Control over Multi-Scale Self-Organization-Based Processes under the Extreme Tribological Conditions of Cutting through the Application of Complex Adaptive Surface-Engineered Systems
Abstract
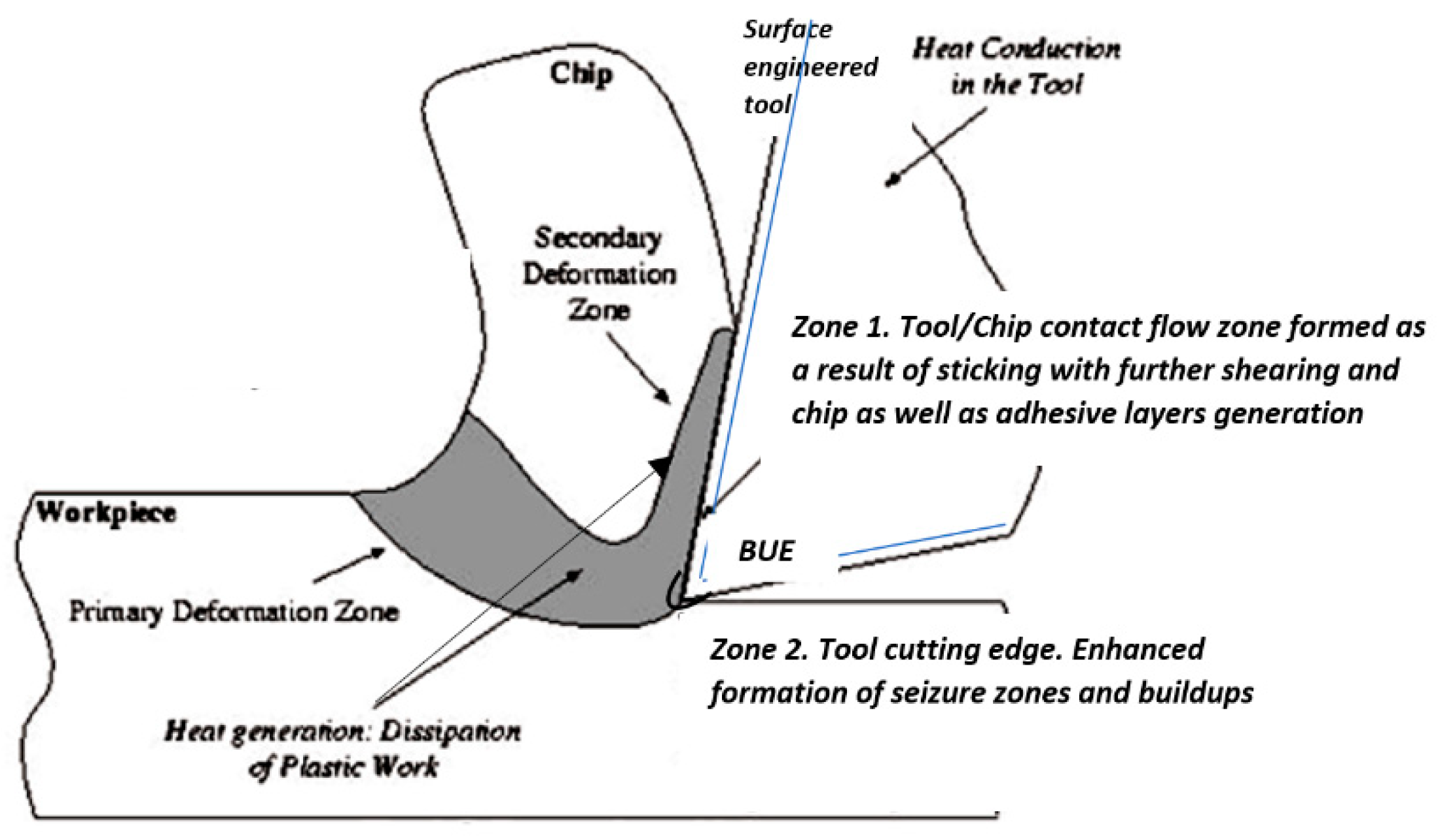
1. A Schematic Presentation of the Cutting Process
- Formation of twinning zones on the worn surfaces of the cutting tools [18];
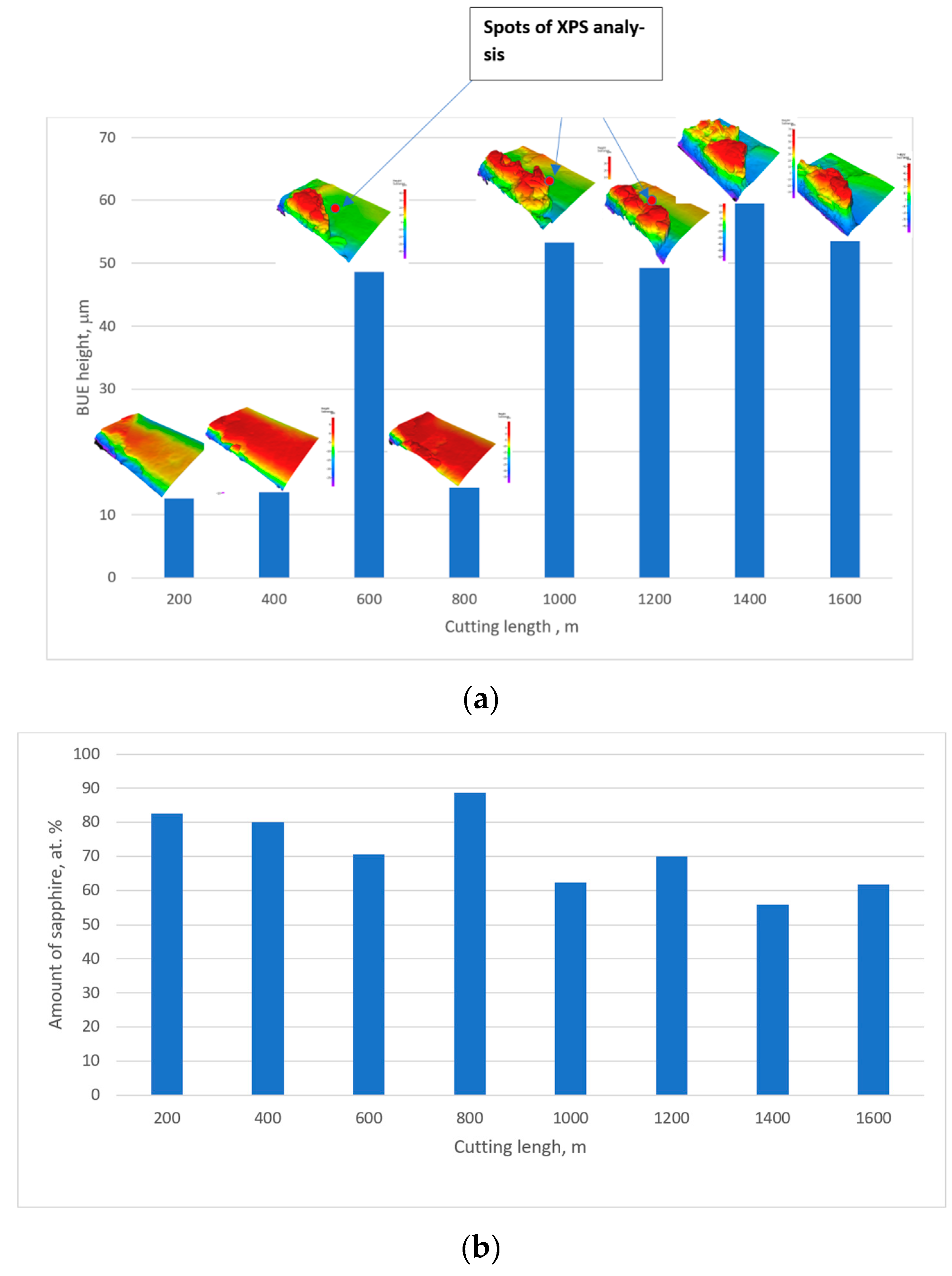
- Formation of adhesive layers (a microscale μm process), which gradually progress from the adhesive interaction between the workpiece and the tool (Figure 2) to the formation of buildups over the course of a seizure process [19]. This results in the formation of a buildup edge (BUE), which is a macroscale (tens of microns) cyclic process combining selforganized criticality (SOC) and selforganization (SO) [18,20,21,22,23,24,25].
