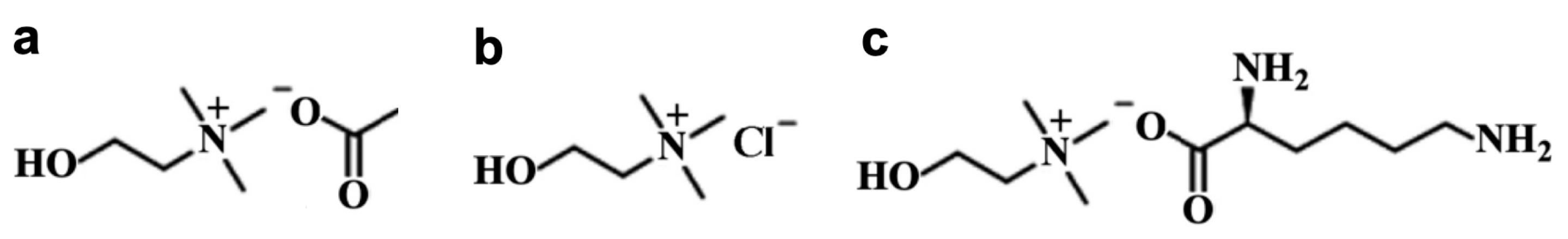Abstract
Ionic liquid molecules exhibit a variety of properties that are well suited for use as lubricants or additives for lubricants, since they form tribolayers that reduce friction and wear. As additives in the design of new water-based biolubricants, ionic liquids present the advantages of polar nature to use in aqueous lubrication, whilst being biocompatible and with null toxicity, opening up the opportunity to develop novel biolubricants. Choline is a cation present in numerous ionic liquids and is widely recognized for its water solubility, biodegradability, low toxicity, and role as a green solvent in different applications. This work presents the comparative studies of several water-based biolubricants and thin-layer films on stainless steel using a low proportion of Choline-based ionic liquids. The results of friction and wear using water-based biolubricants with 1 wt% of different Choline-based ionic liquids showed good tribological performance. In addition, Choline Lysinate, an amino-acid ionic liquid which is biocompatible, nontoxic, and biodegradable, presented excellent performance and was used as a precursor of thin-layer films on stainless steel showing outstanding behavior in pin-on-disc configuration and sapphire/stainless-steel contacts. Subsequent X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirmed the presence of a tribolayer containing the amino acid compound on the metallic surface.
1. Introduction
The potential use of ionic liquids (IL) as lubricants or additives for lubricants has been widely established by numerous authors in recent decades [1,2,3]. Research efforts on IL have previously covered numerous attractive fields, including the use as green solvents, biocatalysts, fuel cells, or energetic materials amongst others [4]. The use of IL as lubricants is driven by the particularly good tribological performance of different sliding contacts with applications engineering, i.e., ceramic–steel, ceramic–ceramic, or aluminum–steel.
Typically, IL exhibit a broad liquid range from −100 °C to as high as 350 °C; they present practically no vapor pressure with ineligible volatility and null pollution to air, are non-flammable below the decomposition temperature, and present a high thermal stability; the ability to self-assembly in films on metallic surfaces to prevent direct asperity–asperity contacts provides solid arguments for their use in lubrication [5,6].
Water-based biolubricants (WBB) are low-cost lubricants offering efficient cooling performance. Their principal applications involve processes such as rolling operations or metalworking, and they are environmentally friendly in comparison to mineral-oil based liquid lubricants. Moreover, WBB can avoid the production of oil fumes, oil pollution, and waste [7,8]. However, the low viscosity and corrosive behavior of WBB are the main challenges in the development of these lubricants. The key to producing these new lubricants is the well-balanced use of additives such as antioxidants, anti-foaming agents, viscosity index improvers, and especially those additives that focus on tribological performance to reduce friction, wear, and tribocorrosion.
Two general categories of additives are used in this field: water-soluble organic compounds as well as solid particles. These compounds perform effectively with polar lubricants since this additive generates a stable lubricating film on surfaces of the materials in contact under relative motion. This film formed by the compound molecules is adsorbed onto the surface materials by electrostatic attraction [9,10]. Water-soluble organic compounds including the use of IL is an example of this. Several studies have been developed to obtain new lubricants using IL in aqueous solutions. Abbot et al. used imidazolium IL in metals-mild steel contacts with varied results [11]. Protic IL based on ethanol-ammoniums with long-chain fatty acids at 1 wt%, coupled with nanodiamond or graphene, were used as additives to obtain novel water-based lubricants and to improve tribological performance [12,13,14,15,16].
In this effort to develop new WBB and driven by the use of biocompatible and biodegradable ionic liquids as additives, Choline-based IL exhibit excellent properties that make them potential candidates for additives in this kind of lubricant. Choline is a quaternary ammonium compound that is used as a cation in the synthesis of biocompatible ionic liquids [17]. It can be obtained from natural resources and is widely recognized for its water solubility, biodegradability, low toxicity, and its role as a green solvent in different applications [18,19]. Choline-based IL offer excellent thermal stability and conductivity and have been used in biomedical applications and as eco-friendly alternatives in lubrication systems [20,21,22]. Those characteristics have led to Choline becoming a promising and versatile cation in new-generation ionic liquids [22,23].
One of the most widely used Choline-derived IL is Choline Chloride, which was proposed by Abbott et al. as the main component for the formation of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) [24]. DES have since been extensively studied in various fields, including tribology, for their potential as green lubricants [25,26].
Another IL derived from the Choline cation is Choline Acetate, which, when combined with hydrogen bond donors such as urea or glycerol, forms DES, with potential as an environmentally friendly lubricant [27]. Furthermore, DES based on Choline Acetate have been shown to reduce friction and wear, outperforming other DES and traditional lubricants [28].
The Lysine anion derived from Lysine amino acid forms Choline Lysinate, which is a biocompatible IL [29,30]. This IL is used in biomass pretreatments to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis by improving lignin solubility [31,32], and its low toxicity and versatility make it valuable in pharmaceutical, biotechnological, and industrial applications [33,34,35]. It has also shown promising results as a sustainable lubricant in tribology in steel–steel contact tests with CO2 absorption [36].
In present work, various water-based biolubricants were formulated using Choline-based IL as additives in a small proportion of 1 wt%. Their tribological performance was studied using tribopairs of sapphire and stainless steel in a pin-on-disc configuration, and the Choline Lysinate demonstrated the best capacity for reducing the friction coefficient and wear rate. The worn surfaces were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The outstanding performance of the lubricant based on Lysine led us to prepare a thin layer by evaporation on the stainless-steel surfaces, which showed superior tribological performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Preparation of Water-Based Biolubricants
The solid Choline Acetate (purity > 95%) and Choline Chloride (purity > 99%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Burlington, MA, USA) with water contents of <1 and <5 wt%, respectively. Liquid Choline Lysinate was acquired from the company Proionic (Grambach, Austria) with >95% of purity and water content <2 wt%, which was confirmed by Karl Fisher titration. The molecular structure of each compound is shown in Figure 1.
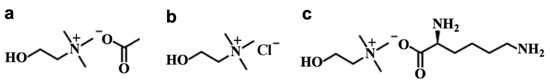
Figure 1.
Chemical structure for (a) Choline Acetate; (b) Choline Chloride; (c) Choline Lysinate.
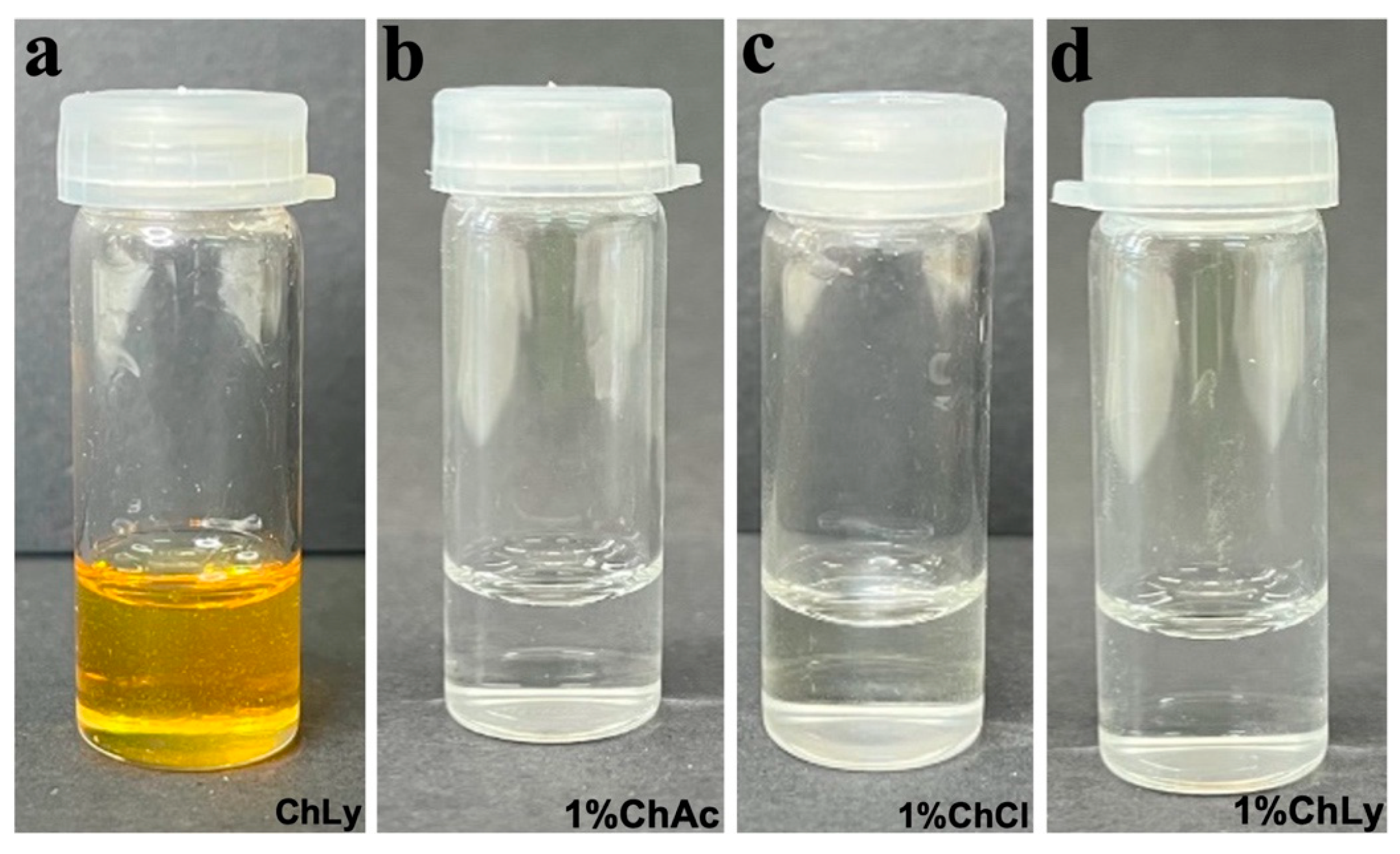
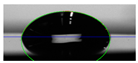
The water used in the preparation of the water-based biolubricants (WBB) was of type II purity obtained using a Milli-Q® Advantage A10 from Millipore Corporation (Burlington, MA, USA). The preparation of each WBB with the IL at 1 wt% involved adding the IL to type II water at room temperature, using magnetic stirring for thirty minutes to obtain homogeneous solutions. The abbreviations used for the WBB are shown in Figure 2, together with close-up images of the biolubricants seven days after preparation, with a mostly transparent and clear appearance. The neat Choline Lysinate presented a clear mustard-yellow color (see Figure 2a). The WBB were very stable, and no deposition or phase segregation appeared in one week.
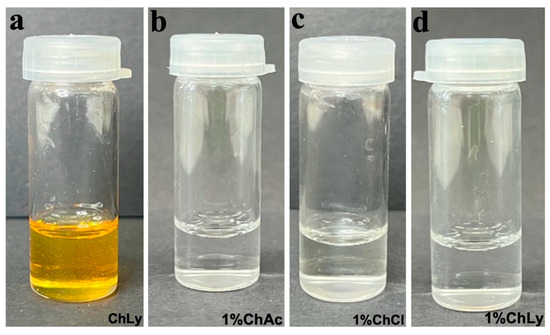
Figure 2.
Close-up images of (a) neat ChLy; (b) 1%ChAc; (c) 1%ChCl; (d) 1%ChLy.
