Investigation of Wear Behavior in Self-Lubricating ABS Polymer Composites Reinforced with Glass Fiber/ABS and Glass Fiber/Carbon Fiber/ABS Hybrid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Fabrication Using Hybrid Manufacturing Technique
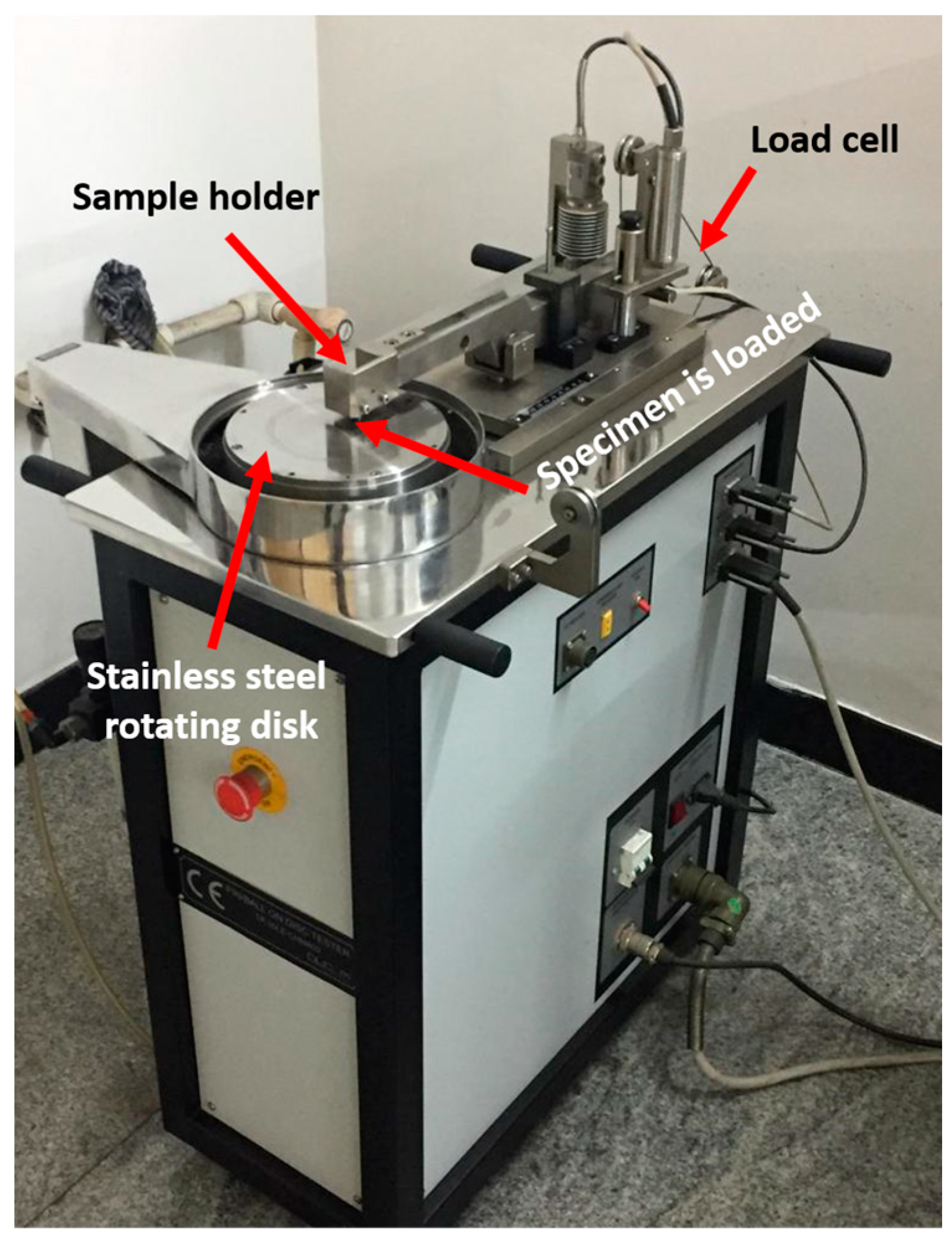
2.3. Wear Test
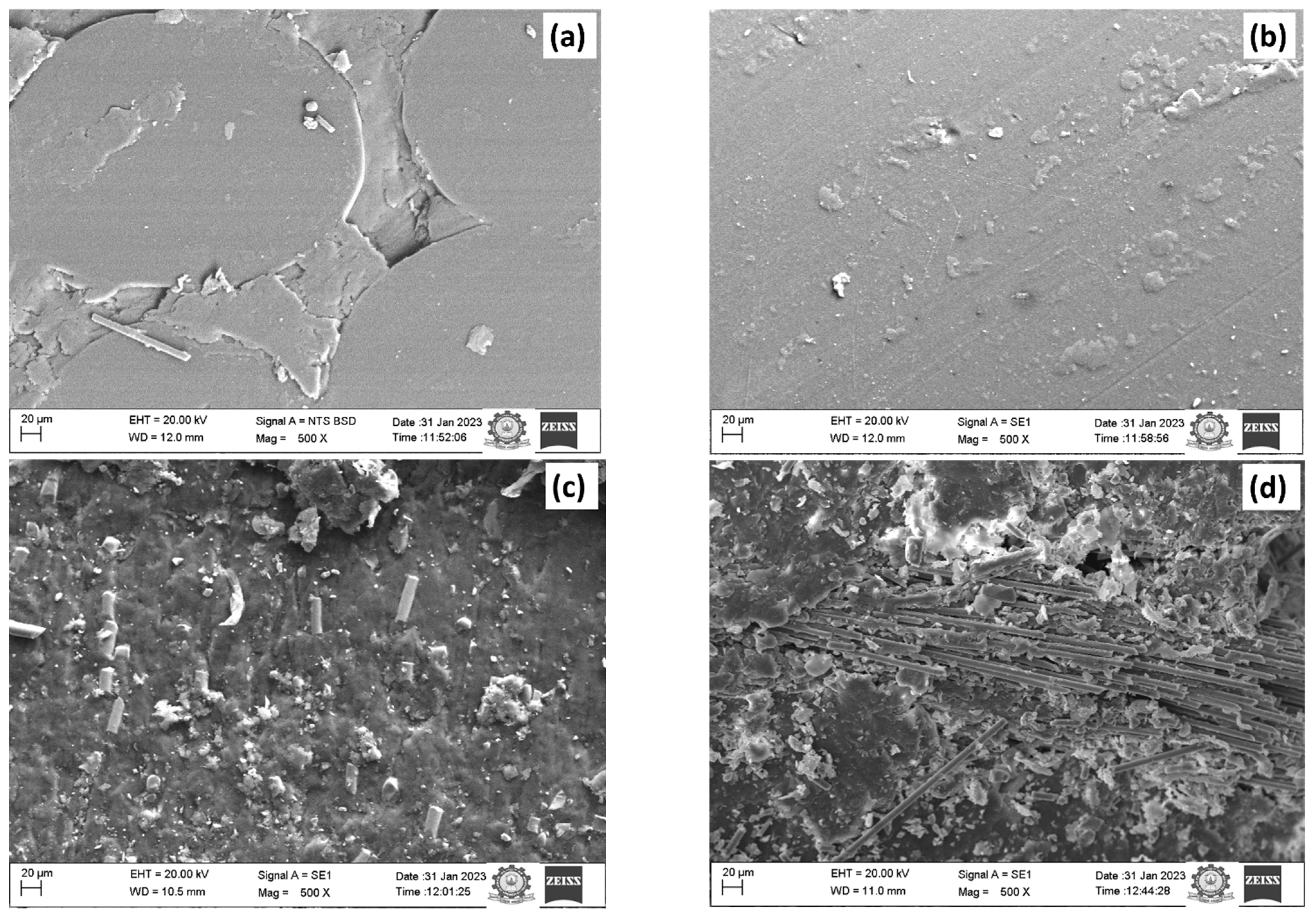
