Effect of Nozzle Geometry on Erosion Characteristics in Abrasive Water Jet: Experimental and Numerical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulation and Result Analysis of Nozzles
2.1. Mathematical Modeling of Nozzles
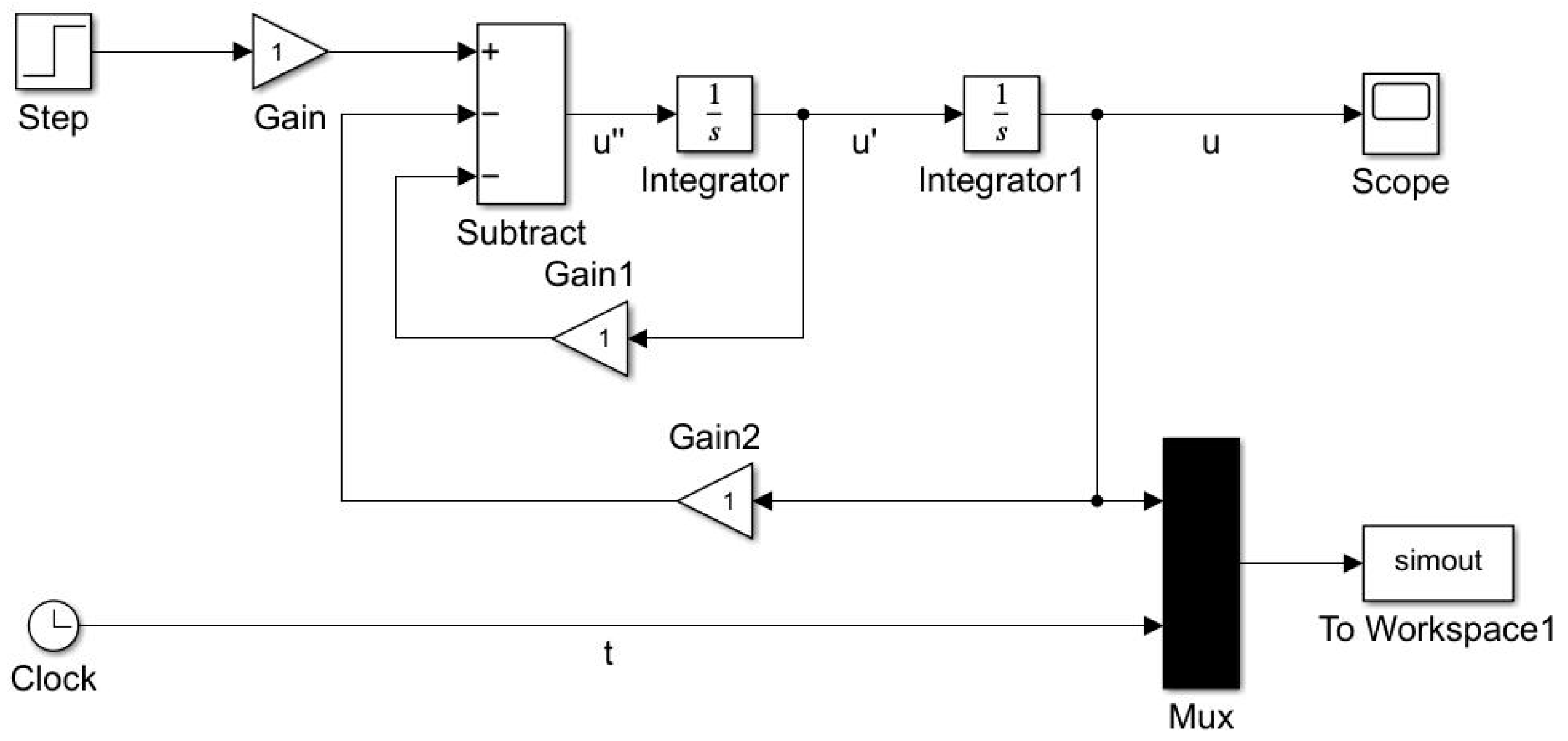
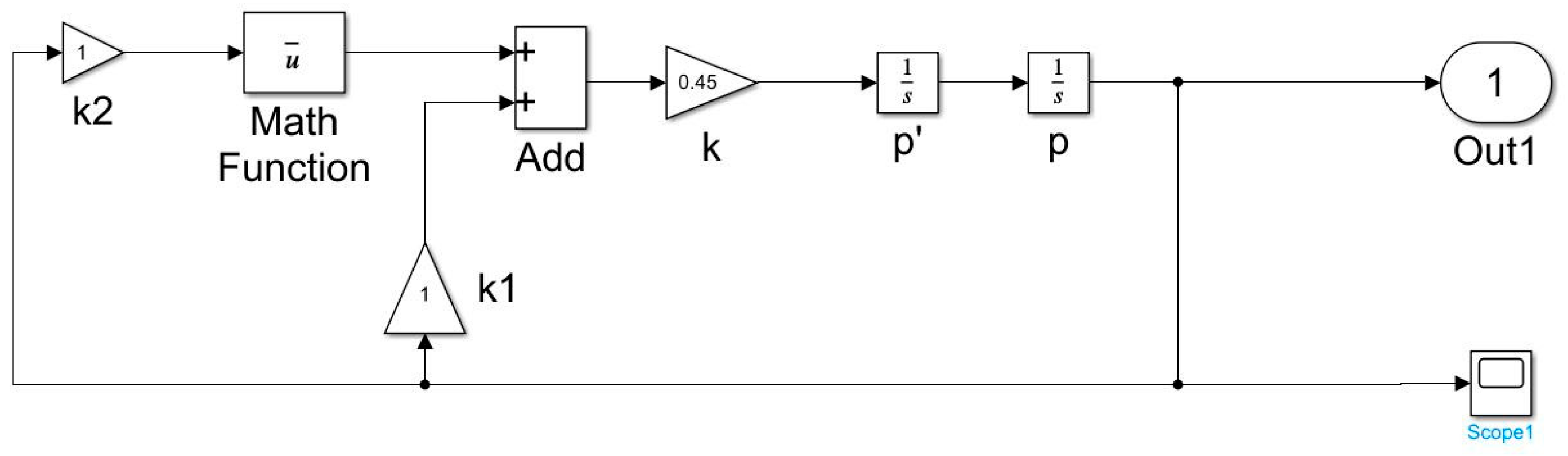
2.2. Matlab Simulation of Nozzle
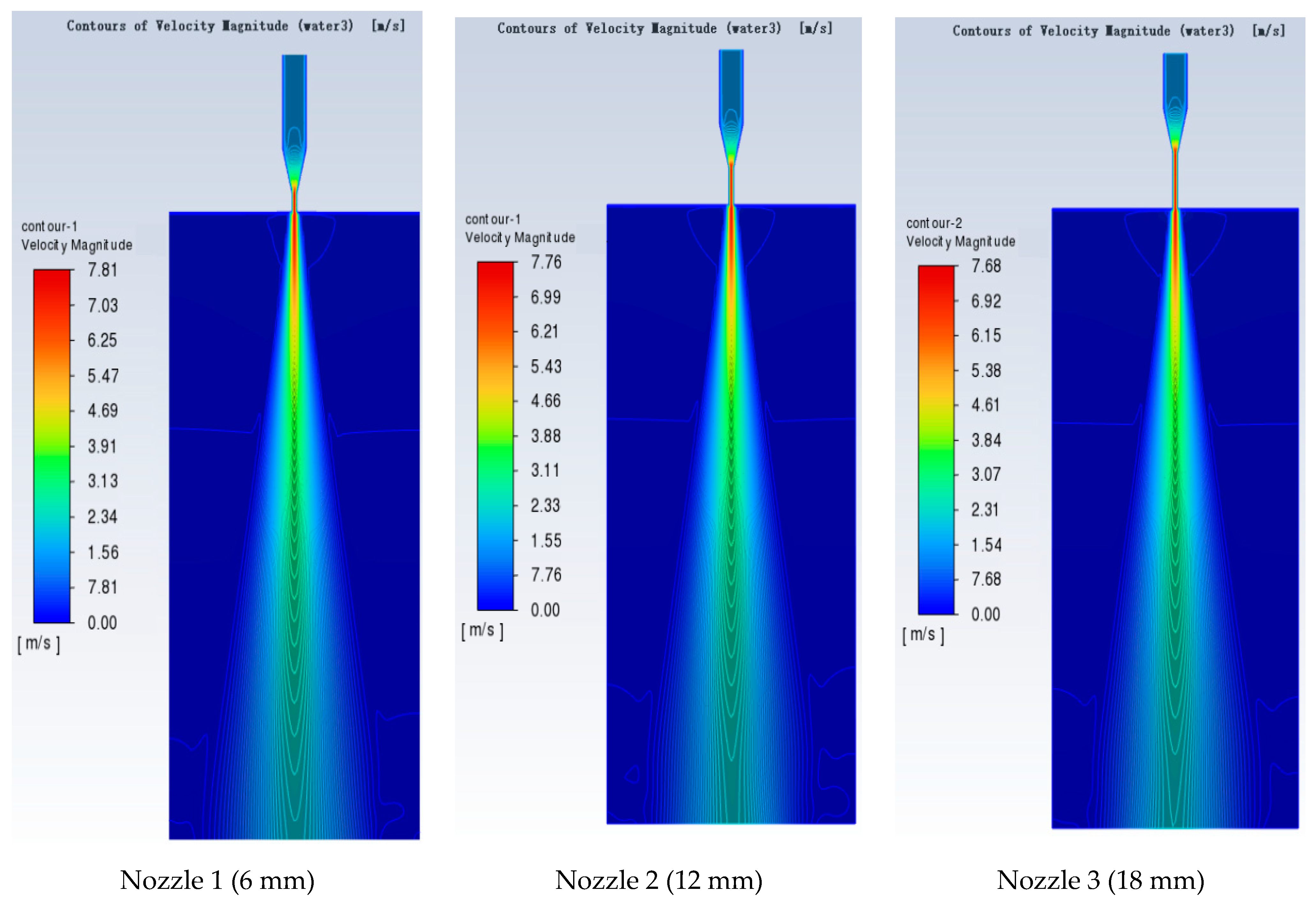
2.3. Fluent Analysis of Different Structure Nozzles
3. Experiments
3.1. Experimental Equipment
3.2. Experimental Methods
4. Results and Discussions
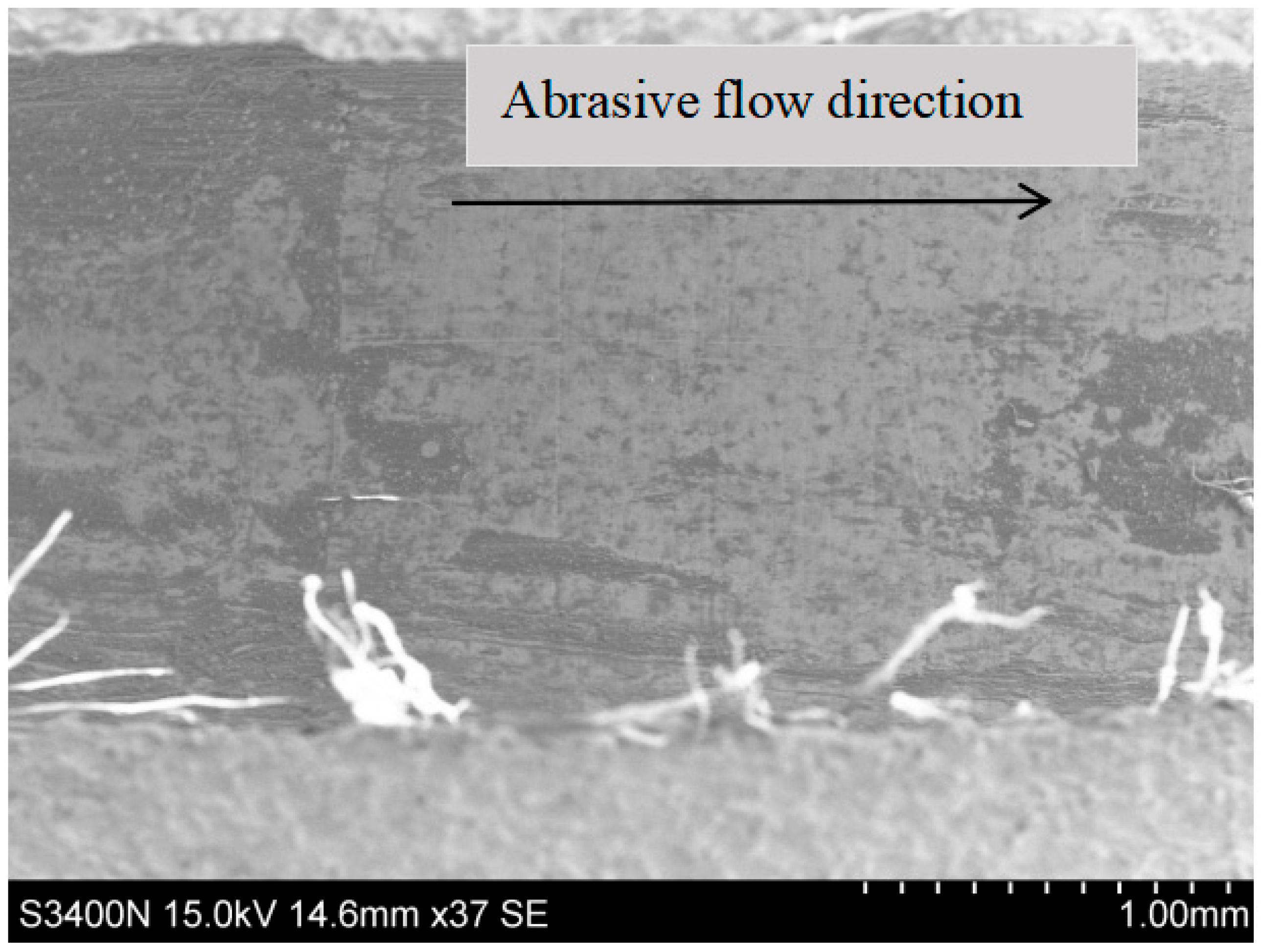
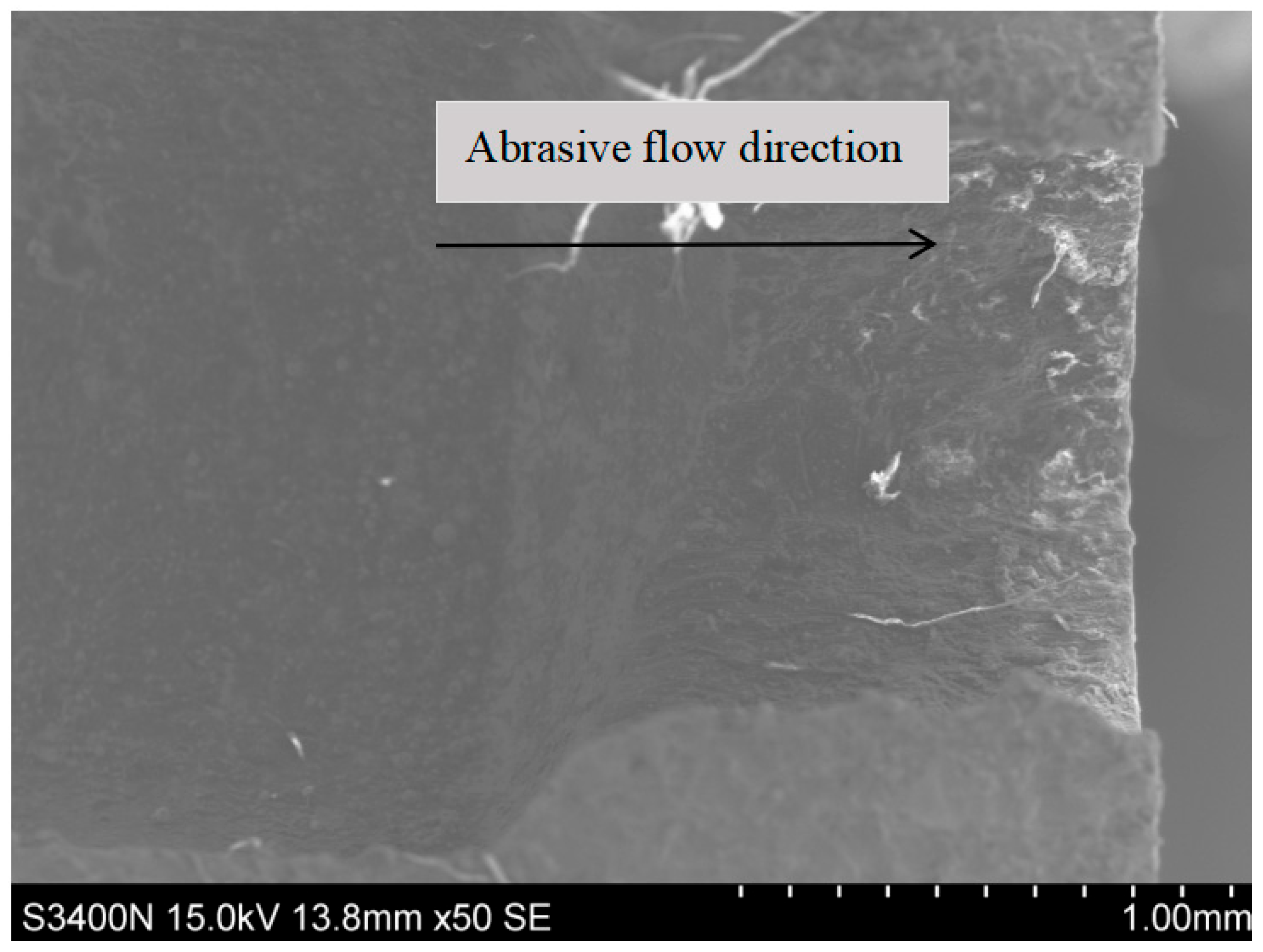
4.1. Nozzle Erosion Distribution
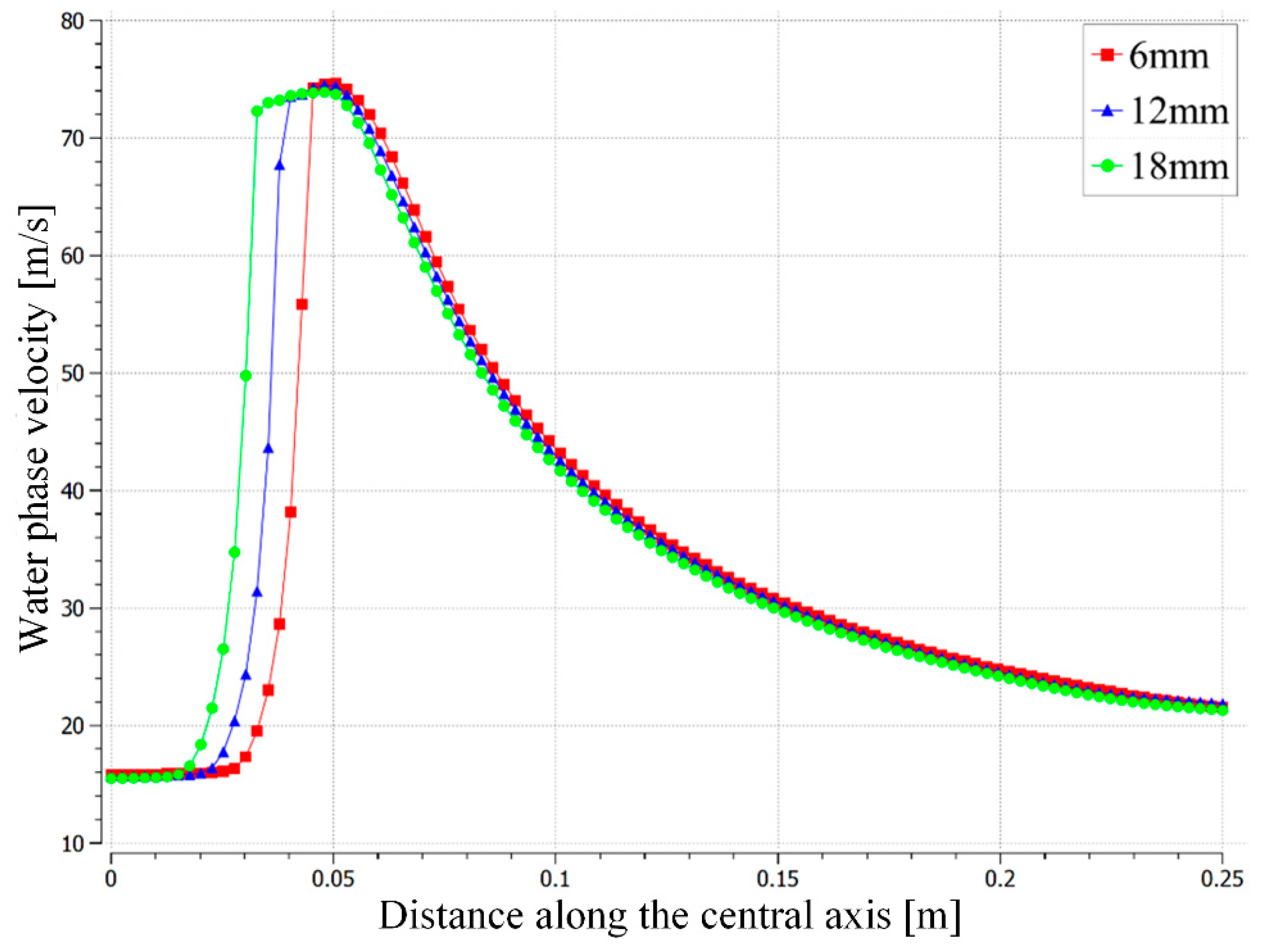
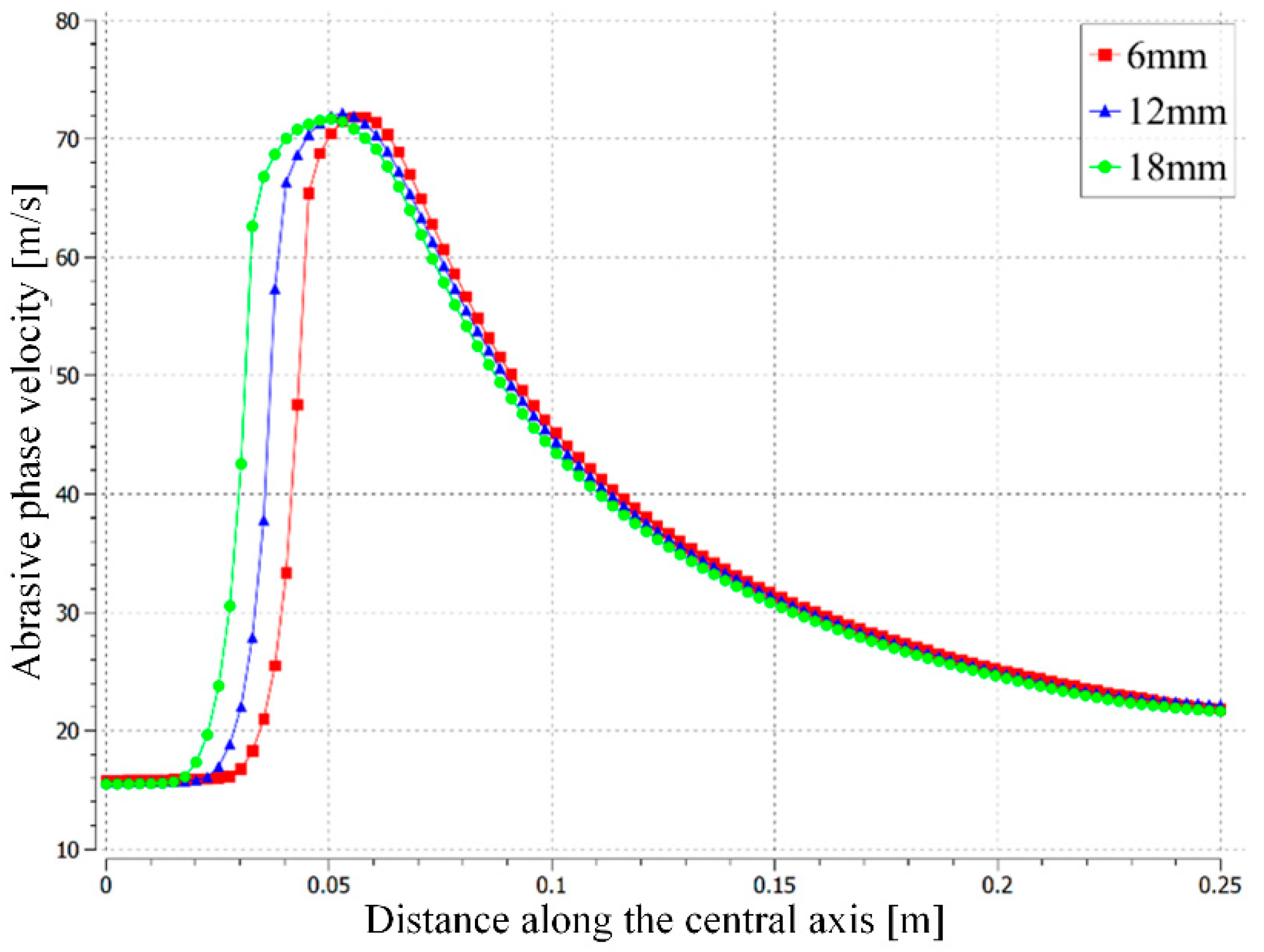
4.2. Analysis of Abrasive Flow Trajectory
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Numerical and experimental study on the duration of nozzle starting of the reflected high-enthalpy shock tunnel. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Ren, W.; Yao, F.; Cheng, B.; Sun, Z.; Deng, H.; Gao, K. Prediction of gas-solid nozzle performance based on CFD and response surface methodology. Powder Technol. 