2.2. Preparation of Thin-Layer Samples
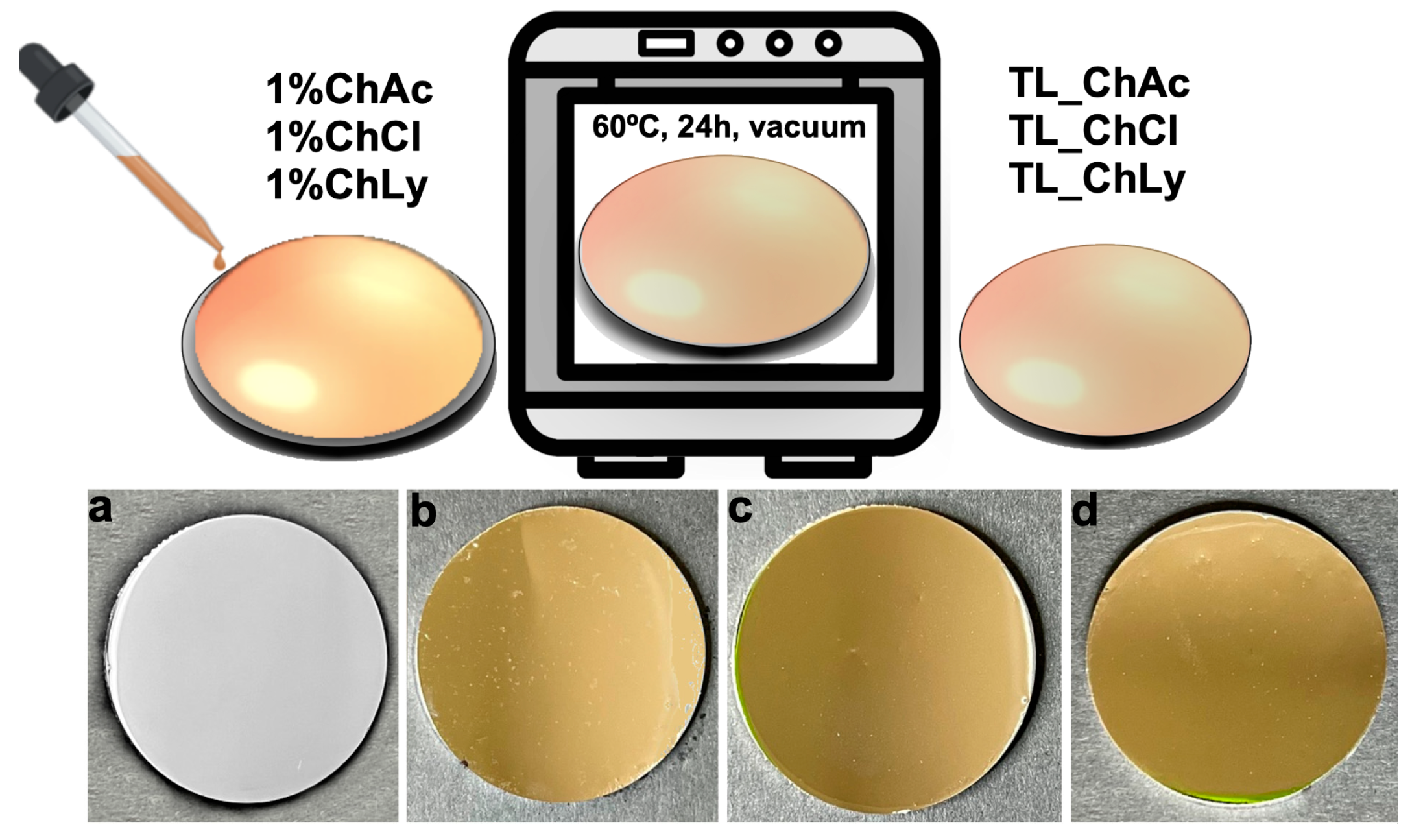
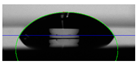
The thin-layer samples were obtained through the addition of WBB drop by drop until they completely covered the stainless-steel surface (0.5 mL). Subsequently, the samples were placed in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h. After evaporation of the water content, a homogenous thin layer remained on the substrate. Figure 3 shows the preparation steps and close-up images of the final thin-layer samples for each biolubricant. The abbreviations corresponding with the thin-layer samples used the prefix TL_ as follows: TL_ChAc, TL_ChCl and TL_ChLy.
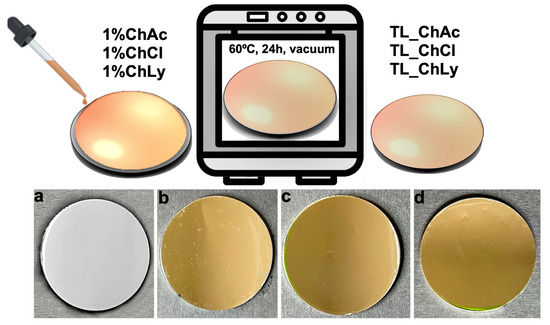
Figure 3.
Preparation steps of thin-layer samples and close-up images. (a) Stainless-steel disc, (b) TL_ChAc, (c) TL_ChCl; (d) TL_ChLy on the stainless-steel substrate.
2.3. Characterization of the Water-Based Biolubricants
The dynamic viscosity measurements of the biolubricants were carried out at room temperature using a rheometer AR-G2 from TA Instruments (New Castle, DE, USA) in a cone-plate geometry with a shear range of 10–100 s−1.
The dynamic light scattering technique was used to study the aggregation state of the WBB by measuring fluctuations in light intensity resulting from the Brownian motion to detect suspended particles. This was performed with an AutoSizer 4800 from Malvern Instruments (Worcestershire, UK) using a cell type ZFT5110 at 25 °C and a wavelength of 488 nm with a laser intensity of 40 mW. A standard based on a polystyrene monodisperse solution of 200 nm was used as the reference (Sigma-Aldrich cat. no. 95581). Data processing was carried out with the software PCS v1.61, and the measurements were repeated three times to check their reproducibility.
A digital pH meter HI98180 from Hanna Instruments (Woonsocket, RI, USA) was employed to determine the pH of the WBB. Calibration was carried out using buffer solutions of pH 4.01 and 7.01, and the results shown in Table 1 are the arithmetic mean of three measurements at room temperature.

Table 1.
pH values of the biolubricants at room temperature.
2.4. Tribological Tests
The friction coefficients and wear rates using the water-based biolubricants and the thin layers were determined at room temperature with a pin-on-disc Anton Paar TRB3 tribometer (Graz, Austria) and a stainless-steel AISI 316L disc (25 mm diameter; 2.5 mm thick; E = 193 GPa; 218 HV) and sapphire ball (1.5 mm diameter; 99.9% Al2O3; E = 445 GPa, 1750 HV). Discs were polished with the vibratory polishing device Qpol Vibro from QATM (Mammelzen, Germany), to a roughness Ra < 0.03 µm. Subsequently, the discs were cleaned using n-hexane, acetone, and air dried before tests.
Only 0.2 mL of biolubricant was added at the beginning of the test with no further amount added. Tribological tests were carried out at a normal load of 1 N with a mean Hertz contact pressure of 1.3 GPa, at a velocity of 0.1 m/s and a sliding distance of 1500 m; temperature was 23 ± 2 °C and relative humidity was 55 ± 4%.
Wear rates were determined with the disc volume loss following testing, using the scar profiles, as previously described [37]. Experimental parameters such as sliding radius, load, velocity, distance, temperature, and humidity were employed in testing the WBB and the thin-layer samples. The results are the arithmetic means of at least three tests per biolubricant.
2.5. Surface Analysis
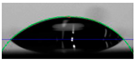
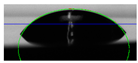
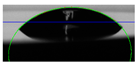
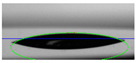
The biolubricant wettability on the discs was studied using a DSA 30 Drop Shape Analyzer from Kruss (Hamburg, Germany). Three µL was placed on the stainless-steel surface using a syringe and then a photograph of the sample was taken, followed by a further image 5 min later. The contact angles were determined with the slope to the drop at the interface line.
The wear-track volume loss was measured by means of a non-contact 3D profilometer model Talysurf CLI from Taylor Hobson (Leicester, UK).
After each test, the discs and sapphire balls were studied using a scanning electronic microscope, ZEISS Crossbeam 350 (Jena, Germany); elemental analyses were carried out with an energy-dispersive X-ray detector, Ultim Max, from Oxford Instrument (Abingdon, UK).
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed on the stainless-steel discs after the tests with the thin-layer sample TL_ChLy utilizing the SPECS FLEXPS-E spectrometer (Berlin, Germany). The elemental spectra were obtained using an Al Kα source (1486.7 eV), with a spot size of 300 μm, a bias voltage of 150 eV, and the C1s binding energy at 285.0 eV as the reference. Spectra were analyzed with the Specslab Prodigy ISQAR software (ver 4.100.1-r111001) modules.
2.6. Corrosion Tests
Two mL of biolubricant was placed onto the stainless-steel disc surface, which was then stored for a month at room temperature, and no evidence of corrosion, pitting, or cracks was found.
Furthermore, we examined the corrosive capacity of these biolubricants, as per the recommendations of the standard ASTM: D4627–22: Iron Chip Corrosion for Water–Miscible Metalworking Fluids. The procedure involved placing cast iron chips of 18 mesh, corresponding to a size below 1 mm, in contact with the biolubricants.
The corrosion test began using a filter paper with 1.5 g of cast iron chips put in a Petri dish, with 3 mL of water-based biolubricant samples soaking the paper. The Petri dishes were stored for 24 h at room temperature. The chips were then taken out, and the filter paper was washed with deionized water. The presence of final rust on the paper allowed us to compare the ability of the biolubricant to produce corrosion on the chips. The test was repeated twice for each sample.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Tests of the Biolubricants
The wettability of the WBB samples, expressed as the contact angle of a drop on the stainless-steel surface, is shown in Table 2. The wettability is also relevant in mixed and boundary lubrication regimes, and the presence of small angles suggests better wettability and that the biolubricant can spread more easily on the metallic surface. In our study, the lubricant 1%ChAc initially presented a small contact angle of 26.1° with a decrease after 5 min to 15.6°, which represents a variation of 40.2%. However, water, 1%ChCl, and 1%ChLy both initially and after 5 min showed reductions of 12.0°, 14.4°, and 3.9°, respectively. The 1%ChCl biolubricant showed the highest contact angle of all the tested samples.

Table 2.
Contact angles.
The dynamic viscosity confirmed the Newtonian behavior of the WBB, in the range of a shear rate of 10–100 s−1; the data are presented in Table 3 and show values similar to that of water.

Table 3.
Dynamic viscosity (mPa·s).