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscope
3. Results and Discussion
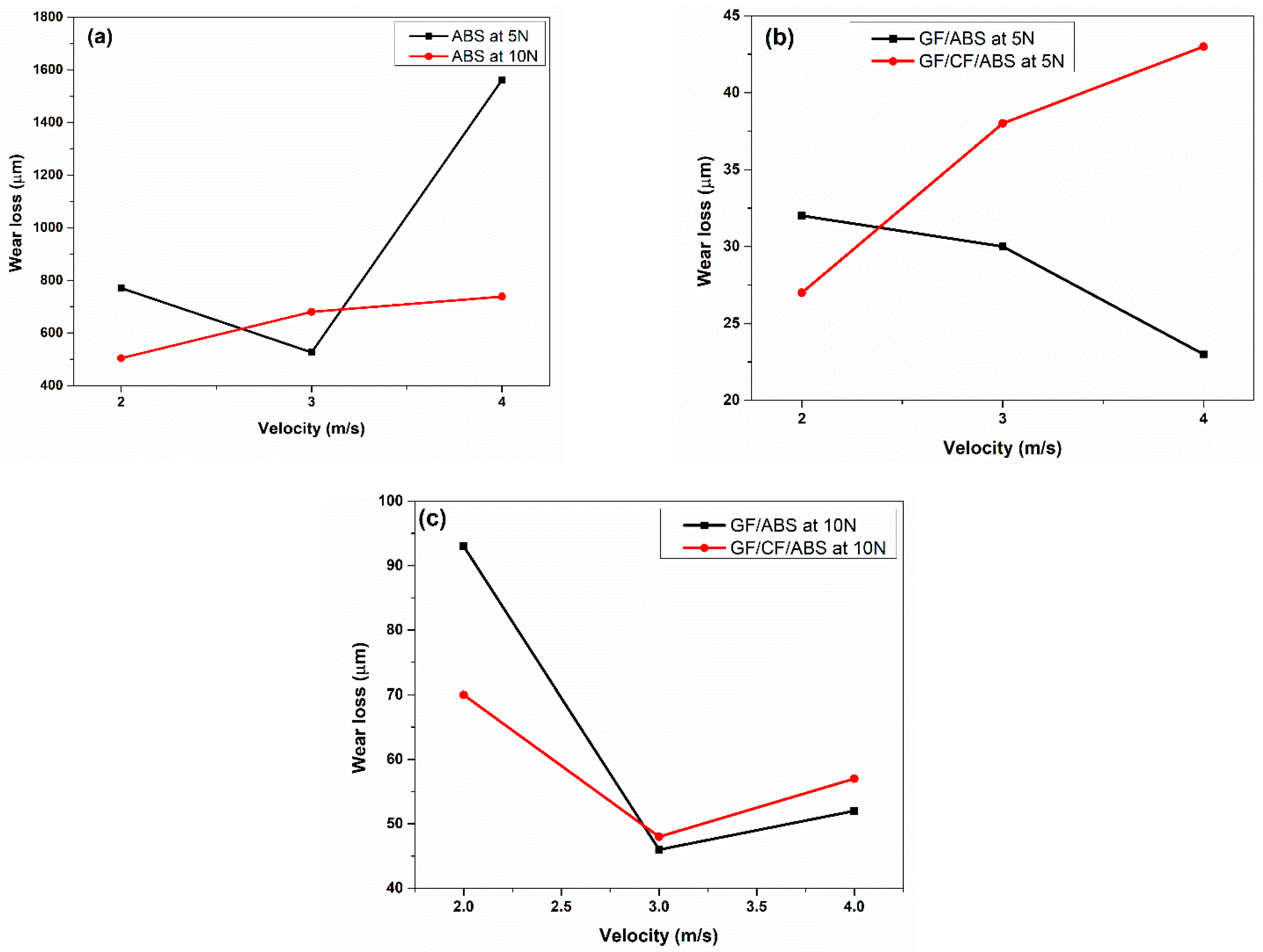
Wear Test
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The study found that the wear loss of the composite laminates was lower compared to that of the ABS samples. The GF/ABS composite laminates exhibited the lowest wear loss of 23 µm (5 N and 4 m/s) among all the tested samples. However, the wear loss increased as the load increased from 5 N to 10 N for both the GF/ABS and GF/CF/ABS samples. These findings indicate that the addition of glass and carbon fibers to the ABS matrix could improve the wear resistance of the resulting composites.
