Abstract
This study proposes a composite-surfactant-assisted method for preparing Fe3O4 water-based nanolubricants to enhance environmental and tribological performance in rolling applications. The dispersion stability of nanoparticles in the suspension was analyzed. The optimal concentration of the nanolubricant was identified. In addition, the reaction mechanism between nanoparticles and water-based nanolubricants was discussed. The experimental results demonstrated that the lubricant containing 6 wt% Fe3O4 nanoparticles exhibited the best anti-friction and anti-wear performance. The aqueous lubricant with composite surfactants showed improved dispersion stability, with its Zeta potential increasing to −43.45 mV, and the intensity curve exhibited a single peak. Through contact angle measurements, wettability was also significantly improved. The molecular interactions of composite surfactants in the prepared water-based nanolubricants were investigated using numerical simulations. The water-based nanolubricant containing composite surfactants displayed enhanced adsorption capacity on Fe3O4 crystals. Compared to other surfactants, the Fe3O4 water-based nanolubricant prepared with composite surfactants exhibited stable dispersion properties. Therefore, composite surfactants can enhance the stability and wettability of water-based nanolubricants. This method enables the preparation of high-performance water-based rolling nanolubricants.
1. Introduction
Rolling is the most common machining method in the field of metal processing, and the research on rolling lubricants has always been the focus of scholars. With the development of nanotechnology, it is possible to increase the lubrication properties of rolling lubricants by adding nanoparticles [1,2]. Recent studies have demonstrated that molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets synthesized via a solvothermal method exhibit exceptional anti-wear performance in oil-based lubricants. Their layered structure facilitates the formation of a continuous protective film at the friction interface, significantly reducing wear scar diameter [3]. This provides critical insights for the application of nano-sulfides in water-based lubricants by optimizing dispersion processes using surfactants. However, with the addition of nanoparticles [4] in the traditional oil-based lubricating oil, although good and stable dispersion performance can be obtained, in a high temperature and high-speed working environment, lubricating oil easily produces harmful gases; the basic solution of an oil-based lubricating has a high cost, and its wettability is difficult to ensure. The long-chain molecules of oil result in strong cohesion and low mobility, making it difficult to spread on solid surfaces, while the short-chain molecules of water, combined with their polarity, allow for rapid adaptation to surface morphology, leading to stronger wettability. Therefore, the emergence of water-based lubricants effectively solves the abovementioned problems, and the gas generated by its work in a high-temperature environment is more environmentally friendly, and the basic solution is easier to obtain at low cost and has good wettability. For example, the water-based lubricant containing 4.0 wt% TiO2 nanoparticles demonstrated the lowest rolling force and thinnest oxide scale in the hot rolling of microalloyed steel. The reductions in rolling force, surface roughness and oxide thickness by 8.1%, 53.7% and 50% respectively [5], validate the comprehensive performance advantages of water-based lubricants under high-temperature conditions. However, the preparation of water-based nanolubricants with a good lubrication performance requires reasonable preparation methods and appropriate nano-additives [6].
Selecting suitable nano-additives and dispersing them effectively and stably in water-based rolling lubricants has become the goal of researchers. To start, Fe, Cu, Co, and other nano-scale particles are added to the lubricating oil to improve its lubrication effect [7,8,9,10,11], but the stability of metals is poor these easily oxidize under a high-temperature and high-pressure working environment, and the lubrication effect is unstable. At the same time, the preparation of nano-scale metal particles is difficult and the preparation cost is high, which is not conducive to large-scale industrial production. Subsequently, nano-scale SiO2 as a more common non-metallic oxide material, because of its high physical strength and strong chemical stability, is added as an additive to the lubricant to improve the lubrication performance [12,13,14,15], but the smaller scale of nano-SiO2 production cost is higher, and it is not easy to remove after metal processing. Nano-scale sulfides [16], diamond [17], rare earth [18], and other materials are used as additives to improve the lubrication effect of lubricating oil, but the relevant problem is that nanoparticles easily agglomerate and cannot be stably dispersed in the base solution, which has not been solved, and the relevant mechanism of using surfactants to disperse nanoparticles has not been fully explained.
With the continuous research and development of nanolubricants, researchers have found that adding a certain amount of surfactants can improve the stability [19,20,21,22] of nanoparticles dispersed in lubricating oil. As a traditional surfactant, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) has been used to disperse nano-copper oxide, which can have good dispersion stability in suspension under the condition of effectively controlling the pH of the solution. The surface modification of nano-copper with sodium dodecyl sulfate was carried out to obtain good dispersion properties [23] in ethylene glycol. Then, sodium dodecyl sulfate was also used to prepare the water-based nano-fluid of aluminum oxide, and the influence [24] of surfactant on its dispersion stability was analyzed. By increasing the concentration of Na+ ions in Fe3O4 crystals, the researchers used a sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to improve the stability of nanoparticle dispersion, but the content of hydroxide ions in the solution was too large, and the solution was in a strong alkaline state [25]. Oleic acid is also a more common surfactant. The use of oleic acid to modify nano-scale ZnO particles results in excellent dispersion stability of the nanofluid [26]. Researchers have employed various surfactants for the surface modification of ZnO nanoparticles to enhance their dispersion stability. Through Zeta potential analysis, SDBS was identified as the most effective surfactant, resulting in the smallest average aggregate size [27]. In recent years, researchers have found that the dispersion modification of nanoparticles by using composite surfactants has a good effect. At a certain temperature, the mixed-use of sodium polyacrylate and SDBS to disperse MoS2 nanoparticles will obtain a good dispersion of water-based nano-lubrication fluid, which has excellent resistance and wear resistance [16]. In this study, Fe3O4 nanoparticles were stably dispersed in water-based lubricants, and sodium oleate and sodium laurate composite surfactants were used to modify the surface of the particles, seeking a more stable dispersion effect.
With the development of rolling lubrication technology, water-based lubricants have been widely used for their unique advantages. Water-based lubricants not only have a low raw material cost, simple preparation method, and easy recycling, but also work at high temperatures, do not easily produce toxic and harmful gases, and have superior environmental protection performance. At the same time, in the process of rolling steel sheets, there is a lot of oxide scrap, as its main component is Fe3O4, and how to efficiently recycle these wastes has become an urgent problem to be solved. Fe3O4 is obtained through the collection and purification of the iron oxide scale. After undergoing steps such as nanoparticle synthesis and size control, surface functionalization, and lubricant integration, Fe3O4 nanoparticles are ultimately produced. In this study, the main waste of iron oxide Fe3O4 produced in the rolling process of steel was used as raw material to prepare a water-based nano-rolling lubricant, which not only meets the lubrication function, but also improves the rolling efficiency and reduces the production cost, and effectively solves the problem of harmful pollutants produced by the lubricating medium under high temperature and high pressure. Nano-scale Fe3O4 particles have high [28] physical strength, good supporting performance on the surface of the friction pair, and can effectively fill the area with surface defects, which can effectively promote the lubricant to reduce resistance and wear resistance. The nanolubricant prepared by composite surfactant has good particle stability and good wettability on the surface of common metals. Therefore, Fe3O4 water-based nano-rolling lubricant can be used in the lubrication system of the metal rolling process to reduce roll wear and effectively improve the quality of the metal surface.
2. Research Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
The main raw materials for preparing a water-based nano-rolling lubricant are as follows: 20 nm Fe3O4 nanoparticles, sodium oleate, sodium laurate, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS), and deionized water. The required material parameters are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The Fe3O4 (≥99.8%, 10 nm; ≥99.8%, 20 nm; ≥99.8%, 30 nm) nanoparticles with different diameters used in the experiments were purchased from Nangong Extreme Pressure Material Co., Ltd. (Xingtai, China).

Table 1.
Physical parameter of Fe3O4 nanoparticles.

Table 2.
Chemical parameters of surfactant.
2.2. Experimental Scheme
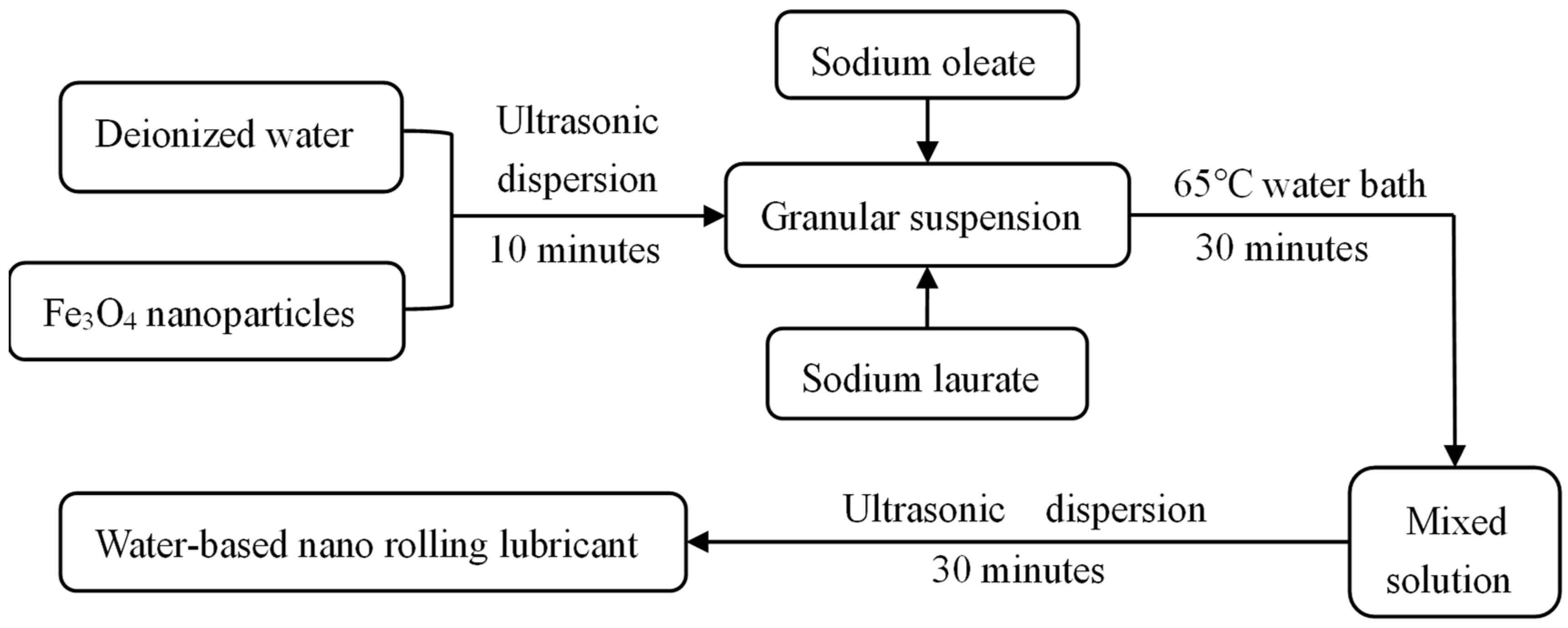
In this study, according to the method and theory of solution preparation, a preparation method of a water-based Fe3O4 nanolubricant was proposed [29]. A compound anionic surfactant was used to prepare the Fe3O4 water-based nano-rolling lubricant, and the lubricant was prepared by ultrasonic dispersion and a constant temperature water bath device, as shown in Figure 1. Firstly, the nano-particles were fully mixed with deionized water by an ultrasonic dispersion device, and the agglomerated nano-particles were effectively dispersed. Then, the composite surfactant, which is made of sodium oleate and sodium laurate at a 1:1 mass ratio, was added to the particle suspension. In a constant temperature water bath at 65 °C, it was ensured that the surfactant was fully coated onto the nanoparticles. Finally, the coated nanoparticles were evenly dispersed into the water-based solution by an ultrasonic dispersion device.
