Study on Temperature Field Distribution of a High-Speed Double-Helical Gear Pair with Oil Injection Lubrication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Calculation Methods
2.1. CFD Theoretical
2.1.1. Basic Control Equations
2.1.2. Multiphase Flow Model
2.1.3. Turbulence Model
2.2. Heat Flux Density Calculation
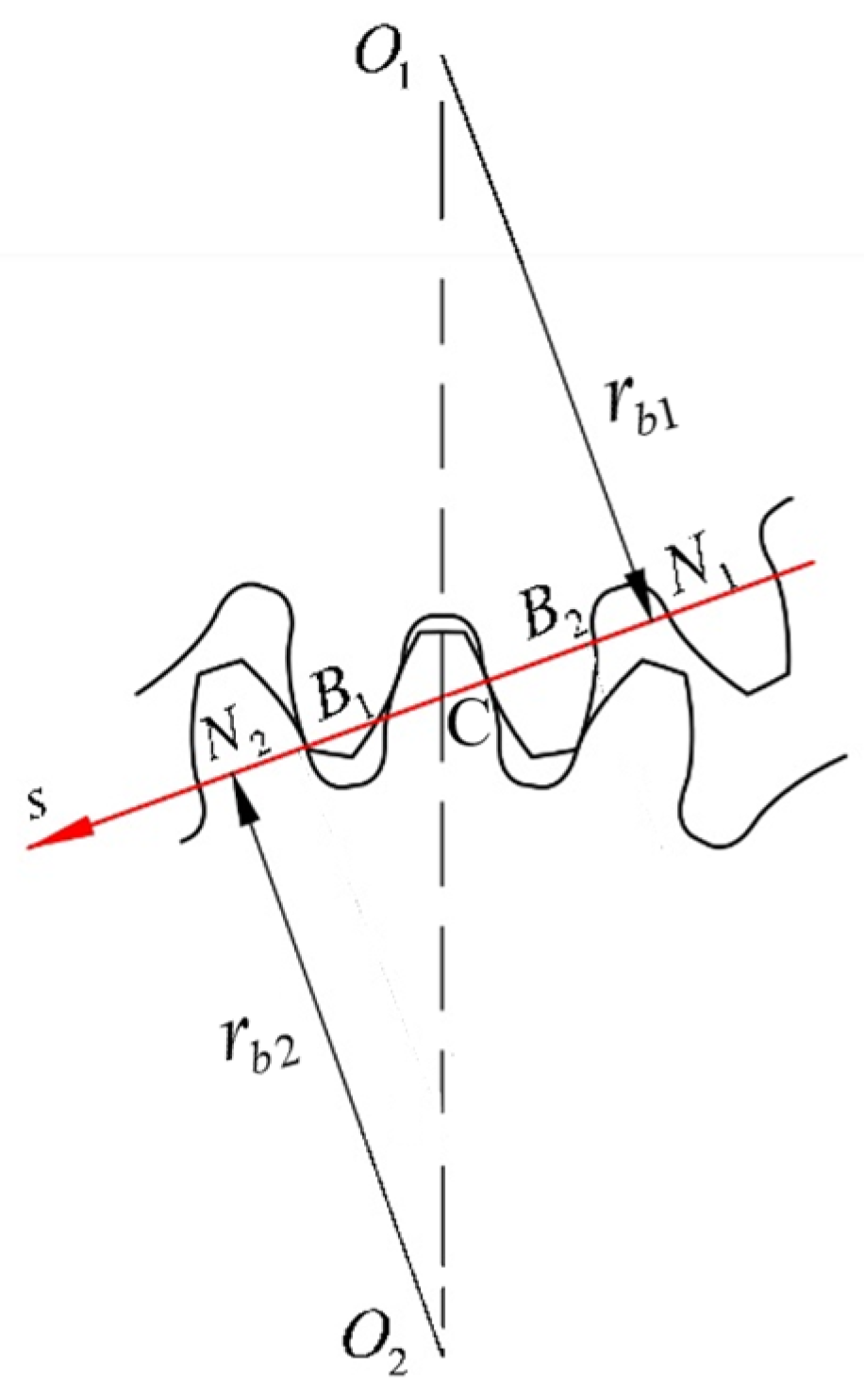
2.2.1. Radius of Curvature at Meshing Position
2.2.2. Velocity at Meshing Position
2.2.3. Contact Line Length
2.2.4. Normal Load on Tooth Surface
2.2.5. Average Contact Pressure on Tooth Surface
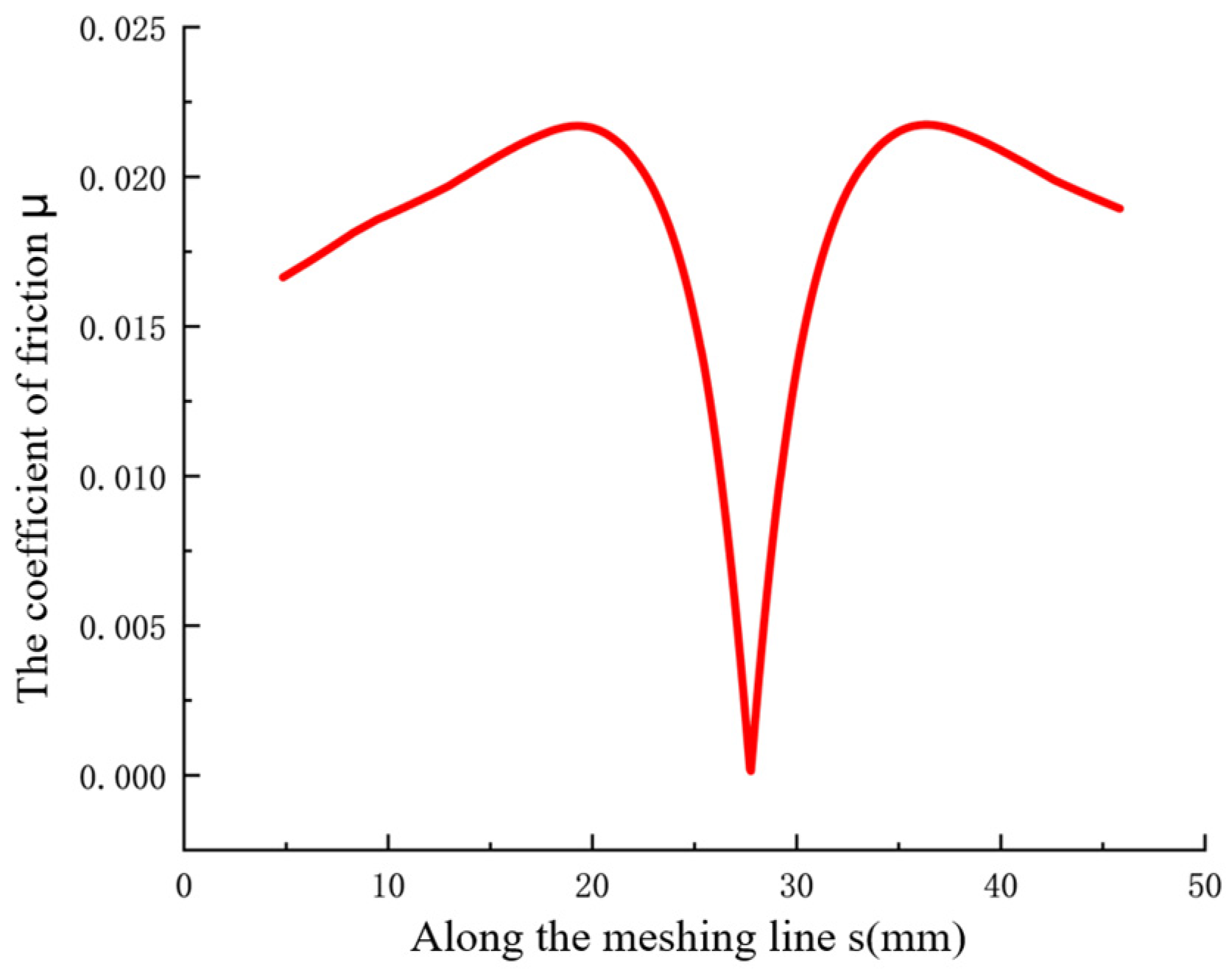
2.2.6. Tooth Surface Friction Coefficient
2.2.7. Calculation of Average Frictional Heat Flux Density on Tooth Surface
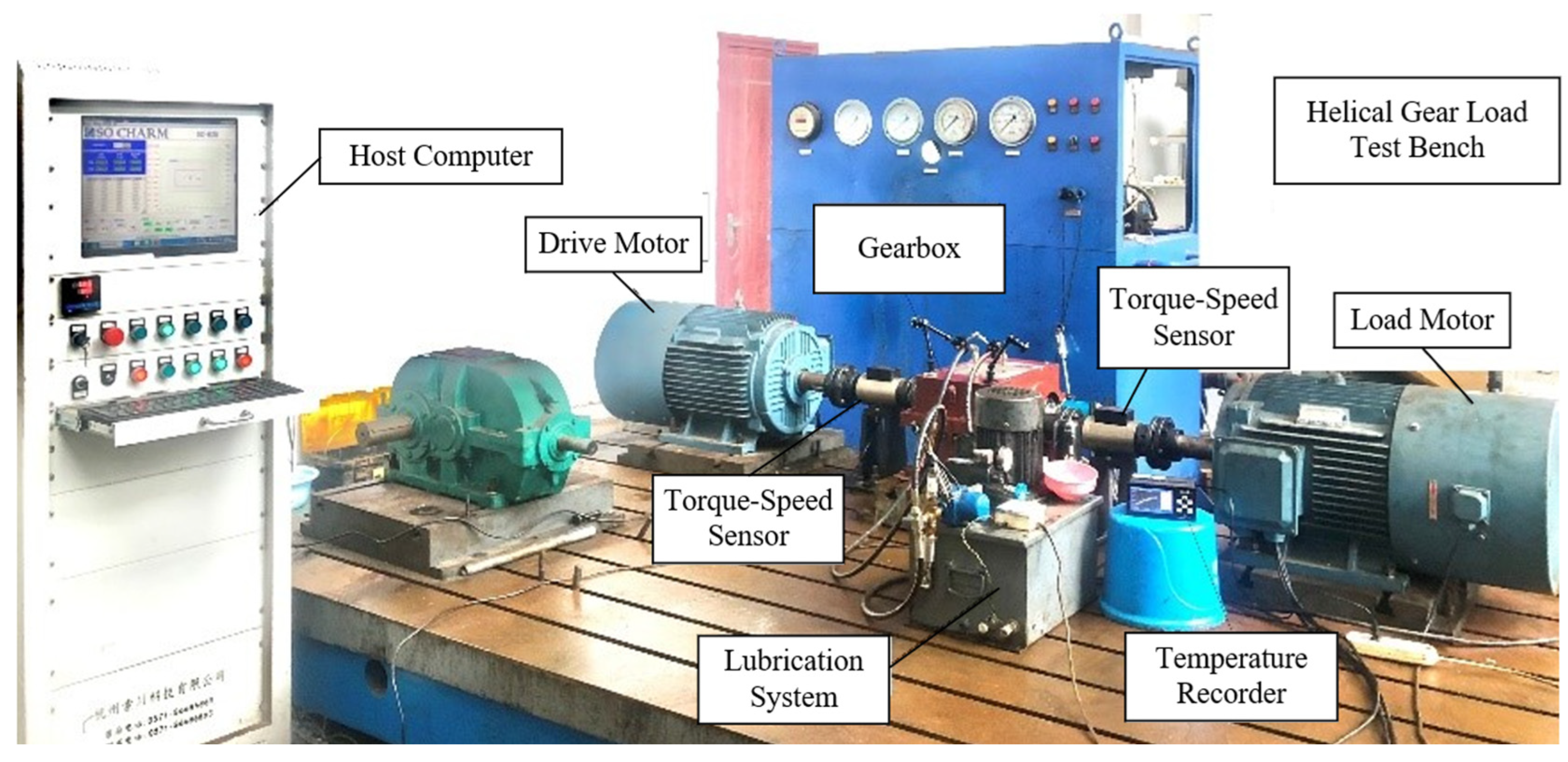
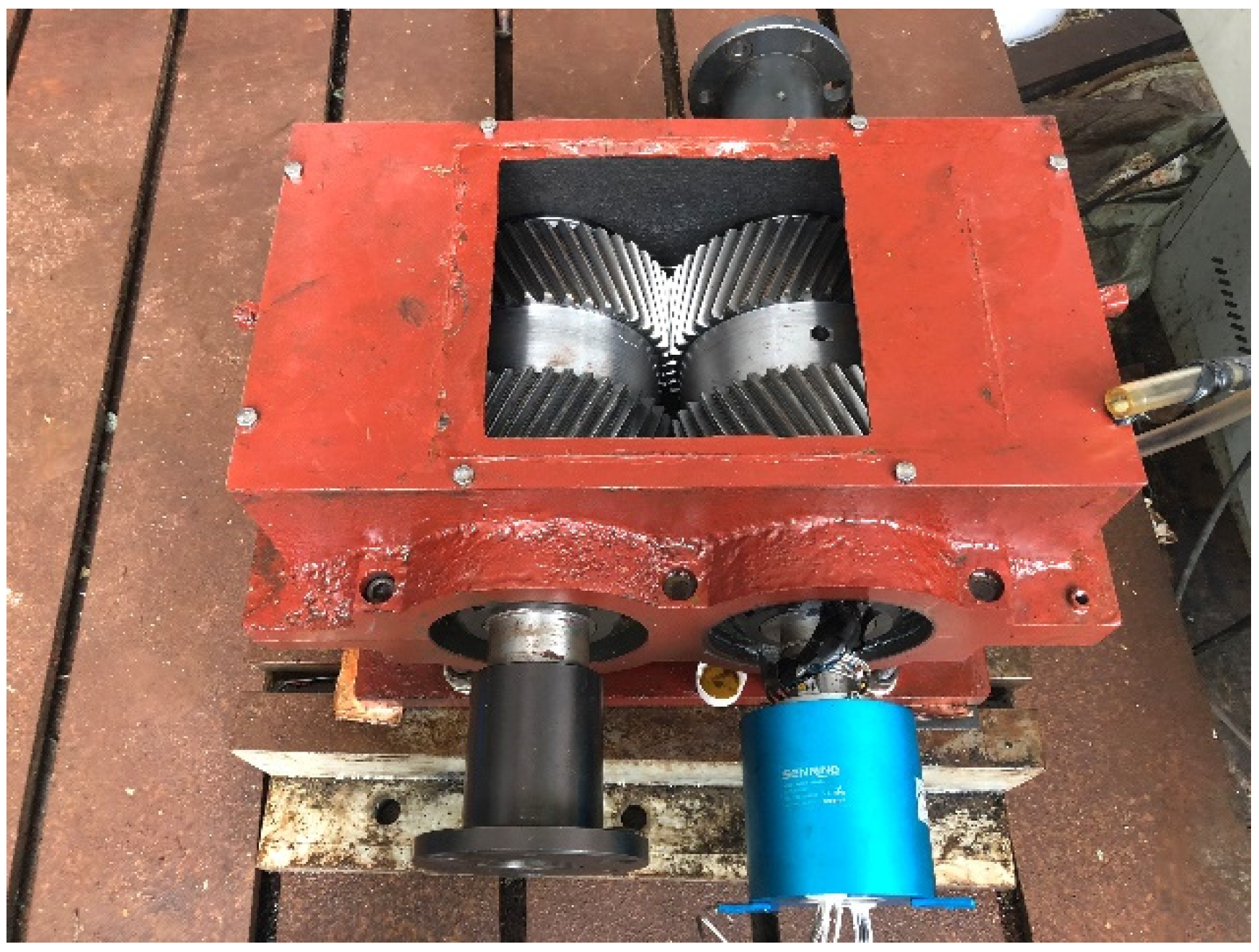
3. Verification of Numerical Method
- Adjustable jet parameters;
- Real-time temperature monitoring of the double-helical gear;
- User-friendly operation, ensuring safety and reliability through digital control.
4. Simulation Model
4.1. Double-Helical Gear Jet Lubrication Simulation Model
4.2. Temperature Field Simulation Model for Double-Helical Gears
5. Simulation Analysis Results
5.1. Lubrication Simulation Results Analysis
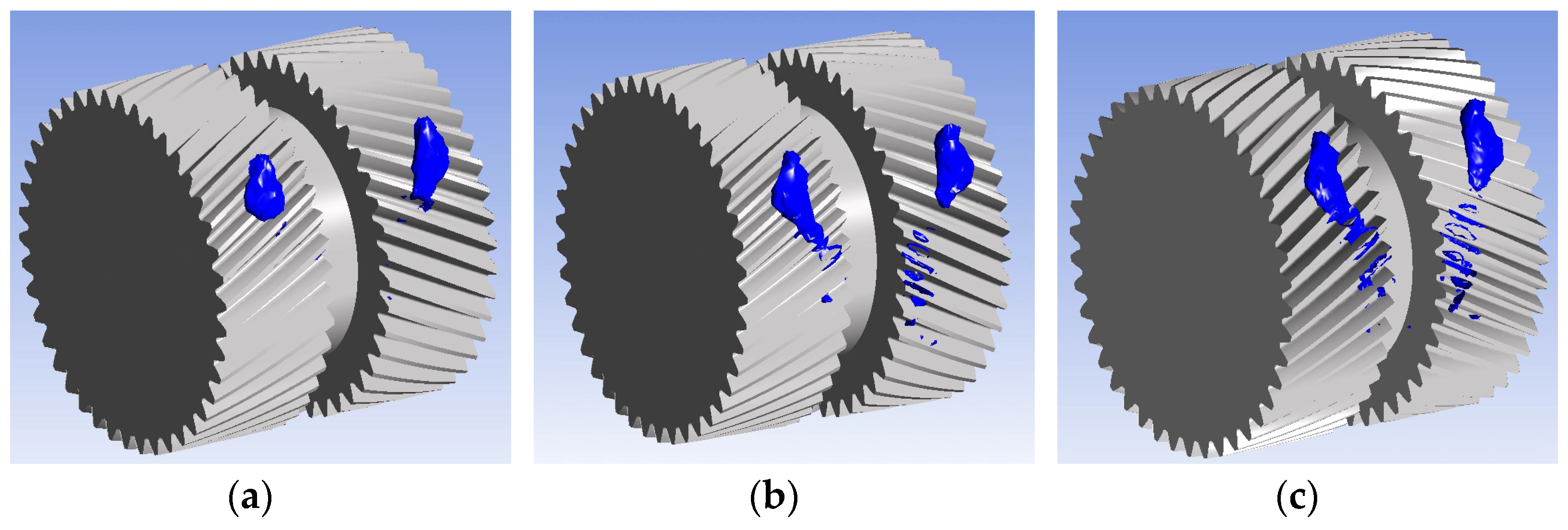
5.1.1. Jet Velocity
5.1.2. Jet Diameter
5.1.3. Gear Rotation Speed
5.2. Temperature Field Simulation Result Analysis
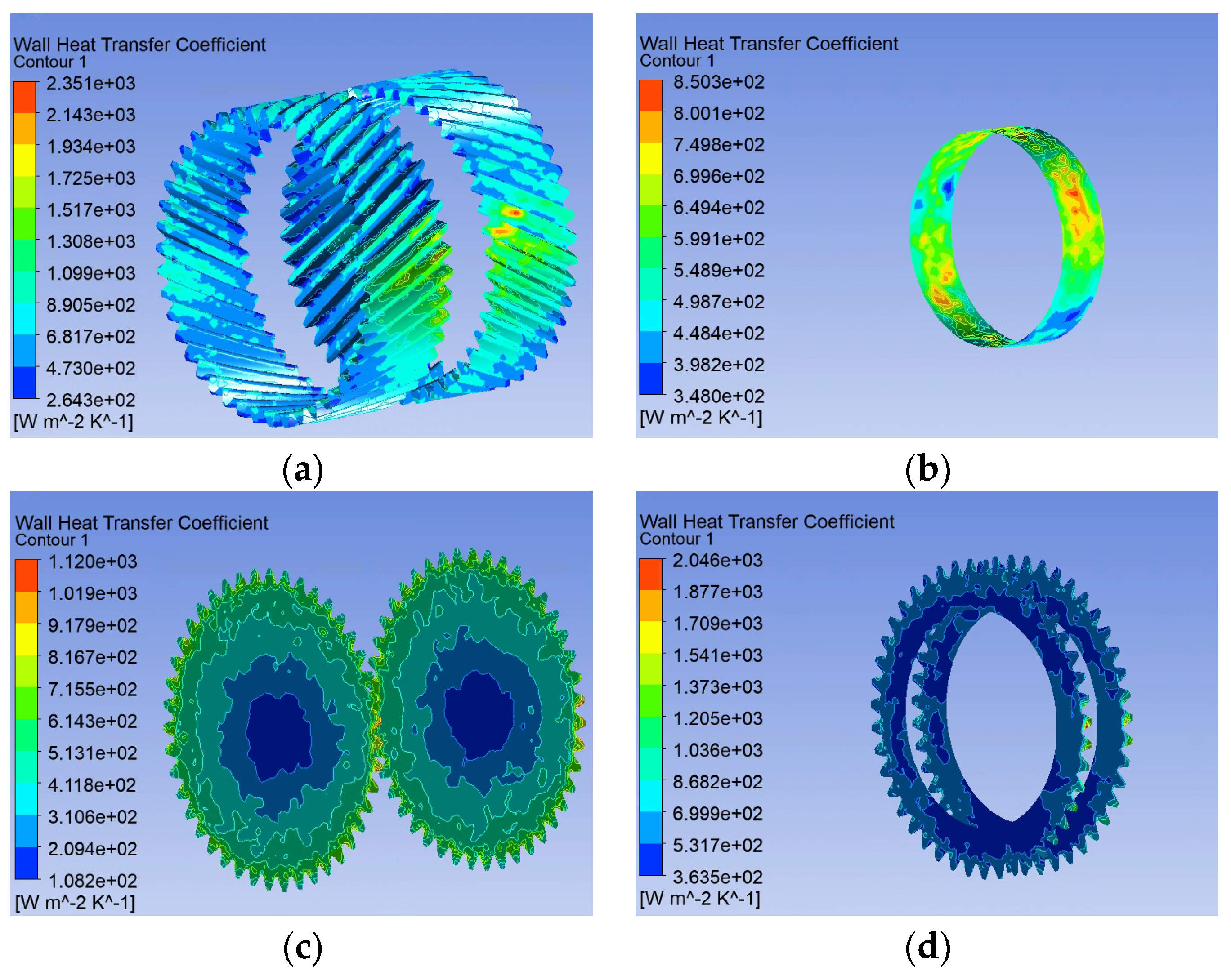
5.2.1. Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient Calculation
5.2.2. Calculation of Heat Flux Density for Double-Helical Gears
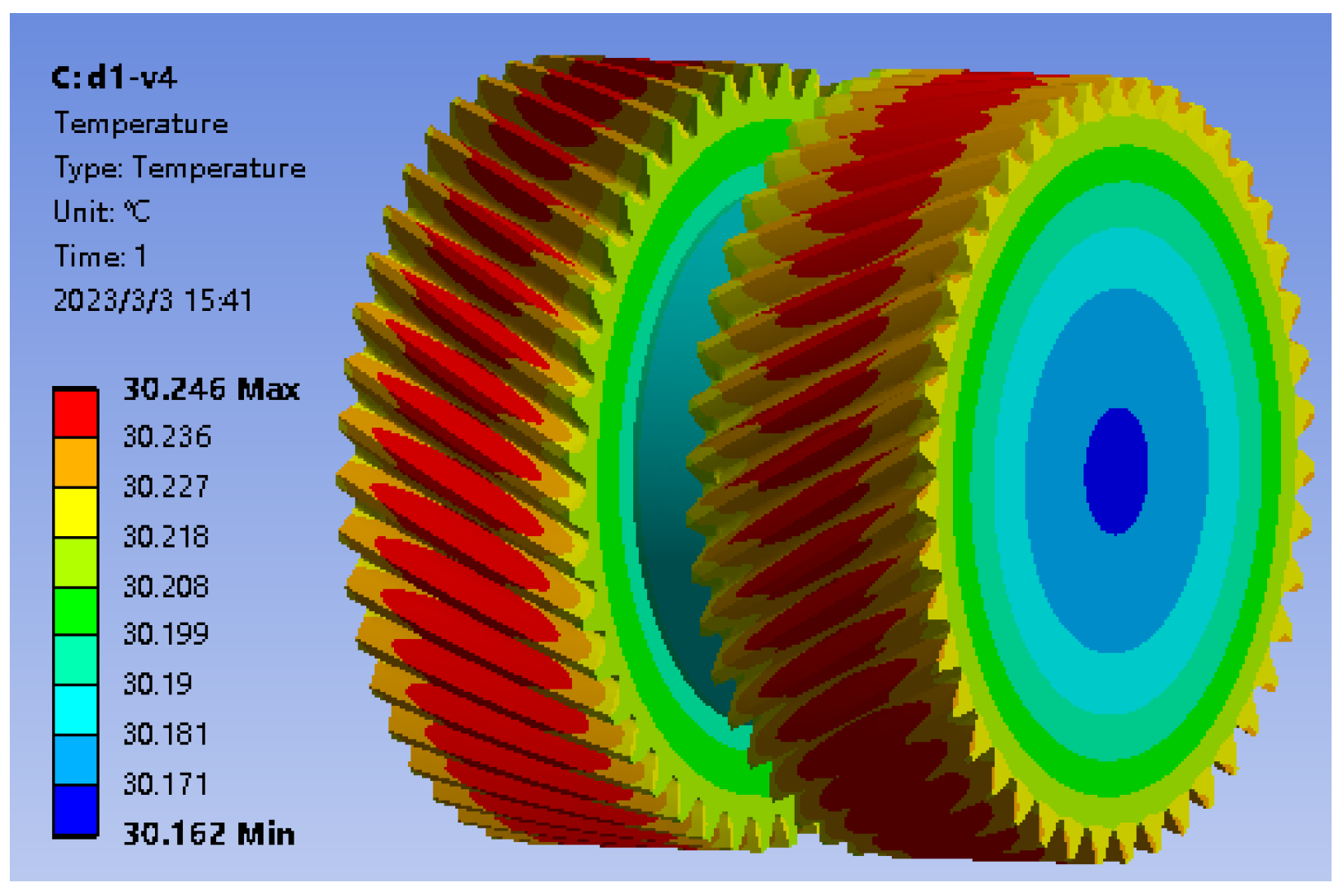
5.2.3. Temperature Field Simulation Solution
5.2.4. Analysis of Parameters Affecting the Steady-State Temperature Field Distribution
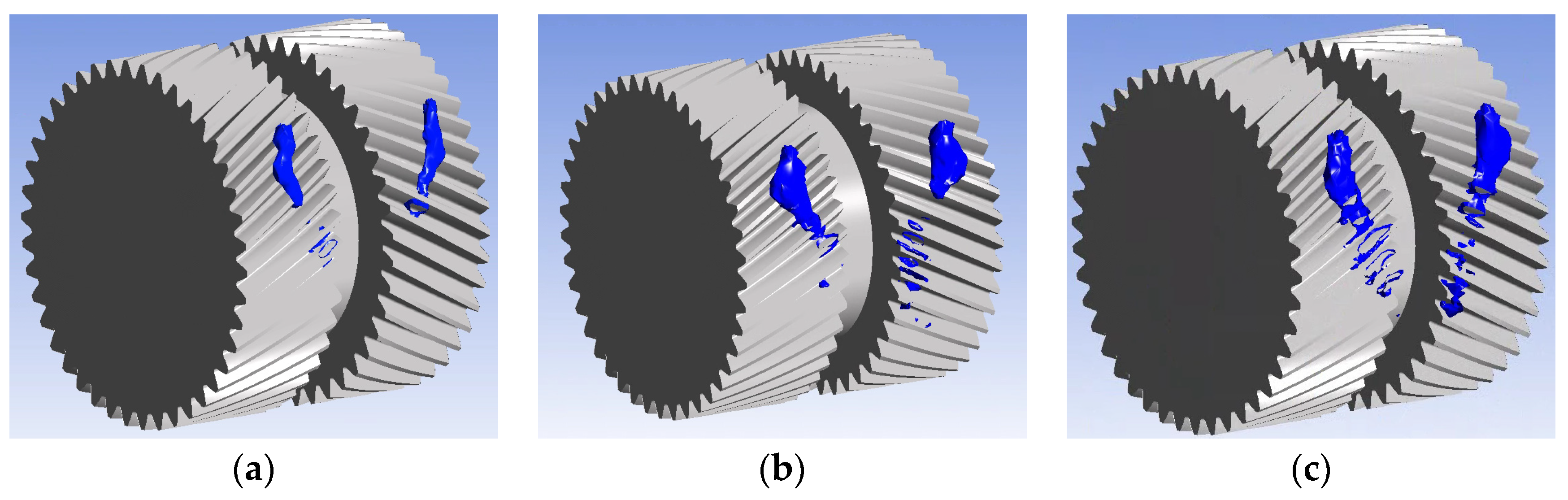
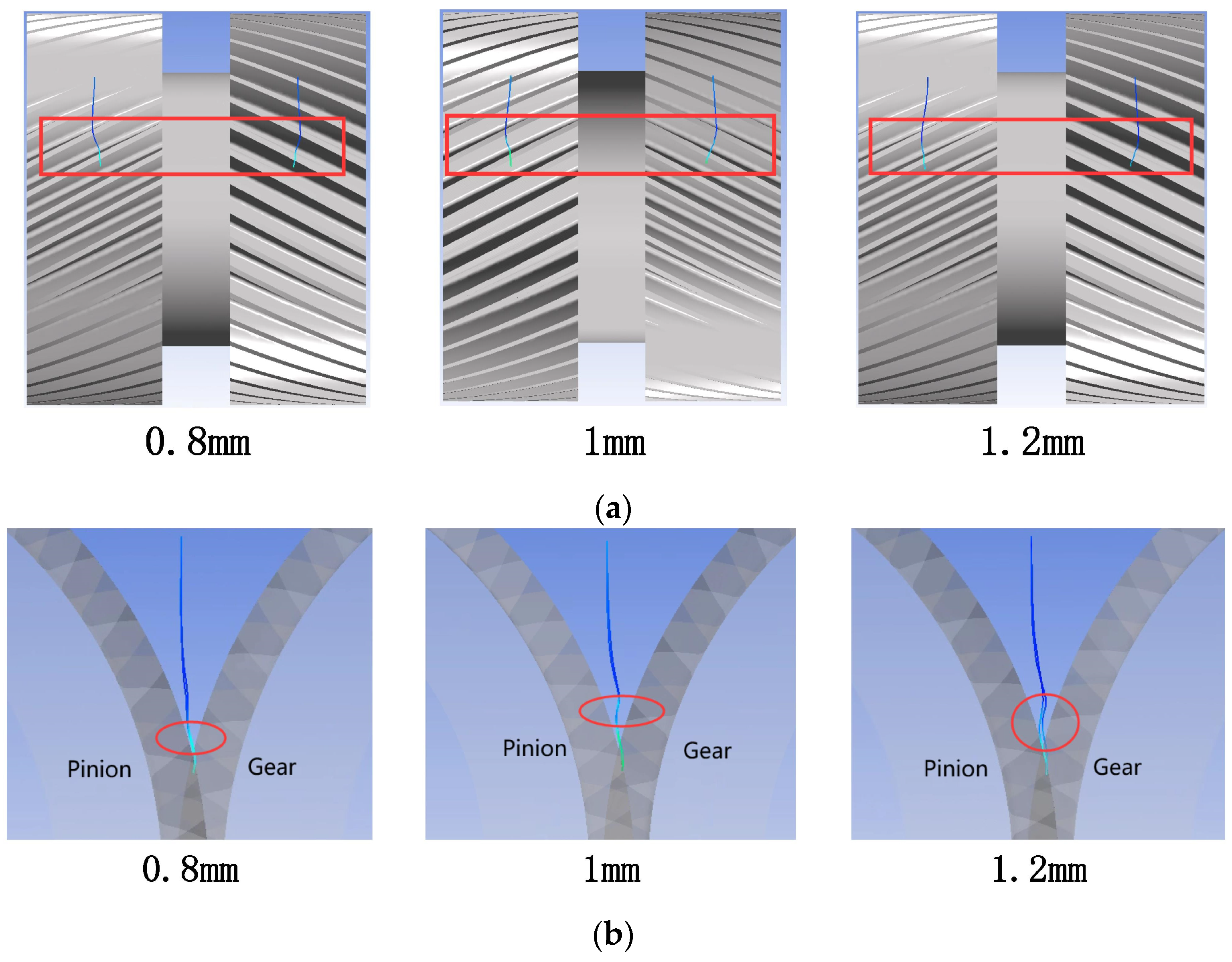
