Abstract
Owing to their low cost and environmentally friendly nature, water-based lubricants have benefits over oil-based ones. However, the appropriate additive package is indispensable in improving its tribological properties. In the current study, we have investigated the friction and wear reduction ability of bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium oleate protic ionic liquid (PIL) in a glycerol aqueous lubricating fluid. The tribo-tests were performed using a ruby–steel friction pair acting in reciprocation mode. The coefficient of friction and wear were the main characteristics of the evaluation. Analysis of the physical properties of the investigated lubricating samples and worn surface analysis were performed to reveal a more detailed picture. The study shows that the investigated PIL can significantly reduce friction and wear. The most suitable concentration of PIL was 0.5%, where friction and wear were reduced 2.6 and 15.8 times, respectively. Using the investigated PIL facilitates a sliding coefficient of friction as low as 0.039. It was hypothesized that the formation of the adsorption layer and metal soap was responsible for this. Further studies could be directed toward higher load and speed applications.
1. Introduction
Recently, the world’s community has been affected by energy cost fluctuations. Therefore, at present, energy-saving technologies are of great interest, more so than ever. Many studies have confirmed that solving tribological problems can reduce energy loss and contribute to the solution of environmental issues [1,2]. Moreover, it will result in improved performance and extended mechanical system service life, reducing downtime due to replacing worn parts. Lubrication is crucial to minimize friction and, consequently, the energy required. The liquid lubrication provides friction and wear reduction, eliminates corrosion, provides the cooling of interacting surfaces, and offers many more benefits, depending on the application. Moreover, in the specific cases of lubrication, ultra-low-friction and superlubricity were achieved at micro and macro scales [3,4,5].
Generally, lubricants can be divided into oil-based and water-based. Oil-based lubricants are the most common. However, most of them have ecological issues regarding the environment. Due to their low cost, nontoxicity, and prevalence, water-based lubricants have been found in widespread industrial applications. To enhance the viscosity of water-based lubricating fluids, they are diluted with higher-viscosity substances such as glycerol, polyethylene glycol, and vegetable oil [6]. Additives must also be introduced to improve corrosion prevention, friction and wear reduction, foaming control, and many other properties [7]. Undoubtedly, these additives must be water-soluble. Moreover, to ensure environmental acceptability, the additives must be environmentally friendly [8].
Recently, protic ionic liquids (PILs) have become attractive due to their environmentally friendly nature and promising tribological response [9,10,11]. Most of the studied PILs are halogen-free and contain only oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen elements [12]. In some cases, phosphorus and borate are presented in the cation. Fatty acids, such as stearic and oleic, are used in synthesizing PILs, which are the renewable counterpart. Current studies of PIL-loaded water-based lubricating fluids show improved lubricity and wettability. Moreover, metal corrosion was also reduced [13,14].
The tribological studies performed confirm the ability to form physically adsorbed layers and/or tribochemical reactions with the surface. Yang et al. [15] explored amino acid-based PILs as additives in aqueous lubricants. A remarkable reduction in friction and wear was reported. Zheng et al. [13] also obtained similar positive results by using ammonium-based PILs as additives in an aqueous glycol solution. In both cases, the polarity of ionic liquid molecules was responsible for a positive response. Bjorling et al. [5,9] investigated a [Choline] [Proline] protic ionic liquid as a neat lubricant and an additive in an aqueous glycerol solution. It was found that the investigated PIL possessed a low pressure–viscosity coefficient, which was responsible for its excellent tribological performance. Moreover, it showed superlubricity when it was used as an additive. Espinosa et al. [11] also reported ultra-low friction using a PIL as an additive in water to lubricate a sapphire–stainless steel friction pair in continuous sliding mode. The adsorption layer and formation of metal–ammonium complexes were noted to be responsible for this.
