Abstract
In the present work, Ni-10 wt.%TiO2 self-lubricating composite sinters were prepared via a powder metallurgy. Commercially available powder of nickel and non-commercial nanometric titanium dioxide (approx. 30 nm size) produced by the microwave method was used. The produced sinters were characterized by evenly distributed TiO2 particles in a nickel matrix and a hardness of approx. 110 HV5. Pin-on-disc wear tests at room temperature and 600 °C were carried out. Light Microscopy (LM), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), and X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) were used to characterize the wear mechanism of sintered materials. The coefficient of friction of the Ni-10 wt.% TiO2—Inconel®625 friction pair tested at room temperature was approx. 0.52. At the test temperature of 600 °C, the same friction pair had a friction coefficient of 0.35. The main wear mechanisms in dry friction conditions at 23 °C were cutting and ploughing. At the test temperature of 600 °C, formation of tribofilm on the surfaces of the friction pair was observed, which reduces the wear by friction.
1. Introduction
Friction is an indispensable phenomenon that occurs during the operation of machine parts. In many cases, it is an unfavorable occurrence and is responsible for the precipitated wear of machine parts and tools, leading to their failure, and thus to high exploitation costs. In order to reduce the frictional resistance of cooperating elements, oils and plastic greases are introduced [1,2]. Moreover, modifications with various additives of existing oils and plastic greases can be applied [3,4,5]. Nanoparticles used as additives in oil lubricants show in experimental results that they deposit on the friction surfaces and improve the tribological properties of the base oil, reducing wear, even at low concentrations [3,4,5,6]. The authors in the work [4] have made an extensive review of additives of nanometric solid lubricants to various liquids, including oils. They have shown that nanoparticles can operate as nano-sized ball bearings with a rolling and sliding motion, mend surface defects, micro-polish, and create low-shear tribofilms to reduce friction and wear loss. In the work [5], the authors have analyzed the effect of adding nanoparticles on the coefficient of friction (COF) for synthetic and bio-lubricating greases. Based on the literature review, they have found that the optimal concentration of nanoparticles of solid lubricants in greases resulted in a lower COF compared to greases without nanoparticle additives. In the literature, there are many studies concerning the use of TiO2 additive in various oils and its positive influence on tribological properties [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Based on tribological studies [14], the authors have found that nano-TiO2/fluorinated reduced graphene oxide as lubricant additives showed a low COF and excellent wear resistance. The influence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles as an additive to oils was investigated by Ilie and Covaliu [15]. The technology proposed by them solved the problem of poor solubility of TiO2 in oil, thus obtaining better anti-wear properties in the base oil. The lubrication mechanism of water-based nanolubricants containing nano-TiO2 in hot rolling of steel is attributed to the synergistic effect of the lubricating film, rolling, polishing, and mending [16]. Apart from metal oxides, the modification of oils with nanoparticles, e.g., titanium, is also observed [17]. Unfortunately, oils and greases may not be used in some applications, such as high temperature or high vacuum. Another disadvantage of this type of lubricant is the problems associated with environmental pollution, practically from the moment of their production up to their disposal. These problems do not apply to solid lubricants, which can be successfully used in demanding operating conditions such as high temperature. Solid lubricants that can operate at high temperatures include, among others, calcium and barium fluorides [18,19,20], calcium sulfates [21,22], and metal oxides [23,24]. The most commonly used solid lubricants that can be used at elevated temperatures are transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) such as MoS2 and WS2 as well as hBN and graphite [25,26,27]. Solid lubricants can be introduced directly into the friction junction or introduced from the material of the cooperating element while being released from it during friction and spreading on the surfaces of the friction pair. There are many methods of producing materials containing solid lubricants in the matrix or in the coatings. These include PVD techniques, thermal spraying, laser alloying, and powder metallurgy [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. The tribological properties of the sprayed TiO2/CNTs coatings were investigated in [32]. The addition of carbon nanotubes reduced the friction coefficient and was in the range of 0.50–0.55 compared to the values of 0.52–0.87 for the TiO2 coating itself. Li et al. [34] have produced NiCr-Mo-Bi2O3/TiO2 composites from micrometric-sized powders. They have conducted tribological tests at the temperature of 800 °C. They found that the excellent tribological properties were obtained due to the formation of the Bi4Ti3O12 phase on the worn surfaces. The coefficient of friction was 0.2–0.3, depending on the amount of added oxides Bi2O3/TiO2 (10.20.30 wt.%). In the work [35], the beneficial effect of TiO2 on tribological properties of the butt-welded AA5083 aluminum alloy was investigated. The authors have observed that the increased hardness, tensile strength, and wear resistance were mainly due to the uniform dispersion of TiO2 nanoparticles in the matrix and their anchoring of the grain boundaries. Zhao et al. [27] have used nano-Cu and h-BN solid lubricants. The produced laser-welded nickel-based coatings were characterized by increased wear resistance. In the literature, there is little research on the production of sinters with TiO2 and they concern commercially available oxides only. In the work [36], the authors have produced sinters containing the addition of nano-TiO2 oxide in the CoCr matrix in the amount of 2, 4, and 6 wt.