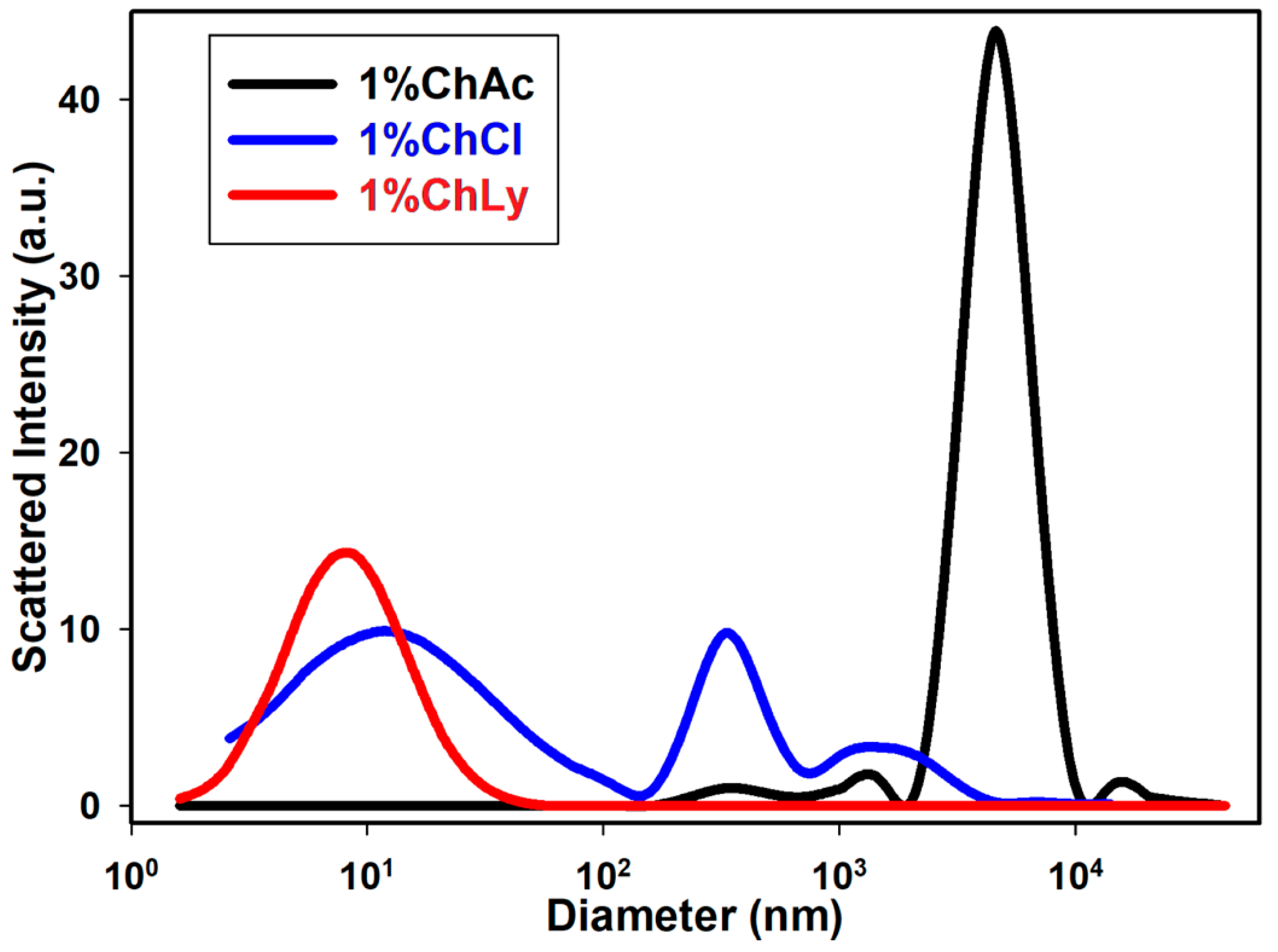
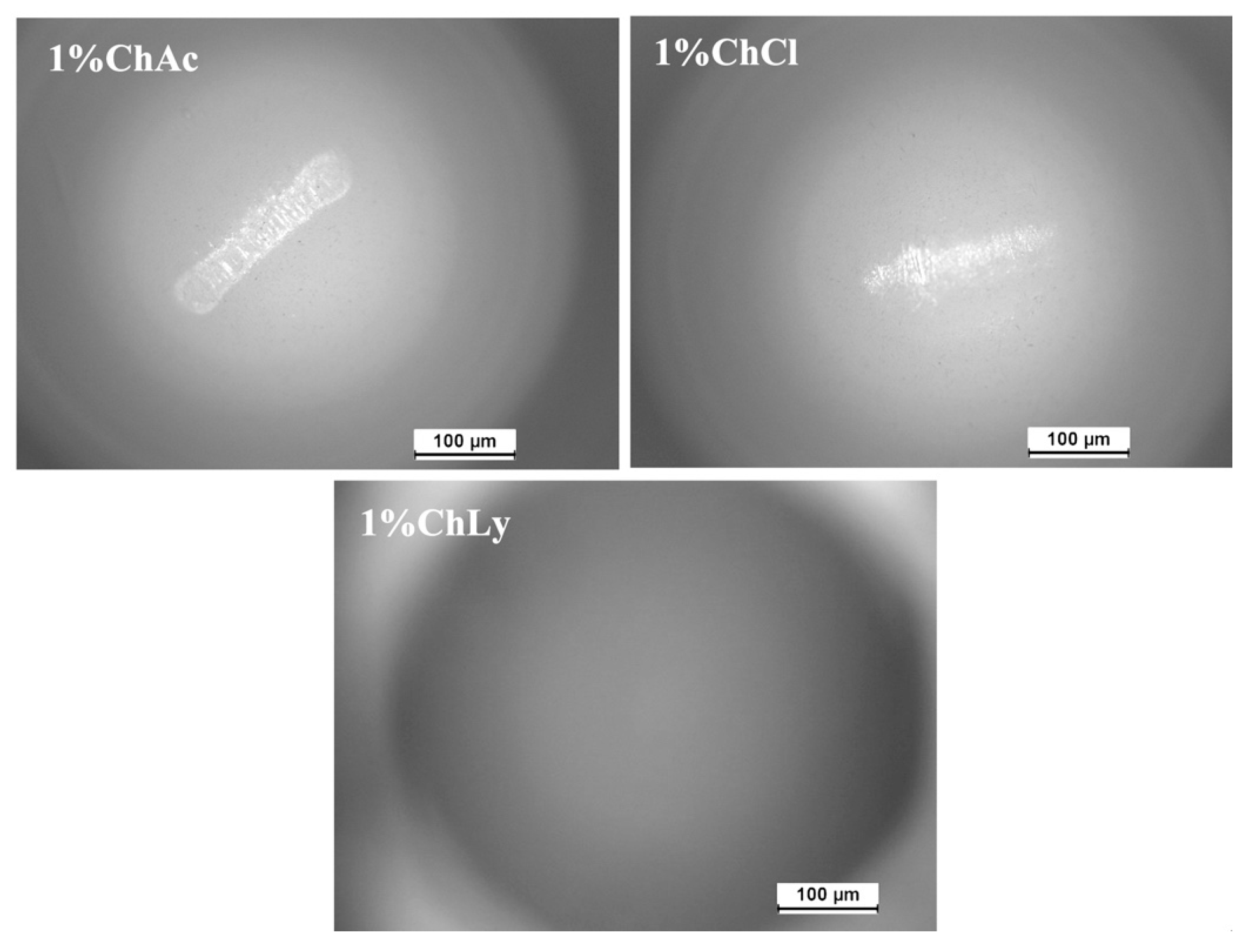
The dynamic light scattering (DLS) test measures the size distribution range of particles in water-based biolubricants. Figure 4 shows that the biolubricant 1%ChLy had the smallest particles (below 10 nm) with a single distribution. In contrast, the biolubricant 1%ChCl exhibited three distributions across a range of sizes, while the lubricant 1%ChAc presented a distribution with a size three orders of magnitude higher than that of 1%ChLy.
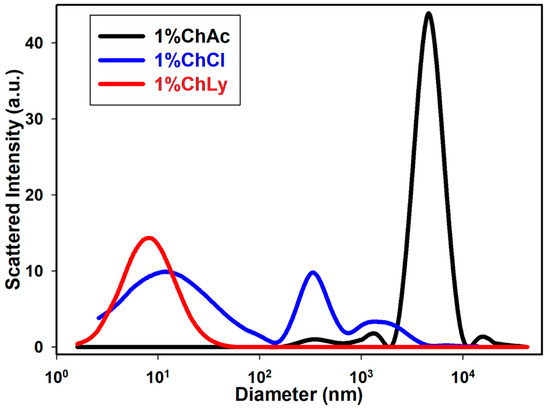
Figure 4.
Dynamic light scattering test for the lubricants 1%ChAc, 1%ChCl, and 1%ChLy.
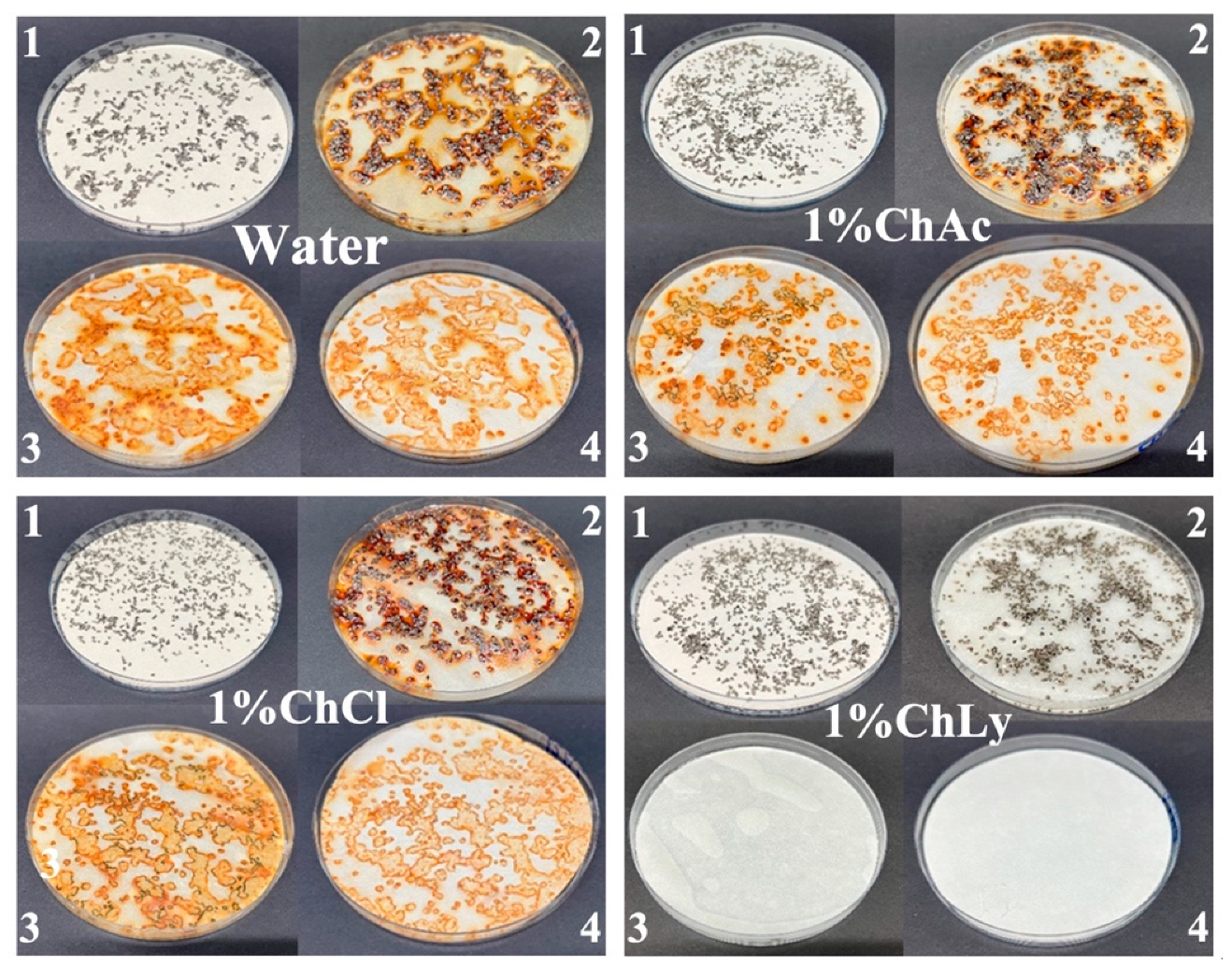
The results of corrosion tests on cast iron chips using the ASTM standard: D4627–22 showed that the water-based biolubricant 1%ChLy acted as an inhibitor against corrosion. The absence of rust spots on the filter paper in comparison with the other biolubricants or water was noteworthy. In contrast, the pattern of the test results with water, 1%ChAc, and 1%ChCl was very different, with clear evidence of corrosion. The alkaline pH = 11.33 of the 1%ChLy biolubricant induces an extremely low corrosion rate in cast irons by passivation. Moreover, the capacity of amino acids to adsorb and form a layer on transition metals and oxides makes these compounds act as inhibitors of corrosion in steels [38,39], extending this study into fields such as biochemistry, nanotechnology, or metallic implants in biomedicine [40,41,42,43]. Figure 5 shows the images of each biolubricant sample in comparison with deionized water.
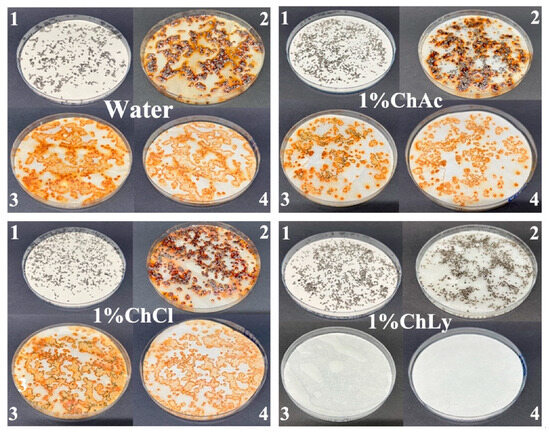

Figure 5.