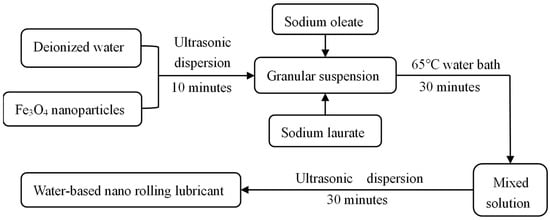
Figure 1.
Preparation method of water-base rolling lubricant.
The particle stability of water-based solutions prepared by different surfactants was analyzed by a potential analyzer, the wettability of the solutions related to different surfactants on the surface of copper and aluminum plates were measured by a contact angle-measuring instrument, and the related properties of the composite anionic modification method were characterized.
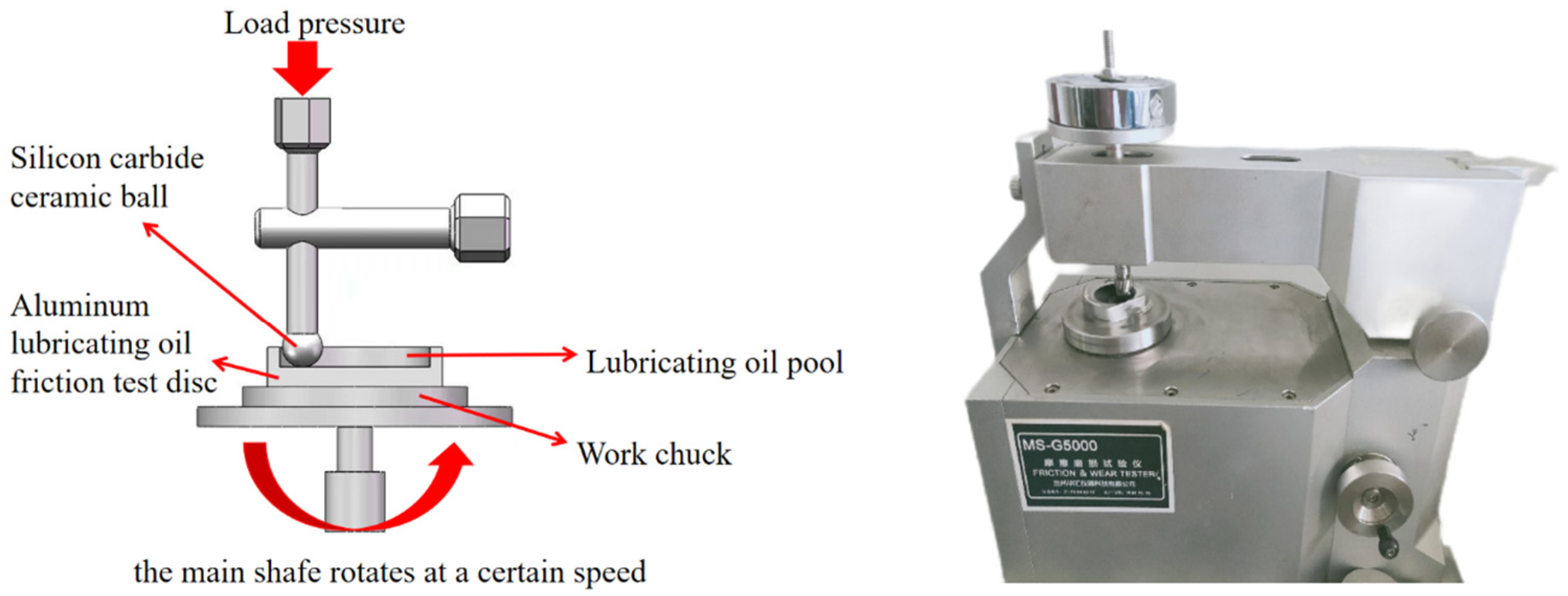
The tribological properties of water-based nano-rolling lubricants with different particle concentrations were tested by a universal friction and wear-testing machine. The structure of the friction and wear-testing machine is shown in Figure 2. The model of the universal friction and wear tester is MS-G5000, which was produced in January 2019 by Lanzhou Huahui Instrument Technology Co., LTD (Lanzhou, China). Its related performance indicators are shown in Table 3. The aluminum testing disc to be tested was machined by CNC, and the testing disc was fixed above the workpiece chuck. The experiment utilized brand-new silicon carbide balls with polished surfaces. The average value of the surface roughness of the aluminum disk used in the experiment was 0.0708, as measured by the instrument. A water-based lubricating liquid containing different particle concentrations was added to the lubricating pool area of the testing disc so that the test silicon carbide ball was in contact with the bottom of the lubricating pool of the testing disc at a certain load pressure, and the testing disc was rotated at a certain speed by driving the spindle. Thus, the influence of the concentration of nanoparticles on the tribological properties of lubricants was analyzed. The friction and wear traces were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy to explore the mechanism of friction reduction and wear resistance of nanoparticles. The water-based lubricant was applied in the lubrication system of four high micro-rolling mills, and the experiment of aluminum plate rolling was carried out. The surface roughness of the aluminum plate was measured by a surface-roughness-measuring instrument under different rolling forces, and the lubrication effect of the water-based nano-rolling lubricant was analyzed.
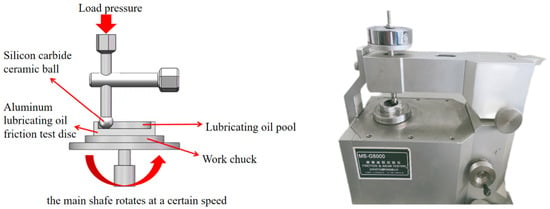
Figure 2.
Structure diagram of friction and wear-testing machine.

Table 3.
Measuring range of technical parameters of MS-G5000 friction and wear-testing machine.
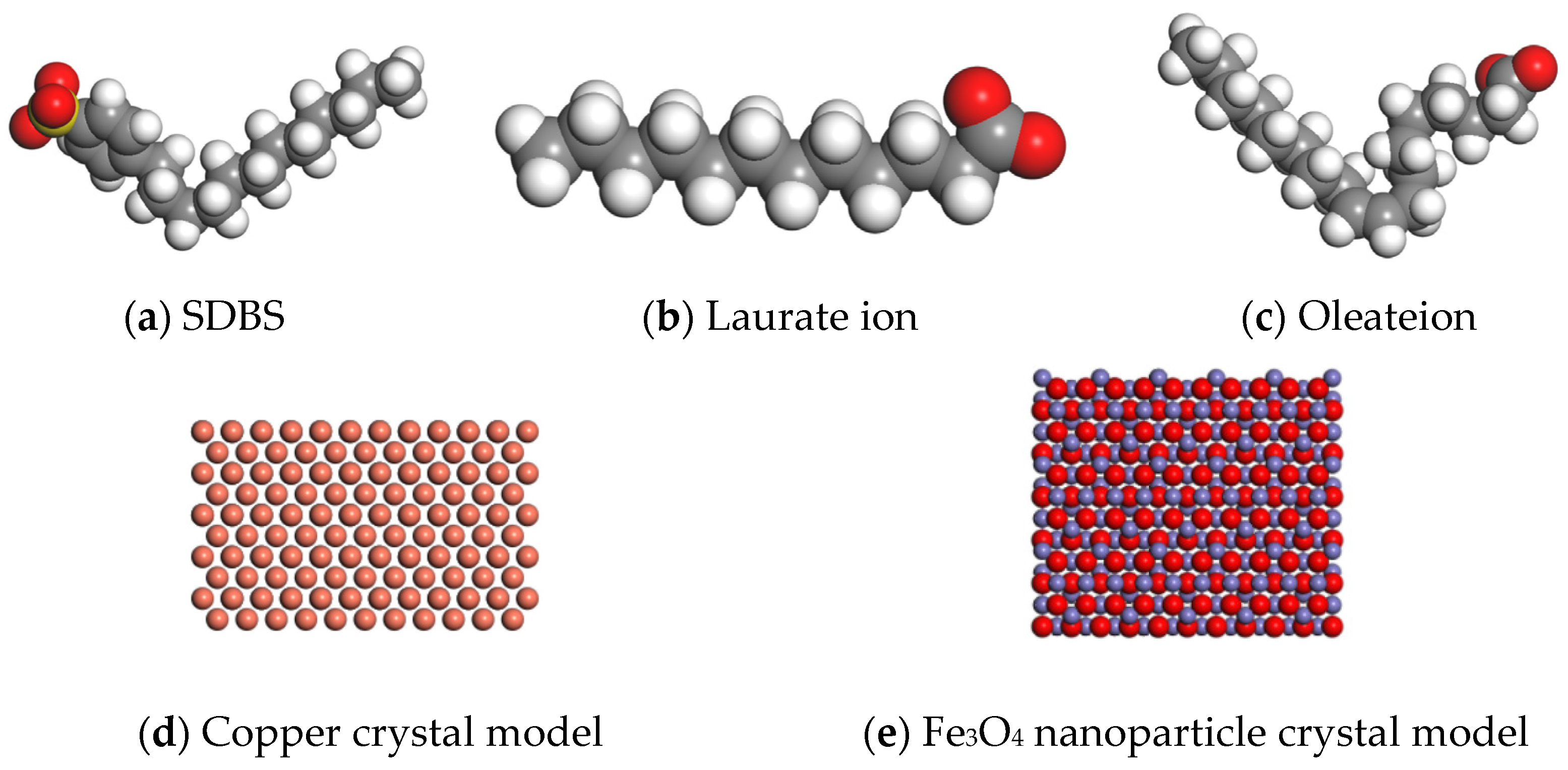
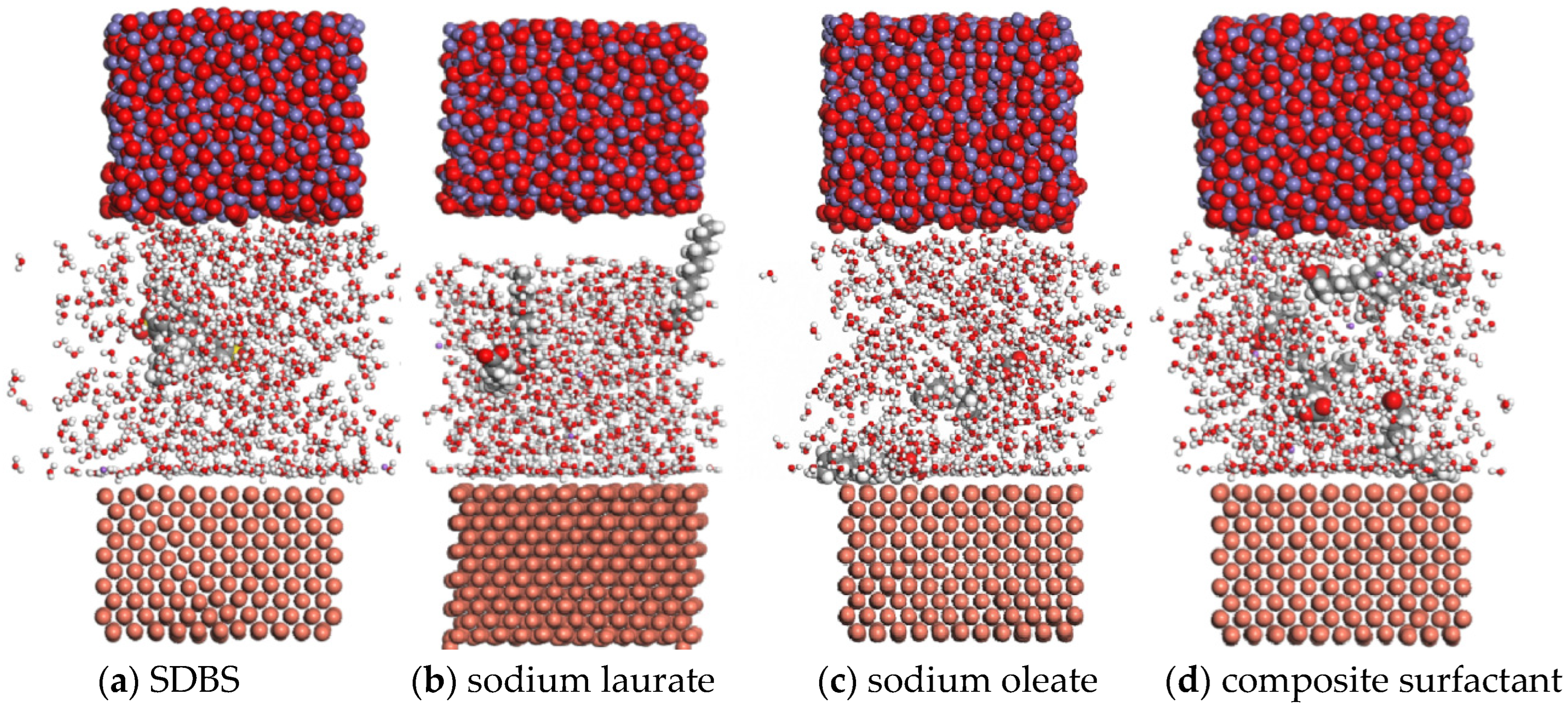
We applied nanoscale lubrication technology in the field of non-ferrous metals, conducting relevant tests on both copper and aluminum. Tribological tests were performed on aluminum discs, and the application mechanisms related to copper were also discussed. Based on the theory of molecular dynamics, the simulation of water-based Fe3O4 nanolubricants containing different surfactants during the rolling of the copper strip was carried out by numerical analysis. In the molecular dynamics simulation module of the simulation software Materials Studio, COMPASS II was selected as the molecular simulation force field, and molecular structural models and crystal models of different materials were established, as shown in Figure 3. The molecular model of SDBS is shown in Figure 3a; the molecular model of laurate is shown in Figure 3b; the molecular model of oleate is shown in Figure 3c; the surface model of copper crystal [0, 0, 1] is shown in Figure 3d; the surface model of Fe3O4 nanoparticle crystal [0, 0, 1] is shown in Figure 3e.
