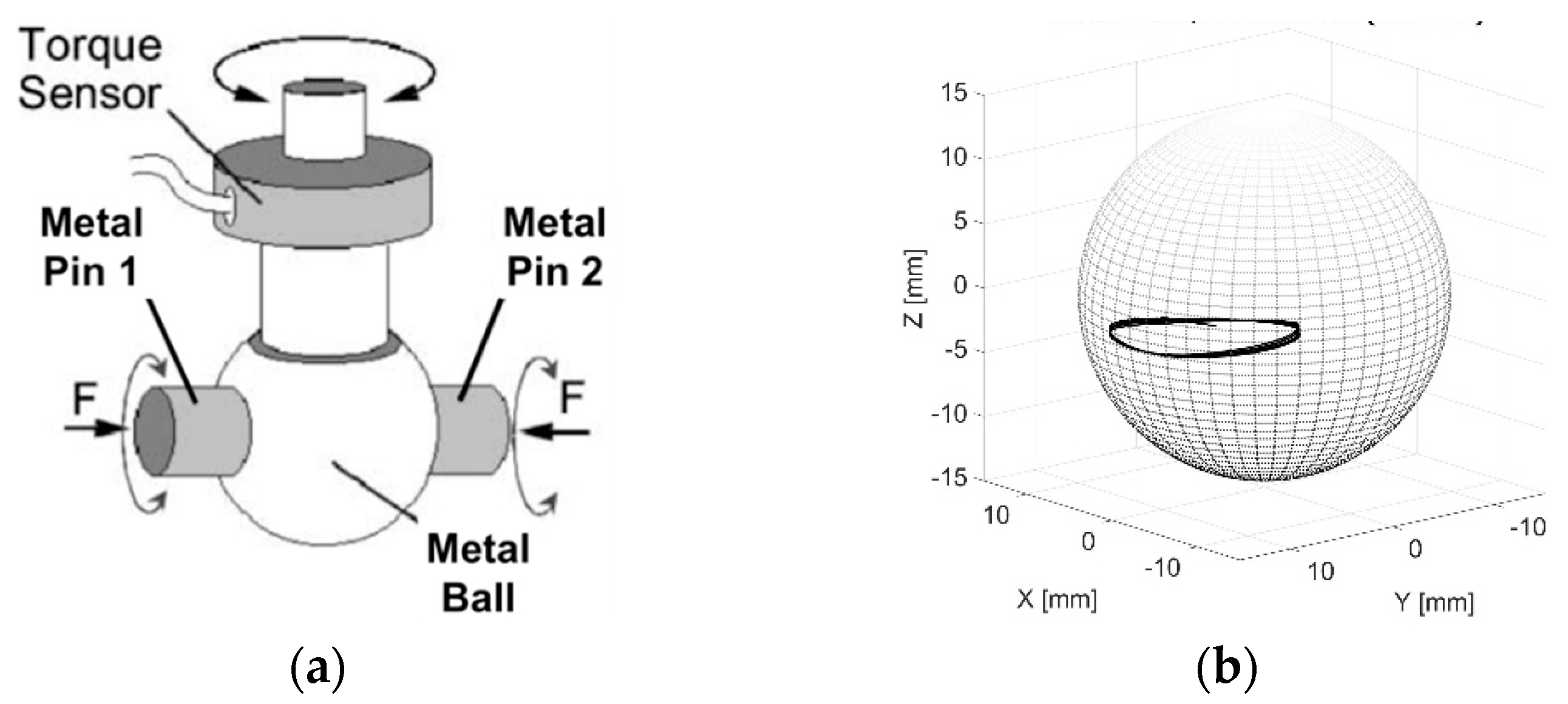
2.2. Laboratory Tribosystem and Analyses
2.3. Definition of Wear Rate
2.4. Modelling of Contact Conditions
2.4.1. Lubrication Regime
2.4.2. Dry Micro Contact Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Material Loss
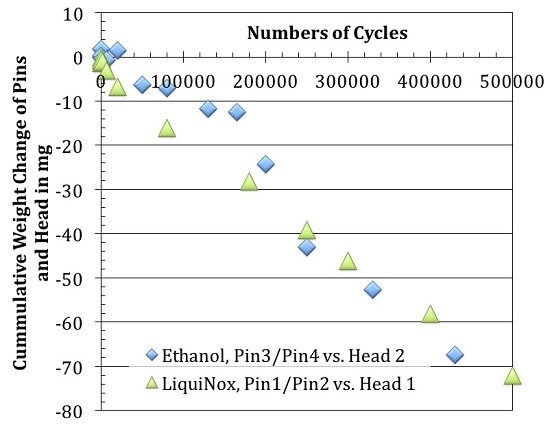
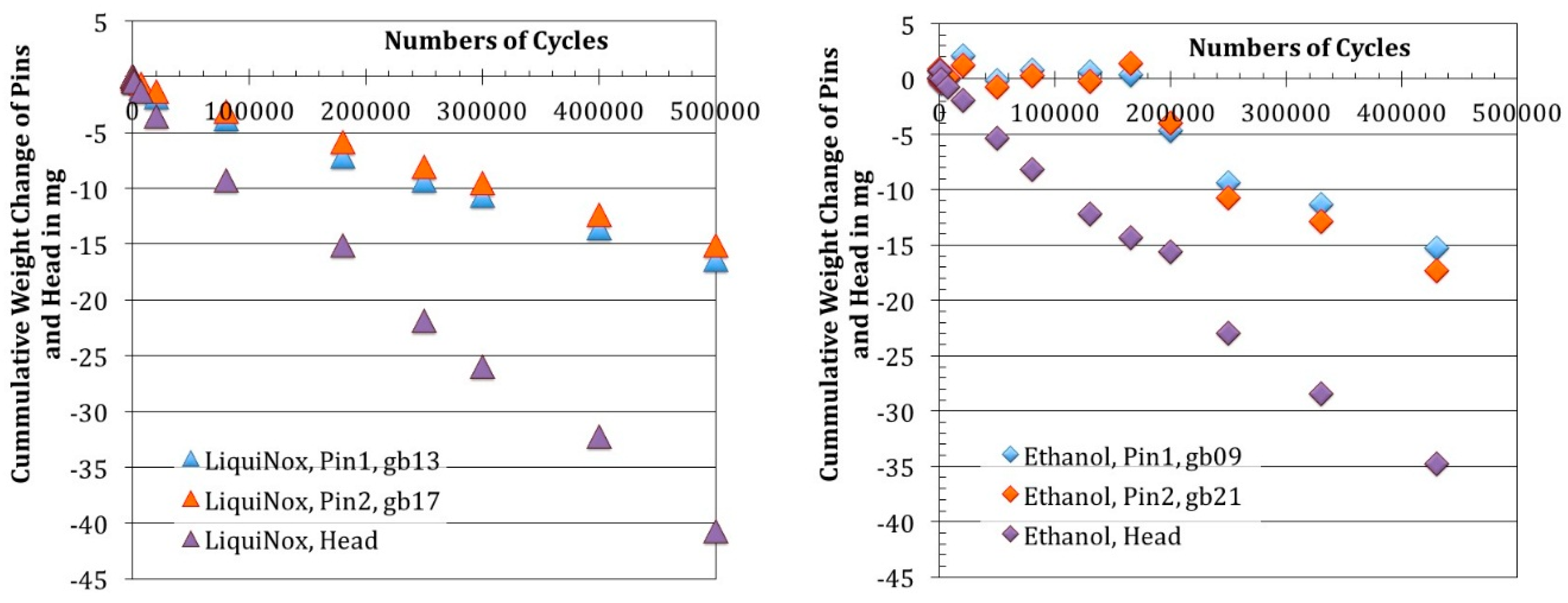
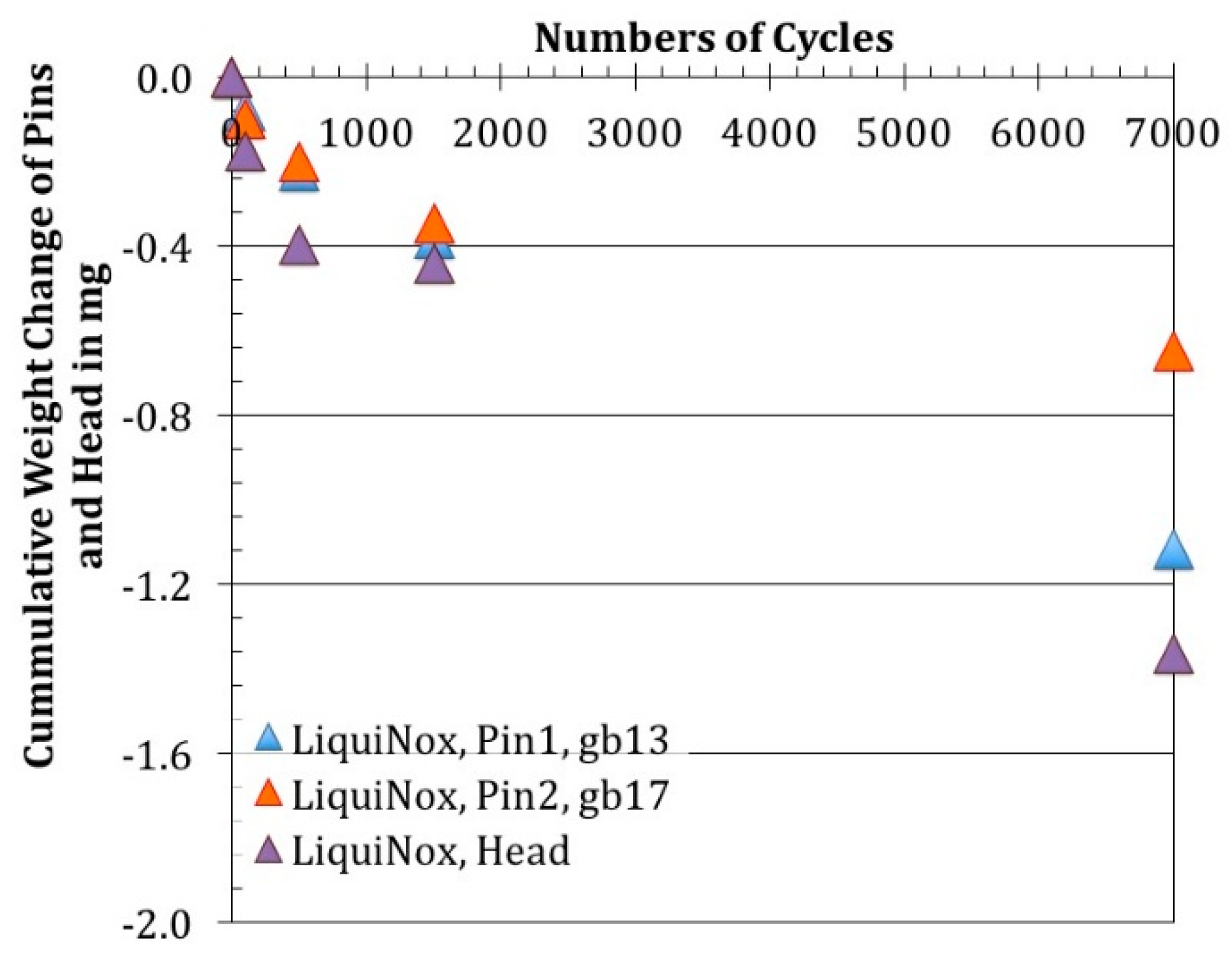
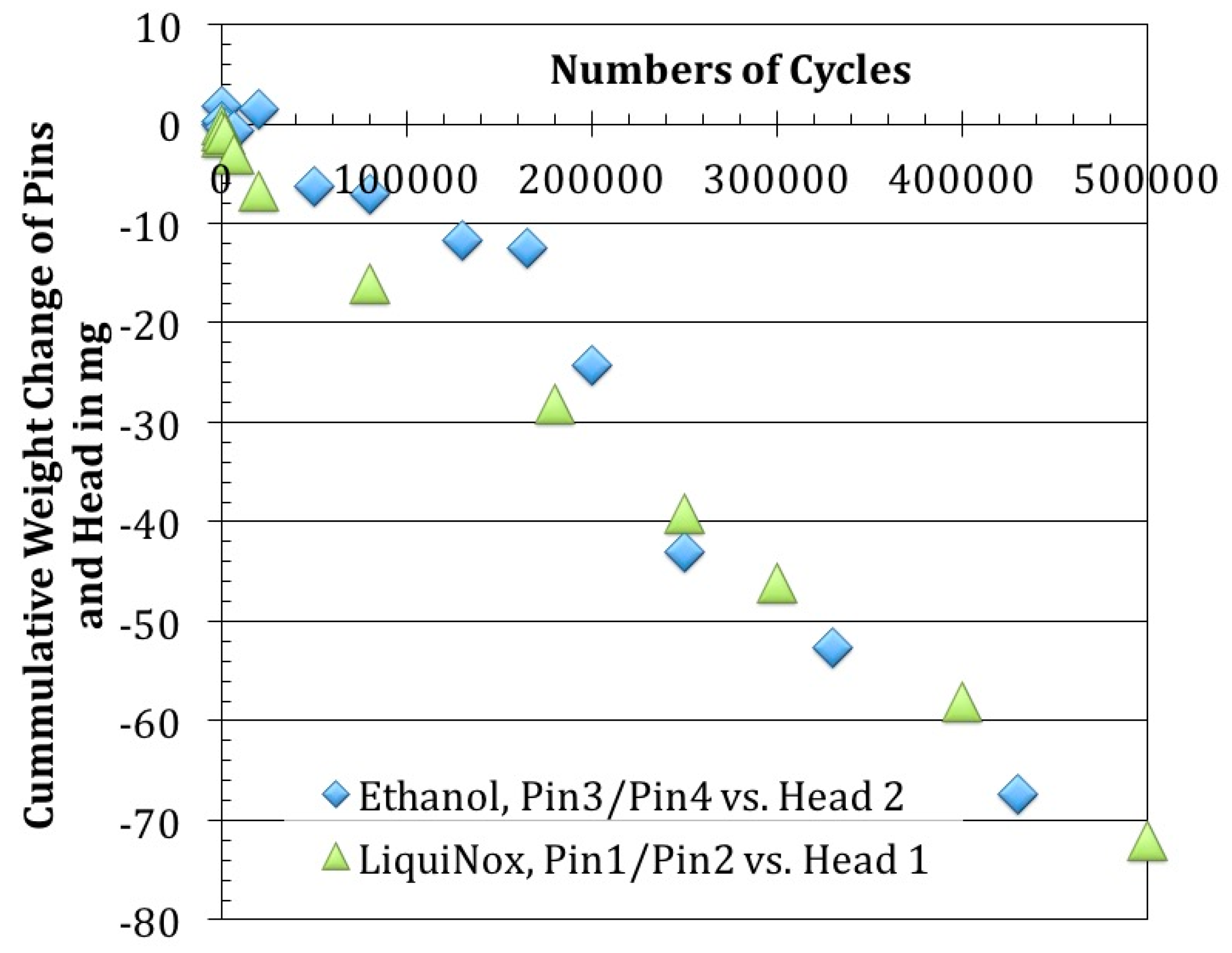
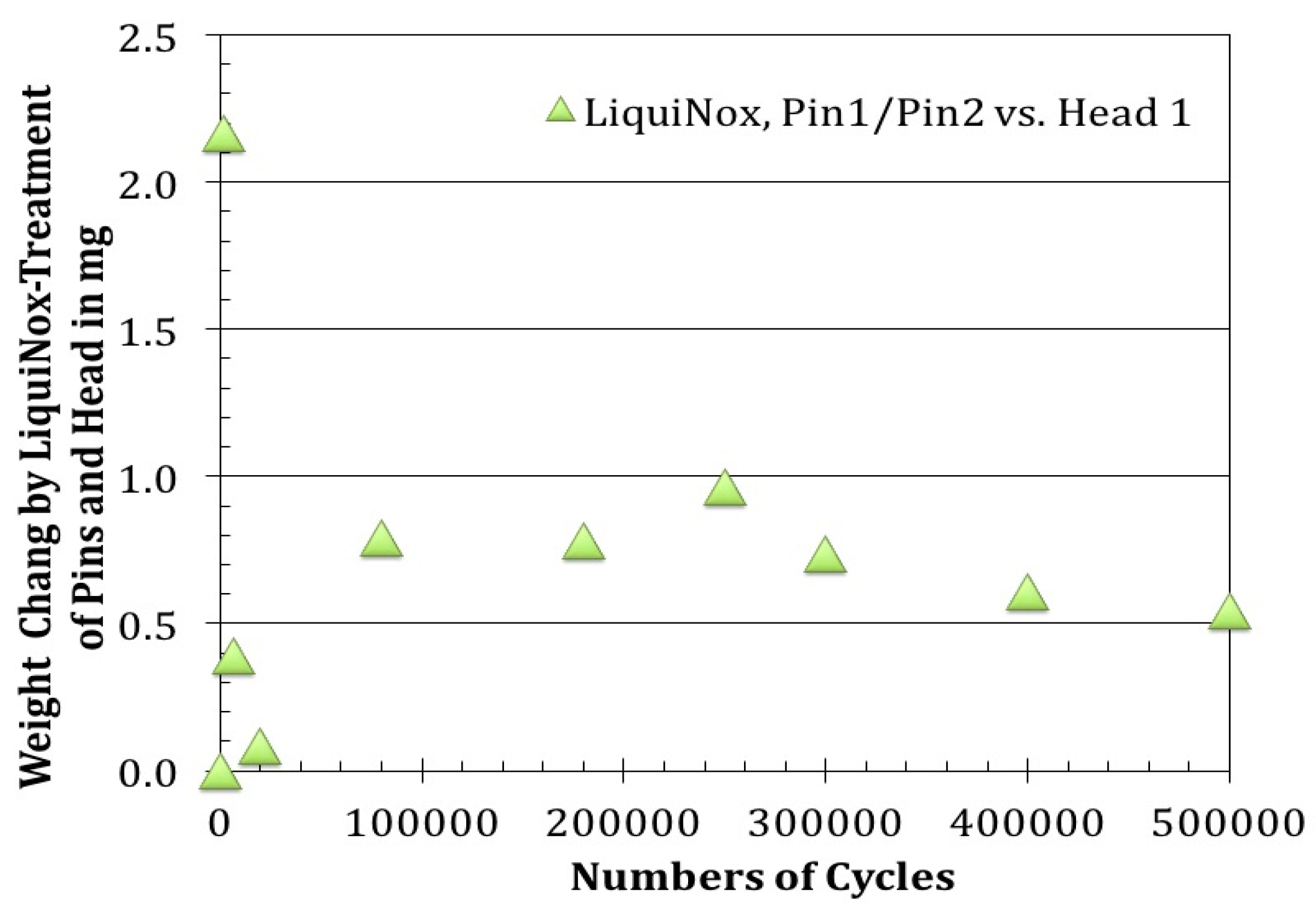
3.1.1. Weight Changes after Removal of Organic Surface Residues (LiquiNox Cleaning)
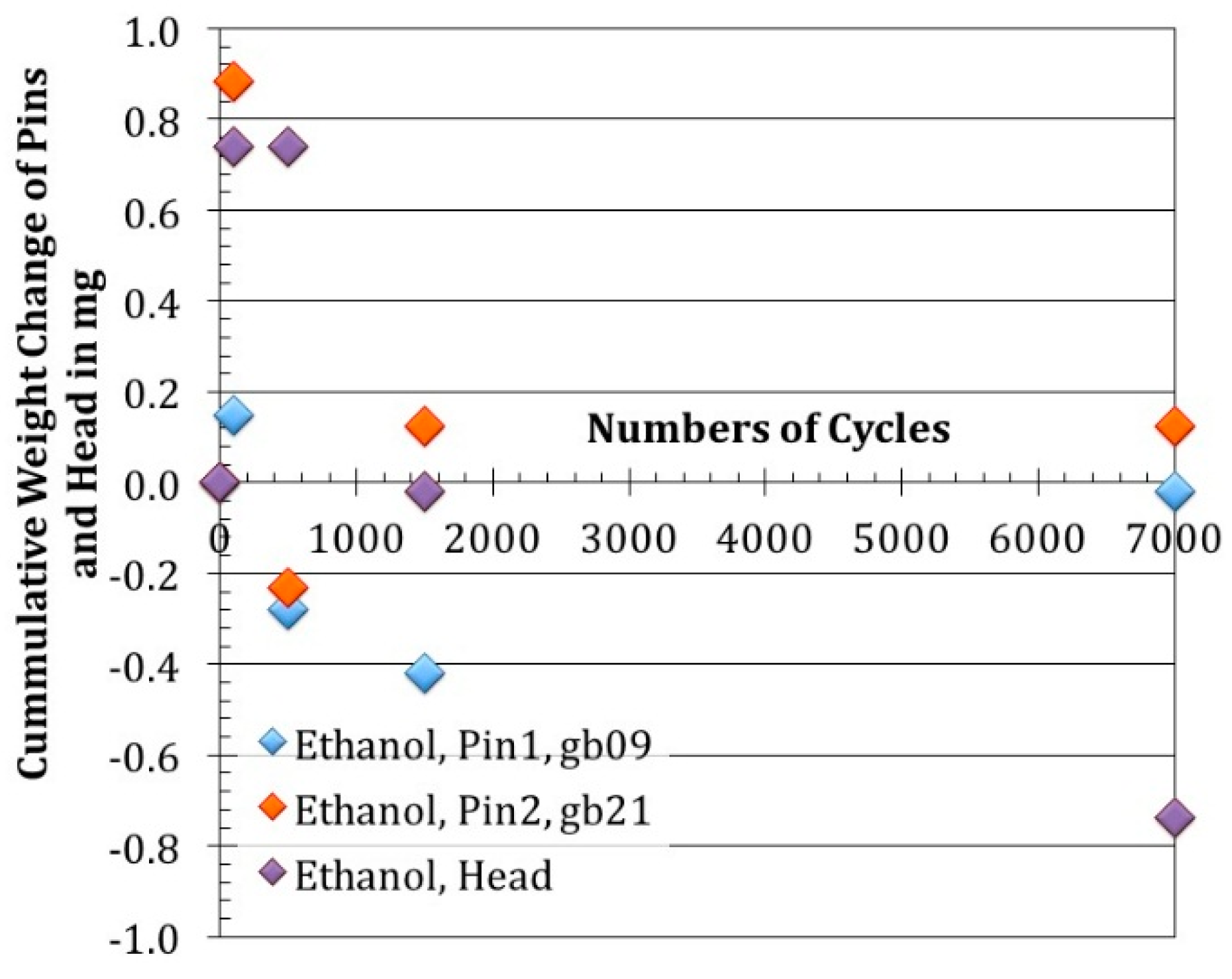
3.1.2. Weight Changes after Removal of Loose Debris (Ethanol Cleaning)
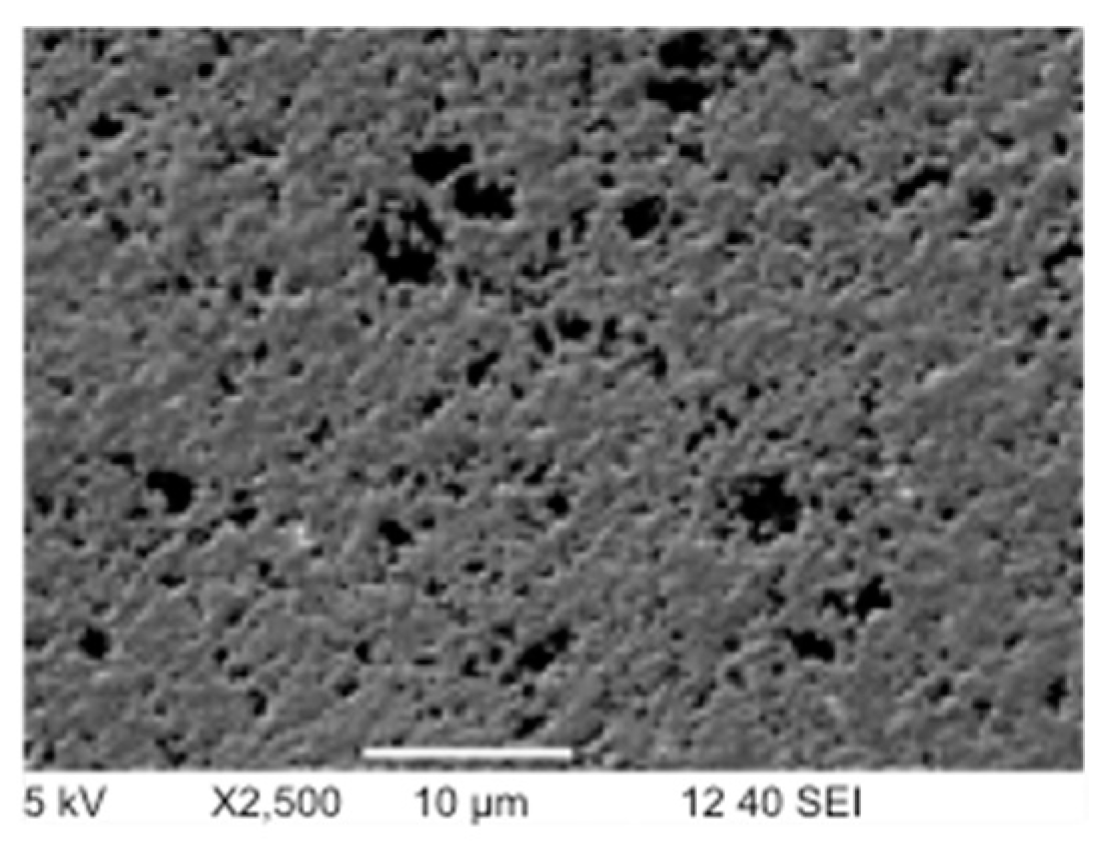
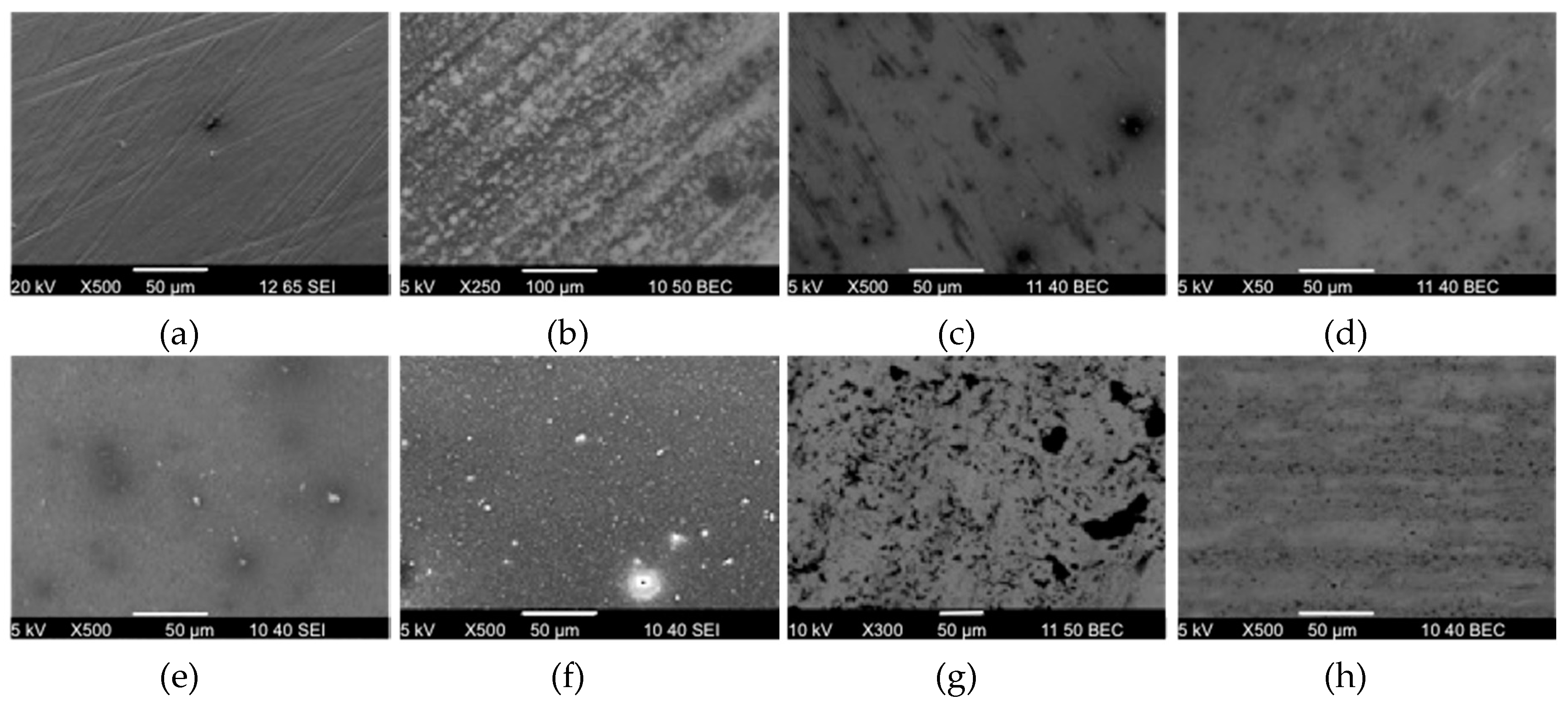
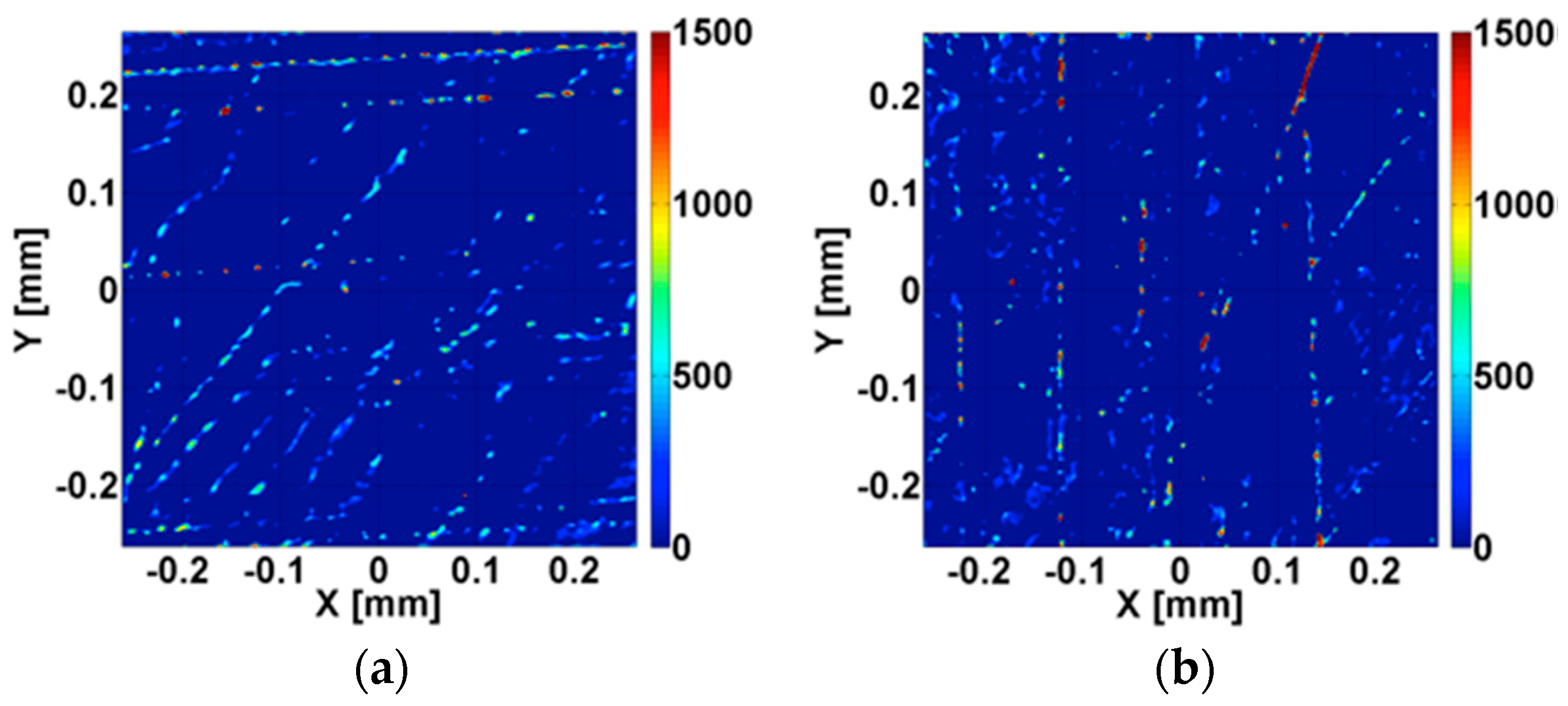
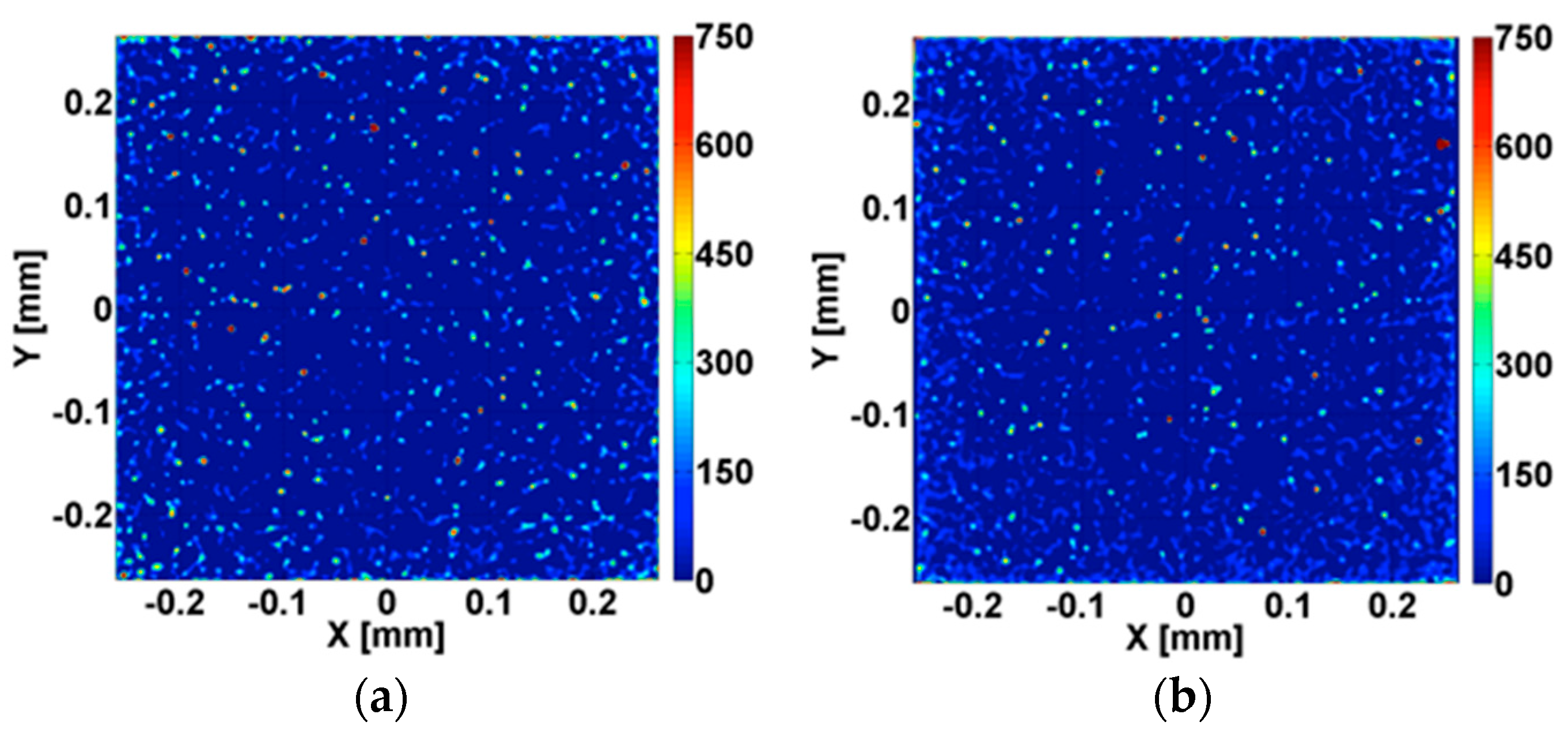
3.2. Wear Appearances
3.2.1. Wear Appearances after Ethanol- and after LiquiNox-Cleaning of Pin 1/Pin 2 vs. Head 1 (gb13/gb17 vs. 20258)
3.2.2. Wear Appearances after Ethanol-Cleaning of Pin 3/Pin 4 vs. Head 2 (gb09/gb21 vs. 20257)
3.3. Lubrication Regime
4. Discussion
4.1. Wear Mechanisms and Tribological Behavior
4.2. Contact Conditions and Tribological Behavior
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurtz, S.M.; Ong, K.L.; Lau, E.; Greenwald, A.S.; Bozic, K.J. Prevalence of Metal-on-Metal Bearings in the United States. In Metal-on-metal Total Hip Replacement Devices—stp1560; Kurtz, S.M., Greenwald, A.S., Mihalko, W.M., Lemons, J.E., Eds.; ASTM International: Wear Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bozic, K.J.; Kurtz, S.; Lau, E.; Ong, K.; Chiu, V.; Vail, T.P.; Rubash, H.E.; Berry, D.J. The epidemiology of bearing surface usage in total hip arthroplasty in the united states. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlock, M.M.; Bishop, N.; Zustin, J.; Hahn, M.; Ruther, W.; Amling, M. Modes of implant failure after hip resurfacing: Morphological and wear analysis of 267 retrieval specimens. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haan, R.; Pattyn, C.; Gill, H.S.; Murray, D.W.; Campbell, P.A.; De Smet, K. Correlation between inclination of the acetabular component and metal ion levels in metal-on-metal hip resurfacing replacement. J. Bone Joint Surg.Ser. B 2008, 90, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.J.; Muirhead-Allwood, S.; Porter, M.; Matthies, A.; Ilo, K.; Maggiore, P.; Underwood, R.; Cann, P.; Cobb, J.; Skinner, J.A. Which factors determine the wear rate of large-diameter metal-on-metal hip replacements? Multivariate analysis of two hundred and seventy-six components. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. Vol. 2013, 95, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannemann, F.; Hartmann, A.; Schmitt, J.; Lützner, J.; Seidler, A.; Campbell, P.; Delaunay, C.P.; Drexler, H.; Ettema, H.B.; García-Cimbrelo, E.; et al. European multidisciplinary consensus statement on the use and monitoring of metal-on-metal bearings for total hip replacement and hip resurfacing. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2013, 99, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, M.A.; Sprecher, C.; Hauert, R.; Täger, G.; Fischer, A. Tribochemical reaction on metal-on-metal hip joint bearings—A comparison between in vitro and in vivo results. Wear 2003, 255, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.A.; Mathew, M.T.; Laurent, M.P.; Nagelli, C.; Liao, Y.; Marks, L.D.; Pourzal, R.; Fischer, A.; Jacobs, J.J. Tribochemical Reactions in Metal-on-metal Hip Joints Influence Wear and Corrosion. In ASTM STP 1560 Symposium on Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Replacement Devices; Kurtz, S., Greenwald, A.S., Mihalko, W.M., Clemson, J.E., Eds.; ASTM: West Conshohocken. PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1560 STP, pp. 292–309. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Pourzal, R.; Wimmer, M.A.; Jacobs, J.J.; Fischer, A.; Marks, L.D. Graphitic tribological layers in metal-on-metal hip replacements. Science 2011, 334, 1687–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesketh, J.; Ward, M.; Dowson, D.; Neville, A. The composition of tribofilms produced on metal-on-metal hip bearings. Biomaterials 2013, 35, 2113–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourzal, R.; Martin, E.J.; Vajpayee, S.; Liao, Y.; Wimmer, M.A.; Shull, K.R. Investigation of the role of tribofilms in self-mating cocrmo systems utilizing a quartz crystal microtribometer. Tribol. Int. 2014, 72, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Sharp, J.; Rana, A.; Thompson, R.; Rainforth, W.M.; Cook, R.B. Sub-surface characterisation of tribological contact zone of metal hip prostheses. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büscher, R.; Täger, G.; Dudzinski, W.; Gleising, B.; Wimmer, M.A.; Fischer, A. Subsurface microstructure of metal-on-metal hip joints and its relationship to wear particle generation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 72, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourzal, R.; Catelas, I.; Theissmann, R.; Kaddick, C.; Fischer, A. Characterization of wear particles generated from cocrmo alloy under sliding wear conditions. Wear 2011, 271, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourzal, R. Possible Pathways of Particle Formation in Cocrmo Sliding Wear. Ph.D. Thesis, University Duisburg-Essen, Duisburg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Godet, M. The third-body approach: A mechanical view of wear. Wear 1984, 100, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, D.A. Transfer, mixing and associated chemical and mechanical processes during the sliding of ductile materials. Wear 2000, 245, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, D.A.; Karthikeyan, S. The evolution of tribomaterial during sliding: A brief introduction. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 39, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.A.; Nassutt, R.; Lampe, F.; Schneider, E.; Morlock, M.M. A New Screening Method Designed for Wear Analysis of Bearing Surfaces Used in Total Hip Arthroplasty. In ASTM STP 1346 Alternative Bearing Surfaces in Total Joint Replacement; Jacobs, J.J., Craig, T.L., Eds.; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1998; Volume 1346, pp. 30–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer, M.A.; Loos, J.; Heitkemper, M.; Fischer, A. The acting wear mechanisms on metal-on-metal hip joint bearings—in vitro results. Wear 2001, 250, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, D.; Jin, Z.M. Metal-on-metal hip joint tribology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H J. Eng. Med. 2006, 220, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallian, T.E. On competing failure modes in rolling contact. ASLE Trans. 