%. It was found that with increasing TiO2 content, the hardness of the sinters increased, and their density decreased. The authors of the paper [37] have observed a positive effect on the tribological properties of the steel sinter with the addition of TiO2 oxide nanoparticles and in the TiO2-graphene system. Kumar R. et al. [38] have investigated the sliding wear resistance of metal–ceramic composites with a composition of 50 wt.% Ti—50 wt.% TiBw. The authors observed a synergistic lubricating behavior of TiO2 and boric acid B(OH)3 at temperatures of 700–900 °C. The formation of the glazed layer reduced the friction. The coefficients of friction were 0.88 at room temperature, 0.24 at 700 °C, and 0.18 at 900 °C. The review in [39] proves that the search for new self-lubricating materials working at high temperatures was a good direction. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a very well-known and widely researched material due to its chemical structure stability, biocompatibility, and favorable physical properties [35]. Moreover, the oxide is non-toxic and has bactericidal properties, and can prevent the development of bacterial flora on the surfaces of the cooperating surfaces, which may change the coefficient of friction. It is assumed that the beneficial tribological effect of TiO2 results from its structure at the atomic level and oxygen vacancies [37]. In this work, nickel sintered materials containing a solid lubricant in the form of titanium oxide TiO2 obtained by the powder metallurgy were produced. Nickel and nickel-based alloys are very important to modern industry. Due to their high corrosion resistance as well as heat resistance, they are used in aviation gas turbines, steam turbine power plants, nuclear power systems, chemical and petrochemical industries, as well as heat resistant applications, among others. Non-commercial, nanometric titanium oxide produced by the microwave method was used. The products obtained via microwave pathways are characterized by high yield and purity, because a shorter reaction time reduces the chance of undesirable side products. Most importantly, microwave heating is considered as an efficient way to control the heating in many processes since it requires less energy than conventional methods [40]. The wear mechanism of the examined sinters was determined using light microscopy (LM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersion spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Sinter
Commercially available nickel powder (99.7% purity, Sigma Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) was used for the matrix material of the sinters. Titanium (IV) chloride was used as the precursor for in situ microwave fabrication of TiO2. The preparation of the TiCl4 solution was carried out in distilled water in an ice-water bath according to the procedure previously reported by Zhang et al. [41]. The concentration of titanium (IV) chloride was adjusted to 1%. Subsequently, 1 g of urea was added to the 50 cm3 TiCl4 solution prepared in the previous step. During microwave heating, urea was decomposed into carbon dioxide and ammonia, which was a hydrolysis promoter and enabled in situ synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles during microwave irradiation. Following the urea dissolution, the solution was transferred to a microwave reactor (Discover 2.0, CEM, Matthews, NC, USA) and heated with a maximum power of 300 W until a temperature of 200 °C was reached; it was maintained at this temperature for 1 min. The obtained titanium dioxide was filtered and washed, and finally dried at 80 °C for 12 h. The morphologies of the used powders are shown in Figure 1; the micro-scale nickel powder has a dendritic structure, and TiO2 powder is in the form of agglomerates. TiO2 nanoparticles have a spherical shape and size between 20–45 nm. In the first step, the powder mixture (Ni and 10 wt.% TiO2) was tumble milled for 1 h. Then, the moldings were manufactured by pressing powder mixtures at a pressure of 1.17 GPa. In the next stage, sintering was carried out at 1000 °C for 3 h in a tube furnace under an argon atmosphere. Sinters were cooled in the furnace at 25 °C/h rate. The produced sinters had a height of 5 mm and diameter of 4 mm. Figure 2 shows the XRD patterns of pure nickel powder, nano-TiO2 powder, and sintered material.

Figure 1.
The nickel (a) and dioxide titanium (b) powders, SEM.
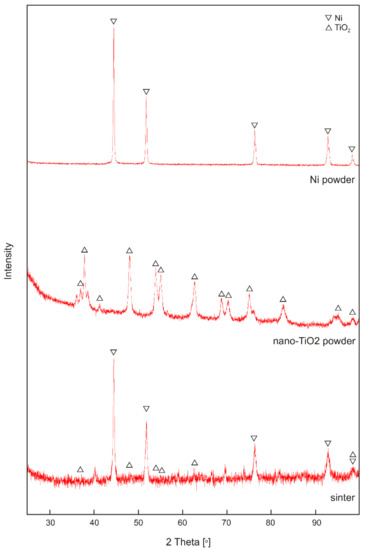
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of powders and sinter.
2.2. Microstructure and Hardness
The microstructure of the produced sinters was observed with a scanning electron microscope (Mira 3, Tescan, Brno, The Czech Republic). The Vickers hardness tester (Falcon 500, INNOVATEST, Maastricht, The Netherlands) was used to measure the hardness of the sinters. The Vickers hardness tests were carried out with a load of 5 kgf and a time of 15 s. Metallographic observations and hardness tests were carried out on metallographic samples prepared from sinters. The metallographic samples were ground with a sandpapers of decreasing grain size and finally polished. Ten hardness measurements were made.
2.3. Wear Tests
The friction wear tests of sinters at room temperature and 600 °C were used with a pin-on-disc tribometer (T-21, Lukasiewicz Research Network—IST, Radom, Poland). Inconel®625 nickel alloy with a diameter of 25.4 mm and a height of 4 mm was used as counter-sample. Friction tests under dry friction conditions were carried out at a load of 5 N for 1 h at a linear speed of 0.1 m/s. Each wear test was repeated three times. During the tests, the friction forces for the friction pairs (sintered material (pin)—Inconel®625 (disc) were recorded. The friction coefficients were determined from the Equation:
where: μ—friction coefficient, Ff—friction force [N]; Fl—load applied [N].