As water-based lubricants become more attractive, systematic studies are particularly important [6]. Moreover, most of the performed studies focus on the lubrication of metallic friction pairs [5,13,15,16,17,18,19,20] and only a few deal with the lubrication of ceramics [10,11,21,22,23,24], which are increasingly attractive for high-performance applications in severe environments. In the current study, we aim to investigate the friction and wear reduction behavior of a bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium oleate protic ionic liquid in a glycerol aqueous lubricating fluid. The ruby-bearing steel friction pair acting in reciprocation mode was employed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
An aqueous glycerol solution (W:GL) was used as a base lubricating fluid. It was prepared by mixing deionized waster and glycerol (1:1 by wt.). The analytically pure anhydrous glycerol was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium oleate protic ionic liquid (PIL) was synthesized following the methodology explained in previous papers [25,26]. Briefly, the synthesis procedure can be described as follows: oleic acid was dropwise introduced into preheated diethanol amine under continuous mixing. The neutralization reaction occurred, resulting in the amine salt, a viscous yellow liquid. The mixture was stirred for 24 h, keeping the same conditions to complete the reaction. The main physicochemical properties, chemical structure, and appearance of the synthesized PIL are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties, structural formula, and visual appearance of investigated PIL.
Five concentrations of PIL in the base lubricating fluid, namely 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 1.5 wt.%, were prepared and studied. A magnetic stirrer operating at 200 rpm at room temperature was employed to prepare lubricating samples. The visual appearance of the investigated lubricating samples is shown in Figure 1. The PIL was soluble for all the investigated concentrations. With the increased PIL concentration, the solution became yellowish.

Figure 1.
The appearance of the investigated lubricating fluids.
2.2. Physicochemical Properties
The kinematic viscosity and density of the investigated lubricating fluids were tested using an SVM 3000 Anton Paar viscometer (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria). Four repetitions were made for each specimen.
2.3. Tribological Properties
A ball-on-plate reciprocating tribometer was employed to evaluate the lubricity of the investigated samples. During the tribo-test, a ruby ball (φ 6 mm) was rubbed against a steel E-52100 plate (φ 10, thickness—3 mm). The ball had a hardness of 1570–2170 (according to technical specifications). The plate surface had a hardness of 190–200 HV30 and a roughness of 20 nm. The main tribo-test conditions were as follows: reciprocation frequency—15 Hz; load—4 N; stroke length—1000 μm; test temperature—25 °C. Moreover, 2 mL of sample was introduced in the friction zone to submerge the friction pair fully. Before the experiments, all the parts in contact with the investigated sample were washed in an ultrasonic bath in toluene and acetone. The tribo-test duration was 30 and 120 min. Tribo-tests were repeated at least two times. The coefficient of friction (COF) variation during the tribo-test was continuously recorded with a frequency of 2 Hz. The mean COF was calculated using the data from the last 10 min of the tribo-test.
2.4. Analysis of the Worn Surfaces
After the tribo-test, the ball and plate surfaces were observed using a Nikon ECLIPSE MA 100 optical microscope (OM) (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) and a Hitachi 3400 N scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Bruker Quad 5040 energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis (Bruker, Berlin, Germany) was employed to inspect the wear scar composition. Before the inspection, the specimens were rigorously cleaned in ethanol. After the tribo-test, the cross-section profile of the wear scars was measured using a Mahr GD-25 stylus profilometer (Mahr GmbH, Göttingen, Germany). The wear volume was calculated following the procedure described in ASTM G133. Briefly, the area of the cross-section profile was calculated in a few locations along the wear scar. Then, the average area of the cross-sections was multiplied by the length of the wear scar, and the wear volume was obtained.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties
The relationship between the lubricants’ viscosity and the PIL concentration at 25 °C is presented in Figure 2. The addition of the viscous PIL increased the lubricants’ viscosity, which followed a linear trend in the investigated concentration interval. The linear trend also showed the good solubility of the PIL in a base fluid. Due to the good tribological response, which will be discussed in further sections, samples having 0.5% PIL were examined in more detail. Their viscosity and density were measured at the temperature range from 20 to 70 °C (Figure 3). The viscosity and density decreased with the increased test temperature, following exponential and linear trends. It must be noted that the temperature significantly influences the viscosity rather than the concentration. During the tribo-test, the local temperature in the contact area was expected to rise; therefore, the viscosity decreased, leading to a lower energy loss.
