Abstract
The influence of laser-alloyed stainless steel coatings on the properties of the surfaces of cast iron discs, such as friction-induced vibration and noise, friction coefficient, residual stress, hardness, and corrosion resistance, was investigated in this study. The experimental results show that after laser alloying, the surface hardness of the cast iron discs increased significantly. The residual stresses on the surfaces of the laser-alloyed discs changed from tensile to compressive residual stresses, while any compressive residual stresses increased by more than six times. Most of the laser-alloyed discs demonstrated better performance in friction-induced vibration and noise damping and friction reduction. Metallographic observation and XRD (X-ray diffraction) analysis results show that the laser-alloyed layer is mainly a mixture of acicular martensite and dendritic material, while the phase composition of laser-treated discs is mainly martensitic, [Fe, Ni], Fe3Si, Cr23C6, and austenite, which plays a significant role in the improvement of the properties of the laser-alloyed cast iron in physics, tribology and corrosion resistance. This research has significance for the laser surface treatment of various cast irons and steels, which is an increasingly important manufacturing technology in the vehicle friction brake industry.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of laser technology, laser surface modification has been applied widely as a metal surface treatment due to its advantages of high efficiency and environmental acceptability. These techniques include laser quenching [1], laser cladding [2], and laser surface alloying [3].
Laser cladding, particularly at higher speeds, is popular in additive manufacturing [4,5,6,7]. Comprehensive studies have been carried out on the surface modification of various materials using laser alloying, for example, on cast irons [8,9,10], steels [11,12], non-ferrous metals [13,14,15], and alloys [16,17,18]. Furthermore, the mechanisms of wear resistance of laser-alloyed coatings have been studied in references [8,11,12,13], and the corrosion resistance of metallic materials with different laser-alloyed coatings investigated in [19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. For example, in order to improve the corrosion resistance of industrially pure copper, researchers prepared various coatings including Ni and Ti [13,15,22,23]. Ravnikar et al. [24] reported that the TiB2/TiC/Al coatings could effectively improve the corrosion resistance of an aluminum alloy. Smolina et al. [25] showed that rhenium coatings could significantly improve the corrosion resistance of cobalt-based alloy surfaces.
The hardness and other properties of laser-alloyed coatings have also been investigated [26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Paczkowska [26] reported that the hardness of Si coatings was higher than that of the Ti, SiN and Co coatings at more than 900 HV0.1. Lont et al. [27] found that titanium coatings can improve the surface hardness and erosion resistance of ductile iron. Paczkowska et al. [28] reported that increasing the cooling rate results in a higher surface hardness of the coatings. Jiru et al. [29] fabricated coatings containing manganese elements on the surface of aluminum plates which resulted in an increase in surface hardness by about four times and a reduction of wear by 30%. Bartkowska et al. [30] reported that the micro-hardness of mixed coatings of B and Mo was superior to that of a single coating of these elements. Makuch et al. [31] laser-alloyed composite coatings with B and Nb powders and reported that the hardness and wear resistance of nickel-based alloys were significantly increased. Yu et al. [32] reported that the average hardness of the coating was about four times that of the Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy substrate and that the anti-wear performance of these coatings was significantly better than that of the titanium alloy substrate.
In this study, in order to improve the mechanical damping, anti-corrosion, and other tribological properties of the gray cast iron, various stainless steel surface coatings were laser alloyed onto gray cast iron discs. An orthogonal experimental method was used to design the laser processing parameters, and 12 discs with different processing parameters and different stainless steel coatings were fabricated for tribological, dynamical, and electrochemical tests. In addition, microstructure observation and phase change analysis of the laser-alloyed coatings were carried out with metallographic observation and XRD (X-ray diffraction) analysis to explore the mechanisms of both vibration and noise reduction and corrosion resistance. The surface-coating fabricating methodology used in this study was significantly different than that in our previous studies [33] and the properties of the laser-alloyed coatings were remarkably improved.
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Laser Alloying Material
The substrates for the laser alloying were gray cast iron (HT250) discs with a diameter of 69.5 mm and a thickness of 9.5 mm. In order to identify the best stainless steel that can be used for the laser alloying, three different stainless steels, namely 304, 316, and 430 powders, were used in this study. Stainless steel contains a high proportion of Cr and Ni so that it has excellent performance in anti-corrosion. The element compositions of the three chosen stainless steel powders are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Element composition of stainless steel (wt.%).
2.2. Laser Alloying
The HT250 substrates were sanded with 240# metallographic sandpapers to polish the surfaces of the mechanically machined cast iron discs, then they were cleaned with acetone. Anhydrous ethanol and polyvinyl alcohol powders were used as coating bonding agents; these were mixed with the stainless steel powder and then the mixture was put uniformly on the surface of the gray cast iron disc with a fine brush, controlling the pre-coating to the same thickness of about 0.5 mm using a ruler and through observation. The samples were then placed in a clean environment at a constant room temperature for 24 h to air dry. The thickness of the coating was then carefully checked and, if necessary, gently polished with sandpapers to control the coating thickness to around 0.5 mm. Laser alloying was then carried out. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram of laser surface alloying processing.