2. Thermodynamic Analysis of Entropy Production
3. Selforganization Processes That Develop during Cutting with Coated Cemented Carbide Tools
3.1. Selforganization during PVD Coating Deposition on the Substrate of the Cutting Tool
3.2. Various Selforganization Processes during Wear on the Surface of Cutting Tools
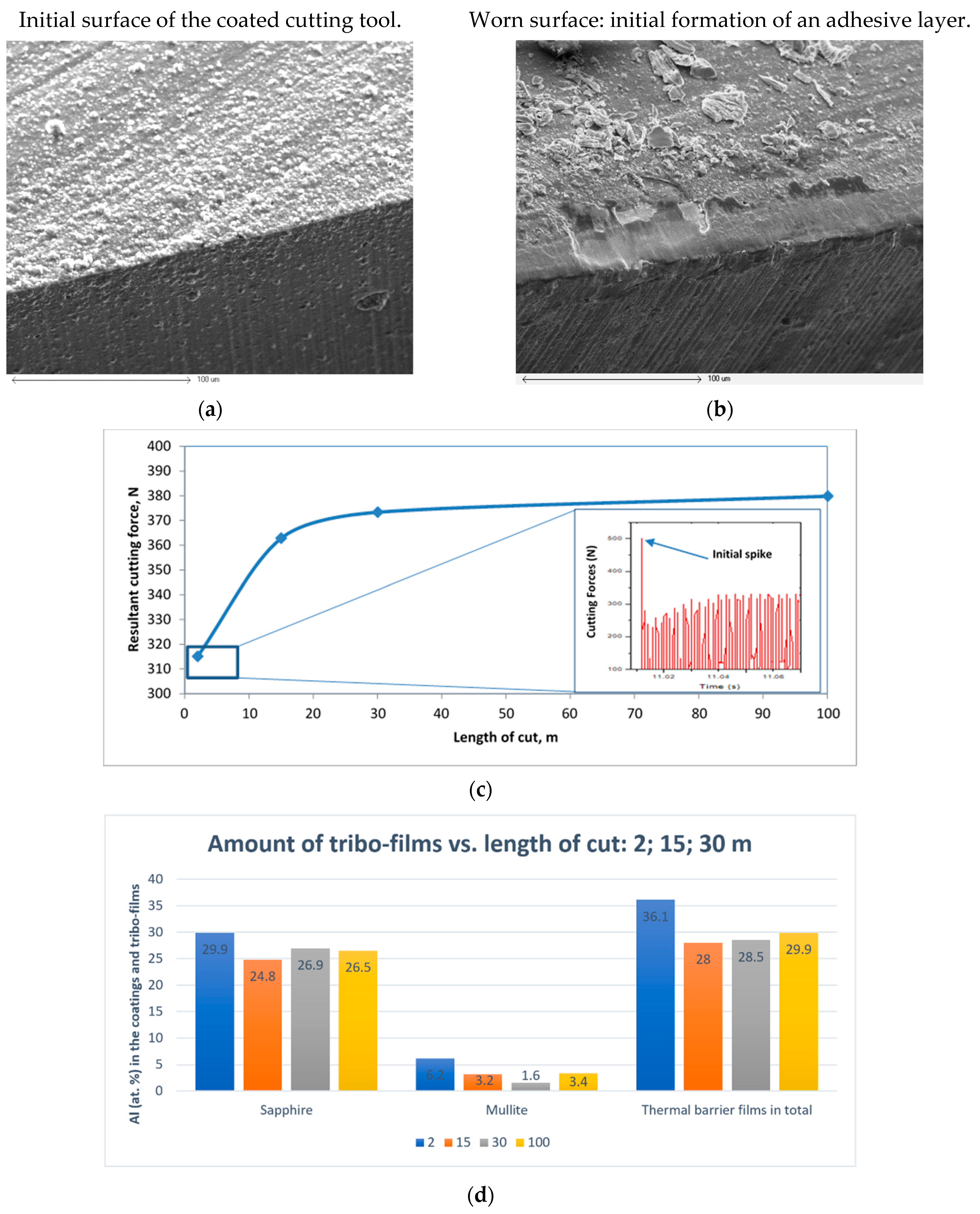
3.2.1. Tribofilm Formation
3.2.2. Lubricating Tribo-Oxides
- A.
- Magnéli phases.
- B.
- Oxides with metallic properties at elevated temperatures.
- C.
- Tribo-oxides that transform into a liquid phase at high operating temperatures.
- D.
- Mixed action tribo-oxides (thermal barrier/lubricating).
- E.
- Thermal barriers.
3.3. Multiscale Selforganization-Based Processes That Occur on the Tool Surface during Cutting
- -
- The tool/chip contact flow zone (zone 1) formed due to sticking accompanied by further shearing and generation of chips as well as adhesive layers on the surface of the tool (a microscale process);
- -
- Zones of intensified seizure (zone 2) with further formation of a BUE within regions of the rake surface closest to the cutting edge (a microscale SOC/SO process).