The results of the wear tests were presented in the form of graphs of the friction coefficients as a function of test time. The relative mass losses were calculated from the Equation:
where: Δm—mass loss [g], mi—initial mass [g], mf—final mass [g].
2.4. Tests of Wear Surface and of Worn Debris
The surface of the sintered materials and counter-samples after the tests, as well as worn debris, were tested with SEM (Mira3, Tescan, Brno, The Czech Republic) and the EDS X-ray microanalyzer (Ultim Max 65, Oxford Instruments, High Wycombe, UK). In order to limit the interaction volume, an accelerating voltage of 12 kV was used. A beam intensity (BI) of 15 and a dead time (DT) of 18–22% were used in the EDS analysis. Quantitative and qualitative tests of the chemical composition of the surface of sintered materials and worn debris were carried out. The element concentrations were also presented in the form of mono-color EDS maps and a color scale. In the case of the color scale, the colors correspond to the concentration of the selected element; white pixels indicate the highest concentration of the element and black areas correspond to zero concentration. Numerical values on these maps correspond to the number of counts. Phase composition tests were carried out on the surface of the sinters after the friction process was performed using a diffractometer (Empyrean, PANalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands) equipped with a copper lamp (X-ray wavelength λ = 1.54060 Å) and an X’Celerator detector. Diffractograms were recorded at room temperature, in an angular range of 25–100° 2 Theta, in steps of 0.0170°. The phase analysis of the obtained diffractograms was carried out in the HighScore program with the PDF-4 database.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 3 shows the microstructure of the molding and the sinter. They are characterized by an even distribution of TiO2 particles in the form of agglomerates. Their size reaches approx. 90 µm. In the BSE images, titanium oxides are visible as darker phases (Figure 3a,c–f). The observations were confirmed by examining the chemical composition using the EDS method in the form of a titanium concentration distribution map (Figure 3g,h). The lack of oxides in some places is probably due to their removal during the preparation of the metallographic sample. The microstructure of the nickel matrix before the sintering process is characterized by an adhesive connection of dendritic grains and titanium dioxide particles between them (Figure 3a,b). After the sintering process, the characteristic boundaries between the nickel grains are not visible (Figure 3c–f). This proves that the sintering process was carried out properly. The nickel matrix creates a continuous structure free of defects (i.e., in the form of cracks). The bond between the oxides and the matrix is only adhesive. Therefore, during the cooperating of the sinter and the counter-sample, free release of oxides will take place. The introduction of TiO2 nanoparticles to the soft matrix resulted in an increase in hardness from about 66 HV for pure nickel sinter [18] to about 110 HV for Ni-10 wt.% TiO2 sinter.
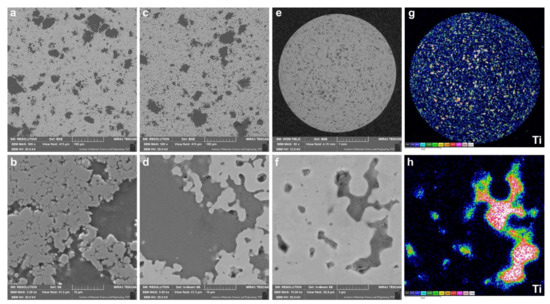
Figure 3.
Microstructure of the molding (a,b), sinter (c–f), and EDS distribution map of titanium concentration (g,h).
Figure 4 shows the test results of the friction coefficient as a function of time. The tests were carried out both at room temperature and at 600°C. In the case of the sinter cooperating with the Inconel®625 counter-sample at the test temperature of 23 °C, three stages are clearly visible in the figure. The first stage was the grinding-in phase of the friction pair, and the time of this period was approximately 500 s. In the second stage, fluctuations in the friction coefficient between 0.48 and 0.53 were observed. The average coefficient of friction during this period was 0.51. After the test time of approx. 2200 s, the fluctuations of the friction coefficient increased from approx. 0.46 to approx. 0.64. The average coefficient of friction in this stage was 0.52. Such changes in the friction coefficient result from complex wear mechanisms, which will be described later in this work. The nature of the changes in the coefficient of friction tested at 600 °C was different (Figure 3). In this case, three stages were also observed. The grinding-in stage was similar and lasted to approx. 500 s. Then, a reduction in the friction coefficient and its fluctuations in the range of 0.30–0.53 was observed. After the test time of approx. 1200 s, the friction coefficient stabilized at the level of approx. 0.30–0.38. The average coefficient of friction in this test stage was 0.35. Our previous research [18] showed that for the nickel-Inconel®625 friction pair tested at room temperature, the average coefficient of friction was 0.75; at the test temperature of 600 °C, it was 0.54. The coefficient of friction for the Ni-10 wt.% TiO2-Inconel®625 friction pair was also lower compared to the nickel sinters containing the solid lubricant in the form of calcium fluoride, which was 0.46. Similar coefficients of friction at the test temperature of 600 °C for CoCr sinters containing nano-TiO2 in a friction pair with Si3N4 were obtained by other authors [36]. Before and after the friction process, the samples and counter-samples were weighed to determine the change in their mass. In Figure 5, the results in the form of relative mass losses are shown. The relative mass loss for sinters and counter-samples tested at room temperature was 0.08149 and 0.00053, respectively. In the case of the test at the temperature of 600 °C, the relative mass loss of the sinters and counter-samples was lower and amounted to 0.02276 and 0.00002, respectively. The relative mass loss for the counter-sample at the test temperature of 600 °C was below zero. This proves that the mass of the counter-sample increased during the test, which was caused by the smearing of removed particles of the sinter, especially titanium dioxide nanoparticles, on the counter-sample surface. That is confirmed by the next test results presented below.