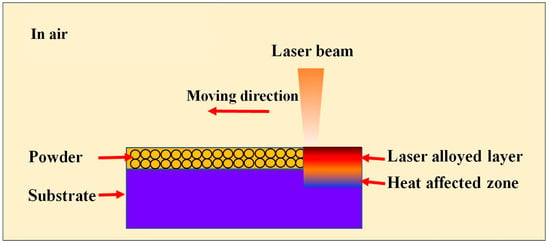
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of laser surface alloying.
The mechanical and tribological properties of the laser-alloyed layer are significantly dependent on the substrate material, the alloying coating material and the laser processing parameters. In accordance with the orthogonal design method, a three-factor (coating material, laser power and scanning speed) with a three-level orthogonal design was used and three additional discs were added for comparison (discs 10, 11 and 12). The laser alloying processing parameters and DOE (design of experiments) arrangement are shown in Table 2. The numbers in brackets in the first column of Table 2 are the LAI values which indicate the laser energy density used in the laser alloying processing; while the numbers in brackets in other columns are the levels in the orthogonal design. The laser-alloyed discs after polishing are presented in Figure 2.

Table 2.
Laser alloying DOE arrangement.
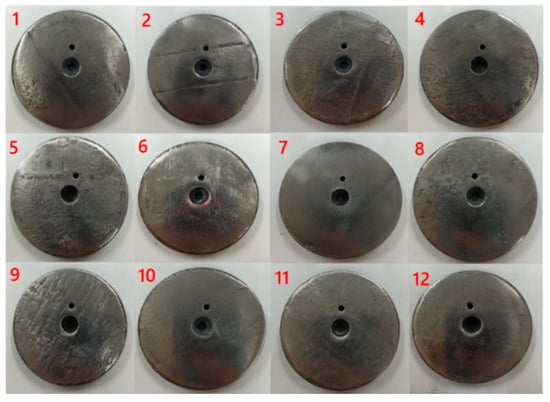
Figure 2.
Cast iron discs with laser-alloyed coating after surface polishing. 1–12. disc 1–12.
2.3. Tribological and Dynamical Tests
2.3.1. Tribological Test
To investigate the tribological properties of the cast iron discs with laser-alloyed coatings, a multifunctional friction and wear tribometer (manufactured by Bruker Technology Co., Ltd., Billerica, MA, USA) was employed. In these tribological tests, the sliding frictional contact pair consisted of an upper stationary GCr15 bearing steel ball and a lower rotating cast iron disc with or without a laser-alloyed surface coating. The operational parameters were kept constant under dry conditions, viz. normal load of 20 N, relative sliding speed of 1 m/s and test duration of 100 s.
2.3.2. Dynamical Test
While in the tribological tests, the friction-induced vibrations and noise were measured using a triaxial accelerometer (Kistler-8766A50M5, Shanghai, China) and a microphone (sound pressure sensor INV9206, BOINV, Beijing, China) using the DASP (data acquisition and signal processing) system developed by Beijing Oriental Institute of Vibration and Noise (BOIVN, Beijing, China). More details of the experimental setup for the tribological and dynamical tests can be found in Sai et al. [33].
2.4. Hardness Measurement
The surface hardness of the laser-alloyed discs was measured by means of an HRS-150 Rockwell hardness tester manufactured by Shanghai Shangcai Testing Machine Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China; while the micro-hardness of the discs was tested using the HXD-1000TMS digital hardness tester manufactured by Shanghai Taiming Optical Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. In the micro-hardness measurements, a 3 N normal load was applied and maintained for 15 s.
2.5. Residual Stress Measurement
The residual stresses of the untreated and the twelve laser-alloyed discs were measured by means of a TEC-4000 X-ray diffraction system (TEC Materials Testing, Knoxville, TN, USA). Three points were selected on each of the discs to be tested and the residual stresses in both radial and tangential directions at each point were measured and repeated three times; the residual stresses measured on the three selected points were averaged in each direction separately.
2.6. Metallographic Observation
Metallographic observations were carried out by a Leica DMI8A inverted metallographic microscope (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany). The specimens used for the metallographic observations were machined to the dimensions of 30 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm via wire cutting. The specimens were ground using sandpaper and then polished to mirror-like surfaces using velvet and polishing paste by means of a polishing machine. Before the metallographic observations the surfaces of the specimens were wiped with 4% dilute nitric acid solution.
2.7. XRD Analysis
An X-ray diffractometer (manufactured by Bruker Technology Co., Ltd., Billerica, MA, USA) was employed to analyze the phase changes in the laser-alloyed coatings. In this study, the X-ray source was cu-kα, the working voltage of the X-ray tube was 35 kV, the acceleration voltage was 40 kV, the range of scanning angle was 0–80° and the scanning speed was 5°/min. After the measurements, the measured data were exported using the JADE6.0 software from the testing system.