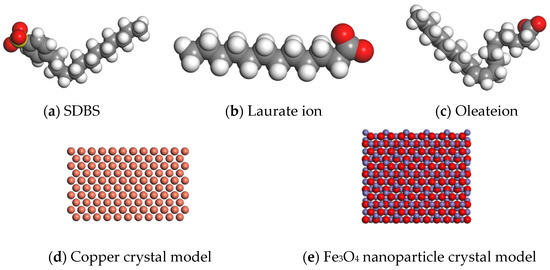
Figure 3.
The model of different materials in a molecular dynamic simulation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dispersion Stability Test of Water-Based Lubricant
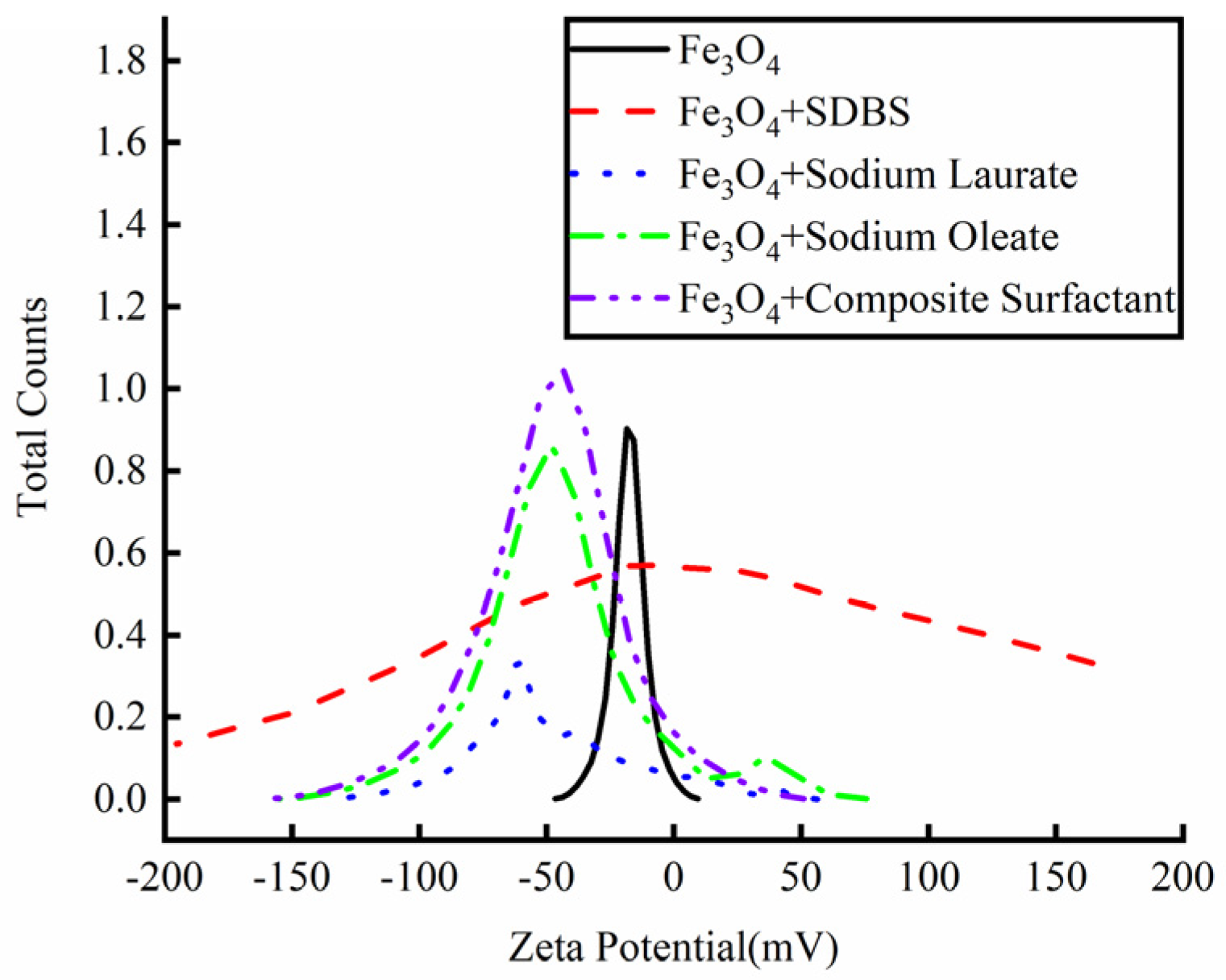
Aqueous nanoparticles with different surfactants were prepared and the dispersion stability of the nanoparticles was analyzed by a potential analyzer, as shown in Figure 4. When only Fe3O4 nanoparticles were added to the aqueous solution, the highest potential was −16.52 mV and there was only one peak value, indicating that most of the particles were unstable in the deionized aqueous solution. With the addition of different kinds of surfactants to the solution, the potential intensity of the particles in the solution showed different changes. When SDBS was added into the solution as a surfactant to modify the Fe3O4 nanoparticles, the maximum potential value of the solution was −0.86 mV, indicating that the addition of SDBS not only did not coat the nanoparticles, but destroyed the stability of the aqueous solution, and the nanoparticles were more prone to sedimentation and agglomeration. Sodium laurate was added to the solution as a surfactant alone, and the maximum potential value of the solution was −52.74 mV, indicating that laurate could modify the nanoparticles well, and the solution was more stable. However, two peaks were found by observing the potential intensity curve. When the potential value was −32.74 mV, the solution contained particles of a certain strength. Therefore, the existence of these particles will have a certain impact on the stability of the solution. When sodium oleate was added to the nanoparticle solution, the maximum potential value of the solution appeared at −48.04 mV, indicating that oleate ions had a certain effect on the modification of the nanoparticles and the solution became more stable. However, like sodium laurate, a certain number of particles appeared in the solution when the potential value was 34.47 mV, and these particles destroyed the stability of the solution. When sodium laurate and sodium oleate were added into the solution as composite surfactants to modify the nanoparticles, the maximum potential of the solution appeared at −43.45 mV, and the potential strength curve of the particles in the solution contained only one peak. Therefore, most of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles were statically dispersed in the water-based solution under the action of the surfactant. Therefore, this study intends to use composite surfactants to modify the surface of the nanoparticles and prepare a water-based nano-rolling lubricant.
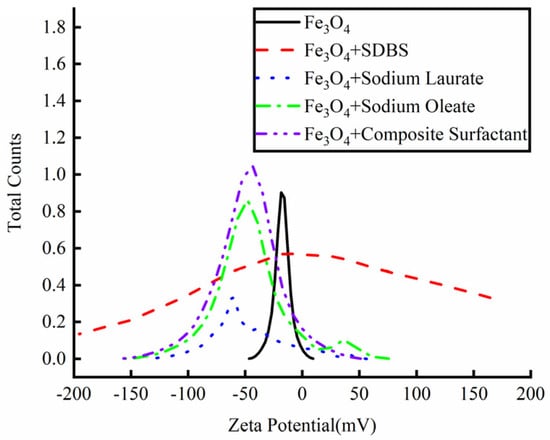
Figure 4.
Zeta potential strength of different active agent solutions.
3.2. Wettability Test of Water-Based Lubricant
The wettability of a rolling lubricant is an important index to measure its adsorption and spreading ability on the surface of the material. Good wettability can effectively spread the lubricant between the roll and the rolled piece, and at the same time, the lubricant can quickly enter the rolling deformation area through dynamic pressure, effectively improve the rolling quality, avoid roll wear, and reduce rolling power consumption. Therefore, it is of great significance to test the wettability of the rolling lubricant.