Effect of Jet Speed on the Temperature Field
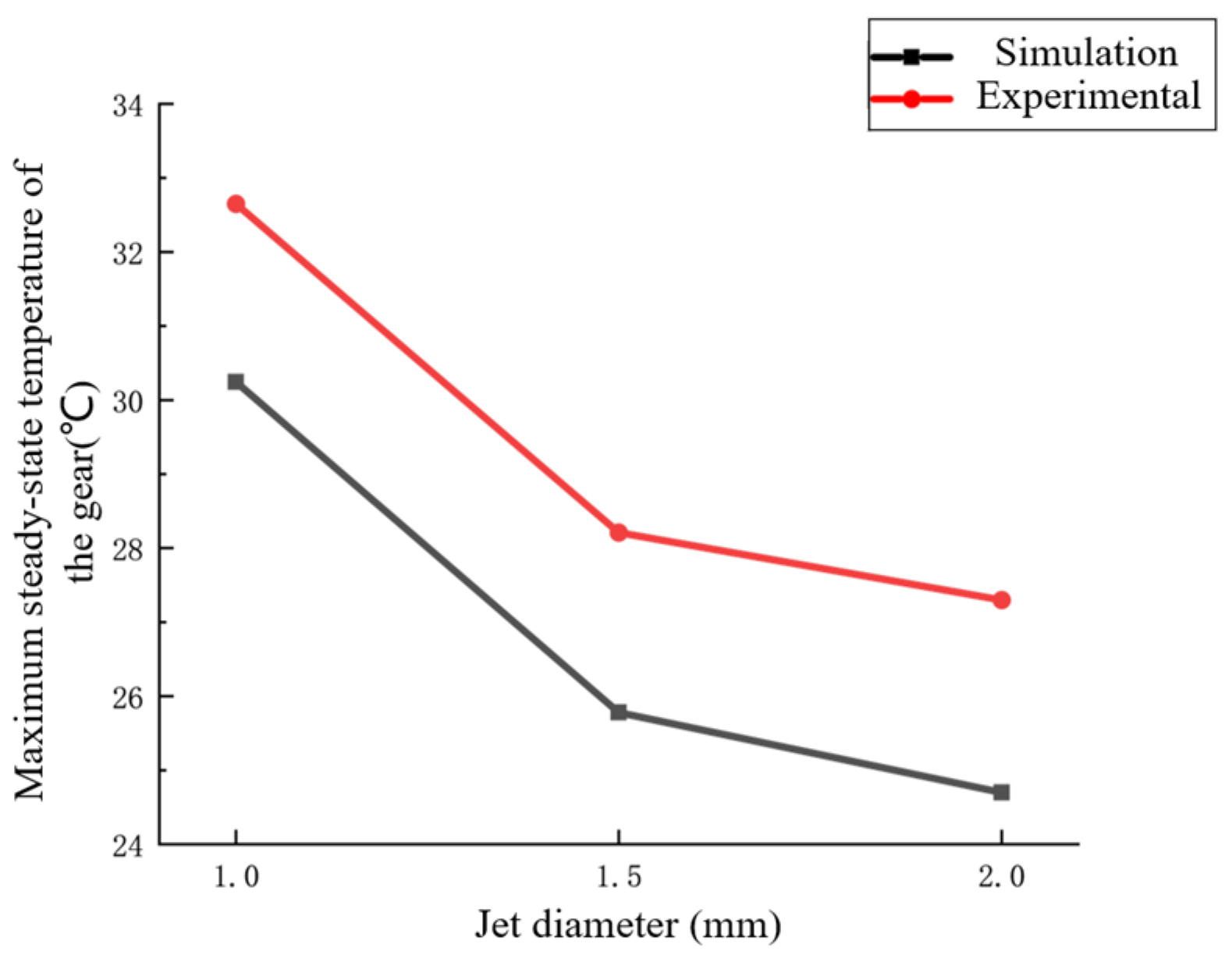
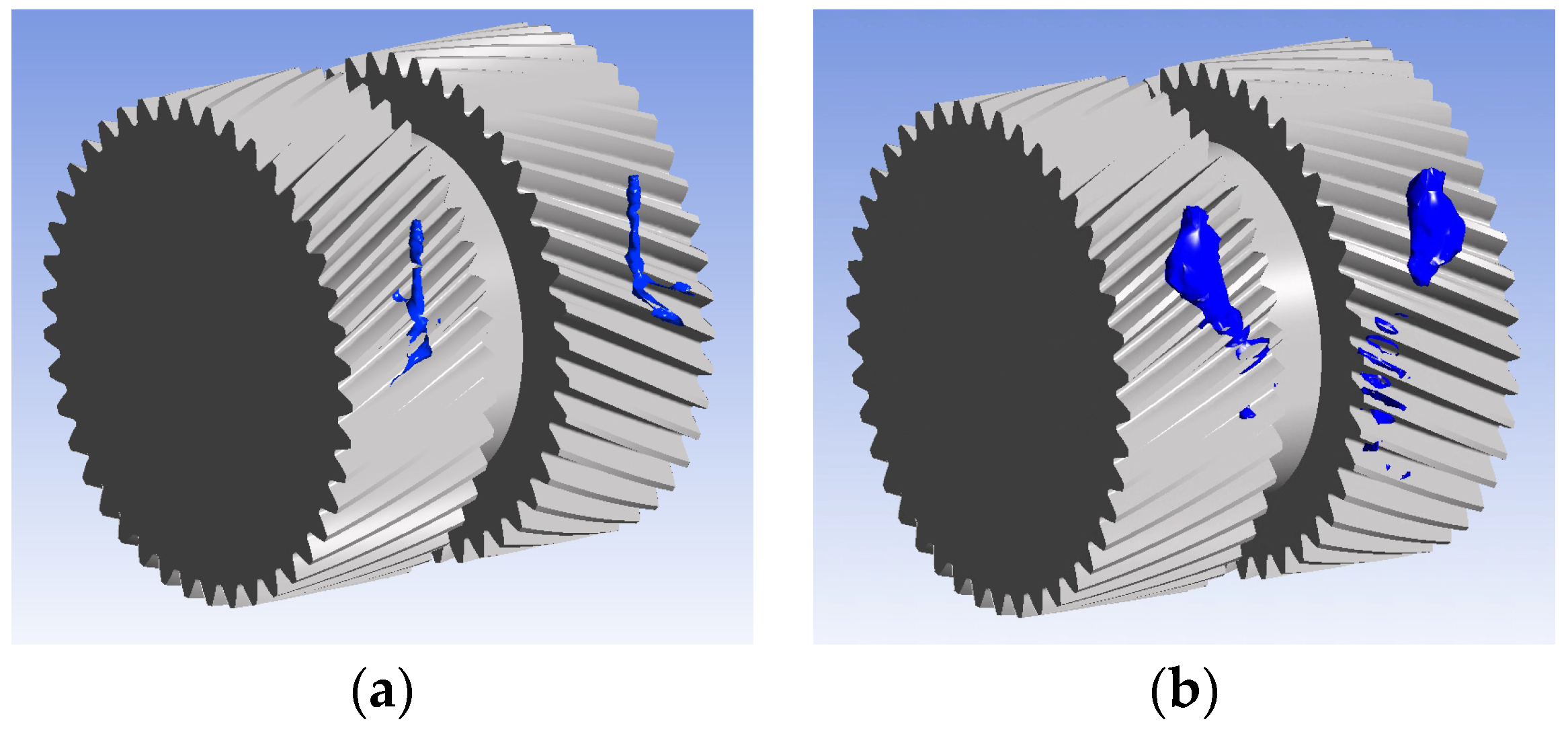
Effect of Jet Diameter on the Temperature Field
Effect of Gear Speed on the Temperature Field
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, D.; Chen, G. Current situation and prospect of gear transmission technology. J. Mech. Eng. 1993, 29, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Development dynamics of gear manufacturing technology. Manuf. Technol. Mach. Tool 1994, 3, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, M.; Sosa, M.; Olofsson, U. Efficiency and temperature of spur gears using jet lubrication compared to dip lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2017, 231, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, H. Einspritzschmierung bei Zahnradgetrieben. In FVA Forschungshefte Heft 156; Forschungsvorhaben Nr. 44111; Institut fur Maschinenkonstruktion und Getriebebau der Universit at Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Massini, D.; Fondelli, T.; Facchini, B.; Tarchi, L.; Leonardi, F. High Speed Visualizations of oil Jet Lubrication for Aero-engine Gearboxes. Energy Procedia 2016, 101, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, E.; Kromer, C.; Schwitzke, C.; Bauer, H.J. Experimental investigation of the oil jet heat transfer on meshing spur gears. In Proceedings of the 5th Conference of the International Society for Air Breathing Engines, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 25–30 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdani, M.; Soteriou, M.C. A novel approach for modeling the multiscale thermo-fluids of geared systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 72, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Morvan, H.P.; Simmons, K. Two Phase Computational Study of Flow Behaviour in a Region Within an Aeroengine Gearbox. In Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 45738, p. V05CT16A021. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, X.; Hong, S.; Li, P.; Wu, M. Influences of an oil guide device on splash lubrication performance in a spiral bevel gearbox. Tribol. Int. 2019, 136, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.C.; Kromer, C.; Cordes, L.; Schwitzke, C.; Bauer, H.J. CFD study of oil-jet gear interaction flow phenomena in spur gears. Aeronaut. J. 2020, 124, 1301–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, S.; Morvan, H.; Simmons, K. Investigation of Oil Jet Impingement on a Rotating Gear Using Lattice Boltzman Method (LBM). In Proceedings of the 2018 Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Oslo, Norway, 11–15 June 2018; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 50985, p. V001T01A028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Stanic, M.; Hartono, E.A.; Chernoray, V. Numerical simulations of oil flow inside a gearbox by Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) method. Tribol. Int. 2018, 127, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.; Szewc, K.; Maurya, V. Multi-Phase Gearbox Modelling Using GPU-Accelerated Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Method. In Proceedings of the 2019 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 July–1 August 2019; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 59049, p. V03AT03A008. [Google Scholar]
- Akin, L.S.; Mross, J.J.; Townsend, D.P. Study of lubricant jet flow phenomena in spur gears. J. Lubr. Technol. 1975, 97, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.P.; Akin, L.S. Study of lubricant jet flow phenomena in spur gears-out of mesh condition. J. Mech. Des. 1978, 100, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, X.