2.8. Electrochemical Test
The electrochemical experiments were carried out with the Gamry Electrochemical Station (Model Interface 1010E, Gamry, Warminster, PA, USA). The anodic and cathodic polarization curves of laser-alloyed cast iron samples were measured using the potentiodynamic scanning method with a scanning speed of 2 mV/s. In these experiments, the temperature was maintained at a room temperature of 26 °C and the specimen was placed in 3.5% NaCl electrolyte solution as the working electrode before measuring the potentiodynamic polarization curves.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Friction-Induced Vibrations and Noise
Figure 3 shows the friction-induced vibrations in the frequency domain; it can be seen that there is a significant resonant peak at about 800 Hz in all of the tests which is a natural frequency of the tribometer. Compared with the original cast iron disc, the vibration peaks of the laser-alloyed discs are all reduced. The peaks of the vibration acceleration of discs 2, 5, 9, and 11 are lower than that of other discs in Figure 3a–d, respectively, indicating that these four discs have better vibration damping performance and that disc 9 is the best.
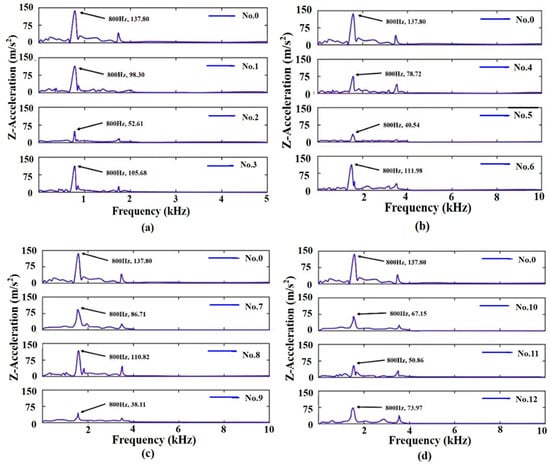
Figure 3.
Frequency spectra of tribometer vibrations induced by sliding contacts of bearing steel balls and discs: (a) no. 0, 1–3; (b) no. 0, 4–6; (c) no. 0, 7–9; (d) no. 0, 10–12.
Figure 4 presents the frequency spectra of measured friction-induced noise. The peak in the noise of the original cast iron disc occurs at about 1900 Hz, with a peak sound pressure of 0.87 Pa. The friction-induced noise levels of all laser-alloyed discs are lower than that of the disc without a laser-alloyed coating. Discs 9 and 11, in which the sound pressures are reduced by more than 72%, have a better noise reduction performance than other discs in this study.
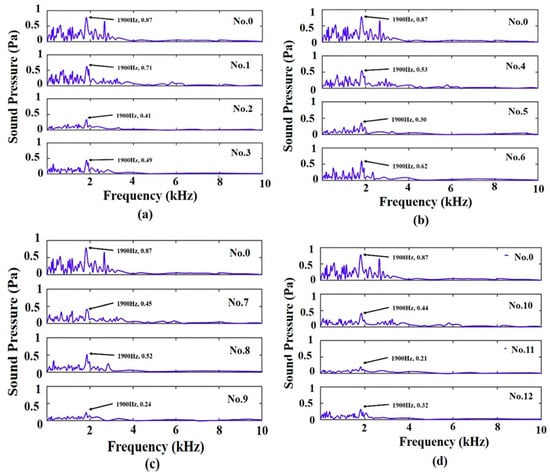
Figure 4.
Frequency spectra of frictional noise induced by sliding contacts of bearing steel balls and discs: (a) no. 0, 1–3; (b) no. 0, 4–6; (c) no. 0, 7–9; (d) no. 0, 10–12.
Table 3 shows the RMS (root mean square) values of the amplitudes of friction-induced vibrations and noise. It can be seen from Table 3 that the RMS of friction-induced vibrations and noise of discs 2, 5, 9, and 11 are smaller than those of the other discs in Figure 3 and Figure 4a–d, respectively; disc 9 has the most significant reduction in friction-induced vibrations (72.4%) and the second largest reduction in friction-induced noise (72.4%); while disc 11 has the largest (75.8%) reduction in friction-induced noise and the third largest (63.1%) reduction in friction-induced vibrations.

Table 3.
RMS of friction-induced vibrations and noise from bearing steel balls sliding contact with cast iron discs.
Recalling the laser alloying parameters shown in Table 2, it may be concluded that the optimum parameters of laser alloying for obtaining the most efficient coatings in vibration and noise damping are laser-alloying power in the range of 3000–3500 W and laser scanning speed of 250 mm/min. To explain why disc 9 has the best performance in vibration and noise damping, a further investigation on residual stresses of all the discs with and without laser-alloyed coating was carried out and will be presented in Section 3.4. The microstructure and phase changes in the laser-alloyed discs were investigated using the metallographic observation and XRD analysis and are presented in Section 3.5 and Section 3.6, respectively.
