Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding
Abstract
1. Introduction
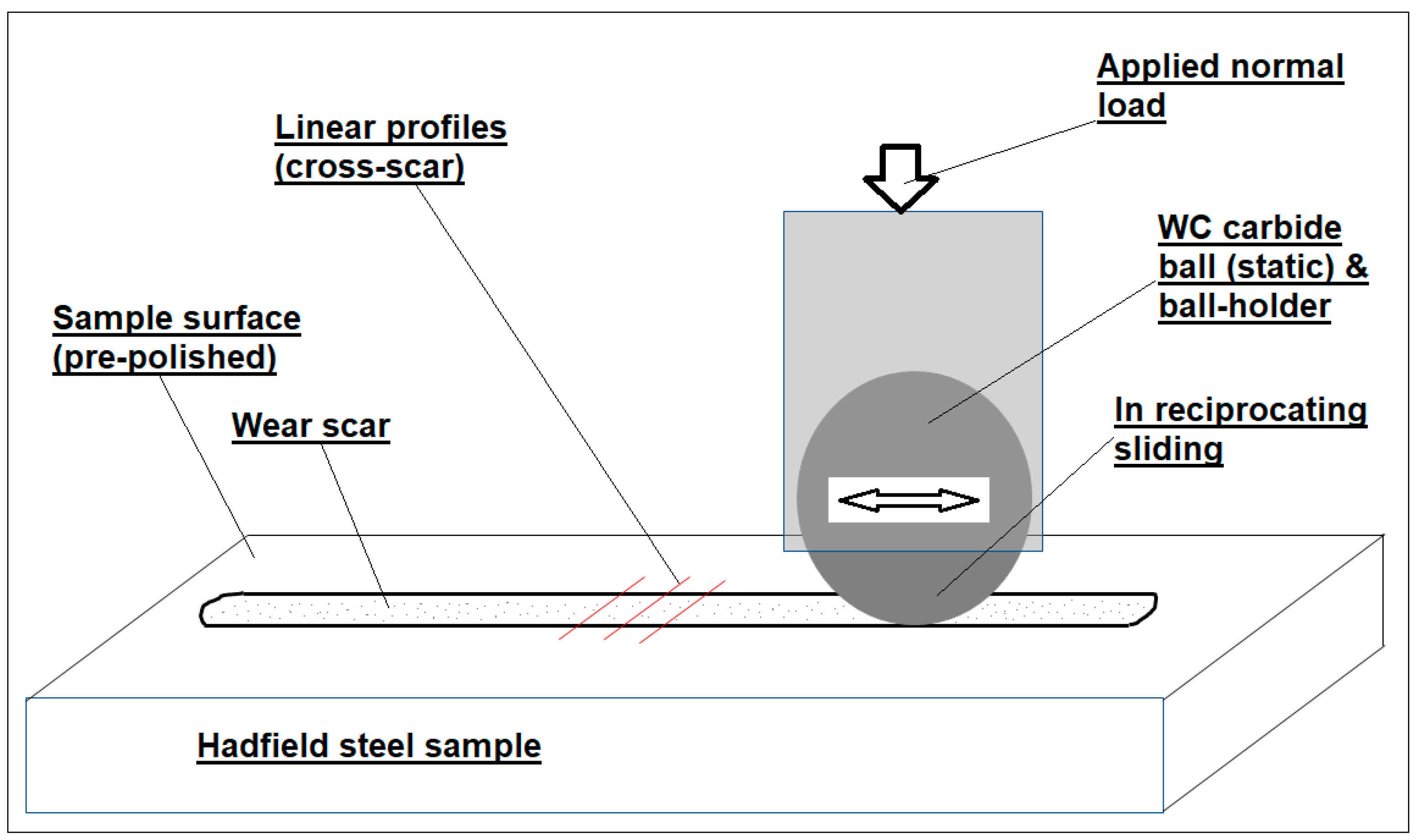
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results
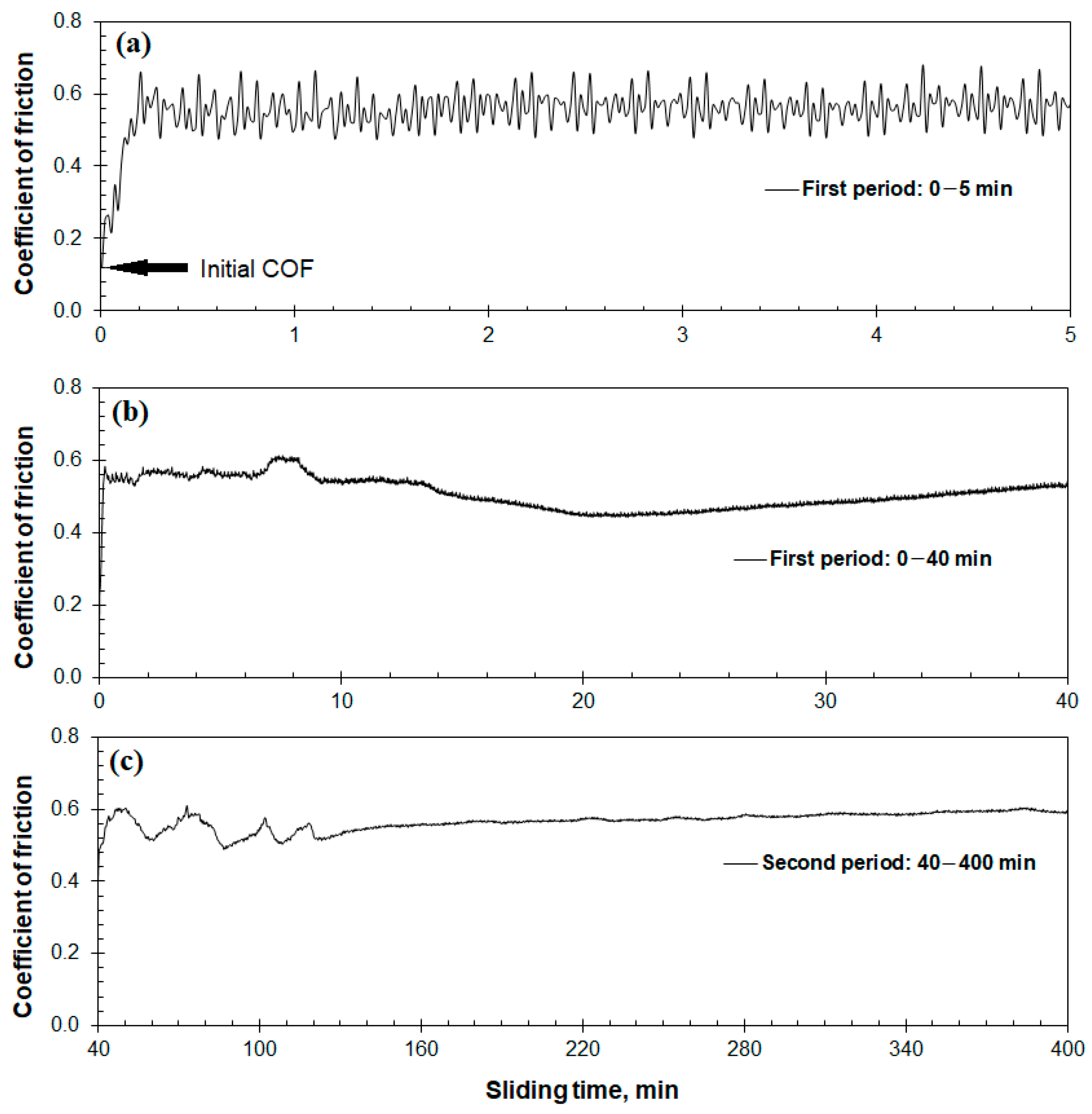