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Y. Simulation study on oil jet lubrication of high-speed gears. Lubr. Seal 2019, 44, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, S.; Han, X. Normal and tangential oil film stiffness of modified spur gear with non-Newtonian elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, L. Analysis of oil jet lubrication for high-speed hk gear pairs. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 38, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, B.; Ding, Y. Analysis of oil jet lubrication for high-speed gearboxes under negative pressure based on, C.F.D. Mech. Transm. 2024, 48, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Yao, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Tao, X. Optimal nozzle orientation design for high linear speed gears based on CFD method. Lubr. Seal 2023, 48, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Jia, J.; Ouyang, B.; Bian, J. Determination of an optimal oil jet nozzle layout for helical gear lubrication: Mathematical modeling, numerical simulation, and experimental validation. Complexity 2020, 2020, 2187027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, W.; Tang, W.; Guo, M.; Guo, X. Factors influencing the deviation of oil nozzle jet direction. J. Aerosp. Power 2012, 27, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Fatourehchi, E.; Shahmohamadi, H.; Mohammadpour, M.; Rahmani, R.; Theodossiades, S.; Rahnejat, H. Thermal analysis of an oil jet-dry sump transmission gear under mixed-elastohydrodynamic conditions. J. Tribol. 2018, 140, 051502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Dang, H.; Zou, Z.; Tang, W.; Yue, Z. Study on aerodynamic power loss of high-speed spiral bevel gears. Mech. Transm. 