3.2. Coefficients of Friction
Figure 5 presents the observed coefficients of friction (COFs) in the dry sliding of contacts between the GCr15 bearing steel balls and the cast iron discs without or with laser-alloyed coatings under a normal load of 20 N, a sliding speed of 1 m/s and for a testing period of 100 s. The COFs of all discs with laser-alloyed coatings, except discs 6 and 8, are smaller and more stable than that of the original disc without coating, which may partly contribute to the vibration and noise reduction in the discs with laser-alloyed coatings. Figure 5a shows that the COFs of discs 1–3 are significantly smaller than that of the original disc 0 after 20 s of testing, and the COFs of many discs are almost constant for about 80 s and then slightly increase, possibly due to the wear of friction pair. However, it can be observed from Figure 5b,c that the COFs of discs 6 and 8 are significantly larger than that of other discs in Figure 5b,c, which is possibly due to the larger LAI (laser alloying index) values of 21 and 18 (as shown in Table 2) used in the laser alloying treatment, respectively, i.e., excessive laser energy was absorbed by discs 6 and 8, which resulted in the relative higher surface hardness and residual stress. Here, the LAI value was defined as the ratio of laser-alloying power to the product of laser-scanning speed and laser spot area.
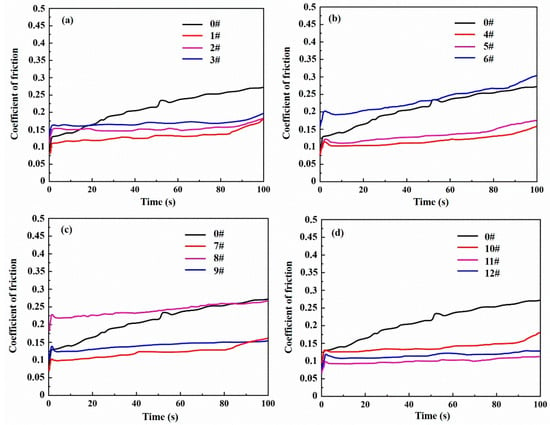
Figure 5.
COFs between a bearing steel balls and discs: (a) no. 0, 1–3; (b) no. 0, 4–6; (c) no. 0, 7–9; (d) no. 0, 10–12.
In summary, the COFs of all the laser-alloyed discs increase quickly in the first 2 s, and then increase gradually over the whole testing period. Discs 1, 4, 7, and 11 have smaller COFs than other laser-alloyed discs in the same Figure. The COFs of all the laser-alloyed discs are more stable than that of the disc without laser-alloyed coating and this plays an important role in the reduction in friction-induced vibrations and noise. The gradual increase of COFs of laser-alloyed discs with the increase in sliding distance is due to the wear of the upper specimen (the GCr15 bearing steel ball), whereas for the disc without laser-alloyed coating it is due to the wear of the lower specimen (the gray cast iron disc). Notwithstanding its potential importance, as the extent of the quantitative wear of the disc with laser-alloyed coating was too little to be measured, it will not be discussed further.
3.3. Hardness
3.3.1. Surface Hardness
The surface hardness of all the laser-alloyed discs and the original disc was measured by means of an HRS-150 Rockwell hardness tester (Shanghai Shangcai Testing Machine Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), the data of which are presented in Figure 6. The results show that the hardness of all laser-alloyed discs increased significantly; the averaged surface hardness of disc 9 is the largest (76.3 HRC) which is 7.6 times that of the original cast iron disc.
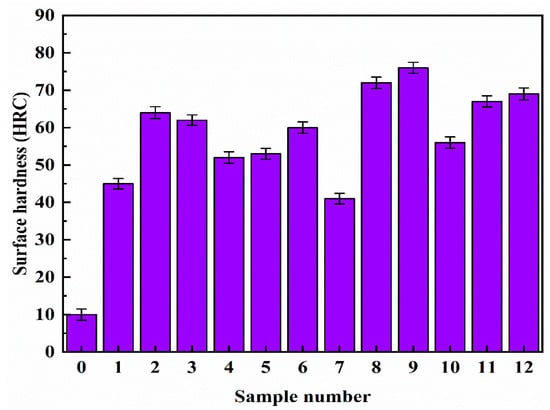
Figure 6.
Surface hardness of discs with and without laser-alloyed coating.
3.3.2. Micro-Hardness
Figure 7 presents the internal hardness profile of the laser-alloyed discs which was measured by means of a digital hardness tester (Shanghai Taiming Optical Instrument Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China) with a normal load of 3 N and a dwell time of 15 s. Figure 7a illustrates that the hardness of the laser-alloyed region is as much as 3.5 times that of the substrate. The micro-hardness values of discs 2 and 6 are significantly larger than those of discs 1, 3, 4, and 5; the hardened depth of laser-alloyed discs is about 0.9 mm.
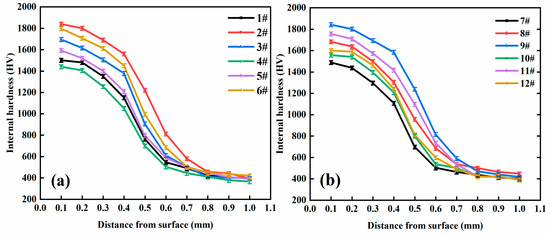
Figure 7.