3.1. The Friction and Wear Properties
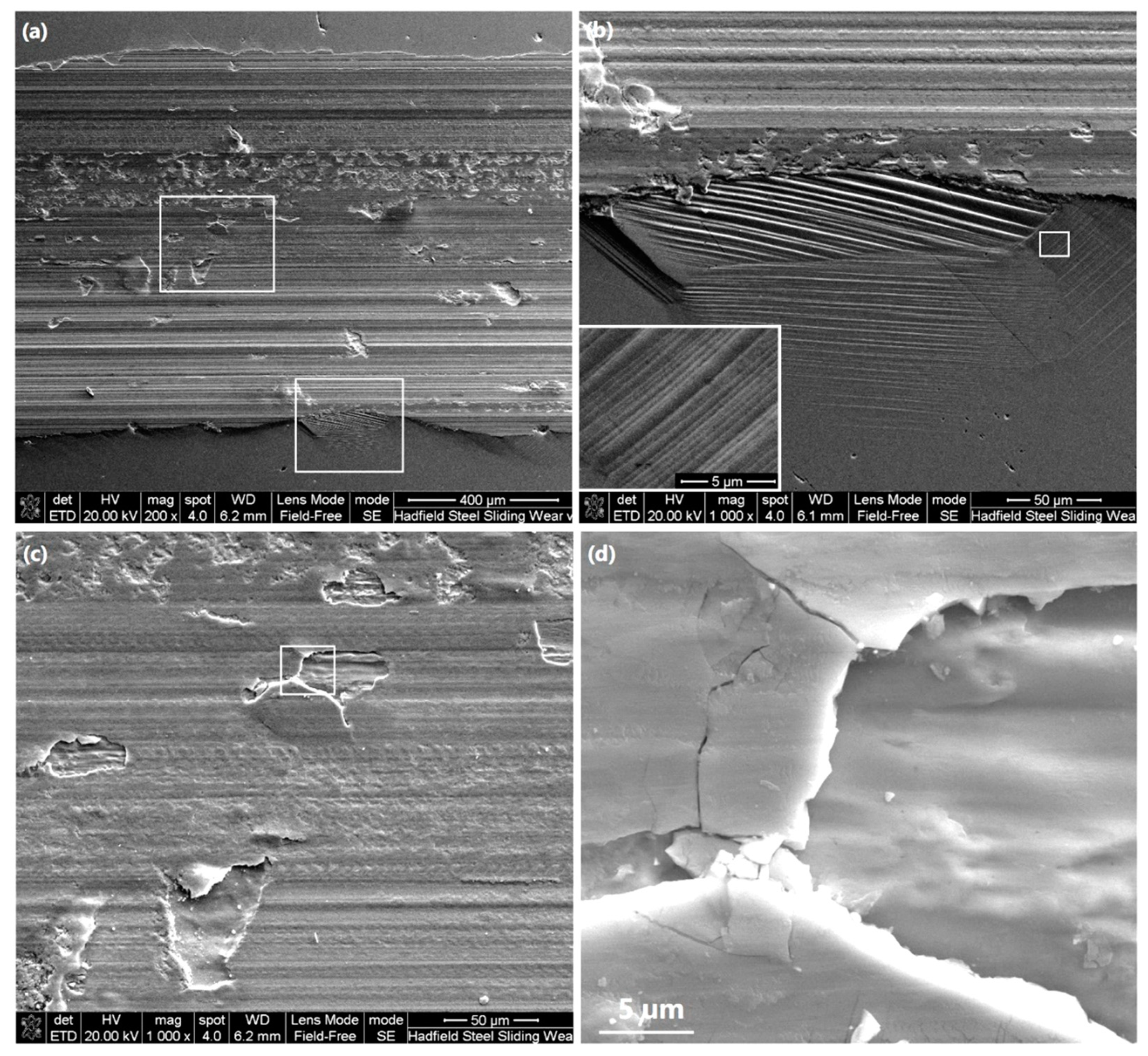
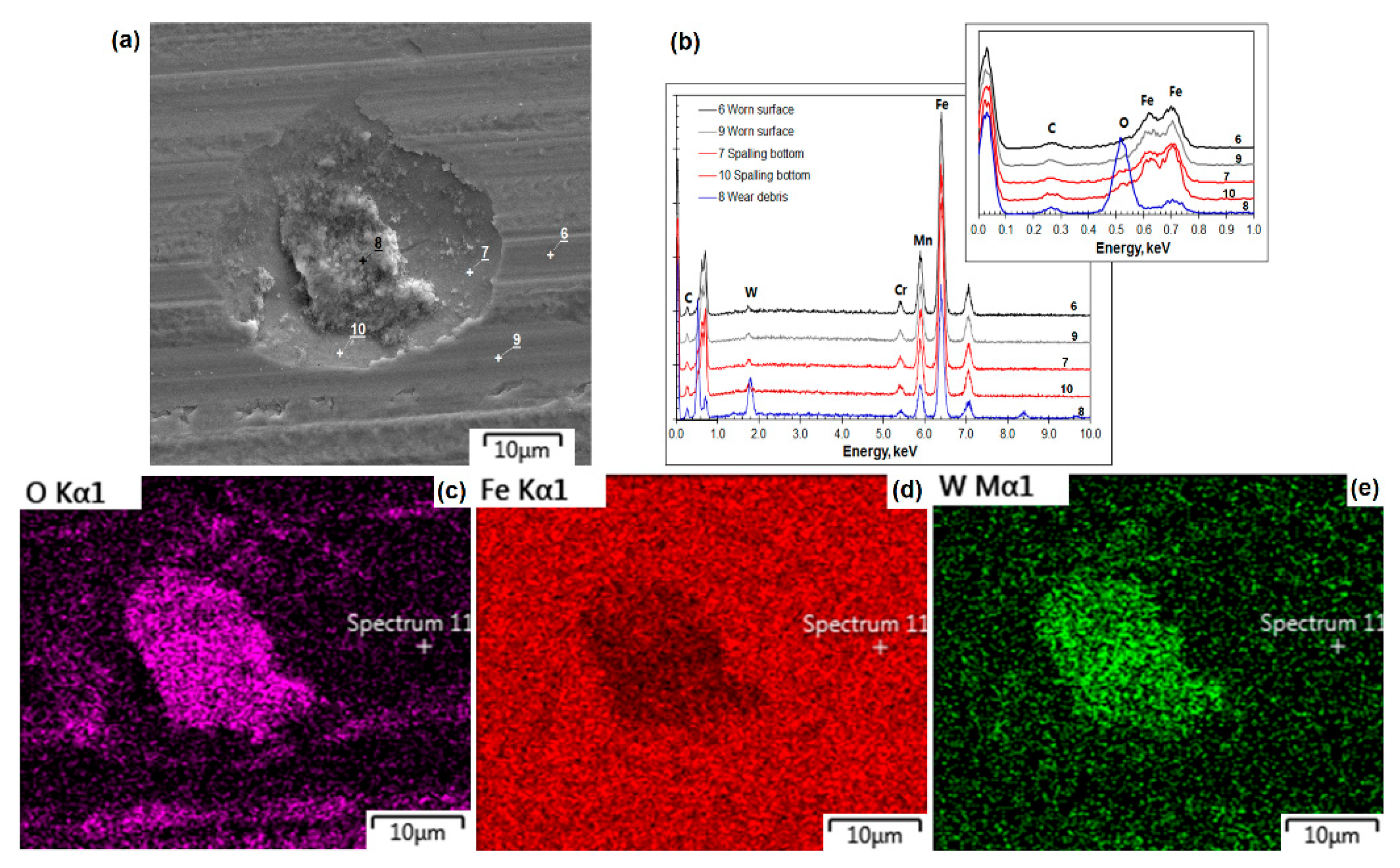
3.2. SEM and EDX Analyses of Worn Surfaces
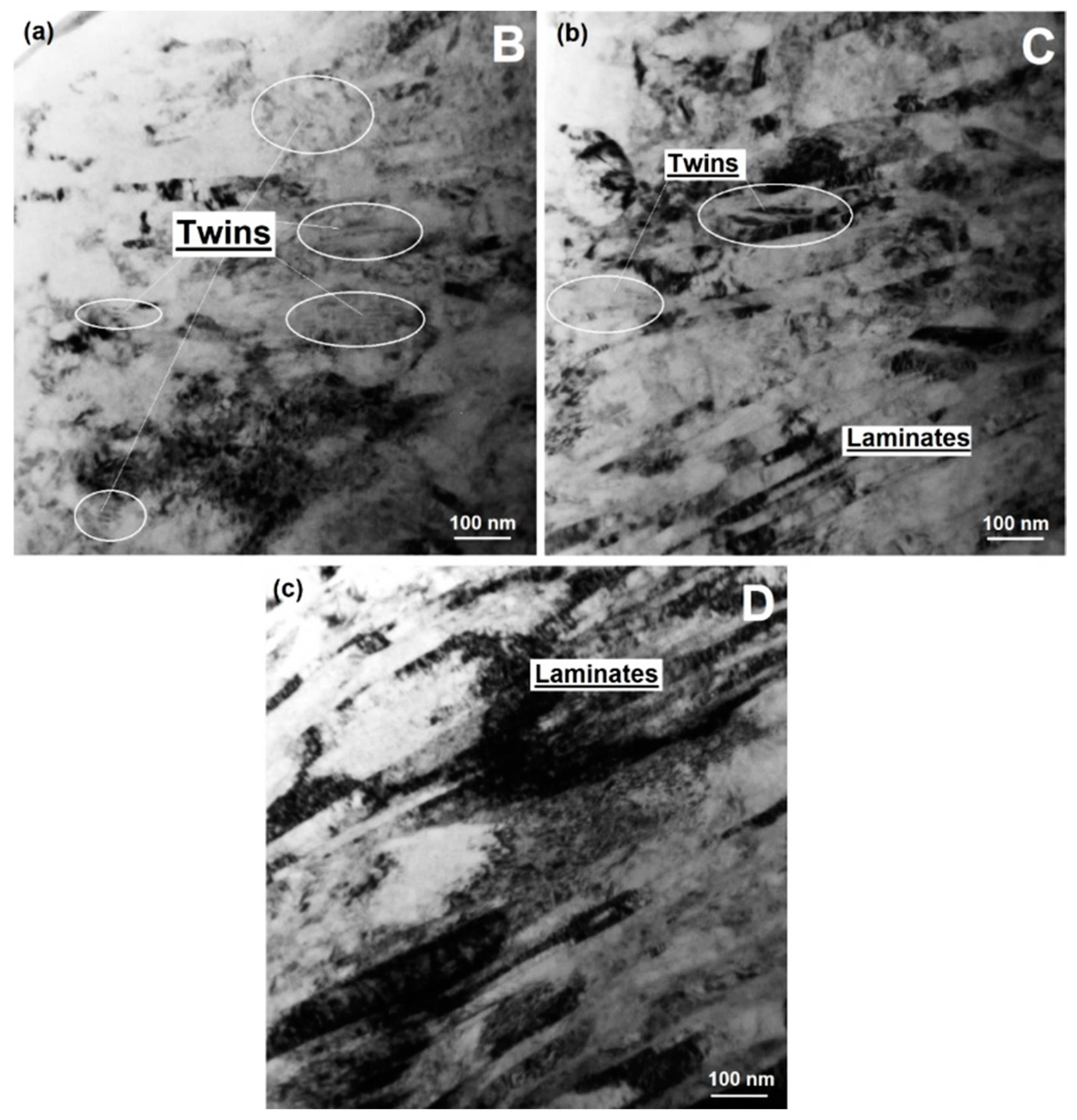
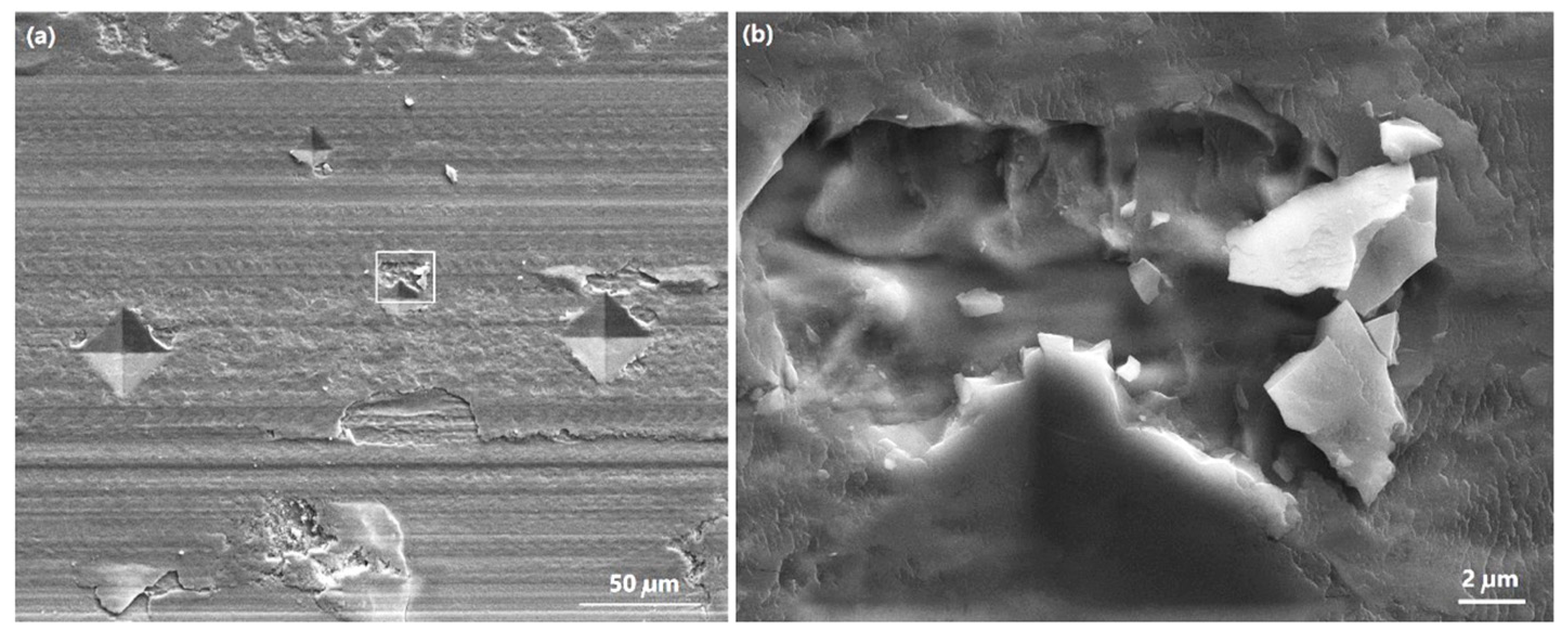
