Tribological Behaviour of Hypereutectic Al-Si Composites: A Multi-Response Optimisation Approach with ANN and Taguchi Grey Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
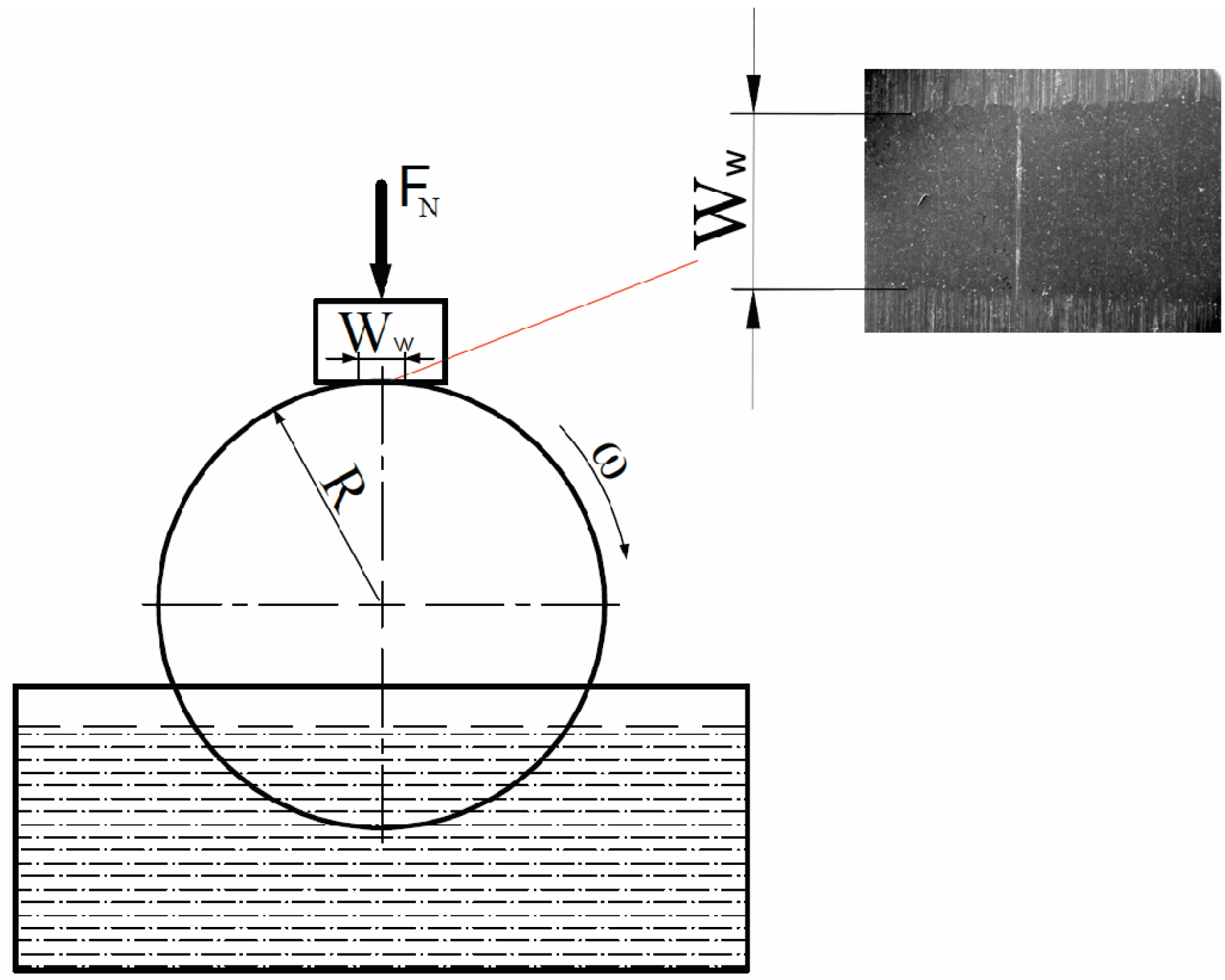
2. Materials and Methods
3. Design of Experiment and Optimisation
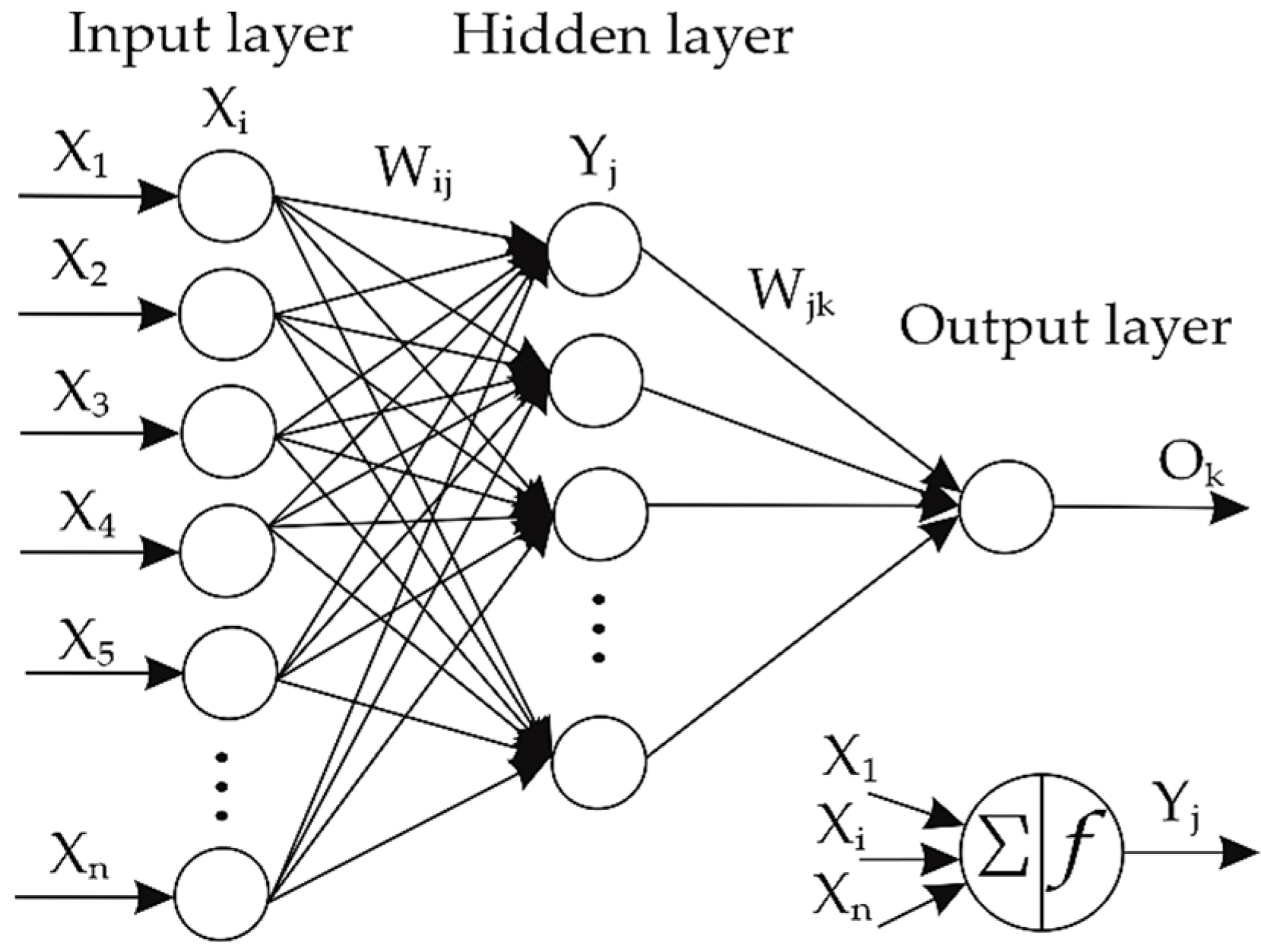
3.1. Artificial Neural Networks
3.2. Taguchi Design
3.3. Grey Relational Analysis
 are maximum and minimum value of experiment response, and Yi (k) is the reference value.