Micro-hardness of laser-alloyed discs. (a) no. 1–6; (b) no. 7–12.
Similarly, Figure 7b shows that the subsurface micro-hardness of discs 9 and 11 is significantly higher than that of discs 7, 8, 10, and 12. The hardening depth of discs 8 and 9 is about 1.0 mm—while the hardening depth of discs 7, 10, 11, and 12 is about 0.8 mm.
Since the surface hardness of the discs had been already determined, in the measurement of the internal hardness of those discs with laser-alloyed coatings, the start point was 0.1 mm from the surface of the coatings. It can be seen from Figure 7 that the internal hardness of the discs is significantly decreased in the positions that are around 0.4 mm from the surfaces of the coatings, indicating that the thickness of the coatings is about 0.4 mm.
3.4. Residual Stress
Figure 8 presents the mean residual stresses of the untreated and the twelve laser-alloyed discs, with these values being measured by means of a TEC-4000 X-ray diffraction system (Bruker Technology Co., Ltd., Billerica, MA, USA). It shows that compressive stresses are recognized only in the case of the laser-alloyed discs, whereas the residual stresses of the original cast iron disc are tensile. Both the tangential and radial residual stresses of discs 6, 9 and 12 are significantly larger than that of other laser-alloyed discs. Considering that discs 9 and 12 have the best performance in vibration and noise reduction in this study, it is reasonable to suggest that the extent of surface residual stress in the disc has a significant effect on the dynamic property (vibration and noise damping) of laser-alloyed coatings on cast iron.
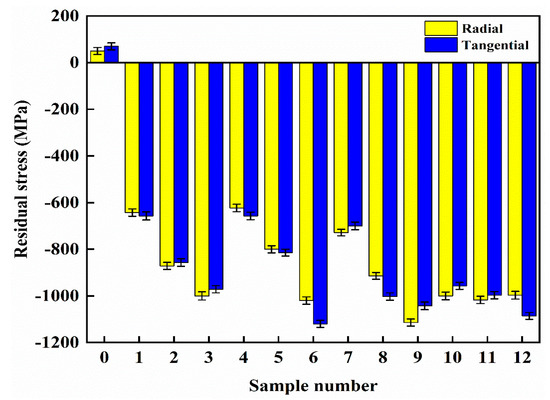
Figure 8.
Measured residual stress of cast iron disc with and without laser-alloyed coating.
3.5. Metallographic Observation
Figure 9a illustrates the microstructures of discs 0 and 9 observed using metallographic microscopy. Three zones were visible in the laser-alloyed layer: a phase alloy layer, a heat affected layer and a matrix layer. Because the heating and cooling rates of laser alloying are faster than traditional heat treatments, the finer and more uniform structures were formed in the laser-alloyed layer of the disc. It can be seen from Figure 9b,c that the composition of the laser-alloyed layer is mainly acicular martensite and ledeburite compared to the structures of the untreated disc in Figure 9d. The martensite has a body-centered tetragonal crystal structure that contributes to the superior mechanical and tribological properties of the laser-alloyed structures.
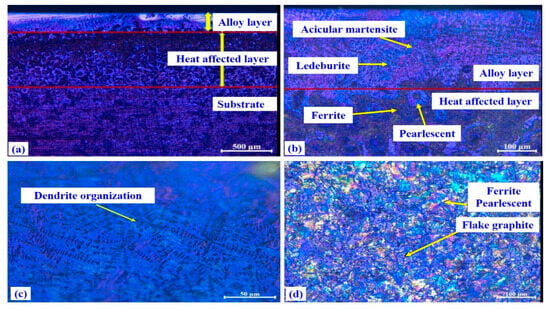
Figure 9.
Disc cross-section microstructures. (a) laser-alloyed disc 9; (b) magnified observation of (a); (c) magnified laser-alloyed area; (d) untreated cast iron disc 0.
3.6. XRD Analysis
The phase analyses of the original disc 0 and laser-alloyed discs 8, 9, and 11 are shown in Figure 10, from which it can be seen that the phase composition of the original disc 0 is mainly austenite, Fe3Si and [Fe, Ni], while the phase composition of discs 8, 9, and 11 is mainly austenite, martensitic, [Fe, Ni], Fe3Si, and Cr23C6.
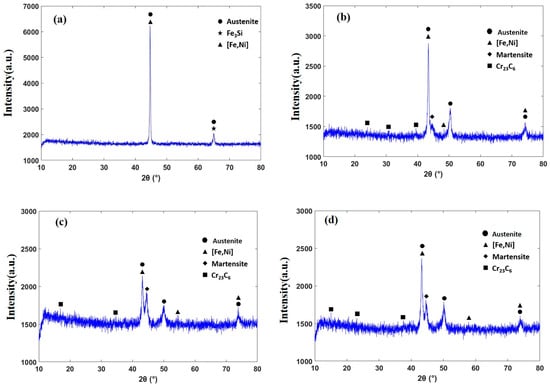
Figure 10.