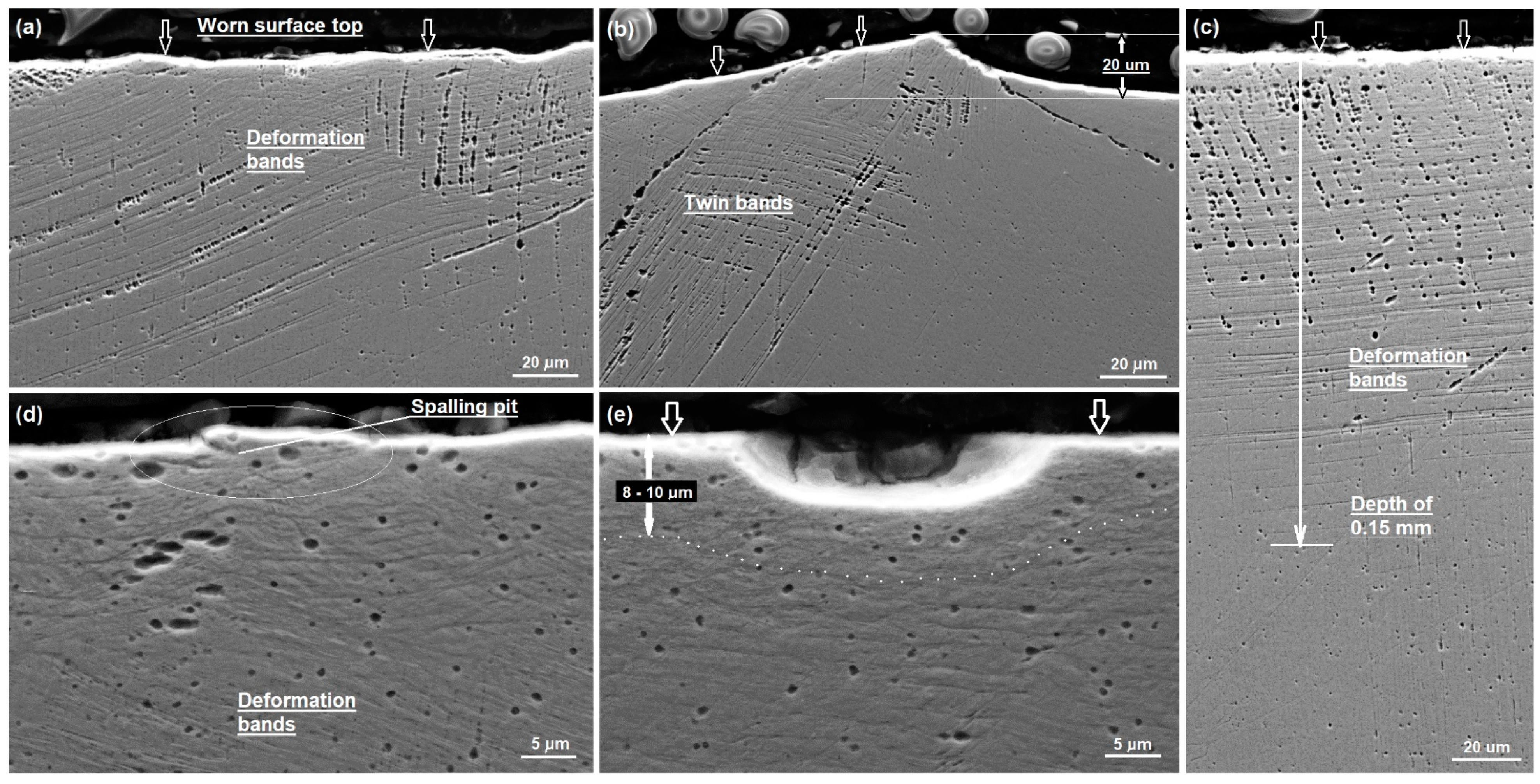
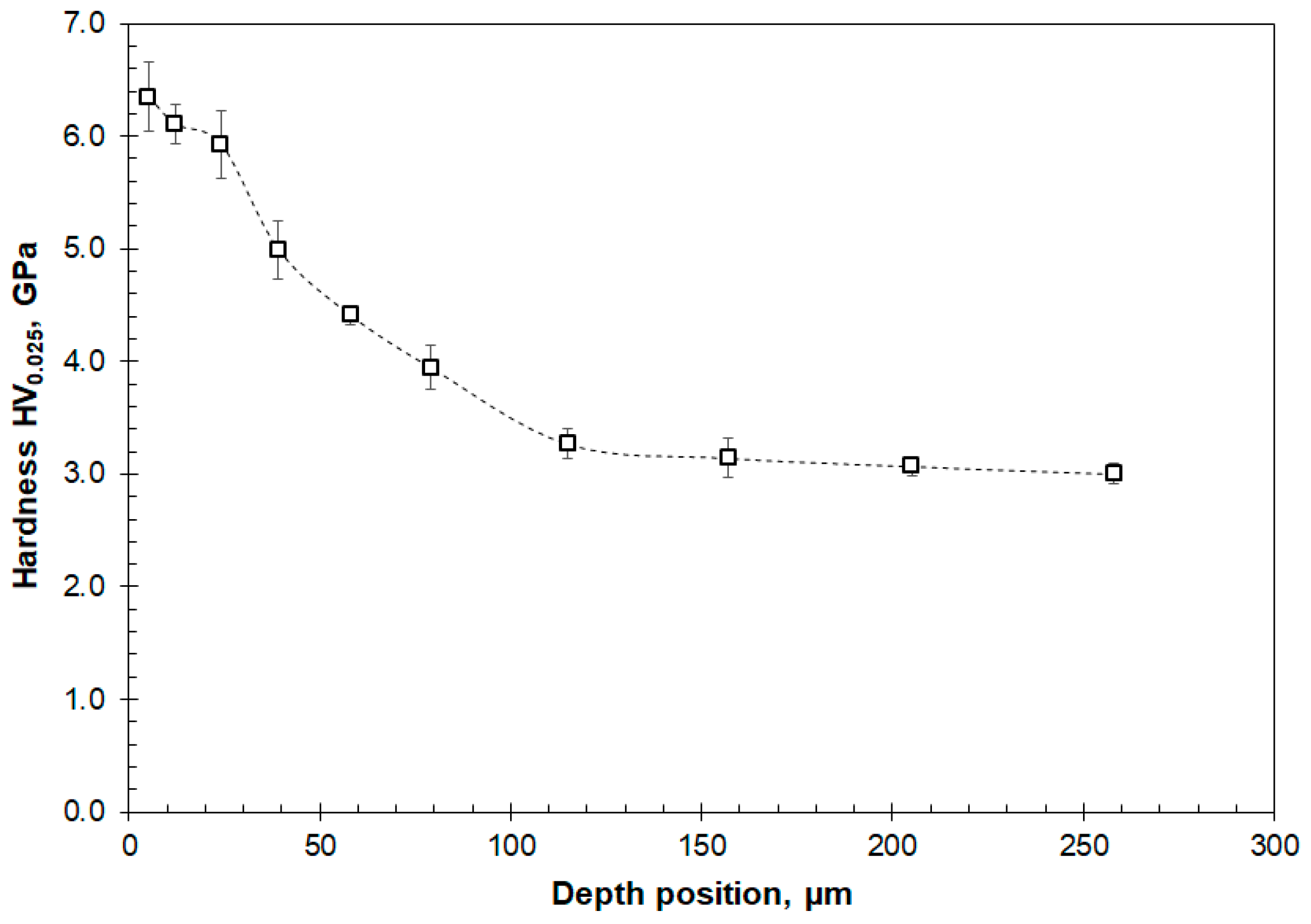
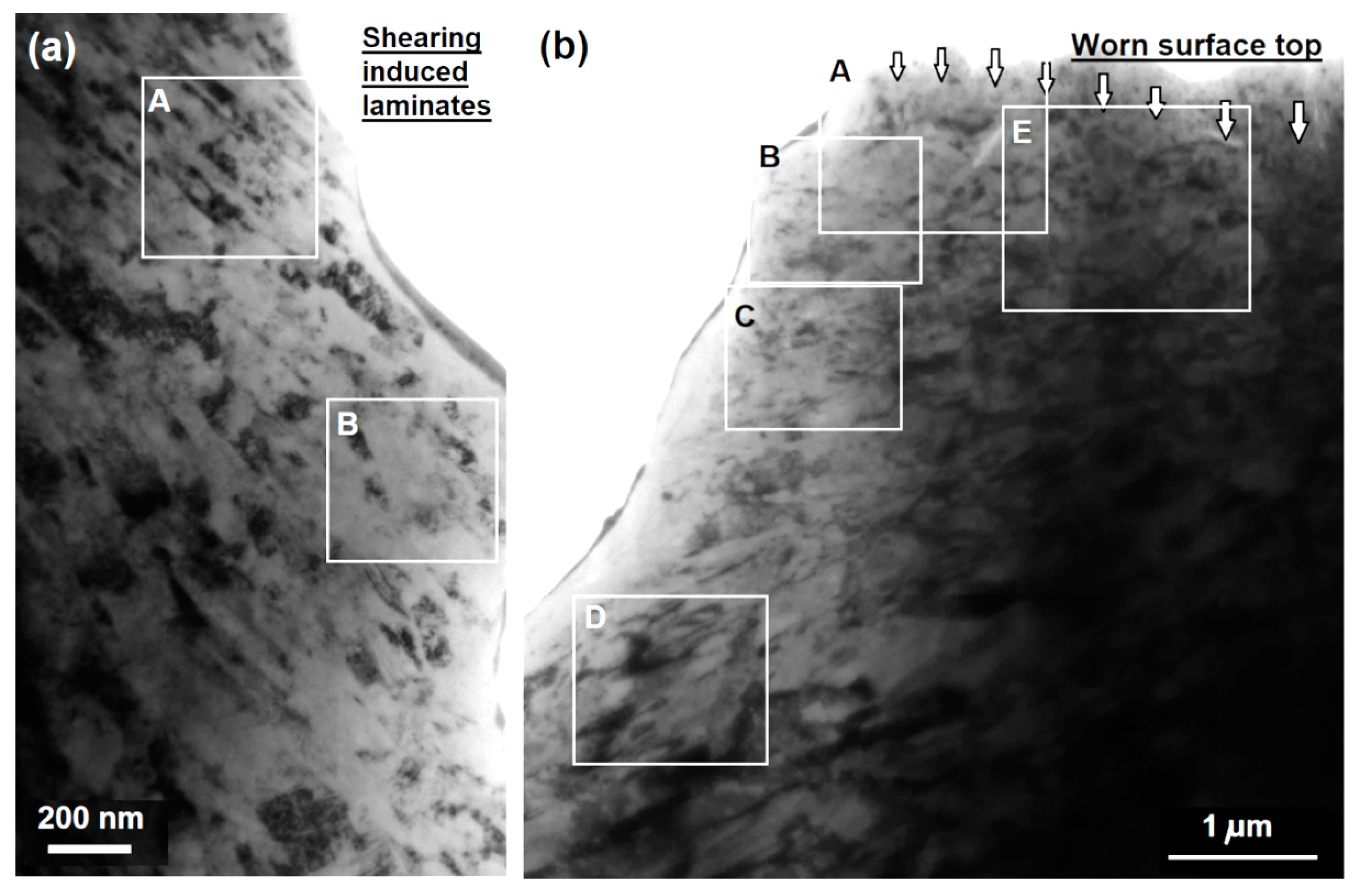
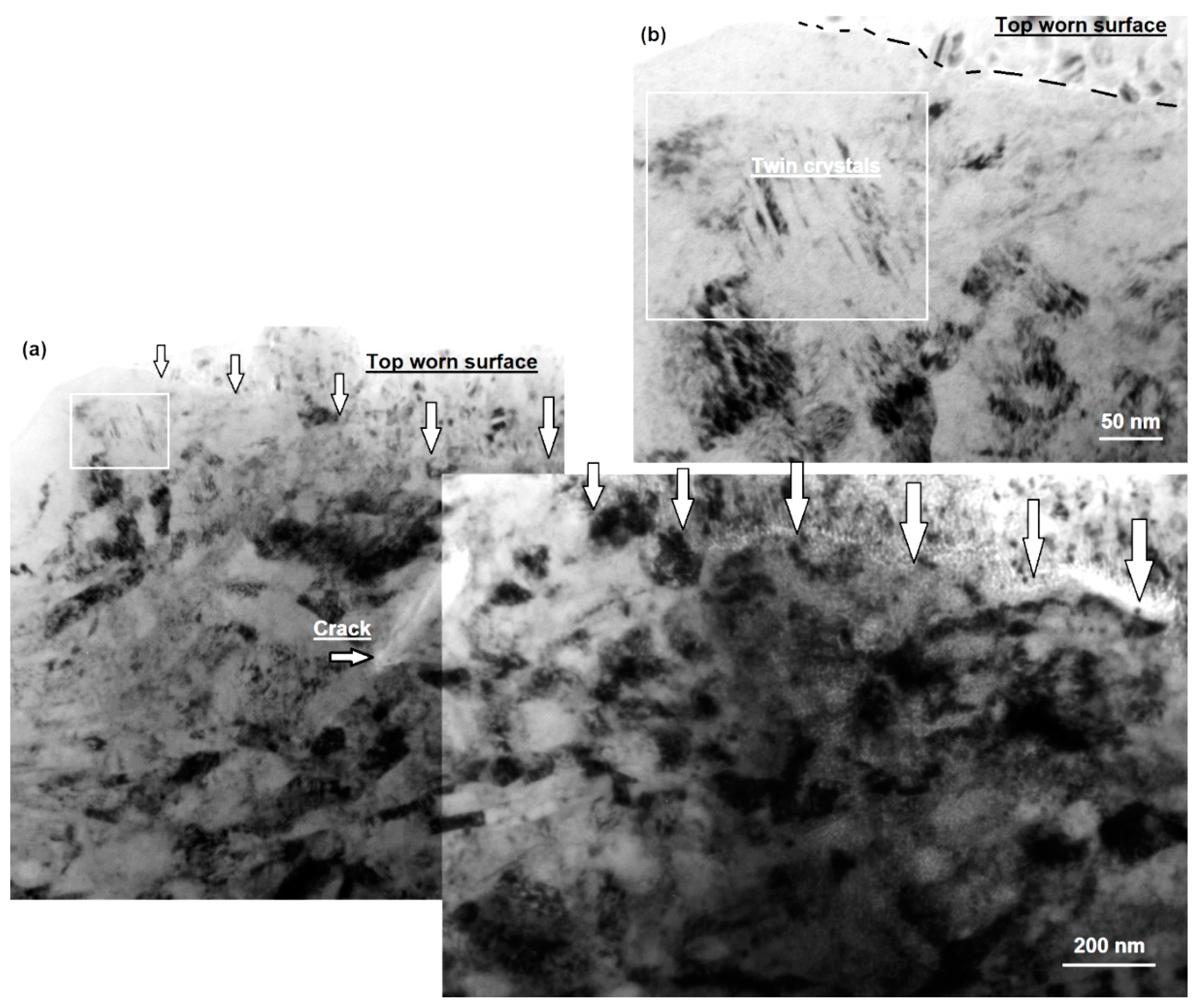
3.3. Cross-Sectional SEM, Microhardness and TEM Analyses of Worn Surfaces