are maximum and minimum value of experiment response, and Yi (k) is the reference value.4. Results and Discussion
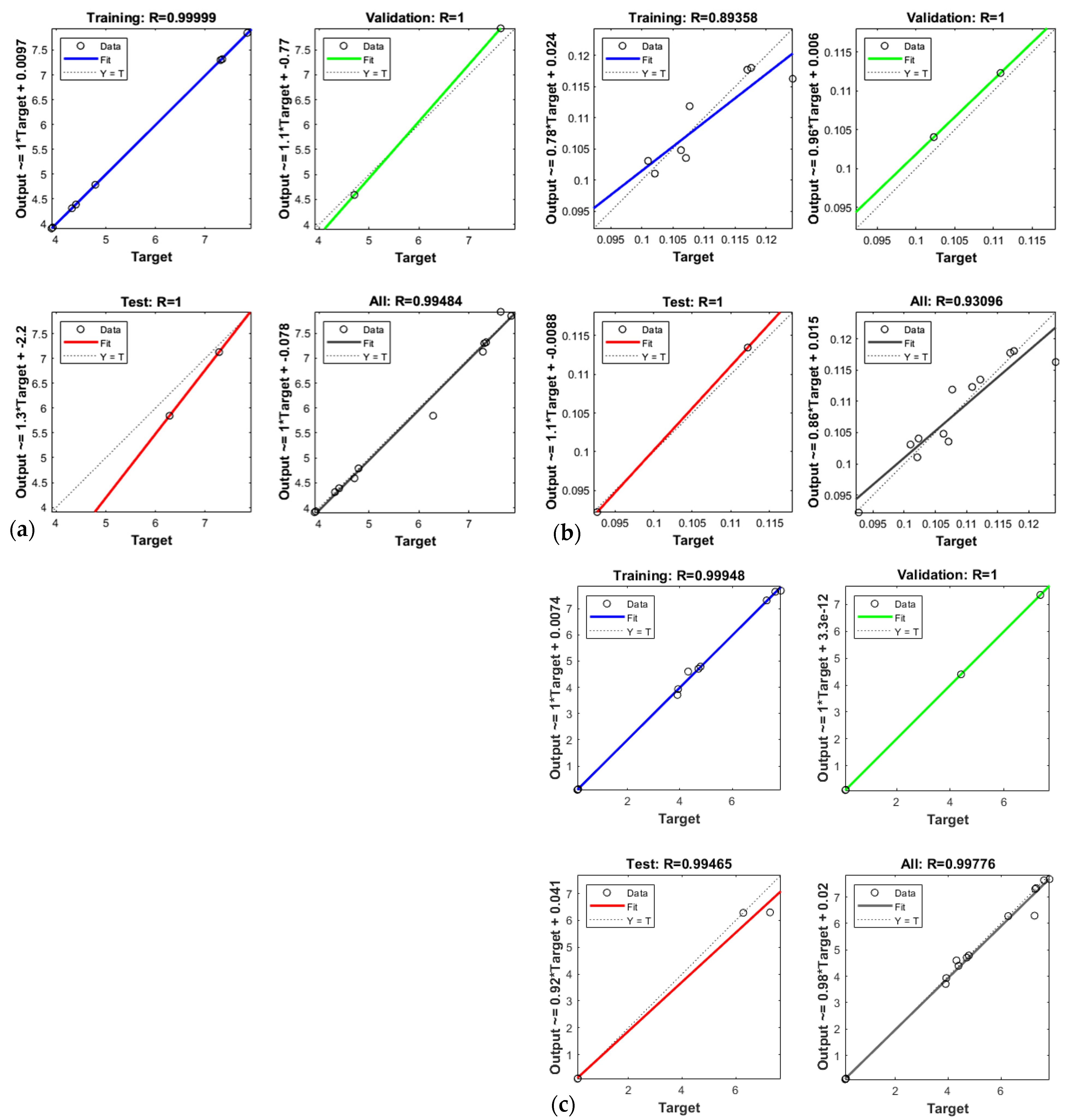
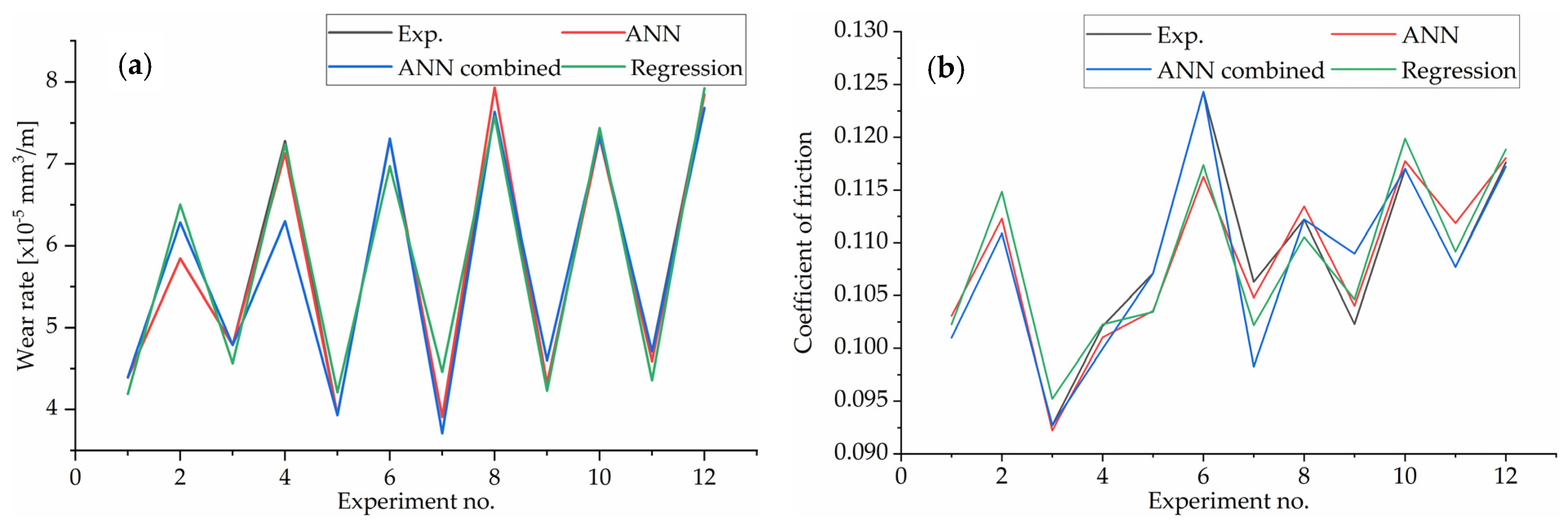
4.1. Artificial Neural Network Analysis
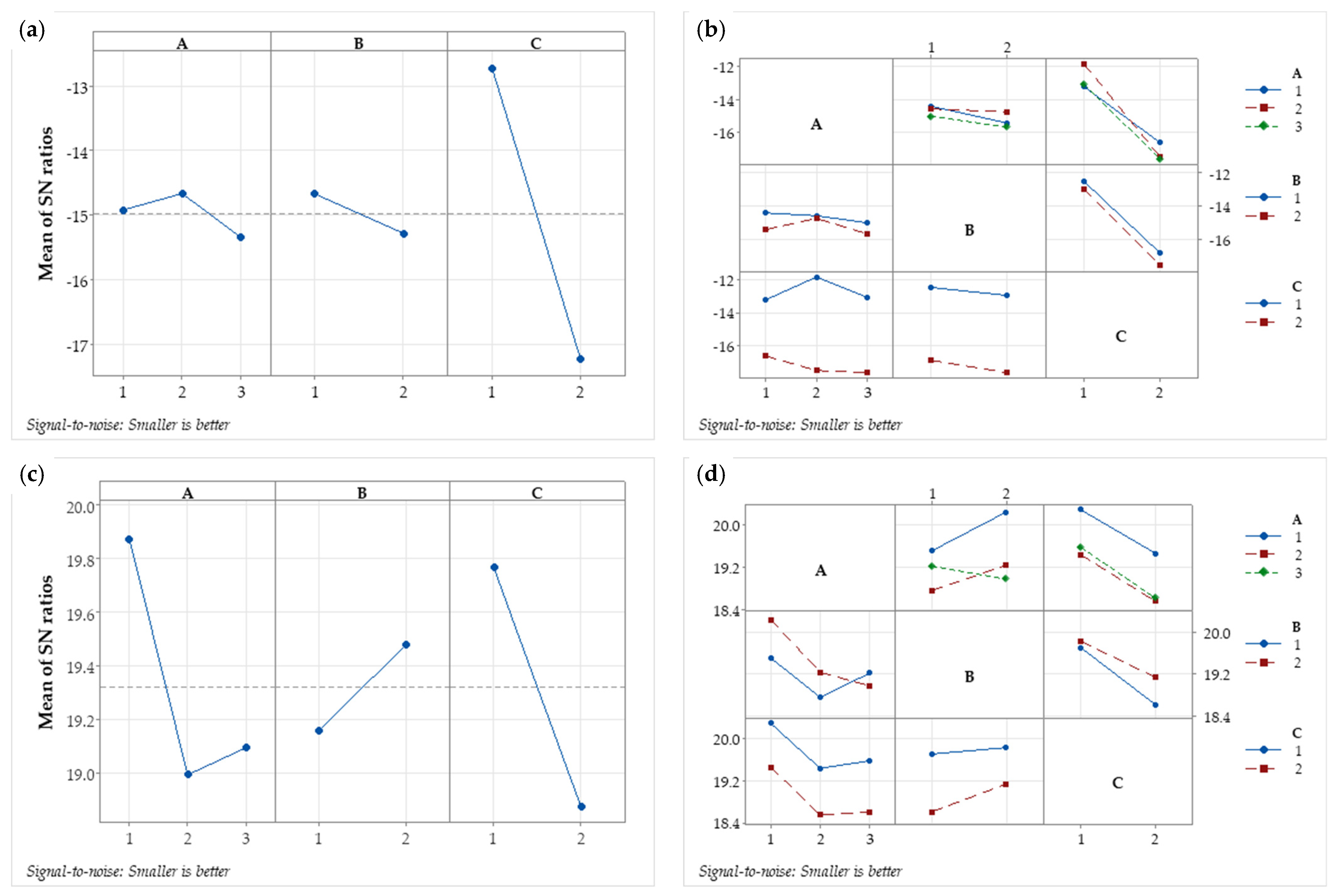
4.2. Taguchi Grey Analysis
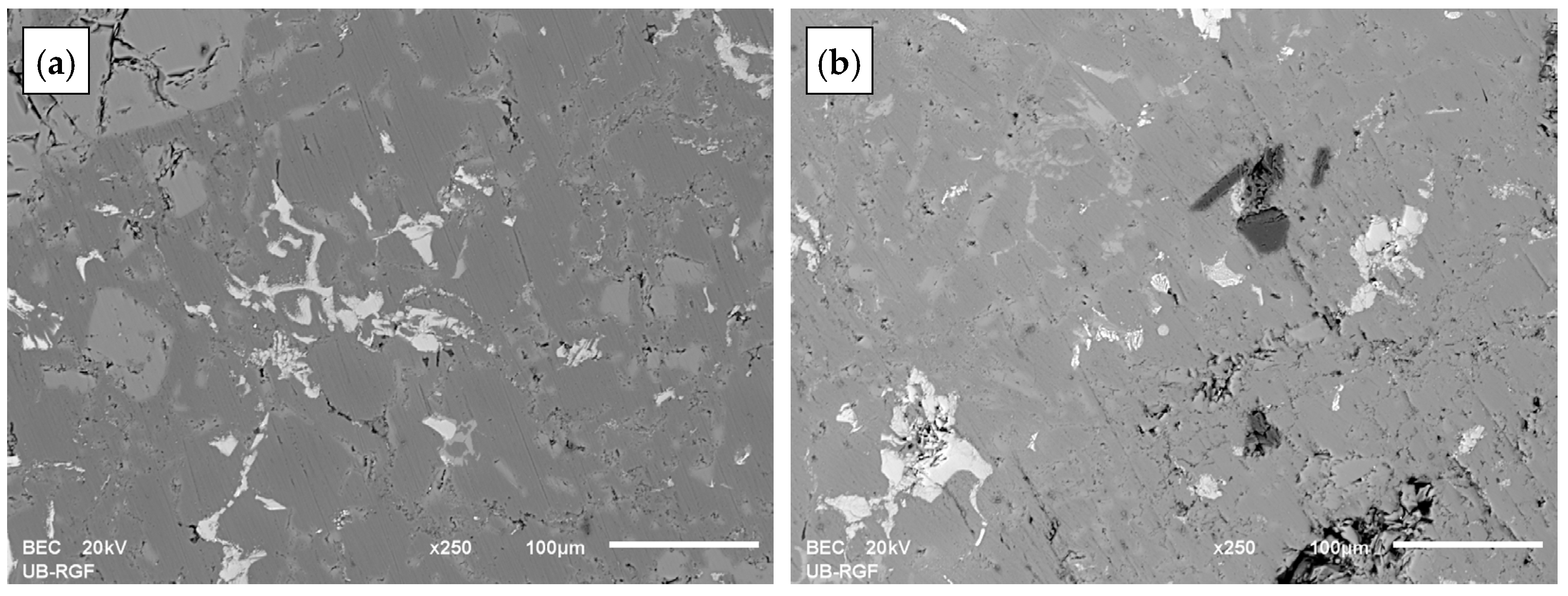
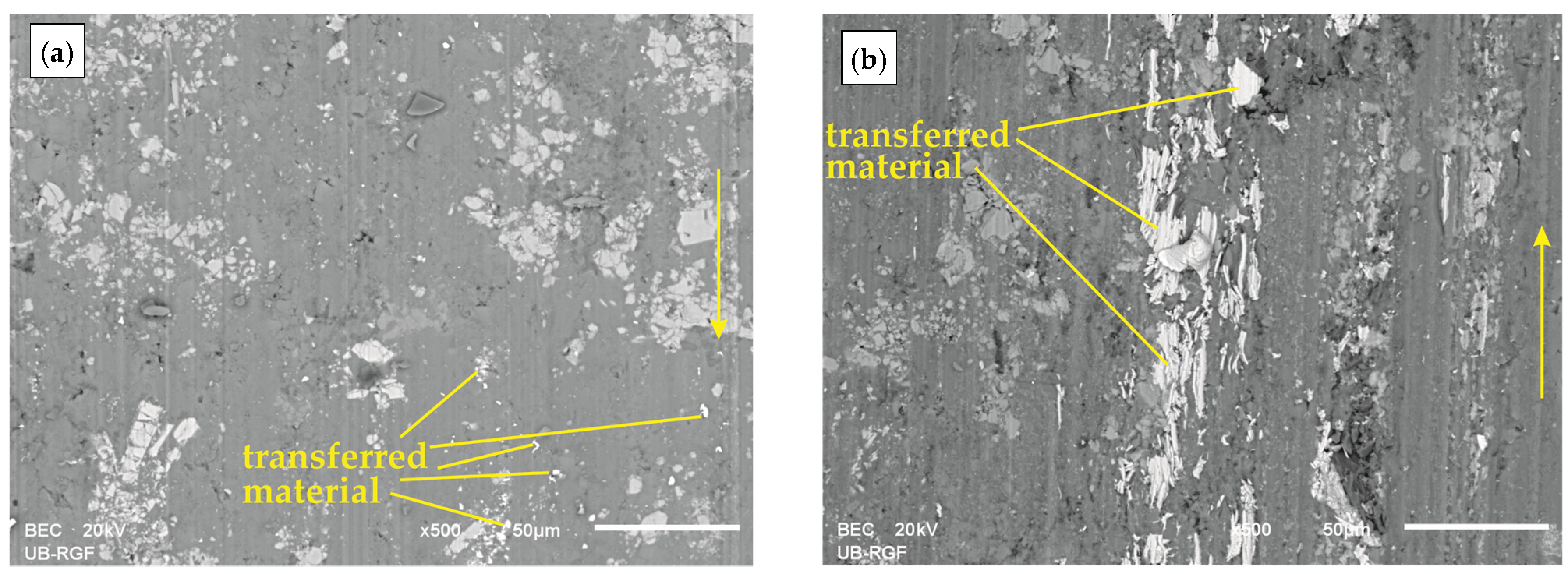
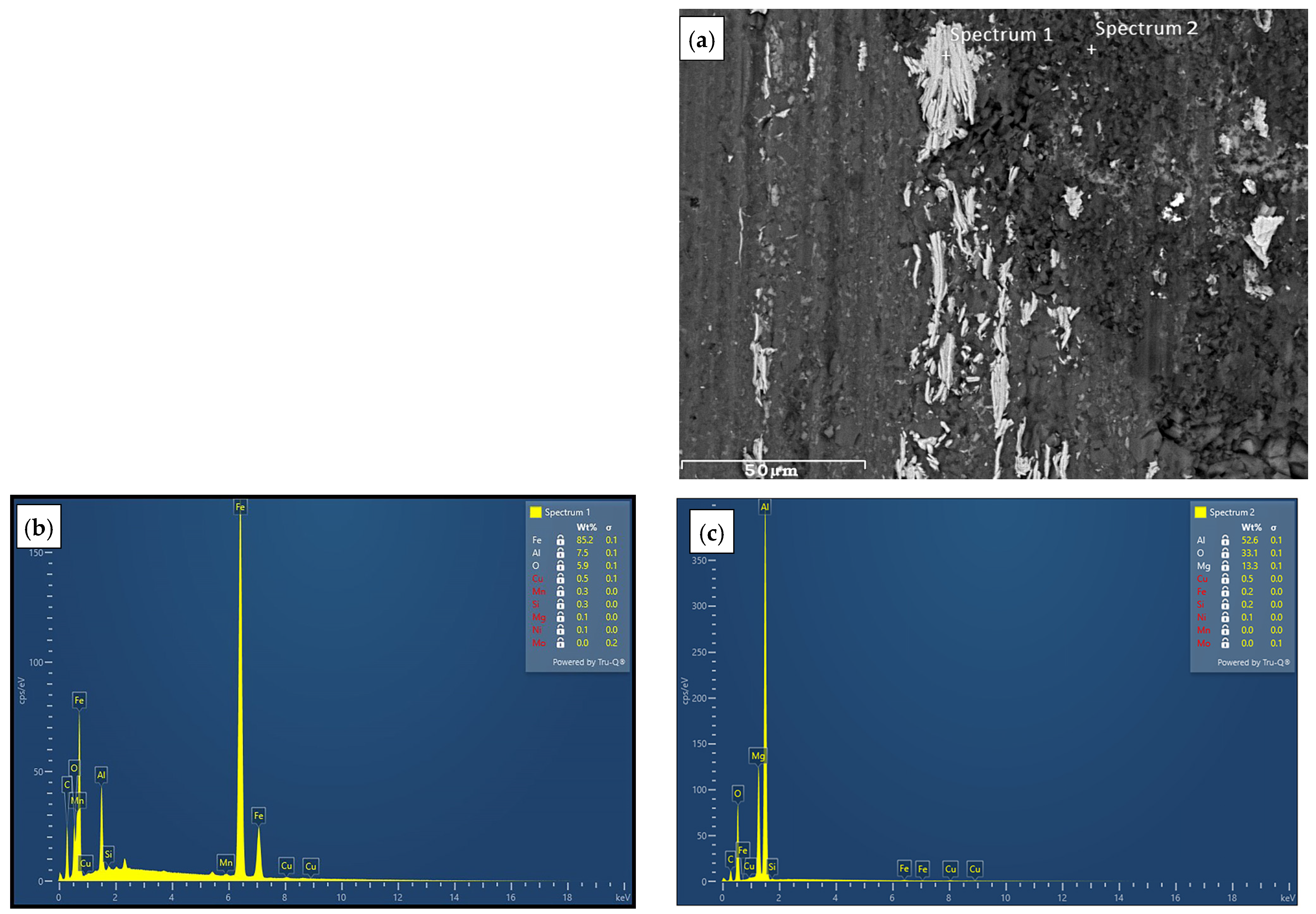
4.3. Worn Surfaces
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joseph, R. Davis Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys. In Alloying: Understanding the Basics; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 351–416. ISBN 978-0-87170-744-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jorstad, J.; Apelian, D. Hypereutectic Al-Si Alloys: Practical Casting Considerations. Int. J. Met. 2009, 3, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wei, M.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y. Morphologies of Primary Silicon in Hypereutectic Al-Si Alloys: Phase-Field Simulation Supported by Key Experiments. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladinović, S.; Stojanović, B.; Gajević, S.; Vencl, A. Hypereutectic Aluminum Alloys and Composites: A Review. Silicon 2023, 15, 2507–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleck, W.; Dziallach, S.; Meuser, H.; Püttgen, W.; Uggowitzer, P.J. Material Aspects of Steel Thixoforming. In Thixoforming: Semi-solid Metal Processing; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 43–104. ISBN 978-3-527-62396-9. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, N.; Ahmad, A. An Overview of Thixoforming Process. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 257, 12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, Y. Cooling Slope Casting and Thixoforming of Hypereutectic A390 Alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 207, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmat-Ardakan, A.; Liu, X.; Ajersch, F.; Chen, X.-G. Wear Behaviour of Hypereutectic Al–Si–Cu–Mg Casting Alloys with Variable Mg Contents. Wear 2010, 269, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasa, L.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M. Effect of Composition and Processing Route on the Wear Behaviour of Al–Si Alloys. Scr. Mater. 2002, 46, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasa, L.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M. Wear Behaviour of Eutectic and Hypereutectic Al–Si–Cu–Mg Casting Alloys Tested against a Composite Brake Pad. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 363, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, V.; Gupta, A.; Pandey, O.P. Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Tempered (T4 and T6) Hypereutectic Aluminum Alloy-Based Composites. Silicon 2023, 15, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, T.V.S.; Dwivedi, D.K.; Jain, N.K. Adhesive Wear of Stir Cast Hypereutectic Al–Si–Mg Alloy under Reciprocating Sliding Conditions. Wear 2009, 266, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, X.; Jin, Y. A Comparison of the Sliding Wear Behavior of a Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy Prepared by Spray-Deposition and Conventional Casting Methods. Wear 2004, 256, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemraj, S.; Jha, A.K.; Ojha, S.N. Tribo-Mechanical Behavior of Complex Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy Compressed through a Converging Die at Elevated Temperatures. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 76509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Shi, Y.; Yu, B. Effect of Squeeze Casting on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectic Al-xSi Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Setchi, R.; Evans, S.L. Synthesis and Characterisation of Advanced Ball-Milled Al-Al2O3 Nanocomposites for Selective Laser Melting. Powder Technol. 2016, 297, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazahery, A.; Abdizadeh, H.; Baharvandi, H.R. Development of High-Performance A356/Nano-Al2O3 Composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 518, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajević, S.; Miladinović, S.; Ivanovic, L.; Skulić, A.; Stojanović, B. A Review on Mechanical Properties of Aluminium-Based Metal Matrix Nanocomposites. Tribol. Mater. 2023, 2, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durai, T.G.; Das, K.; Das, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Al Matrix Composites Reinforced by in Situ Alumina Particulates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 445–446, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, B.; Gajević, S.; Kostić, N.; Miladinović, S.; Vencl, A. Optimization of Parameters That Affect Wear of A356/AlO Nanocomposites Using RSM, ANN, GA and PSO Methods. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2022, 74, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Ezatpour, H.R.; Beygi, H. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Al2O3 Micro and Nano Composites Fabricated by Stir Casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 8765–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirala, A.; Soren, S.; Kumar, N.; Dwivedi, V.K.; Kaushal, D.R. A Comprehensive Review on Stir Cast Al-SiC Composite. Int. Conf. Mech. Energy Technol. 2020, 21, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.S.; Purohit, R.; Soni, V.K.; Das, S. Characterization of Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Aluminium Alloy-SiC Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, A.; Gopalakrishnan, S. A Study on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Aluminium 1100 Alloys 6% of RHAp, BAp, CSAp, ZnOp and Egg Shellp Composites by ANN. Silicon 2021, 13, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, Ş.; Karakoç, H. Investigation of Surface Roughness in the Milling of Al7075 and Open-Cell SiC Foam Composite and Optimization of Machining Parameters. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekka, K.K.; Chauhan, S.R. Varun Dry Sliding Wear Characteristics of SiC and Al2O3 Nanoparticulate Aluminium Matrix Composite Using Taguchi Technique. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith Arul Daniel, S.; Pugazhenthi, R.; Kumar, R.; Vijayananth, S. Multi Objective Prediction and Optimization of Control Parameters in the Milling of Aluminium Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites Using ANN and Taguchi-Grey Relational Analysis. Def. Technol. 2019, 15, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.Z.; Khan, S.; Sarmah, P. Optimization of Powder Metallurgy Processing Parameters of Al2O3/Cu Composite through Taguchi Method with Grey Relational Analysis. J. King Saud Univ.