XRD patterns of discs. (a) untreated cast iron disc 0; (b) no. 8; (c) no. 9; (d) no. 11.
The multiple diffraction peak intensities of discs 8, 9, and 11, shown in Figure 10, suggest that some new compounds were developed via laser alloying, and the phase composition changed from a simple compound to complex compounds of C, Si, Ni, Cr and Fe, i.e., the microstructures of the laser-alloyed layer were mainly acicular martensite and ledeburite [33].
It can also be observed that, compared with the original disc 0, the diffraction peak intensities of discs 8, 9, and 11 are decreased in various degrees, suggesting that a single element in the basic structure is transformed into a compound consisting of C, Fe, Cr and Ni via laser alloying. Meanwhile, the half peak widths of the diffraction peaks of discs 8, 9, and 11 (2θ = 45°) increased, which suggests that, after laser alloying, the microstructure composition of the gray cast iron disc with the laser-alloyed stainless steel coating becomes refined and the microstructure grain size is decreased.
Compared with other specimens, the diffraction peaks of disc 9 have lower intensities and wider peak widths, which indicates that the microstructures of disc 9 have smaller grains. From Section 3.5, it can be seen that the microstructures of disc 9 consist of fine dendrite crystals: the finer the grain, the more grain boundaries, the larger the resistance when the dislocations occur, and thus this structure exhibits larger damping for the friction-induced vibrations and noise. In addition, the graphite on the surface of the gray cast iron matrix dissolves and forms a dendritic structure with the Fe element in the melt pool via laser alloying.
The above phase analysis suggests that the phase compositions of the discs were changed after laser alloying which resulted in an improvement in the dynamical and tribological performance of the laser-alloyed discs.
3.7. Electrochemical Testing
Figure 11 shows the potentiodynamic polarization curves of samples 0–12 in the 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. It can be seen from Figure 11 that the initial corrosion voltage of the samples or discs after laser alloying is higher than that of the disc without laser alloying. In the anode area, the laser-alloyed disc samples have a significant active-dissolution area, a stable-passivation area and an over-passivation area, while the current density of the disc sample without laser alloying increases steadily with the increase in corrosion voltage. The enhanced value of Ecorr indicates more nobility of laser-alloyed discs and the decrease in Icorr value shows the lower corrosion rate. This suggests that the laser-alloyed layer prevents anions in the electrolyte solution from passing through the disc surface.
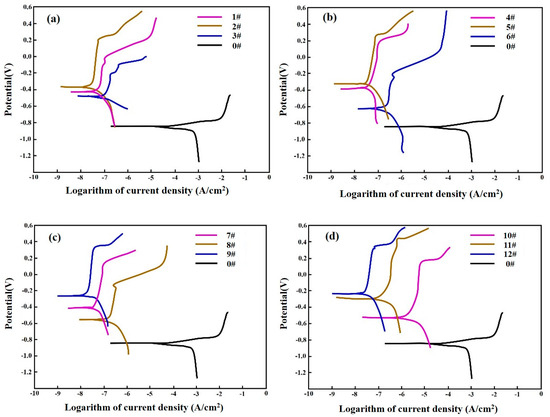
Figure 11.
Potentiodynamic polarization curves of discs: (a) no. 1–3, no. 0; (b) no. 4–6, no. 0; (c) no. 7–9, no. 0; (d) no. 10–12, no. 0.
Thus, it can be concluded that the laser-alloyed stainless steel layers improve the anti-corrosion property of the gray cast iron discs. The corrosion resistance of discs 2, 5, 9 and 11 are significantly higher than that of other discs with the same coating materials, suggesting that the corrosion resistance is related to the laser-alloying parameters and coating material. In this study, the corrosion resistance of material in descending order is 316, 304, and 430 stainless steel.
4. Analysis
In order to analyze the effect of laser alloying materials and laser processing parameters on the performance of laser-alloyed discs, the range analysis and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were carried out. There are three factors of A (coating material), B (laser power), and C (laser scanning speed) with three levels for each factor. The L9(33) orthogonal design was employed for the experimental testing and the experimental data suitable for analysis are presented in Table 4, where the residual stress of each disc is the average of the measured radial and tangential residual stresses.

Table 4.
Experimental results from orthogonal experiments L9(33).
Based on a preliminary analysis, it can be concluded that the three factors of coating material, laser power, and laser scanning speed have no significant effect on the friction-induced vibrations and noise. This is because the mechanical properties of these three coating materials are quite similar, and the variation in the laser processing parameters are not significant. Therefore, only the residual stress and polarization resistance of the laser-alloyed discs have been used in the following range and ANOVA analyses to analyze the significance of the three factors and obtain the optimal coating material and laser alloying parameters.