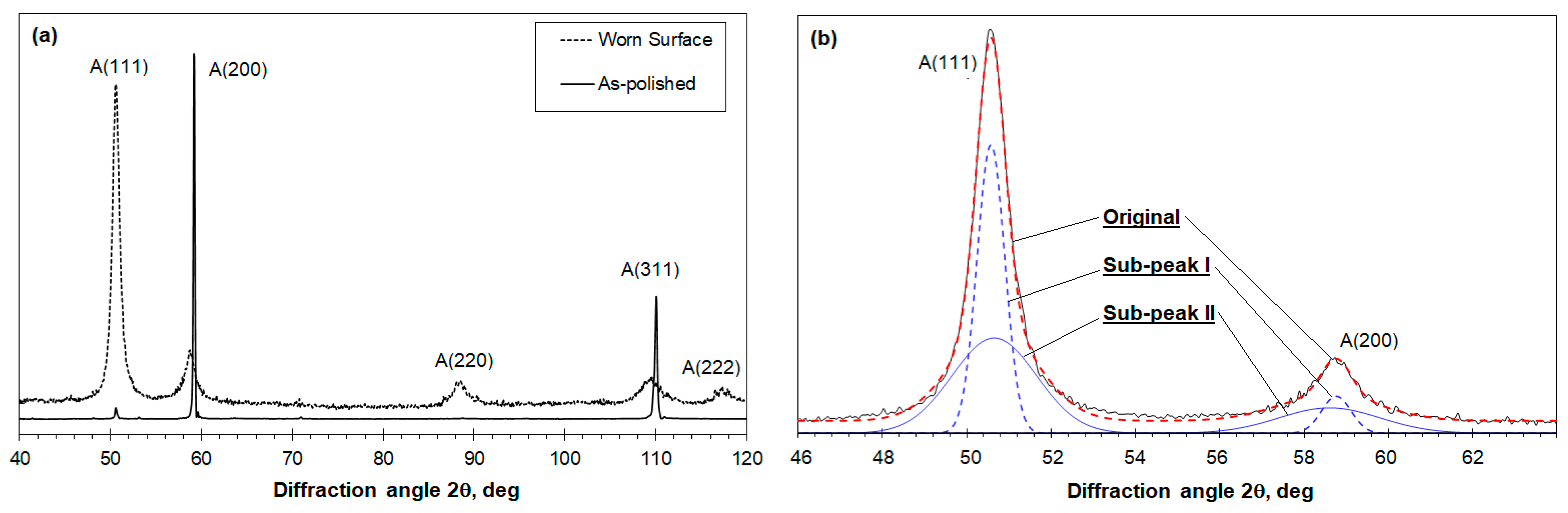
3.4. X-ray Diffraction Analyses of Worn Surfaces
4. Discussion
4.1. The Friction and Wear Properties of Hadfield Steel
4.2. Sliding-Induced Microstructure Evolution and Strain Hardening
4.3. Spalling Wear and Its Relation to the Sliding-Induced Surface Embrittlement
5. Conclusions
- The Hadfield steel showed a coefficient of wear in the scale of 10−14 m3·N−1·m−1 and a coefficient of friction of 0.5–0.6.
- The steel still retained its austenitic structure in the sliding wear without any detectable evidence of deformation-induced martensite transformation.
- The steel encountered severe plastic deformation beneath the worn surface. The deformation led to significant work hardening and surface embrittlement. Deformation-induced spalling wear was found as the predominant wear mechanism. Tribo-oxidation was also observed in the resultant wear debris.