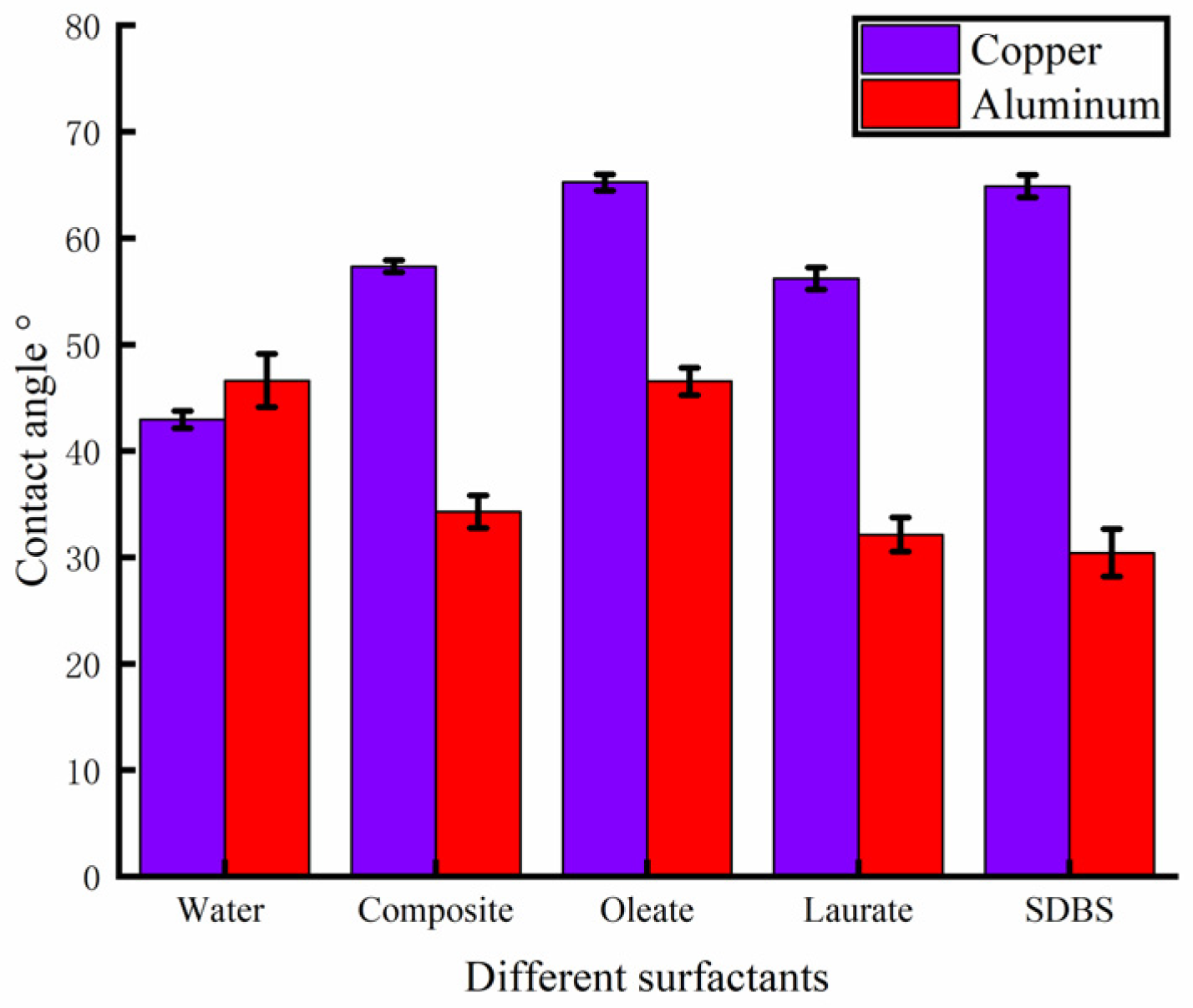
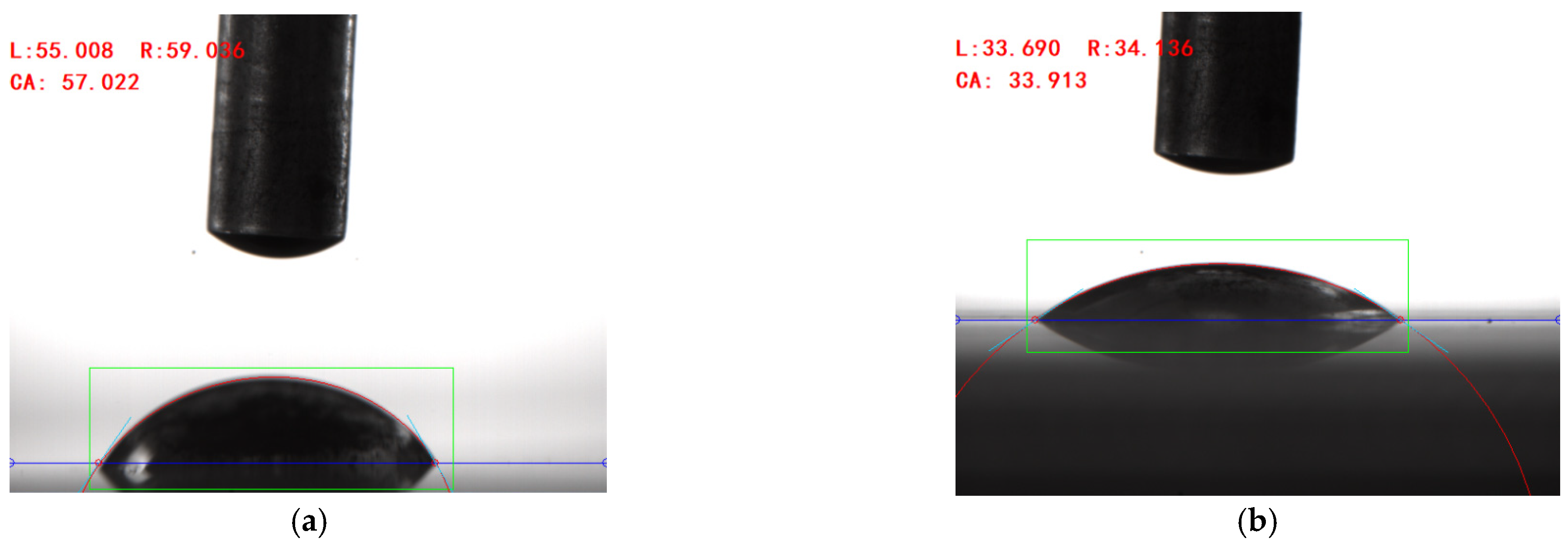
A contact angle-measuring instrument was used to measure the contact angle of the solution prepared with different surfactants on the surface of the rolled copper plate and the aluminum plate, and the results are shown in Figure 5. After many measurements, the wettability of the solution added with surfactants on the surface of the copper plate to be processed was reduced compared with that of deionized water. The mean contact angle of the composite surfactant solution was 57.34°, and the contact angle measured in one test was 57.02°, as shown in Figure 6a, indicating better wettability. On the surface of the aluminum plate to be processed, compared with deionized water, the wettability of the solution with the addition of composite active agent, sodium laurate, SDBS, and other active agents was improved. The mean contact angle of the composite active agent solution on the surface of the aluminum plate was 34.30°, and the contact angle measured in one test was 33.91°, as shown in Figure 6b, showing good wettability. Therefore, the water-based nano-rolling lubricant prepared in this study has good wettability on the surface of copper plate and aluminum plate. When rolling copper/aluminum sheets, the lubricant has good spreading and adsorption properties, which can effectively enter the processing area to protect the surface of the roll and rolled parts, improve the rolling quality, and reduce the rolling power consumption.
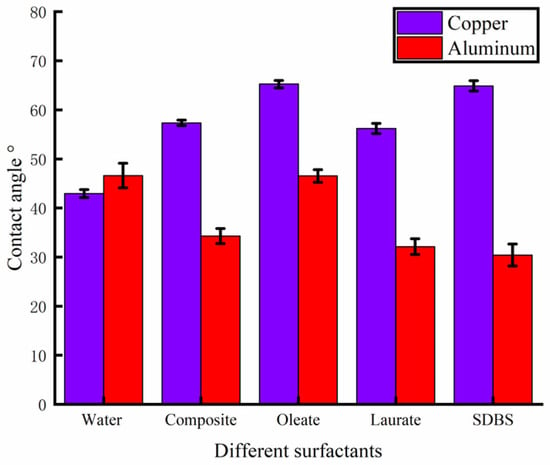
Figure 5.
Contact angle between different surfactants and copper/aluminum surface.
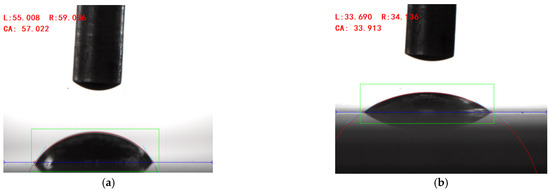
Figure 6.
Contact angle of water-based nano-rolling lubricant on copper/aluminum surface. (a) Contact angle between water-based rolling lubricants and copper surface. (b) Contact angle of water-based rolling lubricant on the surface of aluminum plate.
