Graphene-Family Lubricant Additives: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tribological Behaviors of Graphene-Family Additives
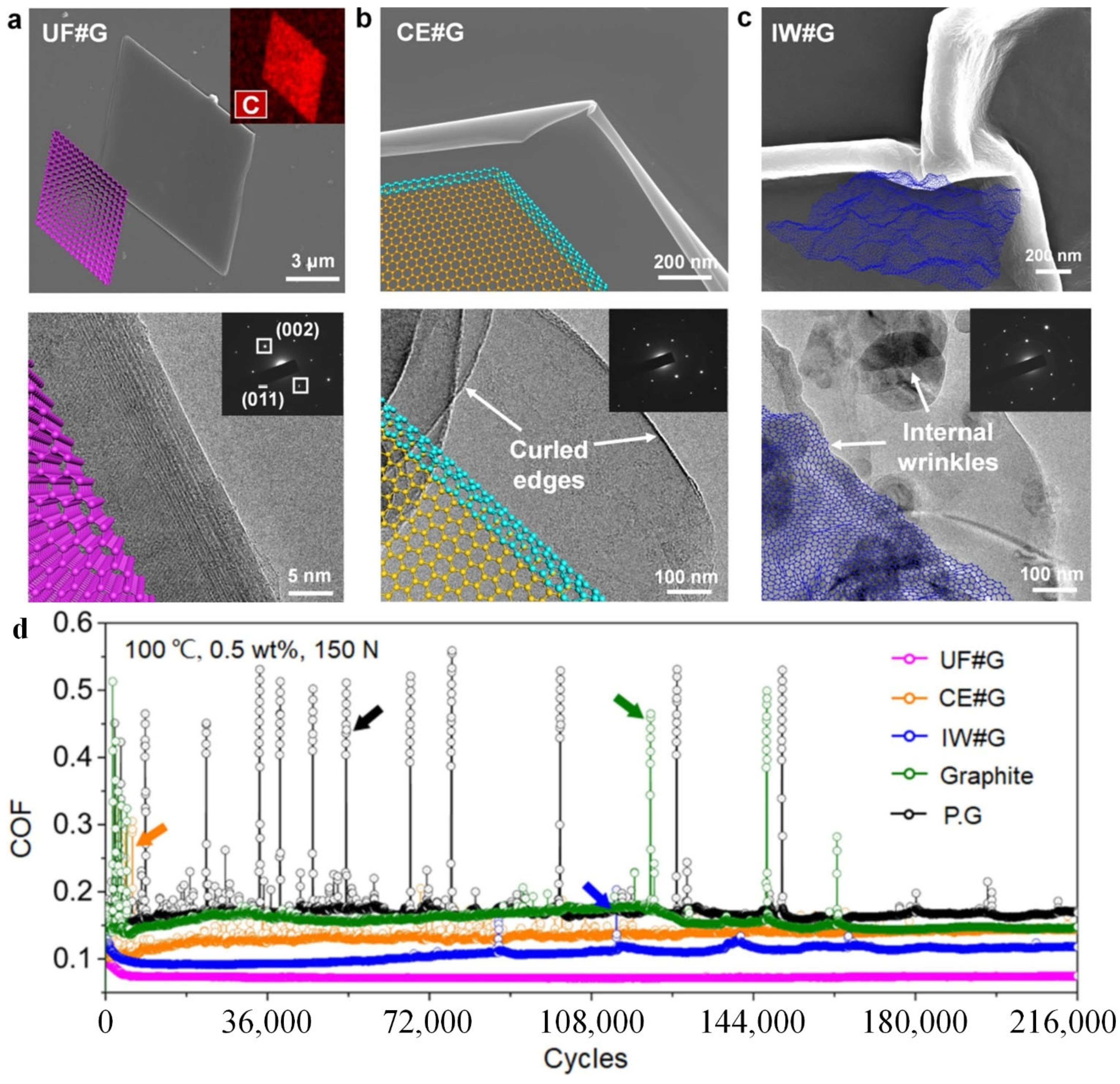
2.1. Pristine Graphene and Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
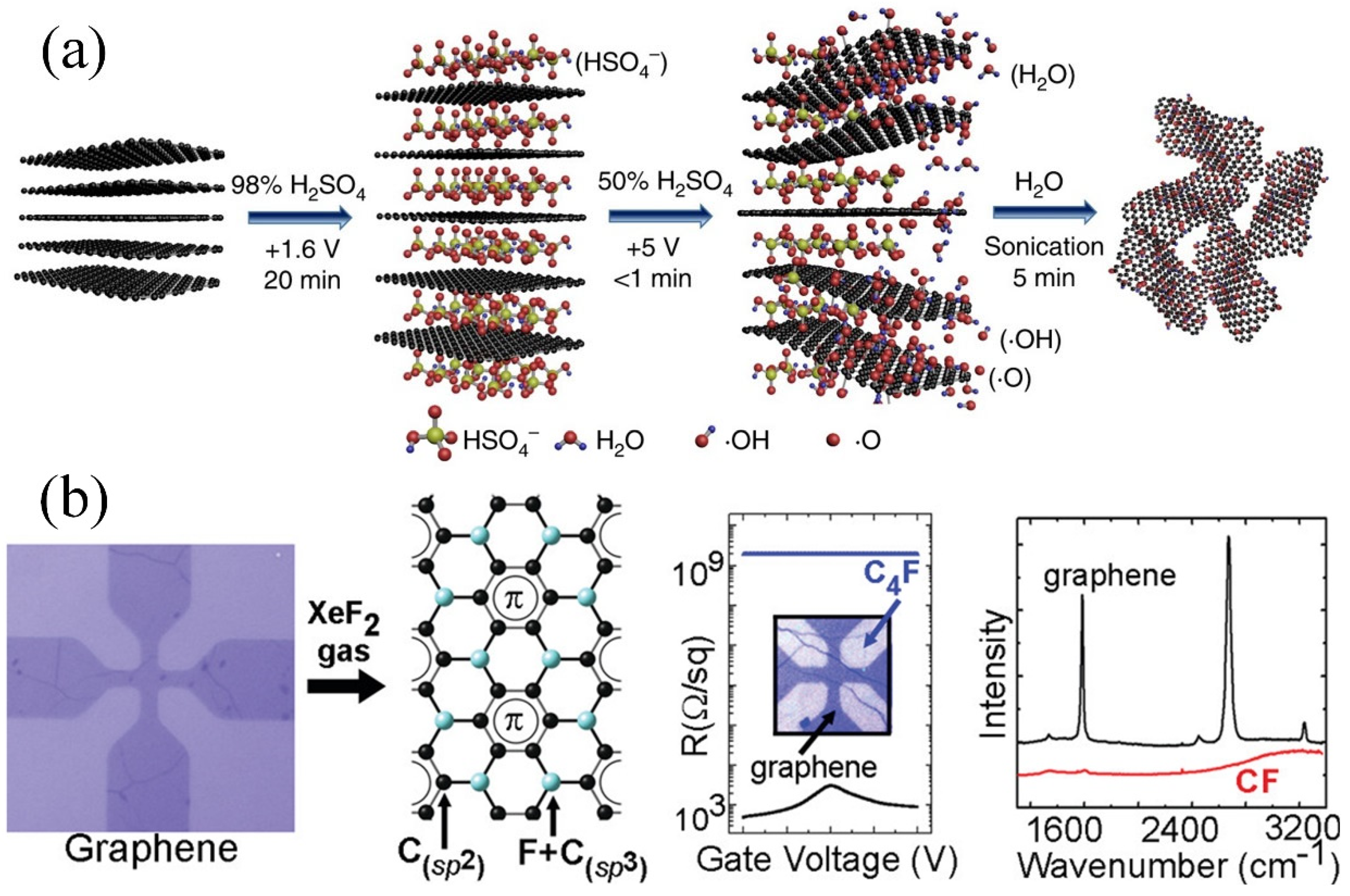
2.2. Functionalized Graphene
2.3. Synergy between Graphene-Family and Other Nanomaterials
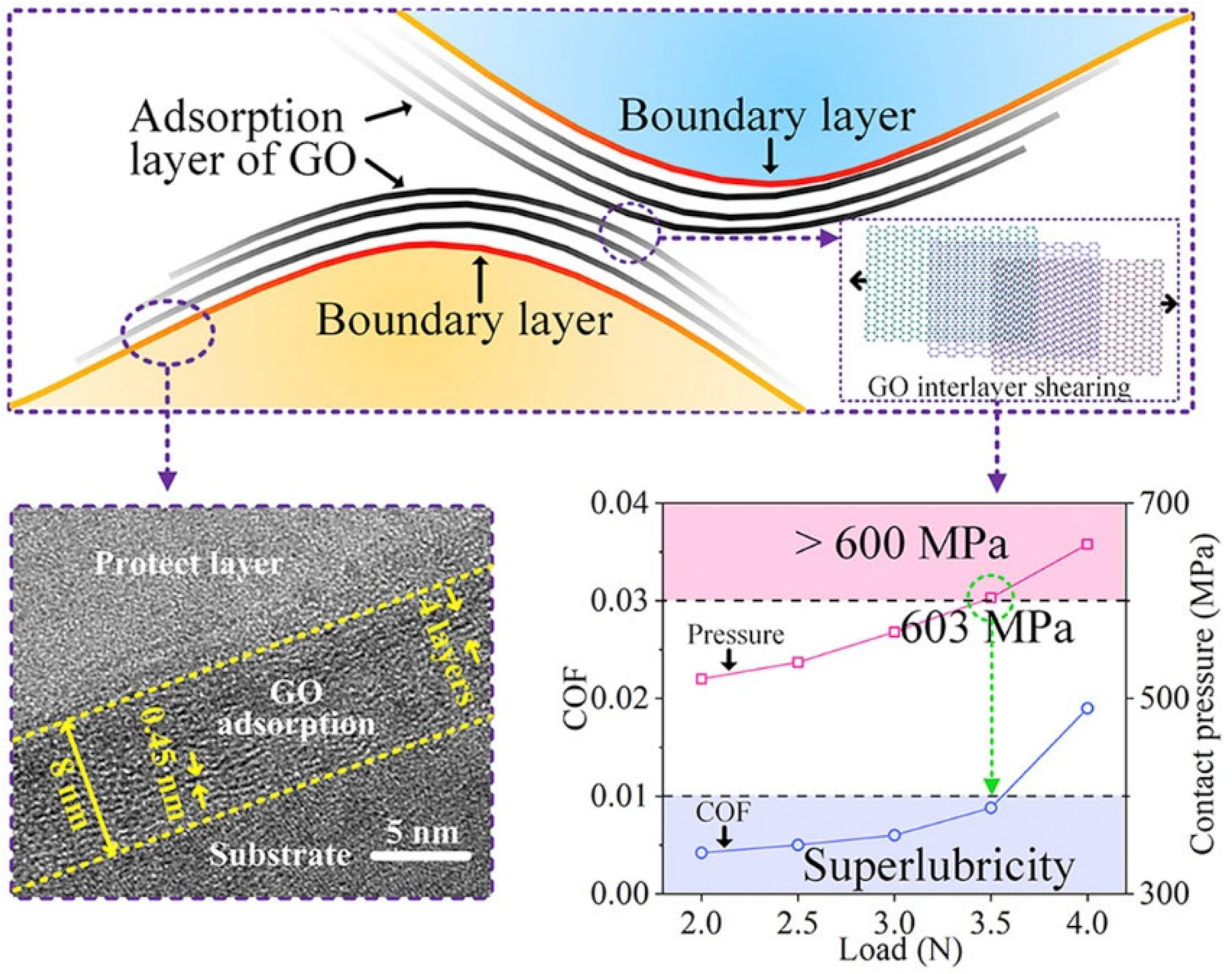
2.4. Lubrication Mechanisms of Graphene-Family Materials as Additives
2.5. Engineering Applications of Graphene-Family Materials as Additives
3. Conclusions and Perspectives
- For graphene-family additives, dispersion stability is an important issue related to the instability in oil or water-based lubrication systems. However, the high temperature introduced wear debris, and the material degradation all have potential influence on the long-term stability of graphene-family additives, which still need further investigation.
- The cost of graphene-family materials is still high for industrial applications. Developing a large-scale, low-cost preparation process is important for the practical application of graphene-family materials as additives.
- There is still a lack of widely accepted criteria for the designing of graphene-family materials as additives. For example, the optimized parameters such as particle size, layer numbers, types, and concentration of functional groups for specified application condition are still unclear. An in-depth investigation of the fundamental mechanisms and advanced techniques [163,164,165] for the guidance of designing and application of graphene-family materials as additives is needed in the future.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Ma, L. Origin of friction and the new frictionless technology—Superlubricity: Advancements and future outlook. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J. Superlubricity Behavior with Phosphoric Acid–Water Network Induced by Rubbing. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9413–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Liskiewicz, T.; Yerokhin, A.; Korenyi-Both, A.; Zabinski, J.; Lin, M.; Matthews, A.; Voevodin, A.A. Fretting wear behavior of duplex PEO/chameleon coating on Al alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 352, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Kato, T.; Yang, X.-A.; Wu, S.; Wang, R.; Nosaka, M.; Luo, J. Evolution of tribo-induced interfacial nanostructures governing superlubricity in a-C:H and a-C:H:Si films. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yi, S.; Ge, X.; Chen, X.; Luo, J. Enhancement of friction performance of nanocomposite fluorinated graphene and molybdenum disulfide coating by microdimple array. Carbon 2020, 167, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Deshmukh, S.A.; Sankaranarayanan, S.K.R.S.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Macroscale superlubricity enabled by graphene nanoscroll formation. Science 2015, 348, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, W. Nanodiamond plates as macroscale solid lubricant: A “non-layered” two-dimension material. Carbon 2022, 198, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Yi, S.; Ge, X.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J. Shear-Induced Interfacial Structural Conversion Triggers Macroscale Superlubricity: From Black Phosphorus Nanoflakes to Phosphorus Oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 31947–31956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Jiao, J.; Yang, K.; He, T.; Chen, R.; Zhu, W. Experimental and numerical exploration on the nonlinear dynamic behaviors of a novel bearing lubricated by low viscosity lubricant. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 182, 109349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhu, W. Theoretical and experimental exploration on the micro asperity contact load ratios and lubrication regimes transition for water-lubricated stern tube bearing. Tribol. Int. 2021, 164, 107105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Zeng, X. Water lubrication of graphene oxide-based materials. Friction 2022, 10, 977–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Sahu, A.K.; Rao, K.B. Development of Doped Carbon Quantum Dot-Based Nanomaterials for Lubricant Additive Applications. Lubricants 2022, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cai, M.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Soft-nanocomposite lubricants of supramolecular gel with carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 7654–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Fal’ko, V.I.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P.R.; Schwab, M.G.; Kim, K. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 2012, 490, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, X.; Li, J. Graphene lubrication. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 20, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Deshmukh, S.A.; Sankaranarayanan, S.K.R.S.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Extraordinary Macroscale Wear Resistance of One Atom Thick Graphene Layer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6640–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.-K.; Jang, H.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J. Chemical Vapor Deposition-Grown Graphene: The Thinnest Solid Lubricant. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5107–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Gao, L.; Yao, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xie, X.; Qiao, S.; Wang, G.; Ma, T.; Di, Z.; et al. Robust ultra-low-friction state of graphene via moiré superlattice confinement. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Kwon, S.; Park, J.Y.; Salmeron, M. Superlubric Sliding of Graphene Nanoflakes on Graphene. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gao, T.; Luo, J. Superlubricity of Graphite Induced by Multiple Transferred Graphene Nanoflakes. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Luo, J. Superlubricity of Graphite Sliding against Graphene Nanoflake under Ultrahigh Contact Pressure. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, T.; Bostwick, A.; Seyller, T.; Horn, K.; Rotenberg, E. Controlling the Electronic Structure of Bilayer Graphene. Science 2006, 313, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, D.C.; Nair, R.R.; Mohiuddin, T.M.G.; Morozov, S.V.; Blake, P.; Halsall, M.P.; Ferrari, A.C.; Boukhvalov, D.W.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Geim, A.K.; et al. Control of Graphene’s Properties by Reversible Hydrogenation: Evidence for Graphane. Science 2009, 323, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.H.; Hersam, M.C. Room-temperature molecular-resolution characterization of self-assembled organic monolayers on epitaxial graphene. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, A.; Ohta, T.; Seyller, T.; Horn, K.; Rotenberg, E. Quasiparticle dynamics in graphene. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Non-covalent functionalization of graphene sheets by sulfonated polyaniline. Chem. Comm. 2009, 13, 1667–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Otyepka, M.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Chandra, V.; Kim, N.; Kemp, K.C.; Hobza, P.; Zboril, R.; Kim, K.S. Functionalization of Graphene: Covalent and Non-Covalent Approaches, Derivatives and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6156–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Luo, J. Fluorinated Graphene: A Promising Macroscale Solid Lubricant Under Various Environments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 40470–40480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Luo, J. Enhancement of friction performance enabled by synergetic effect between graphene oxide and molybdenum disulfide. Carbon 2019, 154, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Luo, C.; You, S.; Chen, X.; Mo, Y.; Zhu, H. Research progress of surface-modified graphene-based materials for tribological applications. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Wei, Q.; Huang, K.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W. Green synthesis of graphene oxide by seconds timescale water electrolytic oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Burgess, J.S.; Junkermeier, C.E.; Badescu, S.C.; Reinecke, T.L.; Perkins, F.K.; Zalalutdniov, M.K.; Baldwin, J.W.; Culbertson, J.C.; Sheehan, P.E.; et al. Properties of Fluorinated Graphene Films. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3001–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel-Gaon, M.; Nguyen, N.H.A.; Sgroi, M.F.; Pullini, D.; Gili, F.; Mangherini, D.; Pruna, A.I.; Rosicka, P.; Sevcu, A.; Castagnola, V. In vitro and environmental toxicity of reduced graphene oxide as an additive in automotive lubricants. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6539–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, V.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Ramaprabhu, S. Graphene-Based Engine Oil Nanofluids for Tribological Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4221–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.-B.; Zhang, S.-W. The Tribological Properties of Multi-Layered Graphene as Additives of PAO2 Oil in Steel–Steel Contacts. Lubricants 2016, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.B.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Yue, W.; Zhu, M.H. Combined Effect of Textured Patterns and Graphene Flake Additives on Tribological Behavior under Boundary Lubrication. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanes, J.; Avilés, M.-D.; Saurín, N.; Espinosa, T.; Carrión, F.-J.; Bermúdez, M.-D. Synergy between graphene and ionic liquid lubricant additives. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, J.; He, Y.; Luo, J. Mild thermal reduction of graphene oxide as a lubrication additive for friction and wear reduction. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, T.; Shen, Y.; Lei, W.; Xu, X.; Liang, L.; Waqar, H.S.; Lin, B.; Tian, Z.Q.; Shen, P.K. Reduced friction and wear enabled by arc-discharge method-prepared 3D graphene as oil additive under variable loads and speeds. Wear 2020, 462–463, 203495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Chu, K.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Qi, S. Synergistic effects of 3D porous graphene and T161 as hybrid lubricant additives on 316 ASS surface. Tribol. Int. 2021, 161, 107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Luo, J. Influence of the micromorphology of reduced graphene oxide sheets on lubrication properties as a lubrication additive. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Gu, L.; Jian, R. Lubrication mechanism of graphene nanoplates as oil additives for ceramics/steel sliding components. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 16935–16942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiu, S.S.K.; Yusup, S.; Soon, C.V.; Arpin, T.; Samion, S.; Kamil, R.N.M. Tribological investigation of graphene as lubricant additive in vegetable oil. J. Phys. Sci. 2017, 28, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaumik, S.; Paleu, V.; Pathak, R.; Maggirwar, R.; Katiyar, J.K.; Sharma, A.K. Tribological investigation of r-GO additived biodegradable cashew nut shells liquid as an alternative industry lubricant. Tribol. Int. 2019, 135, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Cheng, J.; Huo, C.; Zhao, G. Improving the lubricity of a bio-lubricating grease with the multilayer graphene additive. Tribol. Int. 2020, 150, 106386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, E.; Westbroek, R.; Leckner, J.; Jacobson, S.; Rudolphi, Å.K. Grease-lubricated tribological contacts—Influence of graphite, graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide as lubricating additives in lithium complex (LiX)- and polypropylene (PP)-thickened greases. Wear 2021, 486–487, 204107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Li, Q.; Kalb, W.; Liu, X.