Abstract
Surface functionalization by topographic micro- and nano-structures in order to achieve unique properties, like super-hydrophobicity or ultrahigh light absorption, is a common strategy in nature. In this paper, direct laser interference patterning (DLIP) is presented as a promising tool allowing for the generation of such surface patterns on technical surfaces in order to mimic these biological surfaces and effects. Friction optimization and antibacterial effects by DLIP are exemplarily described. Topographic surface patterns on the micro- and nano-scale demonstrated a significant reduction in the coefficient of friction and bacterial adhesion. It was shown that in both cases, the control of the contact area between surfaces or between surface and bacteria is of utmost importance.
1. Introduction
Over millions of years of evolution, nature creates organisms with very unique properties. Natural phenomena, such as the self-cleaning effect of lotus leaves [1], the attachment mechanisms of geckos [2], the non-fogging and super-hydrophobic eyes of mosquitos [3], the super-hydrophobic legs of water striders [4], the colorful wings of butterflies [5,6] or the surprising mechanical properties of spider’s silk [7], provide very interesting solutions for specific problems. Based on these unique properties, many researchers around the world have sought to imitate/mimic these natural solutions (being called biomimetic) and transfer these to technological problems in order to improve properties, like wetting, friction, adhesion or optical properties [8,9].
Inspired by biological systems with an outstanding property, the key issue to mimic this system is to understand the connection between the material’s properties, the structure on different scales ranging from the nano- to the macro-scale, as well as the resulting macroscopic properties. Based on this understanding, a solution for specific technological problems can be designed [10]. Detailed studies of the aforementioned phenomena have clearly demonstrated that these properties cannot be only traced back to the intrinsic properties of the material. Special micro- and/or nanostructures, as well as hierarchical/multi-scale surfaces also contribute to a large extent to these effects [9,10,11]. For example, the self-cleaning and anti-adhesion effect of the lotus leaf can be explained by a combined chemical (epicuticular wax) and topographical effect (hierarchical surface structure) [12]. The excellent mechanical and adhesive properties of the gecko’s foot are based on a multi-scale surface ranging from the milli- to the nano-meter regime in combination with a rigid, as well as hydrophobic material (β-keratin) [9].
Moreover, the non-fogging and super-hydrophobic compound eyes of mosquitos can be explained by hierarchical surface structures, as demonstrated by Gao et al. [3]. The colors of the wings of a butterfly are caused by variations in the dielectric constant induced by specific microstructures [5,13]. In addition to these effects, tailored surface structures are a common and effective strategy in nature to prohibit the colonization of bacteria and biofilm formation in liquid media [14]. Known examples for this kind of behavior can be found in plant leaves, gecko feet, shark skin, insect wings, fish scales and spider silk, only to name a few [15]. Some of these structured surfaces not only prevent the attachment of bacteria, but also show an active bactericidal activity. The antibacterial effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria of the cicada wing for example was attributed exclusively to a specific nanotopography rather than chemical effects [16].
From this brief summary, it can be deduced that specific surface structures/patterns might be the key issue in order to create unique antimicrobial, adhesive or frictional properties. In the tribological community, many research groups around the world study the influence of laser-patterned surfaces on the frictional response. As far as dry friction is concerned, most of this work is related to the trapping of wear debris in order to avoid third body interaction and reducing the contact area (for example, lowered stiction in magnetic storage disks) [17,18,19,20,21]. Youquiang et al. investigated the influence of laser-patterned surfaces in frictional pairs Si3N4/TiC sliding against steel. They found a reduction in the coefficient of friction (COF) of 22.1% and a reduced wear rate of ~37% [22]. Moreover, Borghi et al. performed laser patterning on nitrided steel surfaces and could demonstrate a decrease in the COF of about 10% due to embedded wear particles [23]. Wang et al. studied the influence of groove spacings (produced by a femtosecond laser) between 15 and 300 µm on the frictional response in stainless steel parts. These authors related the different findings to the ploughing, adhesion and surface roughness contributions of the COF. Larger groove spacings lead to smaller area densities and, thus, to an increase in the real contact area, which results in an increased COF. Additionally, all laser-treated samples had lower wear rates in comparison to the unpatterned reference [24]. Gachot et al. investigated the influence of the pattern orientation for stainless steel surfaces that were treated by direct laser interference patterning (DLIP). The authors concluded that the role of alignment is of utmost importance. It turned out that slightly misaligned surfaces have a smaller COF than perfectly-oriented surfaces due to the reduced contact area [25,26]. Additionally, Rosenkranz et al. continued this work also for larger sliding cycles (up to 20,000 cycles) in order to study degradation effects of the patterned surfaces in more detail. They could show that the laser patterns still exist even after longer sliding times and that there is a general tendency for smaller COF’s in the case of perpendicular compared to parallel sliding to the line patterns due to a reduced contact area, which is in good agreement with He et al. [27,28]. Recently, Yu et al. published research work on pattern orientation effects for nano- and micro grooved surfaces. They defined a relative pattern size, which is simply the ratio between the groove width b and the radius R of the used tip. They could show that this ratio strongly determines the frictional behavior under parallel or perpendicular orientation to the grooves. It could be stated that for a ratio of b/R < 10−3, the COF is smaller for the perpendicular and higher for the parallel sliding direction along the grooves [29]. They finally concluded that the contributing factors to the friction anisotropy are mainly the contact area, the stiction length, the energy barrier and the surface contact stiffness in the respective directions.
Structured or hierarchical surfaces can be produced by lithography [30], replica molding combined with etching [31] or laser processing [32,33]. In this context, laser interference patterning is an interesting technique, which typically produces periodic surface patterns with feature sizes in the micron range. In previous publications, the authors could demonstrate that these surfaces can significantly tailor the antimicrobial and tribological properties of surfaces [25,27,34,35]. In order to shed some light on this interesting patterning technique, the theoretical background is summarized in Section 2.1. Afterwards, the influence of the produced surface patterns on the antimicrobial effect and frictional properties under dry sliding is elucidated.
2. Results and Discussion
In the first section of this chapter, the underlying physical principle of DLIP will be introduced and explained in detail. In the following sections, the effect of the produced patterns on the tribological and antimicrobial properties will be summarized.
2.1. Physical Principle of DLIP
The underlying physical principle of DLIP is interference, since at least two coherent laser beams are superimposed in order to create a defined intensity distribution, thus resulting in a certain surface topography. The superimposed sub-beams can be described as monochromatic, linearly-polarized plane waves. Consequently, the total electric field (Etot) is given by:
where Ej0 denotes the amplitude of each sub-beam, k the wave number, t the time, ω the angular frequency, r the direction of propagation and n the number of superimposed sub-beams. After the analysis of the scalar product of the vectors k and r, as well as under the assumption that ω is equal to zero, the total electric field can be written as:
In Equation (2), αj and βj represent the angles of the superimposed sub-beams with respect to the interference-plane.
The spatial intensity distribution Itot can be expressed by:
where c is the speed of light and ε0 the dielectric vacuum permittivity, respectively.
Based on the following assumptions:
the spatial intensity distribution for two-beam interference (n = 2) is given by:
which represents a two-dimensional surface pattern with a characteristic periodicity. This periodicity can be defined as:
where λ presents the wavelength of the used laser and θ is the angle between the interfering sub-beams.
Following the procedure, the resulting intensity distribution for two-, three- and four-beam interference can be calculated.
As can be seen in Figure 1, the result of two-beam interference is a sinusoidal intensity distribution, whereas three-, as well as four-beam interference end up in a dot-like intensity distribution.
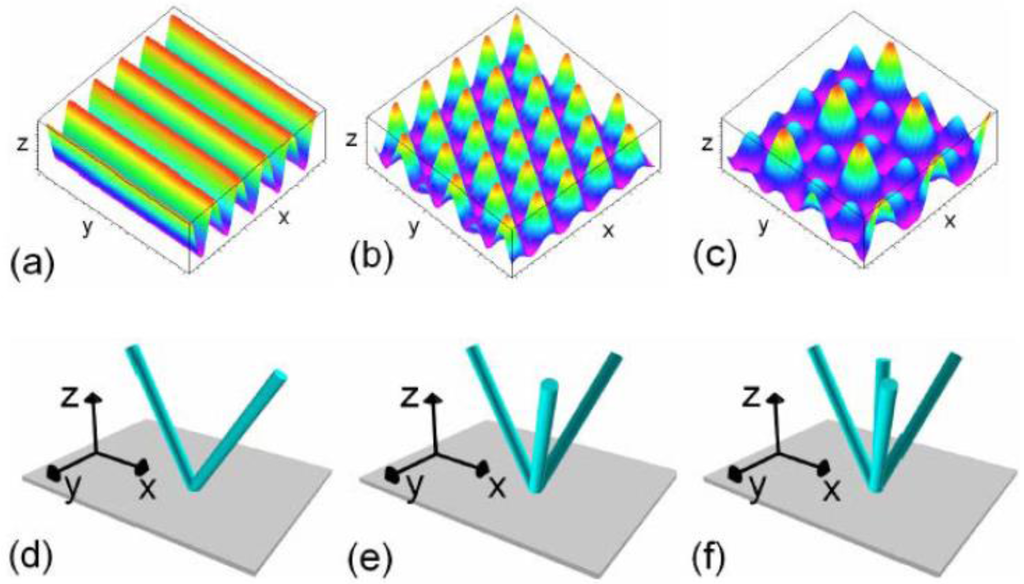
Figure 1.
(a,b,c) Calculated intensity distribution for two-, three- and four-beam interference; (d,e,f) the respective beam configurations for two-, three- and four-beam interference [36].
Figure 1.
(a,b,c) Calculated intensity distribution for two-, three- and four-beam interference; (d,e,f) the respective beam configurations for two-, three- and four-beam interference [36].