—Eng. Sci. 2020, 32, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Bhowmik, A.; Biswas, A. Tribological Performance Optimization of Al2024-TiB2 Composites Using Grey-Taguchi Approach. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2022, 35, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, S.K.; Suri, N.M.; Kant, S.; Pankaj. A Review on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Graphite Reinforced Self Lubricating Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2018, 56, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, B.C.; kumar, J.; Singh, H. Fabrication and Characterisation of Al2O3/Aluminium Alloy 6061 Composites Fabricated by Stir Casting. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwath, P.; Xavior, M.A. Processing Methods and Property Evaluation of Al2O3 and SiC Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites Based on Aluminium 2xxx Alloys. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Ezatpour, H.R.; Torabi Parizi, M. Comparison of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of A356 Aluminum Alloy/Al2O3 Composites Fabricated by Stir and Compo-Casting Processes. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković, S.; Stojanović, B.; Babić, M.; Vencl, A.; Bobić, I.; Vadászné Bognár, G.; Vučetić, F. Parametric Optimization of the Aluminium Nanocomposites Wear Rate. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 41, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dochev, B.; Panov, I.; Dimova, D. Study of the Retention of the Modifying Effect of a Nanodiamond Nanomodifier on the Structure of AlSi18 Alloy. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 2980, 60013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmat-Ardakan, A.; Ajersch, F. Effect of Conventional and Rheocasting Processes on Microstructural Characteristics of Hypereutectic Al–Si–Cu–Mg Alloy with Variable Mg Content. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Konishi, H.; Li, X. Al2O3 Nanoparticles Induced Simultaneous Refinement and Modification of Primary and Eutectic Si Particles in Hypereutectic Al–20Si Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 541, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Li, X. Preparationand Characterization of Hypereutectic Al-20wt.%Si-4.5wt.%Cu Nanocomposites with Al2O3 Nnanoparticles. In Research and Markets, Proceedings of the TMS 2011 140th Annual Meeting and Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings: General Paper Selections, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 March 2011; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- El Mahallawi, I.; Shash, Y.; Rashad, R.M.; Abdelaziz, M.H.; Mayer, J.; Schwedt, A. Hardness and Wear Behaviour of Semi-Solid Cast A390 Alloy Reinforced with Al2O3 and TiO2 Nanoparticles. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 5171–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahallawi, I.S.; Shash, A.Y. Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance of Semisolid Cast Al2O3 Nano Reinforced Hypo and Hyper-Eutectic Al–Si Composites. In Properties and Characterization of Modern Materials; Öchsner, A., Altenbach, H., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 13–30. ISBN 978-981-10-1602-8. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.; Jarfors, A.E.W.; Dahle, A.K. Formation of Iron-Rich Intermetallic Phases in Al-7Si-Mg: Influence of Cooling Rate and Strontium Modification. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 4148–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J. Formation of Intermetallic Phases in Al-10Si-0.3Fe Based Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, Technischen Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, C.; Caram, R.; Botta, W.F.; Kiminam, C.; Bolfarini, C. Intermetallic Compounds in the Al-Si-Cu System. Acta Microsc. 2003, 12, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Warmuzek, M. Chemical Composition of the Ni-Containing Intermetallic Phases in the Multicomponent Al Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 604, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojević, S.; Savić, S.; Maric, D.; Stopka, O.; Krstić, B.; Stojanovic, B. Correlation between Emission and Combustion Characteristics with the Compression Ratio and Fuel Injection Timing in Tribologically Optimized Diesel Engine. Teh. Vjesn. 2022, 29, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminaga, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ratnak, S.; Kusaka, J.; Youso, T.; Fujikawa, T.; Yamakawa, M. A Study on Combustion Characteristics of a High Compression Ratio SI Engine with High Pressure Gasoline Injection; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.K.; Brahma, A.; Dutta, K. Prediction of Mechanical Properties of Al-Si-Mg Alloy Using Artificial Neural Network. Sādhanā 2021, 46, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khishe, M.; Parvizi, G.R. Artificial Neural Networks, Concept, Application and Types. In Neural Networks; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–30. ISBN 978-1-5361-7188-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tosh, C.R.; Ruxton, G.D. (Eds.) Modelling Perception with Artificial Neural Networks; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-521-76395-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zohuri, B.; Moghaddam, M. Neural Network Driven Artificial Intelligence: Decision Making Based on Fuzzy Logic; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-5361-2114-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Gururaj, S. Conceptual Cost Modelling for Sustainable Construction Project Planning—A Levenberg–Marquardt Neural Network Approach. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2019, 13, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Manivannan, I. Evaluation of Tribological Process Parameters of Al6061 + Nano Sic + Gr Hybrid Nano Composites Using Taguchi Technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsy, B.; Nwobi-Okoye, C.; Chukwuemeka, E.; Uche, R. Multi Objective Optimization of Novel Al-Si-Mg Nanocomposites: A Taguchi-ANN-NSGA-II Approach. J. Eng. Res. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, M.; Dwivedi, D.K.; Sehgal, R.; Bhat, I. Effect of Iron on Wear Behavior of As-Cast and Heat-Treated Hypereutectic Al–18Si–4Cu–0.5Mg Alloy: A Taguchi Approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2014, 228, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marode, R.V.; Pedapati, S.R.; Lemma, T.A.; Loyte, A.; Devarajan, Y.; Thandavamoorthy, R. Influence of Silicon Carbide on Microhardness and Corrosion Behavior of AZ91/SiC Surface Composites Processed through Friction Stir Processing: Multi-Response Optimization Using Taguchi-Grey Relational Analysis. Silicon 2023, 15, 6921–6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Priyadarshan; Ghosh, S.K. Statistical and Artificial Neural Network Technique for Prediction of Performance in AlSi10Mg-MWCNT Based Composite Materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 273, 125136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, V.; Pandey, O.P. Wear and Friction Behavior of Gr/Sn Solid Lubricated Dual Reinforced AMCs. Silicon 2022, 14, 5629–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouei, V.; Shabestari, S.G.; Saghafian, H. Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of Hypereutectic Al–Si Piston Alloys Containing Iron-Rich Intermetallics. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, K.P.; Majhi, J.; Sahoo, S.K.; Pattnaik, S.C. The Microstructural and Wear Properties Improvement by Manganese Addition in Al-14Si Hypereutectic Alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 5934–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, E.; Varghese, T.; Rajan, T.P.D.; Pai, B.C. Reciprocating Wear Analysis of Magnesium-Modified Hyper-Eutectic Functionally Graded Aluminium Composites. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, P.R.; Thanigaivelan, R.; Thiraviam, R.; Pradeep Kumar, K. Performance Studies on Hybrid Nano-Metal Matrix Composites for Wear and Surface Quality. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2023, 41, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.; Aydın, F.; Sun, Y.; Zengin, H.; Akinay, Y. Wear Resistance and Tribological Properties of GNPs and MWCNT Reinforced AlSi18CuNiMg Alloys Produced by Stir Casting. Tribol. Int. 2021, 164, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Alpas, A.T. Ultra-Mild Wear of a Hypereutectic Al–18.5wt.% Si Alloy. Wear 2008, 265, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, B.S. Investigation of Tribological and Mechanical Properties Al2O3–SiC Reinforced Al Composites Manufactured by Casting or P/M Method. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, D. Improvement of tribological properties of A356-Al2O3 cast composites by heat-treatment. J. Al-Azhar Univ. Eng. Sect. 2018, 13, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Factor and Label | Unit | Level I | Level II | Level III |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of micro-reinforcement (A) | – | matrix only (1) | 3 wt.% Al2O3 (2) | 3 wt.% SiC (3) |
| Amount of Al2O3 nanoparticles (B) | wt.% | 0 (1) | 0.5 (2) | – |
| Normal load (C) | N | 100 (1) | 200 (2) | – |
| Exp. no | Imput Factor | Experiment | ANN Combined 3-5-2 Logsig | ANN 3-15-1 Logsig | ANN 3-6-1 Tansig | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | WR × 10−5 [mm3/m] | CoF | WR × 10−5 [mm3/m] | CoF | Error WR | Error CoF | WR × 10−5 [mm3/m] | Error | CoF | Error | |||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 4.3969 | 0.101 | 4.3969 | 0.101 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 4.3899 | 0.0070 | 0.1031 | −0.0021 | ||||||||
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 200 | 6.2826 | 0.1109 | 6.2826 | 0.1109 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 5.8444 | 0.4382 | 0.1123 | −0.0014 | ||||||||
| 3 | 1 | 0.5 | 100 | 4.7872 | 0.0927 | 4.7872 | 0.0927 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 4.7882 | −0.0010 | 0.0922 | 0.0005 | ||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.5 | 200 | 7.2794 | 0.1021 | 6.2973 | 0.0999 | 0.9821 | 0.0021 | 7.1276 | 0.1518 | 0.1010 | 0.0011 | ||||||||
| 5 | 2 | 0 | 100 | 3.9305 | 0.1071 | 3.9305 | 0.1071 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 3.9282 | 0.0023 | 0.1036 | 0.0035 | ||||||||