2024, 442, 119871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Lee, K. Modelling of abrasive particle energy in water jet machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar]
- Tamannaee, N.; Spelt, J.K.; Papini, M. Abrasive slurry jet micro-machining of edges, planar areas and transitional slopes in a talc-filled co-polymer. Precis. Eng. 2016, 43, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, T.; Nguyen, D.; Baldi, L.; Gijs, M. Glass reflow on 3-dimensional micro-apertures for electrophysiological measurements on-chip. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2007, 3, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstensen, A.; Seipp, T.; Nadarajah, C. Life management of pressure swing absorbers, in proceedings of asme. Press. Vessel. Pip. Conf. 2023, 2, pvp2023. [Google Scholar]
- Akkurt, A. Cut front geometry characterization in cutting applications of brass with abrasive water jet. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 19, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Wang, H.; Dong, H.; Guo, Y.; Ke, Y. Numerical research on multi-particle movements and nozzle wear involved in abrasive waterjet machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 2845–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yao, S.; Yun, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y. Simulation and Optimization of the Nozzle Section Geometry for a Suspension Abrasive Water Jet. Machines 2022, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kainuma, S.; Yang, M.Y.; Kim, A.; Ikeda, T.; Toyota, Y.; Arakawa, T. Advancements in abrasive water-jet treatment for efficient surface cleaning and comprehensive corrosion removal in steel structures. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.; Peng, J.M.; Li, Y.L.; Ge, D.; Li, J.M. Performance prediction of solid particle erosion in fluidic oscillators for fluidic hammers based on CFD-DPM. Powder Technol. 