2.2. Surface Patterns for an Improved Tribological Performance
In the tribological community, it is well known that artificial surface patterns can significantly improve the tribological performance under dry and lubricated conditions. Under full fluid film conditions (hydrodynamic lubrication), these patterns can produce an additional hydrodynamic pressure, thus leading to an enhanced load-carrying capacity [37,38]. With regard to boundary and mixed lubrication, patterned surfaces can store oil in order to act as a secondary oil source or trap wear particles to reduce abrasive wear. This can lead to an increase in the oil film lifetime or to an improved wear behavior [39,40,41,42]. Regarding dry friction, surface patterns typically reduce the contact area and store wear particles, thus lowering the resulting coefficient of friction (COF) and avoiding stiction, as well as improving adhesion [21,43]. Furthermore, as already discussed in the Introduction and pointed out by Nosonovsky et al. and Gebeshuber, surface structures play a significant role in biological systems and, consequently, also in biotribology [20,44].
2.2.1. How to Achieve Quasi-Periodic Penrose-Like Surface Patterns
After the first patterning step (0°), the sample can be rotated by 90° and a second line-like pattern can be superimposed, thus resulting in a cross-like surface pattern. As already published by the authors in a previous manuscript, these patterns can be used to tailor the tribological performance, especially under mixed lubrication [35].
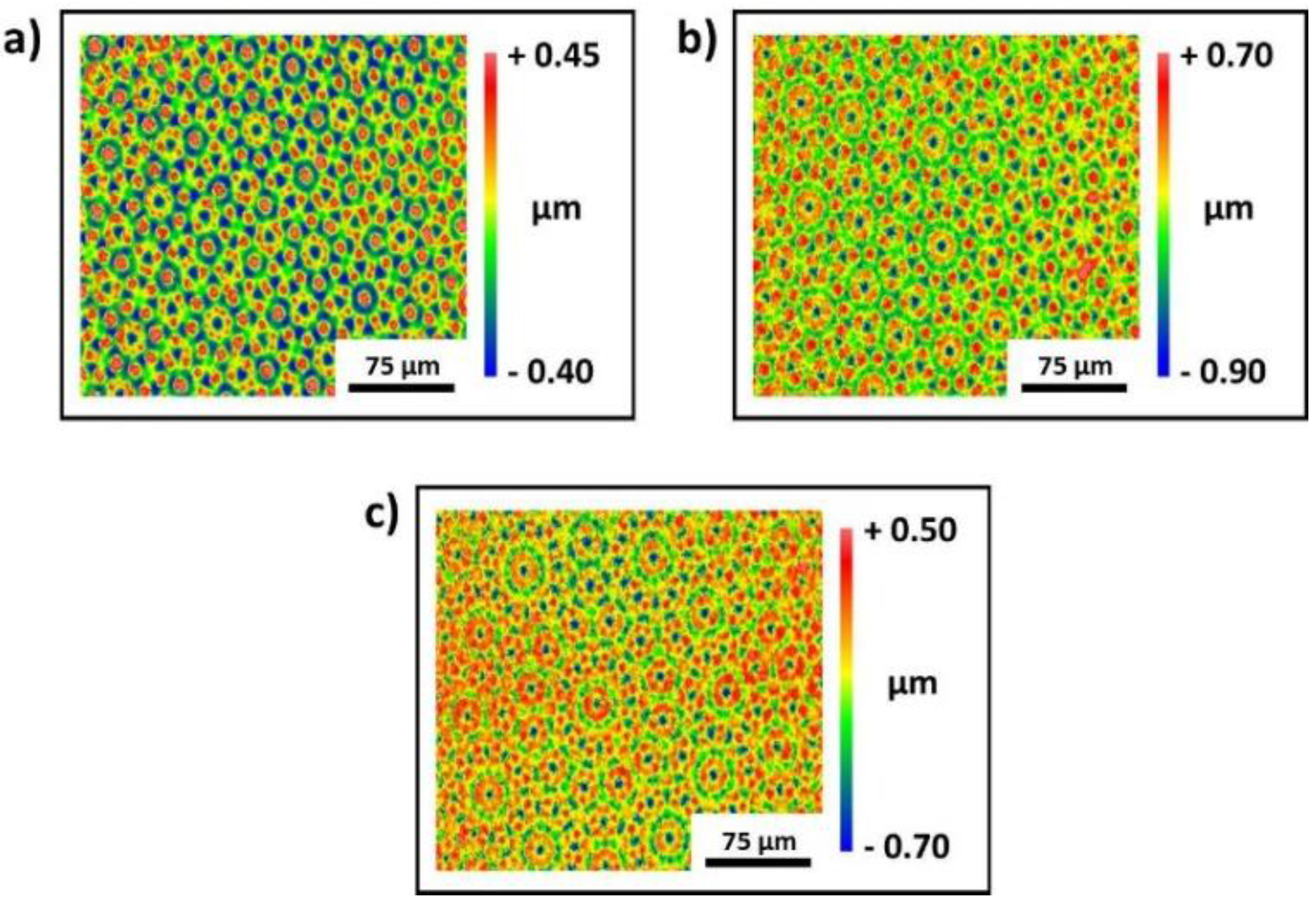
By means of a multi-step process, Penrose patterns with different symmetries can be produced by DLIP. As can be seen in Figure 2, quasi-periodic patterns typically have an 8-, 10- or 12-fold symmetry.
In order to create a quasi-periodic Penrose pattern with an eight-fold symmetry (Figure 2a), it is necessary to superimpose four line-like surface patterns with different rotation angles (0°, 45°, 90° and 135°). Penrose patterns with 10- or 12-fold symmetry can be produced by a five- or six-step process with a rotation angle of 36° or 30°, respectively. It is worth mentioning that these patterns do not have a three-dimensional translation symmetry, which makes them very interesting for tribological applications under dry friction due to reduced geometrical interlocking [45,46].
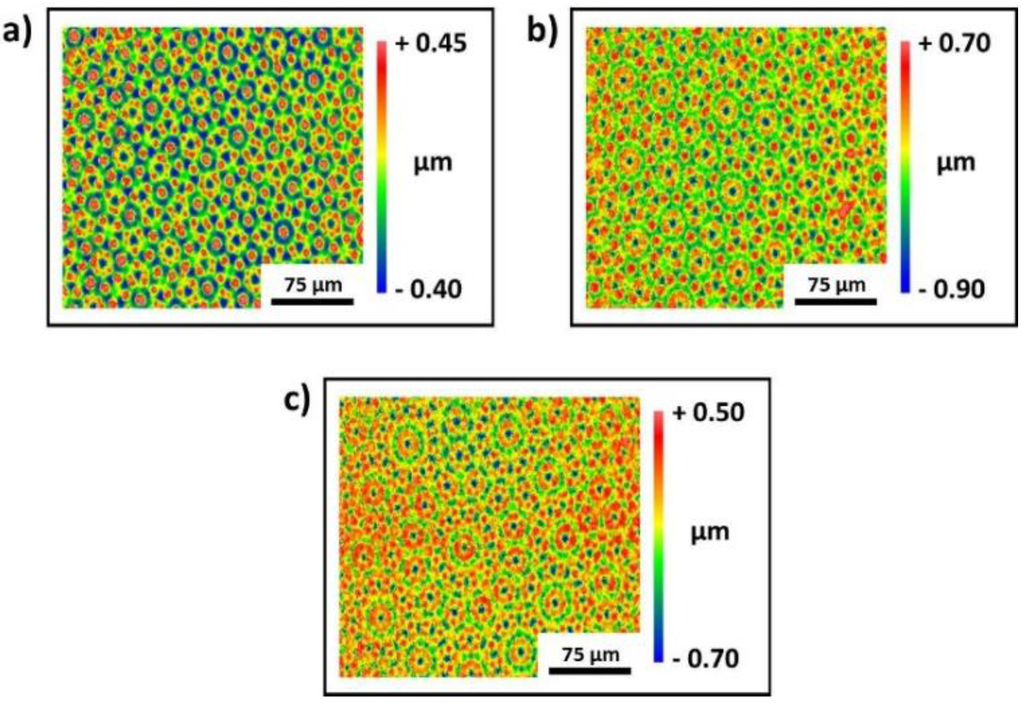
Figure 2.
Two-dimensional images of quasi-periodic Penrose-like surface patterns with 8-fold (a), 10-fold (b) and 12-fold (c) symmetry measured by white light interferometry (WLI).
Figure 2.
Two-dimensional images of quasi-periodic Penrose-like surface patterns with 8-fold (a), 10-fold (b) and 12-fold (c) symmetry measured by white light interferometry (WLI).
2.2.2. Effects under Dry Friction
In order to study the tribological performance under dry sliding conditions, line-like surface patterns with different periodicities (2, 5, 7 and 8 µm) were fabricated by DLIP. After the laser patterning, the produced surface patterns were analyzed by WLI (Figure 3) in order to investigate the shape of the produced surface patterns.
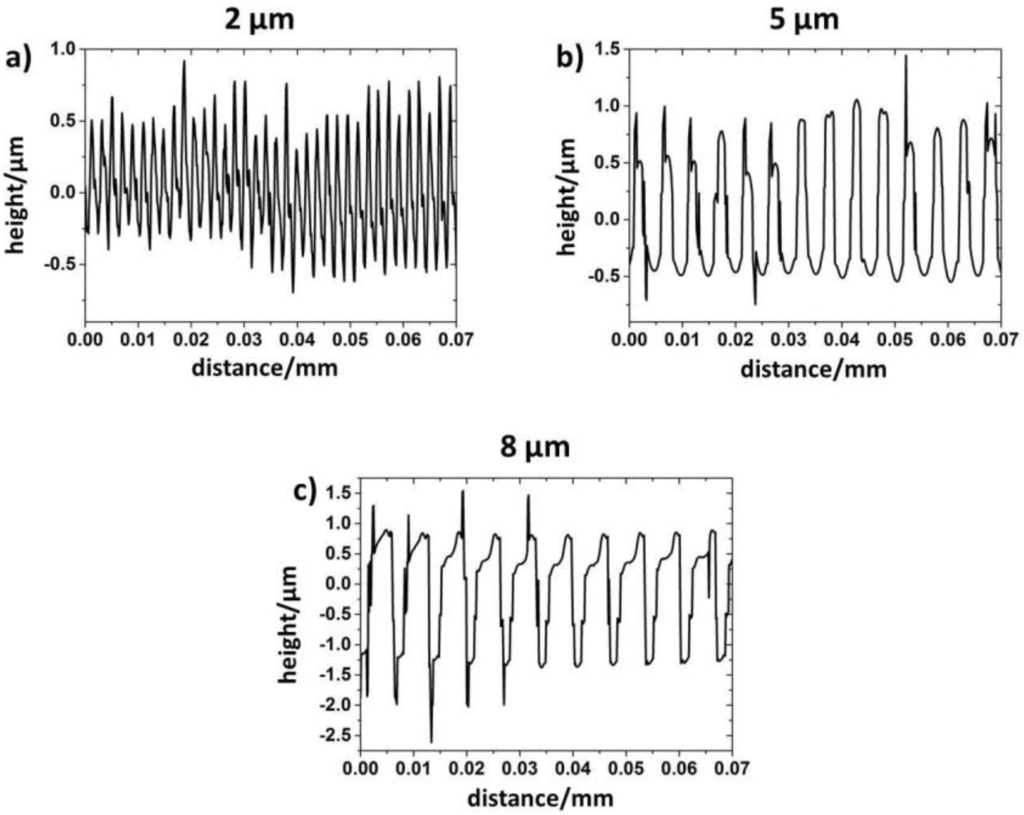
Figure 3.