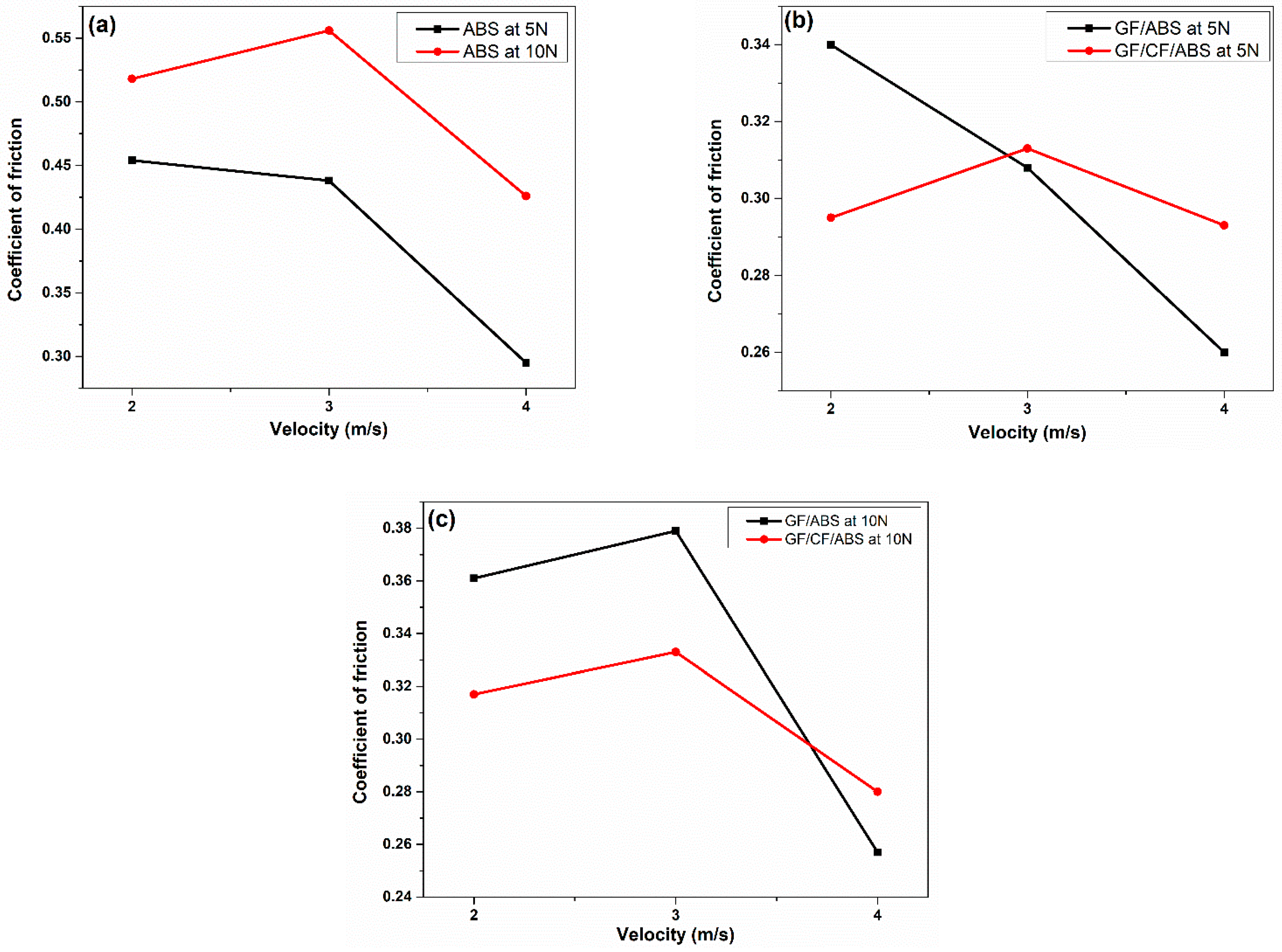
- The coefficient of friction of the ABS samples was lower, with a value of 0.295 at 4 m/s under a 5 N load. The composite laminates also showed a lower coefficient of friction at 4 m/s for both 5 N and 10 N loads. Among the different loaded samples, the GF/ABS samples showed the lowest coefficient of friction.