4.1. Range Analysis
Table 5 shows the range analysis results of the L9(33) orthogonal tests, where the R value indicates the significance of the factor and the optimal level of each factor can be determined from the maximum k value in the factor column. Based on the values of R, the significance order of each factor for the residual stress is B > A > C, indicating that the laser alloying power is the most significant factor influencing the residual stresses, followed by coating material and, finally, laser scanning speed.

Table 5.
Range analysis of residual stress.
Based on the calculated values of k in Table 5, the optimal combination of factors and levels for residual stress is A3B3C1, i.e., the maximum residual stress may be obtained when the coating material is 430 stainless steel, laser power is 3500 W, and scanning speed is 200 mm/min.
Similarly, it can be seen from Table 5 that the significance order of the three factors for the polarization resistance is A > C > B, and the optimal combination of factors and levels is A2B2C3, i.e., the maximum polarization resistance may be obtained when the coating material is 316 stainless steel, laser power is 3000 W, and scanning speed is 300 mm/min, which is consistent with the analysis in Section 3.7
4.2. Analysis of Variance
The analysis of variance (ANOVA) distinguishes between the effects of test factors and fluctuations in test results due to experimental error, and estimates the magnitude of the effect of each factor [34]. In this study, an ANOVA analysis is used to examine the effects of coating material, laser alloying power, and laser scanning speed on the residual stress and polarization resistance.
Table 6 shows the ANOVA outcome of the L9(33) orthogonal test results. It can be seen that the F ratio in factor B is greater than all the F threshold values, i.e., factor B has a most significant effect on residual stress of laser-alloyed discs. This indicates that the laser power is the most significant factor influencing the residual stress of the laser-alloyed technique and this is consistent with the results of the range analysis.

Table 6.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA).
It can be seen from Table 6 that factor A has a significant effect on the polarization resistance, i.e., the coating material has the most significant effect on the corrosion resistance performance of the laser-alloyed discs. The Cr and Ni elements in stainless steel powders are the main reason for the increased corrosion resistance, which is again consistent with the results of the range analysis. And the action of laser energy makes the coating organization fine and homogeneous, which also hinders the corrosion of the coating via Cl-ions.
5. Conclusions
In this study, three different stainless steel powers were laser-alloyed on the surfaces of gray cast iron discs and their surface and sub-surface properties were investigated by means of various macro- and micro-scale characterizations, including dynamical and tribological tests, electrochemical analysis, metallographic observation and XRD analysis. The conclusions may be drawn as follows.
- (1)
- The laser alloying power is the most important effect factor on the surface and internal hardness of discs, and the LAI value also can be an important index determining the surface and internal hardness of discs, provided that the laser alloying power is beyond a threshold, e.g., 3000 W in this study.
- (2)
- Laser alloying significantly increased the residual stress on the surface of cast iron discs and changes it from tensile to compressive, which plays a significant role in the vibration and noise damping and anti-corrosion performance.
- (3)
- Discs 9 and 11 have the best vibration and noise reduction performance in all of the laser-alloyed discs, suggesting that the laser alloying parameters can be optimized to obtain the laser-alloyed coatings with excellent vibration and noise damping property.
- (4)
- The ANOVA analysis shows that the laser power is the most significant factor influencing the residual stress, and that coating material has the most significant effect on the corrosion resistance performance of the laser-alloyed discs.
- (5)
- This research has significance for the laser alloying of various cast irons, steels and other metals, which is an increasingly important technology in the vehicle friction brake manufacturing industry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W.; methodology, S.W.; validation, S.W. and J.W.; formal analysis, J.H. and Y.Z.; investigation, J.H. and Y.Z.; resources, S.W.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, S.W. and J.W.; supervision, S.W.; project administration, S.W. and C.G.; funding acquisition, S.W. and C.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partly funded by the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No.: 18060502400), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai Municipality (No.: 21ZR1445000).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, B.; Pan, Y.; Barber, G.; Wang, R. Phase transformation of austempered and quench-tempered gray cast irons under laser surface hardening treatment. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2021, 34, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, A.; Rodrigo, P. An introduction on the laser cladding coatings on magnesium alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, A.; Kotkowiak, M.; Makuch, N.; Kulka, M. Wear behavior of self-lubricating boride layers produced on Inconel 600-alloy by laser alloying. Wear 2019, 426–427, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Li, R.; Chen, Z.; Gu, J.; Tian, Y. A comparative study on microstructure and properties of traditional laser cladding and high-speed laser cladding of Ni45 alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gui, W.; Nie, B.; Bi, W.; Zhong, C.; Xue, Y.; Luan, B. Elimination of elemental segregation by high-speed laser remelting for ultra-high-speed laser cladding Inconel 625 coatings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 4118–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Bi, W.; Zhong, C.; Wu, T.; Gui, W. A comparative study on microstructure and properties of ultra-high-speed laser cladding and traditional laser cladding of Inconel625 coatings. Materials 2022, 15, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuominen, J.; Kiviö, J.; Balusson, C.; Raami, L.; Vihinen, J.; Peura, P. High-speed laser cladding of chromium carbide reinforced Ni-based coatings. Weld. World 2023, 67, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyaprakash, N.; Yang, C.