Enhancing the Lubrication Performance of Steel–Steel Contacts Using a Novel Ionic Liquid Based on Phosphate Ammonium Salt as an Oil Additive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Synthesized, and Characterizations
2.2. Tribological Tests
3. Results and Discussion
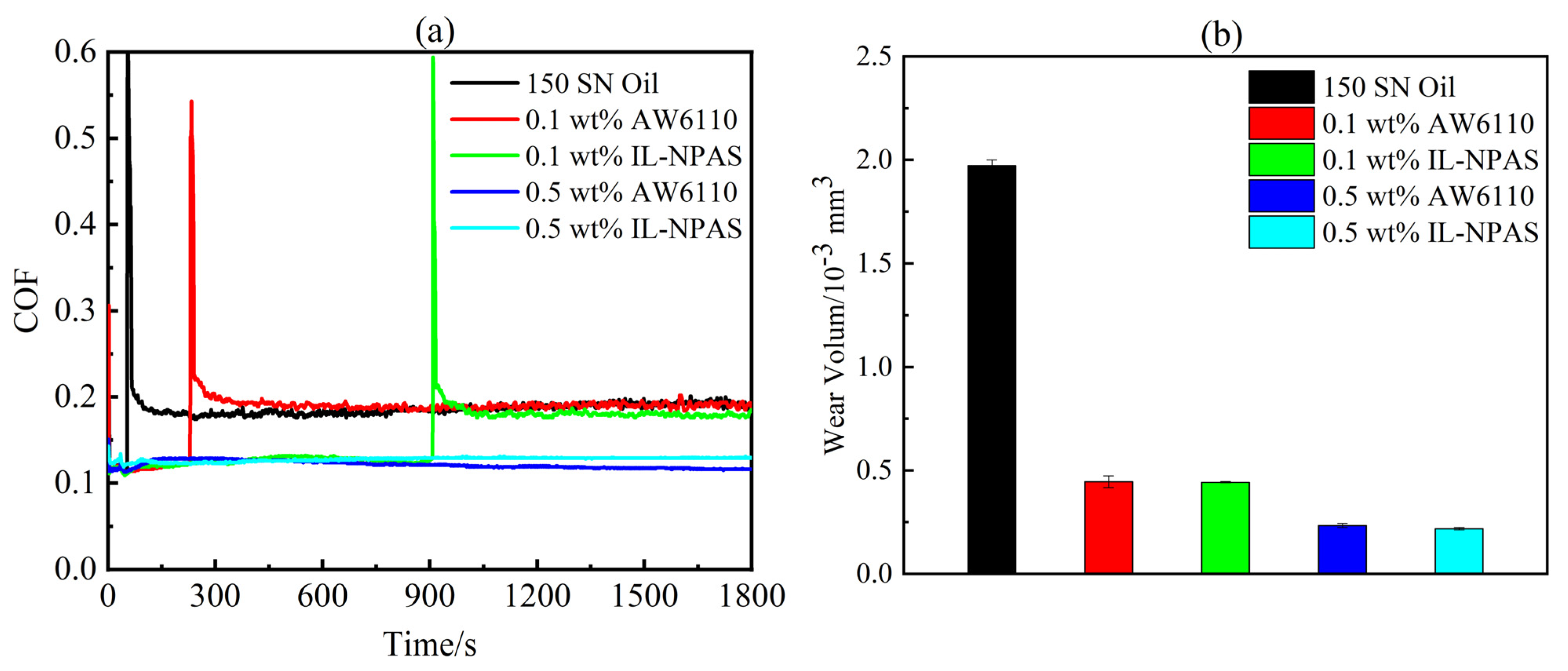
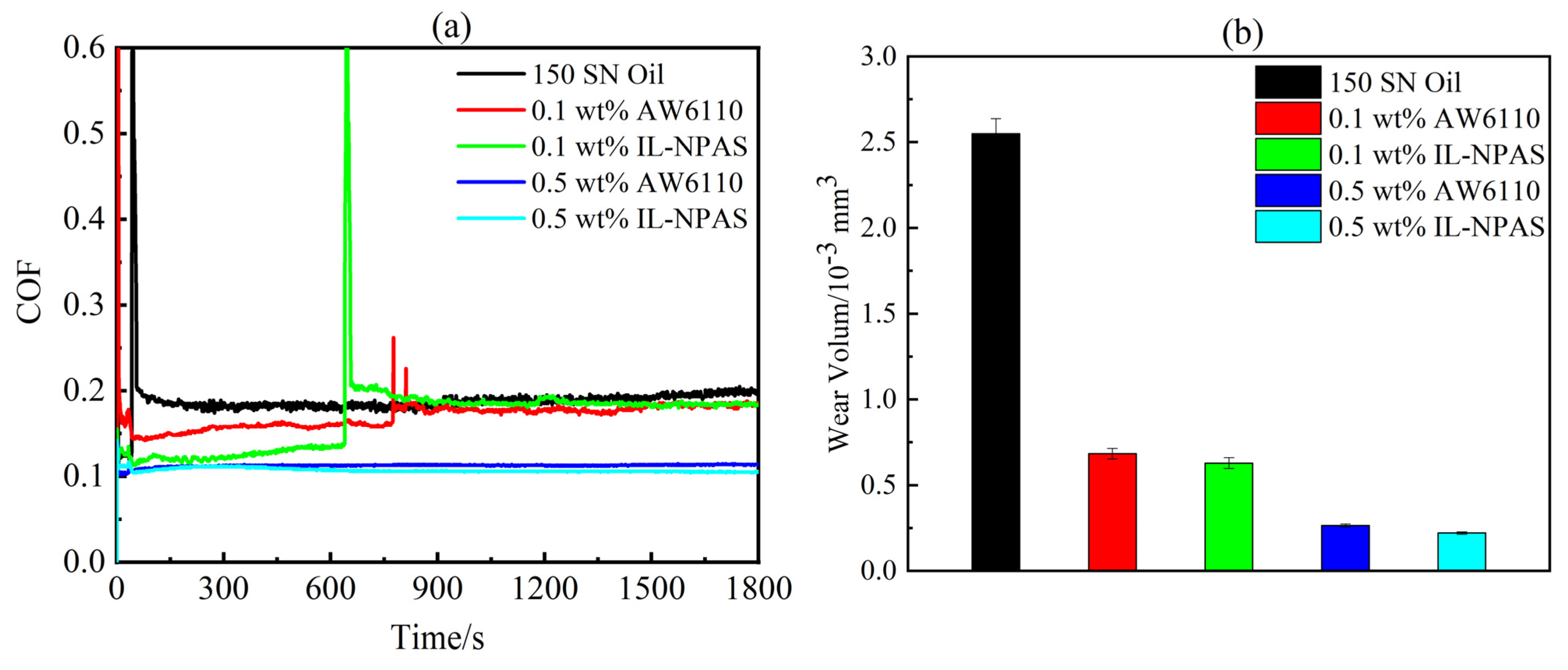
3.1. Tribological Properties
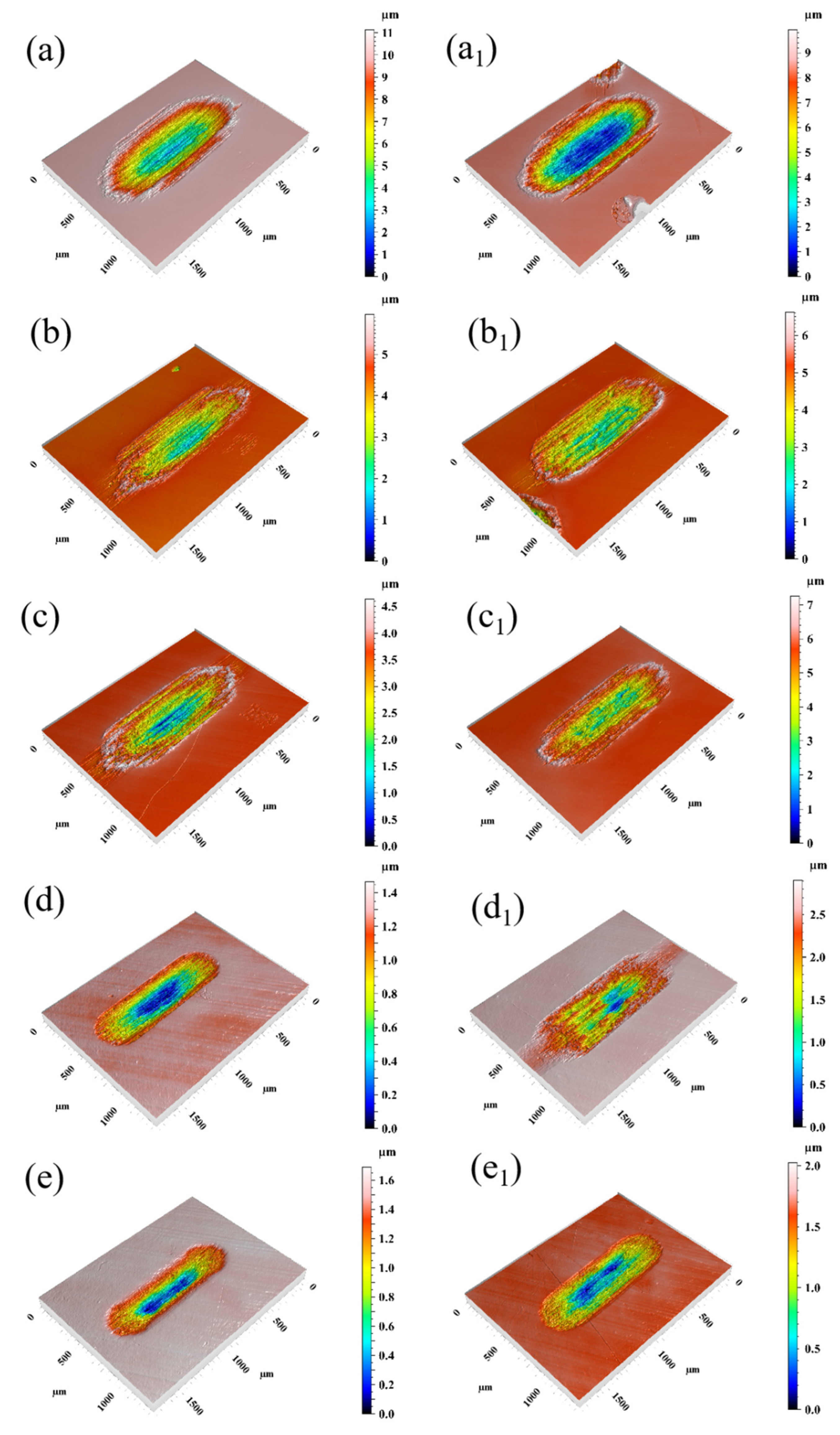
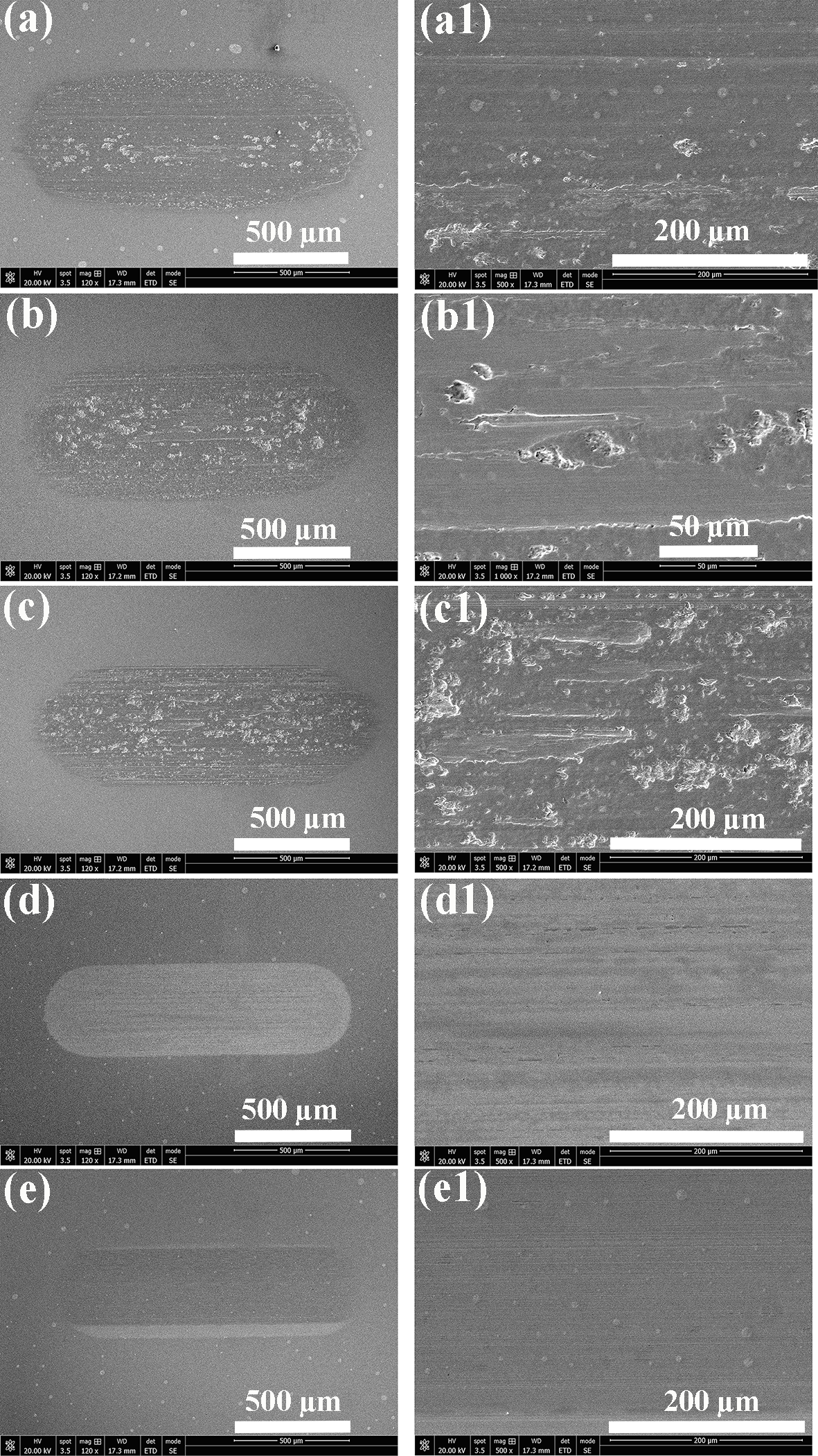
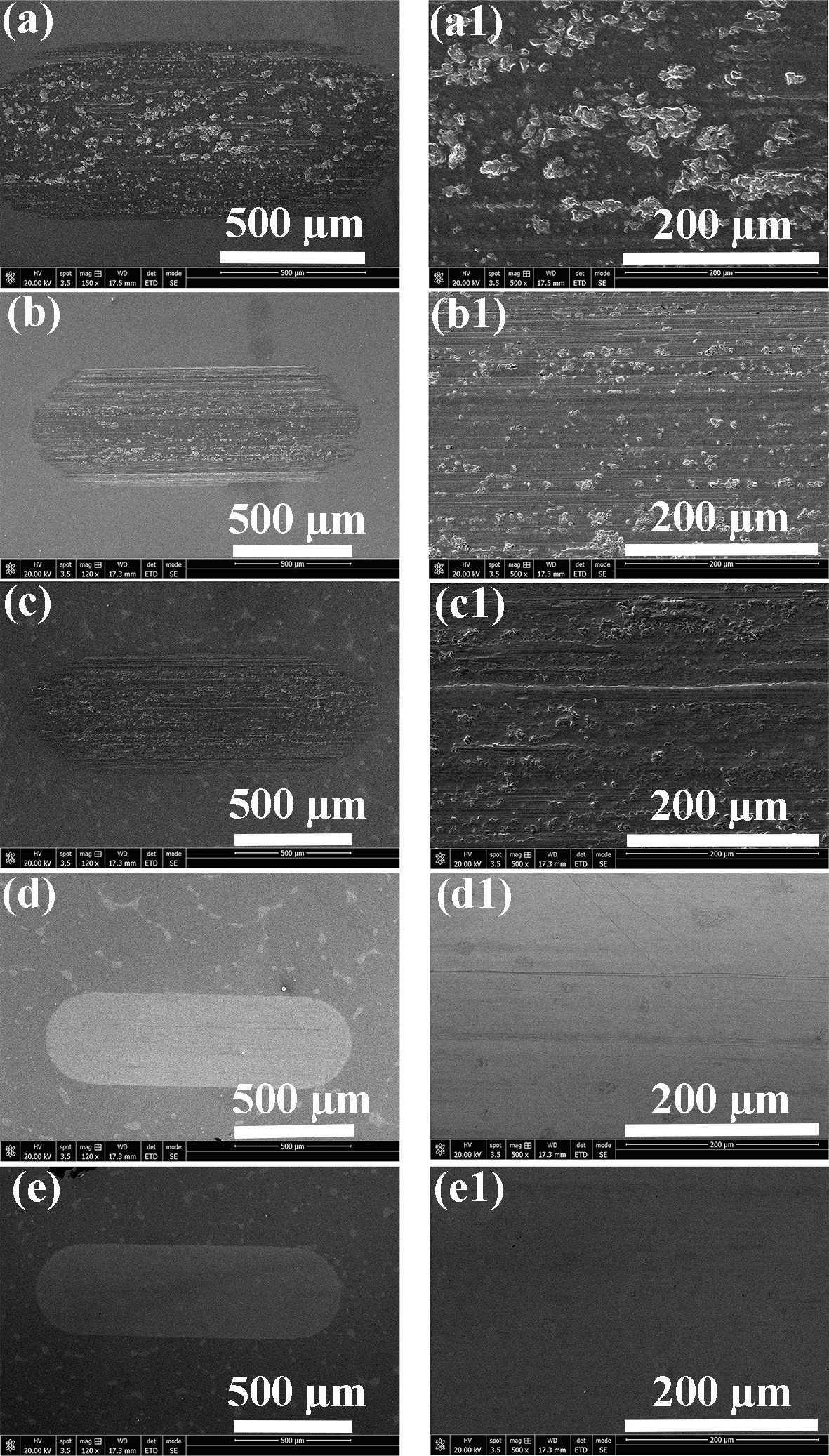
3.2. Morphological Characterization
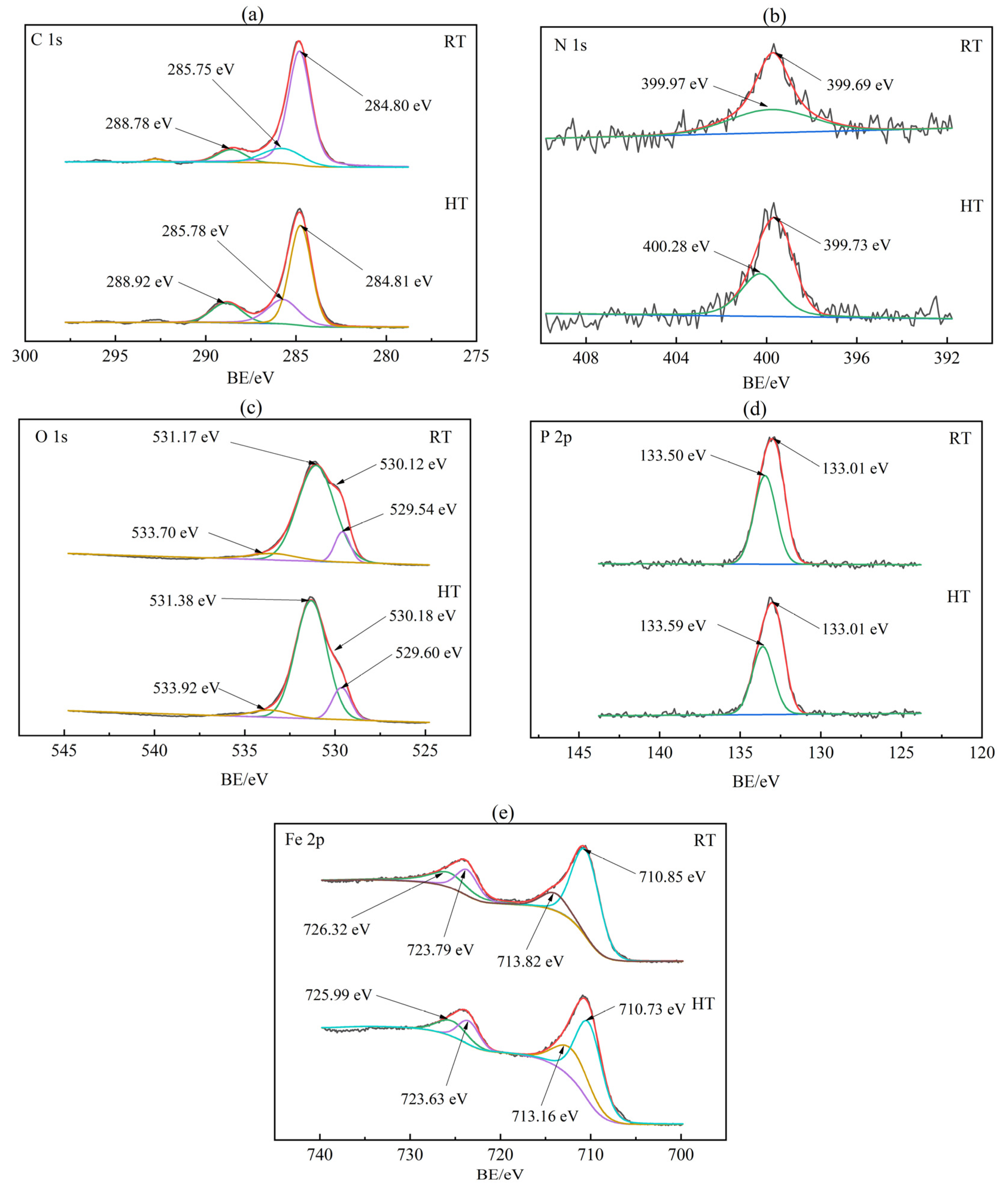
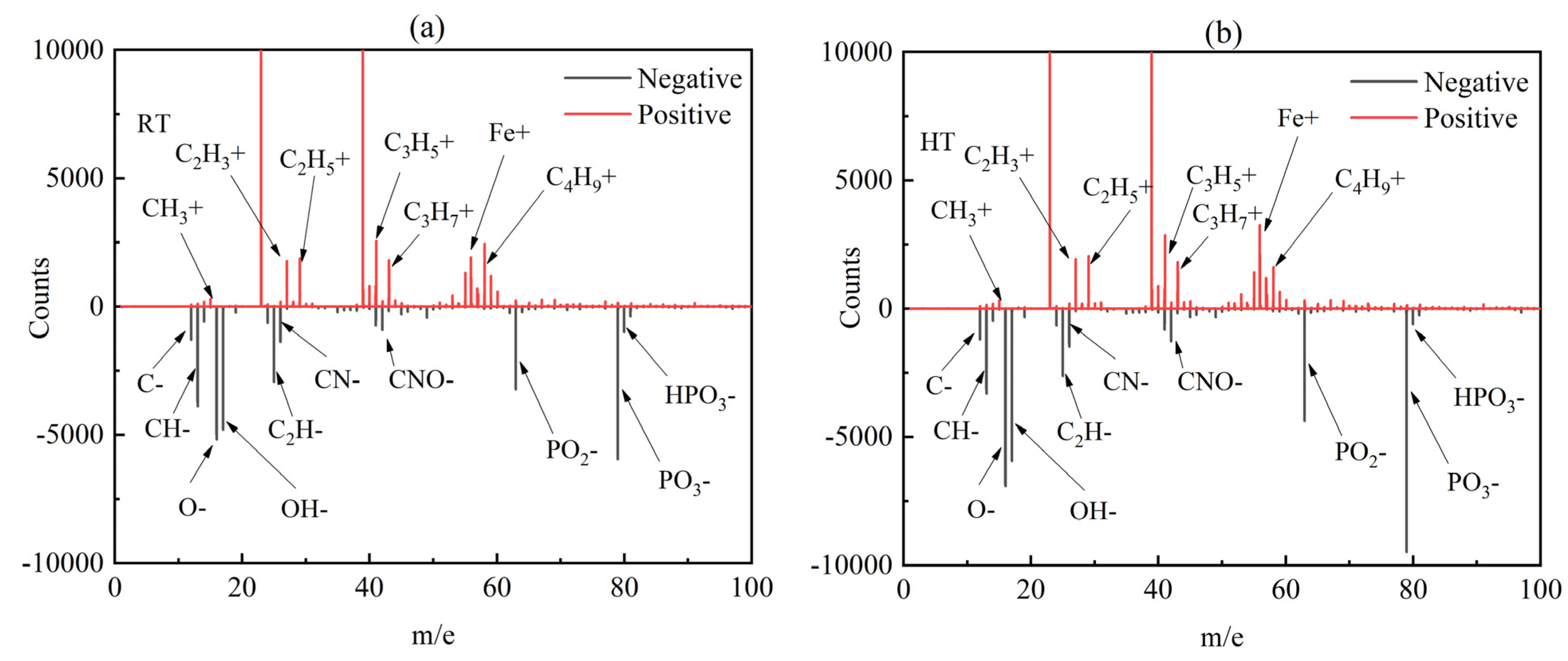
3.3. Wear Resistance Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Ma, L. Origin of friction and the new frictionless technology—Superlubricity: Advancements and future outlook. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, E.; Morris, N.; Leighton, M.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H. Multiscale friction in lubricant-surface systems for high-performance transmissions under mild wear. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Mai, L.; Qingping, C.; Turkson, R.F.; Bicheng, C. Improving the tribological characteristics of piston ring assembly in automotive engines using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanomaterials as nano-lubricant additives. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, J. Ionic liquids as lubricant additives: A review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontham, V.; Padmaja, K.V.; Madhu, D. Synthesis of ricinoleate anion based ionic liquids and their application as green lubricating oil additives. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, B.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Wang, R.; Yan, X.; Yu, B.; Yu, Q.; Cai, M. Performance of oil-soluble ionic liquids as novel lubricant additives. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L. Physicochemical properties of ionic liquids. In Ionic Liquids Further UnCOILed; Plechkova, N.V., Seddon, K.R., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, H.; Fang, X.; Li, H. The development status and future trends of lubricant additives technology: Based on patents analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.R.; Chauhan, K.V.; Rawal, S.; Patel, N.P.; Subhedar, D. Advances and challenges in bio-based lubricants for sustainable tribological applications: A comprehensive review of trends, additives, and performance evaluation. Lubricants 2025, 13, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Liang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Q.; Hu, S.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Development of a high-performance lubricant based on halogen-free phosphonium ionic liquid for electrified vehicle transmissions. Tribol. Int. 2026, 214, 111206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, G.; Lin, H.; Tang, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y. Multi-dimensional nano-additives for their superlubricity: Tribological behaviors and lubrication mechanisms. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 12, 2400796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adavodi, R.; Dini, G. Benzotriazoium bis (2-ethylhexyl) phosphate ionic liquid as a catalyst and multifunctional lubricant additive: Synthesis, optimization, characterization, and tribological evaluation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 7995–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Qin, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Lin, H.; Han, S. Tribological properties and synergistic lubrication mechanism between tetramethyl dodecyl diisooctyl phosphate ionic liquids and molybdenum-based metal organic frameworks additives. Wear 2025, 576–577, 206137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Abdelkareem, M.A.A.; Elagouz, A.; Xianjun, H. In Nanotechnology in the Automotive Industry; Song, H., Nguyen, T.A., Yasin, G., Singh, N.B., Gupta, R.K., Eds.; Chapter 32—Nanolubricant additives. Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 675–711. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, B.; Pochopien, B.A.; Wright, D.S. The chemistry, mechanism and function of tricresyl phosphate (TCP) as an anti-wear lubricant additive. Lubr. Sci. 2016, 28, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W. The Tribology and Chemistry of Phosphorus-Containing Lubricant Additives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; He, Z.; Xie, F.; Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Han, S.; Yang, S. Study of tribological synergistic effect of N-containing heterocyclic borate ester with tricresyl phosphate as rapeseed oil additive. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2020, 57, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Duan, F. Tribological Properties of Tricresyl Phosphate Blended in Base Oils between Iron-Based Surfaces. Langmuir 2025, 41, 29064–29075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Electro-controlled friction and tribofilm formation on electrified steel surfaces lubricated with an N/P-based ionic liquid additive under sliding conditions. Wear 2025, 580–581, 206251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wan, S.; Zhu, Q.; Tieu, A.K.; Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Cowie, B. Tribochemical behavior of phosphate compounds at an elevated temperature. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 25742–25751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dolocan, A.; Morales-Collazo, O.; Sadowski, J.T.; Celio, H.; Chrostowski, R.; Brennecke, J.F.; Mangolini, F. Lubrication mechanism of phosphonium phosphate ionic liquid in nanoscale single-asperity sliding contacts. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Nie, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, N.; Said, Z. Extreme pressure and antiwear additives for lubricant: Academic insights and perspectives. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeck, O.; Givens, J.; Williams, E. On the mechanism of boundary lubrication. II. Wear prevention by addition agents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1940, 177, 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, E.; Battersby, J. Application of adsorption/reaction mechanism to load-carrying results. ASLE Trans. 1974, 17, 268–270. [Google Scholar]
- Oshio, T. Anti-Wear Properties and Mechanisms of Dialkyl Phosphonates in Ester Base Oils. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, Écully, France, 2023. Available online: https://bibliotheque.ec-lyon.fr/documents/TH_2023ECDL0029.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Johnson, D.W.; Hils, J.E. Phosphate Esters, Thiophosphate Esters and Metal Thiophosphates as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants 2013, 1, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Liu, W. Tribochemistry and the development of AW and EP oil additives—A review. Lubr. Sci. 1994, 7, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveira-Suarez, A.; Tomala, A.; Grahn, M.; Zaccheddu, M.; Pasaribu, R.; Larsson, R. The influence of base oil polarity and slide–roll ratio on additive-derived reaction layer formation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2011, 225, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, X. Hydroquinone bis (diphenyl phosphate) as an antiwear/extreme pressure additive in polyalkylene glycol for steel/steel contacts at elevated temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 7419–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Mori, S. Concept of molecular design towards additive technology for advanced lubricants. Lubr. Sci. 2007, 19, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Suo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, F.; Wang, L. The synergistic effect