An AI-Extended Prediction of Erosion-Corrosion Degradation of API 5L X65 Steel
Abstract
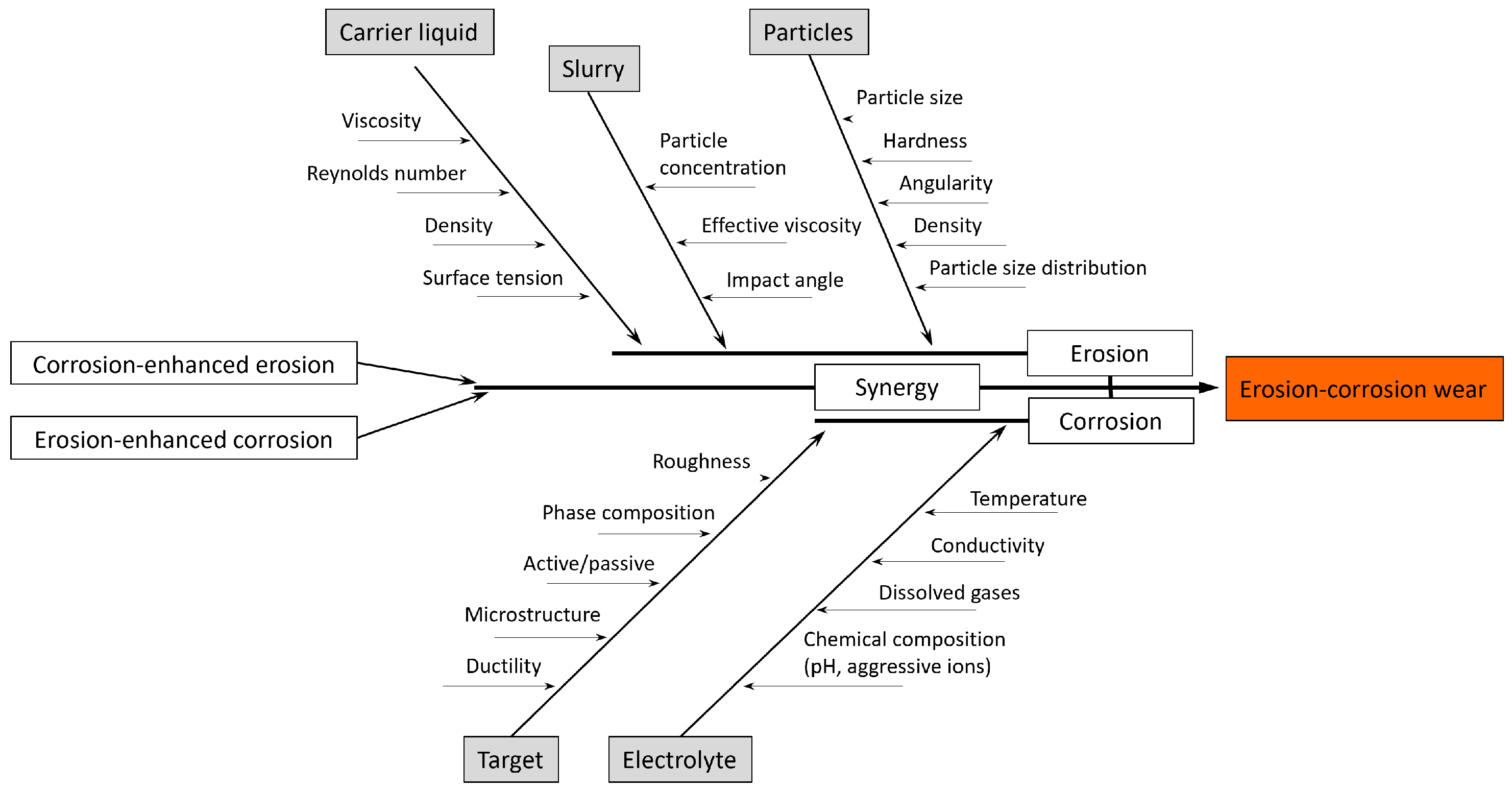
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Methods
2.1. Experimental Determination of E-C Wear
2.1.1. Experiment Design
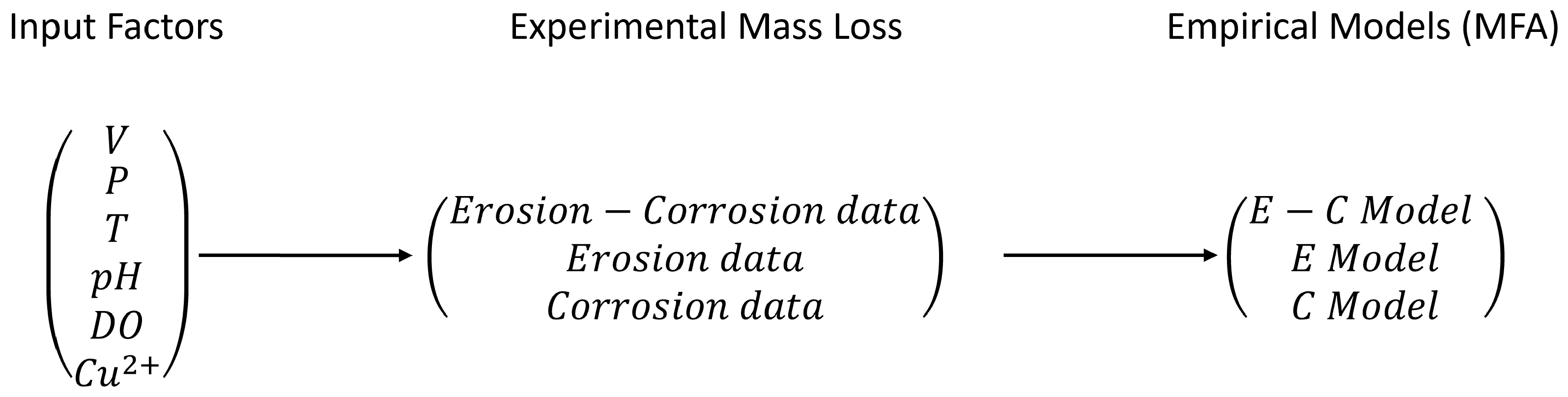
2.1.2. Multifactorial Analysis of Experimental Data
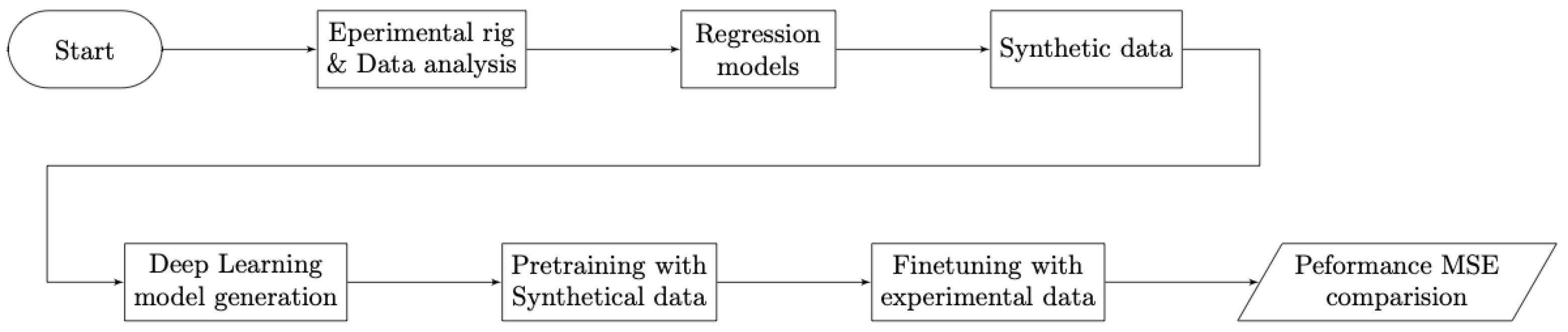
2.2. E-C Neural Network
2.2.1. Model Architecture
2.2.2. Pre-Training Using Synthetic Data
2.2.3. Fine-Tuning, Validation and Evaluation
2.2.4. Sensibility Analysis of E-C NN
3. Results
3.1. MFA Model of E-C Wear
3.2. MFA Model of Stand-Alone Erosion Wear
3.3. MFA Model of Stand-Alone Corrosion Wear
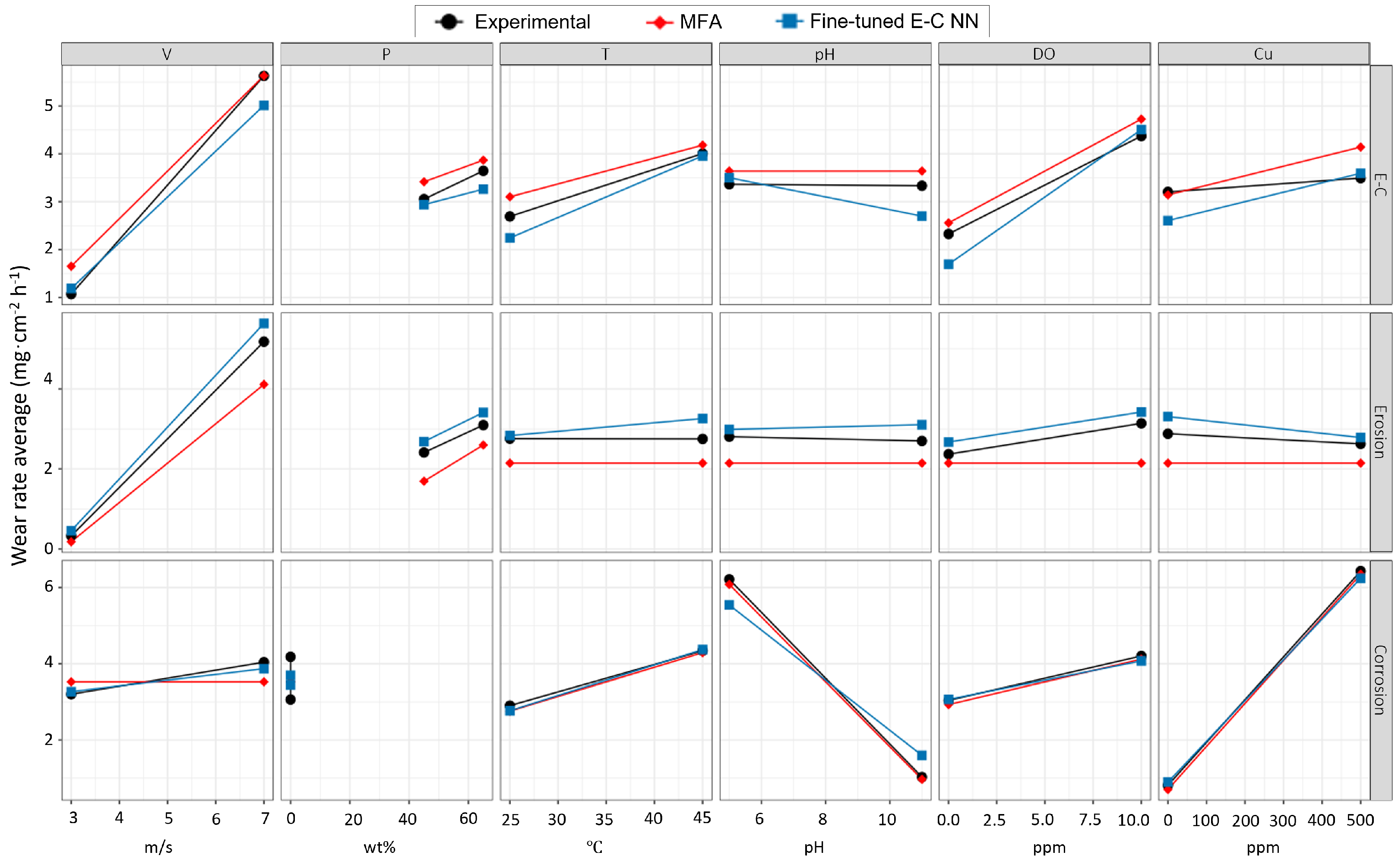
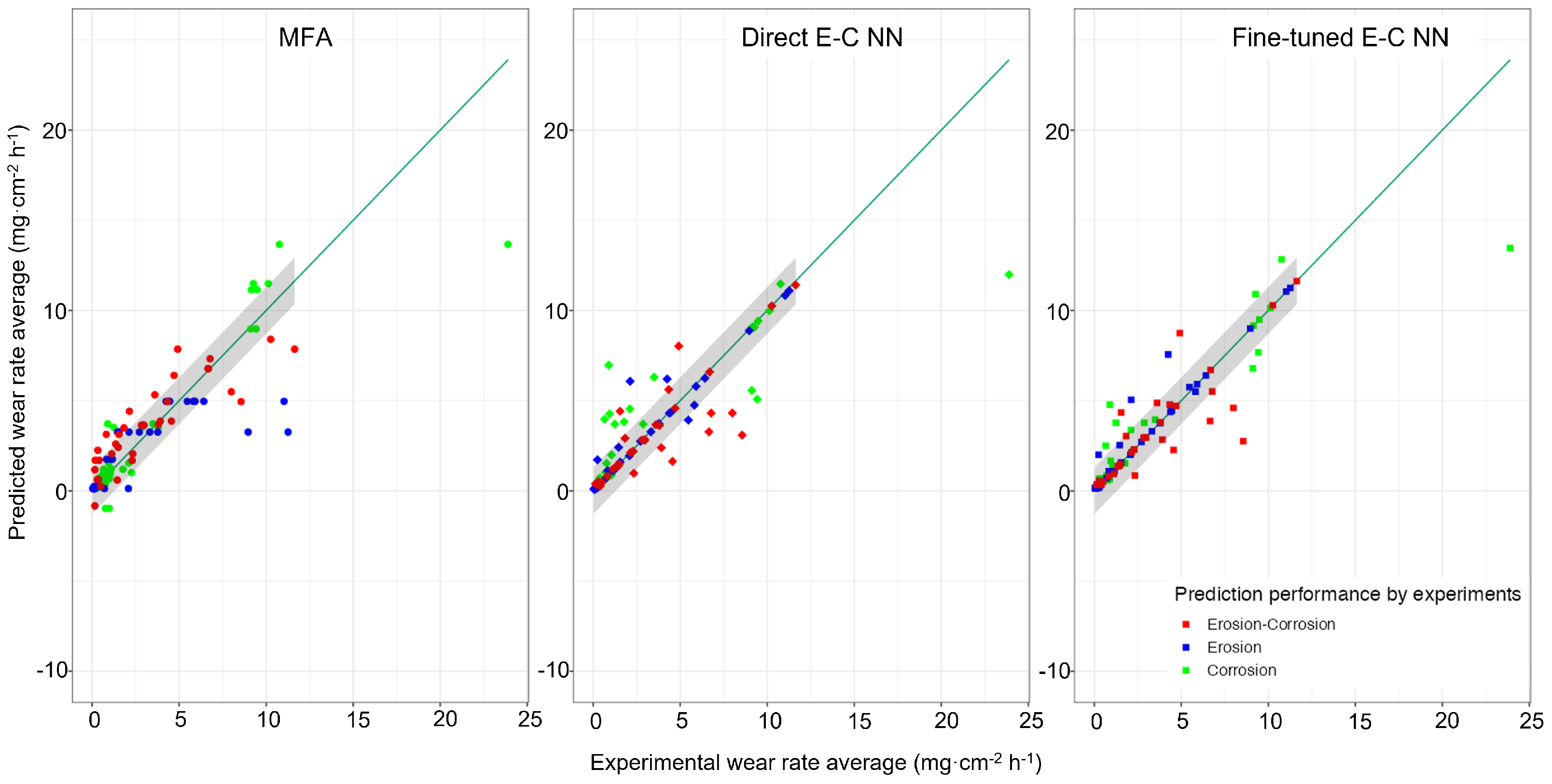