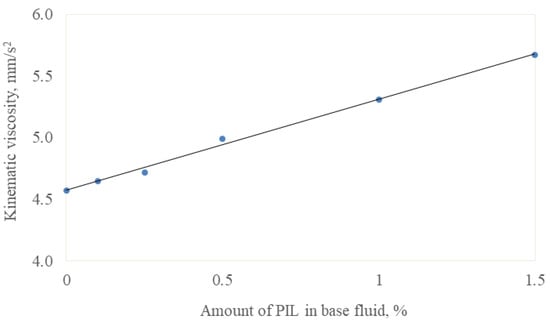
Figure 2.
Kinematic viscosity (blue dots) and its trendline at 25 °C as a function of additive concentration.
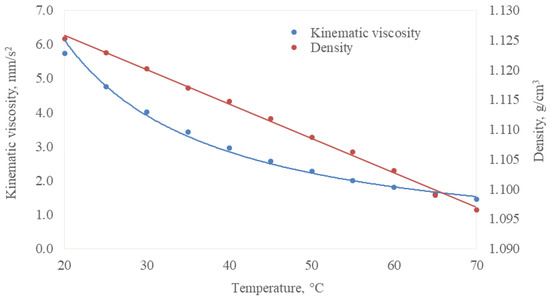
Figure 3.
Kinematic viscosity and density of lubricating fluid W:GL + PIL 0.5 as a function of temperature.
3.2. Friction Evaluation
The COF defines a lubricant’s ability to reduce the energy losses arising between contacting surfaces during their relative motion. Therefore, low-COF lubricants will minimize energy loss and frictional heat. In the present case, the PIL additive significantly reduced the COF, reaching mean values as low as 0.05. Friction variations observed during the tests and mean values calculated from the last 10 min of the tribo-test are presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively.
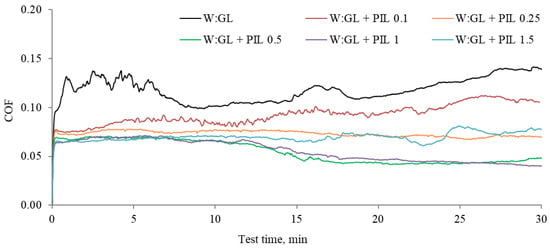
Figure 4.
Variations of the COF as a function of test time observed during the tribo-tests.
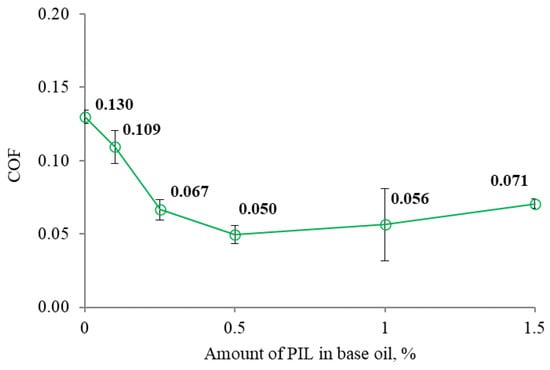
Figure 5.
The mean COF as a function of the amount of PIL.
The additive-free water–glycerol solution demonstrated high and unstable friction. Introducing the PIL additive reduced and stabilized the friction. The COF gradually decreased when the amount of the PIL additive increased; however, a particular additive concentration is essential for optimum results (Figure 5). The lowest COF was observed at the additive concentration of 0.5%. A low and high COF was observed during the repetitions of the lubrication sample having 1% of PIL. Therefore, the mean COF at this point had high variation (Figure 5). Considering that further increases in the amount of PIL resulted in more strongly increased friction, we assumed that there was a threshold for the optimum PIL concentration. Analyzing the COF variation during the test (Figure 4), it was observed that additive-loaded samples had similar initial COF patterns. At the onset of the tribo-test, COFs rose, indicating the running-in conditions. After a few minutes, the COFs stabilize. The 0.1% concentration was insufficient to keep surfaces separated, resulting in the increased COF. Applying 0.25% led to a relatively stable COF thought the test time. The concentrations of 0.5 and 1% resulted in stable friction, which, after 15 min of the test, decreased, reaching COF values as low as 0.035. With the increased concentration up to 1.5%, the friction reduction process was interrupted, and the COF, after 15 min, became unstable. Although the COF at some concentrations was higher, it was still lower than that observed during lubrication with the additive-free base fluid. The most significant COF reduction of 61.5% was observed during lubrication with 0.5% PIL-loaded base fluid.