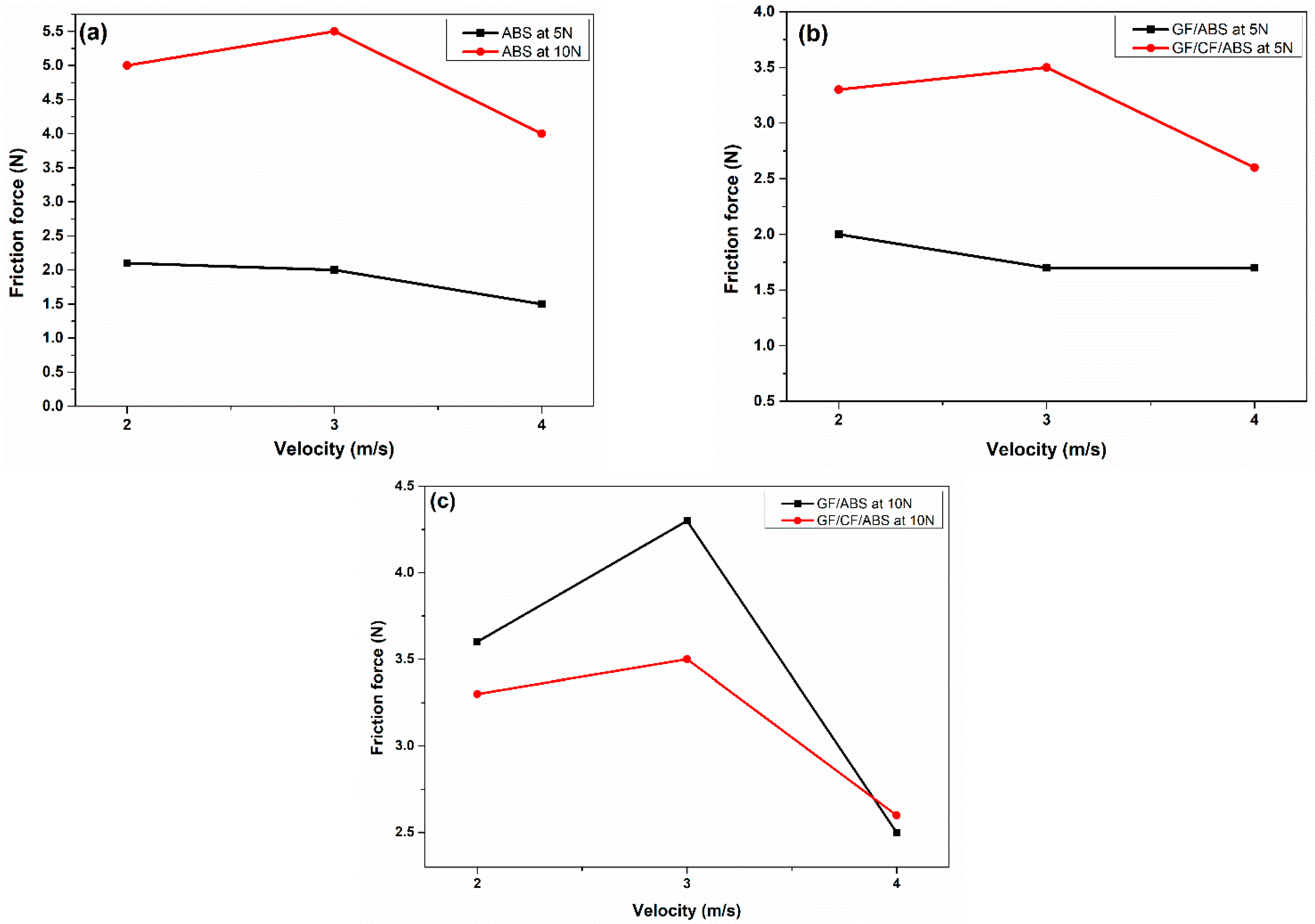
- The ABS samples showed lower friction force values at 2 m/s to 4 m/s under 5 N of load, with a friction force of 1.5 measured for ABS samples (5 N and 2 m/s). In the composite laminates, the GF/ABS exhibited a lower friction force under a 5 N load. When the load was increased from 5 N to 10 N, the friction force increased.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleirscher, M.; Wolfberger, A.; Schlögl, S.; Hołyńska, M.; Hausberger, A. Accelerated Thermo-Catalytic Degradation of Perfluoropolyether (PFPE) Lubricants for Space Applications. Lubricants 2023, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavamurthy, R.; Tambrallimath, V.; Rajhi, A.A.; Ahmed, R.S.; Patil, A.Y.; Khan, T.M.Y.; Makannavar, R. Influence of Solid Lubricant Addition on Friction and Wear Response of 3D Printed Polymer Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilberoglu, U.M.; Gharehpapagh, B.; Yaman, U.; Dolen, M. Current Trends and Research Opportunities in Hybrid Additive Manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 623–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Dhokia, V.G.; Nassehi, A.; Newman, S.T. A Review of Hybrid Manufacturing Processes—State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2013, 26, 596–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, P.; Foteinopoulos, P.; Papacharalampopoulos, A.; Bikas, H. Addressing the Challenges for the Industrial Application of Additive Manufacturing: Towards a Hybrid Solution. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2018, 1, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, T.J.; Harrysson, O.L.A. Overview of Current Additive Manufacturing Technologies and Selected Applications. Sci. Prog. 2012, 95, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamez, M.B.A.; Taha, I. A Review of Additive Manufacturing Technologies and Markets for Thermosetting Resins and Their Potential for Carbon Fiber Integration. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvez, S.; Santos, P.; Parente, J.M.; Silva, M.P.; Reis, P.N.B. 3D Printed Continuous Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA Composites: A Short Review. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2020, 25, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, N.; Jain, P.K. 3D Printed Carbon Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites: A Review. Mater Today Proc. 2020, 43, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Lee, M.S.; Kang, C.G. The Fabrication of a Hybrid Material Using the Technique of Hot-Press Molding. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findik, F. Latest Progress on Tribological Properties of Industrial Materials. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 218–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Rajini, N.; Jawaid, M.; Winowlin Jappes, J.; Thariq, M.; Siengchin, S.; Sukumaran, J. A Review on Tribological Properties of Natural Fiber Based Sustainable Hybrid Composite. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2017, 231, 1616–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, B.; Chandramohan, G.; Samapthkumaran, P.; Seetharamu, S.; Vynatheya, S. Friction and Wear Characteristics of Carbon-Epoxy and Glass-Epoxy Woven Roving Fiber Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2006, 25, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, H.; Nakao, N.; Kuwashiro, S.; Matsuda, S. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites from Acrylic Polymer Matrices: Interfacial Adhesion and Physical Properties. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. High Performance Polymers and Engineering Plastics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781118016695. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnasamy, S.; Thiagamani, S.M.K.; Muthu Kumar, C.; Nagarajan, R.; Shahroze, R.M.; Siengchin, S.; Ismail, S.O.; Indira, I.D. Recent Advances in Thermal Properties of Hybrid Cellulosic Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandapani, A.; Krishnasamy, S.; Muthukumar, C.; Thiagamani, S.M.K.; Nagarajan, R.; Siengchin, S. Plastics in Marine Engineering. Ref. Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2020, 4, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophia, O.; Joyce, R.S.; SuetYin, S.; Evonne, T. Preferred Fiber and Materials Market Report 2021; Textile Exchange: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hausberger, A.; Stiller, T.; Kappl, C.; Hensgen, L.; Grün, F. Improving the Tribological Properties of Technical Polymers with Metal Sulphide Compounds. Lubricants 2021, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morampudi, P.; Namala, K.K.; Gajjela, Y.K.; Barath, M.; Prudhvi, G. Review on Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 43, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. Glass Fibre Sizing: A Review; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 127, ISBN 0044141548. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, S.; Rosenkranz, A. Carbon Nanomaterials—Promising Solid Lubricants to Tailor Friction and Wear. Lubricants 2019, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujah, C.O.; von Kallon, D.V.; Aigbodion, V.S. Tribological Properties of CNTs-Reinforced Nano Composite Materials. Lubricants 2023, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.-S.; Jin, F.-L.; Rhee, K.Y.; Hui, D.; Park, S.