Cross-sectional profiles of laser-patterned line-like surfaces having a periodicity of 2 (a), 5 (b) and 8 µm (c) measured by WLI.
Figure 3.
Cross-sectional profiles of laser-patterned line-like surfaces having a periodicity of 2 (a), 5 (b) and 8 µm (c) measured by WLI.
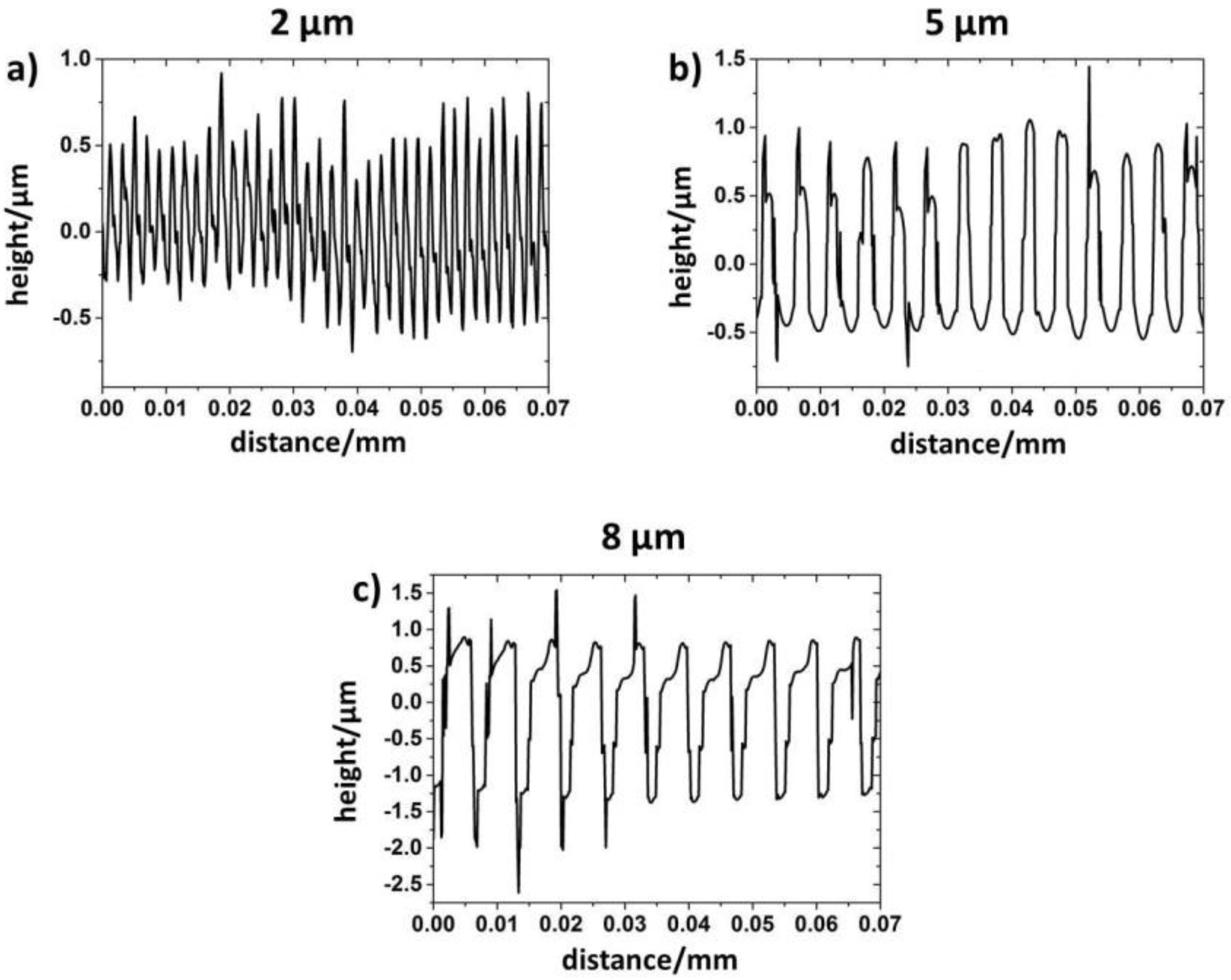
As can be seen in Figure 3, clear differences in the surface profiles can be observed as a function of the adjusted periodicity. In the case of periodicity of 2 µm (Figure 3a), a more spiky surface profile with sharp asperities can be found. An increase in the pattern periodicity leads to the formation of a more plateau-like surface profile (Figure 3b,c). In order to precisely describe the produced surface patterns, selected roughness parameters, such as the Swedish height H, the root-mean-square roughness Rq and the skewness Rsk, were measured by WLI (Table 1).

Table 1.
Topographic parameters of laser-patterned aluminum samples measured by WLI. The Swedish height H is a well-suited parameter to indicate the structural depth of the laser-patterned surfaces.
| Sample | H/µm | Rq/nm | Rsk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polished reference | 0.030 ± 0.005 | 20 ± 3 | −1.44 ± 0.33 |
| Line pattern P = 2 µm | 1.58 ± 0.27 | 547 ± 56 | 0.73 ± 0.16 |
| Line pattern P = 5 µm | 1.88 ± 0.34 | 579 ± 116 | 0.65 ± 0.13 |
| Line pattern P = 7 µm | 2.98 ± 0.37 | 936 ± 89 | 0.25 ± 0.09 |
| Line pattern P = 8 µm | 2.87 ± 0.36 | 978 ± 76 | 0.53 ± 0.06 |
As can be seen in Table 1, the topographic analysis demonstrates no significant differences. The Swedish height H and Rq increase with increasing periodicity. Similar findings have already been published by Lasagni et al. [33]. The skewness Rsk for the polished reference sample is negative, indicating a good load-bearing capability being typical for polished surfaces. In contrast to that, the skewness value of all laser-treated specimens is positive, which can be traced back to spikier surface profiles.
The experiments under dry friction were performed as a function of the relative alignment of the line-like surface pattern with respect to the sliding direction of the tribological counter body. Two different alignments, namely “para” (parallel) and “perp” (perpendicular), were tested. In the case of the para-orientation (Figure 4a), the sliding direction of the ball is aligned parallel to the line-like pattern, whereas “perp” indicates a sliding direction being perpendicular to the surface pattern (Figure 4b). Furthermore, a small normal load of 100 mN was used in order to avoid any wear features.
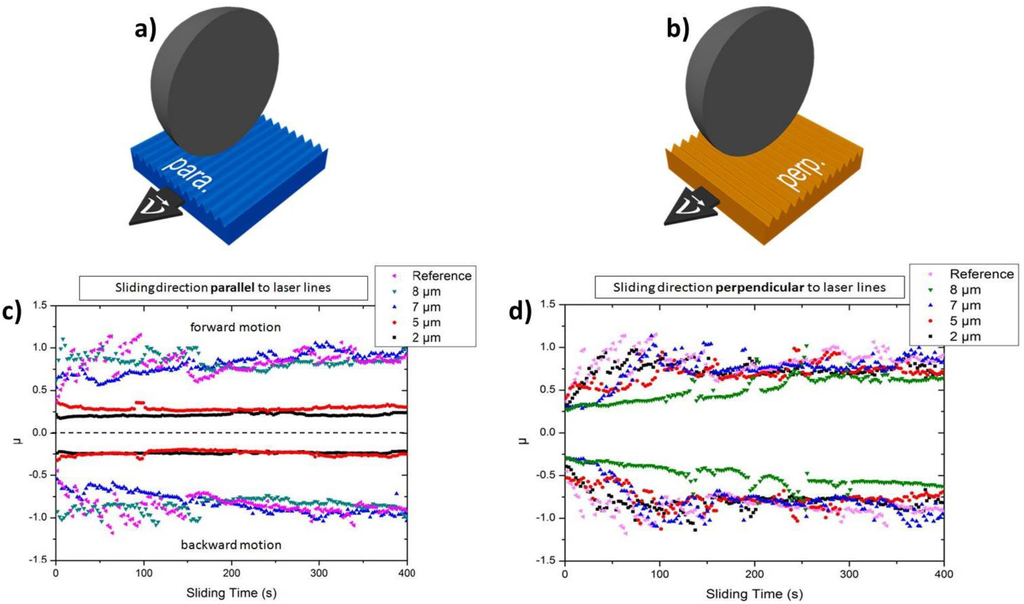
Figure 4.
(a,b) Schematic illustrations of the parallel (para-) and perpendicular (perp-) alignment; (c,d) temporal evolution of the coefficient of friction (COF) of the polished reference and line-like surface patterns with different periodicity for the para- and perp-alignment.
Figure 4.
(a,b) Schematic illustrations of the parallel (para-) and perpendicular (perp-) alignment; (c,d) temporal evolution of the coefficient of friction (COF) of the polished reference and line-like surface patterns with different periodicity for the para- and perp-alignment.