3.3. Frictional Performance Test of Water-Based Lubricants
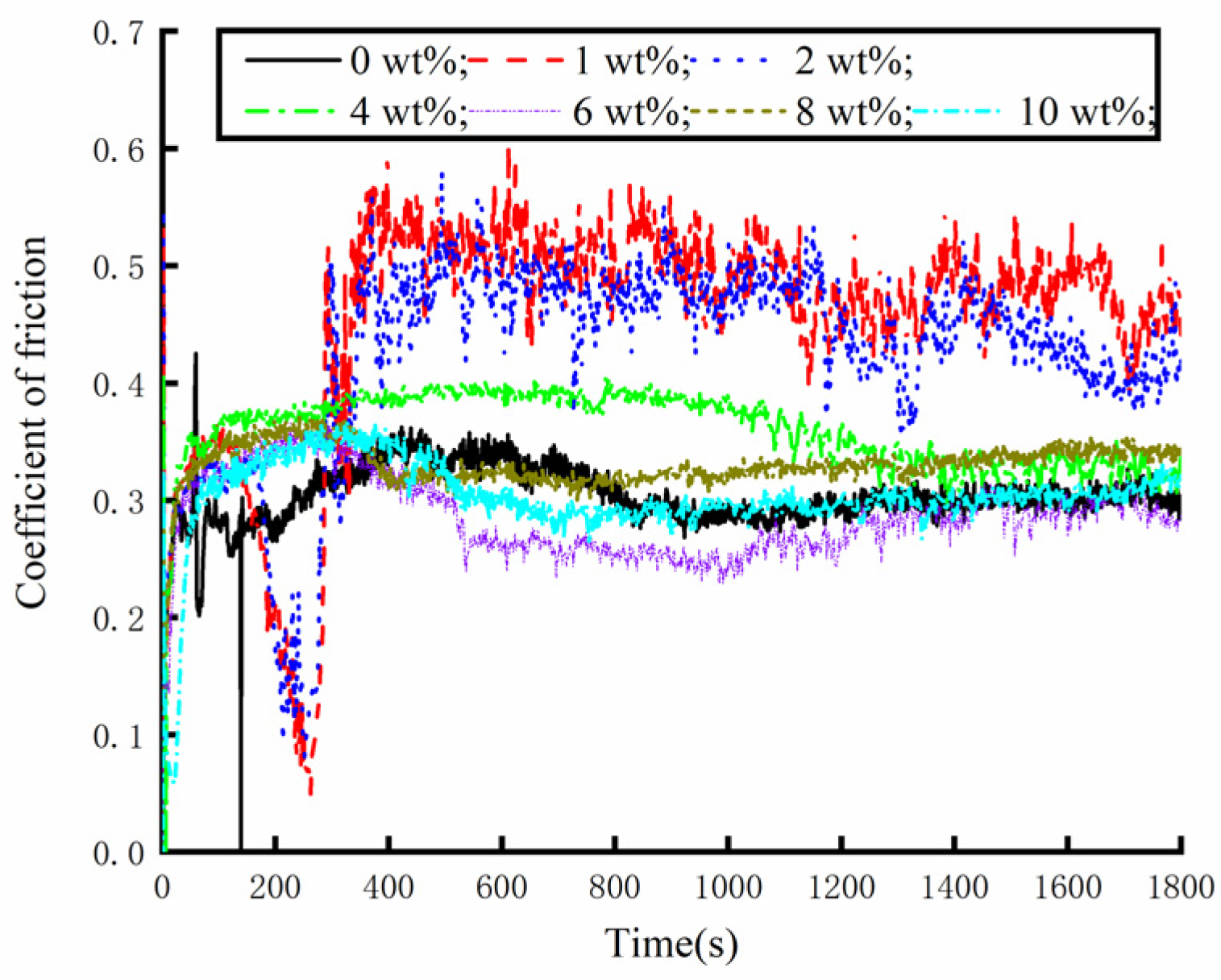
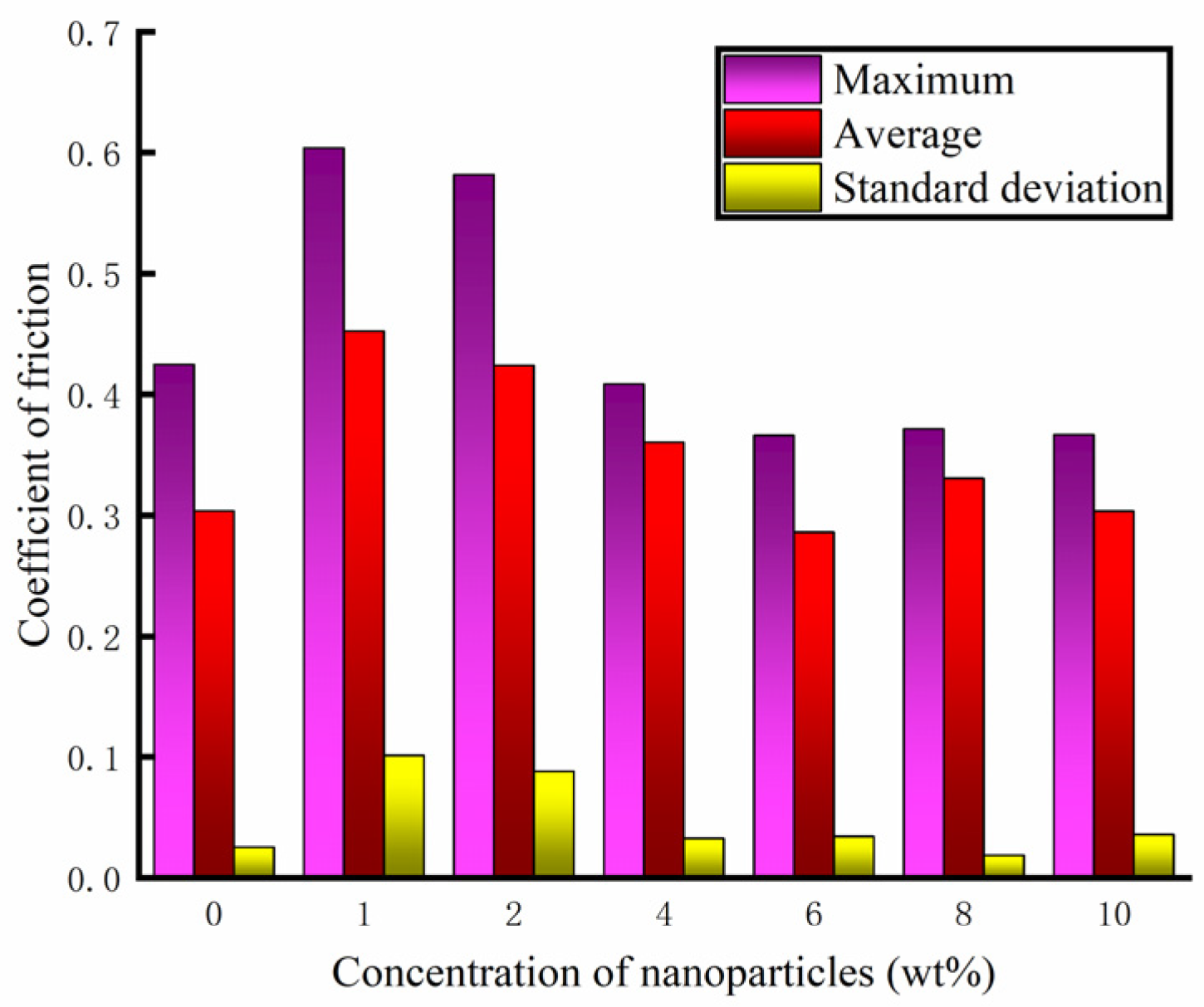
The friction and wear-testing machine was used to test different concentrations of water-based nano-rolling lubricants. The load mass added above the silicon carbide ball was 500 g, the spindle speed was 300 r/min, and the test duration was 30 min. During the friction and wear tests, the friction force between the silicon carbide ball and aluminum workpiece was measured, and the friction coefficient was calculated. The friction coefficient of the water-based lubricant containing different Fe3O4 nanoparticle concentrations is shown in Figure 7. When the nanoparticle concentration is lower than 4 wt%, the nanoparticle destroys the fluidity of the water-based lubricant, making the lubricant drag reduction and wear resistance worse. At the same time, it can be seen from the figure that the tribological properties of 1 wt% and 2 wt% are very unstable. The lubricant has good anti-wear performance within 5 min before the test, and the friction performance decreases greatly after 5 min. When the particle concentration is 6 wt%, the lubricant has the best drag reduction and wear resistance effect, and the friction coefficient is the smallest. The water-based nanolubricant shows good lubrication characteristics within 30 min of the test. Under the action of compound surfactants, the 6 wt% nanoparticle concentration not only ensures sufficient dispersion of particles to prevent agglomeration but also forms a continuous and stable protective film that isolates the friction contact surfaces, thereby significantly reducing frictional wear. When the lubricant particle concentration exceeds 6 wt%, increased particle loading intensifies the agglomeration phenomena. This results in the formation of large solid particles within the friction pair, which subsequently deteriorates the lubrication performance. Especially when the concentration increases to 8 wt%, during the test time, the friction coefficient of silicon carbide ball and aluminum test disk is greater than that of the water-based solution with a particle concentration of 6 wt%. Through the analysis of the friction coefficient data obtained during the test time, the maximum value, average value and standard deviation of the friction coefficient under different particle concentrations of the lubricant are obtained, as shown in Figure 8. The standard deviation of different particle concentrations is controlled below 0.1; so, the deviation degree of the data is small and the reliability is high. As can be seen from Figure 8, when the particle concentration is 6 wt%, the maximum value and average value of the friction coefficient are the smallest. Therefore, when the concentration of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in a water-based lubricant is 6 wt%, the drag reduction and wear resistance of the lubricant are the best.
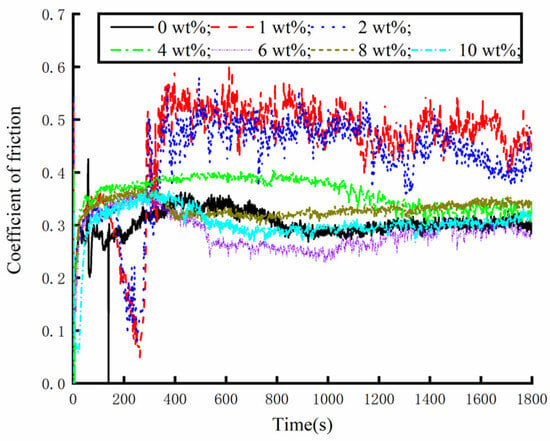
Figure 7.
Friction coefficient of different water-based nanolubricants in tribometer testing.
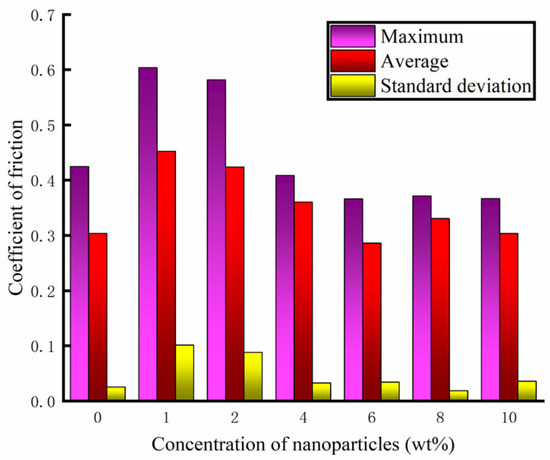
Figure 8.
Numerical statistics of friction coefficient.