of novel anti-wear additive 1,3,4-thiadiazole mixed ammonium salt and MoDTC on tribological properties of FeCoCrNiMn alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 38, 5235–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Yu, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhou, F. Ionic liquid lubricants: When chemistry meets tribology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7753–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhvaryu, A.; Erhan, S.; Perez, J. Tribological studies of thermally and chemically modified vegetable oils for use as environmentally friendly lubricants. Wear 2004, 257, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Improving tribological performance of electrified steel interfaces in e-mobility systems using ash-sulfur-less oil additives based on amine salts-phosphoric esters. Tribol. Int. 2025, 205, 110561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King Industries, I. Product Data Sheet for Amine Salts of Aliphatic Phosphoric Acid Esters (NA-LUBE® AW-6110). 2023. Available online: https://www.kingindustries.com/assets/1/6/NA-LUBE_AW-6110_PDS.pdf?1126 (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Itoh, T. Ionic liquids as tool to improve enzymatic organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10567–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, D.; Wang, X. In situ synthesized phosphate-based ionic liquids as high-performance lubricant additives. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.D.; Milne, N. Ashless phosphorus–containing lubricating oil additives. In Lubricant Additives; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 157–196. [Google Scholar]
- Truhan, J.J.; Qu, J.; Blau, P.J. A rig test to measure friction and wear of heavy duty diesel engine piston rings and cylinder liners using realistic lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhill, W.C.; Luo, H.; Meyer, H.M., III; Ma, C.; Chi, M.; Papke, B.L.; Qu, J. Tertiary and quaternary ammonium-phosphate ionic liquids as lubricant additives. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 63, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, E.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Cheng, S. Tribological performance of fatty acid ammonium ionic liquids as anti-wear additives in water-based fluids. Tribol. Int. 2024, 194, 109565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J. Design of Ionic Liquid Based Additives for Integration with Modern Lubrication Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, A.E.; Yunis, R.; Armand, M.B.; Pringle, J.M.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Towards phosphorus free ionic liquid anti-wear lubricant additives. Lubricants 2016, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, C.; Yu, Q.; Yu, B.; Cai, M.; et al. Halogen-free functional quaternary ammonium-based ionic liquid as an ecofriendly corrosion inhibitor for Q235 steel in acids. Langmuir 2024, 40, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Sastry, M.; Sarpal, A.; Jain, S. Characterization of nitrogen and phosphorous componenets in a multifunctional lubricant additive by NMR and IR techniques. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 1997, 53, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Ewen, J.P.; Latorre, C.A.; Gattinoni, C.; Khajeh, A.; Moore, J.D.; Remias, J.E.; Martini, A.; Dini, D. Substituent effects on the thermal decomposition of phosphate esters on ferrous surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 9852–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Fang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hu, L. Combining in-situ quadrupole mass spectrometer analyses: Study on the structure–activity relationship and lubrication mechanisms of ammonium phosphate ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 413, 125998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Song, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Laxative inspired ionic liquid lubricants with good detergency and no corrosion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, R.; Stelmakh, O.