-Z.; Berger, H.; Carpick, R.W.; Hone, J. Frictional Characteristics of Atomically Thin Sheets. Science 2010, 328, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Q.; Carpick, R.W.; Gumbsch, P.; Liu, X.Z.; Ding, X.; Sun, J.; Li, J. The evolving quality of frictional contact with graphene. Nature 2016, 539, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hou, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, X.-Q.; Li, Q. Tuning friction to a superlubric state via in-plane straining. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24452–24456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Sun, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Toward high load-bearing, ambient robust and macroscale structural superlubricity through contact stress dispersion. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 431, 133548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ju, P.; Ji, L.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. Toward Robust Macroscale Superlubricity on Engineering Steel Substrate. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J. High-quality ultra-flat reduced graphene oxide nanosheets with super-robust lubrication performances. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 135620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Xie, G. Ultralow concentration of graphene oxide nanosheets as oil-based lubricant additives. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 498, 143683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lai, W.; Liu, X. Toward Excellent Tribological Performance as Oil-Based Lubricant Additive: Particular Tribological Behavior of Fluorinated Graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28828–28838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, G.; Shit, S.; Hirani, H.; Kuila, T.; Murmu, N.C. Tribological behavior of dodecylamine functionalized graphene nanosheets dispersed engine oil nanolubricants. Tribol. Int. 2019, 131, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gan, C.; Han, Z.; Yan, H.; Chen, D.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Fan, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, M. High dispersivity and excellent tribological performance of titanate coupling agent modified graphene oxide in hydraulic oil. Carbon 2020, 165, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Fan, X.; Li, W.; Zhu, M.; Peng, J.; Li, H. In situ modified multilayer graphene toward high-performance lubricating additive. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24399–24409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, C.; Niu, Q.; An, C. In Situ Alkylated Graphene as Oil Dispersible Additive for Friction and Wear Reduction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 9029–9034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungse, H.P.; Gupta, K.; Singh, R.; Sharma, O.P.; Sugimura, H.; Khatri, O.P. Alkylated graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide: Grafting density, dispersion stability to enhancement of lubrication properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 541, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Ye, C.; Chen, Y.; Jin, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, H. Dependence of the lubrication enhancement of alkyl-functionalized graphene oxide and boric acid nanoparticles on the anti-oxidation property. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 649, 129521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Liang, T.; Chen, D.; Li, W.; Fan, X.; Tang, G.; Lin, B.; Zhu, M. Phosphonium-organophosphate modified graphene gel towards lubrication applications. Tribol. Int. 2020, 145, 106180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.A.; Bagheri, S. Highly oil-dispersed functionalized reduced graphene oxide nanosheets as lube oil friction modifier. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 222, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, A.; Mungse, H.P.; Sharma, O.P.; Singh, R.K.; Khatri, O.P. Chemically functionalized graphene for lubricant applications: Microscopic and spectroscopic studies of contact interfaces to probe the role of graphene for enhanced tribo-performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J. Modified graphene as novel lubricating additive with high dispersion stability in oil. Friction 2021, 9, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungse, H.P.; Khatri, O.P. Chemically Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Novel Material for Reduction of Friction and Wear. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 14394–14402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yi, X. Long-term stably dispersed functionalized graphene oxide as an oil additive. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 39230–39241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, A.; Mungse, H.P.; Khatri, O.P. Surface chemistry of graphene and graphene oxide: A versatile route for their dispersion and tribological applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 283, 102215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Liang, T.