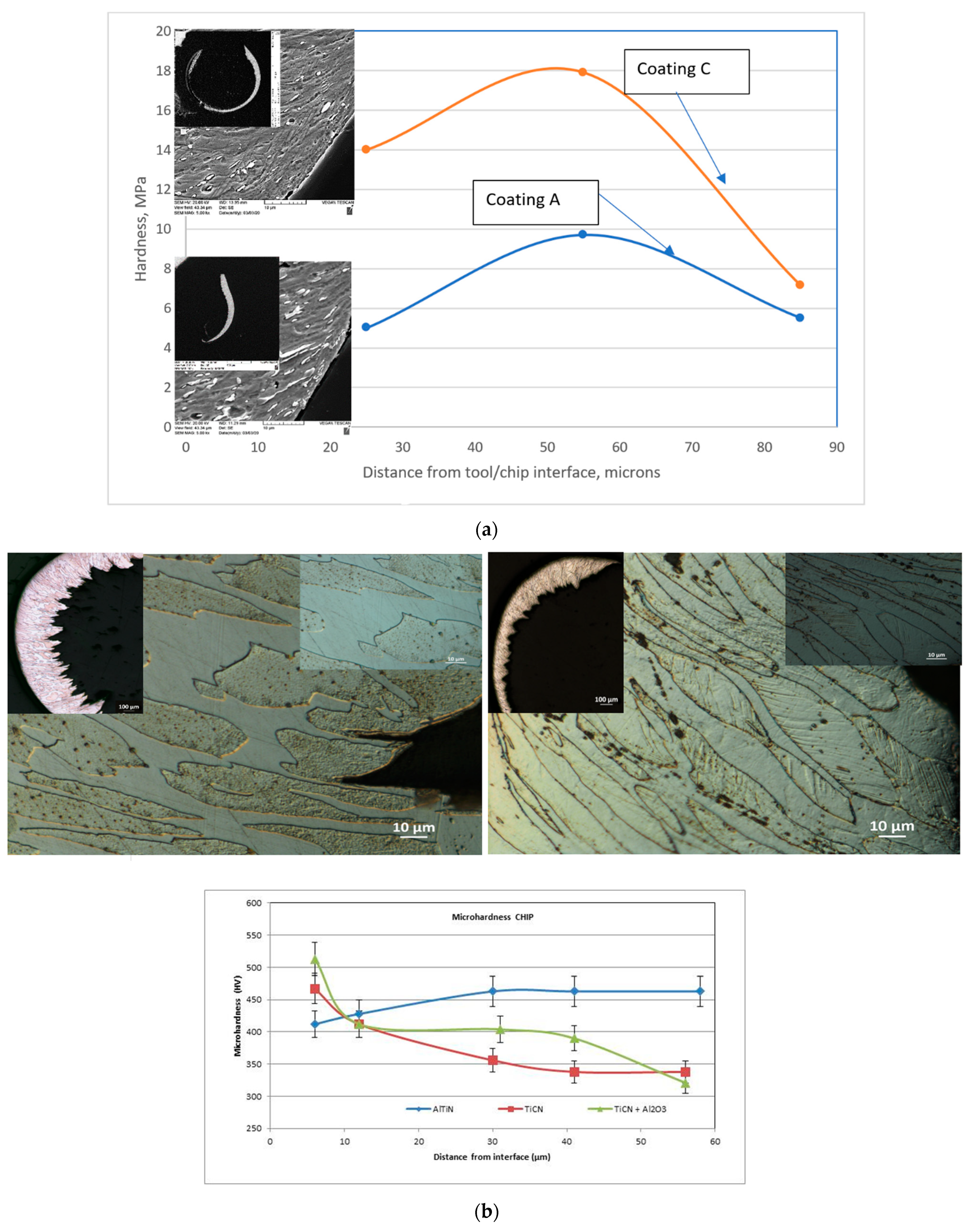
3.3.1. Adhesive Layers and Edge Buildup
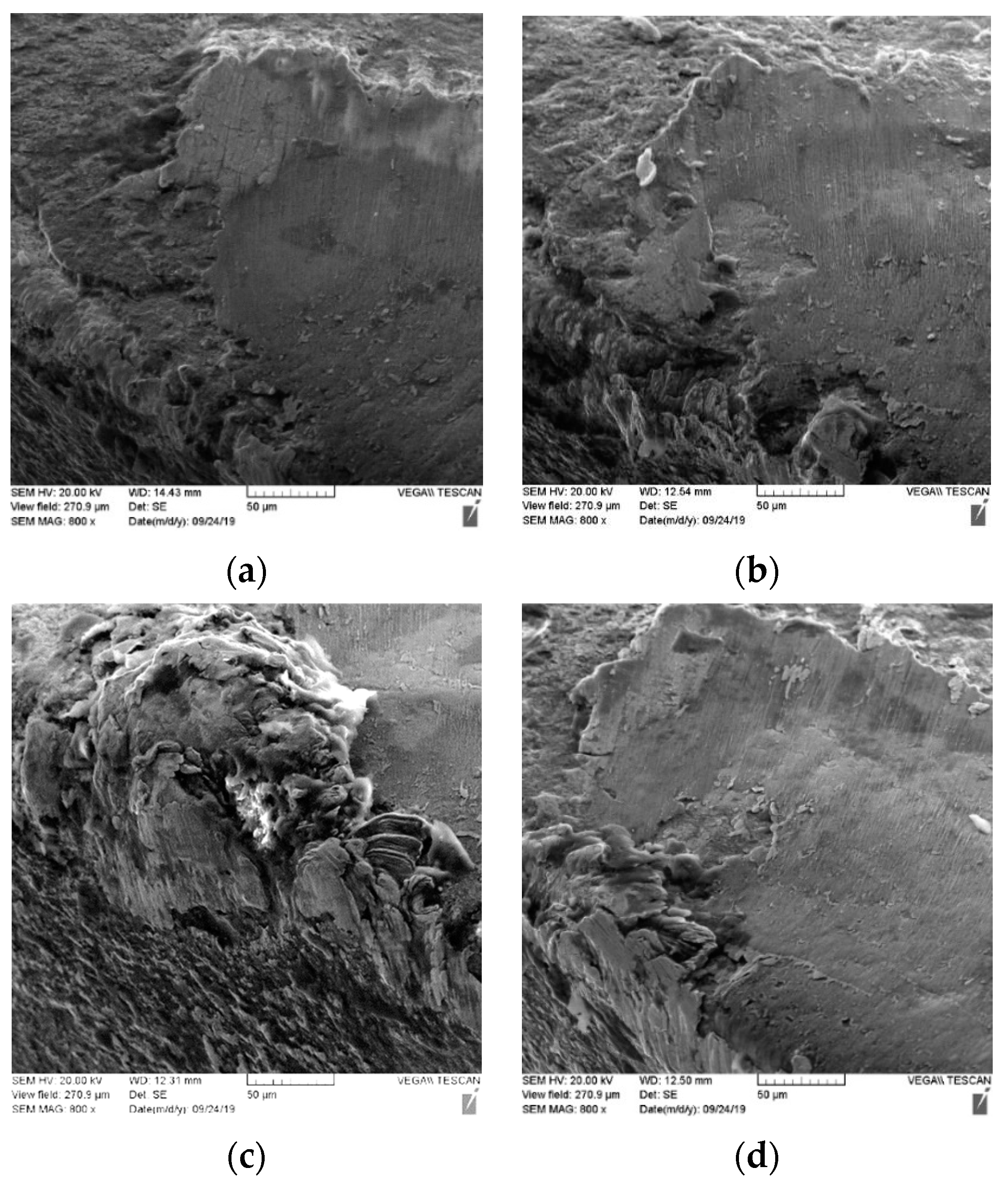
3.3.2. Chips
4. Complex Adaptive Surface-Engineered Systems Capable of Enhancing Multiscale Selforganization Phenomena during Cutting, Such as the Latest Generation of PVD Coatings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SO | Selforganization process |
| SOC | Selforganized criticality |
| PVD | Physical vapor deposition |
| HEAC | High entropy alloy coatings |
| HREELS | High-resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| BUE | Buildup edge |
References
- Vaz, M., Jr. On the Numerical Simulation of Machining Processes. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. 2000, 22, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Totten, G.E. Self-Organization during Friction: Advanced Surface-Engineered Materials and Systems Design; Tailor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Prigogine, I. Time, Structure, and Fluctuations. Science 1978, 201, 777–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehn, J.-M. Toward Self-Organization and Complex Matter. Science 2002, 295, 2400–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, P.; Tang, C.; Wiesenfeld, K. Self-organized criticality. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovsepian, P.; Kok, Y.N.; Ehiasarian, A.P.; Haasch, R.; Wen, J.-G.; Petrov, I. Phase separation and formation of the self-organised layered nanostructure in C/Cr coatings in conditions of high ion irradiation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleck, H.; Schier, V. Multilayer PVD coatings for wear protection. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1995, 76–77, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Kovalev, A.; Veldhuis, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Endrino, J.; Gershman, I.S.; Rashkovskiy, A.; Aguirre, M.H.; Wainstein, D.L. Spatio-temporal behaviour of atomic-scale tribo-ceramic films in adaptive surface engineered nano-materials. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopezky, C.V.; Andreeva, A.V.; Sukhomlin, G.D. Multiple twinning and specific properties of Σ = 3n boundaries in f.c.c. crystals. Acta Metall. Mater. 1991, 39, 1603–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Muñoz, L.; García-Guinea, J.; Beny, J.M.; Rouer, O.; Campos, R.; Sanz, J.; De Moura, O.J. Mineral self-organization during the orthoclase-microcline transformation in a granite pegmatite. Eur. J. Miner. 2008, 20, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogachev, I.M.; Mints, R.I. Increasing of Cavitation Resistance of Machine Parts; Mashinostroenie: Moscow, Russia, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Alfyorova, E.A.; Lychagin, D.V. Self-organization of plastic deformation and deformation relief in FCC single crystals. Mech. Mater. 2018, 117, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, A. Thermodynamics of Open Systems, Self-Organization, and Crystal Plasticity; Kettunen, P.O., Lepisto, T.K., Lehtonen, M.E., Eds.; Strength of Metals and Alloys (ICSMA 8); Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Castany, P.; Hao, Y.L.; Gloriant, T. Plastic deformation via hierarchical nano-sized martensitic twinning in the metastable β Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn alloy. Acta Mater. 2000, 194, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Bellon, P. Microstructural self-organization triggered by twin boundaries during dry sliding wear. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 6673–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.A.; Nesterenko, V.F.; LaSalvia, J.C.; Xue, Q. Shear localization in dynamic deformation of materials: Microstructural evolution and self-organization. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 317, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolf, P. Machinability Comparison between Two Different Grades of Titanium Alloys under Diverse Turning and Cooling Conditons: Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-5Al-5V-5Mo-3Cr. Master’s Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Gershman, I.S.; Locks, E.; Paiva, J.M.; Endrino, J.L.; Dosbaeva, G.; Veldhuis, S. The Relationship between Cyclic Multi-Scale Self-Organized Processes and Wear-Induced Surface Phenomena under Severe Tribological Conditions Associated with Buildup Edge Formation. Coatings 2021, 11, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushe, N.; Gershman, I. Compatibility of Tribosystem. In