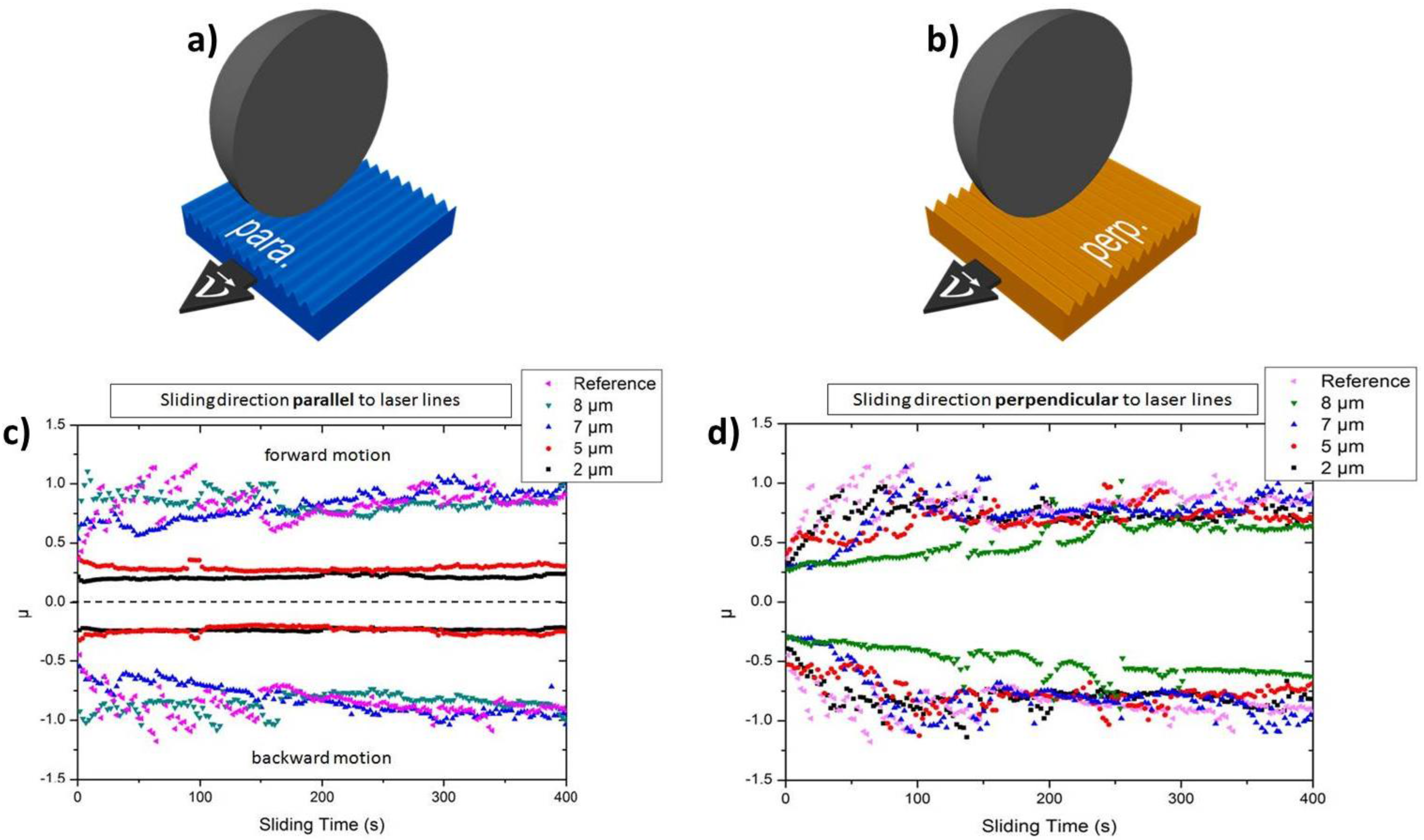
As can be observed in Figure 4c, the COF of the polished reference and of the line-like pattern with a periodicity of 7 and 8 µm fluctuates around one. In contrast to that, the COF of the surface patterns having a periodicity of 2 and 5 µm is about 0.25 and stable over time. Therefore, it can be concluded that the line-like surface pattern can lead to a significant friction reduction by a factor of roughly four under dry conditions. On the contrary, the effect of the periodicity is not very pronounced for the perp-alignment, as can be seen in Figure 4d. It is worth mentioning that the COF of the reference is in the same range compared to the para-configuration. Furthermore, all samples roughly start from the same initial COF. From the literature, it is well known that the frictional response for para- and perp-alignments can be quite different [28,47,48]. Recently, Yu et al. were able to demonstrate that the contact area, the stiction length, the energy barrier and the contact stiffness are the most influencing factors for the frictional behavior with respect to these two extreme cases [29]. The increased corrugation of the surface topography in the perpendicular direction obviously plays a role in terms of COF fluctuation. It is also worth mentioning that, after the tribological experiments, both the substrate and the counter body were studied by light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and WLI. However, no pronounced wear features have been observed. Furthermore, no generated transfer layer could be detected by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
In order to describe this behavior from the theoretical point of view, half-space simulations based on a multi-level and multi-integration approach were performed on laser-patterned line-like surfaces in collaboration with the tribology group of the Imperial College in London. As can be seen in Figure 5, the contact between a smooth sphere and a patterned aluminum plane is analyzed as a function of the periodicity.
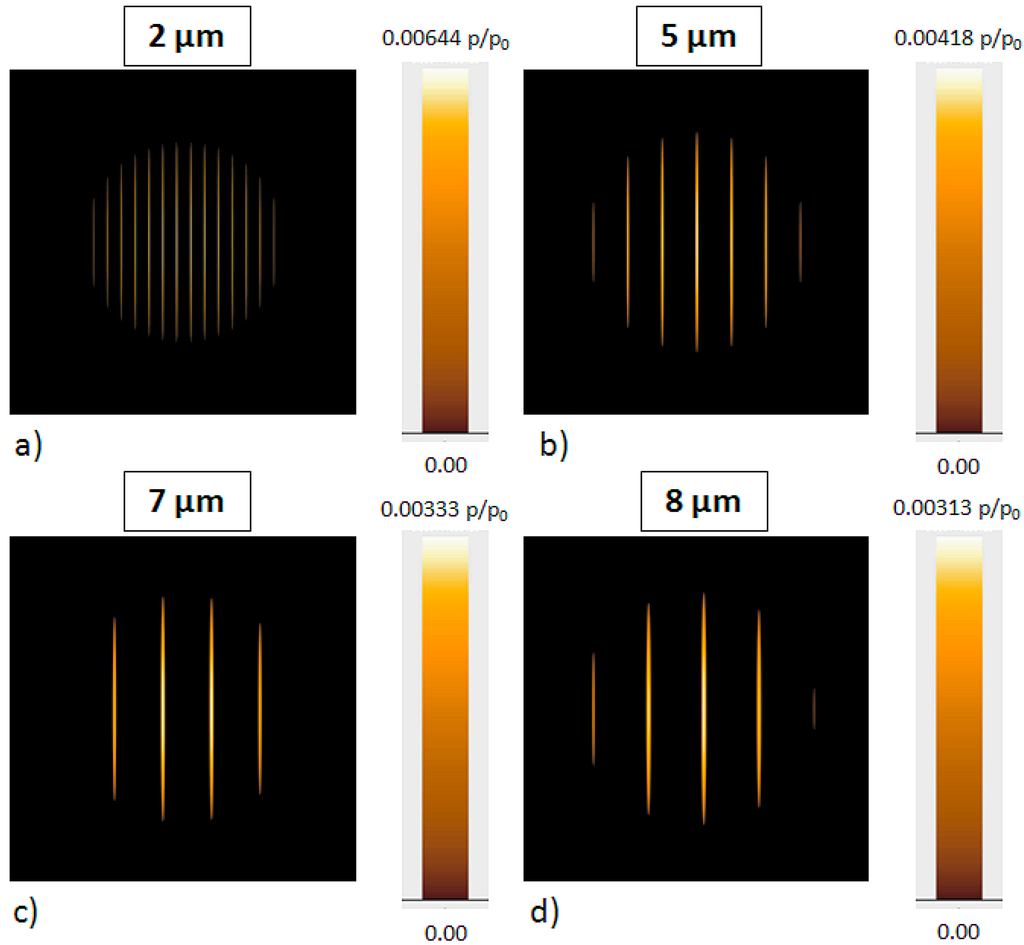
Figure 5.
Simulated contact pressure distributions for line-line surface patterns with 2 (a), 5 (b), 7 (c) and 8 µm periodicity (d) based on a multi-level and multi-integration approach using a finite-element mesh with 2048 × 2048 nodes. The color code highlights the normalized contact pressure. The normalization is done using the Hertzian contact pressure p0.
Figure 5.
Simulated contact pressure distributions for line-line surface patterns with 2 (a), 5 (b), 7 (c) and 8 µm periodicity (d) based on a multi-level and multi-integration approach using a finite-element mesh with 2048 × 2048 nodes. The color code highlights the normalized contact pressure. The normalization is done using the Hertzian contact pressure p0.
By means of the numerical simulation, the acting contact pressure, the number of asperities in contact and the contact area can be evaluated. The results of the numerical simulation are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of the numerical results for the laser-patterned surface with different periodicities.
| Periodicity/µm | Number of Asperities | Contact Area/µm2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 14 | 29.48 |
| 5 | 7 | 44.38 |
| 7 | 4 | 50.58 |
| 8 | 5 | 55.81 |
The numerical results clearly demonstrate that the number of asperities in contact increases from five (line-like pattern with periodicity of 8 µm) to 14 (line-like pattern with periodicity of 2 µm) with decreasing periodicity. However, the contact area shows exactly the opposite trend, which correlates very well with the experimental findings of the para-alignment.
2.3. Antibacterial Surface Structures for Implant Materials
Infections originating in bacterial biofilms pose a major problem, as bacteria generally tend to colonize any available surface rather than staying in the planktonic state [49]. In the human body, bacterial biofilms preferably develop on inert surfaces or dead tissue, which makes implant materials a primary target for bacterial attachment after insertion [50]. It is therefore imperative to provide some kind of antimicrobial properties to implant surfaces, which should at least last for a few weeks after surgery. In addition to release-based strategies [51], intrinsic antibacterial properties are also added to implant surfaces by bio-inspired topographical design [52].