The behavior of the COF when surfaces were lubricated with the base fluid having 0.5% of PIL was particularly interesting. Therefore, we extended the experiment to 2 h. The COF variations observed during the repetitions of this experiment are shown in Figure 6.
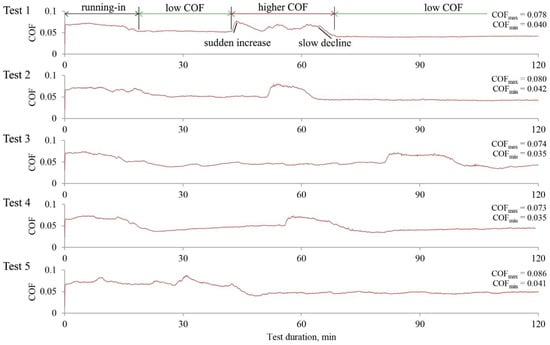
Figure 6.
Variations of the COF as a function of test time were observed during the extended tribo-tests when lubricating with PIL-loaded (0.5%) base fluid.
It was found that the COFs were not stable throughout the test time. A similar 15 to 20 min running-in period was observed in all test repetitions except Test 5, which took 45 min to stabilize. At the stable low-friction periods, the COF had a mean value of 0.039. Unfortunately, the low-friction periods were interrupted, and the COFs reached higher values (0.078). Although the COF in these periods increased, its values did not exceed that observed at the onset of the tests. After some time, the friction decreased, and the low-friction period followed. The decreased COF, reaching the same low-friction value, means that the interruption was not caused by the evaporation of water or wear. Instead, it was related to physicochemical processes during surface interaction. The reason for such behavior could be found by analyzing the tribo-film formation/removal process, as described in the next section.
3.3. Wear Evaluation
The observed wear as a function of the PIL concentration is presented in Figure 7. The wear was significantly reduced and followed the friction tendency in all the investigated PIL concentrations except 0.1%. The minimum wear was observed after lubrication with 0.5% PIL-loaded base fluid. At this point, the wear volume was 15.8 times lower than that observed in the case of the additive-free sample. A further increase in the amount of PIL resulted in higher wear.
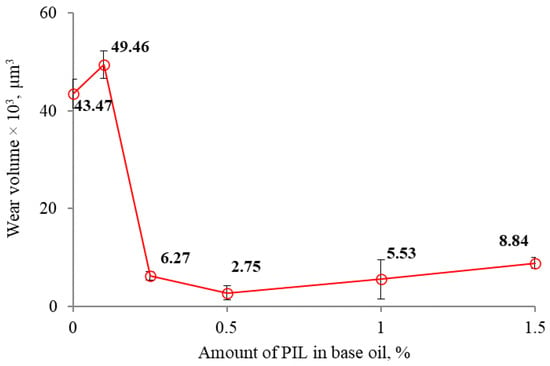
Figure 7.
The mean wear volume as a function of PIL concentration.
The cross-section profiles of wear scars on the plate are presented in Figure 8. The introduction of the PIL resulted in pushed-out metal at the boundaries of the wear scar. The material at the edges was particularly evident in the cases of 0.1 and 1.5%, which underwent higher wear. The low-wear-possessing surfaces were smoother, reflected by lower friction.
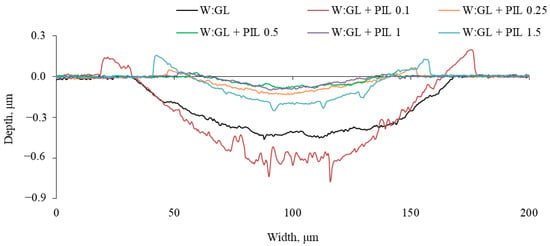
Figure 8.
Cross-section profiles of wear scars on the plate observed after the tribo-test of investigated lubricating fluids.