Close-up images of test results under ASTM D4627 corresponding to deionized water, and the biolubricants 1%ChAc, 1%ChACl, and 1%ChLy. The sequence of the process was as follows: 1. lubricants and chips on the filter paper, 2. after 24 h at room temperature, 3. chips removed and washed, and 4. dried filter paper.
3.2. Tribological Characterization of WBB
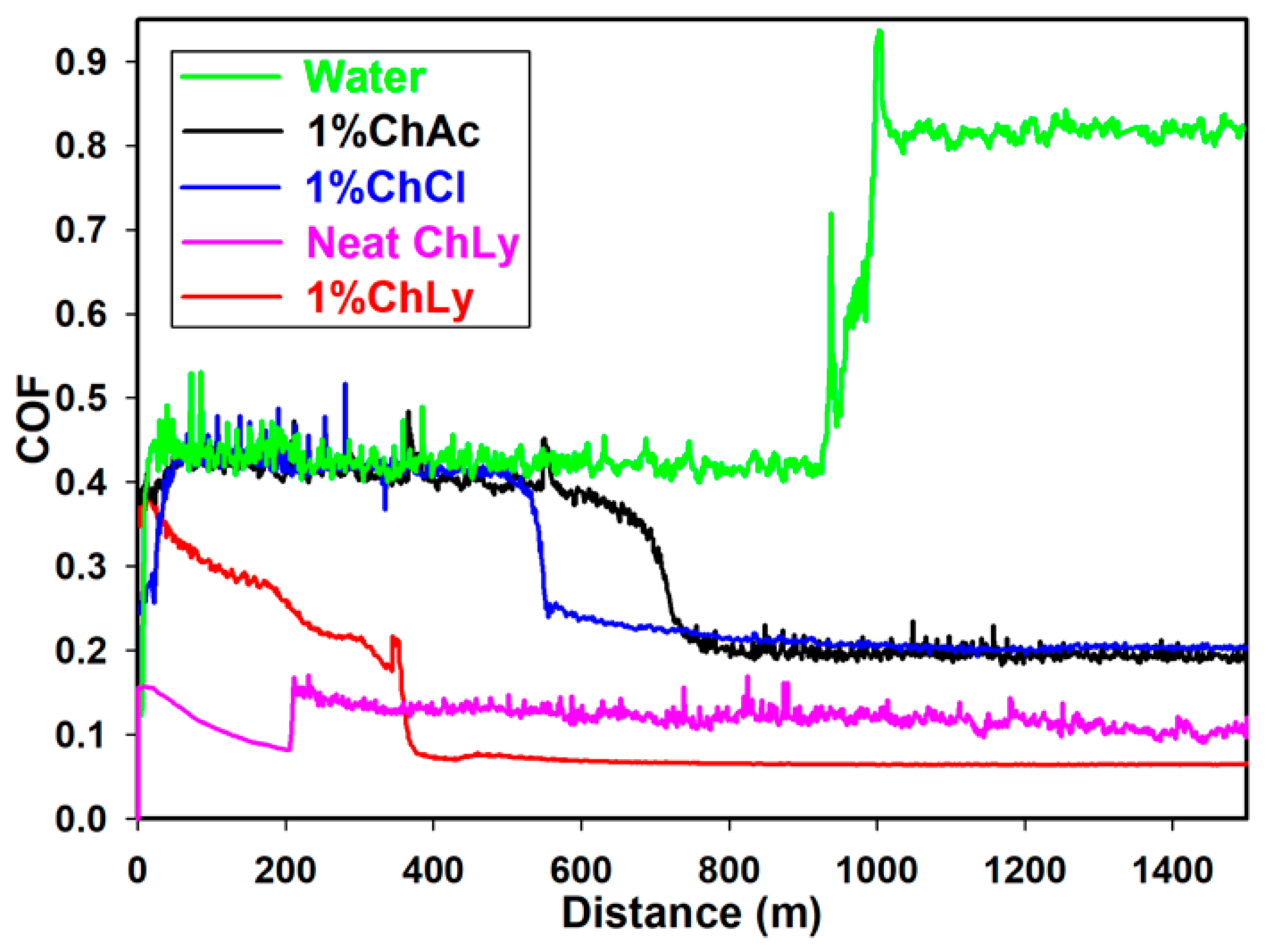
Figure 6 presents the plots of friction coefficients as a function of the sliding distance in the pin-on-disc tests at room temperature. A cursory observation of the plot showed similar behavior for the three WBB and neat ChLy, where an initial stage was followed by a transition to a lower plateau and a stable friction coefficient, in contrast to the test water, which had an unexpectedly sharp increment of friction.
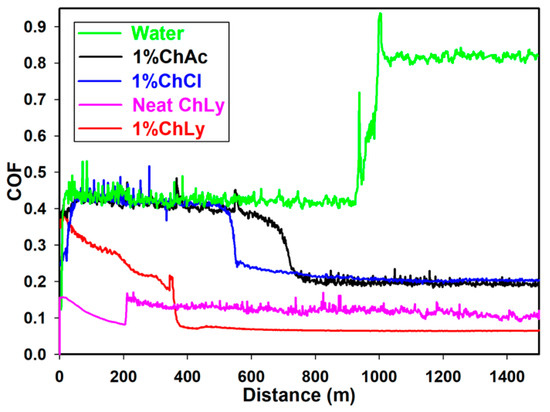
Figure 6.
Friction coefficients for water, 1%ChAc, 1%ChCl, neat ChLy, and 1%ChLy along 1500 m.
The initial values of friction were 0.420 for water, 1%ChAc, and 1%ChCl. However, the biolubricant 1%ChLy already presented a lower and decreasing value, falling to a low plateau at 0.068.
As the sliding distance progressed, there was a drop in friction coefficient owing to evaporation of the water content; this relevant role of water evaporation during friction tests had been previously observed in studies using solutions of protic IL [12,13] and polyalkylene glycols [44].
This friction fall happened at 365 m for 1%ChLy, after which a friction value of 0.068 was reached. For the biolubricants 1%ChAc and 1%ChCl, the drop in friction coefficient did not occur until 726 and 573 m, respectively, with a plateau close to 0.200. For neat water, complete evaporation occurred at 983 m and the friction then presented an abrupt increase to a high friction coefficient with a direct contact between stainless steel and sapphire.
In the case of neat ChLy, we also observed two stages due to the presence of water in the IL, as confirmed by Karl Fisher analysis. The neat IL showed a plateau friction value of 0.117 from 200 m until test completion at 1500 m.
The reduction in friction of 1%ChLy in comparison to water was 92% and 66% compared to 1%ChAc and 1%ChCl. Table 4 summarizes data about the evolution of friction coefficient during the initial stage (running-in) and the distance where friction changes toward the plateau stage (steady-state).

Table 4.
Friction data of the WBB.
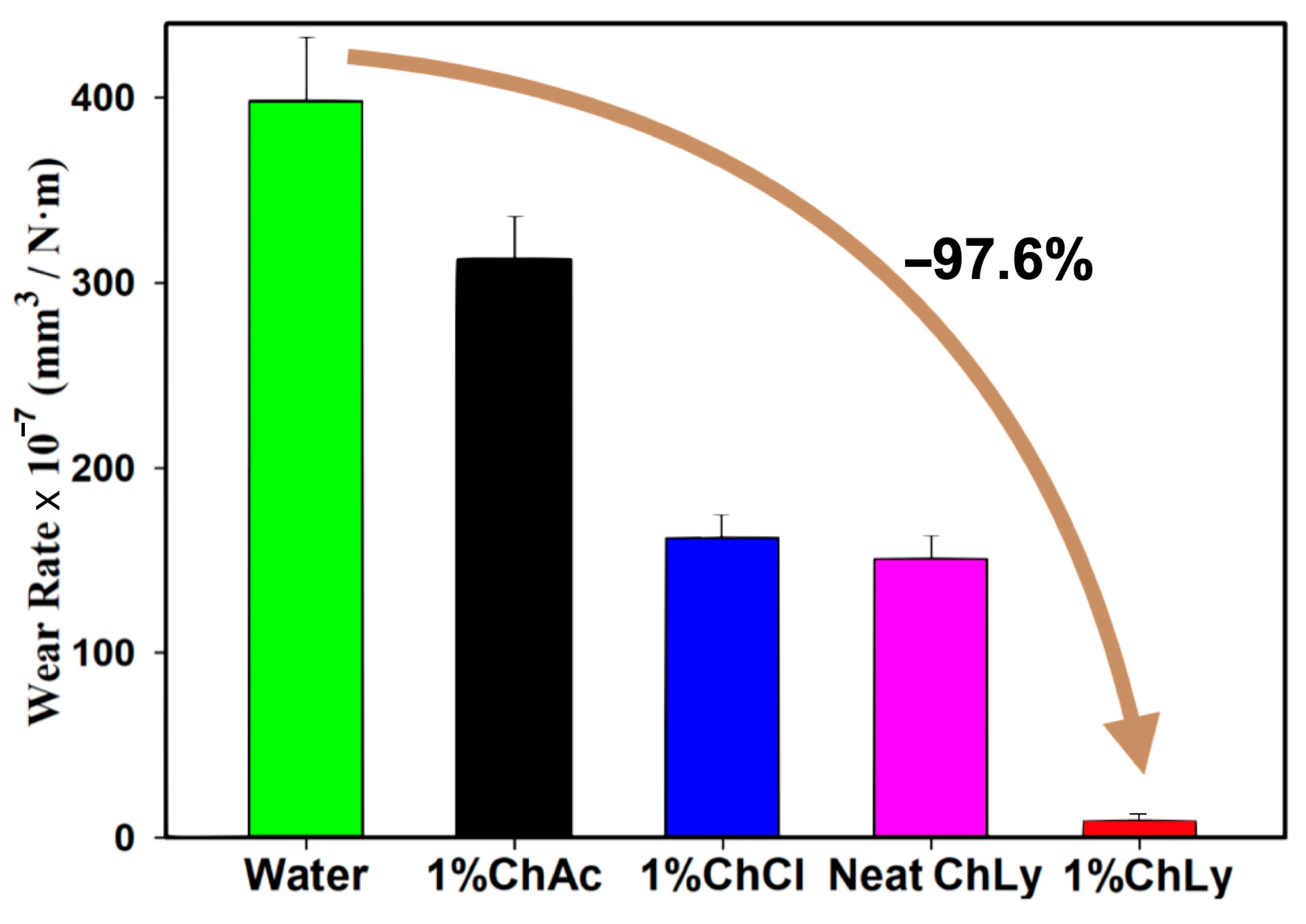
The evaluation of wear rates after the test using the non-contact profilometer also showed the potential of the 1%ChLy as an excellent biolubricant in terms of wear reduction, with a very low wear rate and reductions in orders of magnitude with respect to the rest of the biolubricants tested. Figure 7 and Table 5 represent the average wear rates for all the WBB after three tests. 1%ChLy showed a decrease in the wear rate of 97.6% compared to water and of 93.6% for neat ChLy.
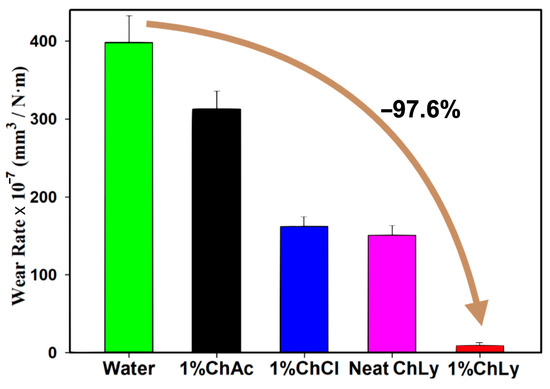
Figure 7.
Wear rates of the biolubricants tested.

Table 5.
Wear rates, mm3/N·m, and standard deviations for the WBB.