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M. Ultra-dispersive monolayer graphene oxide as water-based lubricant additive: Preparation, characterization and lubricating mechanisms. Tribol. Int. 2021, 155, 106768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ge, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q. PEGlated graphene as nanoadditive for enhancing the tribological properties of water-based lubricants. Carbon 2018, 137, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-J.; Li, N. Frictional behavior of oxide graphene nanosheets as water-base lubricant additive. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 105, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Kondo, M.; Nishina, Y.; Fujii, M. Anti-Wear Effect of Graphene Oxide in Lubrication by Fluorine-Containing Ionic Liquid for Steel. Tribol. Online 2015, 10, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, H.; Nishina, Y.; Alias, A.A.; Fujii, M. Tribological properties of monolayer graphene oxide sheets as water-based lubricant additives. Carbon 2014, 66, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Huang, S.; Yun, J.-H.; Jiang, Z.; Stokes, J.; Jiao, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, H. The pH-dependent structural and tribological behaviour of aqueous graphene oxide suspensions. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Fu, T.; Yue, Q.; Liu, H.; Ma, S.; Cai, M.; Zhou, F. Graphene oxide/brush-like polysaccharide copolymer nanohybrids as eco-friendly additives for water-based lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2021, 157, 106895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, L. High-performance lubricant additives based on modified graphene oxide by ionic liquids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 452, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Gan, C.; Li, X.; Feng, P.; Ma, X.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M. Electrochemical preparation of modified-graphene additive towards lubrication requirement. Tribol. Int. 2021, 161, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Fan, K. Bioinspired three-dimensional and multiple adsorption effects toward high lubricity of solvent-free graphene-based nanofluid. Carbon 2022, 188, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Chiashi, S.; Maruyama, S.; Choi, J. Macroscale tribological properties of fluorinated graphene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 432, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, S. Covalent Functionalization of Fluorinated Graphene and Subsequent Application as Water-based Lubricant Additive. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7483–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; He, Z.; Song, H.; Liang, H.; Liu, D.; Dong, C.; Jia, W. Fluorinated graphene oxide nanosheet: A highly efficient water-based lubricated additive. Tribol. Int. 2019, 140, 105867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Lai, W.; Gao, S.; Qin, J.; Liu, X. Towards enhanced tribological performance as water-based lubricant additive: Selective fluorination of graphene oxide at mild temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 531, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Wu, C.; Chang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Yu, C. Solvent-free preparation of hydrophilic fluorinated graphene oxide modified with amino-groups. Mater. Lett. 2019, 237, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, X.; Zheng, G.; Zeng, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, T.; Zhang, Y. Tribological performances of highly dispersed graphene oxide derivatives in vegetable oil. Tribol. Int. 2018, 126, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, V.; Kalyani; Umrao, S.; Rastogi, R.B.; Kumar, R.; Srivastava, A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Tribological Evaluation of TiO2-Reinforced Boron and Nitrogen co-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide Based Hybrid Nanomaterials as Efficient Antiwear Lubricant Additives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11698–11710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Guo, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, G. Significantly enhancing tribological performance of epoxy by filling with ionic liquid functionalized graphene oxide. Carbon 2018, 136, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Gu, L.; Song, B.; Wang, L. Investigation of the tribological behavior of graphene oxide nanoplates as lubricant additives for ceramic/steel contact. Tribol. Int. 2018, 128, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, X. Superlubricitive engineering—Future industry nearly getting rid of wear and frictional energy consumption. Friction 2020, 8, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J. Superlubricity of carbon nanostructures. Carbon 2020, 158, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Li, J.; Luo, R.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J. Macroscale Superlubricity Enabled by the Synergy Effect of Graphene-Oxide Nanoflakes and Ethanediol. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 40863–40870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J. Macroscale superlubricity under extreme pressure enabled by the combination of graphene-oxide nanosheets with ionic liquid. Carbon 2019, 151, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Chai, Z.; Shi, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, W. Liquid Superlubricity Enabled by the Synergy Effect of Graphene Oxide and Lithium Salts. Materials 2022, 15, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Chai, Z.; Shi, Q.