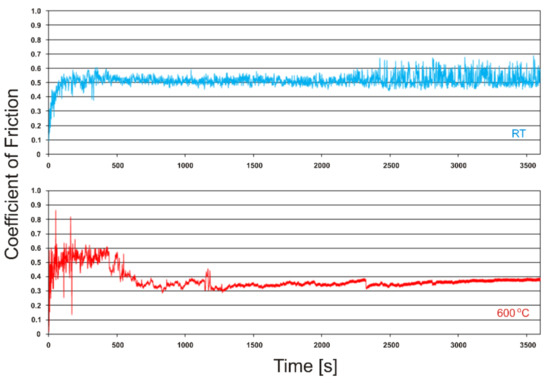
Figure 4.
Coefficient of friction vs. time of friction of self-lubricating composite cooperating with Inconel®625-alloy at room temperature and 600 °C.
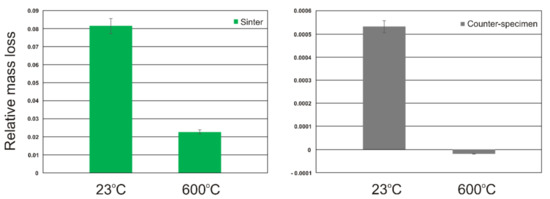
Figure 5.
Relative mass loss of sinters and counter-samples at room temperature and 600 °C.
Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 show the results of microscopic observations of the wear surfaces of both nickel sinters with TiO2 and counter-samples. The surface of the sinters after the friction wear test at room temperature is very developed (Figure 6a,b and Figure 7a–e). The main wear mechanism of the sinter tested at 23 °C is abrasion and ploughing. Moreover, a significant amount of worn debris is visible, in the form of black particles (Figure 6a,b). The SEM pictures taken in the backscattered electrons contrast (BSE) additionally show the areas of TiO2 located in the sinter. The surface appearance is different after the friction wear test at the temperature of 600 °C. In the LM image (Figure 6c,d) regular scratches are visible, and the surface has a regular blue-gray color. SEM observations (Figure 7g,h) at higher magnifications show slight delamination of the outer sinter surface layer. In BSE contrast, an almost uniform gray color of the surface is visible, which indicates the formation of a lubricating film on the surface. Areas with a lighter shade of gray are characterized by a smaller thickness of the tribofilm. The amount of worn debris is minimal, which is confirmed by the relative mass losses. The results of the observation of the counter-sample surface after the wear test at 23 °C are shown in Figure 6e,f and Figure 8. On the worn surface, a significant amount of worn debris was observed. The BSE image shows dark-colored worn debris corresponding to titanium dioxides, and worn debris with no considerable difference in color, which are wear products from sinter and Inconel®625. The ploughing and cutting are noted on the wear tracks of Inconel®625. In addition, smeared worn debris and–in some places–micro-polishing are visible. On the surface of the counter-sample, after testing at the temperature of 600 °C Figure 6g,h and Figure 9), micro-cutting and micro-polishing are visible. Observations in BSE contrast show the smearing of TiO2 on the worn surface. This is clearly visible in the form of darker shades of gray. The worn surface is smoother than the worn surface of Inconel®625 when tested at room temperature. In the wear track, there are also areas indicative of ploughing. The wear pattern also shows ploughing areas that were formed in the initial stage of the test, i.e., during the grinding-in period.
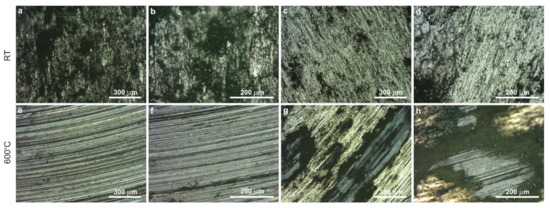
Figure 6.
Worn surface of sinters and counter-samples after friction wear tests at 23 °C—sinter (a,b), counter-sample (c,d) and at 600 °C—sinter (e,f), counter-sample (g,h), LM.
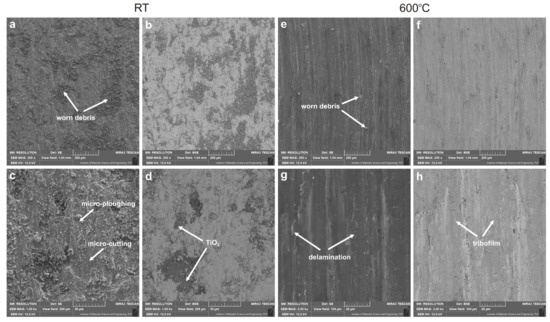
Figure 7.