One straight-forward approach in materials design is aiming at surface structures that actively destroy bacteria. Ivanova et al. generated so-called black silicon surfaces, on which Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as endospores were efficiently killed [53]. The black color originates from a needle-like nanostructure of the silicon surface, on which bacteria were impaled upon attachment. Similar effects were observed on titanium coatings, which were sputtered under glancing incidence angle (GLAD) by Sengstock et al. [54]. The specific sputtering setup used also induced a needle-like nanoroughness, which was attributed with a supposedly mechanical, bactericidal effect. In this study, Gram-positive bacteria with a thicker cell wall were found to be more resistant than Gram-negative cells against the proposed killing mechanisms [54]. Both studies claim to be inspired by the topography-related antimicrobial properties of insect wings [16]. A possible model describing the destructive interaction of topographical insect wing structures with bacteria has been proposed by Pogodin et al. According to their observations, nanopillars on the cicada wing with a diameter of 60 nm, a height of 200 nm and a spacing of approximately 170 nm may stretch the bacteria envelope until it tears. They propose the structural size of those pillars and the bacterial cell wall properties as governing parameters for the observed, purely physic-mechanical killing mechanism.
Besides an active bactericidal effect, bacteria repelling surfaces may as well be considered antibacterial. The relation between topographical surface design and bacterial adhesion is all but trivial and is subject of numerous studies [55,56]. A general consensus seems to be that structures on the nanoscale, thus smaller than bacteria, tend to inhibit bacterial adhesion, and topography features larger than bacteria may favor adhesion [55,56]. Although to this end, some studies rebutting this rule can also be found [14,57]. Patterned surfaces with features of about the same size as bacteria may cause different effects depending on the specific interaction between single bacteria and topography [56,58]. In order to apply anti-adhesive and in this sense antibacterial properties to implant materials, surface functionalization presumably needs to aim towards structures of a few microns in size or smaller. Following this approach, Levandowska et al. generated nanotube structures on titanium by an electrochemical surface treatment, which resulted in a decrease in bacterial attachment and at the same time enhanced fibroblast adhesion [59].
As laser interference surface structuring allows for surface patterns in the micron and sub-micron range, it is an ideal tool to investigate and tailor the bacterial attachment on surfaces. In spite of this potential, only very few studies using laser surface patterning to influence bacterial adhesion and antibacterial properties were conducted so far. Wagner et al. investigated the biofilm formation on line-like laser patterned steel surfaces [60]. They suspect that the 5-µm laser pattern periodicity used was too large compared to bacterial size for anti-adhesive effects to take place. Valle et al. observed that a regular laser pattern (periodicity of 5 µm) may enhance bacterial adhesion in contrast to a contact-inhibiting, irregular, non-laser surface pattern on polystyrene [61]. So far, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, the effect of the laser pattern of exactly the bacterial size has not been investigated nor has a clear mechanism of action been defined.
2.3.1. DLIP to Investigate Bacterial Killing
In previous experiments, DLIP surfaces have been used to clarify the role of bacterial adhesion to a metallic surface during the so-called contact killing of bacteria [34]. Bacterial adhesion experiments performed on metallic surfaces (see Figure 6a) proved that about 90% percent of bacteria adhere to the sample surface already after 90 min (dotted line), which becomes apparent by the plateau values after 90 min. Standardized antimicrobial testing procedures, according to the Environmental Protection Agency of the U.S., should at least last for 2 h [62]. Bacterial adhesion to surfaces therefore plays a major role during must studies on antibacterial surface effects.
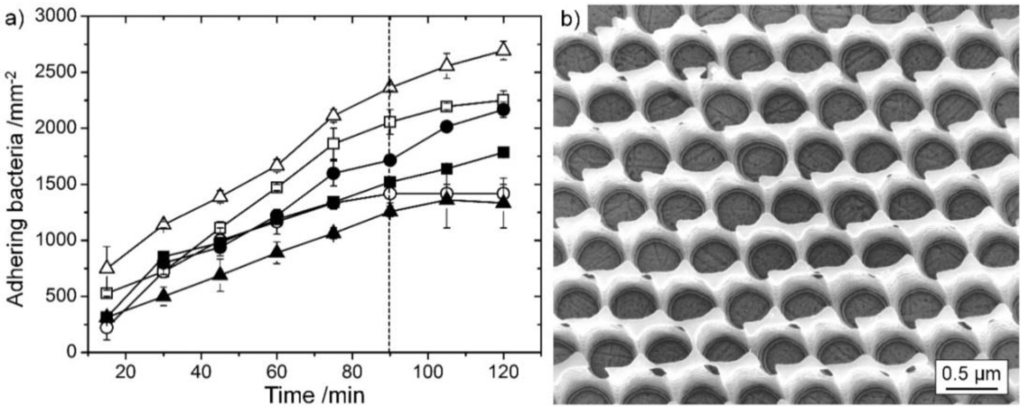
Figure 6.
(a) Bacterial adhesion per surface determined on several polished stainless steel (filled symbols) and brass (empty symbols) samples; (b) contact-inhibiting, inert arrays generated by direct laser interference patterning (DLIP) on polished copper [34].
Figure 6.
(a) Bacterial adhesion per surface determined on several polished stainless steel (filled symbols) and brass (empty symbols) samples; (b) contact-inhibiting, inert arrays generated by direct laser interference patterning (DLIP) on polished copper [34].
In order to shine light on the actual role of bacterial adhesion for actively antimicrobial effects, inhibitory array structures have been generated by DLIP on metallic copper (see Figure 6b) [34]. In this experiment, DLIP patterns were tailored in a way (lateral periodicity of 700 nm) that bacteria adhering to the surface could not get in contact with the metallic copper. It became clear that the direct contact to a metallic surface promotes contact killing.
These experiments emphasize the role of bacterial attachment on intrinsically antibacterial materials, as well as for passively antibacterial, anti-adhesive surface concepts.
2.3.2. DLIP Induces Antibacterial Surface Effects
On this behalf, we investigated on a possible antibacterial surface functionalization by DLIP in terms of lowered bacterial adhesion. For this purpose, line-like topographical surface structures with a periodicity of about 2 µm were generated on polymer and homogeneously covered with a gold layer to provide an inert metallic surface, as shown in Figure 7a. Initial bacterial adhesion on this surface was measured for 2 h by microscopic means and compared to a flat gold reference surface.
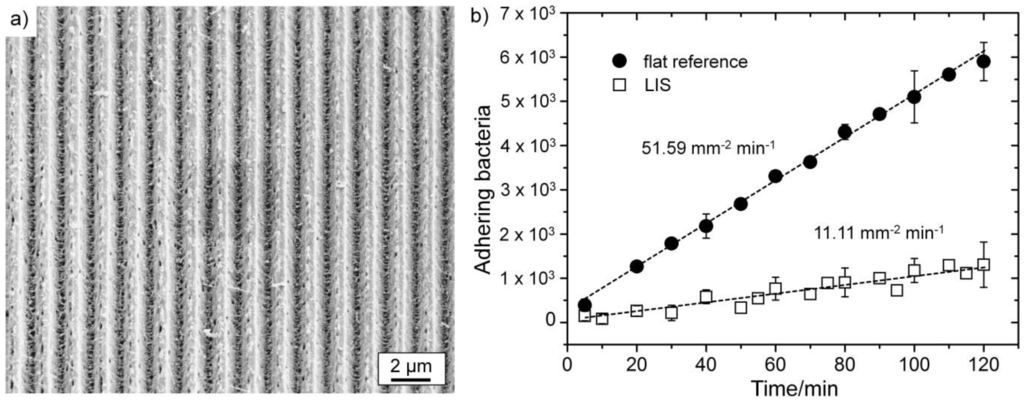
Figure 7.
(a) Laser interference-patterned, gold-coated surface; (b) reduced bacterial adhesion on DLIP surface compared to a flat reference surface.
Figure 7.
(a) Laser interference-patterned, gold-coated surface; (b) reduced bacterial adhesion on DLIP surface compared to a flat reference surface.
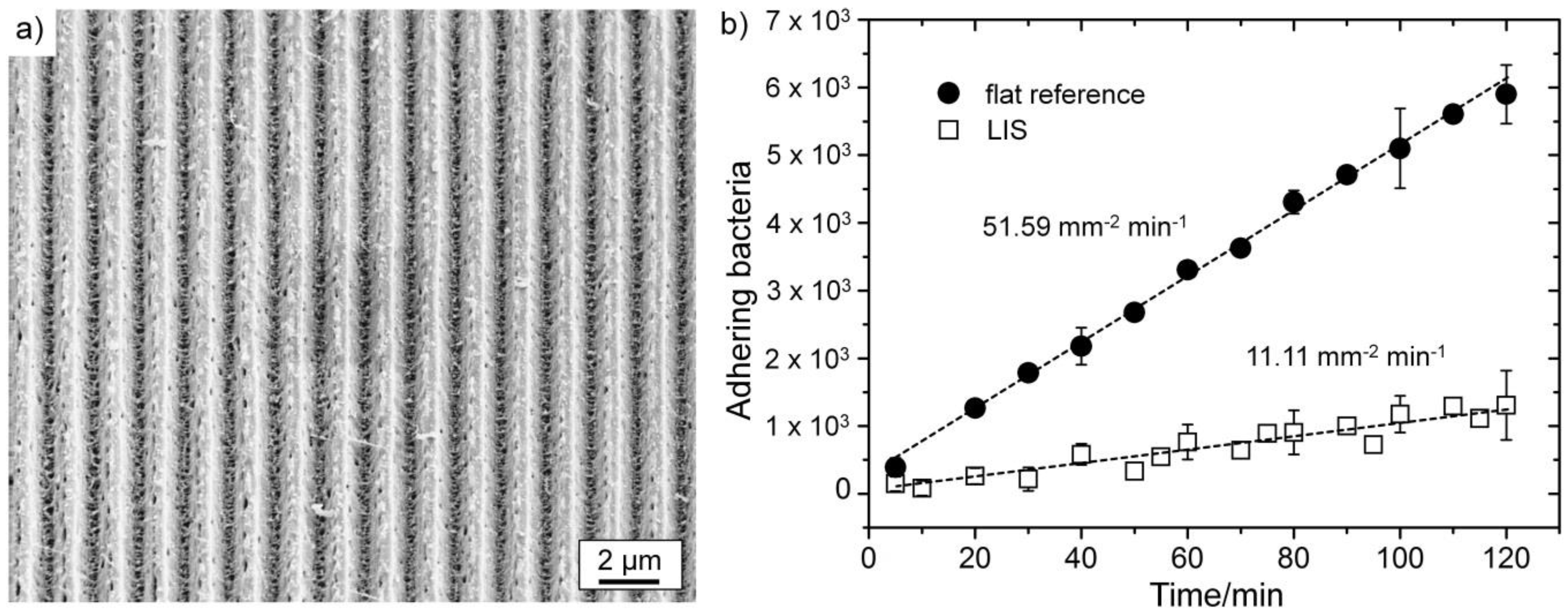
Both surfaces showed linearly increasing bacterial adhesion over time. The number of attaching bacteria on the laser-patterned surface was reduced about 80% compared to the non-treated surface, which is clearly depicted by the calculated adhesion rates of 51.59 and 11.11 mm−2·min−1 (see Figure 7b). The applied laser surface patterning thus resulted in a clear antibacterial effect.