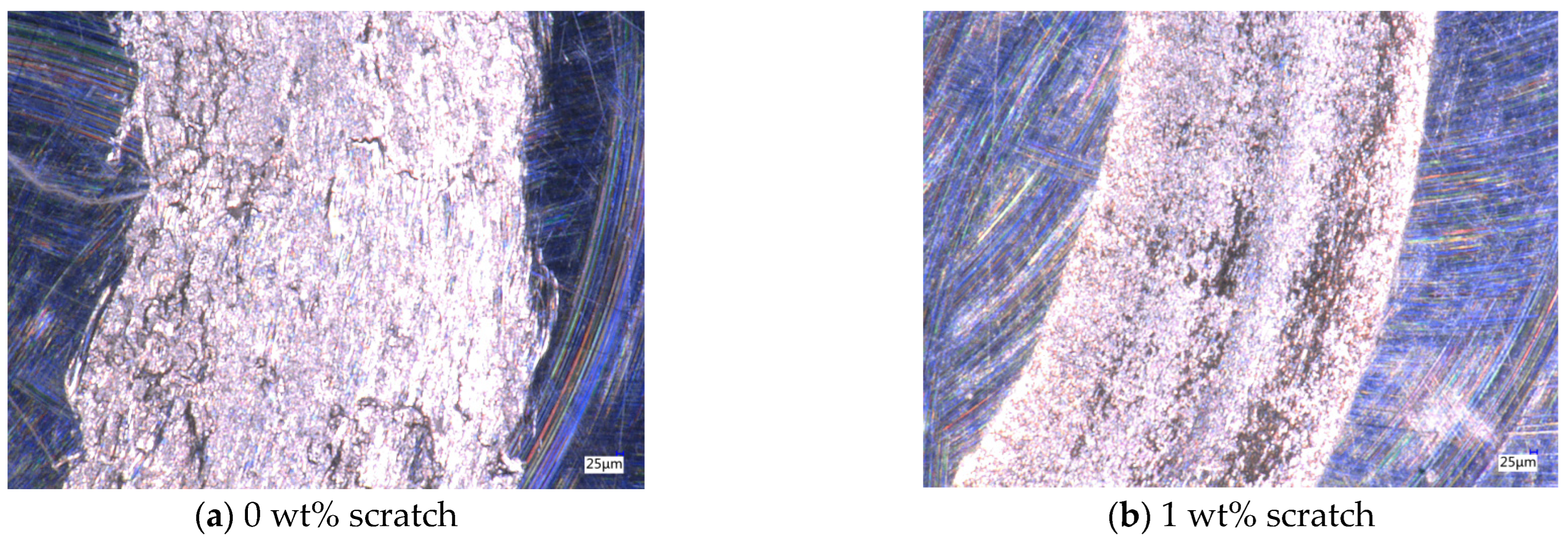
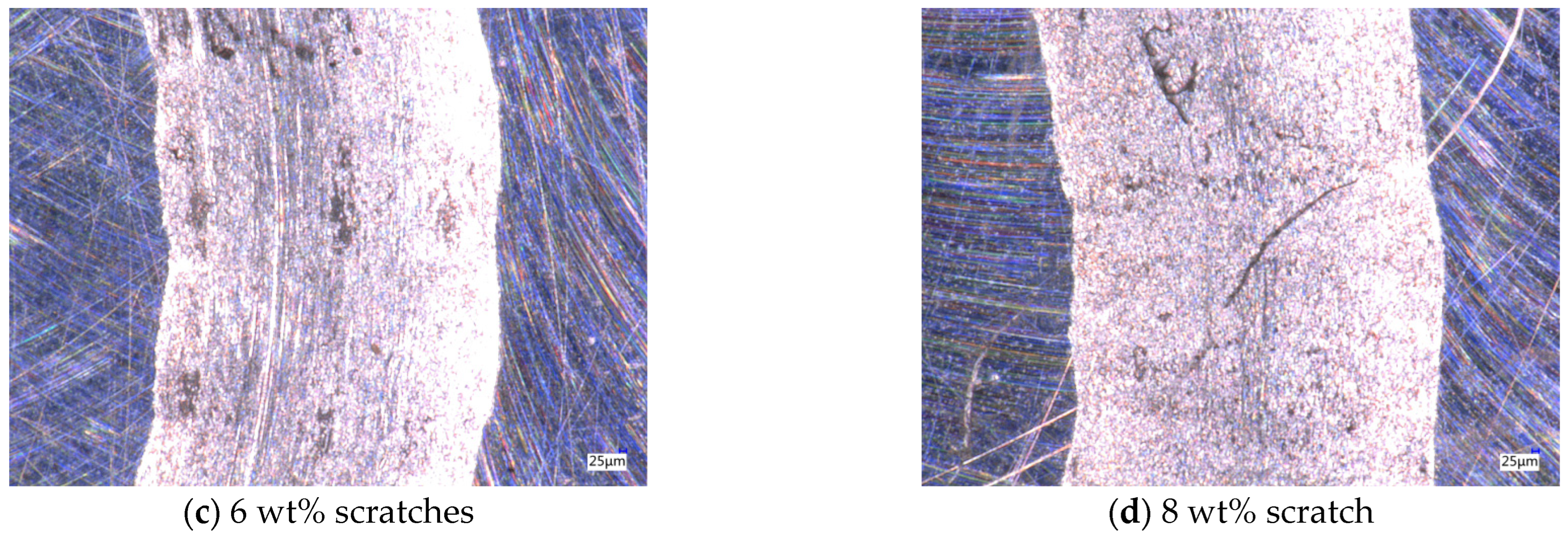
After the friction and wear test, the friction marks of the aluminum testing disc were observed by using a depth-of-field microscope, as shown in Figure 9. The average friction values for different particle concentrations remain close to each other over extended time ranges, but in the 0–400 s time period, there is a sharp shift in the friction values, which leads to an increase in friction in this time period, and ultimately leads to a different wear profile. Without nanoparticles added to the base solution, the friction marks in the aluminum disk are very rough and the edges are very irregular, as shown in Figure 9a. With the addition of nanoparticles, the inside of the friction marks becomes smoother, but when the concentration of nanoparticles is low, a wider gully appears in the middle of the friction marks. The lubricant particle concentration is not enough to form an effective protective film on the surface of the test workpiece; so, a wider gully appears, and, at the same time, the nanoparticles are deposited in the gully, as shown in Figure 9b. When the concentration is 6 wt%, the width of the gully is significantly reduced, the deposition phenomenon is reduced, and the lubricant has a good lubrication effect, as shown in Figure 9c. When the concentration is 8 wt%, due to the increase in nanoparticle concentration, the agglomeration phenomenon increases, and large particles appear in the lubricant, thus causing scratches on the surface of the friction pair perpendicular to the motion trajectory, as shown in Figure 9d. Therefore, by observing the scratches on the test disc in the friction and wear test, it can be determined that when the concentration of Fe3O4 nanoparticles is 6 wt%, the friction and wear performance of the water-based nano-rolling lubricant is the best.
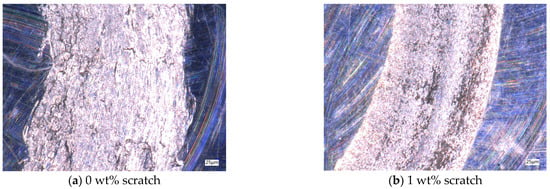
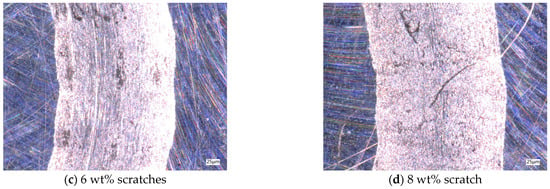
Figure 9.
Scratches on aluminum test plate for friction and wear test.
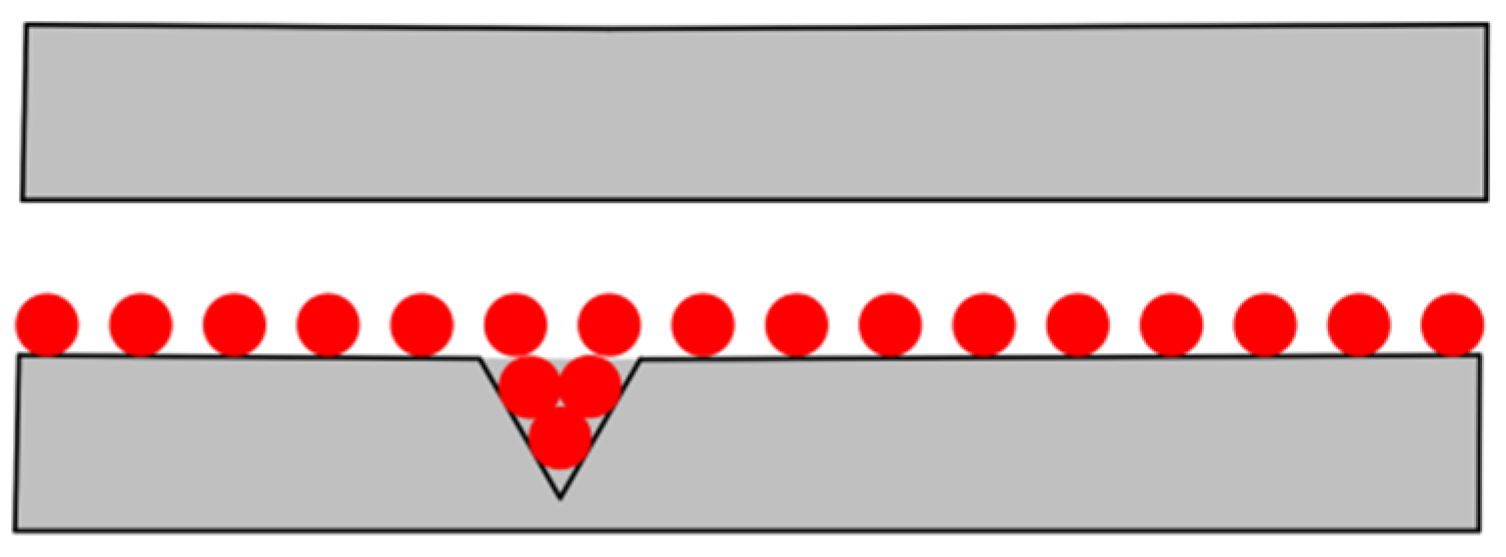
When the water-based nano-rolling lubricant is applied to the surface of the friction pair for lubrication, it is generally believed that the presence of nanoparticles can make the lubricant evenly distributed on the surface of the friction pair, and, at the same time, fill the parts with poor quality on the surface of the friction pair to ensure low friction resistance during the working process, as shown in Figure 10. Due to the high hardness of Fe3O4 nanoparticles, they can form a supporting effect between the roll and the rolled part, effectively prevent roll wear, and improve the processing quality of the rolled part. In order to further explore the lubrication mechanism of the nanolubricant, this study tested the friction marks on the aluminum test disc in the friction and wear test.
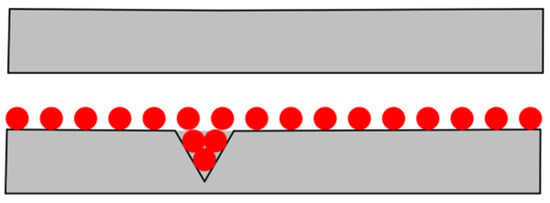
Figure 10.
Lubrication mechanism of nanoparticles in friction pair.