1967, 10, 418–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seller, P.C.; Dowson, D.; Wright, V. The rheology of synovial fluid. Rheol. Acta 1971, 10, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, D.; McKinley, G.; Scott, R.D.; Spector, M. Rheology of joint fluid in total knee arthroplasty patients. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2002, 20, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Laurent, M.; Johnson, T.; Blanchard, C.; Crowninshield, R. The influences of lubricant and material on polymer/CoCr sliding friction. Wear 2003, 255, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Myant, C.W.; Underwood, R.; Cann, P.M.; Hart, A. Inlet protein aggregation: A new mechanism for lubricating film formation with model synovial fluids. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H J. Eng. Med. 2011, 225, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myant, C.; Underwood, R.; Fan, J.; Cann, P.M. Lubrication of metal-on-metal hip joints: The effect of protein content and load on film formation and wear. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 6, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myant, C.; Cann, P. In contact observation of model synovial fluid lubricating mechanisms. Tribol. Int. 2013, 63, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbka, M.; Nečas, D.; Hartl, M.; Křupka, I.; Urban, F.; Gallo, J. Visualization of lubricating films between artificial head and cup with respect to real geometry. Biotribology 2015, 1–2, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, I.; Spinu, S. A simplified model for pressure distribution in elastic—Perfectly plastic contact. Ann. Oradea Univ. 2010, XIX, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Willner, K. Fully coupled frictional contact using elastic halfspace theory. ASME J. Tribol. 2008, 130, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, I.A.; Keer, L.M. A numerical method for solving rough contact problems based on the multi-level multi-summation and conjugate gradient techniques. Wear 1999, 231, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. A versatile method of discrete convolution and FFT (DC-FFT) for contact analyses. Wear 2000, 243, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L. Determination of the sampling interval in surface roughness measurements with implications to engineering tribo-surface characterization and evaluation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. J. Eng. Tribol. 2009, 223, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickel, D.; Fischer, A. The alteration of micro-contact parameters during run-in and their effect on the specific dissipated friction power. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milocev, I.; Remckar, M. In vivo production of nanosized metal wear debris formed by tribochemical reaction as confirmed by high-resolution tem and xps analyses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 91, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zum Gahr, K.H. Microstructure and Wear of Materials; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, T.F.J. Review of oxidational wear. Part I: The origins of oxidational wear. Tribol. Int. 1983, 16, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, D.; Mischler, S.; Stemp, M. Electrochemical methods in tribocorrosion: A critical appraisal. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 3913–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, D.A.; Hammerberg, J.E. Mechanical Mixing and the Development of Nanocrystalline Material During the Sliding of Metals. In Advanced Materials in the 21st Century: The 1999 Julia R. Weertman Symposium; Chung, Y.W., Dunand, D.C., Liaw, P., Olson, G.B., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999; pp. 465–474. [Google Scholar]
- Mischler, S.; Debaud, S.; Landolt, D. Wear-accelerated corrosion of passive metals in tribocorrosion systems. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Wu, J.H.; Rigney, D.A. The Role of Vorticity in the Formation of Tribomaterial During Sliding. In MRS Fall Meeting, Symposium on Nanoscale Materials and Modeling-Relations Among Processing, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties; Anderson, P.M., Foecke, T., Misra, A., Rudd, R.E., Eds.; MRS: Warrendale, PA, USA; Boston, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 821, pp. 9.6.1–9.6.6. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram, N.K.; Guo, Y.; Chandrasekar, S. Mesoscale folding, instability, and disruption of laminar flow in metal surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Sundaram, N.; Mahato, A.; Compton, D.W.; Chandrasekar, S. Folding and transitions in plastic deformation in metal sliding and machining. In Proceedings of the 41st North American Manufacturing Research Conference 2013, NAMRC 2013, Madison, WI, USA, 10–14 June 2013; pp. 458–462.