2021, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Song, C.; Zhu, C.; Tan, C.; Guo, W. Modeling and analysis of transmission efficiency of high-speed wheel-side reducers for electric vehicles. J. Chongqing Univ. 2019, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velex, P.; Ville, F. An analytical approach to tooth friction losses in spur and helical gears influence of profile modifications. J. Mech. Des. 2009, 131, 101008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, H. The dissipation of frictional heat. Appl. Sci. Res. Sect. A 1955, 5, 151–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobe, T.; Kato, M. A study on flash temperatures on the spur gear teeth. J. Eng. Ind. 1974, 96, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S. A refined solution to the thermal-elastohydrodynamic lubrication of rolling and sliding cylinders. Asle Trans. 1965, 8, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Xiao, K.; Wang, J.; Pu, W.; Cao, W. A numerical method to investigate the temperature behavior of spiral bevel gears under mixed lubrication condition. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 147, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhai, P.F.; Ding, L. Analysis of Thermal Characteristic of Spur/Helical Gear Transmission. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. 2019, 11, 021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Shao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C. Dynamic Thermal Behavior of Two-Stage Gear Transmission System. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2021, 9, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Transient temperature field of helicopter transmission system spiral bevel gears under oil starvation conditions. J. Aerosp. Power 2020, 35, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, T.; Zhu, C.; Wei, P.; Xu, Y. Study on service temperature prediction model of high-speed gears in aviation. Mech. Transm. 