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Functionalized graphene-oxide nanosheets with amino groups facilitate macroscale superlubricity. Friction 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Ge, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W. Quantum dots of graphene oxide as nano-additive triggers macroscale superlubricity with an extreme short running-in period. Mater. Today Nano 2022, 18, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; Ma, T.-B.; Hu, Y.-Z.; Wang, H. Atomic-scale friction in graphene oxide: An interfacial interaction perspective from first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 125436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; Ma, T.-B.; Hu, Y.-Z.; Wang, H.; Shao, T.-M. Ab Initio Study of the Friction Mechanism of Fluorographene and Graphane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 12520–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, T.; Colas, G.; Filleter, T. Effect of Humidity and Water Intercalation on the Tribological Behavior of Graphene and Graphene Oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22537–22544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, P.; Selyanchyn, R.; Tanaka, H.; Darekar, D.; Staykov, A.; Fujikawa, S.; Lyth, S.M.; Sugimura, J. Macroscale Superlubricity of Multilayer Polyethylenimine/Graphene Oxide Coatings in Different Gas Environments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27179–27187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Ge, X.; Yi, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J. Macroscale Superlubricity Achieved on the Hydrophobic Graphene Coating with Glycerol. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 18859–18869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Ding, S.; Luo, J. Macroscale superlubricity of Si-doped diamond-like carbon film enabled by graphene oxide as additives. Carbon 2021, 176, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Dearn, K.D.; Zheng, X.; Yao, L.; Hu, X. Synergistic lubricating behaviors of graphene and MoS2 dispersed in esterified bio-oil for steel/steel contact. Wear 2015, 342–343, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsadi, M.; Bagheri, S.; Ismail, N.A. Nanocomposite of functionalized graphene and molybdenum disulfide as friction modifier additive for lubricant. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 244, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Wu, X.; Zhao, G.; Wang, X. Nanosized MoS2 deposited on graphene as lubricant additive in polyalkylene glycol for steel/steel contact at elevated temperature. Tribol. Int. 2017, 110, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.A.; Chowdhury, Z.Z.; Johan, M.R.; Zulkifli, N.W.M. MoS2-Functionalized Graphene Composites—Potential Replacement for Lubricant Friction Modifier and Anti-Wear Additives. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Lou, W.; Zhao, G.; Wu, X.; Wang, X. MoS2 nanoparticles grown on carbon nanomaterials for lubricating oil additives. Friction 2021, 9, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S. One-pot synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/molybdenum disulfide heterostructures with intrinsic incommensurateness for enhanced lubricating properties. Carbon 2017, 115, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Geng, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Z. Synergistic Lubricating Behaviors of 3D Graphene and 2D Hexagonal Boron Nitride Dispersed in PAO4 for Steel/Steel Contact. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1901893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Sahoo, R.R. Covalently Linked Hexagonal Boron Nitride-Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites as High-Performance Oil-Dispersible Lubricant Additives. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 10941–10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J. Synergistic tribological behaviors of graphene oxide and nanodiamond as lubricating additives in water. Tribol. Int. 2019, 132, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, P.; Sobhan, C.B.; Chakravorti, S. Improved tribological behavior of lubricating oil dispersed with hybrid nanoparticles of functionalized carbon spheres and graphene nano platelets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 540, 148402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wu, Y.-p.; Li, Z.-y.; Cai, Z.-b. Tribological properties of WS2/graphene nanocomposites as lubricating oil additives. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14060–14068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Chen, G.; Huang, P. Lubricating performances of graphene oxide and onion-like carbon as water-based lubricant additives for smooth and sand-blasted steel discs. Friction 2020, 8, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, Y.; Su, F.; Chen, Y. Au/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Synthesized in Supercritical CO2 Fluid as Energy Efficient Lubricant Additive. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39549–39559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.; Jia, X.H.; Zhang, Z.Z. Facile synthesis of copper/polydopamine functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposites with enhanced tribological performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 324, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, P.; Li, W.; Luo, T.; Cao, B. Mono-dispersed Ag/Graphene nanocomposite as lubricant additive to reduce friction and wear. Tribol. Int. 2020, 146, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Liang, T.; Li, W.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M. Amine-terminated ionic liquid modified graphene oxide/copper nanocomposite toward efficient lubrication. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 491, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Ji, X.; Li, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/Cu nanoparticle composites and their tribological properties. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 26086–26093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.; Chen, M.; Xiao, C.; Huang, W.; Sundararajan, S. Microtribological behavior of Mo and W nanoparticle/graphene composites. Wear 2018, 414–415, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Su, F.; Chen, Y. Supercritical Fluid Synthesis and Tribological Applications of Silver Nanoparticle-decorated Graphene in Engine Oil Nanofluid. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Ni, J.; Li, H.; Shao, X. Synthesis, characterization and tribological properties of Cu/reduced graphene oxide composites. Tribol. Int. 2015, 88, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Su, F.; Chen, Y. Synthesis of nano-Cu/graphene oxide composites by supercritical CO2-assisted deposition as a novel material for reducing friction and wear. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Su, F.; Li, Z. Boundary and Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Behaviors of Nano-CuO/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite as an Efficient Oil-Based Additive. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10322–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; He, A.; Yun, J.-H.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Jiao, S.; Huang, H. Synergistic tribological performance of a water based lubricant using graphene oxide and alumina hybrid nanoparticles as additives. Tribol. Int. 2019, 135, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.J.R.A. Preparation of a reduced graphene oxide/zirconia nanocomposite and its application as a novel lubricant oil additive. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 91802–91812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Luo, J. In Situ Green Synthesis of the New Sandwichlike Nanostructure of Mn3O4/Graphene as Lubricant Additives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 36931–36938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, W.; Yan, T.; Liang, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X. Tribological performances of copper perrhenate/graphene nanocomposite as lubricating additive under various temperatures. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 100, 296–309. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Gao, L.; Xie, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Zu, G.; Ran, X. Tribological properties and anti-wear mechanism of ZnO@graphene core-shell nanoparticles as lubricant additives. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghani, W.; Karim, M.S.A.; Bagheri, S.; Amran, N.A.M.; Gulzar, M. Enhancing the Tribological Behavior of Lubricating Oil by Adding TiO2, Graphene, and TiO2/Graphene Nanoparticles. Tribol. Trans. 2019, 62, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ge, C.; Wang, C.; Li, S. Tribological behavior of graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanocomposites for additives in water-based lubricants. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2022, 30, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S. Preparation of a highly effective lubricating oil additive–ceria/graphene composite. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 47096–47105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G. Solvent-free ionic nanofluids based on graphene oxide-silica hybrid as high-performance lubricating additive. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 471, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Geng, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, G. Enhanced Tribological Performance of Aminated Nano-Silica Modified Graphene Oxide as Water-Based Lubricant Additive. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6444–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lei, W.; Tang, W.; Ouyang, T.; Liang, L.; Tian, Z.Q.; Shen, P.K. Synergistic friction-reduction and wear-resistance mechanism of 3D graphene and SiO2 nanoblend at harsh friction interface. Wear 2022, 488–489, 204175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yan, J.; Ji, H. Tribological Performance of an Imidazolium Ionic Liquid-Functionalized SiO2@Graphene Oxide as an Additive. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 50573–50583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Zhang, B.; Luo, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z. Preparation, characterization, and tribological properties of silica-nanoparticle-reinforced B-N-co-doped reduced graphene oxide as a multifunctional additive for enhanced lubrication. Friction 2021, 9, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Elomaa, O.; Johansson, L.-S.; Hannula, S.-P.; Koskinen, J. Lubricating properties of silica/graphene oxide composite powders. Carbon 2014, 79, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Tirth, V.; Kamel, B.M. Tribological characterization and rheology of hybrid calcium grease with graphene nanosheets and multi-walled carbon nanotubes as additives. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 6178–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, B.M.; El-Kashif, E.; Hoziefa, W.; Shiba, M.S.; Elshalakany, A.B. The effect of MWCNTs/GNs hybrid addition on the tribological and rheological properties of lubricating engine oil. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, T.; Tang, W.; Pan, M.; Tang, J.; Huang, H. Friction-reducing and anti-wear properties of 3D hierarchical porous graphene/multi-walled carbon nanotube in castor oil under severe condition: Experimental investigation and mechanism study. Wear 2022, 498–499, 204302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.; Hirani, H.; Kuila, T.; Murmu, N.C.J.N. Nanolubricants dispersed with graphene and its derivatives: An assessment and review of the tribological performance. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3458–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; D’Agostino, V.; Petrone, V.; Ciambelli, P.; Sarno, M. Graphene oxide nanosheets as effective friction modifier for oil lubricant: Materials, methods, and tribological results. J. ISRN Tribol. 2013, 2013, 425809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.-L.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Preparation, characterization, and tribological properties of oleic diethanolamide-capped zinc borate-coated graphene oxide composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 705, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. Modification of Graphene Platelets and their Tribological Properties as a Lubricant Additive. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, W. Multilayer Graphene as a Lubricating Additive in Bentone Grease. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 55, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Shen, Z.; Yi, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, S. In-situ exfoliated graphene for high-performance water-based lubricants. Carbon 2016, 96, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetto, D.; Restuccia, P.; Ballestrazzi, A.; Righi, M.C.; Rota, A.; Valeri, S. Surface passivation by graphene in the lubrication of iron: A comparison with bronze. Carbon 2017, 116, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ren, T.; de Vries, E.; van der Heide, E. The emulsifying and tribological properties of modified graphene oxide in oil-in-water emulsion. Tribol. Int. 2017, 105, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Cai, Z.-b.; Shen, M.-x.; Li, Z.-y.; Zhu, M.-h. Investigation of the tribology behaviour of the graphene nanosheets as oil additives on textured alloy cast iron surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, X.; Lee, K.-R. Tailoring the Nanostructure of Graphene as an Oil-Based Additive: Toward Synergistic Lubrication with an Amorphous Carbon Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43320–43330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, W.; Li, J.; Ma, M.; Luo, J. Molecular Origin of Superlubricity between Graphene and a Highly Hydrophobic Surface in Water. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 2978–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, W.; Tang, X.-Z.; Yang, L.; Bai, L. A molecular dynamics study on the synergistic lubrication mechanisms of graphene/water-based lubricant systems. Tribol. Int. 2022, 167, 107356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, K.-R.; Wang, A. Insights into friction dependence of carbon nanoparticles as oil-based lubricant additive at amorphous carbon interface. Carbon 2019, 150, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, A.; Lee, K.-R. Insights into Superlow Friction and Instability of Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbon/Fluid Nanocomposite Interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35173–35186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.; Koltonow, A.R.; He, X.; Jang, H.D.; Wang, Q.; Chung, Y.-W.; Huang, J. Self-dispersed crumpled graphene balls in oil for friction and wear reduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Sun, J.; Bao, Y. Preparation, characterization and tribological mechanism of nanofluids. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12599–12609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zin, V.; Agresti, F.; Barison, S.; Colla, L.; Fabrizio, M. Influence of Cu, TiO2 Nanoparticles and Carbon Nano-Horns on Tribological Properties of Engine Oil. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3590–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurutuza, A.; Marinelli, C. Challenges and opportunities in graphene commercialization. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, N.; Adidharma, H.; Fan, M. Graphene: A review of applications in the petroleum industry. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 167, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.K.; Khalid, M.; Javeed, A.; Rashmi, W.; Gupta, T.C.S.M.; Chan, A. Heat transfer and tribological performance of graphene nanolubricant in an internal combustion engine. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldin, V.; da Silva, L.R.R.; Houck, C.F.; Gelamo, R.V.; Machado, Á.R. Effect of Graphene Addition in Cutting Fluids Applied by MQL in End Milling of AISI 1045 Steel. Lubricants 2021, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, T.; Zhang, R.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, W. MQL milling of TC4 alloy by dispersing graphene into vegetable oil-based cutting fluid. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 99, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Li, G.; Ding, S.; Mo, J. Performance and mechanisms of graphene oxide suspended cutting fluid in the drilling of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. J. Manuf. Processes 2017, 29, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Dixit, A.R.; Tiwari, A.K.; Pramanik, A.; Mandal, A. Performance evaluation of alumina-graphene hybrid nano-cutting fluid in hard turning. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kałużny, J.; Świetlicka, A.; Wojciechowski, Ł.; Boncel, S.; Kinal, G.; Runka, T.; Nowicki, M.; Stepanenko, O.; Gapiński, B.; Leśniewicz, J.; et al. Machine Learning Approach for Application-Tailored Nanolubricants’ Design. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, B.; Wang, L.; Pu, H.; Chan, M.K.Y.; Chen, J. Understanding, discovery, and synthesis of 2D materials enabled by machine learning. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 1899–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Kordijazi, A.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Nosonovsky, M. Machine learning models of the transition from solid to liquid lubricated friction and wear in aluminum-graphite composites. Tribol. Int. 2022, 165, 107326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