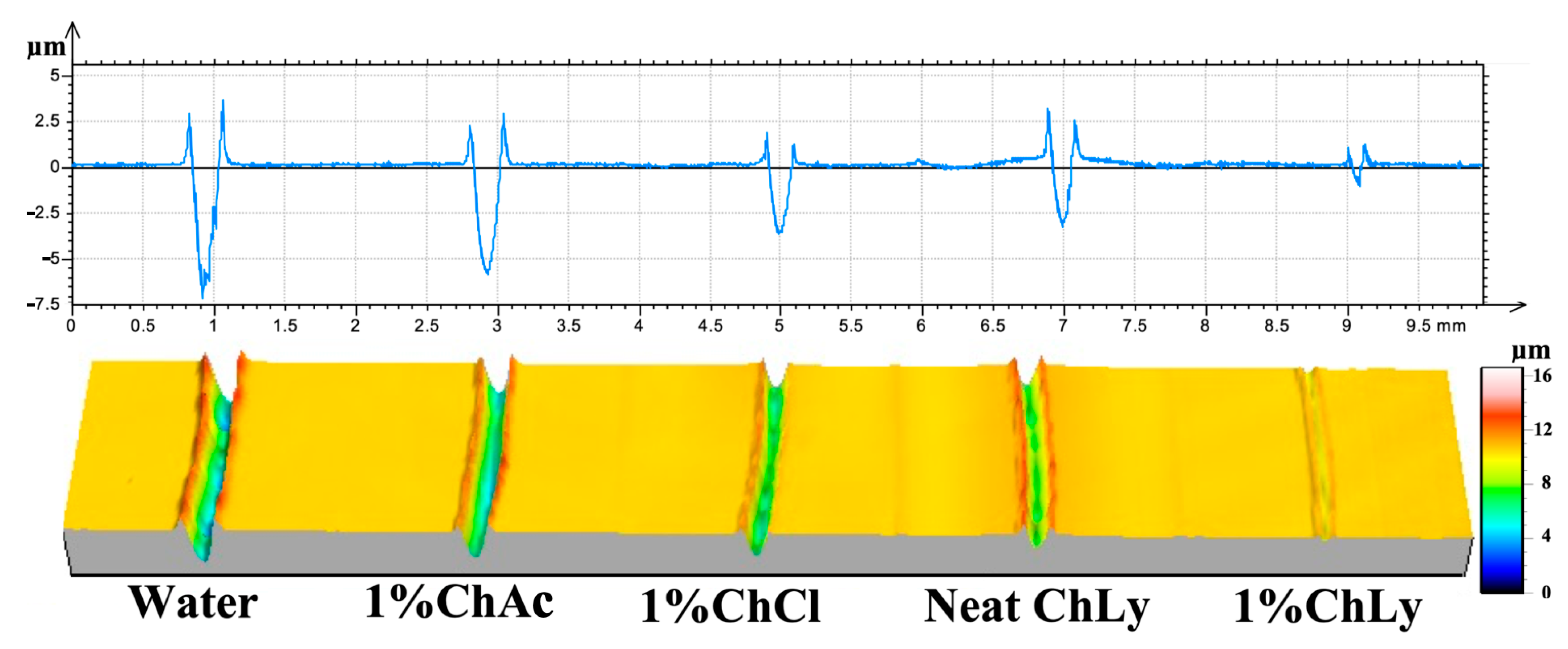
Figure 8 shows the 2D profiles and 3D images from the non-contact profilometer of the wear tracks for each WBB. The effective protection of the biolubricant 1%ChLy against surface damage is noticeable from the profiles of the wear tracks for the WBB, where the wear track in the case of 1%ChLy shows negligible damage on the surface in comparison to the rest of the biolubricants.
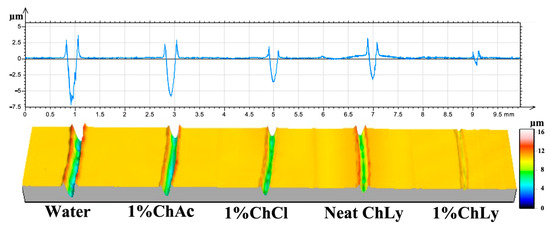
Figure 8.
Two-dimensional profiles and three-dimensional confocal images of the representative wear tracks.
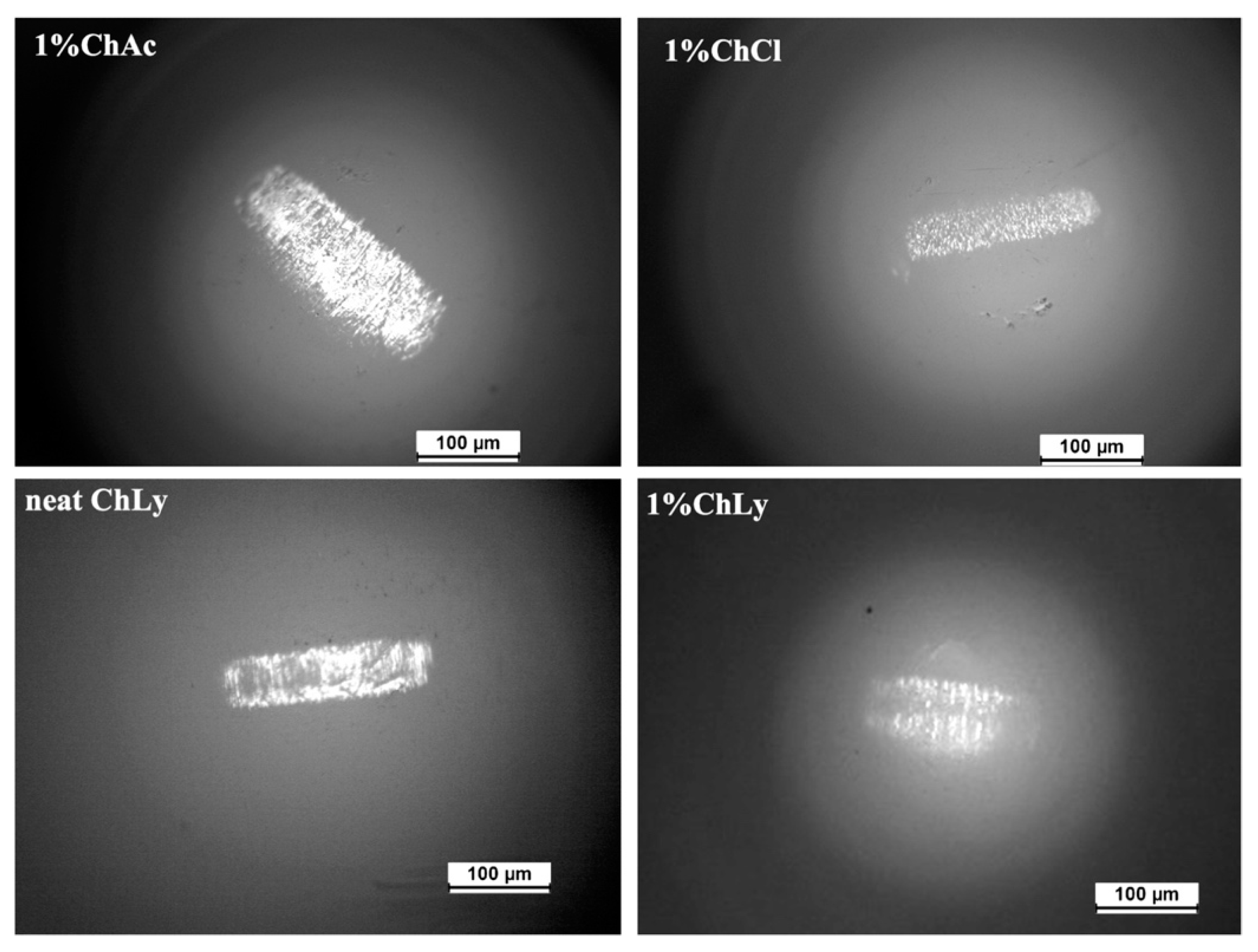
Furthermore, the sapphire balls were also studied with the optical microscope (see Figure 9). Wear scars were clearly observed on the balls, with minimal damage in the case of 1%ChLy after the test. No material transfer was detected during the observation.
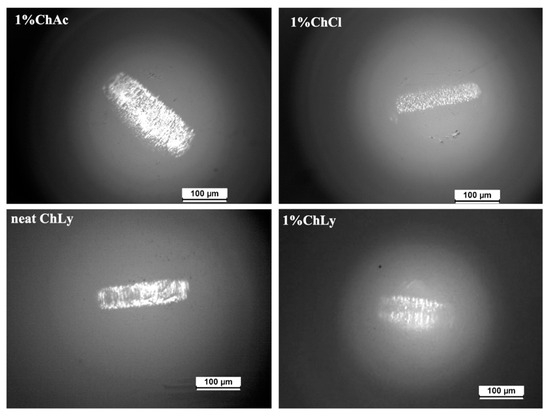
Figure 9.
Micrographs of sapphire balls for 1%ChAc, 1%ChCl, neat ChLy, and 1%ChLy.
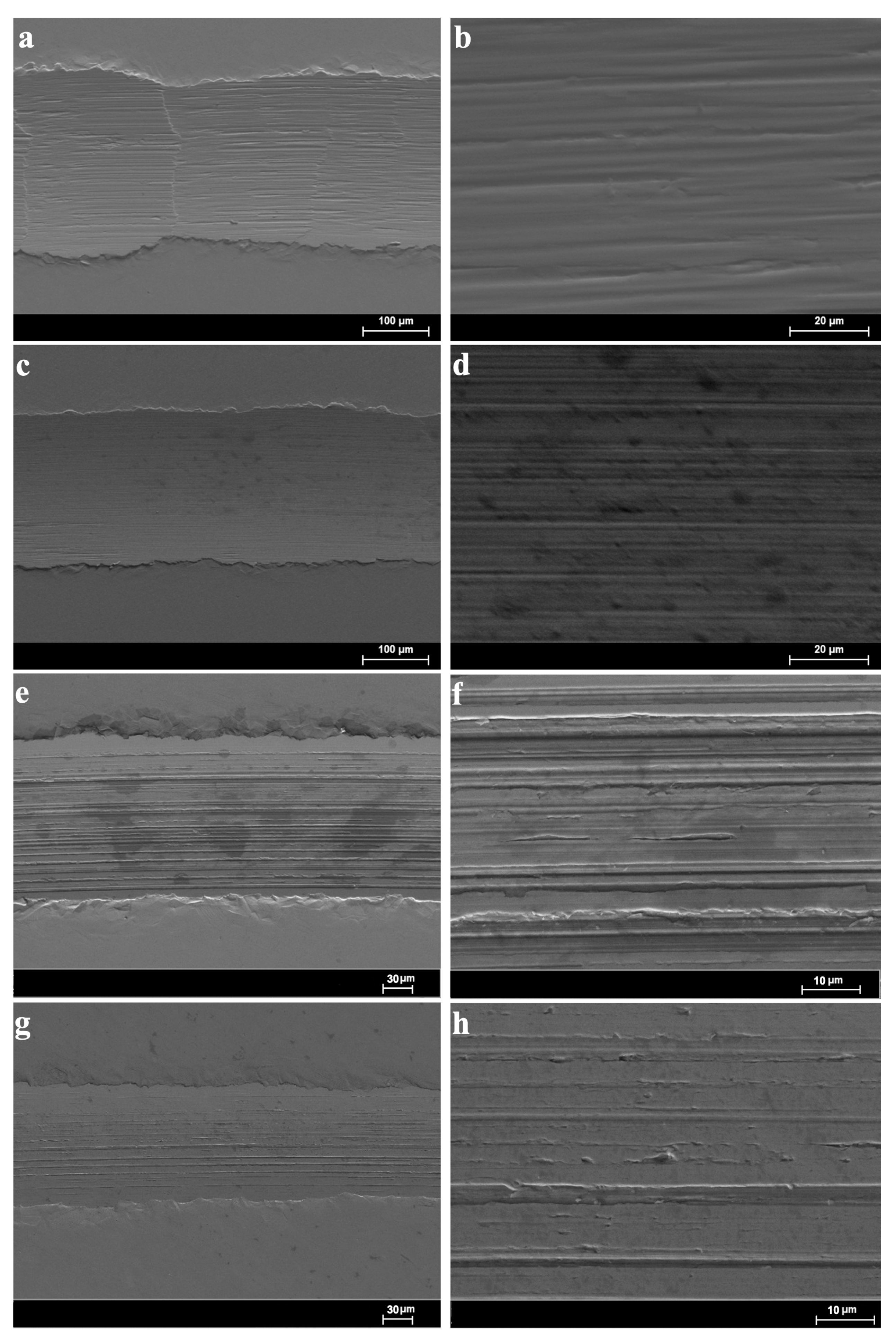
Figure 10 shows the results of the observation of the wear tracks using the SEM at two magnifications. In all the cases, the morphology inside of the wear tracks denoted parallel and aligned linear grooves; these are compatible with a mild abrasive wear mechanism caused by successive runs of the sapphire ball on the disc. The width and the visible damage inside of the wear tracks are clearly higher for 1%ChAc, 1%ChCl, and neat ChLy in comparison with 1%ChLy.