Self-Organization during Friction: Advanced Surface-Engineered Materials and Systems Design; Fox-Rabinovich, G., Totten, G.E., Eds.; Tailor and Fransis: Milton Park, UK, 2006; pp. 59–79. [Google Scholar]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Bhushan, B. Thermodynamics of surface degradation, self-organization and self-healing for biomimetic surfaces, Philosophical transactions of the royal society A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1607–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Kabaldin, Y.G.; Kojevnikov, N.V.; Kravchuk, K.V. HSS cutting tool wear resistance study. J. Frict. Wear 1990, 11, 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, Y.S.; Paiva, J.M.; Bose, B.; Veldhuis, S.C. New observations on built-up edge structures for improving machining performance during the cutting of super duplex stainless steel. Tribol. Int. 2019, 137, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.S.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Paiva, J.M.; Wagg, T.; Veldhuis, S.C. Effect of Built-Up Edge Formation during Stable State of Wear in AISI 304 Stainless Steel on Machining Performance and Surface Integrity of the Machined Part. Materials 2017, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emel’yanov, S.G.; Yatsun, E.I.; Shvets, S.V.; Remnev, A.I.; Pavlov, E.V. Influence of Buildup in Lathe Processes on Tool Life and Surface Quality. Russ. Eng. Res. 2011, 31, 1276–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershman, I.; Gershman, E.; Mironov, A.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Veldhuis, S. Application of self-organizaiton phenomenon in the development of wear resistant materials. Rev. Entropy 2016, 18, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Zhao, J.; Song, X.; Xu, L.; Guo, Z. Study on Self Organization During Cutting Process of Coating Tools; Key Laboratory of High Efficiency and Clean Mechanical Manufacture of MOE, CHN, Machine Tools: Junoan, China, 2015; pp. 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.; Cheng, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, G. Self-organization wear characteristics of MTCVD-TiCN-Al2O3 coated tool against 300M steel. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 13214–13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Kovalev, A.; Gershman, I.; Wainstein, D.; Aguirre, M.H.; Covelli, D.; Paiva, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Veldhuis, S. Complex Behavior of Nano-Scale Tribo-Ceramic Films in Adaptive PVD Coatings under Extreme Tribological Conditions. Entropy 2018, 20, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.G.; Xue, S.F.; Jiang, M.Q.; Tong, X.H.; Dai, L.H. Modeling of periodic adiabatic shear band evolution during high-speed machining Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Plast. 2013, 40, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.; Patel, S.K. Effect of chip sliding velocity and temperature on the wear behaviour of PVD AlCrN and AlTiN coated mixed alumina cutting tools during turning of hardened steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loladze, T.N. Strength and Wear Resistance of Cutting Tools; Mashinostroenie: Moscow, Russia, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Kovalev, A.; Aguirre, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Veldhuis, S.; Gershman, I.; Rashkovskiy, A.; Endrino, J.; Beake, B.; Dosbaeva, G.; et al. Evolution of self-organization in nano-structured PVD coatings under extreme tribological conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 297, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroka, E.B. Ensuring stability of PVD coatings by producing a discrete topography with preset parameters. J. Superhard Mater. 2009, 31, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veprek, S. Superhard and functional nanocomposites formed by self-organization in comparison with hardening of coatings by nergetic ion bombardment during their deposition. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2003, 5, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
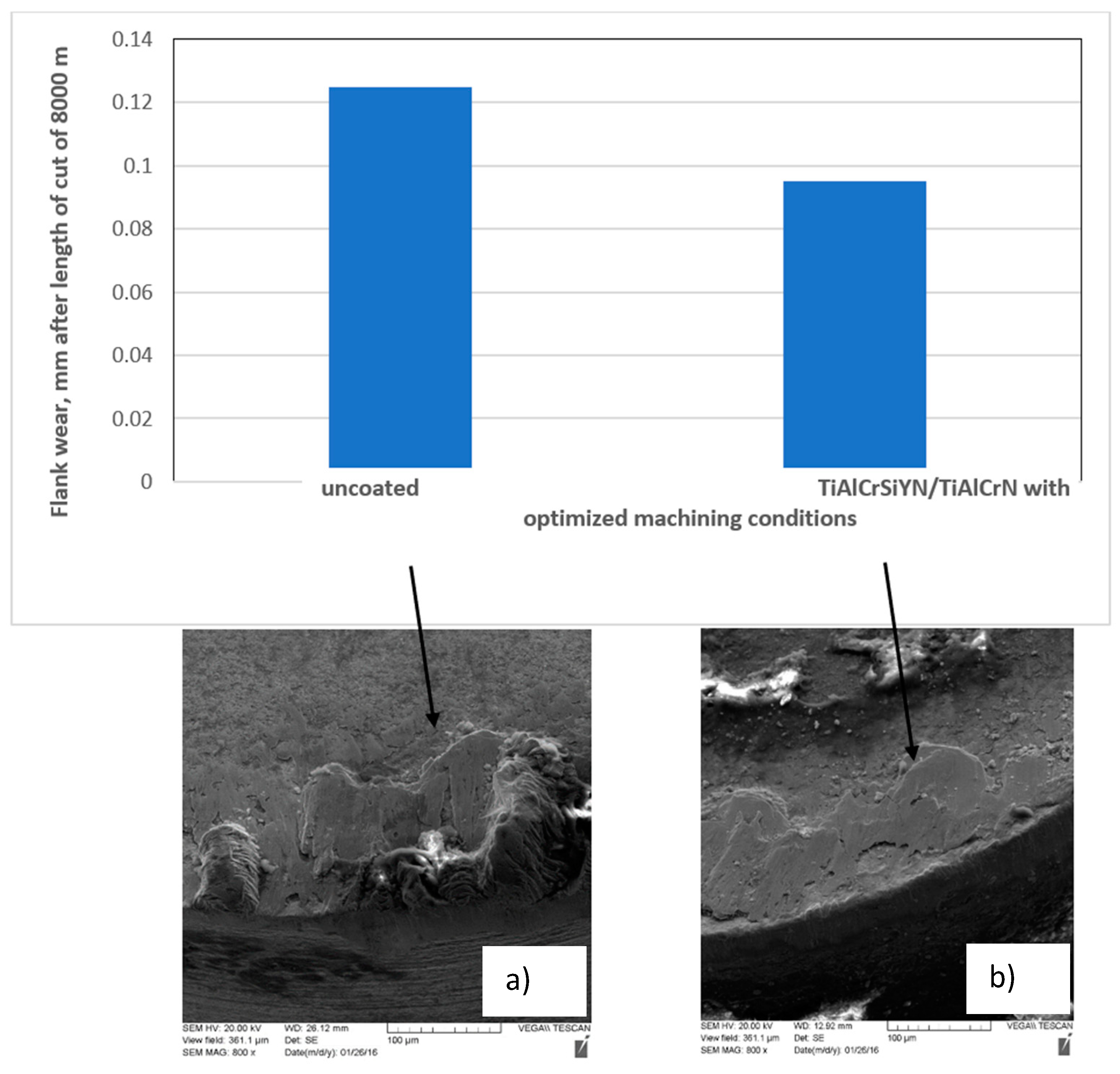