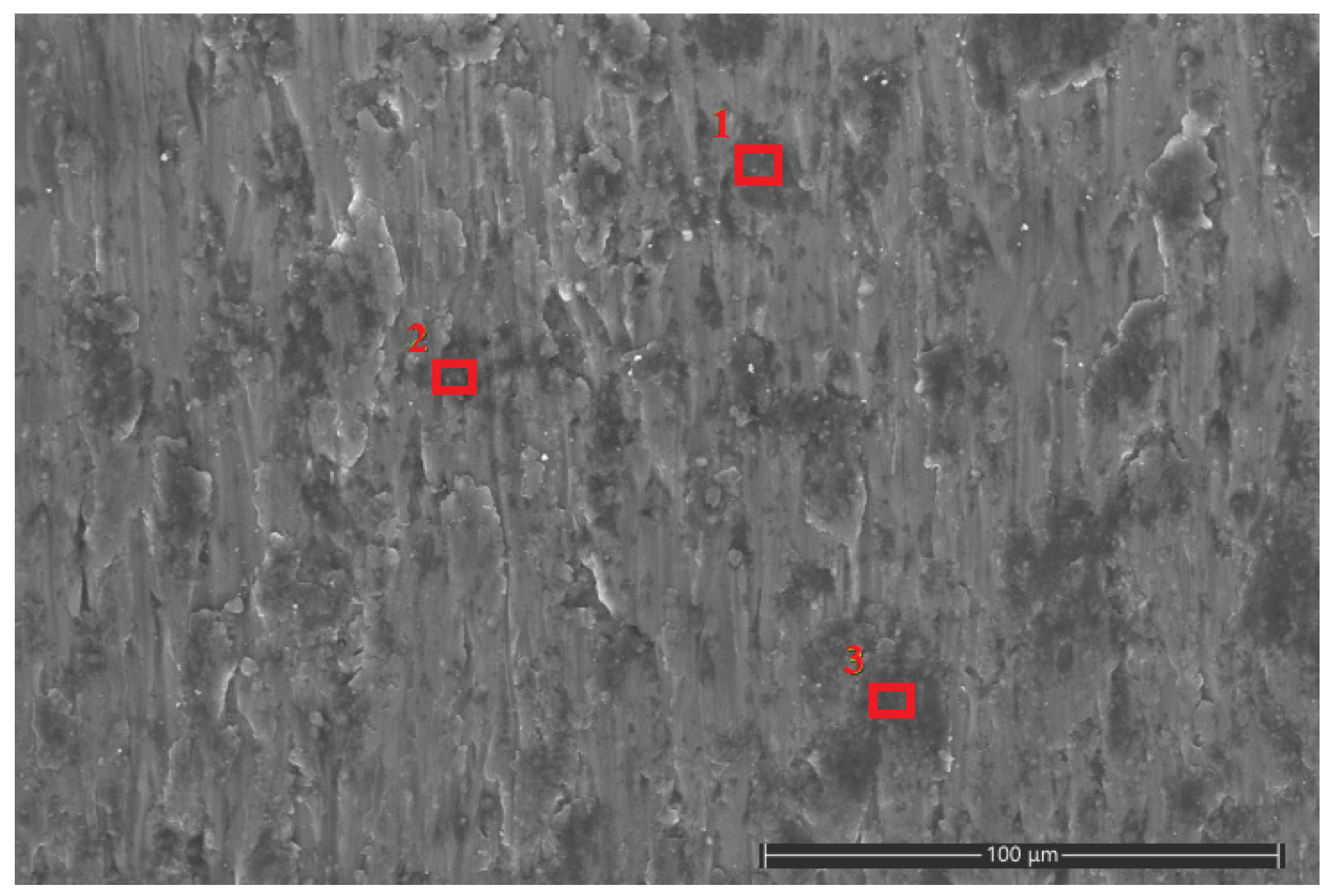
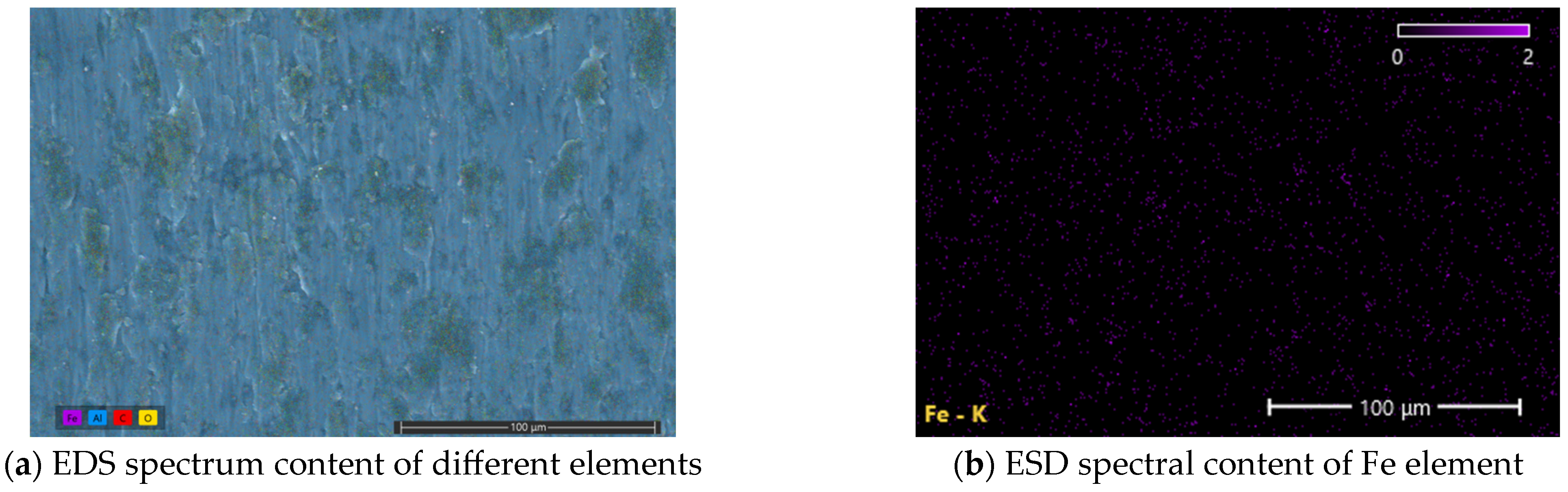
Based on the lubrication mechanism, it is inferred that the black residue in the scratches of the test disk is Fe3O4 nanoparticles. In order to further study the lubrication mechanism of the water-based nano-rolling lubricant prepared in this study, the scratch area was analyzed by energy spectrum using scanning electron microscopy. Marks of the friction and wear test of the water-based nanolubricant with a concentration of 6 wt% were analyzed by energy spectrum analysis. Three points with darker colors were selected for point scanning, and the contents of different metal elements at the three points were analyzed, as shown in Figure 11. The locations of the three red squares in the figure are the three sample points we selected. According to EDS scanning analysis, the three points of scratches all contain a certain amount of Fe element; the specific content is shown in Table 4.
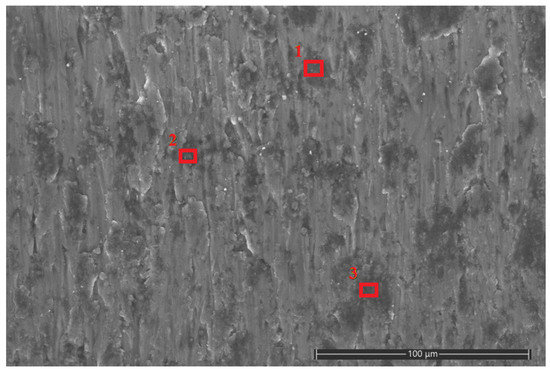
Figure 11.
Scratches of aluminum test plate in SEM. The locations of the three red squares in the figure are the three sample points we selected.

Table 4.
Content of different elements in selected three points.
At the same time, EDS surface scanning was carried out for the areas where scratches were observed. The scanning results are shown in Figure 12. Through analysis, it can be seen that there are certain iron elements in the internal areas of scratches of the aluminum test disc, and these iron elements are concentrated in the positions where surface defects exist. These particles are filled in the area with defects on the surface of the friction pair to reduce the expansion of the defect location. At the same time, in the smooth area of the friction pair, support is formed to protect the surface of the friction pair.
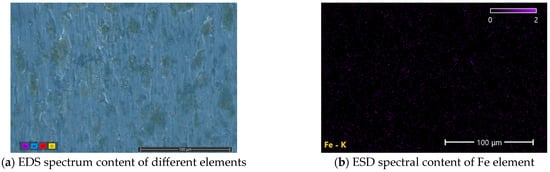
Figure 12.
EDS spectral scan results of scratches in aluminum test plate.
3.4. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
Based on the theory of molecular dynamics, the lubrication state of the Fe3O4 water-based nano-rolling lubricant on the surface of a copper plate was simulated in this paper. When the lubricant contacts the copper plate for 80 ps, the energy is essentially stable. In order to analyze the influence of different surfactants on the lubricant, the molecular dynamic trajectory diagram of the lubricant in contact with the copper surface at 80 ps is shown in Figure 13. When SDBS is selected as a surfactant, the lubricant base liquid molecules are fully dispersed between the nanoparticle and the surface to be processed, but water molecules with lower energy are mainly concentrated on the surface of the nanoparticle, as shown in Figure 13a.
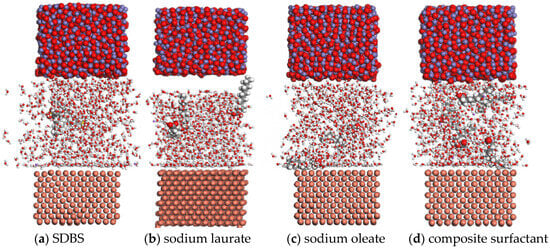
Figure 13.
Molecular dynamic trajectories of a lubricant prepared with different surfactants in contact with a copper plate at 80 ps.
When sodium laurate is added to the lubricant as a surfactant, most of the base solution is adsorbed by the copper surface, and the nanoparticles are free in the base solution, which makes it difficult to achieve the lubrication effect, as interatomic position changes of copper atoms in the surface layer occur due to the adsorption of sodium laurate on the surface, as shown in Figure 13b. When sodium oleate is used as a surfactant to prepare a lubricant, the basic solution has good dispersion performance between the nanoparticles and the surface to be processed. At the same time, oleate molecules with large energy are adsorbed on the surface of the workpiece to be processed, which can improve the processing lubrication effect of the lubricant. However, water molecules with small energy are mainly adsorbed on the surface of the nanoparticles. Therefore, it is difficult for nanoparticles to have a good lubrication effect when oleic acid is the surfactant, as shown in Figure 13c. When the composite active agent of sodium oleate and sodium laurate is used as a surfactant, the lubricant has a good dispersion on the surface of the nanoparticles and the workpiece; while laurate increases the adsorption ability of the base solution to the nanoparticles, oleate enhances the adsorption ability of the workpiece surface to the lubricant, which can make the nanolubricant have a good lubrication effect, as shown in Figure 13d.