Worn surface of sinters after friction wear tests at 23 °C (a–d), and at 600 °C (e–h), SEM.
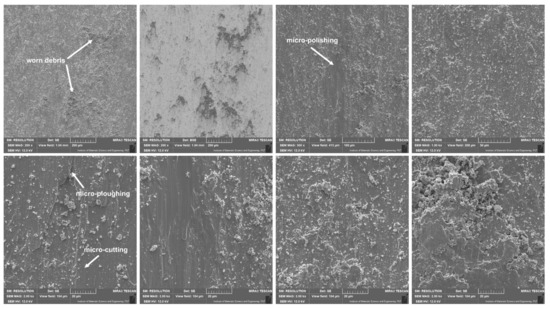
Figure 8.
Worn surface of counter-samples after friction wear tests at room temperature, SEM.
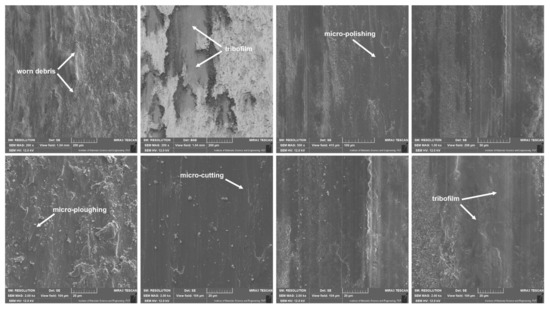
Figure 9.
Worn surface of counter-samples after friction wear tests at 600 °C, SEM.
The study of the chemical composition of EDS (Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14, Table 1) confirmed the formation of tribofilm on the surface of the sinters at the test temperature of 600 °C. On the sinter surface after wear test at room temperature (to 7.5 wt.%), an increased content of chromium was observed compared to the content of chromium on the worn surface at temperature of 600 °C (0.1 wt.%). This proves that the counter-sample had a significant role in the friction and abrasion process. Titanium was observed on the whole surface of the sinter, but mainly in loose TiO2 particles and anchored in the matrix. On the surface of the sinter tested at the temperature of 600 °C, the smearing of TiO2 is clearly visible. The distribution of titanium concentration and the quantitative analysis show the different thickness of the tribofilm formed during the wear test. The titanium content was between 0.5 and 3.8 wt. %. The distributions of the concentrations of elements on the surfaces of the counter-samples depending on the test temperature are shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13. The result of the quantitative analysis is presented in Table 1. Based on the SEM observations and EDS maps, as well as the quantitative analysis, it was found that for the counter-samples at room temperature after the wear test, TiO2 is present in its original form, i.e., nanoparticles and agglomerates. The formation of tribofilm in some places in the wear track was confirmed on the worn surface of the Inconel®625 alloy after the test at 600 °C. For this counter-sample, an increased content of nickel and oxygen is observed in the areas where there is also an increased content of titanium. It proves the smearing of the sintered material in the wear track, the release of TiO2 nanoparticles, and further formation of a tribofilm. Based on the XRD tests (Figure 15), it was found that during the testing of the Ni-10 wt.% TiO2—Inconel®625 friction pair at room temperature on the sinter surface, apart from the original components (TiO2, Ni), there is also the presence of phases composed of elements derived from the counter-specimen material, such as Cr2O3, NiMoO4 and γ. A similar phase composition was found on the sinter surface after the friction wear test at the temperature of 600 °C. In the case of Cr2O3 and NiMoO4 oxides, there is a slight shift of the peaks towards the lower angles. This can probably be attributed to a lower coefficient of friction, which leads to less local deformation caused by stress and thus to larger d-spacing of the crystal structure compared to sinter tested at room temperature. Figure 16 and Table 2 show the results of tests of worn debris. Based on the SEM observations and EDS tests (Figure 16a–d, Table 2), it was found that the worn debris for the friction pair tested at 23 °C were loose Inconel®625 particles and oxide particles. The particle size of the worn debris is as high as 200 µm. In case of a friction pair tested at 600 °C, the particle size is about 10–20 µm and they contain mainly nickel, titanium, and oxygen. This proves the low wear of counter-sample in this case. It should be noted that the wear of the sinter is low, which was confirmed by the relative mass losses test.
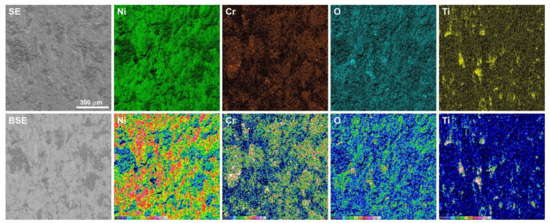
Figure 10.
EDS maps of element concentration distributions on the sinter surface after friction wear test at room temperature.
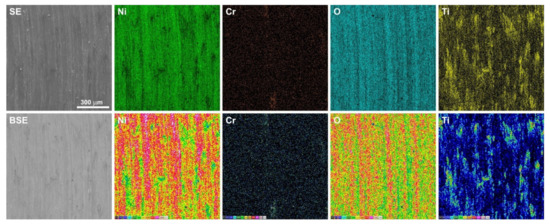
Figure 11.
EDS maps of element concentration distributions on the sinter surface after friction wear test at 600 °C.