Whitehead et al. proposed in theory that, with a decreasing number of contact points for bacteria to a structured or rough surface, the bacterial adhesion may also decrease [63]. The generated laser interference patterns were specifically designed in a way that the valleys of the structures are minimally smaller than the applied bacteria, therefore offering only the edges as initial points of attachment. Similar effects are expected for even smaller periodicities. The observed bacteria-repelling effect is believed to originate in a reduced number of possible contact points for the tested bacteria on the structured surface, following the mechanism proposed by Whitehead et al. [63].
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
Adhesion experiments depicted in Figure 6 were performed on polished inert stainless steel (AISI 304) and polished brass (CuZn23Al3Co) with a roughness Ra = 5 ± 2 nm for both. For the bacterial adhesion experiments shown in Figure 7, flat, spin-coated polyimide films (Ra = 2 ± 1 nm) were PVD coated with an approximately 10-nm gold layer or laser interference patterned at 890 mJ/cm2 with line-like topography and then coated. The bacteria used were Escherichia coli K12 (Figure 6) and Staphylococcus carnosus (Figure 7) concentrations of about 2 × 105 mL−1 bi-distilled. A flow box setup was used in both experiments, which allowed counting bacteria in situ by microscopic means.
Commercially available, flat aluminum bulk samples with a technical purity of 99.5% (round plates with a diameter of 25 mm) were used for the laser surface patterning and the subsequent tribological experiments under dry sliding conditions (Figure 4). The specimens were grounded and polished in order to have a good surface finish (Table 1).
3.2. Laser Interference Patterning (DLIP)
A high power pulse solid-state Nd:YAG laser with a fundamental wavelength of 1064 nm, a pulse duration of 10 ns and a repetition rate of 10 Hz is used for the surface patterning. The experimental set-up for two-beam interference can be seen in Figure 8.
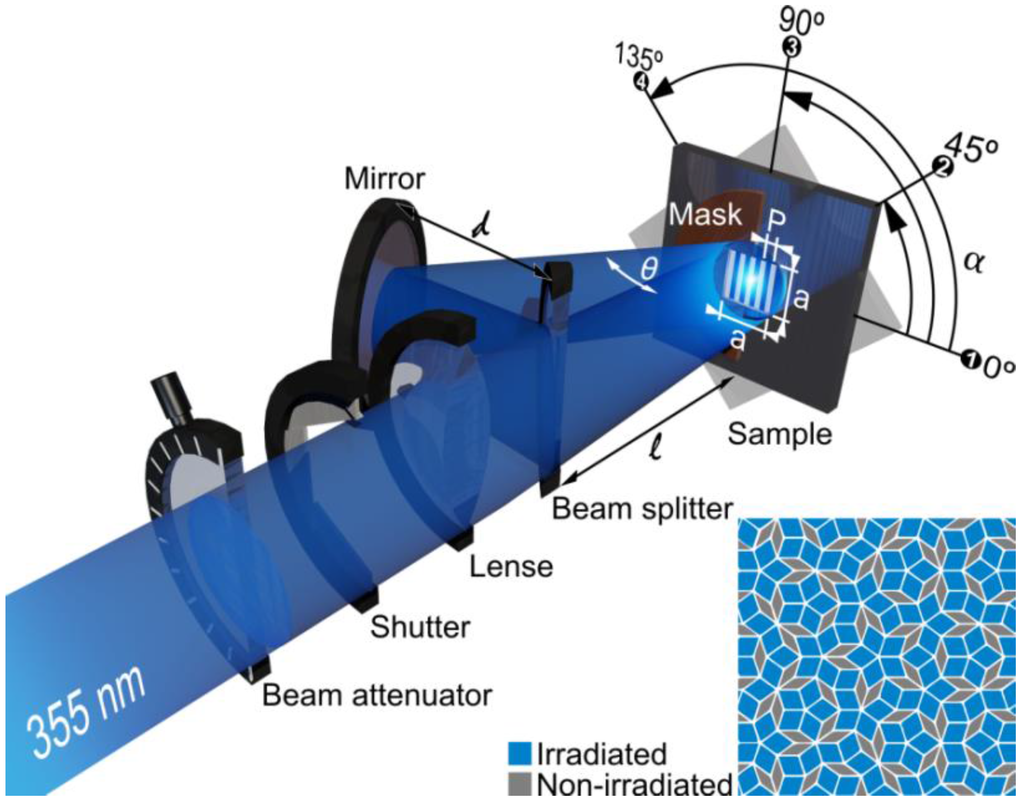
Figure 8.
Schematic illustration of the experimental set-up for two-beam interference. By a multi-step process, the generation of quasi-periodic Penrose-like surface patterns is possible as schematically depicted in this figure.
Figure 8.
Schematic illustration of the experimental set-up for two-beam interference. By a multi-step process, the generation of quasi-periodic Penrose-like surface patterns is possible as schematically depicted in this figure.
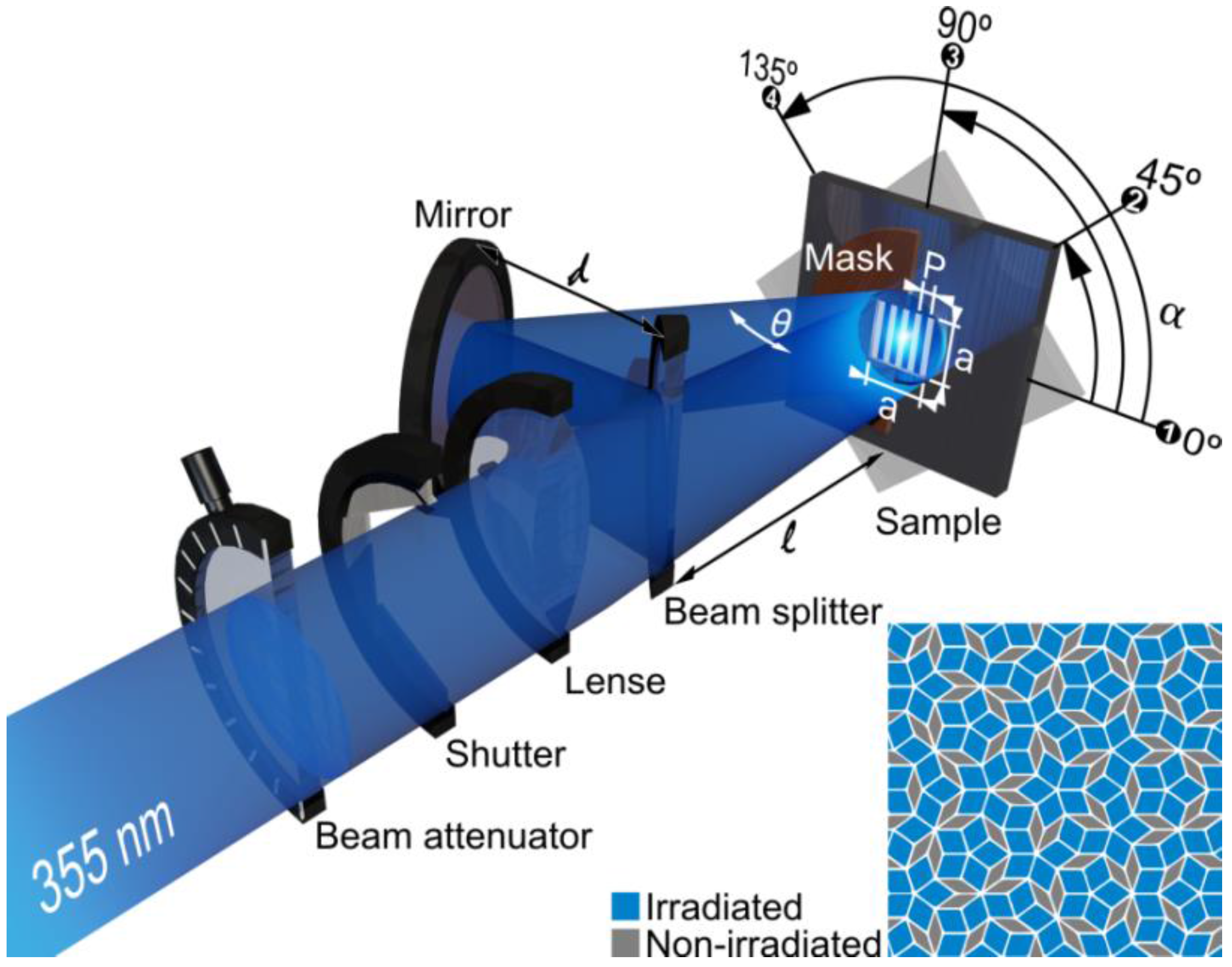
By means of harmonic generation, a laser wavelength of 355 nm can be produced, which is typically used for the patterning process. As can be seen in this figure, the primary beam travels through an attenuator in order to adjust the energy of the beam. Afterwards, this beam passes a shutter to precisely select the number of pulses used for the surface patterning. A lens can be used in order to increase the laser fluence. Finally, the primary beam is split into two sub-beams by means of a suitable beam-splitter, and these sub-beams interfere with each other on the surface of the sample. The result of two-beam interference is a sinusoidal, line-like surface pattern with a characteristic periodicity P. As already demonstrated in Equation (6), the periodicity is mainly dependent on the laser wavelength used and the angle between the interfering sub-beams. It is important to mention that the positions of the maximum laser intensity correspond to the topographical minima positions and vice versa.