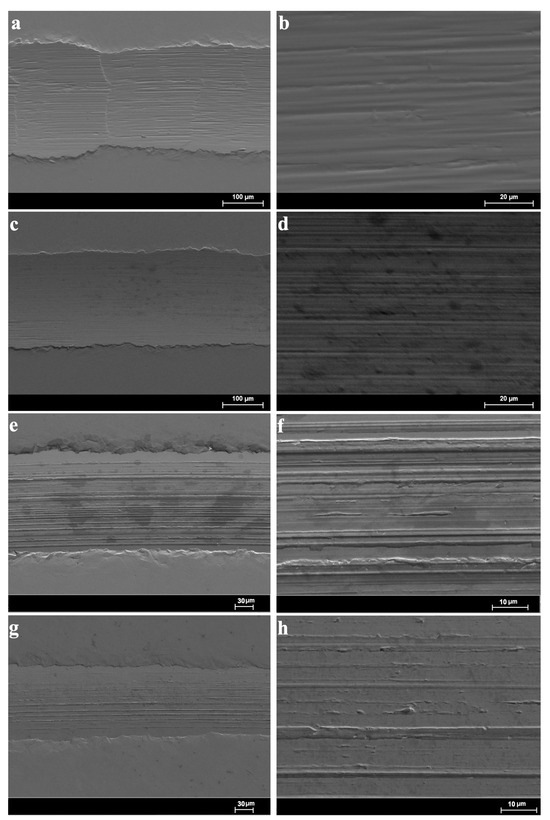
Figure 10.
Low and high magnification SEM micrographs of the wear tracks: (a,b) 1%ChAc; (c,d) 1%ChCl; (e,f) neat ChLy; and (g,h) 1%ChLy.
Following the study of damage on the metallic discs, analysis inside and outside the wear tracks was carried out using the EDX probe; Table 6 shows the obtained data. It is worth mentioning that the oxygen content was higher inside than outside the wear tracks in all the cases except for that of the neat ChLy. It is likely that the predominant presence of water in the WBB provoked the start of an oxidation process, assisted by the continuous passes of the ceramic ball under load.

Table 6.
Elemental analysis (wt%) by EDX inside and outside of the wear tracks.
3.3. Tribological Characterization of Thin Layers
1%ChLy demonstrated the best tribological properties. This biolubricant exhibited outstanding performance in terms of friction coefficient and wear rate, with minimal damage on the sample discs. The high free energy of adsorption of the IL on the surface assists in reducing slip and preventing direct contact between counterfaces, leading to a lower friction coefficient and wear rate. Additionally, the very small particle size increases the surface area of the ionic liquid in solution. This excellent performance was achieved quickly as the water evaporated during the test. Given that previous studies had shown that the use of a thin layer of protic IL gave notable tribological performance [12,13], we decided to develop thin layers of the water-based biolubricants and test their tribological properties under the same conditions.
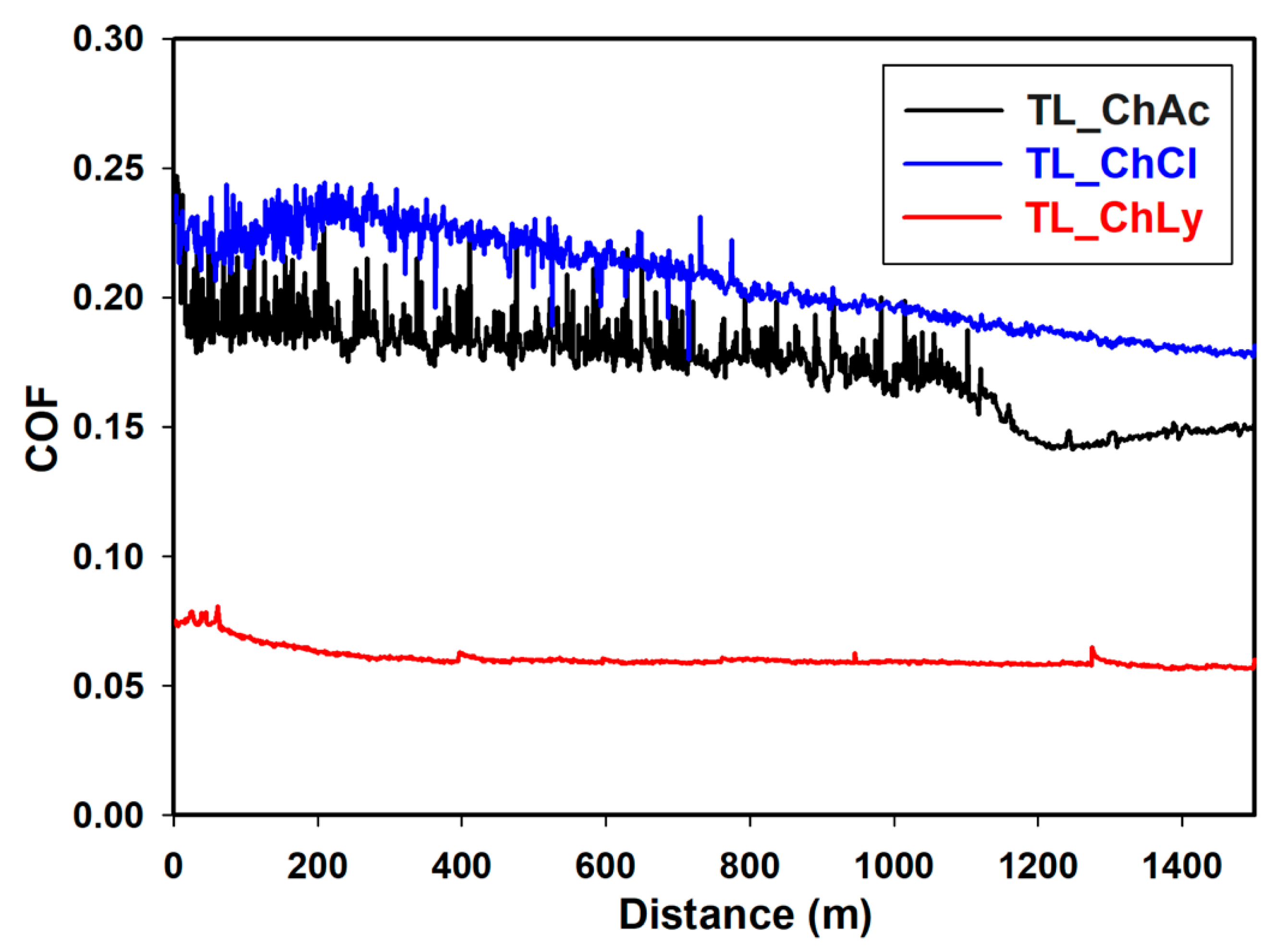
The plots of the friction coefficients of the thin layers of WBB are shown in Figure 11. The sample TL_ChLy presented excellent performance, even better than the water-based 1%ChLy biolubricant, with a value of 0.054. This was significantly lower than the two preceding samples, TL_ChAc and TL_ChCl, which had friction coefficients close to 0.200 and exhibited a prominent stick-slip effect.
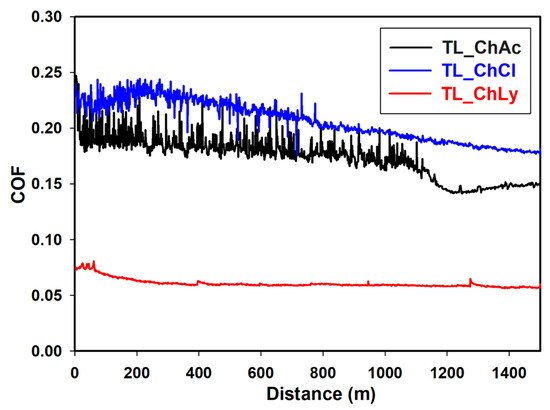
Figure 11.
Friction coefficient TL_ChAc, TL_ChCl, and TL_ChLy samples along 1500 m.
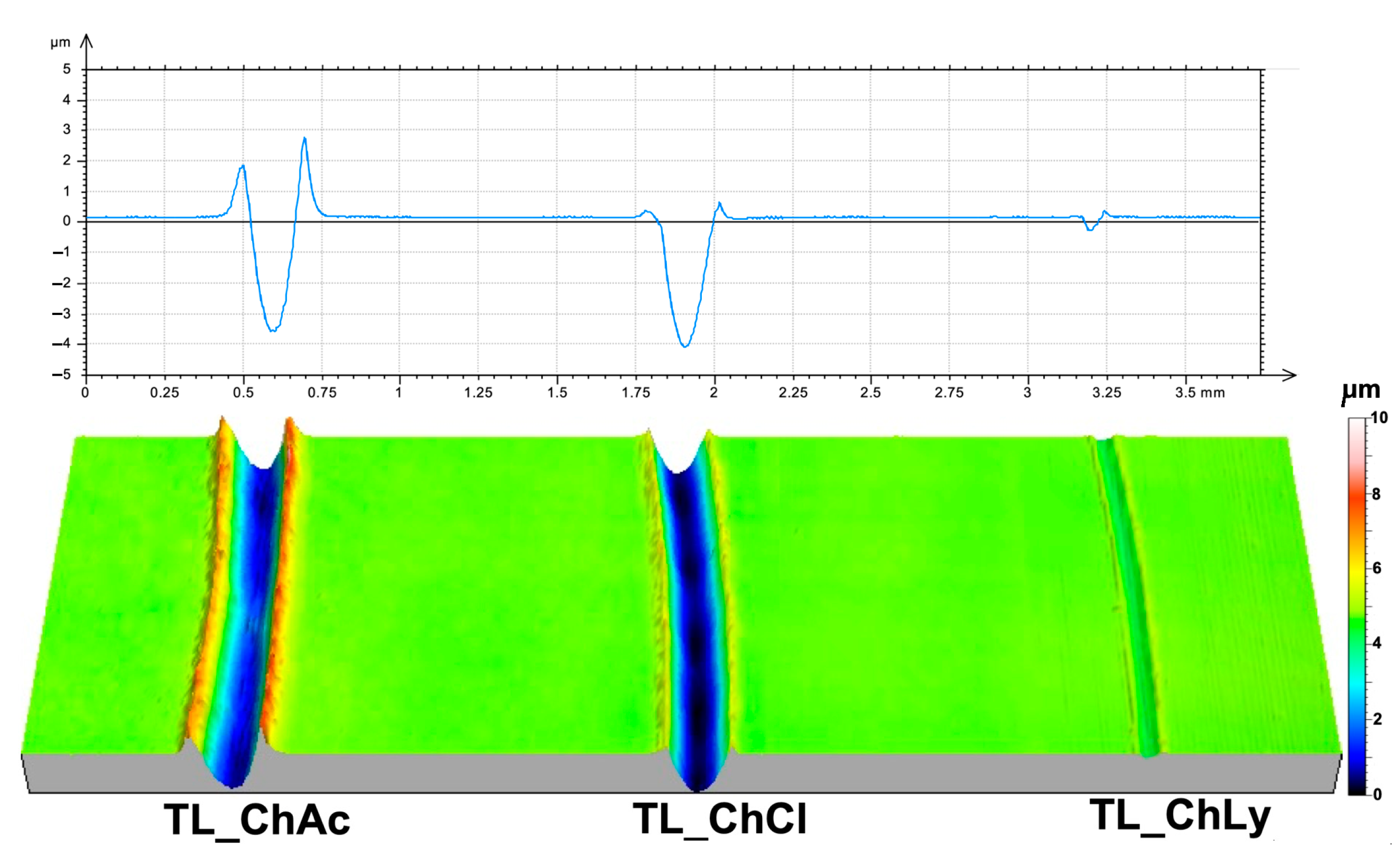
The study of the damage to the metallic surface of the discs once again revealed the good performance of TL_ChLy, with practically negligible damage, as shown in Table 7. Compared to TL_ChAc, the reduction in wear rate was 97.7%. Figure 12 shows the wear profiles and 3D images of the wear scars on the surfaces of the thin layers.

Table 7.
Friction coefficients and K; wear rates on thin-layer samples.
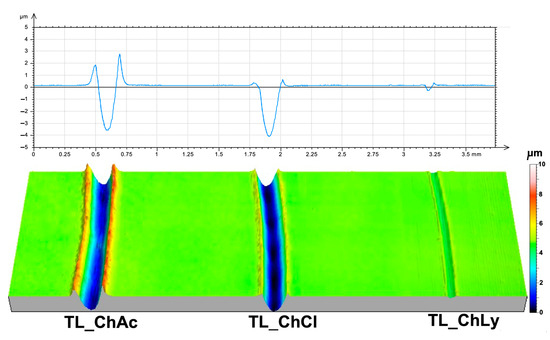
Figure 12.