3.4. E-C NN Model Predictions
4. Discussion
4.1. Validity of Synthetic Data
4.2. Applicability of E-C NN
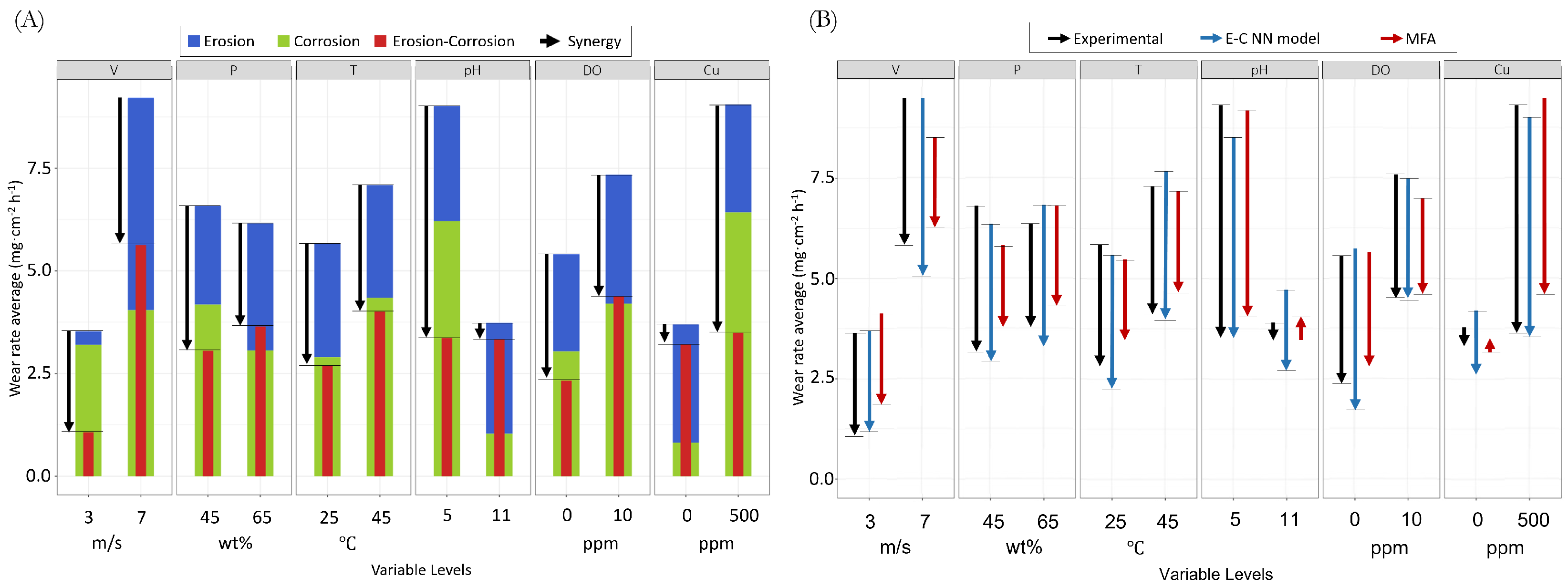
4.3. E-C Synergy
5. Conclusions
- -
- Combination of experimental data with synthetic data generated by the MFA model provides a larger and more diverse dataset, enhancing the training process and improving the generalisation of the applicability and the capabilities of the ANN model in the specific field of E-C studies.
- -
- The ANN shows a superior performance compared to the MFA counterpart as assessed by the mean and median squared errors (MSE). The performance is further improved by including a pre-training step, reducing the mean and median MSE from 3.623 to 2.535, and 0.019 to 0.005, respectively, as compared with 3.694 and 0.345, respectively, of the MFA.
- -
- The ANN trained on E-C data, i.e., the E-C NN, is capable of generalising the importance of experimental parameters without overemphasizing noise in the data, as shown by the absence of global overfitting.
- -
- The errors of the E-C NN predictions are consistently lower than the stand-alone experimental errors, indicating that the model provides highly confident predictions within the factor ranges, outperforming the predictions obtained using MFA.
- -
- Velocity emerges as the predominant factor across all wear mechanisms studied in this work, underscoring the necessity for future focused and deterministic investigations on the specific impact of this parameter in each wear mechanism.