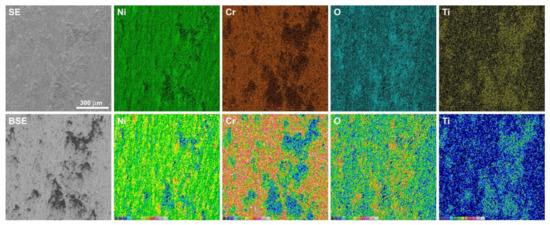
Figure 12.
EDS maps of element concentration distributions on the Inconel®625 surface after friction wear test at room temperature.
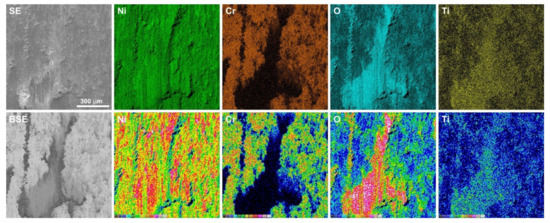
Figure 13.
EDS maps of element concentration distributions on the Inconel®625 surface after friction wear test at 600 °C.
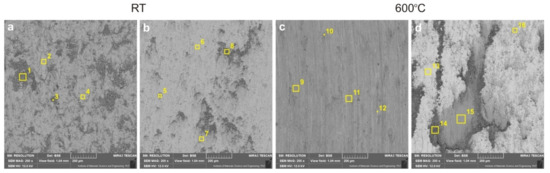
Figure 14.
Surface of friction pairs with marked areas of EDS analysis of sinters (a,c) and Inconel®625 (b,d).

Table 1.
The chemical composition of worn surfaces (according to Figure 14).
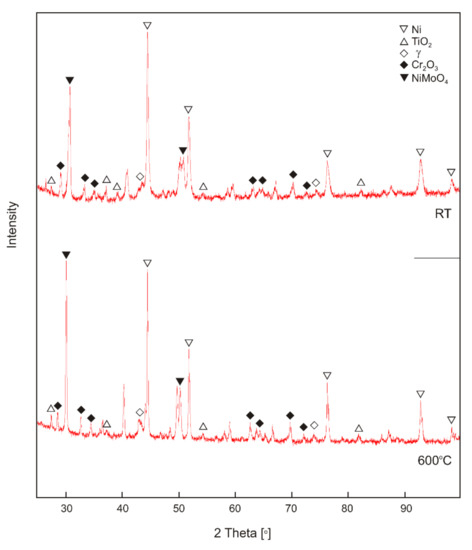
Figure 15.
XRD patterns of worn surfaces.
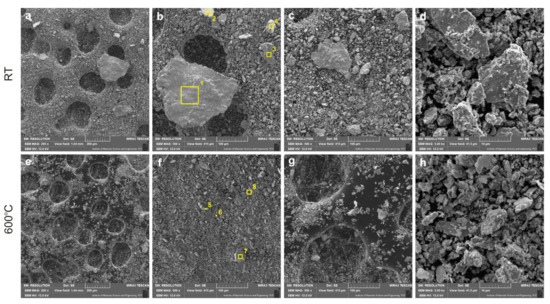
Figure 16.
Worn debris, test temperature 23 °C (a–d), 600 °C (e–h).

Table 2.
The chemical composition of worn debris (according to Figure 16b,f).
Based on the results, the wear mechanism of the Ni-10 wt.% TiO2—Inconel®625 friction pair was proposed (Figure 17). This mechanism can be divided into four stages. The first two stages were the same at the test temperature of 23 °C and 600 °C. In the initial stage, grinding-in occurs. The unevenness of the surface of counter-samples and sinters are sheared, and TiO2 nanoparticles are released. In addition, the surface of Inconel®625 was oxidized, and Cr2O3 and NiMoO4 oxides were formed and then removed during successive rotations of the pin on the disc and were part of the worn debris. After their removal, the surface was re-oxidized. The presence of these oxides was confirmed by XRD analysis. Then, the worn debris are crumbled into smaller particles followed by the further release of TiO2 particles from the sinter. In both tested temperatures, the process of mending the surfaces by filling the grooves with oxide is observed. In the case of the friction wear test at room temperature, in the third and fourth stages, two interactions of TiO2 nanoparticles are observed—some of them behave like balls in a rolling bearing, and some of them slide on the surface. However, there is no formation of tribofilm. The oxide particles together with other worn debris cause cutting, ploughing, and in some areas, polishing of the surfaces of the friction pair. Moreover, some worn debris are smeared on the friction pair surfaces, and further release of TiO2 occurs. In case of a friction pair operating at a temperature of 600 °C, the formation of a tribofilm composed of titanium oxides in the third stage and the continuous release of oxides from the particles of sinter smeared on the surfaces of the friction pair is observed. In addition, some of the TiO2 oxides and the Cr2O3 and NiMoO4 oxides formed during friction may be responsible for the rolling and sliding effect between the surfaces of the friction pair, which causes their micropolishing. In the fourth stage, tribofilm of various thickness and containing high dispersion worn debris is formed on the surface of the sinter. The proposed wear mechanism will allow for a better understanding of the phenomena occurring during the frictional operation of the Ni-10 wt.% TiO2 sinter—Inconel®625 friction pair and may be transferred to other pairs operating under dry friction conditions in the presence of TiO2.