Two-dimensional and three-dimensional views after the test of the wear scars on the thin layers.
Observation of the wear scars on the sapphire balls after the tests, using optical microscopy, revealed the absence of damage on the ball used in the test with TL_ChLy. Only minimal wear scars were observed on the other thin layers, and no material transfer from the discs to the balls was detected (see Figure 13).
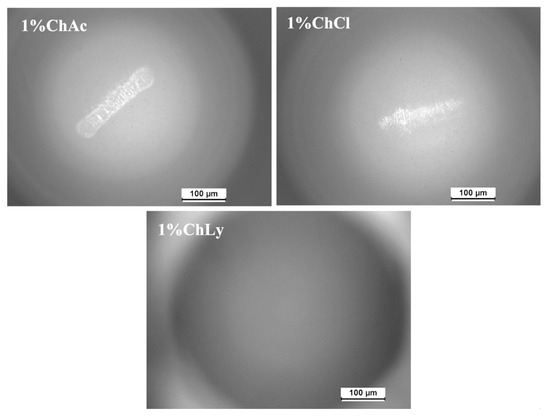
Figure 13.
Wear scars of the ball after the lubrication tests using optical microscopy.
3.4. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
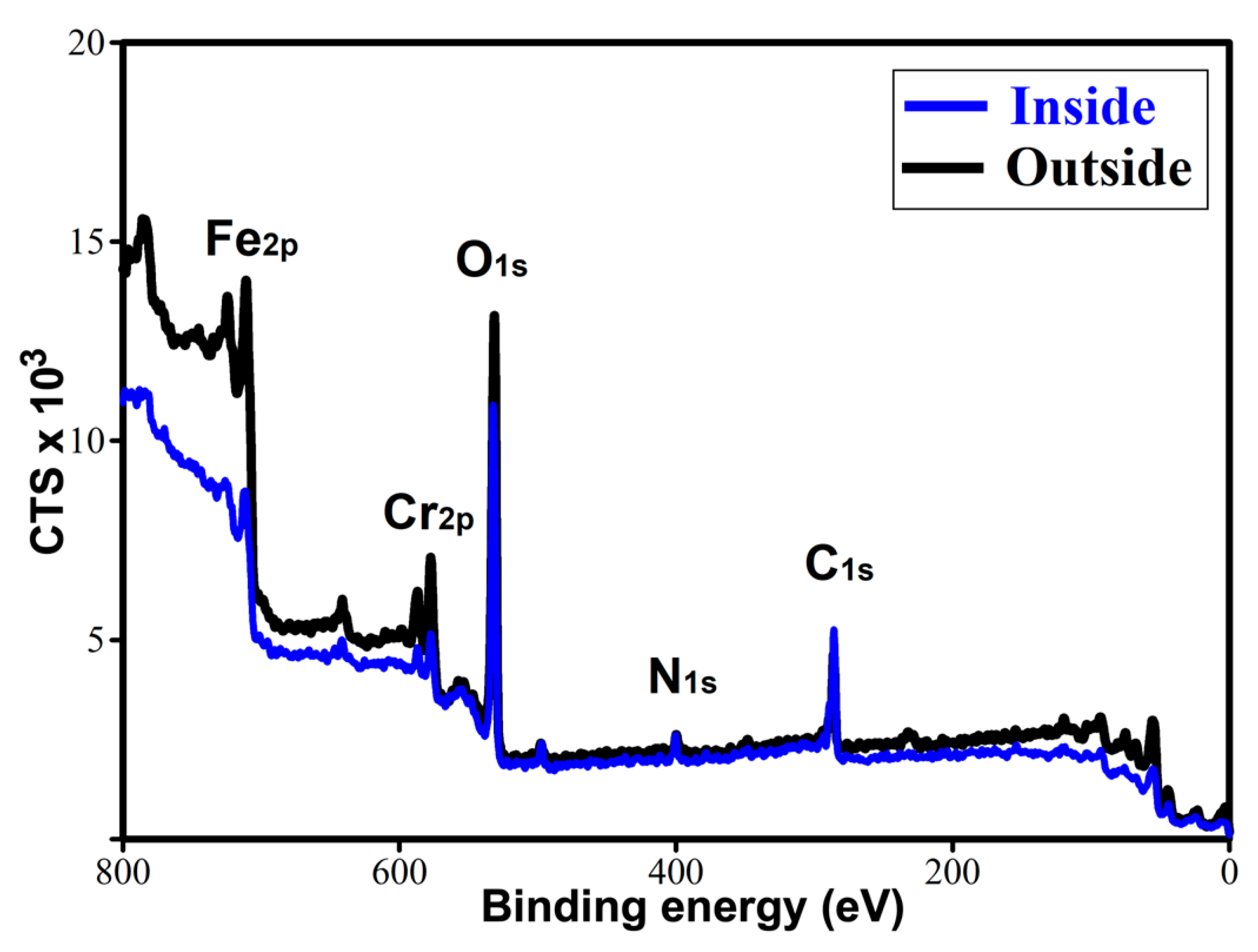
The exceptional tribological performance of TL_ChLy can be attributed to the presence of a tribolayer that interacts with and is adsorbed onto the stainless-steel surface. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) technique was employed to investigate the presence of a tribofilm for TL_ChLy by comparing the analyses conducted outside and inside the wear track after cleaning the surface with ethanol. Figure 14 and Table 8 present the results obtained from the survey analysis of XPS spectra, which was performed out within the binding energy of 0–800 eV, highlighting the principal elements present in the amino-acid ionic liquid, as well as those inherent to the stainless-steel substrate.
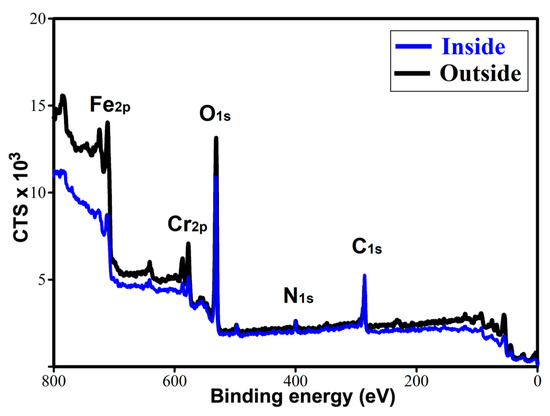
Figure 14.
XPS survey spectra for the TL_ChLy sample inside and outside of the wear track.

Table 8.
Binding energy and atomic percentages inside and outside the wear track after the test on TL_ChLy.
The results are consistent with those previously observed with EDX analysis after the lubrication tests using the WBB, indicating a significantly higher presence of oxygen inside compared to outside.
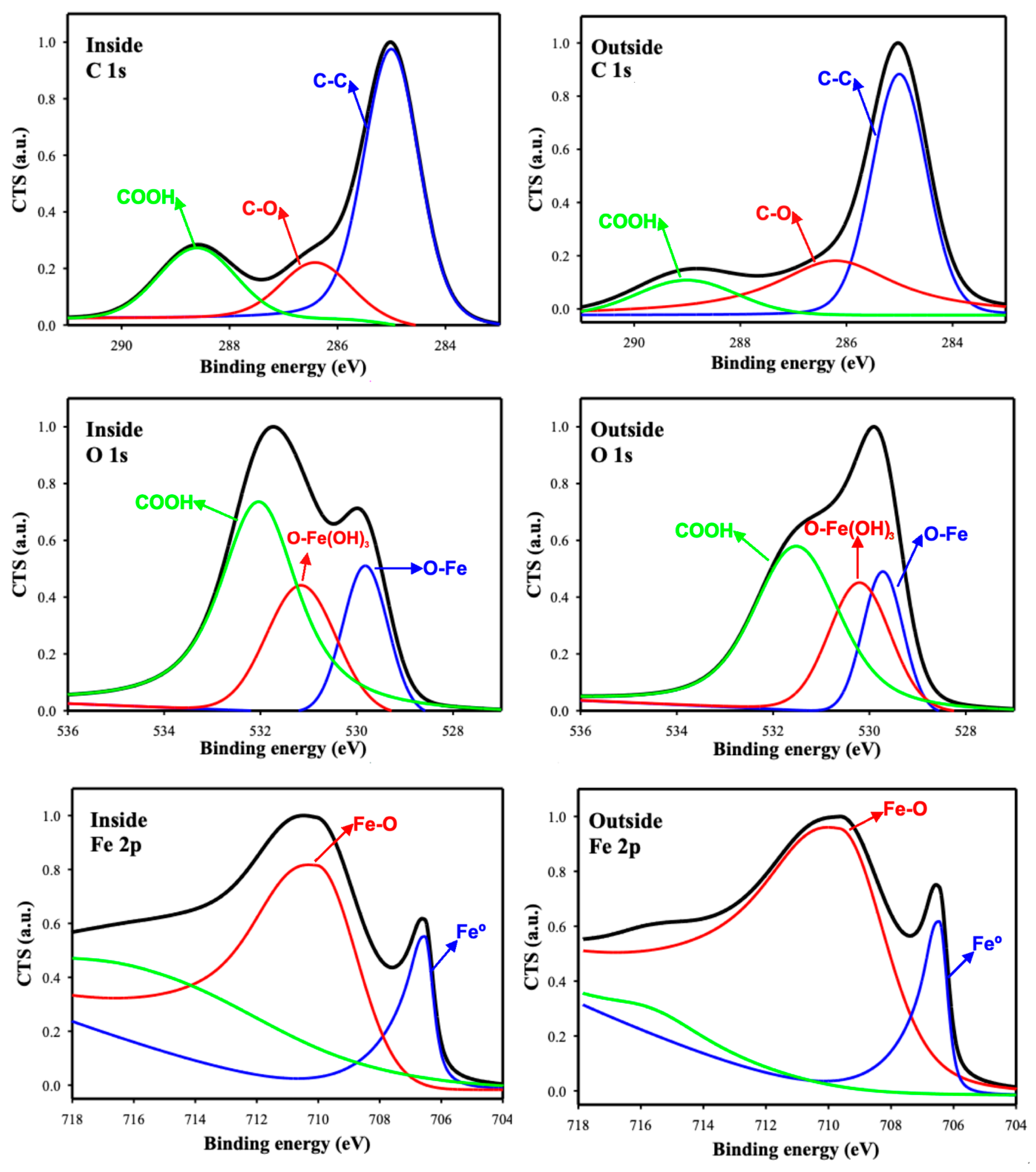
The comparative plots of the high-resolution spectra, both outside and inside the tracks (black), along with the deconvolution spectra results of the chemical states for the ChLy biolubricant, are presented in Figure 15, and confirmed the formation of a tribolayer during the tribological testing.
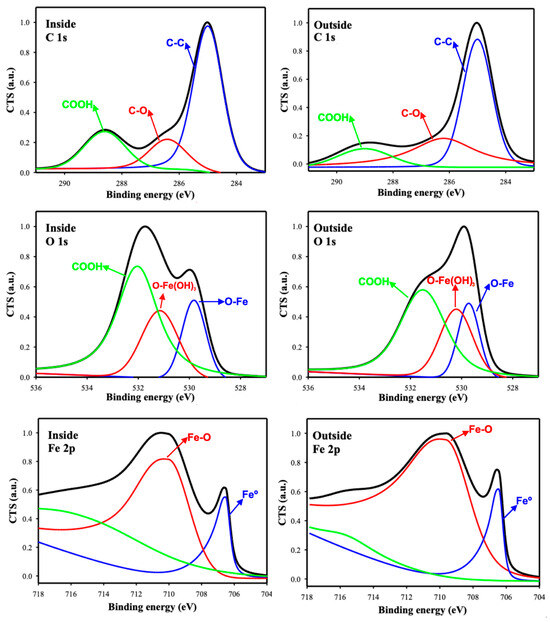
Figure 15.
XPS high-resolution spectra for C, O, and Fe elements, inside and outside the wear scars.
A detailed study of the high-resolution XPS spectra revealed that the carbon atomic percentage was higher inside the track, with C1s peaks in the binding energy range of 290–283 eV. This observation is coherent with ChLy, containing aliphatic C, C-O, and COOH at 285.0, 286.6, and 288.8 eV, respectively [45,46].