- -
- The synergy effect is highly pronounced compared to the stand-alone wear rate impact. Conducting a detailed study to thoroughly understand and model this particular effect, as well as identifying the key factors that significantly influence it, is of paramount importance.
- -
- Exploring the genuine impact of particle concentration and its influence on fluid viscosity in corrosion wear becomes crucial for a comprehensive understanding of corrosion and E-C wear mechanisms.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| E-C NN | Erosion-corrosion neural network |
| MFA | Multifactorial analysis |
| MSE | Meas squared error |
| RSM | Response surface method |
Appendix A
| Order | V | P | T | Exp. Wear | MFA | E-C NN | F-T E-C NN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.1188 | 0.1287 | 0.1139 | 0.1583 |
| 2 | 7 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 1.4600 | 3.2607 | 2.4135 | 2.5356 |
| 3 | 3 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 0.2688 | 0.2327 | 0.2352 | 0.3331 |
| 4 | 7 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5.4693 | 4.9647 | 3.9248 | 5.7540 |
| 5 | 3 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 0.1584 | 0.1287 | 0.1492 | 0.1764 |
| 6 | 7 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1.5477 | 3.2607 | 1.5944 | 1.5708 |
| 7 | 3 | 65 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.2320 | 0.2327 | 0.1816 | 0.1722 |
| 8 | 7 | 65 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 4.4563 | 4.9647 | 4.3497 | 4.4579 |
| 9 | 3 | 45 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 0.0821 | 0.1287 | 0.0964 | 0.1562 |
| 10 | 7 | 45 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 11.2582 | 3.2607 | 11.0948 | 11.2479 |
| 11 | 3 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0.1075 | 0.2327 | 0.1076 | 0.1748 |
| 12 | 7 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 4.3771 | 4.9647 | 4.3075 | 4.3779 |
| 13 | 3 | 45 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0.0849 | 0.1287 | 0.1021 | 0.1549 |
| 14 | 7 | 45 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 3.7751 | 3.2607 | 3.7327 | 3.7596 |
| 15 | 3 | 65 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 0.2575 | 0.2327 | 0.1941 | 0.1765 |
| 16 | 7 | 65 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 4.2498 | 4.9647 | 6.2028 | 7.5619 |
| 17 | 3 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 2.0836 | 0.1287 | 1.9453 | 2.0045 |
| 18 | 7 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 2.7162 | 3.2607 | 2.7509 | 2.7100 |
| 19 | 3 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0.3169 | 0.2327 | 0.3019 | 0.2484 |
| 20 | 7 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 5.8144 | 4.9647 | 4.7506 | 5.4991 |
| 21 | 3 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0.0340 | 0.1287 | 0.1057 | 0.1515 |
| 22 | 7 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 8.9664 | 3.2607 | 8.8790 | 8.9976 |
| 23 | 3 | 65 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 0.2462 | 0.2327 | 1.7233 | 1.9999 |
| 24 | 7 | 65 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 11.0291 | 4.9647 | 10.8320 | 11.0532 |
| 25 | 3 | 45 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 0.1584 | 0.1287 | 0.3864 | 0.2676 |
| 26 | 7 | 45 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 3.3161 | 3.2607 | 3.2726 | 3.3056 |
| 27 | 3 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 0.1584 | 0.2327 | 0.2003 | 0.1757 |
| 28 | 7 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 6.4171 | 4.9647 | 6.2448 | 6.3988 |
| 29 | 3 | 45 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 0.7102 | 0.1287 | 0.6785 | 0.7017 |
| 30 | 7 | 45 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 2.1221 | 3.2607 | 6.0747 | 5.0481 |
| 31 | 3 | 65 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 0.2292 | 0.2327 | 0.1953 | 0.2732 |
| 32 | 7 | 65 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 5.9106 | 4.9647 | 5.7941 | 5.9130 |
| 33 | 5 | 55 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 0.8347 | 1.7535 | 1.1227 | 1.0933 |
| 34 | 5 | 55 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 1.1685 | 1.7535 | 1.1227 | 1.0933 |
| 35 | 5 | 55 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 1.0808 | 1.7535 | 1.1227 | 1.0933 |
| Order | V | P | T | Exp. Wear | MFA | E−C NN | F−T E−C NN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 0 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.3537 | 0.4592 | 0.3669 | 0.3526 |