- Fox-Rabinovitch, G.; Dosbaeva, G.; Kovalev, A.; Gershman, I.; Yamamoto, K.; Locks, E.; Paiva, J.; Konovalov, E.; Veldhuis, S. Enhancement of Multi-Scale Self-Organization Processes during Inconel DA 718 Machining through the Optimization of TiAlCrSiN/TiAlCrN Bi-Nano-Multilayer Coating Characteristics. Materials 2022, 15, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, G.; Mayrhofer, P.; Kutschej, K.; Mitterer, C.; Kathrein, M. Magnéli phase formation of PVD Mo–N and W–N coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 3335–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugscheider, E.; Knotek, O.; Bärwulf, S.; Bobzin, K. Characteristic curves of voltage and current, phase generation and properties of tungsten- and vanadium-oxides deposited by reactive d.c.-MSIP-PVD-process for self-lubricating applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 142–144, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcar, T.; Parreira, N.M.G.; Cavaleiro, A. Tribological characterization of tungsten nitride coatings deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. Wear 2007, 262, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcar, T.; Cavaleiro, A. Structure, mechanical properties and tribology of W–N and W–O coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2010, 28, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storz, O.; Gasthuber, H.; Woydt, M. Tribological properties of thermal-sprayed Magnéli-type coatings with different stoichiometries (TinO2n−1). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 140, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woydt, M.; Skopp, A.; Dörfel, I.; Witke, K. Wear engineering oxides/anti-wear oxides. Wear 1998, 218, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, A. A crystal-chemical approach to lubrication by solid oxides. Tribol. Lett. 2000, 8, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Yamamoto, K.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Kovalev, A.I.; Shuster, L.S.; Ning, L. Self-adaptive wear behavior of nano-multilayered TiAlCrN/WN coatings under severe machining conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleck, H.J. Material selection for hard coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1986, 4, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.I.; Chowdhury, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Beake, B.D.; Bose, B.; Elfizy, A.; Cavelli, D.; Dosbaeva, G.; Aramesh, M.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; et al. Wear behaviour of coated carbide tools during machining of Ti6Al4V aerospace alloy associated with strong built up edge formation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 313, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kovalev, A.I.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Ning, L.; Shuster, L.S.; Elfizy, A. Wear behavior of adaptive nano-multilayered TiAlCrN/NbN coatings under dry high performance machining conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biksa, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Dosbaeva, G.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Elfizy, A.; Wagg, T.; Shuster, L.S. Wear behavior of adaptive nano-multilayered AlTiN/MexN PVD coatings during machining of aerospace alloys. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gu, L.; Tang, G.; Mao, Y. Wear Transition of CrN Coated M50 Steel under High Temperature and Heavy Load. Coatings 2017, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.I.; Bose, B.; Yamamoto, K.; Shuster, L.S.; Paiva, J.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Veldhuis, S.C. Wear performance investigation of PVD coated and uncoated carbide tools during high-speed machining of TiAl6V4 aerospace alloy. Wear 2020, 446–447, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.I.; Bose, B.; Rawal, S.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Veldhuis, S.C. Investigation of the Wear Behavior of PVD Coated Carbide Tools during Ti6Al4V machining with Intensive Built Up Edge Formation. Coatings 2021, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Lin, J.H.; Ho, W.Y. Study on chromium oxide synthesized by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 1998, 332, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayuti, M.; Sarhan, A.A.; Salem, F. Novel uses of SiO2 nano-lubrication system in hard turning process of hardened steel AISI4140 for less tool wear, surface roughness and oil consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 67, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Procházka, J.; Karvánková, P.; Ma, Q.; Niu, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, D.; Xu, K.; Vepřek, S. Comparative study of the tribological behaviour of superhard nanocomposite coatings nc-TiN/a-Si3N4 with TiN. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 194, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dang, H. Surface-modification in situ of nano-SiO2 and its structure and tribological properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 7856–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.B.; Cho, K.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, K.H. Effects of Si content and free Si on oxidation behavior of Ti–Si–N coating layers. Thin Solid Film. 2004, 447–448, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwawut, S.; Saikaew, C.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Surinphong, S. Cutting performances and wear characteristics of WC inserts coated with TiAlSiN and CrTiAlSiN by filtered cathodic arc in dry face milling of cast iron. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 3883–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, N.M.; Vickerman, J.C. Correlation of the emission of SIMS cluster ions with composition and structure from the Al2−xCrxO3 Mixed Oxide Series. Surf. Interface Anal. 1992, 19, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieh, T.G.; Wadsworth, J.; Sherby, O.D. Superplasticity in Metals and Ceramics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Aouadi, S.M.; Gao, H.; Martini, A.; Scharf, T.W.; Muratore, C. Lubricious oxide coatings for extreme temperature applications: A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 257, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.H.; Sasaki, S.; Murakami, T.; Umeda, K. Spark-plasma-sintered ZrO2(Y2O3)-BaCrO4 self-lubricating composites for high temperature tribological applications. Ceram. Int. 2005, 31, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Gershman, I.; Yamamoto, K.; Biksa, A.; Veldhuis, S.; Beake, B.; Kovalev, A. Self-Organization during Friction in Complex Surface Engineered Tribosystems. Entropy 2010, 12, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Gershman, I.S.; Veldhuis, S. Thin-Film PVD Coating Metamaterials Exhibiting Similarities to Natural Processes under Extreme Tribological Conditions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.K.; Trent, E.M. Metal Cutting, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Woburn, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
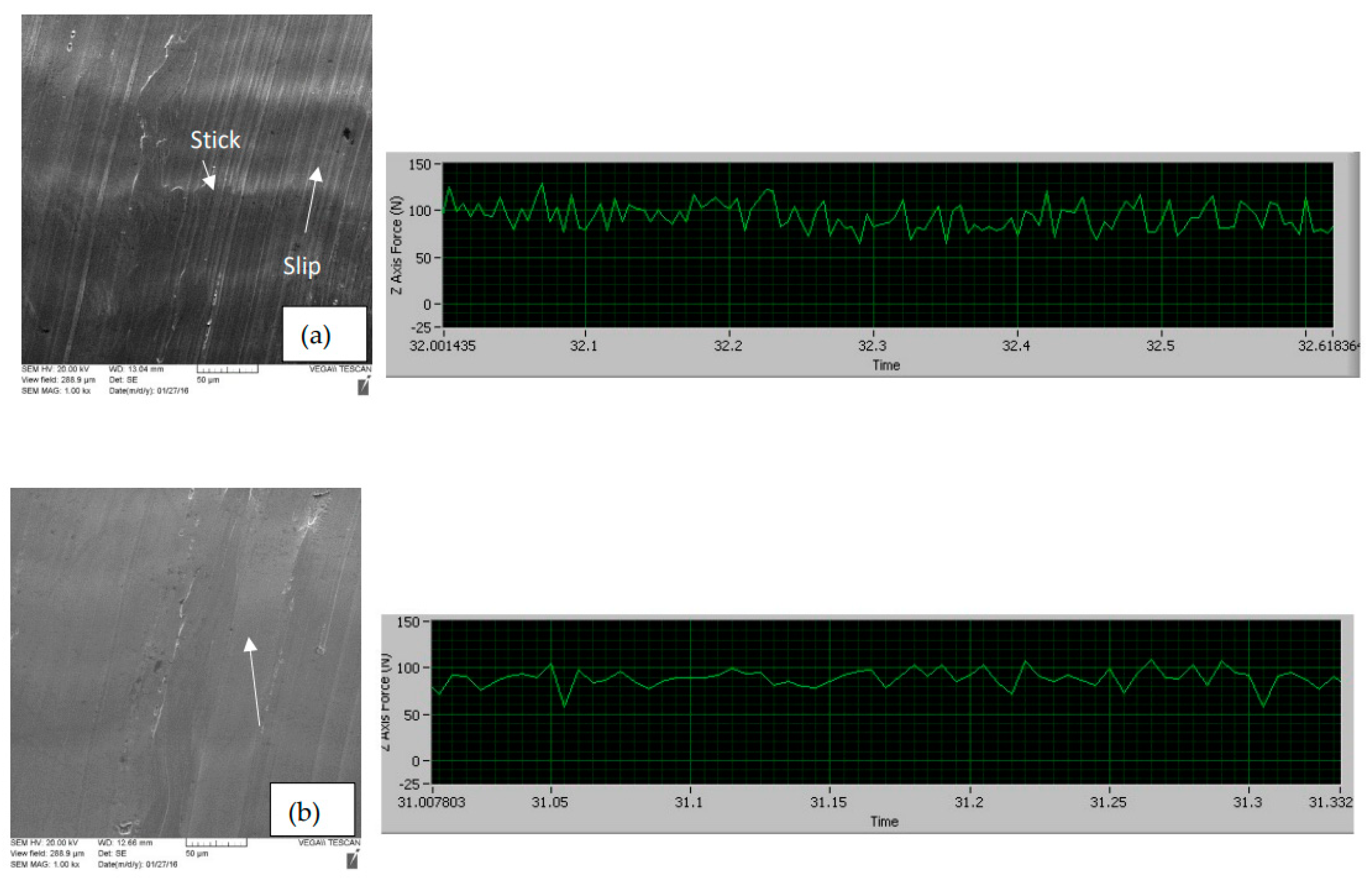
- Chin, J.H.; Chen, C.C. A study of stick-slip motion and its influence on the cutting process. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1993, 35, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingery, W.D. Thermal Conductivity: XIV, Conductivity of Multicomponent Systems. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1959, 42, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Q.; Vassen, R.; Stoever, D. Ceramic materials for thermal barrier coatings. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.; Barsoum, M.W. Fundamentals of Ceramics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Endrino, J.L.; Aguirre, M.H.; Beake, B.D.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Kovalev, A.I.; Gershman, I.S.; Yamamoto, K.; Losset, Y.; Wainstein, D.L.; et al. Mechanism of adaptability for the nano-structured TiAlCrSiYN-based hard physical vapor deposition coatings under extreme frictional conditions. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 064306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, S.; Tsujii, N.; Jiang, Q.; Khaliq, J.; Maruyama, S.; Miranda, M.; Simpson, K.; Mori, T.; Reece, M.J. Ultra low thermal conductivity of disordered layered p-type bismuth telluride. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trent, E.M. Conditions of Seizure at the Tool Work Interface; ISI, Special Report, 94; Iron and Steel Institute: London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Bogatov, A.; Podgursky, V.; Vagiström, H.; Yashin, M.; Shaikh, A.A.; Viljus, M.; Menezes, P.L.; Iosif, S. Gershman Transition from Self-Organized Criticality into Self-Organization during Sliding Si3N4 Balls against Nanocrystalline Diamond Films. Entropy 2019, 21, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldyrev, S.V.; Ferrante, J.; Zypman, F. Dry friction avalanches: Experiment and theory. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 066110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zypman, F.R.; Ferrante, J.; Jansen, M.; Scanlon, K.; Abel, P. Evidense of self-organized criticality in dry sliding friction. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2003, 15, L191–L196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Paiva, J.M.; Gershman, I.; Aramesh, M.; Cavelli, D.; Yamamoto, K.; Dosbaeva, G.; Veldhuis, S. Control of Self-Organized Criticality through Adaptive Behavior of Nano-Structured Thin Film Coatings. Entropy 2016, 18, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, J.M.P., Jr.; Torres, R.D.; Amorim, F.L.; Danielle, C.; Mohammed, T.; Stephen, V.; Goulnara, D.; German, F.-R. Frictional and wear performance of hard coatings during machining of superduplex stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S. Complex Adaptive Systems ESD.83 Research Seminar in Engineering Systems; MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lansing, J.S. Complex Adaptive Systems. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2003, 32, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, K. A Nominal Definition of Complex Adaptive Systems. Chaos Netw. 1996, 8, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.H. Studying Complex Adaptive Systems. Jrl. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2006, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Yamamoto, K.; Beake, B.D.; Gershman, I.S.; Kovalev, A.I.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Aguirre, M.H.; Dosbaeva1, G.; Endrino, J. Hierarchical adaptive nanostructured PVD coatings for extreme tribological applications: The quest for nonequilibrium states and emergent behavior. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2012, 13, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Yamamoto, K.; Beake, B.D.; Kovalev, A.I.; Aguirre, M.H.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Dosbaeva, G.K.; Wainstein, D.L.; Biksa, A.; Rashkovskiy, A. Emergent behavior of nano-multilayered coatings during dry high-speed machining of hardened tool steels. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3425–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Gershman, I.S.; Yamamoto, K.; Aguirre, M.H.; Covelli, D.; Arif, T.; Aramesh, M.; Shalaby, M.A.; Veldhuis, S. Surface/interface phenomena in nano-multilayer coating under severing tribological conditions. Surf. Interface Anal. 2016, 49, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Bose, B.; Yamamoto, K.; Veldhuis, S.C. Effect of Interlayer Thickness on Nano-Multilayer Coating Performance during High Speed Dry Milling of H13 Tool Steel. Coatings 2019, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, G.Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, G.; Sun, J. He-ion irradiation effects on the microstructure stability and size-dependent mechanical behavior of high entropy alloy/Cu nanotwinned nanolaminates. Int. J. Plast. 2020, 133, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beake, B.D. The influence of the H/E ratio on wear resistance of coating systems—Insights from small-scale testing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 442, 128272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Lin, S.J. Breakthrough applications of high-entropy materials. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3129–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, B.S.; Huang, J.L.; Lu, H.H.; Sajgalik, P. Investigation of nanocrystal-(Ti1−xAlx)Ny/amorphous-Si3N4 nanolaminate films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 194, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrebnjak, A.D. The structure and properties of high-entropy alloys and nitride coatings based on them. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, O.V.; Andreev, A.A.; Voevodin, V.N.; Gorban, V.F.; Grigor’ev, S.N.; Volosova, M.A.; Serdyuk, I.V. The bias potential and pressure nitrogen effect on structural stress on the structure stressed state and proper ties of nitride coatings produced from high entropy alloys by the vacuum arc technique. Probl. At. Sci. Technol. 2014, 89, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, M.C.; Yeh, J.W.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. High-Entropy Alloys, Fundamentals and Applications; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lvi, S.; Akhtar, F. High-temperature tribology of CuMoTaWV high entropy alloy. Wear 2019, 426–427, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.J.; Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. Machining Performance of Sputter-Deposited (Al0.34Cr0.22Nb0.11Si0.11 Ti0.22) 50N 50 High-Entropy Nitride Coatings. Coatings 2015, 5, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Fahrenholtz, W.G.; Brenner, D.W. High-Entropy Ultra-High-Temperature Borides and Carbides: A New Class of Materials for Extreme Environments. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2021, 51, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Gao, R.; Yang, Z.H.; Wu, S.T.; Wan, Q. A study on the wear and corrosion resistance of high-entropy alloy treated with laser shock peening and PVD coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 437, 128281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, A.I.; Demchenkov, S.A.; Melnychenko, T.V.; Skorodzievskii, V.S.; Polishchuk, S.S. Effect of structure of high entropy CrFeCoNiCu alloys produced by EB PVD on their strength and dissipative properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 887, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, V.; Stepanov, N.; Zherebtsov, S.; Salishchev, G. Structure and Properties of High-Entropy Nitride Coatings. Metals 2022, 12, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A. High Entropy Alloy Coatings and Technology. Coatings 2021, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

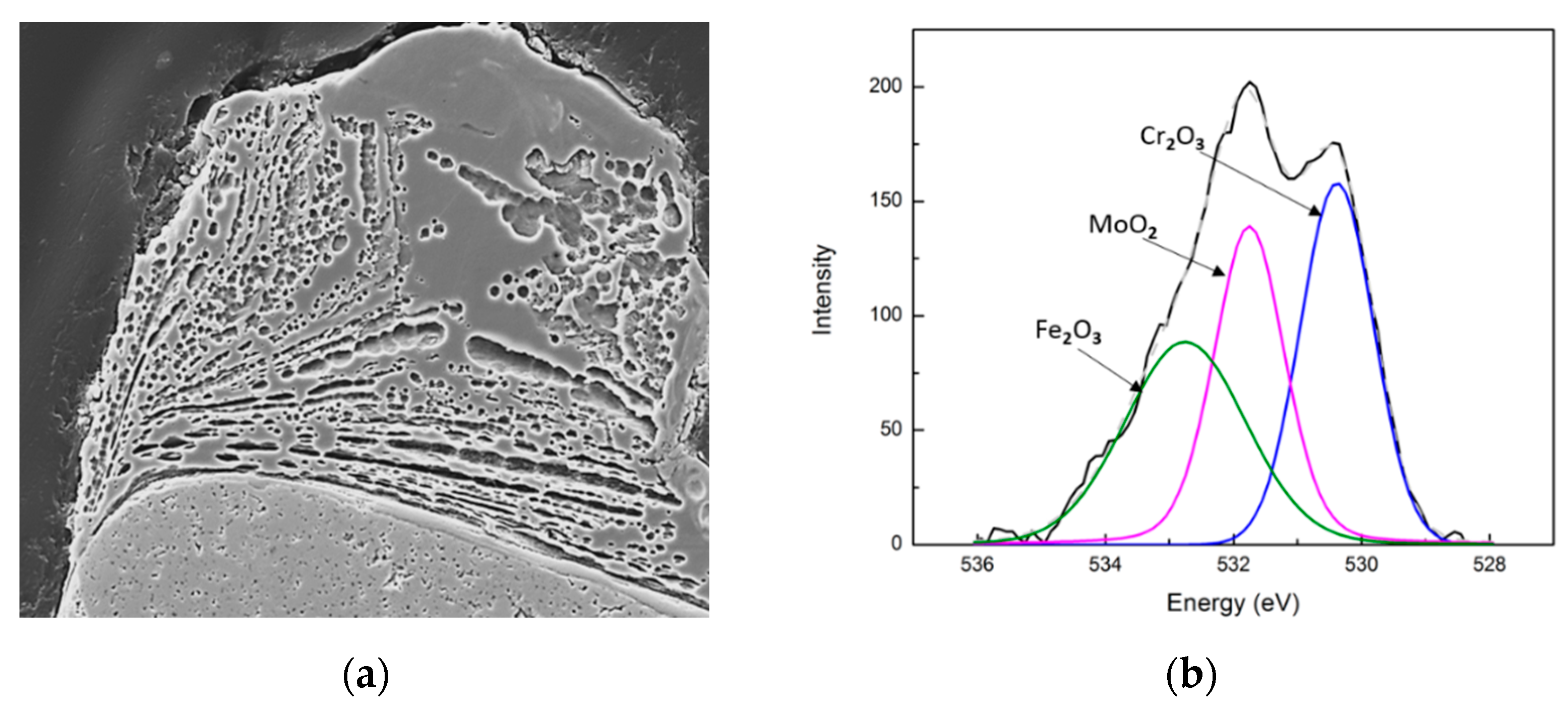
| Types of Tribofilms Formed, Which Control Tool Life | Coating Material | Cutting Conditions | Tool Life Improvement Compared with the Commercial Benchmark | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lubricious | Thermal Barrier | Operation | Speed, m/min | Workpiece Material | ||
| Magnéli (W-O) phases | TiAlCrN/WN nano-multilayer | Ball nose end milling | 220 | H 13, hardened (Hardness of 53-55 HRC) | More than 2x that of a commercial TiAlCrN benchmark | |
| Tribo-oxides with metallic properties at elevated temperatures Nb205 | TiAlCrN/NbN nano-multilayer | Ball nose end milling | 300–400 | H 13, hardened (Hardness of 53–55 HRC) | 4x that of a commercial TiAlCrN benchmark | |
| TiAlN/NbN nano-multilayer | Turning, finishing operation | 40 | Inconel 718 | 60% greater than that of commercial TiAlN | ||
| Tribo-oxides, which transform to a liquid phase at high operating temperatures | ||||||
| 1. B203 | TiB2 monolayer | Turning, roughing operation | 45 | TiAl6V4 | 2x, as compared to commercial TiAlN benchmark | |
| 2. V2O5 | AlTiN/VN nano-multilayer | Turning, finishing operation | 150 | TiAl6V4 | 50%, as compared to commercial TiAlN | |
| 3. MoO3 | AlTiN/MoN | Turning, finishing operation | 40–60 | Inconel 718 | 2x higher and above, as compared to commercial TiAlN | |
| Lubricating/ thermal barriers | ||||||
| 1. Cr-O | CrN | Turning, roughing operation | 45 | TiAl6V4 | 2x higher and above, as compared to uncoated and commercial AlTiN | |
| Turning, roughing operation | 150 | TiAl6V4 | 2.3–1.45x higher and above, as compared to uncoated and commercial AlTiN | |||
| 2. Si-O | TiAlSiN | Face milling | 300 | Cast iron | 2x higher and above, as compared to uncoated tool | |
| Combination of Al2O3 Sapphires,Al6 Si2O13 Mullites, | TiAlCrSiYN/TiAlCrN multilayer | Ball nose end milling | 500–600 | H 13, HRC 52-54 | 2x higher and above, as compared to monolayer TiAlCrSiYN | |
| Y3Al5O12 Garnets, AlCrOx Rubies | Turning, Finishing operation | 40 | Inconel 718 | 2x higher and above, as compared to commercial AlTiN | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Gershman, I.; Goel, S.; Endrino, J.L. Control over Multi-Scale Self-Organization-Based Processes under the Extreme Tribological Conditions of Cutting through the Application of Complex Adaptive Surface-Engineered Systems. Lubricants 2023, 11, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030106
Fox-Rabinovich G, Gershman I, Goel S, Endrino JL. Control over Multi-Scale Self-Organization-Based Processes under the Extreme Tribological Conditions of Cutting through the Application of Complex Adaptive Surface-Engineered Systems. Lubricants. 2023; 11(3):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030106
Chicago/Turabian StyleFox-Rabinovich, German, Iosif Gershman, Saurav Goel, and Jose Luis Endrino. 2023. "Control over Multi-Scale Self-Organization-Based Processes under the Extreme Tribological Conditions of Cutting through the Application of Complex Adaptive Surface-Engineered Systems" Lubricants 11, no. 3: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030106
APA StyleFox-Rabinovich, G., Gershman, I., Goel, S., & Endrino, J. L. (2023). Control over Multi-Scale Self-Organization-Based Processes under the Extreme Tribological Conditions of Cutting through the Application of Complex Adaptive Surface-Engineered Systems. Lubricants, 11(3), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11030106