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y. Wear mechanism of steel materials oxide form conversion at the friction interface conducted by lubricants containing varying hydrogen. Friction 2025, 13, 9440934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; Han, S.; Wang, C. Tribological mechanisms of the synergistic effect between phosphate based ionic liquids and metal-organic frameworks. Wear 2024, 558, 205565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, L.; Li, L.; Pei, L.; Xue, W.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y. Exploring the effect mechanism of alkyl chain lengths on the tribological performance of ionic liquids. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 3184–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Yu, Q.; Ali, M.K.A. Synthesis of a Novel Multifunctional Ionic Liquid Based on Benzotriazole for Enhanced Tribological Performance of Steel Interfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2025, 73, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Guo, C.; Li, Z.; Liang, H. Change of surface oxide layer of pyrite samples prepared by resin embedding polishing method after long-term placement and its effect on TOF-SIMS analysis. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 104124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
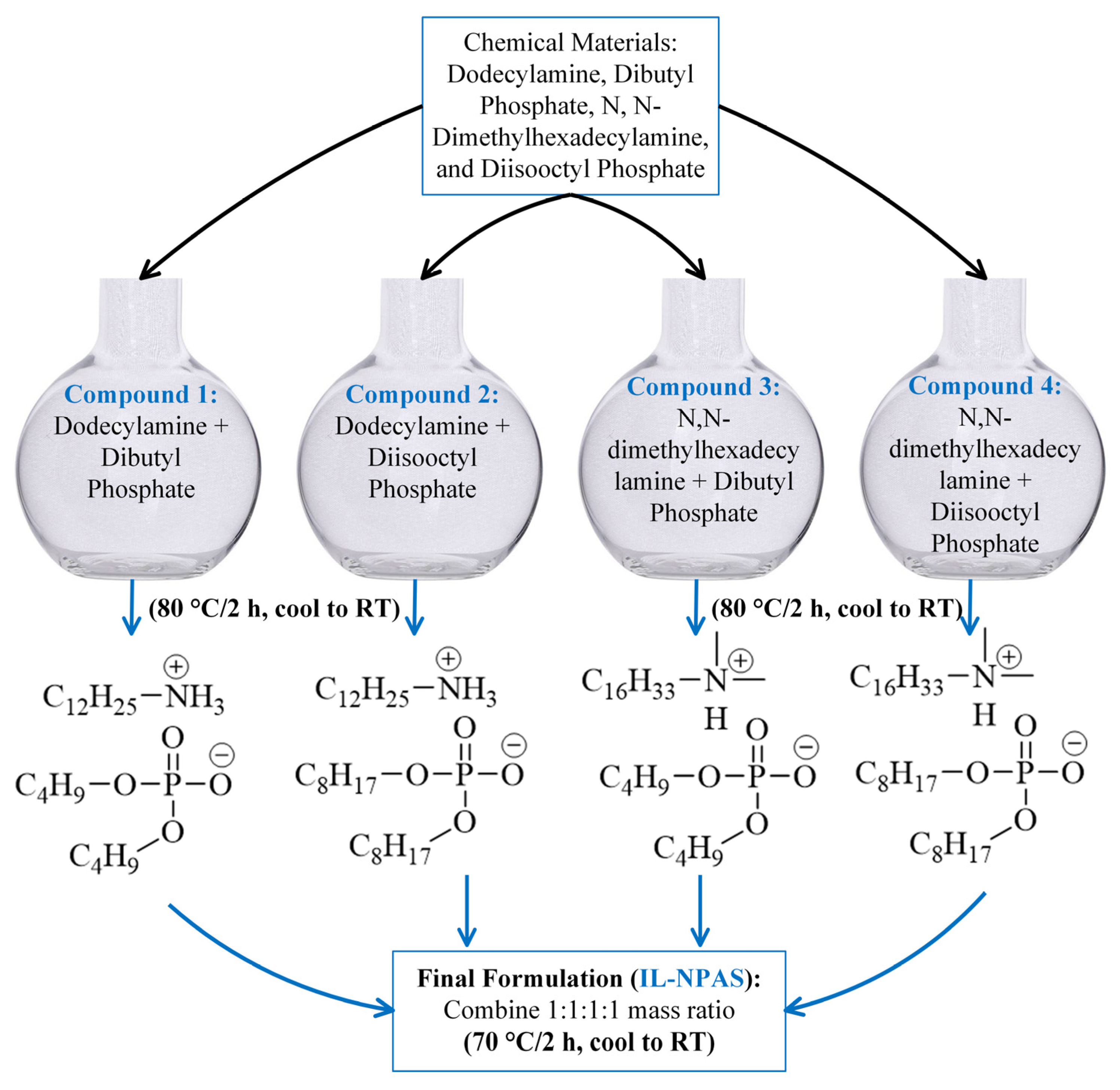
| Reagent | Manufacturer | Purity/% |
|---|---|---|
| Dodecylamine | Chemical Regents | 99 |
| Dibutyl phosphate | Chemical Regents | 99 |
| N,N-dimethylhexadecylamine | Chemical Regents | 98 |
| Diisooctyl phosphate | Chemical Regents | 95 |
| 150 SN | PetroChina | 96 |
| Ethanol | Chemical Regents | 99 |
| Lubricant Sample Name | Kinematic Viscosity (mm2/s) | Viscosity Index | |