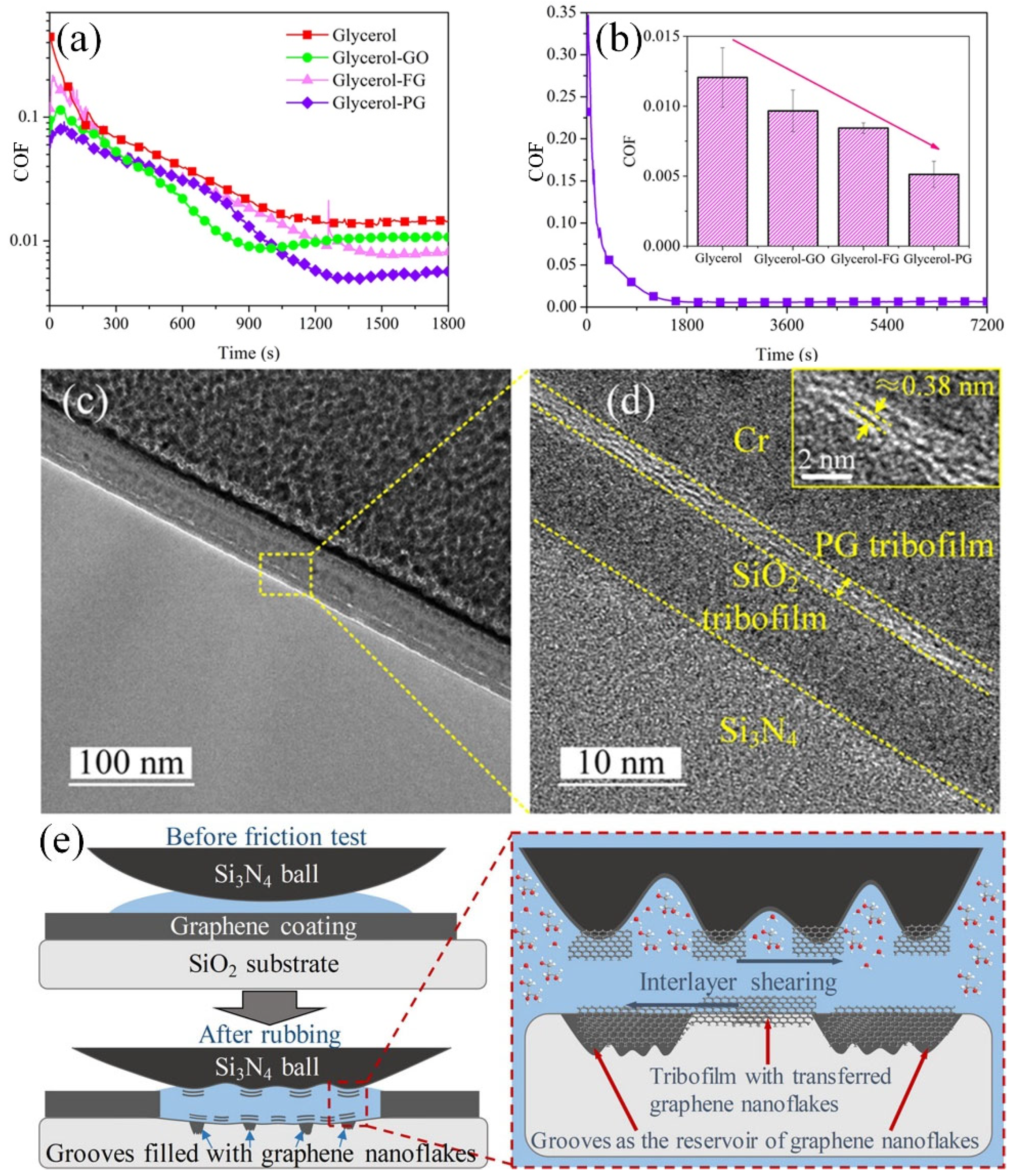
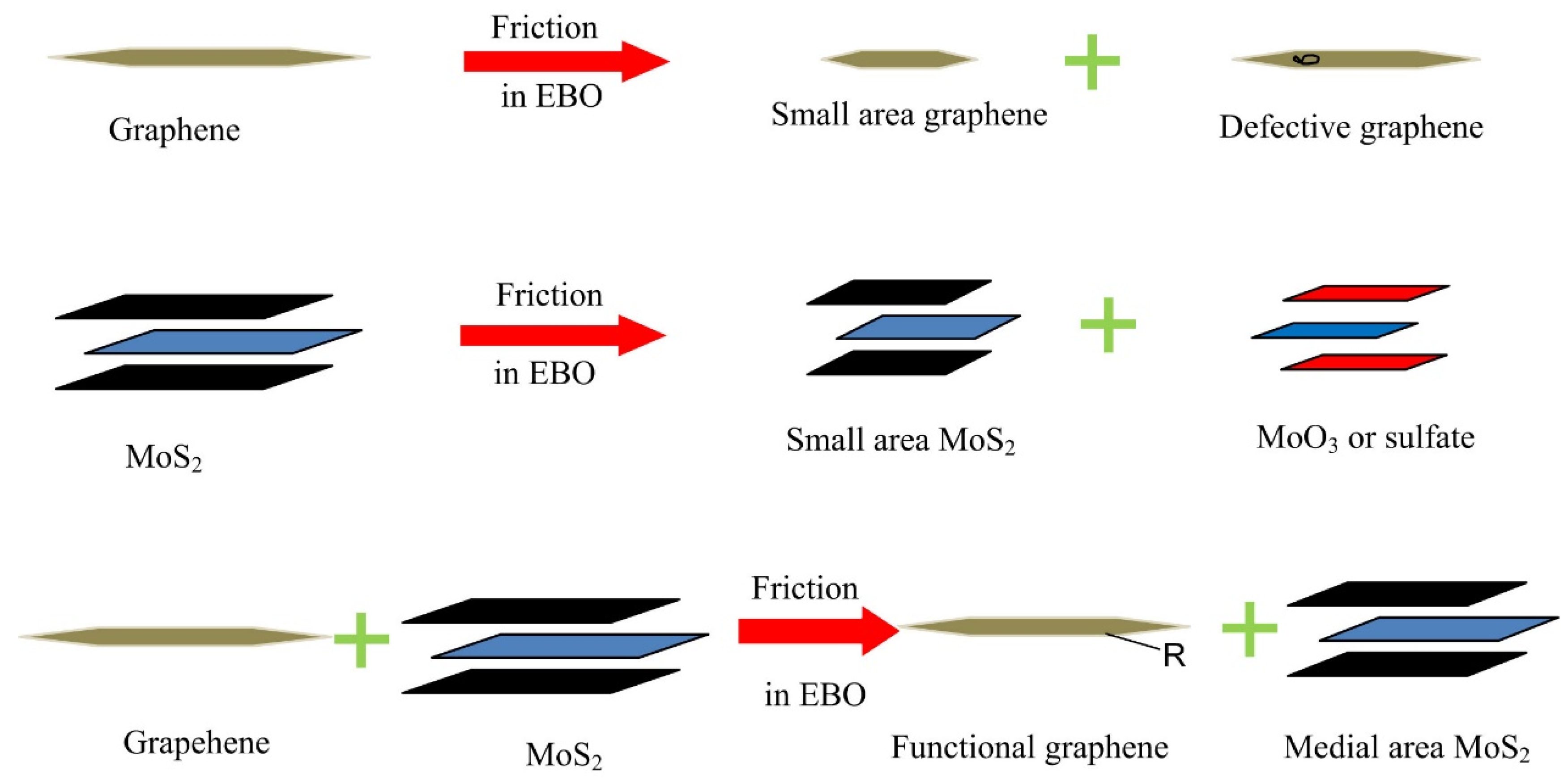


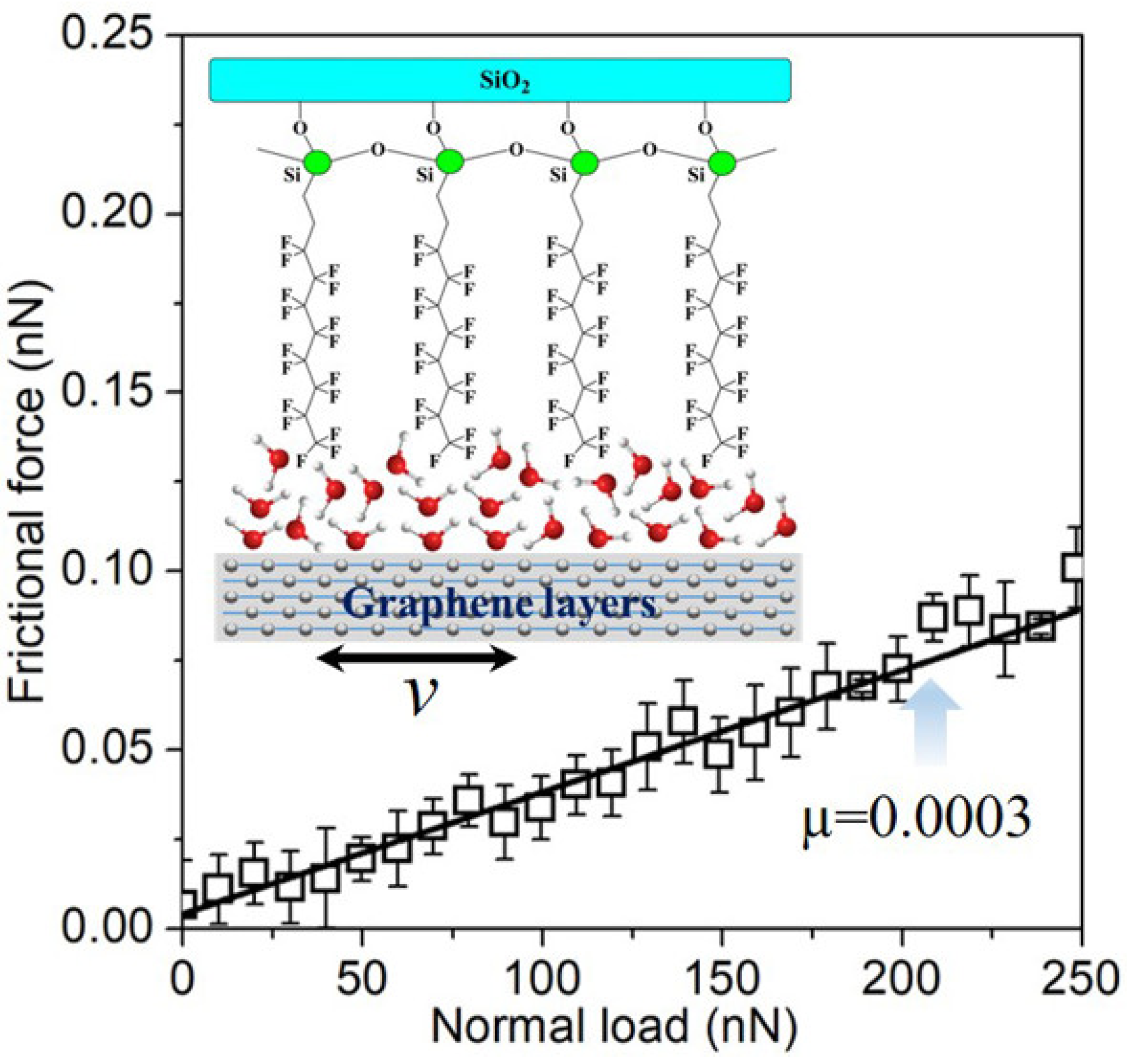
| Additive (Fraction), in Base Liquid | Test Mode | Specimen Details | Test Parameters | Results | Lubrication Mechanisms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COF Reduction | Wear Reduction | |||||
| GO (0.1 wt%), in 150 SN | Upper disk on the lower ball, Rotary | Ball: X45Cr13 steel, 52−54 HRC, Φ8 mm. Disk: X155CrVMo12-1 steel, 60 HRC, Ra 0.5 μm, Φ105 mm, | 0.05−2.1 m/s; 30, 60, 90 N; 25, 50, 80 °C | 30% | 27% | Deposited GO protective layer [140] |
| Zinc borate/GO composite (2 wt%), in 500 SN | Four-ball | — | 1200 rpm; 147 N; Test 2 h | 48.2% | 40% | Protective layer [141] |
| Cu nanoparticles decorated on polydopamine functionalized GO (0.1 wt%), in soybean oil | Ball on disk | Ball: GCr15 steel, Φ9.525 mm, 62 HRC. Disk: 45#steel | 100−500 rpm; 1−12 N; Test 0.5 h | 57% | 27% | Tribolayer [113] |
| Modified graphene (0.075 wt%), in 350 SN | Four-ball | GCr15A steel, Φ12.7 mm, 61 HRC, Test standard: ASTM D4172-82 | 1200 rpm; 147 N; 75 ± 2 °C; Test 1 h | 37% | — | Protective layer [142] |
| Single layer GO (0.06%), in water | Ball on three disks | Ball: Cr alloy steel, Ra 11.1 ± 0.4 nm, 64 HRC. Disk: AISI304 stainless steel, Ra 37.0 ± 6.2 nm, 92 HRB | 50 mm/s; 20 N; sliding 7.5 m | 44.4% | 17.1% | Tribolayer [73] |
| Multilayer graphene (0.1 wt%), in benton grease | Ball on disk, reciprocation | Ball: AISI52100 steel, Φ10 mm, 710 HV. Disk: AISI52100, 664 HV | 100−500 N; 10−50 Hz; Test 0.5 h | 10.4% | 25−50% | Tribolayer [143] |
| Graphene (0.01 wt%), in PAO4 | Ball on disk | Ball: GCr15 steel, Φ9.525 mm. Disk: Bronze contained elliptical dimple (area ratios: 0, 5%, 10%, 20%) | 5 mm/s; 5 N; Sliding 8 mm; 25, 60, 100, 150 °C Test 1.67 h | 78% | 90% | Tribolayer and texturing [36] |
| CeO2-decorated graphene (0.06 wt%), in paraffin oil | Reciprocation, test method: ASTM D6425-05 | Ball: GCr15 steel, Φ10 mm, Ra 20 nm, 62 HRC. Disk: GCr15 steel, 792 HV, Ra: 50 nm | 6 cm/s; 15 Hz; 50 N; 17% RH; Test 0.5 h | 52% | 1.5% | Transfer layer and nanoparticle spacer between graphene sheets [129] |
| ZrO2/rGO composite (0.06 wt%), in paraffin oil | Reciprocation, test method: ASTM D6425-05, | Ball: GCr15 steel, Φ10 mm, Ra 20 nm, 62 HRC. Disk: GCr15 steel, 790−820 HV, Ra 50 nm | 6 cm/s; 50−450 N; 25 ± 5% RH; Test 0.5 h | 56% | 6.4% | Protective layer and ball bearing [123] |
| Graphene (23.8−110 μg/mL), in water | Ball on disk, rotary | Ball: GCr15 steel, Φ9.53 mm. Disk: GCr15 steel | 62.8−251.2 mm/s; 2−15 N; 25 ± 5% RH; Test 0.5 h | 81.3% | 61.8% | Fluid adhesive layer and graphene protective layer [144] |
| Single layer graphene (1 mg/mL), in ethanol | Ball on disk | Ball: 100Cr6 steel, Φ4 mm. Disk: Iron (99.98% pure) and bronze (98% Cu and 2% Sn), Ra 30 nm | 100 mm/s; 1 N; 50% RH | 48% | — | Chemical passivation of iron by graphene [145] |
| Silica/GO composite (0.125 wt%), in EG | Pin on disk, rotary | Ball: AISI420 steel, Φ12.7 mm. Disk: AISI52100 steel, Φ40 mm, Ra < 0.1 μm | 0.008 m/s; 68.9 N; 50% RH; Test 1 h | 38% | 31% | Tribolayer and ball bearing [135] |
| Modified GO, in oil/water emulsion | Ball on ring | Ball: bearing steel, Φ25.4 mm, 65 HRC, Ra 30 ± 10 nm. Ring: AISI52100 steel, 65 HRC, Ra 100 ± 50 nm | 20−200 mm/s; 0.5 N; 25 ± 5% RH; sliding 100 m | 18% | 48% | Transfer layer, adsorption layer, and tribolayer; and the lubricity of emulsion droplets [146] |
| Graphene (0.01 wt%), in Span-80/PAO4 | Ball on disk, reciprocation | Ball: GCr15 steel, Φ4 mm, 766 HV. Disk: RTCr2 alloy cast iron, 220 HV, Ra ≤ 0.03 μm | — | — | 50% on normal surface, 90% on textured surface | Polishing, self-repairing, and tribolayer [147] |
| GO (2 mg/mL) in ethylene glycol aqueous solution | Ball on disk, rotary | Ball: Si3N4, Φ4 mm, Disk: SiO2 | 0.1 m/s; 3 N; 10−25% RH | Superlubricity with COF ≈ 0.004 | 99.5% compared to ethylene glycol aqueous solution | Adsorbed GO; low shear stress between GO layers and the interface between GO and ethylene glycol aqueous solution, and the formation of hydrated networks [89] |
| GO quantum dots (1 mg/mL) in ethylene glycol aqueous solution | Ball on disk, rotary | Ball: Si3N4, Φ20 mm, Disk: sapphire | 0.1 m/s; 15 N; 10−25% RH | Superlubricity with COF of 0.0068 | 90% | Formation of tribofilm containing GO quantum dots [93] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Shi, Q.; Ge, X.; Wang, W. Graphene-Family Lubricant Additives: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives. Lubricants 2022, 10, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10090215
Liu Y, Yu S, Shi Q, Ge X, Wang W. Graphene-Family Lubricant Additives: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives. Lubricants. 2022; 10(9):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10090215
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanfei, Shengtao Yu, Qiuyu Shi, Xiangyu Ge, and Wenzhong Wang. 2022. "Graphene-Family Lubricant Additives: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives" Lubricants 10, no. 9: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10090215
APA StyleLiu, Y., Yu, S., Shi, Q., Ge, X., & Wang, W. (2022). Graphene-Family Lubricant Additives: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives. Lubricants, 10(9), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10090215