| 6 | 2 | 0 | 200 | 7.3077 | 0.1243 | 7.3077 | 0.1243 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 7.2973 | 0.0104 | 0.1163 | 0.0080 | ||||||||
| 7 | 2 | 0.5 | 100 | 3.9063 | 0.1063 | 3.7091 | 0.0983 | 0.1972 | 0.0080 | 3.9081 | −0.0018 | 0.1048 | 0.0015 | ||||||||
| 8 | 2 | 0.5 | 200 | 7.6366 | 0.1122 | 7.6366 | 0.1122 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 7.9297 | −0.2931 | 0.1135 | −0.0013 | ||||||||
| 9 | 3 | 0 | 100 | 4.3165 | 0.1023 | 4.5994 | 0.1089 | −0.2829 | −0.0067 | 4.3140 | 0.0025 | 0.1040 | −0.0017 | ||||||||
| 10 | 3 | 0 | 200 | 7.3432 | 0.117 | 7.3432 | 0.117 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 7.3180 | 0.0252 | 0.1177 | −0.0007 | ||||||||
| 11 | 3 | 0.5 | 100 | 4.7056 | 0.1077 | 4.7056 | 0.1077 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 4.5901 | 0.1155 | 0.1119 | −0.0042 | ||||||||
| 12 | 3 | 0.5 | 200 | 7.8468 | 0.1176 | 7.6817 | 0.1172 | 0.1651 | 0.0004 | 7.8461 | 0.0007 | 0.1180 | −0.0004 | ||||||||
| Exp. no | Taguchi | Grey | |||||||||||||||||||
| S/N for WR | S/N for CoF | norm. WR | norm. COF | delta WR | delta COF | GRC WR | GRC CoF | GRG | Rank | ||||||||||||
| 1 | −12.8629 | 19.9136 | 0.8755 | 0.7373 | 0.1245 | 0.2627 | 0.8006 | 0.6556 | 0.7622 | 5 | |||||||||||
| 2 | −15.9628 | 19.1014 | 0.3970 | 0.4241 | 0.6030 | 0.5759 | 0.4533 | 0.4647 | 0.4563 | 7 | |||||||||||
| 3 | −13.6016 | 20.6584 | 0.7764 | 1.0000 | 0.2236 | 0.0000 | 0.6910 | 1.0000 | 0.7730 | 4 | |||||||||||
| 4 | −17.2419 | 19.8195 | 0.1440 | 0.7025 | 0.8560 | 0.2975 | 0.3687 | 0.6270 | 0.4372 | 8 | |||||||||||
| 5 | −11.8890 | 19.4042 | 0.9939 | 0.5443 | 0.0061 | 0.4557 | 0.9879 | 0.5232 | 0.8646 | 2 | |||||||||||
| 6 | −17.2756 | 18.1106 | 0.1368 | 0.0000 | 0.8632 | 1.0000 | 0.3668 | 0.3333 | 0.3579 | 11 | |||||||||||
| 7 | −11.8353 | 19.4693 | 1.0000 | 0.5696 | 0.0000 | 0.4304 | 1.0000 | 0.5374 | 0.8773 | 1 | |||||||||||
| 8 | −17.6580 | 19.0001 | 0.0533 | 0.3829 | 0.9467 | 0.6171 | 0.3456 | 0.4476 | 0.3727 | 9 | |||||||||||
| 9 | −12.7026 | 19.8025 | 0.8959 | 0.6962 | 0.1041 | 0.3038 | 0.8277 | 0.6220 | 0.7731 | 3 | |||||||||||
| 10 | −17.3177 | 18.6363 | 0.1278 | 0.2310 | 0.8722 | 0.7690 | 0.3644 | 0.3940 | 0.3722 | 10 | |||||||||||
| 11 | −13.4523 | 19.3557 | 0.7972 | 0.5253 | 0.2028 | 0.4747 | 0.7114 | 0.5130 | 0.6588 | 6 | |||||||||||
| 12 | −17.8939 | 18.5919 | 0.0000 | 0.2120 | 1.0000 | 0.7880 | 0.3333 | 0.3882 | 0.3479 | 12 | |||||||||||
| Prediction | WR | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transfer function | tansig | logsig | ||||||||||||
| No. of neurons in the hidden layer | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 20 | ||||
| Regression coefficient | 0.97358 | 0.9895 | 0.98869 | 0.98547 | 0.9316 | 0.97731 | 0.99484 | 0.97145 | 0.99189 | 0.98717 | ||||
| MSE | 0.96924 | 0.99062 | 0.98987 | 0.98697 | 0.96924 | 0.97043 | 0.99927 | 0.97543 | 0.99286 | 0.98494 | ||||
| Prediction | CoF | |||||||||||||
| Transfer function | tansig | logsig | ||||||||||||
| No. of neurons in the hidden layer | 5 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 15 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 15 | ||||
| Regression coefficient | 0.91038 | 0.93096 | 0.92719 | 0.88538 | 0.76831 | 0.88754 | 0.91765 | 0.86306 | 0.75498 | 0.80757 | ||||
| MSE | 0.99988 | 0.99992 | 0.99990 | 0.99986 | 0.99986 | 0.99986 | 0.99990 | 0.99984 | 0.99971 | 0.99971 | ||||