- de Beer, S.; Müser, M.H. Viewpoint—Surface folds make tears and chips. Physics 2012, 5, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, N.; Romero, P.A.; Linsler, D.; Dienwiebel, M.; Stolz, U.; Moseler, M.; Gumbsch, P. Origins of folding instabilities on polycrystalline metal surfaces. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2014, 2, 064004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkirigawa, K.; Kato, K. An experimental and theoretical investigation of ploughing, cutting and wedge formation during abrasive wear. Tribol. Int. 1988, 21, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, D.A.; Glaeser, W.A. The significance of near surface microstructure in the wear process. Wear 1978, 46, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, D.A. Microstructural evolution during sliding. Procs. ASM Sympos. Wear Eng. Mater. 1998, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Büscher, R.; Fischer, A. The pathways of dynamic recrystallization in all-metal hip joints. Wear 2005, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourzal, R.; Theissmann, R.; Williams, S.; Gleising, B.; Fisher, J.; Fischer, A. Subsurface changes of a mom hip implant below different contact zones. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 2, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Weiss, S.; Wimmer, M.A. The tribological difference between biomedical steels and cocrmo-alloys. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 1, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gaytan, S.M.; Murr, L.E.; Martinez, E.; Martinez, J.L.; MacHado, B.I.; Ramirez, D.A.; Medina, F.; Collins, S.; Wicker, R.B. Comparison of microstructures and mechanical properties for solid and mesh cobalt-base alloy prototypes fabricated by electron beam melting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2010, 41, 3216–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.V.; Michael, J.R.; Majumdar, B.S.; Battaile, C.C.; Moody, N.R.; Cordill, M.J.; Jungk, J.M.; Bammann, D.J. Modeling of Friction-Induced Deformation and Microstructures; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA; Livermore, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bosman, R.; Schipper, D.J. Mild wear maps for boundary lubricated contacts. Wear 2012, 280–281, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Finnie, I. Correlations between two-body and three-body abrasion and erosion of metals. Wear 1981, 68, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A. Well-founded selection of materials for improved wear resistance. Wear 1996, 194, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.A.; Laurent, M.P.; Mathew, M.T.; Nagelli, C.; Liao, Y.; Marks, L.D.; Jacobs, J.J.; Fischer, A. The effect of contact load on cocrmo wear and the formation and retention of tribofilms. Wear 2015, 332–333, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myant, C.; Cann, P. On the matter of synovial fluid lubrication: Implications for metal-on-metal hip tribology. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 34, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, M.; Myant, C.; Cann, P.M.; Wong, J.S.S. Synovial fluid lubrication: The effect of protein interactions on adsorbed and lubricating films. Biotribology 2015, 1–2, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Radius in mm | Radial Clearance in µm | Max. Hertzian Contact Pressure in MPa | Ra in µm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol + LiquiNox Cleaning | Pin 1 (gb13) | 13.998 | 1 | °1 | 0.006 |
| Pin 2 (gb17) | 14.029 | 32 | 40 | 0.004 | |
| Head 1 (20258) | 13.997 | – | – | 0.005 | |
| Ethanol Cleaning | Pin 3 (gb09) | 14.025 | 32 | 40 | 0.005 |
| Pin 4 (gb21) | 14.055 | 62 | 60 | 0.004 | |
| Head 2 (20257) | 13.993 | – | – | 0.005 | |
| Main Elements | Body | Head |
| Counterbody | Concave Pins | |
| Interfacial Medium | Bovine Calf Serum | |
| Surrounding Medium and Temperature in °C | Bovine Calf Serum at 37 °C | |
| Tribological Stresses | Type of Loading | Multidirectional Sliding |
| Constant Normal Force in N | 750 | |
| Relative Velocity of the center of the Hertzian contact in mm/s (at 1 Hz) (s.a. Figure 2b) | 25 to 35 | |
| Lubricant | BCS Solution, pH = 7.6 | 588 mL Bovine Calf Serum (BCS), 3.7 g NaCl, 82.4 mg EDTA, 11.12 g Trisaminomethane, 412 mL deionized water (H2O) |
| Cycles | Ra Pin 3 in µm | Ra Head 2 in µm | λ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.021 | 0.092 | 0.0003–0.07 |
| 50,000 | 0.034 | 0.114 | 0.0004–0.09 |
| 430,000 | 0.093 | 0.248 | 0.0003–0.1 |
| Ra Pin 2 in µm | Ra Head 1 in µm | λ | |
| 100 | 0.011 | 0.059 | 0.0004–0.07 |
| 80,000 | 0.004 | 0.054 | 0.0002–0.03 |
| 500,000 | 0.008 | 0.083 | <0.003 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer, A.; Stickel, D.; Schoss, C.; Bosman, R.; Wimmer, M.A. On the Growth Rate of Tribomaterial in Bovine Serum Lubricated Sliding Contacts. Lubricants 2016, 4, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020021
Fischer A, Stickel D, Schoss C, Bosman R, Wimmer MA. On the Growth Rate of Tribomaterial in Bovine Serum Lubricated Sliding Contacts. Lubricants. 2016; 4(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer, Alfons, Daniel Stickel, Christian Schoss, Rob Bosman, and Markus A. Wimmer. 2016. "On the Growth Rate of Tribomaterial in Bovine Serum Lubricated Sliding Contacts" Lubricants 4, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020021
APA StyleFischer, A., Stickel, D., Schoss, C., Bosman, R., & Wimmer, M. A. (2016). On the Growth Rate of Tribomaterial in Bovine Serum Lubricated Sliding Contacts. Lubricants, 4(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020021