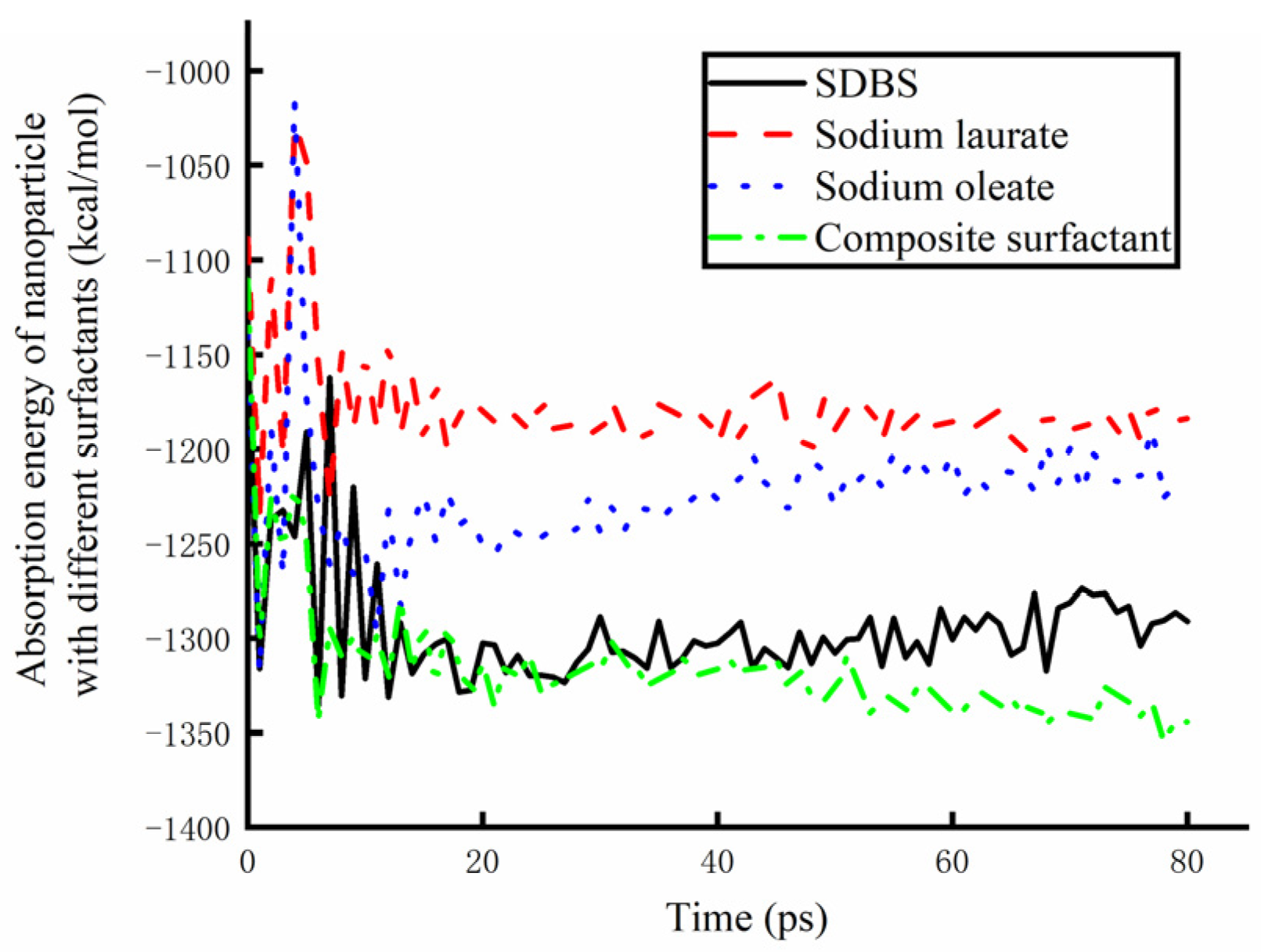
In order to further analyze the lubrication mechanism of water-based nanolubricants, the surface adsorption energy of nanoparticles in lubricants prepared by different surfactants in the molecular dynamic simulation was statistically analyzed, as shown in Figure 14. Starting from the lubricant touching the surface of the copper plate, the adsorption energy of the nanoparticle surface to the base solution reached a stable state after 20 ps. The larger the absolute value of adsorption energy is, the better the adsorption effect is. Therefore, it can be found from the figure that sodium laurate has the worst adsorption effect on nanoparticles, and the composite surfactant has the best adsorption effect on the surface of nanoparticles. Therefore, the Fe3O4 water-based nano-rolling lubricant prepared by the composite surfactant has a good lubrication effect.
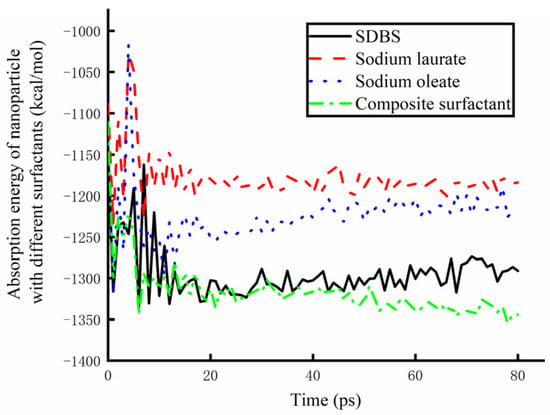
Figure 14.
The absorption energy of nanoparticles in lubricants containing different surfactants.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we developed a novel method for preparing water-based Fe3O4 nanolubricants for rolling applications using composite surfactants, demonstrating enhanced stability of nanoparticle dispersion. The prepared lubricants exhibited excellent wettability on both copper and aluminum surfaces with contact angles of 57.02° and 33.91°, respectively. Notably, the lubricants exhibited excellent drag reduction and anti-wear properties when the concentration of Fe3O4 nanoparticles was increased to 6wt%. The analysis of the lubrication mechanism based on molecular nomenclature theory showed that the composite surfactant enhanced the surface adsorption capacity of Fe3O4 crystals, which improved the lubrication effect of the water-based lubricant. The Zeta potential of the lubricant containing the complex surfactant was −43.45 mV, indicating that the complex surfactant resulted in a significant increase in nanoparticle dispersion stability. After friction and wear tests with this lubricant, the interior of the moat was found to be smoother under a scanning electron microscope. In addition, friction and wear tests showed that the lubricant containing 6 wt% Fe3O4 nanoparticles had higher tribological performance. X-ray energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis confirmed the presence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in the scratches, suggesting that they were uniformly distributed and acted as a separator of friction sub-particles during the lubrication process, which facilitated the formation of lubrication film. The more uniformly the nanoparticles are dispersed, the more favorable the formation of protective film is. The film formation effect was also identified based on the elemental concentration to ensure that the most suitable concentration was found. Numerical simulations of the molecular interactions within the water-based nanolubricant containing the surfactant complex were performed to gain insight into the superior absorption of Fe3O4 crystals by the surfactant complex compared to other surfactants. Together, these findings validate the efficacy of the proposed lubricant in improving tribological performance and provide a theoretical basis for the development of advanced nanolubricant formulations.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.Z. and C.H.; software, Y.Z. and C.H.; formal analysis, Y.Z., Z.L. and C.H.; investigation, Y.Z., Z.L. and C.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. and Z.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z. and Z.L.; supervision, Y.Z.; project administration, Y.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Doctoral Fund of University of science and technology Liaoning. Grant number: 6003000422.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Spikes, H. Friction modifier additives. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 60, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, F.; Barber, G.C.; Zou, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Q. Role of nano-sized materials as lubricant additives in friction and wear reduction: A review. Wear 2022, 490, 204206. [Google Scholar]
- Vattikuti, S.P.; Byon, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Molybdenum Disulfide Nanoflowers and Nanosheets: Nanotribology. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 710462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Jiang, Z. Friction and Wear Characteristics of Fe3O4 Nano-Additive Lubricant in Micro-Rolling. Lubricants 2023, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Kamali, H.; Huo, M.; Lin, F.; Huang, S.; Huang, H.; Jiao, S.; Xing, Z.; Jiang, Z. Eco-Friendly Water-Based Nanolubricants for Industrial-Scale Hot Steel Rolling. Lubricants 2020, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Xia, W.; Cheng, X.; He, A.; Yun, J.H.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Jiao, S.; Huang, L.; et al. Analysis of TiO2 nano-additive water-based lubricants in hot rolling of microalloyed steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 27, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yi, X.U.; Shi, P.; Xu, B.-S.; Wang, X.-L.; Liu, Q. Tribological properties and lubricating mechanisms of Cu nanoparticles in lubricant. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, C.; Hwang, Y.; Park, M.; Lee, J.; Choi, C.; Jung, M. Tribological behavior of copper nanoparticles as additives in oil. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, e124–e127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.S.; Xu, B.S.; Xu, Y.; Gao, F.; Shi, P.-J.; Wu, Y.-X. Cu nanoparticles effect on the tribological properties of hydrosilicate powders as lubricant additive for steel–steel contacts. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 878–886. [Google Scholar]
- Padgurskas, J.; Rukuiza, R.; Prosyčevas, I.; Kreivaitis, R. Tribological properties of lubricant additives of Fe, Cu and Co nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2013, 60, 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Song, S.; Yang, G.; Yu, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, P. Preparation and tribological properties of surface-capped copper nanoparticle as a water-based lubricant additive. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 54, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dang, H. Surface-modification in situ of nano-SiO2 and its structure and tribological properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 7856–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.X.; Chen, C.H.; Kang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Chang, S. Size effects of SiO2 nanoparticles as oil additives on tribology of lubricant. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2010, 62, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Men, X.H. The tribological behaviors of the polyurethane coating filled with nano-SiO2 under different lubrication conditions. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, S.Y.; Bassyony, E.Z.; Sarhan, A.A.D. Development of SiO2 nanolubrication system to be used in sliding bearings. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Sun, J.; He, J.; Yan, X.; Pei, Y. Recycling prospect and sustainable lubrication mechanism of water-based MoS2 nano-lubricant for steel cold rolling process. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123991. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.X.; Kang, Y.; Hwang, R.M.; Shyr, S.; Chang, Y. Tribological properties of diamond and SiO2 nanoparticles added in paraffin. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.N.; Harsha, A.P. Antiwear and extreme pressure performance of castor oil with nano-additives. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2018, 232, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, H.W.; Azmi, W.H.; Usri, N.A.; Mamat, R.; Adam, N. Thermal conductivity and viscosity of Al2O3 nanofluids for different based ratio of water and ethylene glycol mixture. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. Int. J. Exp. Heat Transf. Thermodyn. Fluid Mech. 2017, 81, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Ebata, A.; Teramae, K. Alteration of thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles (dispersion of γ-Al2O3, SiO2 and TiO2 ultra-fine particles). Netsu Bussei 1993, 7, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranmanesh, S.; Mehrali, M.; Sadeghinezhad, E.; Ang, B.C.; Ong, H.C.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. Evaluation of viscosity and thermal conductivity of graphene nanoplatelets nanofluids through a combined experimental–statistical approach using respond surface methodology method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 79, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sonawane, S.S.; Juwar, V. Optimization of conditions for an enhancement of thermal conductivity and minimization of viscosity of ethylene glycol based Fe3O4 nanofluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 109, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zin, V.; Agresti, F.; Barison, S.; Colla, L.; Gondolini, A.; Fabrizio, M. The Synthesis and Effect of Copper Nanoparticles on the Tribological Properties of Lubricant Oils. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2013, 12, 751–759. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.; Jiang, H.; Liu, R.; Zhai, Y. Effects of surfactant on the stability and thermal conductivity of Al2O3/de-ionized water nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 84, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Pati, S.S.; Mahendran, V.; Philip, J. A Simple Approach to Produce Stable Ferrofluids Without Surfactants and with High Temperature Stability. J. Nanofluids 2013, 2, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.U.; Narahari, M.; Theng, J.T.Y.; Pendyala, R. Experimental evaluation of dispersion behavior, rheology and thermal analysis of functionalized zinc oxide-paraffin oil nanofluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 294, 111613. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnakumar, V.; Elansezhian, R. Dispersion stability of zinc oxide nanoparticles in an electroless bath with various surfactants. Mater. Today: Proc. 2022, 51, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Nordin, A.H.; Ahmad, Z.; Husna, S.M.N.; Ilyas, R.A.; Azemi, A.K.; Ismail, N.; Nordin, M.L.; Ngadi, N.; Siti, N.H.; Nabgan, W.; et al. The State of the Art of Natural Polymer Functionalized Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticle Composites for Drug Delivery Applications: A Review. Gels 2023, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Jiang, Z. Preparation, Characterization, and Lubrication Performances of Water-Based Nanolubricant for Micro Rolling Strips. Materials 2024, 17, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).