The fragments of wear scars observed on the plate are shown in Figure 9. All the worn surfaces had specific features corresponding to a particular friction response. The many pits on the additive-free base-fluid-lubricated surface possibly occurred due to adhesion. Together with abrasion, it resulted in high and unstable friction (Figure 4). Applying the smallest amount (0.1%) of additive almost eliminated the adhesion; however, many furrows occurred in the central part of the wear scar. These are also evident in the cross-section profiles (Figure 8). A further increase in the concentration up to 0.25% resulted in a smooth wear scar surface. At a concentration of 0.5%, the worn surface was also smooth, having a patchy appearance. There was almost no pushed-out material at the boundaries of the wear scar. The higher concentrations of 1 and 1.5% increased the width of the wear scars. The pushed-out material appeared at the edges of the wear scars. A few deep furrows occurred on the surface lubricated with 1.5% PIL (Figure 8). These could result from wear debris embedded in the tribo-film and moving with the ball. It must be noted that the wear of the ruby ball in all the performed experiments was negligible. There was only a slight polishing observed on the balls’ wear scar.
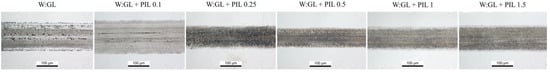
Figure 9.
OM images of the wear scars on the plate observed after lubrication with investigated samples.
We analyzed the worn surface at different periods to identify the lubrication mechanisms behind the low and higher friction. The wear scars on the plate and the ball observed during low- and higher-friction periods are shown in Figure 10. Surface polishing was observed on the ball in the low-friction period (Figure 10a’), whereas in the higher-friction period, some layers were attached to the ball (Figure 10b’). Similarly, the wear scar on the plate observed in the higher-friction period reveals a dense layer, whereas the layer seems uneven in the low-friction period.
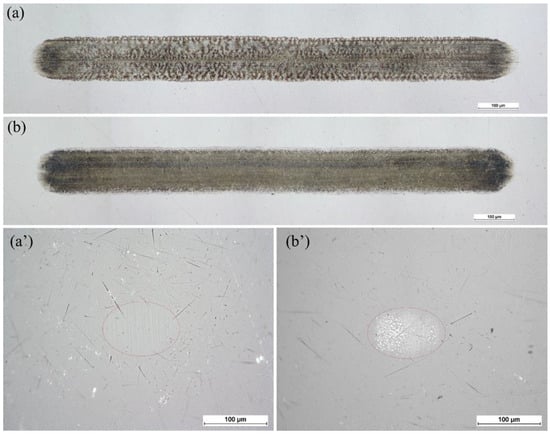
Figure 10.
OM images observed on the plate and the ball at the low (a,a’) and higher (b,b’) friction periods of the test when 0.5% PIL concentration was used.
The SEM images of both wear scars on the plate, and their composition, confirm the presence of a tribo-film (Figure 11). Worn surfaces contain higher amounts of C, O, and N than entire plate surfaces. Comparing these two cases, the tribo-film containing more oxygen and nitrogen was observed in the higher-COF period. The layer was present in both cases. However, in the case of the higher COF, it was thicker and more evenly distributed on the worn surface. It also easily distinguished pushed-out material at the edges of wear scars, which could be the residues of the tribo-film. It must be noted that a small amount of N was observed outside the wear scars, confirming the presence of an adsorbed layer.
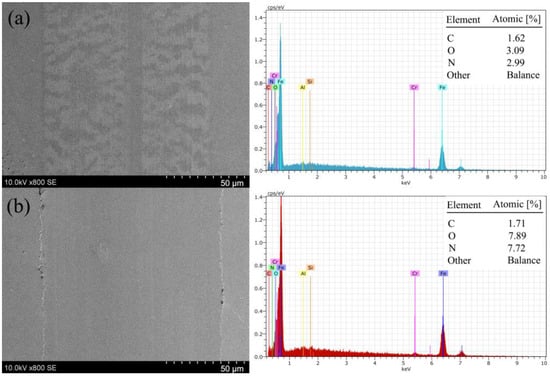
Figure 11.
SEM images and EDS of wear scars on the plate observed in the low (a) and high (b) friction periods. Undamaged surface composition: C—0.89%; O—0.11%; N—0.8%. Other elements refer to Fe, Si, Cr, and Al.