2024, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hu, X.; Fang, T.; Wang, A.; Quan, C. Thermal analysis and experiment of spur gears under time-varying mixed lubrication. J. Mech. Des. Res. 2021, 37, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mironova, T.B.; Prokofiev, A.B.; Sverbilov, V.Y. The finite element technique for modelling of pipe system vibroacoustical char-acteristics. Procedia Eng. 2017, 176, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda-Casanova, V.; Sanchez-Marin, F. A 2D finite element based approach to predict the temperature field in polymer spur gear transmissions. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 133, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.D. Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Basics with Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hirt, C.W.; Nichols, B.D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 1981, 39, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhot, V.; Orszag, S.A.; Thangam, S.; Gatski, T.B.; Speziable, C.G. Development of turbulence models for shear flows by a double expansion technique. Phys. Fluids A Fluid Dyn. 1992, 4, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.E. Development of a generalized mechanical efficiency prediction methodology for gear pairs. In Dissertation Abstracts International; University Microfilms: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, V. Thermo-EHD analysis of lubrication of helical gears. J. Mech. Trans. 1988, 110, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, V. EHD Lubrication of Different Types of Gears; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Handschuh, R.F.; Kicher, T.P. Experimental and Analytical Assessment of the Thermal Behavior of Spiral Bevel Gears; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Lewis Research Center: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1995.