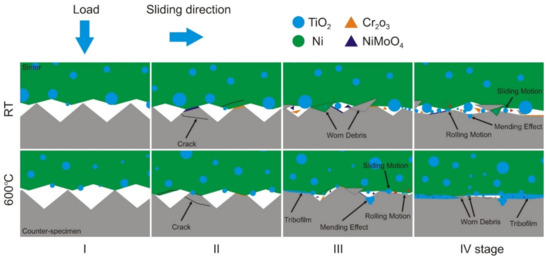
Figure 17.
Wear mechanism of the sinter (Ni-10 wt%TiO2)—Inconel®625 friction pair.
4. Conclusions
In this work, Ni-10 wt.% TiO2 sinters were produced by the powder metallurgy method. The influence of nano TiO2 addition on the tribological behavior and wear mechanism of the nickel sinter at room temperature and 600 °C was investigated. Non-commercial nanometric titanium oxide produced by the microwave method was used. Single particle size was about 30 nm. The following conclusions are drawn:
- The obtained sinters are characterized by an even distribution of TiO2 particles in the form of agglomerates. The nickel matrix creates a continuous structure that is free of cracks.
- The hardness of the sinters containing 10 wt.% nano-TiO2 was about 110 HV.
- The coefficient of friction of the Ni-10 wt.% TiO2—Inconel®625 friction pair tested at room temperature is approx. 0.52. At the test temperature of 600°C, the same friction pair has a friction coefficient of 0.35.
- No self-lubricating effect was observed at room temperature. The main wear mechanisms in dry friction conditions at 23 °C were cutting and ploughing.
- The sinter at the temperature of 600 °C has self-lubricating properties due to the presence of titanium oxide. On the surfaces of the friction pair, the formation of tribofilm was observed, which reduces the wear by friction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P.; formal analysis, A.P, M.K., M.T. and A.K.; funding acquisition, A.P.; investigation, A.P., M.K., M.T. and A.K.; methodology, A.P., M.K., M.T. and A.K.; project administration, A.P.; resources, A.P., M.K., M.T. and A.K.; supervision, A.P.; validation, A.P., M.K., M.T. and A.K.; visualization, A.P.; writing—original draft, A.P.; writing—review & editing, A.P., M.K., M.T. and A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Rector’s Grant of Poznan University of Technology, Poland, grant no. 0513/SIGR/4744.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Agocs, A.; Besser, C.; Brenner, J.; Budnyk, S.; Frauscher, M.; Dorr, N. Engine Oils in the Field: A Comprehensive Tribological Assessment of Engine Oil Degradation in a Passenger Car. Tribol. Lett. 2022, 70, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmaier, H. Increase Service Life for Rail Wheel Bearings—A Review of Grease Lubrication for This Application. Lubricants 2022, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Chauhan, P.; Mamatha, T.G. A review on tribological performance of lubricants with nanoparticles additives. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 25, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, F.; Barber, G.C.; Zou, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Q. Role of nano-sized materials as lubricant additives in friction and wear reduction: A review. Wear 2022, 490–491, 204206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Zahid, R.; Bhutta, M.U.; Khan, Z.A.; Saeed, A. A Review of Friction Performance of Lubricants with Nano Additives. Materials 2021, 14, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, N.; Jothi Saravanan, M.L.; Barathkumar, K.E.; Gokula Kannan, K.; Karthikeyan, R. Development and testing of nano particulate lubricant for worm gear application. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Noor, F.; Farooq, M.; Ong, H.C.; Gul, M.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Bashir, S.; Rizwanul Fattah, I.M.; et al. Effect of Additivized Biodiesel Blends on Diesel Engine Performance, Emission, Tribological Characteristics, and Lubricant Tribology. Energies 2020, 13, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamisa, A.H.; Azmi, W.H.; Yusof, T.M.; Ismail, M.F.; Ramadhan, A.I. Rheological Properties of TiO2/POE Nanolubricant for Automotive Air-Conditioning System. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2022, 90, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Yu, C.; Zhang, L.; Xie, G.; Guo, D.; Luo, J. Intelligent lubricating materials: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 202, 108450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.K.; Dhami, S.S.; Goyal, D.; Chauhan, A. Effect of TiO2 and CuO Based Nanolubricants on the Static Thermal Performance of Circular Journal Bearings. Tribol. Ind. 2021, 43, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, V.; Sanchez, K.; Gonzalez, R.; Alcoutlabi, M.; Ortega, J.A. The Performance of SiO2 and TiO2 Nanoparticles as Lubricant Additives in Sunflower Oil. Lubricants 2020, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suryawanshi, S.R.; Pattiwar, J.T. Tribological performance of commercial Mobil grade lubricants operating with titanium dioxide nanoparticle additives. Ind. Lubric. Tribol. 2019, 71, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghani, W.; Ab Karim, M.S.; Bagheri, S.; Amran, N.A.M.; Gulzar, M. Enhancing the Tribological Behavior of Lubricating Oil by Adding TiO2, Graphene, and TiO2/Graphene Nanoparticles. Tribol. Trans. 2019, 62, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ci, X. TiO2 Nanoparticle/Fluorinated Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheet Composites for Lubrication and Wear Resistance. ASC Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 2, 8732–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, F.; Covaliu, C. Tribological Properties of the Lubricant Containing Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles as an Additive. Lubricants 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Luo, L.; Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Jiao, S.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Z. Performance Evaluation and Lubrication Mechanism of Water-Based Nanolubricants Containing Nano-TiO2 in Hot Steel Rolling. Lubricants 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saini, V.; Bijwe, J.; Seth, S.; Ramakumar, S.S.V. Unexplored solid lubricity of Titanium nanoparticles in oil to modify the metallic interfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 580, 152127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotkowiak, M.; Piasecki, A.; Kulka, M. The influence of solid lubricant on tribological properties of sintered Ni–20%CaF2 composite material. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 17103–17113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yi, M.; Xu, C.; Xiao, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Mechanical property and cutting performance of (W,Ti)C based ceramic composites with the addition of nano-sized CaF2. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 99, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Luo, L.; Guo, F.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, P. High-temperature tribological behavior of Mo and BaF2 added Cr3C2-NiCr matrix composite. Ind. Lubric. Tribol. 2020, 72, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, P.J.; Zabinski, J.S. Sulfate based coatings for use as high temperature lubricants. Tribol. Lett. 1999, 7, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Ouyang, J.; Korenaga, A.; Umeda, K.; Sasaki, S.; Yoneyama, Y. High-Temperature Tribological Properties of Al2O3-X (X: BaCrO4, BaSO4 and CaSO4) Spark-Plasma-Sintered Composites Containing Sintering Additives. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 2614–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.; Jia, J.; Chen, T.; Xin, H.; Shi, Y.; He, N.; Feng, X.; Shi, P.; Lu, C. High temperature tribological behaviors and wear mechanisms of NiAl-MoO3/CuO composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 395, 125910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, S.; Zhou, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, R. Tribological properties of TiAl-Ag-ZnO self-lubricating composites from room temperature to 800 °C. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 056233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Jiang, Y.; Hardell, J.; Prakash, B.; Fanget, Q.F. Influence of service temperature on tribological characteristics of self-lubricant coatings: A review. Front. Mater. Sci. 2013, 7, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, K.P.; Biasoli de Mello, J.D.; Klein, A.N. Self-lubricating composites containing MoS2: A review. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 280–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, K.; Yao, C.; Nie, P.; Huang, J.; Li, Z. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser cladded self-lubricating nickel-base composite coatings containing nano-Cu and h-BN solid lubricants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 359, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seynstahl, A.; Krauß, S.; Bitzek, E.; Meyer, B.; Merle, B.; Tremmel, S. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Tribological Behavior of Magnetron-Sputtered MoS2 Solid Lubricant Coatings Deposited under Industrial Conditions. Coatings 2021, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, A.; Kulka, M.; Kotkowiak, M. Wear resistance improvement of 100CrMnSi6-4 bearing steel by laser boriding using CaF2 self-lubricating addition. Tribol. Int. 2016, 97, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, A.; Kotkowiak, M.; Kulka, M. Self-lubricating surface layers produced using laser alloying of bearing steel. Wear 2017, 376–377, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, A.; Kotkowiak, M.; Kulka, M. The effect of CaF2 and BaF2 solid lubricants on wear resistance of laserborided 100CrMnSi6-4 bearing steel. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 86, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, P.; Ma, G.; Xu, B.; Xing, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Tribological behavior of plasma sprayed carbon nanotubes reinforced TiO2 coatings. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 3660–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, A.; Kotkowiak, M.; Makuch, N.; Kulka, M. Wear behavior of self-lubricating boride layers produced on Inconel 600-alloy by laser alloying. Wear 2019, 426–427, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, y.; Li, C.; Kang, Y.; Hou, X.; Liu, F.; Zhao, S. Improved tribological performance of nickel based high temperature lubricating composites with addition of metallic oxides. Wear 2021, 480–481, 203938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjavadi, S.S.; Alipour, M.; Emamian, S.; Kord, S.; Hamouda, A.M.S.; Koppad, P.G.; Keshavamurthy, R. Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles incorporation to friction stir welded 5083 aluminum alloy on the microstructure, mechanical properties and wear resistance. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, G.; Kou, Z. Nano-TiO2 reinforced CoCr matrix wear resistant composites and high-temperature tribological behaviors under unlubricated condition. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H. M50 Matrix Sintered with Nanoscale Solid Lubricants Shows Enhanced Self-lubricating Properties Under Dry Sliding at Different Temperatures. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Antonov, M.; Liu, L.; Hussainova, I. Sliding wear performance of in-situ spark plasma sintered Ti-TiBw composite at temperatures up to 900 °C. Wear 2021, 476, 203663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Hussainova, I.; Rahmani, R.; Antonov, M. Solid Lubrication at High-Temperatures—A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budarin, V.L.; Shuttleworth, P.S.; Bruyn, M.D.; Farmer, T.J.; Gronnow, M.J.; Pfaltzgraff, L.A.; Macquarrie, D.J.; Clark, J.H. The potential of microwave technology for the recovery, synthesis and manufacturing of chemicals from bio-wastes. Catal. Today 2015, 239, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Gao, L.; Guo, J.K. Preparation and characterization of nanosized TiO2 powders from aqueous TiCl4 solution. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 11, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).