The following friction reduction mechanism is proposed considering the obtained results. Initially, the ionic liquid molecules adsorb on the submerged surfaces (Figure 12a). It was confirmed by EDS analysis that the adsorption of PIL molecules occurs even on the intact surface. The rubbing process initiates a tribo-reaction between the metal and PIL. The adsorbed oleic acid anion most likely reacts with the metal surface, forming a metal soap layer on the plate (Figure 12b) [27,28]. This layer separates interacting surfaces and prevents their direct contact. As a result, friction and wear reduction are achieved.
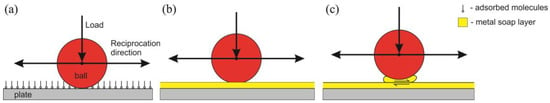
Figure 12.
Proposed lubrication mechanism of PIL in aqueous glycerol solution: (a)—running-in period; (b)—low-friction period; (c)—higher-friction period.
Further, the layer grows and becomes thicker while shearing between its layers occurs. At this point, part of the layer is attached to the ball surface, resulting in intense shearing (Figure 12c). This implies that shearing within the layer requires more energy than the sliding of the ball on the layer. As a result, the friction is increased. The explained process could be distinguished in the extended experimental repetitions from 1 to 4, where a sudden (duration ≈ 1 min) COF rise is observed (Figure 6). Although friction is higher in this period, the more intense wear does not occur because the layer separates interacting surfaces. This additional energy is consumed to shear the layer. Due to shearing, the contact temperature increases, leading to lower lubricating fluids’ viscosity (Figure 3) and disturbing the layer formation equilibrium. Thus, after some time, the layer vanishes from the ball and the friction decreases. The friction slope, which takes approximately five minutes, was observed in the COF variation curves (Figure 6). The proposed mechanism could also explain the low- and higher-friction interchanges while retaining the same COF values.
4. Conclusions
The investigated bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium oleate PIL demonstrated a good tribological response when it was used as an additive in an aqueous glycerol solution to lubricate a ruby-bearing steel friction pair. In light of the observed results, the following conclusions could be drawn:
- The bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium oleate PIL additive was soluble in the aqueous base fluid. With an increased concentration, the viscosity of the lubricating fluid was increased.
- Significant friction and wear reduction were achieved using the investigated PIL additive. At the concentration of 0.5%, 2.6- and 15.8-times friction and wear reductions were reached.
- The positive effect of the additive could be maintained for prolonged time intervals.
- The adsorption of ionic liquid molecules and formation of a metal soap layer were found to be responsible for the good tribological response.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.K.; Investigation, M.G., A.K. and J.T.; Methodology, R.K. and A.K.; Project administration, R.K.; Resources, R.K.; Supervision, R.K.; Validation, R.K., M.G. and A.K.; Visualization, J.T. and A.A.; Writing—original draft, R.K.; Writing—review and editing, R.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grant No. S-MIP-21-61 from the Research Council of Lithuania.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Holmberg, K.; Erdemir, A. Influence of Tribology on Global Energy Consumption, Costs and Emissions. Friction 2017, 5, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, X. Superlubricitive Engineering—Future Industry Nearly Getting Rid of Wear and Frictional Energy Consumption. Friction 2020, 8, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanola, A.; Khanna, N.; Kumar, K. A Critical Review on Liquid Superlubricitive Technology for Attaining Ultra-Low Friction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 165, 112626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C. Unlocking the Secrets behind Liquid Superlubricity: A State-of-the-Art Review on Phenomena and Mechanisms. Friction 2022, 10, 1137–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Björling, M.; Larsson, R.; Shi, Y. Controllable Superlubricity Achieved with Mixtures of Green Ionic Liquid and Glycerol Aqueous Solution via Humidity. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.; Warneke, H.; Webbert, H.; Rodriguez, J.; Austin, E.; Tokunaga, K.; Rajak, D.K.; Menezes, P.L. Water-Based Lubricants: Development, Properties, and Performances. Lubricants 2021, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najiha, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Yusoff, A.R. Environmental Impacts and Hazards Associated with Metal Working Fluids and Recent Advances in the Sustainable Systems: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1008–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartz, W.J. Ecotribology: Environmentally Acceptable Tribological Practices. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björling, M.; Bair, S.; Mu, L.; Zhu, J.; Shi, Y. Elastohydrodynamic Performance of a Bio-Based, Non-Corrosive Ionic Liquid. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreivaitis, R.; Gumbytė, M.; Kupčinskas, A.; Kazancev, K.; Ta, T.N.; Horng, J.H. Investigation of Tribological Properties of Two Protic Ionic Liquids as Additives in Water for Steel–Steel and Alumina–Steel Contacts. Wear 2020, 456–457, 203390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Jiménez, M.; Sanes, J.; Jiménez, A.-E.; Iglesias, M.; Bermúdez, M.-D. Ultra-Low Friction with a Protic Ionic Liquid Boundary Film at the Water-Lubricated Sapphire–Stainless Steel Interface. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximo, G.J.; B N Santos, R.J.; Lopes-da-Silva, A.; Costa, M.C.; A Meirelles, A.J.; Coutinho, A.P. Lipidic Protic Ionic Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 121, 3177–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Zhao, Q.; Ju, C.; Wang, X. The Interaction of Two Anticorrosive Ionic Liquid Additives on the Friction Properties of Water Lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2020, 141, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.D.; Jiménez, A.E.; Sanes, J.; Carrión, F.J. Ionic Liquids as Advanced Lubricant Fluids. Molecules 2009, 14, 2888–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Cai, M.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Q. Amino Acid Ionic Liquids as Anticorrosive and Lubricating Additives for Water and Their Environmental Impact. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Zhang, G.; Ding, T.; Xiang, X.; Li, F.; Ren, T.; Liu, S.; Zheng, L. Tribological Properties and Surface Interaction of Novel Water-Soluble Ionic Liquid in Water-Glycol. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, Z.; Zeng, X.; Ren, T.; de Vries, E.; van der Heide, E. Tribological Properties and Tribochemistry Mechanism of Sulfur-Containing Triazine Derivatives in Water-Glycol. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Ju, C.; Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Yang, C. Synergy between Two Protic Ionic Liquids for Improving the Antiwear Property of Glycerol Aqueous Solution. Tribol. Int. 2020, 141, 105731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J. Controllable Superlubricity of Glycerol Solution via Environment Humidity. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11924–11930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, F.J.; Avilés, M.D.; Nakano, K.; Tadokoro, C.; Nagamine, T.; Bermúdez, M.D. Diprotic Ammonium Palmitate Ionic Liquid Crystal and Nanodiamonds in Aqueous Lubrication. Film Thickness and Influence of Sliding Speed. Wear 2019, 418–419, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Liu, S.; Guo, D.; Wang, Q.; Luo, J. Investigation of the Running-in Process and Friction Coefficient under the Lubrication of Ionic Liquid/Water Mixture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 6408–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Sol, I.; Gámez, A.J.; Rivero, A.; Iglesias, P. Tribological Performance of Ionic Liquids as Additives of Water-Based Cutting Fluids. Wear 2019, 426–427, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, M.-D.; Cao, V.D.; Sánchez, C.; Arias-Pardilla, J.; Carrión-Vilches, F.-J.; Sanes, J.; Kjøniksen, A.-L.; Bermúdez, M.-D.; Pamies, R. Effect of Temperature on the Rheological Behavior of a New Aqueous Liquid Crystal Bio-Lubricant. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Tian, J.; Bai, P.; Li, S.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, W.; Tian, Y. A Novel Comb-Typed Poly(Oligo(Ethylene Glycol) Methylether Acrylate) as an Excellent Aqueous Lubricant. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreivaitis, R.; Gumbytė, M.; Kupčinskas, A.; Kazancev, K.; Makarevičienė, V. Investigating the Tribological Properties of PILs Derived from Different Ammonium Cations and Long Chain Carboxylic Acid Anion. Tribol. Int. 2020, 141, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, V.H.; Mattedi, S.; Martin-Pastor, M.; Aznar, M.; Iglesias, M. Synthesis and Thermophysical Properties of Two New Protic Long-Chain Ionic Liquids with the Oleate Anion. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2010, 299, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furey, M.J.; Kajdas, C.; Kempinski, R. Applications of the Concept of Tribopolymerisation in Fuels, Lubricants, Metalworking, and “minimalist” Lubrication. Lubr. Sci. 2002, 15, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Chung, Y.-W. Encyclopedia of Tribology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).