Regarding the O 1s spectra, the observed peaks can be attributed to the formation of iron (III) oxide and hydroxide, as well as the presence of an organic layer associated with the ionic liquid in the organic acid group [45].
The presence of a lower atomic percentage of Fe 2p inside the wear track, compared to outside, is likely owing to the presence of adsorbed organic molecules, which augment the intensity of the C 1s peaks and lower the intensity of the metal peaks. The Fe 2p high-resolution spectra in Figure 15 also show peaks at 711.0 eV and 706.6 eV, which are attributed to iron (III) hydroxide [47], and the iron originating from the stainless-steel substrate [45,47].
4. Conclusions
In this study, the water-based biolubricant containing 1 wt% of the ionic liquid Choline Lysine exhibits remarkable stability at room temperature, and wettability studies demonstrated that this biolubricant achieves a high contact angle among all tested samples on stainless-steel surfaces. The investigation into the size distribution range of particles in the biolubricant 1% ChLy, utilizing the dynamic light scattering (DLS) technique, revealed a single distribution and an exceptionally small particle size, close to 10 nm. This result indicates an increase in the surface area due to the small size of the particle in solution and suggests the potential to achieve a higher concentration of the biolubricant on the metallic surface. In accordance with the procedure described in ASTM D4627–22, the biolubricant 1%ChLy demonstrated that the additive functions as an inhibitor against corrosion. This effect is likely attributable to the elevated pH value of the solution.
The friction coefficients over a sliding distance of 1500 m for the novel WBB are characterized by two distinct stages. Initially, the friction coefficients were high, but after a period, they decreased, reaching a stable plateau stage with low values of friction. This transition was driven by the evaporation of the water content, which impacted significantly on the tribological performance by increasing the viscosity, thereby greatly enhancing the load-carrying capacity. The potential of 1% ChLy as a WBB was demonstrated by its remarkable friction coefficient, achieving a value of 0.068 in the steady-state stage and causing minimal damage to the stainless-steel surface. In addition, the evaluation of wear rate tests again evidenced the excellent tribological performance of the biolubricant 1% ChLy, with reductions of 97.6% compared to water and 93.6% compared to neat ChLy.
Finally, the preparation of the thin-layer samples, which was a further step to improve tribological performance, involved the evaporation of the water content under vacuum, resulting in a filmy coating that exhibited exceptional behavior. This thin layer demonstrated an impressive friction coefficient of 0.054 and a remarkable wear rate reduction of 97.7% when compared to the other thin-layer samples utilizing ChAc and ChCl. XPS studies confirmed the existence of an adsorbed layer of ChLy on the wear track, corroborating the adsorption of ChLy on the metallic surface, thus lowering the contact between the sapphire ball and the stainless-steel surface.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology F.J.C.-V., M.-D.A. and P.M.; investigation, P.M., M.-D.A. and P.M.M.-R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-D.A., P.M. and F.J.C.-V.; writing—review and editing, F.J.C.-V. and M.-D.B.; funding acquisition, F.J.C.-V. and M.-D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present research was funded by grant PID2021-122169NB-I00 funded by MCIN/AEI 10.13039/501100011033 and by the EU. P.M. recognizes grant PRE2022-102014 funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by EU Next Generation EU/PRTR and P-M.M-R would like to thank Fundación Séneca (Region de Murcia, Spain) for the FPI research grant (21574/FPI/21).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bermúdez, M.D.; Jiménez, A.E.; Sanes, J.; Carrión, F.J. Ionic Liquids as Advanced Lubricant Fluids. Molecules 2009, 14, 2888–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, I. Ionic Liquids in Tribology. Molecules 2009, 14, 2286–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandra, P.; Szerb, E.I.; Lombardo, D.; Algieri, V.; De Nino, A.; Maiuolo, L. A Presentation of Ionic Liquids as Lubricants: Some Critical Comments. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.J.; Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, A.C.F.; Malfreyt, P.; Pádua, A.A.H. Interactions and Ordering of Ionic Liquids at a Metal Surface. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3348–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, J. Ionic Liquids as Lubricant Additives: A Review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomala, A.; Karpinska, A.; Werner, W.S.M.; Olver, A.; Störi, H. Tribological Properties of Additives for Water-Based Lubricants. Wear 2010, 269, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tang, W.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z. Synthesis of Ionic Liquid Decorated Muti-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as the Favorable Water-Based Lubricant Additives. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process 2017, 123, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Warneke, H.; Webbert, H.; Rodriguez, J.; Austin, E.; Tokunaga, K.; Rajak, D.K.; Menezes, P.L. Water-Based Lubricants: Development, Properties, and Performances. Lubricants 2021, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, L.; Jin, Z.; Prakash, B.; Ma, T.; Wang, W. A Review of Advances in Tribology in 2020–2021. Friction 2022, 10, 1443–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Ahmed, E.I.; Harris, R.C.; Ryder, K.S. Evaluating Water Miscible Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Ionic Liquids as Potential Lubricants. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4156–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Jiménez, M.; Sanes, J.; Jiménez, A.E.; Iglesias, M.; Bermúdez, M.D. Ultra-Low Friction with a Protic Ionic Liquid Boundary Film at the Water-Lubricated Sapphire-Stainless Steel Interface. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, M.D.; Carrión-Vilches, F.J.; Sanes, J.; Bermúdez, M.D. Diprotic Ammonium Succinate Ionic Liquid in Thin Film Aqueous Lubrication and in Graphene Nanolubricant. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, M.D.; Carrión, F.J.; Sanes, J.; Bermúdez, M.D. Effects of Protic Ionic Liquid Crystal Additives on the Water-Lubricated Sliding Wear and Friction of Sapphire against Stainless Steel. Wear 2018, 408–409, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, F.J.; Avilés, M.D.; Nakano, K.; Tadokoro, C.; Nagamine, T.; Bermúdez, M.D. Diprotic Ammonium Palmitate Ionic Liquid Crystal and Nanodiamonds in Aqueous Lubrication. Film Thickness and Influence of Sliding Speed. Wear 2019, 418–419, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, M.D.; Cao, V.D.; Sánchez, C.; Arias-Pardilla, J.; Carrión-Vilches, F.J.; Sanes, J.; Kjøniksen, A.L.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Pamies, R. Effect of Temperature on the Rheological Behavior of a New Aqueous Liquid Crystal Bio-Lubricant. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadilohar, B.L.; Shankarling, G.S. Choline Based Ionic Liquids and Their Applications in Organic Transformation. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 234–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiin, C.L.; Yap, K.L.; Ku, A.Z.E.; Chin, B.L.F.; Lock, S.S.M.; Cheah, K.W.; Loy, A.C.M.; Chan, Y.H. Recent Advances in Green Solvents for Lignocellulosic Biomass Pretreatment: Potential of Choline Chloride (ChCl) Based Solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zaid, H.F.; Chong, F.K.; Abdul Mutalib, M.I. Extractive Deep Desulfurization of Diesel Using Choline Chloride-Glycerol Eutectic-Based Ionic Liquid as a Green Solvent. Fuel 2017, 192, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, C.; Yan, X.; Guo, T.; Xiang, W.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Yu, B.; Cai, M.; Zhou, F. Influence of the Molecular Structure on the Tribological Properties of Choline-Based Ionic Liquids as Water-Based Additives under Current-Carrying Lubrication. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 369, 120868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, Y.; Iizuka, Y.; Sekikawa, K.; Ohno, H. Bio Ionic Liquids: Room Temperature Ionic Liquids Composed Wholly of Biomaterials. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 1155–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzani, A.; Karadendrou, M.A.; Kalafateli, S.; Kakokefalou, V.; Detsi, A. Current Trends in Green Solvents: Biocompatible Ionic Liquids. Crystals 2022, 12, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Pang, J.; Iglesias, P. Recent Advances and Challenges of Ionic Liquids in Tribology. In Ionic Liquids—Recent Advances; Bhowmik, P.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Munro, H.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Preparation of Novel, Moisture-Stable, Lewis-Acidic Ionic Liquids Containing Quaternary Ammonium Salts with Functional Side Chains. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1, 2010–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.; Yon Pang, J.-S.; Lau, E. Von A Comparative Study of Thermophysical Properties between Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents and Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 395, 123895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawes, S.D.A.; Hainsworth, S.V.; Blake, P.; Ryder, K.S.; Abbott, A.P. Lubrication of Steel/Steel Contacts by Choline Chloride Ionic Liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 37, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea Mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernaglia, M.; Rivera, N.; Bartolomé, M.; Fernández-González, A.; González, R.; Viesca, J.L. Tribological Behavior of Two Novel Choline Acetate-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 414, 126102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigual, V.; Papa, G.; Rodriguez, A.; Wehrs, M.; Kim, K.H.; Oliet, M.; Alonso, M.V.; Gladden, J.M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Simmons, B.A.; et al. Evaluating Protic Ionic Liquid for Woody Biomass One-Pot Pretreatment + Saccharification, Followed by Rhodosporidium Toruloides Cultivation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Wen, P.; Li, N.; Zong, M.; Ou-Yang, B.; Wu, H. Evaluating the Effects of Biocompatible Cholinium Ionic Liquids on Microbial Lipid Production by Trichosporon Fermentans. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.P.; Hou, X.D.; Li, N.; Zong, M.H. Ionic Liquids from Renewable Biomaterials: Synthesis, Characterization and Application in the Pretreatment of Biomass. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Li, S.; Ma, H.-H.; Zhang, B.-X.; Gao, Y.-F. Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Effective Solvents for Lignin Extraction and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocelluloses. Bioresources 2016, 11, 7672–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.J.; Miao, S.; Imberti, S.; Simmons, B.A.; Atkin, R.; Warr, G.G. Liquid Nanostructure of Choline Lysinate with Water and a Model Lignin Residue. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. The Ratio of Choline Lysine Ionic Liquid Determines the Structure and Digestion of Starch-Oleic Acid Complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; He, Q.; Zhou, G.; Ali, A.; Yu, C.; Yao, S. Choline and Amino Acids-Based Ionic Liquids (CABILs) for the Preparation of New Antibacterial Coating with Loofah and Epoxy Resin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mu, L.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yin, X.; Feng, X.; Lu, X.; Larsson, R.; Shi, Y. Turning the Solubility and Lubricity of Ionic Liquids by Absorbing CO2. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, M.D.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, C.; Pamies, R.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Carrión-Vilches, F.J.; Sanfelix, S.G.; Kjoniksen, A.L. New Water-Ethylene Glycol Lubricants with Stearate Ionic Liquid Crystal Additive. Lubricants 2022, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarenko, N.V.; Kharchenko, U.V.; Zemnukhova, L.A. Effect of Amino Acids on Corrosion of Copper and Steel in Acid Medium. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2011, 84, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ibrahimi, B.; Jmiai, A.; Bazzi, L.; El Issami, S. Amino Acids and Their Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Metals and Alloys. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 740–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qu, X.; Hu, X. Iron-Coordinated L-Lysine–Based Nanozymes with High Peroxidase-like Activity for Sensitive Hydrogen Peroxide and Glucose Detection. Polymers 2023, 15, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pušnik, K.; Peterlin, M.; Cigić, I.K.; Marolt, G.; Kogej, K.; Mertelj, A.; Gyergyek, S.; Makovec, D. Adsorption of Amino Acids, Aspartic Acid, and Lysine onto Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. 2016, 120, 14372–14381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzhitskii, A.; Lazorenko, G.; Nazdracheva, T.; Yavna, V. Comparative Computational Study of L-Amino Acids as Green Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel. Computation 2021, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talha, M.; Ma, Y.; Kumar, P.; Lin, Y.; Singh, A. Role of Protein Adsorption in the Bio Corrosion of Metallic Implants—A Review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, S.; Lohner, T.; Stahl, K. Influence of Water Evaporation on Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication with Water-Containing Polyalkylene Glycols. Friction 2024, 12, 2370–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtis, L.A.; Arcifa, A.; Zhang, P.; Du, J.; Fantauzzi, M.; Rauber, D.; Hempelmann, R.; Kraus, T.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Influence of Water on Tribolayer Growth When Lubricating Steel with a Fluorinated Phosphonium Dicyanamide Ionic Liquid. Lubricants 2019, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database NIST Standard Reference Database Number 20; version 5.0; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fan, Y.; Fan, Z.; Xu, H.; Cui, D.; Xue, C.; Zhang, W. Noble-Metal-Free p-n Heterojunction of Iron(III) Hydroxide and Graphitic Carbon Nitride for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Ceram Int. 2021, 47, 35057–35066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).