| 2 | 7 | 0 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 9.4248 | 8.9749 | 5.0799 | 7.6796 |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 9.1135 | 8.9749 | 5.5686 | 6.7908 |
| 4 | 7 | 0 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.7753 | 0.4592 | 0.7725 | 0.7774 |
| 5 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 10.1265 | 11.4943 | 9.9856 | 10.1459 |
| 6 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2.2664 | 1.0055 | 2.1457 | 2.2700 |
| 7 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.7074 | 1.0055 | 0.6891 | 0.7111 |
| 8 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 9.2663 | 11.4943 | 9.0739 | 10.9060 |
| 9 | 3 | 0 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 0.7668 | −0.9749 | 1.5257 | 0.5824 |
| 10 | 7 | 0 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0.3820 | 0.1906 | 0.7115 | 0.6872 |
| 11 | 3 | 0 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0.2603 | 0.1906 | 0.5175 | 0.6645 |
| 12 | 7 | 0 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 0.9846 | −0.9749 | 1.0360 | 0.9934 |
| 13 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0.4188 | 0.7370 | 0.5629 | 0.5740 |
| 14 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 2.1079 | 1.5445 | 4.5462 | 3.3760 |
| 15 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 0.9479 | 1.5445 | 4.2680 | 1.6610 |
| 16 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0.7158 | 0.7370 | 1.0281 | 0.8493 |
| 17 | 3 | 0 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 9.1503 | 11.1470 | 9.0801 | 9.1590 |
| 18 | 7 | 0 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 1.0044 | 0.6722 | 0.9941 | 0.9995 |
| 19 | 3 | 0 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0.8969 | 0.6722 | 1.0509 | 0.6580 |
| 20 | 7 | 0 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 9.4819 | 11.1470 | 9.4167 | 9.4943 |
| 21 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 1.0554 | 1.2186 | 1.9900 | 1.2875 |
| 22 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 23.8958 | 13.6663 | 11.9901 | 13.4631 |
| 23 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 10.7659 | 13.6663 | 11.4710 | 12.8372 |
| 24 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 1.1035 | 1.2186 | 1.1378 | 1.1175 |
| 25 | 3 | 0 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 0.7498 | 0.4037 | 0.7171 | 0.7379 |
| 26 | 7 | 0 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 0.6564 | 1.1971 | 3.9713 | 2.4994 |
| 27 | 3 | 0 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 1.7712 | 1.1971 | 3.8260 | 1.5332 |
| 28 | 7 | 0 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 0.6593 | 0.4037 | 0.6668 | 0.6620 |
| 29 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 3.4972 | 3.7165 | 6.3058 | 3.9462 |
| 30 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 1.0497 | 0.9500 | 0.8715 | 1.3876 |
| 31 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 0.6366 | 0.9500 | 0.6113 | 0.6354 |
| 32 | 7 | 0 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 0.8941 | 3.7165 | 6.9660 | 4.7817 |
| 33 | 5 | 0 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 1.2421 | 3.5252 | 3.7010 | 3.7723 |
| 34 | 5 | 0 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 3.7942 | 3.5252 | 3.7010 | 3.7723 |
| 35 | 5 | 0 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 2.8719 | 3.5252 | 3.7010 | 3.7723 |
| Order | V | P | T | Exp. Wear | MFA | E-C NN | F-T E-C NN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.1556 | −0.8300 | 0.3622 | 0.3340 |
| 2 | 7 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 2.1447 | 4.4140 | 2.1187 | 2.1424 |
| 3 | 3 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 0.3650 | 0.6220 | 0.3823 | 0.4210 |
| 4 | 7 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 4.5582 | 3.8660 | 1.6334 | 2.2664 |
| 5 | 3 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 0.3282 | 2.2500 | 0.3414 | 0.3573 |
| 6 | 7 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1.8278 | 3.4940 | 2.9187 | 3.0410 |
| 7 | 3 | 65 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.4074 | 1.7020 | 0.2723 | 0.3409 |
| 8 | 7 | 65 | 45 | 5 | 0 | 500 | 4.3403 | 4.9460 | 5.6191 | 4.7799 |
| 9 | 3 | 45 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 0.1556 | 1.1700 | 0.4032 | 0.3479 |
| 10 | 7 | 45 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 1.4996 | 2.4140 | 1.4928 | 1.4864 |
| 11 | 3 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0.2943 | 0.6220 | 0.5036 | 0.5608 |
| 12 | 7 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 3.9159 | 3.8660 | 2.3881 | 2.8404 |