- Long, H.; Lord, A.A.; Gethin, D.T.; Roylance, B.J. Operating temperatures of oil-lubricated medium-speed gears: Numerical models and experimental results. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2003, 217, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Zhang, G.; Luo, W. Analytical simulation of transient contact stress and temperature of rotating gears. J. Mech. Eng. 2004, 40, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.M.; Rocha, D.M.; Martins, R.C.; Magalhães, L.; Seabra, J.H. Finite element method model to predict bulk and flash temperatures on polymer gears. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| −8.916465 | |
| 1.03303 | |
| 1.036077 | |
| −0.354068 | |
| 2.812084 | |
| −0.100601 | |
| 0.752755 | |
| −0.390958 | |
| 0.620305 |
| Parameter | Value (Driving and Driven Gears) |
|---|---|
| Number of Teeth | 43/42 |
| Module (mm) | 3.5 |
| Tooth Width (mm) | 60/60 |
| Pressure Angle (°) | 20 |
| Helix Angle (°) | 26.969 |
| Shaft Hole Radius (mm) | 42/45 |
| Undercut Radius (mm) | 78/76 |
| Undercut Width (mm) | 46 |
| Name | Specific Heat Capacity | Thermal Conductivity | Elastic Modulus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gear | 7980 | 500 | 40 | 2.1 |
| Name | Density | Specific Heat Capacity | Thermal Conductivity | Dynamic Viscosity (Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lubricating Oil | 969.6 | 1960 | 0.14 | 0.03 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Teeth | 43/42 |
| Module (mm) | 3.5 |
| Face Width (mm) | 60 |
| Pressure Angle (°) | 22.5 |
| Helix Angle (°) | 26.969 |
| Standard Center Distance (mm) | 166.9 |