-H.; Duraiselvam, M.; Sivasankaran, S. Comparative study of laser melting and pre-placed Ni-20% Cr alloying over nodular iron surface. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2020, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, S.; Zhou, H.; Tong, X.; Ren, L. Mechanical properties and wear resistance of ZrO2 particulate-reinforced composite layer on compacted graphite cast iron processed by selective laser alloying. J. Laser Appl. 2017, 29, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. Corrosion and wear resistance characteristics of NiCr coating by laser alloying with powder feeding on grey iron liner. Wear 2006, 260, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.F.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.B.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Fabrication and wear behavior of TiC reinforced FeCoCrAlCu-based high entropy alloy coatings by laser surface alloying. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 255, 123571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulka, M.; Mikołajczak, D.; Dziarski, P.; Panfil-Pryka, D. Laser surface alloying of austenitic 316L steel with boron and some metallic elements: Properties. Materials 2021, 14, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.W.; Cristino, V.A.M.; Tam, L.M.; Lo, K.H.; Kwok, C.T. Laser surface alloying of copper with Cr/Ti/CNT for enhancing surface properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, S.; Li, S.; Hu, H.; Fang, Y.; Liu, J.; Dong, W.; Wang, H. Surface hardening of CrCoFeNi high-entropy alloys via Al laser alloying. Mater. Res. Lett. 2021, 9, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, S. Phase evolution and properties in laser surface alloying of FeCoCrAlCuNi high-entropy alloy on copper substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 315, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Vera, M.; Hdz-García, H.; Muñoz-Arroyo, R.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, M.; Ortega, J.A.; Mtz-Enriquez, A.; Hernandez-García, F.; Carrera-Espinoza, R.; Ortega-Ramos, I. Wear resistance of surfaced modified CoCr alloy with stellite alloys and boron carbide coating via laser alloying. Wear 2023, 524–525, 204811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Meng, X.; Dou, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, C. Laser alloying with Fe-B4C-Ti on AA6061 for improved wear resistance. Surf. Eng. 2021, 37, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, A.; Wei, P. Study on wear resistance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy composite coating prepared by laser alloying. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, D.; Bartkowska, A.; Popławski, M.; Przestacki, D. Microstructure, microhardness, corrosion and wear resistance of B, Si and B-Si coatings produced on C45 steel using laser processing. Metals 2020, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, L.; Hao, G. Microstructure and corrosion behaviour of laser-cladded γ-Ni/Mo2Ni3Si alloy coating. Surf. Eng. 2018, 35, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.T.; Lei, W.B.; Wang, Q.J.; Tong, W.P.; Liu, C.S.; Cui, J.Z. Laser surface alloying of low carbon steel using high-entropy alloy precursors. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2016, 23, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.; Kwok, C.; Man, H.; Cheng, F. Corrosion behavior of laser-alloyed copper with titanium fabricated by high power diode laser. Corros. Sci. 2012, 57, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.; Wong, P.; Man, H. Enhancement in corrosion and electrical wear resistance of copper via laser surface alloying with NiTi. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 408, 126804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravnikar, D.; Rajamure, R.S.; Trdan, U.; Dahotre, N.B.; Grum, J. Electrochemical and DFT studies of laser-alloyed TiB2/TiC/Al coatings on aluminium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2018, 136, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolina, I.; Kobiela, K. Characterization of wear and corrosion resistance of stellite 6 laser surfaced alloyed (LSA) with rhenium. Coatings 2021, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczkowska, M. The comparison of the effects of nodular cast iron laser alloying with selected substances. Materials 2022, 15, 7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lont, A.; Górka, J.; Janicki, D.; Matus, K. The laser alloying process of ductile cast iron surface with titanium powder in nitrogen atmosphere. Coatings 2022, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczkowska, M.; Makuch, N.; Kulka, M. The influence of various cooling rates during laser alloying on nodular iron surface layer. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 102, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiru, M.G.; Singh, B. Surface engineered AlMn alloy using laser surface alloying for wear resistance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 110, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowska, A.; Bartkowski, D.; Poplawski, M.; Piasecki, A.; Przestacki, D.; Miklaszewski, A. Microstructure, microhardness, corrosion resistance and chemical composition of Mo, B and Mo-B coatings produced using laser processing. Materials 2020, 13, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuch, N.; Piasecki, A.; Dziarski, P.; Kulka, M. Influence of laser alloying with boron and niobium on microstructure and properties of Nimonic 80A-alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 75, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lu, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C. Microstructure and wear resistance of a composite coating prepared by laser alloying with Ni-coated graphite on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sai, Q.; Hao, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Improving the properties of gray cast iron by laser surface modification. Materials 2023, 16, 5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalçın, B.; Yüksel, A.; Aslantaş, K.; Der, O.; Ercetin, A. Optimization of micro-drilling of laminated aluminum composite panel (Al–PE) using taguchi orthogonal array design. Materials 2023, 16, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).