| 13 | 3 | 45 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0.5008 | 0.2500 | 0.4720 | 0.4893 |
| 14 | 7 | 45 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 7.9959 | 5.4940 | 4.3158 | 4.5988 |
| 15 | 3 | 65 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 500 | 0.1754 | 1.7020 | 0.3715 | 0.3482 |
| 16 | 7 | 65 | 45 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 8.5590 | 4.9460 | 3.0907 | 2.7559 |
| 17 | 3 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 1.3553 | 2.6000 | 1.3859 | 1.3562 |
| 18 | 7 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 3.6047 | 5.3240 | 3.6684 | 4.8792 |
| 19 | 3 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 2.3371 | 2.0520 | 0.9745 | 0.8509 |
| 20 | 7 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 6.6887 | 6.7760 | 6.5905 | 6.7015 |
| 21 | 3 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 2.2975 | 1.6800 | 2.1945 | 2.2997 |
| 22 | 7 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 10.2623 | 8.4040 | 10.2508 | 10.2911 |
| 23 | 3 | 65 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 500 | 1.5449 | 3.1320 | 4.4122 | 4.3425 |
| 24 | 7 | 65 | 45 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 11.6374 | 7.8560 | 11.4157 | 11.6311 |
| 25 | 3 | 45 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 1.4430 | 0.6000 | 1.3731 | 1.3913 |
| 26 | 7 | 45 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 6.7793 | 7.3240 | 4.3113 | 5.5060 |
| 27 | 3 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 1.1318 | 2.0520 | 1.1991 | 0.9393 |
| 28 | 7 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 6.6520 | 6.7760 | 3.2735 | 3.8736 |
| 29 | 3 | 45 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 3.8056 | 3.6800 | 3.6246 | 3.8071 |
| 30 | 7 | 45 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 4.7081 | 6.4040 | 4.5801 | 4.7080 |
| 31 | 3 | 65 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 0.8149 | 3.1320 | 0.8151 | 0.8023 |
| 32 | 7 | 65 | 45 | 11 | 10 | 500 | 4.9175 | 7.8560 | 8.0262 | 8.7464 |
| 33 | 5 | 55 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 2.9794 | 3.6430 | 2.8227 | 2.9507 |
| 34 | 5 | 55 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 2.8351 | 3.6430 | 2.8227 | 2.9507 |
| 35 | 5 | 55 | 35 | 8 | 5 | 250 | 2.9596 | 3.6430 | 2.8227 | 2.9507 |
References
- Moore, P. Ausenco Symposium Outlines Importance of Long Term Mining Slurry Pipeline Management; Ausenco: South Brisbane, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G119-09; Standard Guide for Determining Synergism Between Wear and Corrosion. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, V.; Porter, D.; Kuokkala, V.T. Slurry erosion of steel—Review of tests, mechanisms and materials. Wear 2018, 408, 248–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turenne, S.; Fiset, M.; Masounave, J. The effect of sand concentration on the erosion of materials by a slurry jet. Wear 1989, 133, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.; Hodgkiess, T.; Xu, H. An electrochemical and microstructural assessment of erosion–corrosion of cast iron. Wear 1999, 233, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.W. Particle angularity and its relationship to abrasive and erosive wear. Wear 2000, 241, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, M.; Jana, B. Modelling particulate erosion–corrosion in aqueous slurries: Some views on the construction of erosion–corrosion maps for a range of pure metals. Wear 2004, 256, 986–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desale, G.R.; Gandhi, B.K.; Jain, S. Effect of erodent properties on erosion wear of ductile type materials. Wear 2006, 261, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.R.; Cheng, Y.F. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of X-65 steel in the simulated oil sand slurry. I: Effects of hydrodynamic condition. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Mahdi, E. Studying and comparing the erosion-enhanced pitting corrosion of X52 and X100 steels. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 5692–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.J.K.; Walker, J.C.; Harvey, T.J.; Wang, S.; Rajahram, S.S. Influence of microstructure on the erosion and erosion–corrosion characteristics of 316 stainless steel. Wear 2013, 306, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.M.; Farhat, Z.N.; Ahmed, E.M.; Alfantazi, A.M. Erosion enhanced corrosion and corrosion enhanced erosion of API X-70 pipeline steel. Wear 2013, 302, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Li, D.Y.; Grondin, A. Effects of the dissolved oxygen and slurry velocity on erosion-corrosion of carbon steel in aqueous slurries with carbon dioxide and silica sand. Wear 2013, 302, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, M.; Perolainen, J. Slurry pot investigation of the influence of erodent characteristics on the erosion resistance of austenitic and duplex stainless steel grades. Wear 2014, 319, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.; Toor, I.; Ahmed, W.; Gasem, Z.; Habib, M.; Ben-Mansour, R.; Badr, H. Investigations on the Corrosion-Enhanced Erosion Behavior of Carbon Steel AISI 1020. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 6765–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Alam, T.; Farhat, Z.N.; Mohamed, A.; Alfantazi, A. Effect of microstructure on the erosion behavior of carbon steel. Wear 2015, 332, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, Y. Erosion-enhanced corrosion of stainless steel and carbon steel measured electrochemically under liquid and slurry impingement. Corros. Sci. 2016, 102, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xie, Y.; Islam, A. The Effect of Dissolved Oxygen in Slurry on Erosion–Corrosion of En30B Steel. J. Bio Tribo-Corros. 2017, 3, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvila, R.; Kumaran, S.T.; Khan, M.A.; Uthayakumar, M. A brief review on the erosion-corrosion behavior of engineering materials. Corros. Rev. 2018, 36, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.Z.; Hu, H.X.; Wang, Z.B.; Zheng, Y.G. On the critical flow velocity for erosion-corrosion in local eroded regions under liquid-solid jet impingement. Wear 2019, 423, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messa, G.V.; Wang, Y.; Malavasi, S. A discussion of the test procedures of the API 6AV1 standard based on wear prediction simulations. Wear 2019, 426, 1416–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, J.R.; Stephenson, D.J. Monte Carlo modelling of erosion processes. Wear 1995, 186, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, G.; Arabnejad, H.; Shirazi, S.A.; Mclaury, B.S. A mechanistic model for stochastic rebound of solid particles with application to erosion predictions. Wear 2017, 376, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K. Application of a Stochastic Modelling Framework to Characterize the Influence of Different Oxide Scales on the Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour of Boiler Grade Steel; Technical Report; Indian Academy of Sciences: Karnataka, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- de Moura, B.F.; da Silva, W.B.; de Macêdo, M.C.S.; Martins, M.F. A statistical approach to estimate state variables in flow-accelerated corrosion problems. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2018, 26, 966–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencl, A.; Svoboda, P.; Klančnik, S.; But, A.; Vorkapić, M.; Harničárová, M.; Stojanović, B. Influence of Al2O3 Nanoparticles Addition in ZA-27 Alloy-Based Nanocomposites and Soft Computing Prediction. Lubricants 2023, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalwani, V.; Sharma, P.; Pruncu, C.I.; Unune, D.R. Response surface methodology and artificial neural network-based models for predicting performance of wire electrical discharge machining of inconel 718 alloy. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Abdul Wahab, N. Improved Artificial Neural Network Training Based on Response Surface Methodology for Membrane Flux Prediction. Membranes 2022, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S. Comparison of a response surface method and artificial neural network in predicting the aerodynamic performance of a wind turbine airfoil and its optimization. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.A.; Brahmbhatt, P.K. A Comparative Study of the RSM and ANN Models for Predicting Surface Roughness in Roller Burnishing. Procedia Technol. 2016, 23, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Kiru, M.U.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Umar, A.M.; Linus, O.U.; Arshad, H.; Kazaure, A.A.; Gana, U. Comprehensive Review of Artificial Neural Network Applications to Pattern Recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 158820–158846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Nosonovsky, M. Triboinformatics: Machine learning algorithms and data topology methods for tribology. Surf. Innov. 