| Case | Total Number of Mesh Elements (Million) | Actual Computation Time (h) | Pressure Difference in the Meshing Zone (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.313 | 21.9 | 266,379 |
| 2 | 5.204 | 28.5 | 313,058 |
| 3 | 6.146 | 42.7 | 399,082 |
| 4 | 7.562 | 58.6 | 387,998 |
| Surface | Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient/W/(m2·k) |
|---|---|
| Driving Gear Tooth Surface | 689.13 |
| Driving Gear Flank | 579.45 |
| Driving Gear Outer End Face | 480.78 |
| Driving Gear Inner End Face | 602.05 |
| Driven Gear Tooth Surface | 699.34 |
| Driven Gear Flank | 585.88 |
| Driven Gear Outer End Face | 480.11 |
| Driven Gear Inner End Face | 605.61 |
| Driving Gear Speed (rpm) | Average Heat Flux Density (Driving Gear/Driven Gear) (W/mm2) |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.1328/0.1355 |
| 3000 | 0.1913/0.1951 |
| 4000 | 0.2478/0.2527 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, J. Study on Temperature Field Distribution of a High-Speed Double-Helical Gear Pair with Oil Injection Lubrication. Lubricants 2024, 12, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12090315
Hu X, Yuan Y, Chen J. Study on Temperature Field Distribution of a High-Speed Double-Helical Gear Pair with Oil Injection Lubrication. Lubricants. 2024; 12(9):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12090315
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiaozhou, Yangmei Yuan, and Jie Chen. 2024. "Study on Temperature Field Distribution of a High-Speed Double-Helical Gear Pair with Oil Injection Lubrication" Lubricants 12, no. 9: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12090315
APA StyleHu, X., Yuan, Y., & Chen, J. (2024). Study on Temperature Field Distribution of a High-Speed Double-Helical Gear Pair with Oil Injection Lubrication. Lubricants, 12(9), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12090315