-J. Recent Advances in Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites: A Review. Compos. B Eng. 2018, 142, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchenkov, K.; Vedernikov, A.; Safonov, A.; Akhatov, I. Thermoplastic Pultrusion: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedernikov, A.; Minchenkov, K.; Gusev, S.; Sulimov, A.; Zhou, P.; Li, C.; Xian, G.; Akhatov, I.; Safonov, A. Effects of the Pre-Consolidated Materials Manufacturing Method on the Mechanical Properties of Pultruded Thermoplastic Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattan, R.; Bijwe, J.; Fahim, M. Optimization of Weave of Carbon Fabric for Best Combination of Strength and Tribo-Performance of Polyetherimide Composites in Adhesive Wear Mode. Wear 2008, 264, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijwe, J.; Rajesh, J.J.; Jeyakumar, A.; Ghosh, A.; Tewari, U.S. Influence of Solid Lubricants and Fibre Reinforcement on Wear Behaviour of Polyethersulphone. Tribol. Int. 2000, 33, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Mohan Rao, I.; Bijwe, J. Influence of Fiber Orientation on Abrasive Wear of Unidirectionally Reinforced Carbon Fiber-Polyetherimide Composites. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudin, M.N.; Ramli, F.R.; Alkahari, M.R.; Abdullah, M.A. Comparison of Wear Behavior of ABS and ABS Composite Parts Fabricated via Fused Deposition Modelling. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrishraj, D.; Senthilvelan, T. Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of ABS Composites Reinforced with Nano Zirconia and PTFE. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 7068–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pıhtılı, H.; Tosun, N. Investigation of the Wear Behaviour of a Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Composite and Plain Polyester Resin. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-K.; Du, S.-S.; Li, F.; Xiao, H.-M.; Li, Y.-Q.; Zhang, W.-G.; Hu, N.; Fu, S.-Y. Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Short Glass Fiber and Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polyethersulfone Composites: A Comparative Study. Compos. Commun. 2018, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
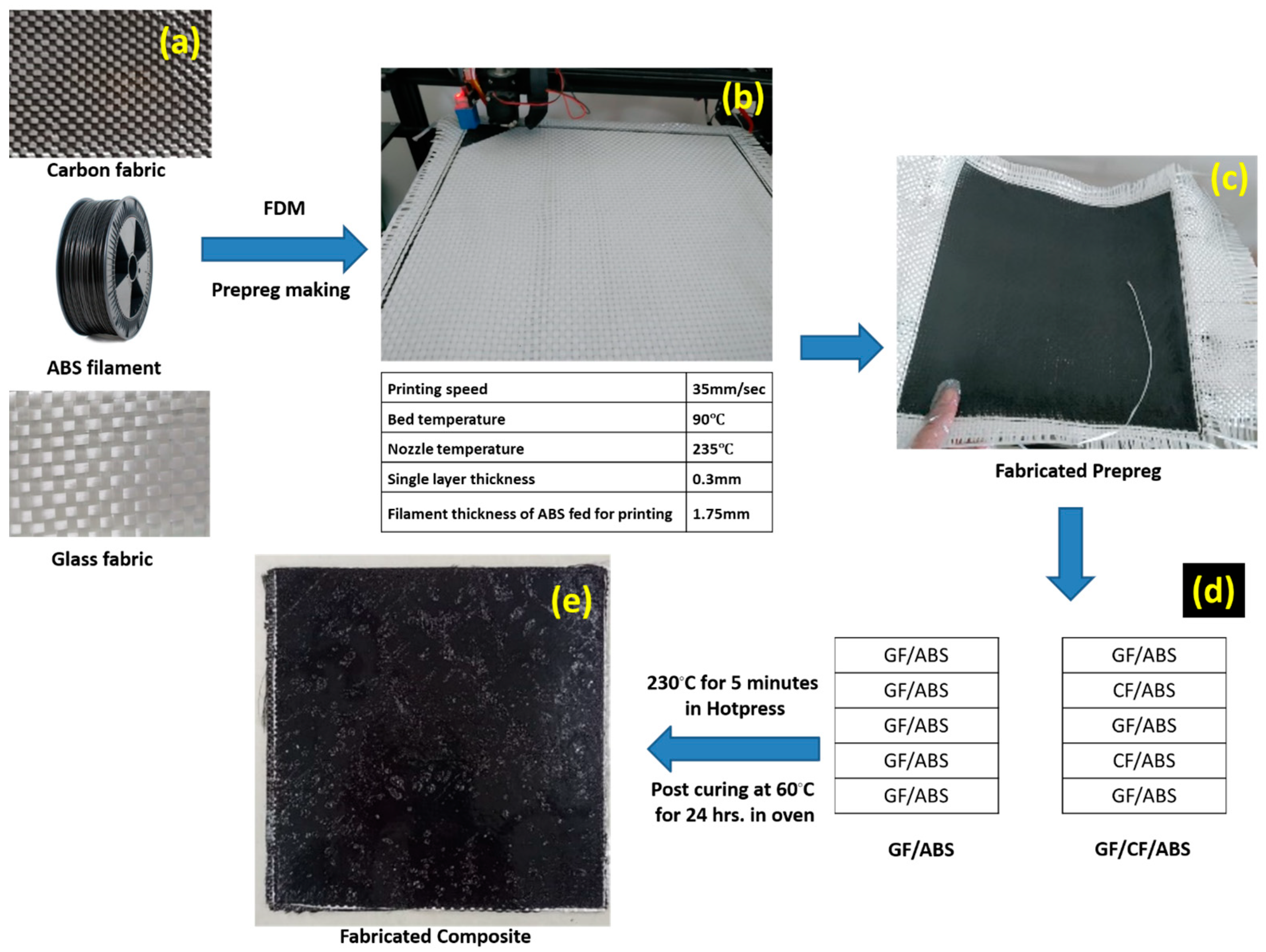

| Parameters | Glass Fiber | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 3100–3800 | 4100 |
| Young’s modulus (GPa) | 80–81 | 240 |
| Elongation at break % | 4.8 | 1.8 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.62 | 1.77 |
| Grams per square meter (GSM) | 300 | 200 |
| Parameters | ABS |
|---|---|
| Tensile strength | ≥43 MPa |
| Flexural strength | ≥70 MPa |
| Flexural modulus | ≥2300 MPa |
| Impact strength (IZOD, 23 °C) | ≥108 J/m (ASTM 256) |
| Elongation at break | ≥30% |
| Layer Details | Matrix and Fiber Details | Composite Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| 1st layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Glass fiber (0.4 mm) | GF/ABS |
| 2nd layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Glass fiber (0.4 mm) | |