As already depicted in Figure 1, by means of three-beam interference, it is possible to create adot-like surface pattern. The experimental set-up for three-beam interference is shown in Figure 9.
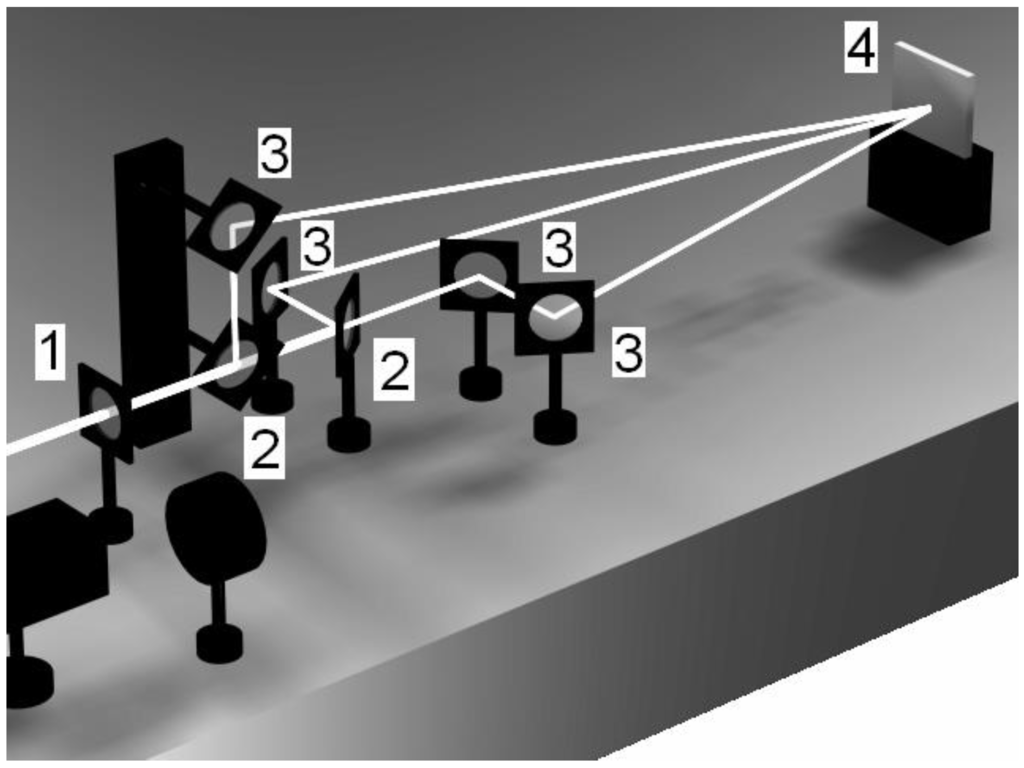
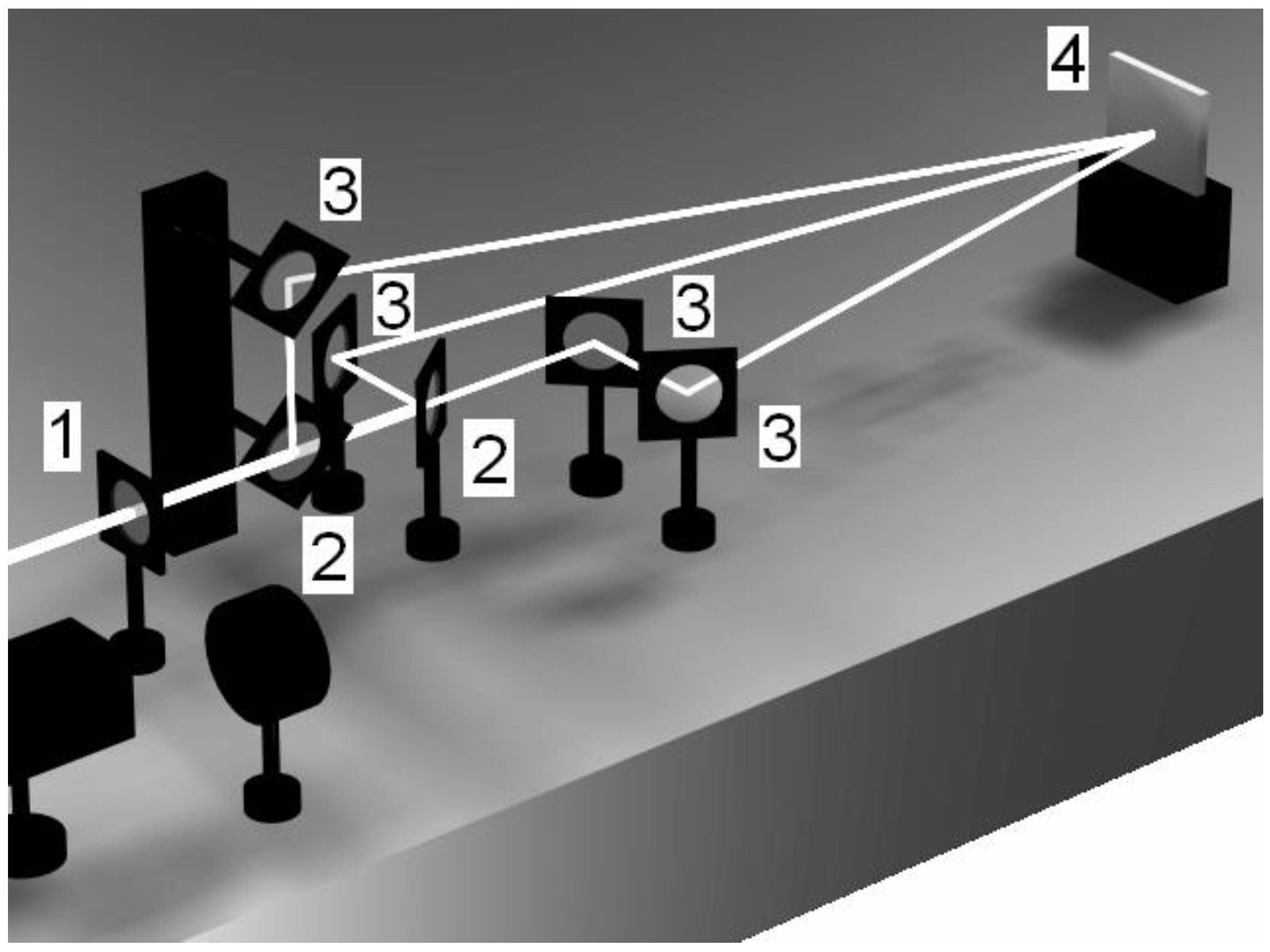
Figure 9.
Experimental set-up for three-beam interference to create dot-like surface patterns. (1) represents a lens in order to increase the laser fluence, whereas (2) and (3) illustrate the positions of the respective beam-splitters and mirror, respectively [36].
Figure 9.
Experimental set-up for three-beam interference to create dot-like surface patterns. (1) represents a lens in order to increase the laser fluence, whereas (2) and (3) illustrate the positions of the respective beam-splitters and mirror, respectively [36].
The periodicity of the dot-like surface pattern can be expressed as:
Consequently, the periodicity of the dot-like surface pattern also depends on the laser wavelength and the angle between the interfering sub-beams.
For the tribological experiments under dry friction, line-like surface patterns with different periodicities (2, 5, 7 and 8 µm) and a structural depth of around 1 µm were produced in order to study the influence of the periodicity on the frictional response. For all laser experiments, a laser fluence of 1500 mJ/cm2 was used in order to create homogenous surface patterns. All of the samples were irradiated under normal atmospheric conditions in air with one single laser shot. After the laser patterning, the homogeneity of the patterns was investigated by WLI and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The obtained experimental results were directly compared to numerical studies done by collaborations partners at the Imperial College (Dr. Simon Medina).
The line-like patterned surfaces for adhesion experiments (lateral periodicity of 2 μm) were generated on polyimide at a laser fluence of about 490 mJ/cm2 and coated with gold (50 nm). Inert contact arrays shown in Figure 6b were generated by laser interference lithography with a spin-coated photo resist (AZ 1518, MicroChemicals GmbH) at a laser fluence of 33 mJ/cm2. In both cases, a laser wavelength of 355 nm was used, which was obtained by second harmonic generation.
3.3. Tribological Experiments
The tribological experiments under dry sliding conditions were conducted using a ball-on-disk configuration in linear reciprocating sliding mode with a stroke length of 0.6 mm, a sliding speed of 1 cm/s and a normal load of 100 mN. A normal load of 100 mN was selected in order to avoid any wear features. The number of cycles was set to 200 cycles. The counter body was a 100Cr6 steel ball with a diameter of 1.5 mm, which is mounted on a stiff cantilever. During the experiment, the deflections of the cantilever in the horizontal and vertical direction are measured using optical fiber displacement sensors, thus being able to calculate the normal and friction force. Temperature and relative humidity were kept constant at 20 ± 2 °C and 45% ± 2%, respectively. The tribological experiments under dry friction were performed as a function of the periodicity of the line-like surface pattern.
4. Conclusions
DLIP is a powerful technique to create different, periodic surface geometries (line-, dot- or cross-like surface patterns) having a periodicity and structural depth in the micron and sub-micron range. In addition to periodic surface topographies, quasi-periodic Penrose-like patterns with 8-, 10- or 12-fold symmetry can be generated by means of a multi-step process.
With regard to the frictional behavior under dry sliding conditions, it could be demonstrated that periodic line-like surface patterns with small periodicities (2 and 5 µm) lead to a significant reduction of the resulting COF. The experimental results fit very well with theoretical calculations showing a decrease in the contact area with decreasing periodicity.
By using DLIP surfaces with lateral periodicities on and below the bacteria scale, the important role of bacteria adhesion for antibacterial surface effects could be demonstrated. Furthermore, an anti-adhesive surface pattern, which could prevent bacterial attachment in the first place, has been realized by DLIP.