2022, 10, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Kokol, M.; Zagoranski, S. Machine learning on small size samples: A synthetic knowledge synthesis. Sci. Prog. 2022, 105, 003685042110297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrionuevo, G.O.; Walczak, M.; Ramos-Grez, J.; Sánchez-Sánchez, X. Microhardness and wear resistance in materials manufactured by laser powder bed fusion: Machine learning approach for property prediction. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, J.; Walczak, M. Multifactorial study of erosion–corrosion wear of a X65 steel by slurry of simulated copper tailing. Tribol. Int. 2018, 126, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G1-03 (Reapproved 2017); Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrike Groemping. FrF2: Fractional Factorial Designs with 2-Level Factors; Ulrike Groemping: Berlin, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lumley, T.; Miller, A. leaps: Regression Subset Selection. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/leaps/leaps.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Kobayashi, M.; Sakata, S. Mallows’ C criterion and unbiasedness of model selection. J. Econom. 1990, 45, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, T.K.; Levy, M.S. Goodness of Prediction Fit for Multivariate Linear Models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1996, 91, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, J.; Walczak, M.; Rohwerder, M. The mechanism of erosion-corrosion of API X65 steel under turbulent slurry flow: Effect of nominal flow velocity and oxygen content. Wear 2019, 438, 203053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.M. Particle velocity and size effects in laboratory slurry erosion measurements OR... do you know what your particles are doing? Tribol. Int. 2002, 35, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, S.; Lohse, D.; Sun, C. High–Reynolds Number Taylor-Couette Turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2016, 48, 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.S.; Liu, B. Hydrodynamic and temperature effects on the flow-induced local corrosion rate in pipelines. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2003, 190, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickel, J.J.; Powell, R.L. Fluid mechanics and rheology of dense suspensions. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2005, 37, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Li, X.F. Effects of particle concentration and physical properties on the apparent viscosity of a suspension of monodisperse concentric core–shell particles. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2020, 84, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
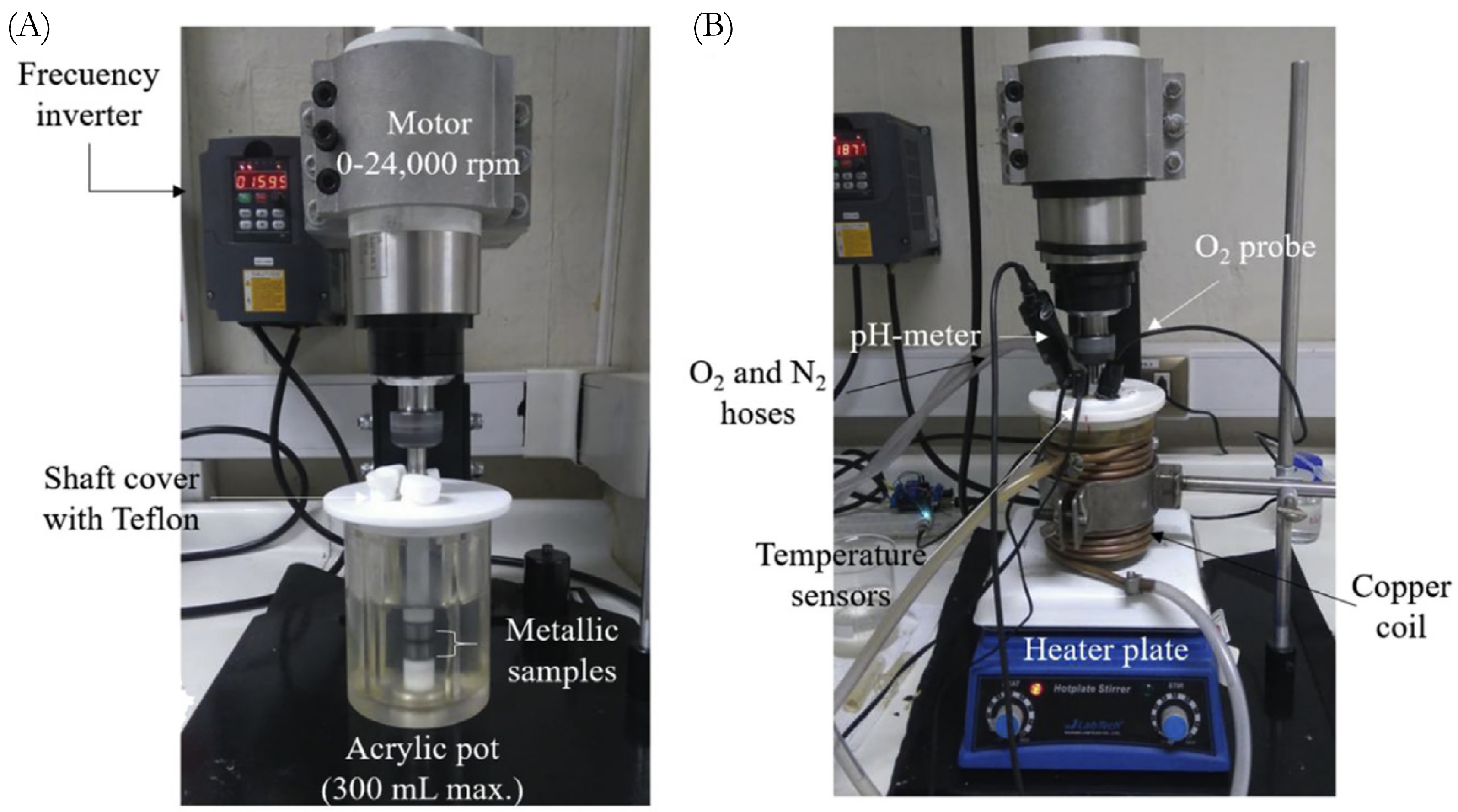

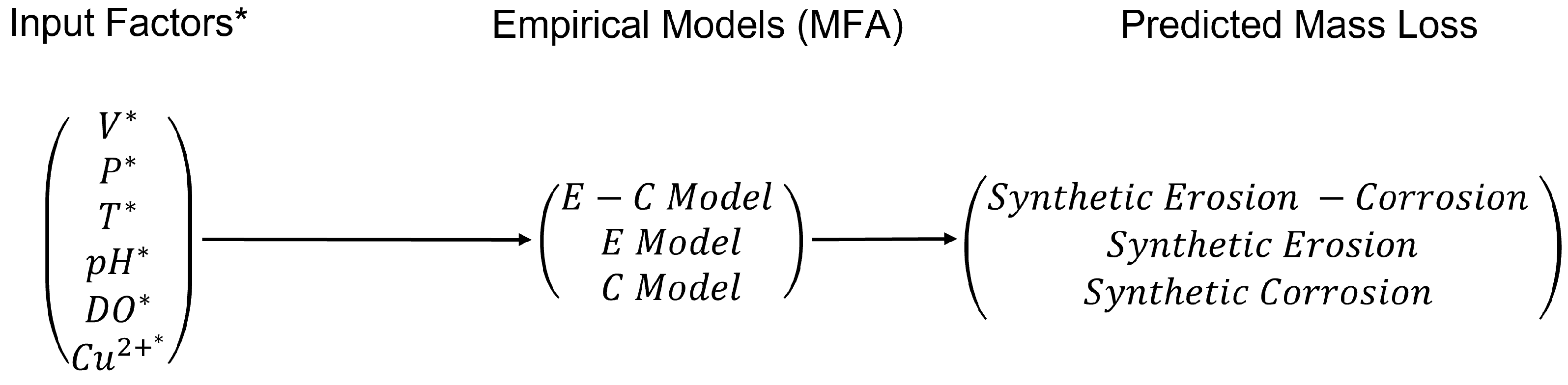
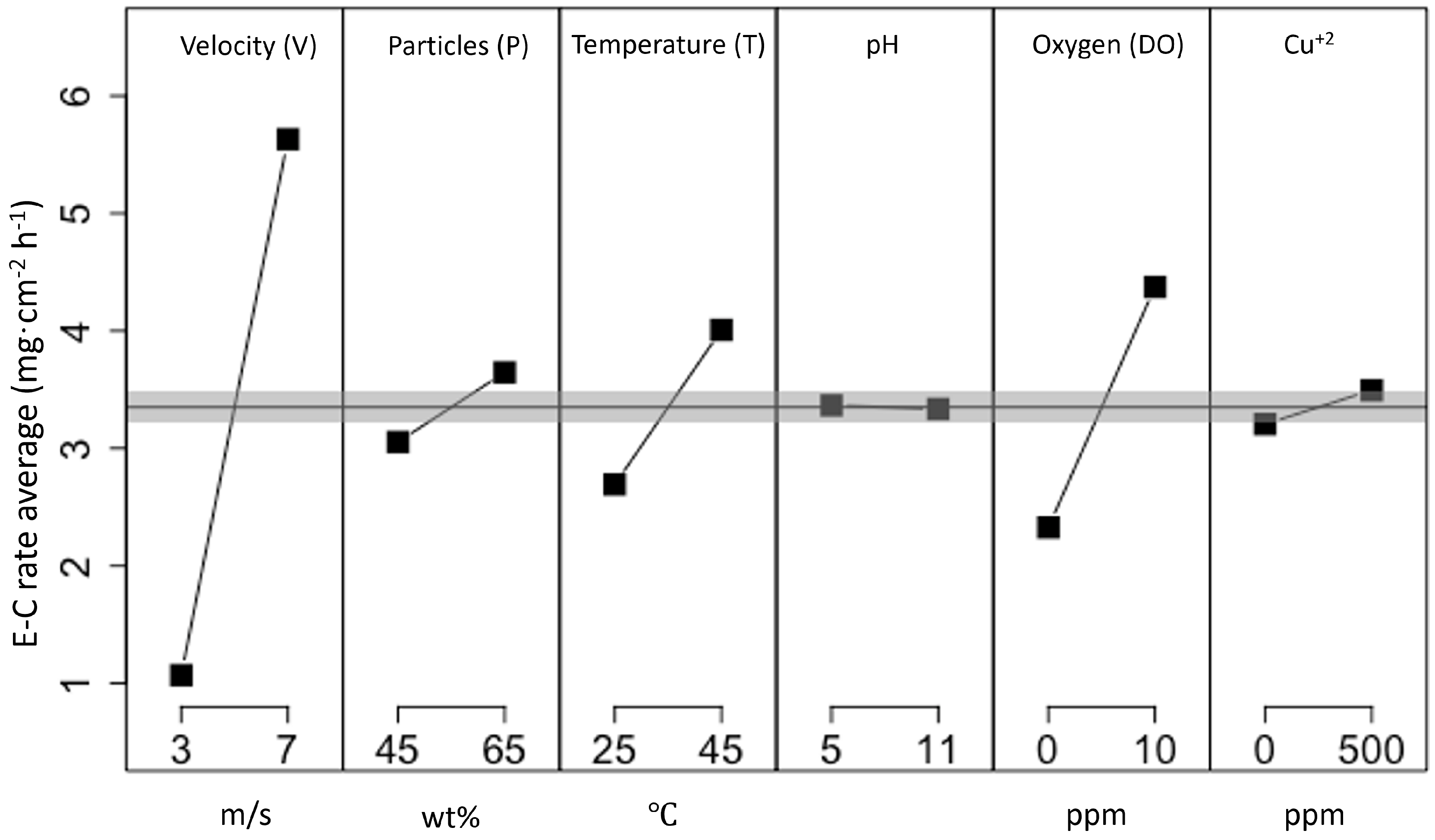
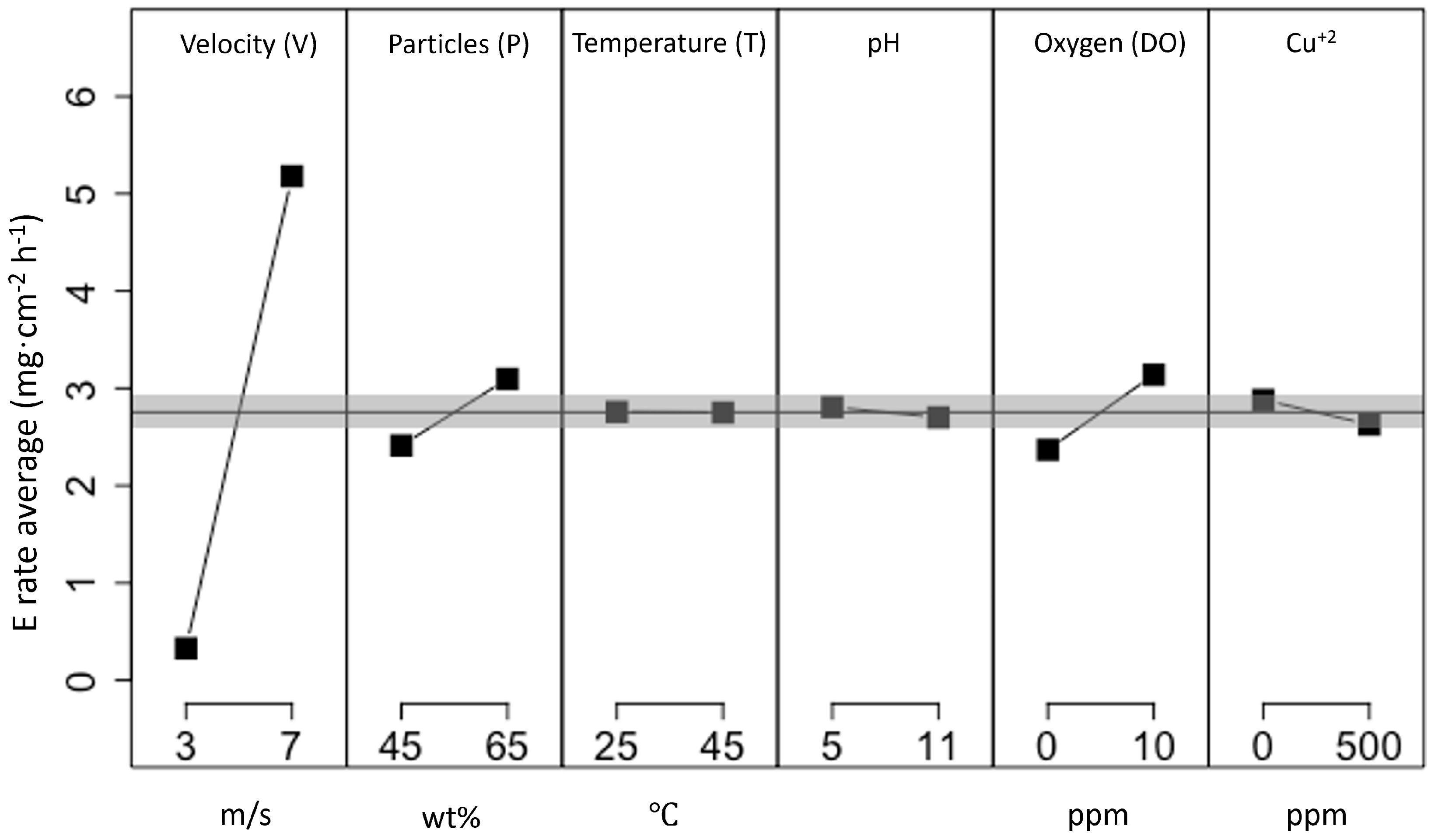

| Factor | Unit | Symbol | Low Level | Central Level | High Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velocity | m/s | V | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| Particles concentration | wt % | P | 45 | 55 | 65 |
| Temperature | C | T | 25 | 35 | 45 |
| pH | pH | 5 | 8 | 11 | |
| Dissolved oxygen | ppm | 0 | 5 | 10 | |
| Copper ion concentration | ppm | Cu | 0 | 250 | 500 |
| MFA | Direct E-C NN | Fine-Tuned E-C NN | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 1st.Qu. | 0.037 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| Median. | 0.345 | 0.019 | 0.005 |
| Mean | 3.694 | 3.623 | 2.535 |
| 3rd.Qu. | 2.519 | 0.909 | 0.202 |
| Max. | 104.642 | 141.747 | 108.842 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinoza-Jara, A.; Wilk, I.; Aguirre, J.; Walczak, M. An AI-Extended Prediction of Erosion-Corrosion Degradation of API 5L X65 Steel. Lubricants 2023, 11, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11100431
Espinoza-Jara A, Wilk I, Aguirre J, Walczak M. An AI-Extended Prediction of Erosion-Corrosion Degradation of API 5L X65 Steel. Lubricants. 2023; 11(10):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11100431
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinoza-Jara, Ariel, Igor Wilk, Javiera Aguirre, and Magdalena Walczak. 2023. "An AI-Extended Prediction of Erosion-Corrosion Degradation of API 5L X65 Steel" Lubricants 11, no. 10: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11100431
APA StyleEspinoza-Jara, A., Wilk, I., Aguirre, J., & Walczak, M. (2023). An AI-Extended Prediction of Erosion-Corrosion Degradation of API 5L X65 Steel. Lubricants, 11(10), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11100431