|---|---|---|---|
| @ 40 °C | @ 100 °C | ||
| IL-NPAS | 469.77 | 35.58 | 109 |
| AW6110 | 491.57 | 35.32 | 114 |
| Base oil (150 SN) | 32.730 | 5.6678 | 112.9 |
| 150 SN oil + 0.5 wt% IL-NPAS | 30.741 | 5.4142 | 111.1 |
| 150 SN oil + 0.1 wt% IL-NPAS | 30.935 | 5.4353 | 111.0 |
| 150 SN oil + 0.5 wt% AW6110 | 30.966 | 5.4400 | 111.1 |
| 150 SN oil + 0.1 wt% AW6110 | 30.859 | 5.4308 | 111.3 |
| Parameter (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| Tribopair materials | Steel–steel Contact |
| Load (N) | 200 |
| Frequency (Hz) | 50 |
| Temperature (°C) | 25/100 |
| Amplitude (mm) | 1 |
| Duration test (min) | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Xie, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Ali, M.K.A. Enhancing the Lubrication Performance of Steel–Steel Contacts Using a Novel Ionic Liquid Based on Phosphate Ammonium Salt as an Oil Additive. Lubricants 2026, 14, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants14010021
Xie J, Hu S, Liu C, Gao Z, Zhang F, Zhang C, Ali MKA. Enhancing the Lubrication Performance of Steel–Steel Contacts Using a Novel Ionic Liquid Based on Phosphate Ammonium Salt as an Oil Additive. Lubricants. 2026; 14(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants14010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Junjie, Shuai Hu, Cunqiang Liu, Ziqiang Gao, Faxue Zhang, Chaoyang Zhang, and Mohamed Kamal Ahmed Ali. 2026. "Enhancing the Lubrication Performance of Steel–Steel Contacts Using a Novel Ionic Liquid Based on Phosphate Ammonium Salt as an Oil Additive" Lubricants 14, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants14010021
APA StyleXie, J., Hu, S., Liu, C., Gao, Z., Zhang, F., Zhang, C., & Ali, M. K. A. (2026). Enhancing the Lubrication Performance of Steel–Steel Contacts Using a Novel Ionic Liquid Based on Phosphate Ammonium Salt as an Oil Additive. Lubricants, 14(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants14010021