| Prediction | WR and CoF combined | |||||||||||||
| Transfer function | tansig | logsig | ||||||||||||
| No. of neurons in the hidden layer | 5 | 10 | 15 | 5 | 10 | 15 | ||||||||
| Regression coefficient | 0.99799 | 0.99022 | 0.98325 | 0.99776 | 0.99167 | 0.99761 | ||||||||
| MSE for WR | 0.98714 | 0.93494 | 0.88919 | 0.98383 | 0.93723 | 0.99488 | ||||||||
| MSE for CoF | 0.99822 | 0.99916 | 0.99761 | 0.99991 | 0.99903 | 0.99864 | ||||||||
| WR | CoF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | A | B | C | Level | A | B | C |
| 1 | −14.92 | −14.67 | −12.72 | 1 | 19.87 | 19.16 | 19.77 |
| 2 | −14.66 | −15.28 | −17.22 | 2 | 19.00 | 19.48 | 18.88 |
| 3 | −15.34 | 3 | 19.10 | ||||
| Delta | 0.68 | 0.61 | 4.50 | Delta | 0.88 | 0.32 | 0.89 |
| Rank | 2 | 3 | 1 | Rank | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value | Percentage Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2 | 0.9367 | 0.9367 | 0.4683 | 12.60 | 0.074 | 1.42 |
| B | 1 | 1.1239 | 1.1239 | 1.1239 | 30.23 | 0.032 | 1.71 |
| C | 1 | 60.7775 | 60.7775 | 60.7775 | 1634.96 | 0.001 | 92.33 |
| A × B | 2 | 0.3605 | 0.3605 | 0.1803 | 4.85 | 0.171 | 0.55 |
| A × C | 2 | 2.4978 | 2.4978 | 1.2489 | 33.60 | 0.029 | 3.79 |
| B × C | 1 | 0.0537 | 0.0537 | 0.0537 | 1.45 | 0.352 | 0.08 |
| Residual error | 2 | 0.0743 | 0.0743 | 0.0372 | 0.11 | ||
| Total | 11 | 65.8244 | 100.00 | ||||
| R-Sq (99.89%) R-Sq(adj) 99.38% | |||||||
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value | Percentage Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2 | 1.84351 | 1.84351 | 0.92176 | 20.36 | 0.047 | 35.00 |
| B | 1 | 0.30925 | 0.30925 | 0.30925 | 6.83 | 0.121 | 5.87 |
| C | 1 | 2.37985 | 2.37985 | 2.37985 | 52.56 | 0.019 | 45.18 |
| A × B | 2 | 0.51399 | 0.51399 | 0.25699 | 5.68 | 0.150 | 9.76 |
| A × C | 2 | 0.00985 | 0.00985 | 0.00493 | 0.11 | 0.902 | 0.19 |
| B × C | 1 | 0.12002 | 0.12002 | 0.12002 | 2.65 | 0.245 | 2.28 |
| Residual error | 2 | 0.09056 | 0.09056 | 0.04528 | 1.72 | ||
| Total | 11 | 5.26703 | 100.00 | ||||
| R-Sq (98.28%) R-Sq(adj) 90.54% | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miladinović, S.; Gajević, S.; Savić, S.; Miletić, I.; Stojanović, B.; Vencl, A. Tribological Behaviour of Hypereutectic Al-Si Composites: A Multi-Response Optimisation Approach with ANN and Taguchi Grey Method. Lubricants 2024, 12, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12020061
Miladinović S, Gajević S, Savić S, Miletić I, Stojanović B, Vencl A. Tribological Behaviour of Hypereutectic Al-Si Composites: A Multi-Response Optimisation Approach with ANN and Taguchi Grey Method. Lubricants. 2024; 12(2):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12020061
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiladinović, Slavica, Sandra Gajević, Slobodan Savić, Ivan Miletić, Blaža Stojanović, and Aleksandar Vencl. 2024. "Tribological Behaviour of Hypereutectic Al-Si Composites: A Multi-Response Optimisation Approach with ANN and Taguchi Grey Method" Lubricants 12, no. 2: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12020061
APA StyleMiladinović, S., Gajević, S., Savić, S., Miletić, I., Stojanović, B., & Vencl, A. (2024). Tribological Behaviour of Hypereutectic Al-Si Composites: A Multi-Response Optimisation Approach with ANN and Taguchi Grey Method. Lubricants, 12(2), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12020061