To conclude, surface patterns generated by DLIP allow an active surface optimization for biological applications in terms of tribological and antibacterial properties.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the work group of Karin Jacobs (Condensed Matter Physics) at the Saarland University and specifically Christian Kreis, as well as Christian Zeitz for excellent experimental support. Furthermore, the authors would like to thank Simon Medina, Andrew Olver and Hugh A. Spikes (Imperial College London) for performing the numerical simulations to evaluate contact pressure and contact area.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, R.; Lu, H.; Li, L.; Kong, Y.; Qi, K.; Xin, J.H. Artificial lotus leaf structures from assembling carbon nanotubes and their applications in hydrophobic textiles. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, B.P.; Messersmith, P.B. A reversible wet/dry adhesive inspired by mussels and geckos. Nature 2007, 448, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yan, X.; Yao, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Jiang, L. The dry-style antifogging properties of mosquito compound eyes and artificial analogues prepared by soft lithography. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2213–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Jiang, L. Biophysics: Water-Repellent Legs of Water Striders. Nature 2004, 432, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potyrailo, R.A.; Ghiradella, H.; Vertiatchikh, A.; Dovidenko, K.; Cournoyer, J.R.; Olson, E. Morpho butterfly wing scales demonstrate highly selective vapour response. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakefield, P.M.; French, V. Butterfly wings: The evolution of development of colour patterns. BioEssays 1999, 21, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, T.; Alsop, R.; Ettershank, G. Adhesiveness of spider silk. Science 1964, 146, 1058–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B. Biomimetics: Lessons from Nature—An Overview. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1445–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, M.K.; Pang, C.; Jeong, H.E.; Kim, H.N.; Yoon, H.; Jung, H.S.; Suh, K.Y. Towards the next level of bioinspired dry adhesives: New Designs and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3606–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Bio-inspired, smart, multiscale interfacial materials. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2842–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Feng, L.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired surfaces with special wettability. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukusic, P.; Sambles, J.R.; Lawrence, C.R. Structural colour: Colour Mixing in Wing Scales of a Butterfly. Nature 2000, 404, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Antibacterial surfaces: The Quest for a New Generation of Biomaterials. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Bio-inspired design of multiscale structures for function integration. Nano Today 2011, 6, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Hasan, J.; Webb, H.K.; Truong, V.K.; Watson, G.S.; Watson, J.A.; Baulin, V.A.; Pogodin, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Tobin, M.J.; et al. Natural bactericidal surfaces: Mechanical Rupture of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Cells by Cicada Wings. Small 2012, 8, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, H.; Yamagami, H.; Sumiya, T.; Okudera, M.; Inada, A.; Terada, A.; Nakamura, T. Contact start/stop characteristics on photolithographic magnetic recording media. Wear 1994, 172, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R; Lambeth, D.N.; Tromel, M.; Goglia, P.; Li, Y. Laser texturing for low-flying-height media. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 5745–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, L.; Moshkovich, A.; Perfilyev, V.; Lapsker, I.; Halperin, G.; Itovich, Y.; Etsion, I. Friction and wear of MoS2 films on laser textured steel surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Bhushan, B. Multiscale friction mechanisms and hierarchical surfaces in nano-and bio-tribology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2007, 58, 162–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamakuri, S.K.; Bhushan, B. Optimization of asperities for laser-textured magnetic disk surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 1997, 40, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Deng, J.; Feng, X.; Yu, S. Effect of laser surface texturing on Si 3 N 4/TiC ceramic sliding against steel under dry friction. Mater. Des. 2013, 52, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, A.; Gualtieri, E.; Marchetto, D.; Moretti, L.; Valeri, S. Tribological effects of surface texturing on nitriding steel for high-performance engine applications. Wear 2008, 265, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. Modulation of dry tribological property of stainless steel by femtosecond laser surface texturing. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 119, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Reinert, L.; Ramos-Moore, E.; Souza, N.; Müser, M.H.; Mücklich, F. Dry friction between laser-patterned surfaces: Role of Alignment, Structural Wavelength and Surface Chemistry. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 49, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodanov, N.; Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Mücklich, F.; Müser, M.H. Contact mechanics of laser-textured surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 50, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Reinert, L.; Gachot, C.; Mücklich, F. Alignment and wear debris effects between laser-patterned steel surfaces under dry sliding conditions. Wear 2014, 318, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.J. Surface texture effect on friction of a microtextured poly (dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS). Tribol. Lett. 2008, 31, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yu, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, W.; He, B.; Wang, Q.J. Understanding topographic dependence of friction with micro-and nano-grooved surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, D.; McCarthy, T.J. Ultrahydrophobic surfaces. Effects of topography length scales on wettability. Langmuir 2000, 16, 7777–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.E.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, H.N.; Moon, S.H.; Suh, K.Y. A nontransferring dry adhesive with hierarchical polymer nanohairs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5639–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mücklich, F.; Lasagni, A.F.; Daniel, C. Laser Interference Metallurgy-using interference as a tool for micro/nano structuring. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 97, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasagni, A.F.; D’Alessandria, M.; Giovanelli, R.; Mücklich, F. Advanced design of periodical architectures in bulk metals by means of Laser Interference Metallurgy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 254, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, S.; Hans, M.; Mücklich, F.; Solioz, M. Contact killing of bacteria on copper is suppressed if bacterial-metal contact is prevented and is induced on iron by copper ions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2605–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Heib, T.; Gachot, C.; Mücklich, F. Oil film lifetime and wear particle analysis of laser-patterned stainless steel surfaces. Wear 2015, 334, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasagni, A.F. Advanced Design of Periodical Structures by Laser Interference Metallurgy in the Micro/Nano Scale on Macroscopic Areas. Ph.D. Thesis, Saarland University, Saarbruecken, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fowell, M.T.; Pegg, I.G.; Olver, A.V.; Gosman, A.D.; Spikes, H.A. Entrainment and inlet suction: Two Mechanisms of Hydrodynamic Lubrication in Textured Bearings. J. Tribol. 2007, 129, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olver, A.V.; Fowell, M.T.; Spikes, H.A.; Pegg, I.G. “Inlet suction”, a load support mechanism in non-convergent, pocketed, hydrodynamic bearings. J. Eng. Tribol. 2006, 220, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Saka, N.; Suh, N.P. Boundary lubrication studies on undulated titanium surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 1989, 32, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, N.; Tian, H.; Suh, N.P. Boundary lubrication of undulated metal surface at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Trans. 1989, 32, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, G.; Romano, V.; Weber, H.P.; Haefke, H.; Gerbig, Y.; Pflueger, E. Laser microstructuring of steel surfaces for tribological applications. J. Appl. Phys. A 2000, 70, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, P.; Koskinen, J.; Varjus, S.; Gerbig, Y.; Haefke, H.; Georgiou, S.; Zhmud, B.; Buss, W. Microlubrication effect by laser-textured steel surfaces. Wear 2007, 262, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Premchandran, N.R.; Zou, M.; Wang, Y.A. Adhesion and friction properties of micro/nano-engineered superhydrophobic/hydrophobic surfaces. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 3801–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeshuber, I.C. Biotribology inspires new technologies. Nano Today 2007, 2, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.E.; Vanossi, A.; Urbakh, M. Origin of friction anisotropy on a quasicrystal surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 074302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Thiel, P.A. Atomic scale friction and adhesion properties of quasicrystal surfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 314012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.L.; Kishore; Kailas, S.V. Effect of roughness parameter and grinding angle on coefficient of friction when sliding Al-Mg alloy over EN8 steel. J. Tribol. 2004, 128, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.L.; Kishore; Kailas, S.V. Studies on friction and transfer layer: Role of Surface Texture. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 24, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZoBell, C.E. The effect of solid surfaces upon bacterial activity. J. Bacteriol. 1943, 46, 36–56. [Google Scholar]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: A Common Cause of Persistent Infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8533–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glinel, K.; Thebault, P.; Humblot, V.; Pradier, C.M.; Jouenne, T. Antibacterial surfaces developed from bio-inspired approaches. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1670–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Hasan, J.; Webb, H.K.; Gervinskas, G.; Juodkazis, S.; Truong, V.K.; Wu, A.H.F.; Lamb, R.N.; Baulin, V.A.; Watson, G.S.; et al. Bactericidal activity of black silicon. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengstock, C.; Lopian, M.; Motemani, Y.; Borgmann, A.; Khare, C.; Buenconsejo, P.J.S.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Ludwig, A.; Köller, M. Structure-related antibacterial activity of a titanium nanostructured surface fabricated by glancing angle sputter deposition. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 195101–195112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploux, L.; Anselme, K.; Dirani, A.; Ponche, A. Opposite responses of cells and bacteria to micro/nanopatterned surfaces prepared by pulsed plasma polymerization and UV-irradiation. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8161–8169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselme, K.; Davidson, P.; Popa, A.M.; Giazzon, M.; Liley, M.; Ploux, L. The interaction of cells and bacteria with surfaces structured at the nanometre scale (Review). Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3824–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jullien, C.; Benezech, T.; le Gentil, C.; Boulange-Petermann, L.; Dubois, P.E.; Tissier, J.P.; Traisnel, M.; Faille, C. Physico-chemical and hygienic property modification of stainless steel surfaces induced by conditioning with food and detergent. Biofouling 2008, 24, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazaka, K.; Jacob, M.V.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Efficient surface modification of biomaterial to prevent biofilm formation and the attachment of microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 95, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, Ż.; Piszczek, P.; Radtke, A.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Kozak, W.; Sadowska, B. The evaluation of the impact of titania nanotube covers morphology and crystal phase on their biological properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.; Friedrich, S.; Stang, C.; Bley, T.; Schilling, N.; Bieda, M.; Lasagni, A.; Boschke, E. Initial phases of microbial biofilm formation on opaque, innovative anti-adhesive surfaces using a modular microfluidic system. Eng. Life Sci. 2013, 14, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.; Burgui, S.; Langheinrich, D.; Gil, C.; Solano, C.; Toledo-Arana, A.; Helbig, R.; Lasagni, A.; Lasa, I. Evaluation of Surface Microtopography Engineered by Direct Laser Interference for Bacterial Anti-Biofouling. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATS Labs. Test Method for the Continuous Reduction of Bacterial Contamination on Copper Alloy Surfaces; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Whitehead, K.A.; Verran, J. The effect of surface topography on the retention of microorganisms. Food Bioprod. Proc. 2006, 84, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