| 3rd layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Glass fiber (0.4 mm) | |
| 4th layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Glass fiber (0.4 mm) | |
| 5th layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Glass fiber (0.4 mm)/3D printed ABS (0.3 mm) |
| Layer Details | Matrix and Fiber Details | Composite Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| 1st layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Glass fiber (0.4 mm) | GF/CF/ABS |
| 2nd layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Carbon fiber (0.4 mm) | |
| 3rd layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Glass fiber (0.4 mm) | |
| 4th layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Carbon fiber (0.4 mm) | |
| 5th layer | 3D printed ABS (0.3 mm)/Glass fiber (0.4 mm)/3D printed ABS (0.3 mm) |
| Type of Composites | Weight (g) | Weight Fraction (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WtG | Wtc | Wtm | WFG | WFc | WFm | |
| Neat ABS | - | - | 140 | - | - | 100 |
| GF/ABS | 136 | - | 84 | 61.84 | - | 38.18 |
| GF/CF/ABS | 81.6 | 65 | 84 | 35.34 | 28.19 | 36.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhandapani, A.; Krishnasamy, S.; Nagarajan, R.; Selvaraj, A.D.A.; Thiagamani, S.M.K.; Muthukumar, C.; Mohammad, F.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Ismail, S.O. Investigation of Wear Behavior in Self-Lubricating ABS Polymer Composites Reinforced with Glass Fiber/ABS and Glass Fiber/Carbon Fiber/ABS Hybrid. Lubricants 2023, 11, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030131
Dhandapani A, Krishnasamy S, Nagarajan R, Selvaraj ADA, Thiagamani SMK, Muthukumar C, Mohammad F, Al-Lohedan HA, Ismail SO. Investigation of Wear Behavior in Self-Lubricating ABS Polymer Composites Reinforced with Glass Fiber/ABS and Glass Fiber/Carbon Fiber/ABS Hybrid. Lubricants. 2023; 11(3):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030131
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhandapani, Aravind, Senthilkumar Krishnasamy, Rajini Nagarajan, Anto Dilip Albert Selvaraj, Senthil Muthu Kumar Thiagamani, Chandrasekar Muthukumar, Faruq Mohammad, Hamad A. Al-Lohedan, and Sikiru Oluwarotimi Ismail. 2023. "Investigation of Wear Behavior in Self-Lubricating ABS Polymer Composites Reinforced with Glass Fiber/ABS and Glass Fiber/Carbon Fiber/ABS Hybrid" Lubricants 11, no. 3: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030131
APA StyleDhandapani, A., Krishnasamy, S., Nagarajan, R., Selvaraj, A. D. A., Thiagamani, S. M. K., Muthukumar, C., Mohammad, F., Al-Lohedan, H. A., & Ismail, S. O. (2023). Investigation of Wear Behavior in Self-Lubricating ABS Polymer Composites Reinforced with Glass Fiber/ABS and Glass Fiber/Carbon Fiber/ABS Hybrid. Lubricants, 11(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030131