2023, 428, 118819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.F.; Ge, Z.L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, W.C.; Li, Z.T.; Tian, C.; Chang, W.X. Experimental and numerical investigation of abrasive water jet nozzle erosion. Powder Technol. 2023, 430, 119031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perec, A. Experimental research into alternative abrasive material for the abrasive water-jet cutting of titanium. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Ou, M.X.; Jia, W.D. The effect of nozzle configuration on the evolution of jet surface structure. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Gao, D.R.; Cheng, M.Z.; Cai, Y.; Guo, L.W. Effect of Special-Shaped Nozzle Structure on Water Jet Performance. Processes 2022, 10, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.C.; Deng, S.S.; Guan, J.F.; Hua, W.X. Experiment and simulation research on abrasive water jet nozzle wear behavior and anti-wear structural improvement. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2017, 39, 2023–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.; Moon, H.K.; Bang, M.; Cho, H.H. Effect of Misalignment at the Flat and Profiled Endwall of Nozzle Guide Vane on Heat Transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 230, 125750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesar, V. Characterisation of inexpensive, simply shaped nozzles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2010, 88, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowruzi, H.; Ghassemi, H. Effects of Nano-nozzles cross-sectional geometry on fluid flow: Molecular dynamic simulation. J. Mech. 2018, 34, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadge, M.; Lohar, G.; Chinchanikar, S. A review on micro-blasting as surface treatment technique for improved cutting tool performance. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 64, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, R.P.; Byers, D.H. Statis pressure, velocity, and noise characteristics of rectangular nozzles for high velocity/low volume exhaust ventilation. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1980, 41, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, R.P.; Byers, D.H. Static pressure and velocity characteristics of circular nozzles for high velocity/low volume exhaust ventilation. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1980, 41, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, R.P.; Erig, M. Airflow Characteristics of Two Symmetric Exhaust Inlets and of a Single Inlet near an External Boundary Surface. Appl. Ind. Hyg. 1988, 3, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Mi, J.Y.; Li, D.; Wang, R.R. Impinging performance of high-pressure water jets emitting from different nozzle orifice shapes. Geofluids 2020, 2020, 8831544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.Q.; Ge, Z.L.; Ren, Q.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, H.Y. Numerical analysis on the flow field structure and deflection characteristics of water jets under nozzle moving conditions. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2020, 14, 1279–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urazmetov, O.; Cadet, M.; Teutsch, R.; Antonyuk, S. Investigation of the flow phenomena in high-pressure water jet nozzles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 165, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.W.; Huang, Z.W.; Li, J.B.; Zhou, Y.S.; Xiong, C. Experimental investigation of internal and external flow fields of jetting nozzles with different structures. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 217, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
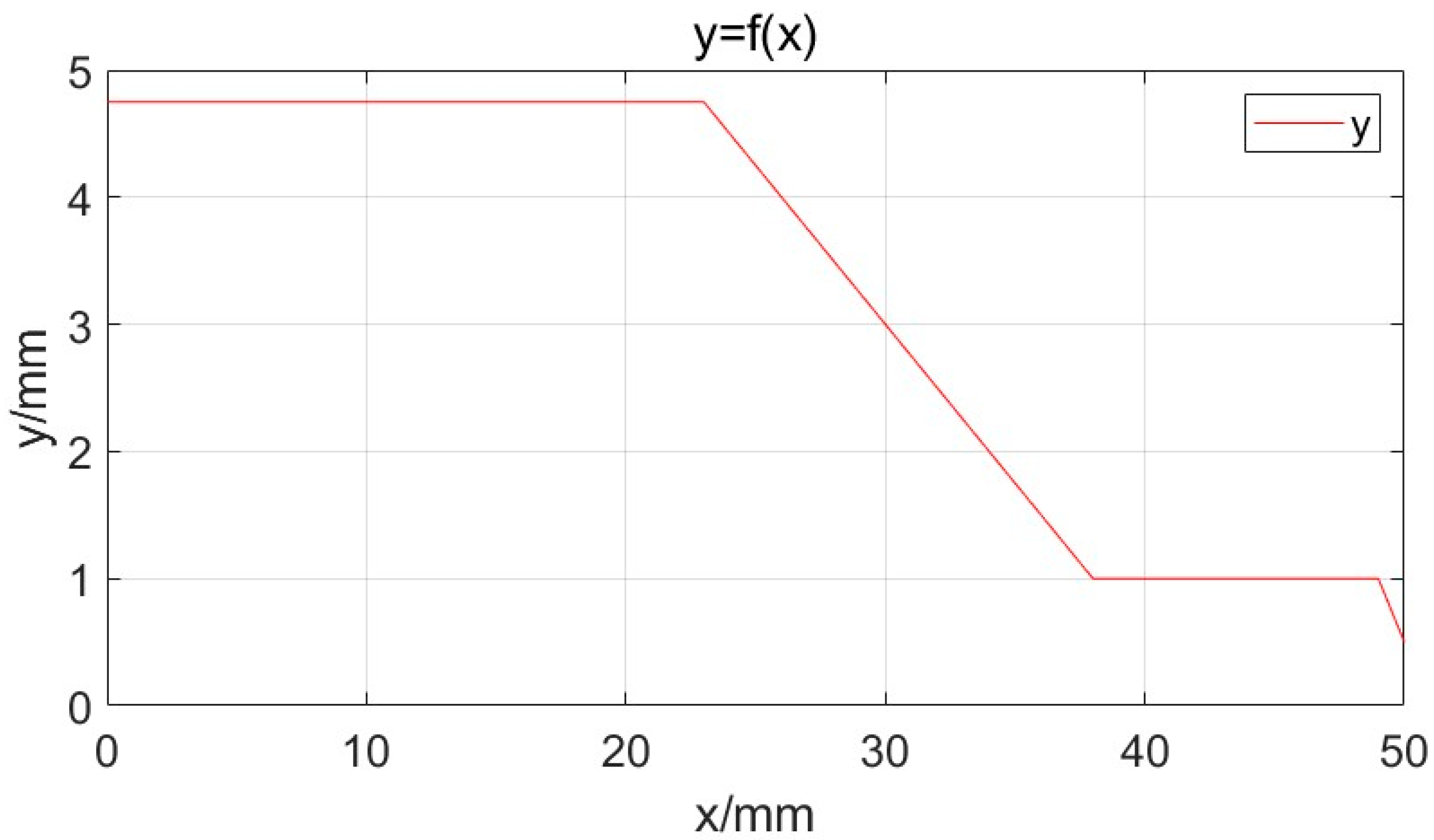
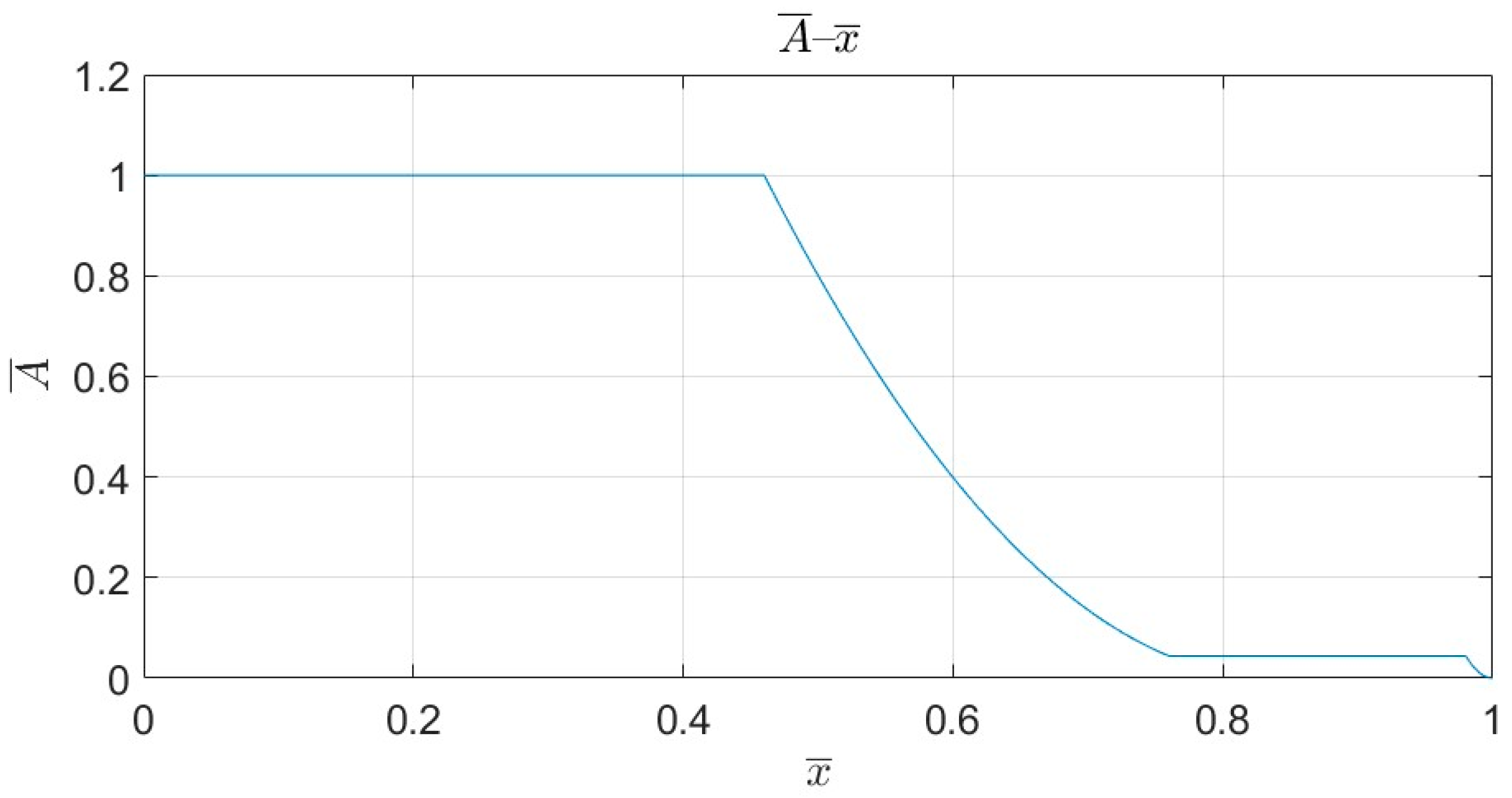
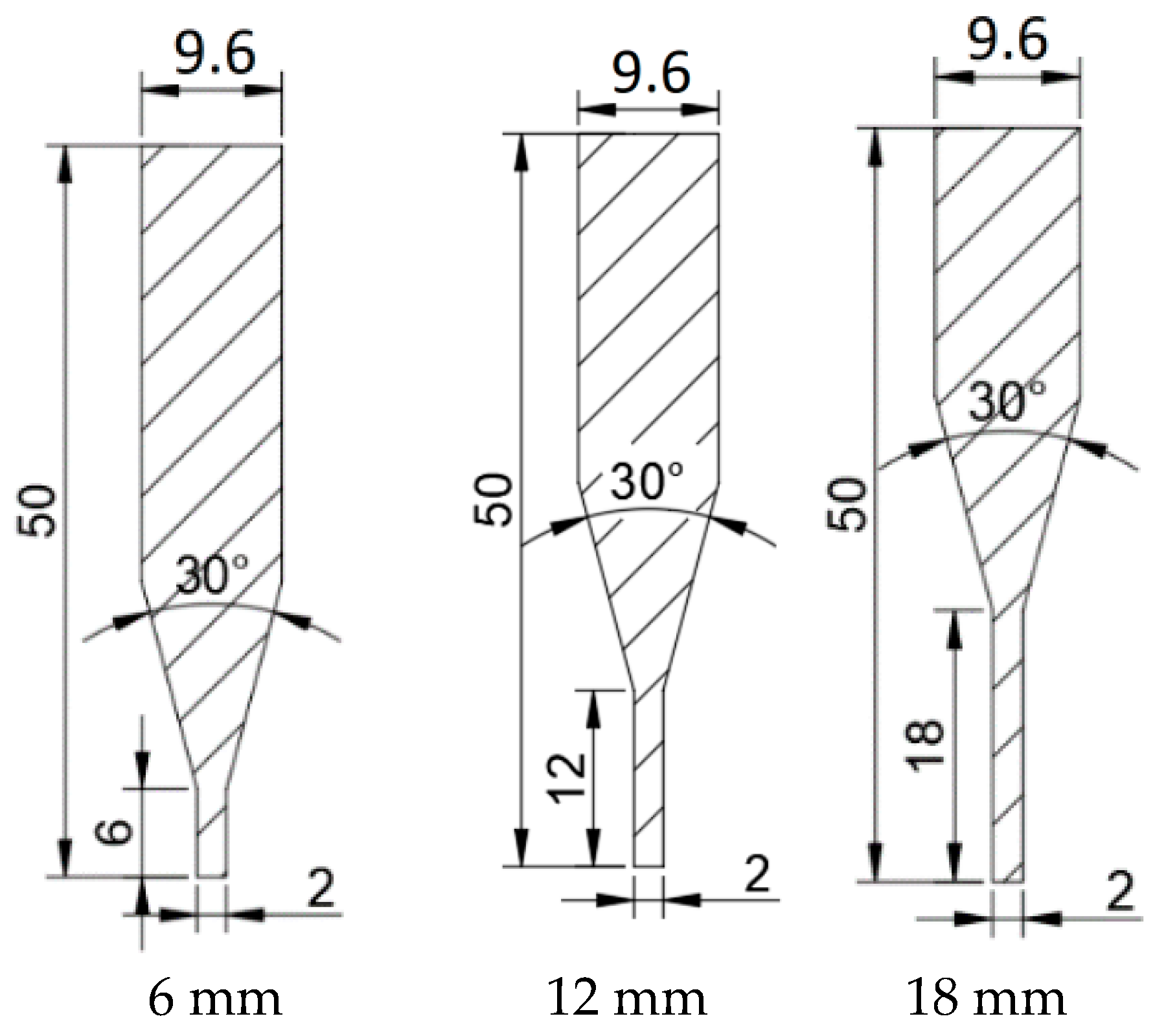


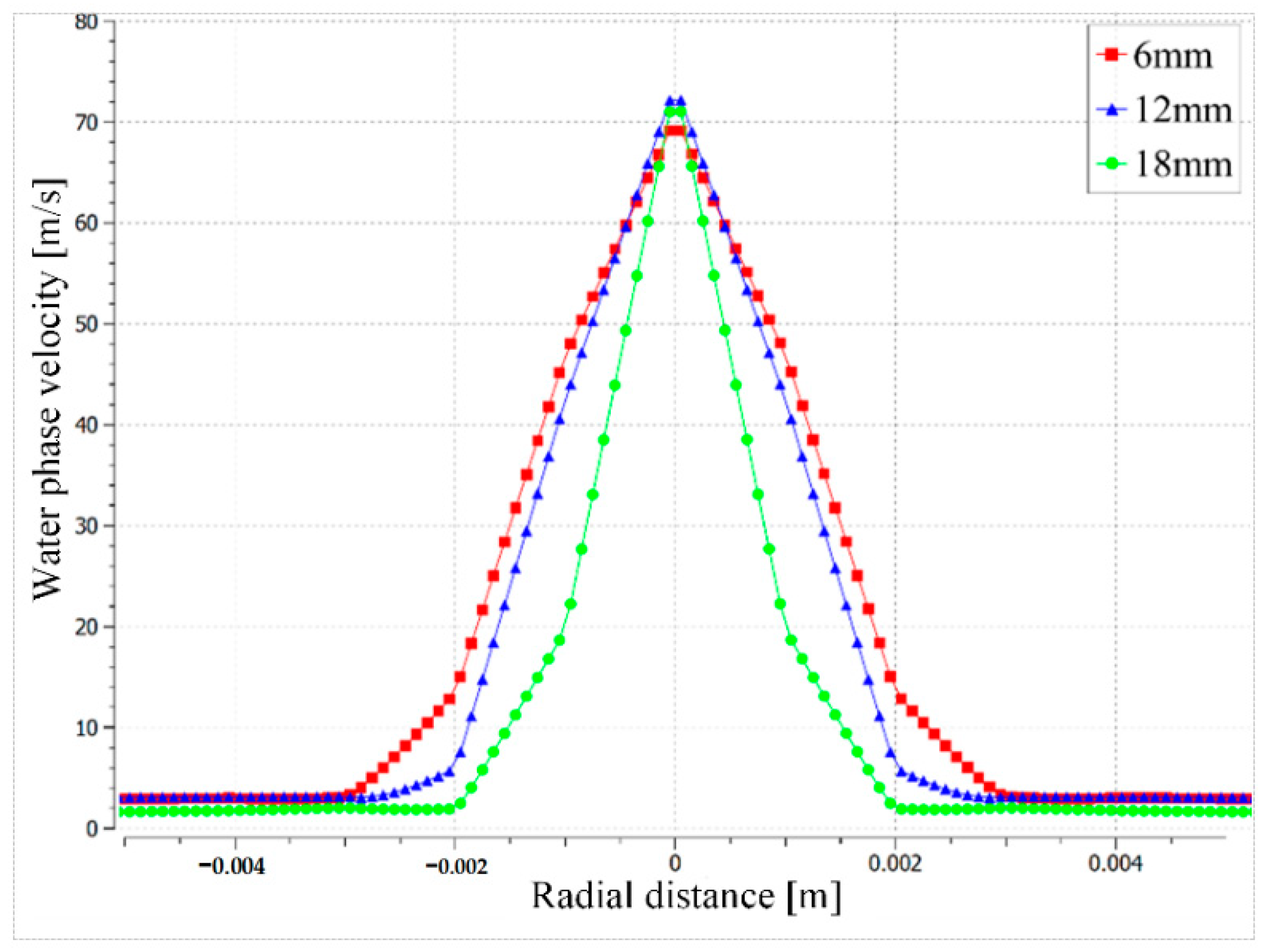
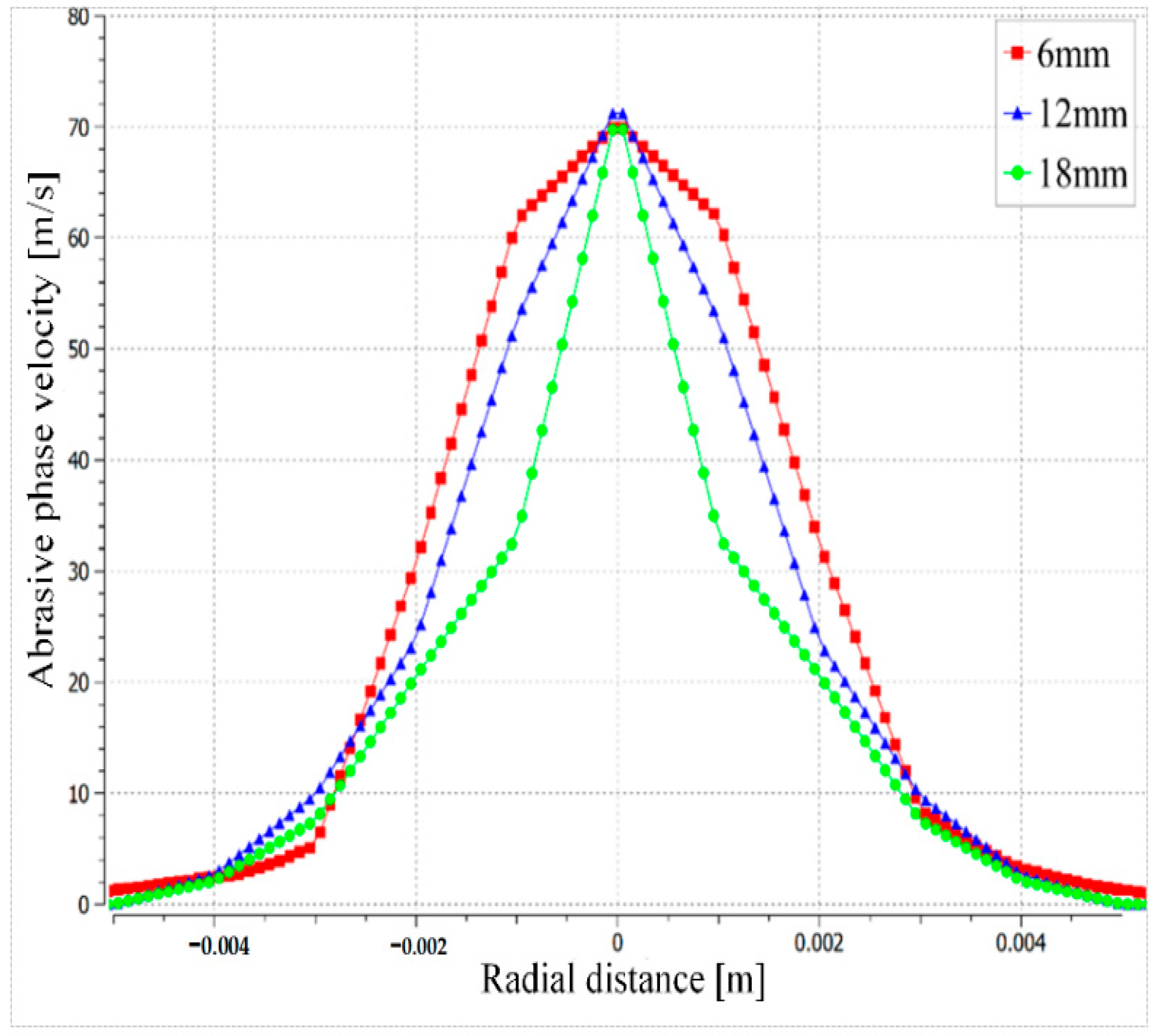





| Overall Length of Nozzle | Inlet Diameter | Contraction Angle | Outlet Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mm | 9.6 mm | 30° | 2 mm |
| Parameter | Experiment Value | Data Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic pressure | 3 MPa | 2~4 MPa |
| Abrasive particle flow rate | 1 g/s | 0.725 g/s~1.25 g/s |
| Abrasive particle diameter | 1 μm | 0.5 μm, 1 μm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Pan, H.; Chen, L. Effect of Nozzle Geometry on Erosion Characteristics in Abrasive Water Jet: Experimental and Numerical Analysis. Lubricants 2025, 13, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13030132
Chen X, Pan H, Chen L. Effect of Nozzle Geometry on Erosion Characteristics in Abrasive Water Jet: Experimental and Numerical Analysis. Lubricants. 2025; 13(3):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13030132
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xuhong, Haihong Pan, and Lin Chen. 2025. "Effect of Nozzle Geometry on Erosion Characteristics in Abrasive Water Jet: Experimental and Numerical Analysis" Lubricants 13, no. 3: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13030132
APA StyleChen, X., Pan, H., & Chen, L. (2025). Effect of Nozzle Geometry on Erosion Characteristics in Abrasive Water Jet: Experimental and Numerical Analysis. Lubricants, 13(3), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13030132