- The surface embrittlement and spalling wear was associated with the deformation-induced nano-heterogeneous microstructure including nano-laminate, nanotwins, and nanocrystalline beneath the worn surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gauzzi, F.; Rossi, M.; Verdini, B. Cold-Working induced martensitic transformation in 12 percent Mn austenitic steel (Hadfield steel). Metall. Ital. 1971, 63, 555. [Google Scholar]
- Tweedale, G.; Paton, W.D.M. Sir Robert Abbott Hadfield F.R.S (1858–1940) and the discovery of manganese steel, Notes and Records. R. Soc. J. Hist. Sci. 1985, 40, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Dastur, Y.N.; Leslie, W.C. Mechanism of work-hardening in Hadfield manganese steel. Metall. Trans. A 1981, 12, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.P.; Wang, W.Y.; Li, J.W.; Wang, A.Q.; Zhao, Y.R.; Li, L.L. Wear Resistant Austenitic Manganese Steels; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Harzallah, R.; Mouftiez, A.; Felder, E.; Harriri, S.; Maujean, J.P. Rolling contact fatigue of Hadfield steel X120Mn12. Wear 2010, 269, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, R.; Das, S.; Das, K. Effect of thermo-mechanical processing on the low impact abrasion and low stress sliding wear resistance of austenitic high manganese steels. Wear 2019, 420, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, F.; Zhu, R.; Lei, T. On the impact abrasive wear of super-high manganese steel. Acta Metall. Sinica 1999, 35, 581–584. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Song, R.; Liu, S.; Feng, Y.; Pei, Z. Wear behaviour and subsurface layer work hardening mechanism of Fe-24. 1Mn-1.21C-0.48Si steel. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, P.C.; Pereira, J.I.; Sinatora, A. Abrasive wear of austenitic manganese steels via jaw crusher test. Wear 2021, 476, 203726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.C.; Pereira, J.I.; Sinatora, A. Subsurface microstructural dynamic recrystallization in multiscale abrasive wear. Wear 2021, 486–487, 204111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, C.; Sehitoglu, H. Strain hardening and heterogeneous deformation during twinning in Hadfield steel. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende-Seco, R.; Artigas, A.; Bruna, H.; Carvajal, L.; Monsalve, A.; Sklate-Boja, M.F. Hardening by Transformation and Cold Working in a Hadfield Steel Cone Crusher Liner. Metals 2021, 11, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychagin, D.V.; Filippov, A.V.; Novitskaya, O.S.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Kolubaev, E.A.; Lychagina, L.L. Deformation of Hadfield steel single crystals by dry sliding friction with the normal load/friction force orientations []/[10] and []/[001]. Tribo. Int. 2020, 147, 106284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychagin, D.V.; Filippov, A.V.; Novitskaya, O.S.; Kolubaev, A.V.; Moskvichev, E.N.; Fortuna, S.V.; Chumlyakov, Y.I. Deformation and wera of Hadfield steel single crystals under dry sliding friction. Wear 2022, 488–489, 204126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lv, B.; Wang, T.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, M.; Luo, H.; Liu, H. Microstructure and properties of purity high Mn steel crossing explosion hardened. ISIJ Int. 2008, 48, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yan, W.; Fang, L.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y. Effect of surface nanocrystallization on abrasive wear properties in Hadfield steel. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2007, 41, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Fang, L.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y. Effect of surface hardening on wear behaviour of Hadfield steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 460–461, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, I.A.; Datta, P.K.; Du, H.L.; Burnell-Gray, J.S.; Pierzgalski, S.; Luo, Q. Studies of high temperature sliding wear of metallic dissimilar interfaces. Tribo Int. 2005, 38, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.G.; Yin, C.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Tang, S.H. Lowering the coefficient of martensitic steel by forming a self-lubricating layer in dry sliding wear. Mater. Res. Exp. 2019, 6, 055024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, J.; Yan, Q.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Kitchen, M.; Bowen, L.; Farmilo, N.; Ding, Y. Sliding wear of medium-carbon bainitic/martensitic/austenitic steel treated by short-term low-temperature austempering. Wear 2021, 476, 203732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z. Friction behaviour and self-lubricating mechanism of low alloy martensitic steel during reciprocating sliding. Wear 2021, 482–483, 203972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, M.; Long, S.L. Formation of nano-laminated structures in a dry sliding wear induced layer under different wear mechanisms of 20CrNi2Mo steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.S.; Li, S.X.; Gao, Q.Y.; Jiang, H.; Lu, S.Y.; Yu, F.; Shu, X.D. Evolution of nano-laminated structure formed by the thermally-assisted plastic deformation in dry sliding wear. Tribo Int. 2019, 140, 105846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, S.M.; Pal, T.K.; Padmanabham, G.; Joshi, S.V. Comparative study on dry sliding wear behaviour of various railroad steels. Trans. ASME J. Tribo 2011, 133, 021602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, L.G.; Chernenko, N.L. Effect of aluminium on the structural transitions and the wear resistance of Hadfield steel under friction. Phys. Met. Metall. 2018, 119, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lv, B.; Ma, H.; Sun, D.; Zhang, F. Wear behaviour and the corresponding work hardening characteristics of Hadfield steel. Tribo Int. 2018, 121, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. A modified X-ray diffraction method to measure residual normal and shear stresses of machined surfaces. Int. J. Adv. Manufact. Technol. 2022, 119, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction; Pearson Education Ltd.: Harlow, UK, 2014; p. 379. [Google Scholar]
- Lahrman, D.F.; Field, R.D.; Darolia, R.; Fraser, H.L. Investigation of techniques for measuring lattice mismatch in a rhenium containing nickel based superalloy. Acta Metall. 1988, 36, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, D.; Gilles, R.; Barbier, B.; Del Genovese, D.; Hasse, B.; Strunz, P.; Wroblewski, T.; Fuess, H.; Rösler, J. Lattice misfit measurement in Inconel 706 containing coherent γ’ and γ” precipitates. Scrip. Mater. 2003, 48, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Chi, K.; Li, S.; Barnard, P. Microstructural Stability and Lattice Misfit Characterisations of Nimonic 263. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 Pressure Vessels & Piping Division Conference (PVP2012), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–19 July 2012; Volume 6, PTS A & B. pp. 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q. A new XRD method to quantify plate and lath martensites of hardened medium-carbon steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Characterization of short-range ordered domains using quantitative X-ray diffraction. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2018, 10, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Oluwafemi, O.; Kitchen, M.; Yang, S. Tribological properties and wear mechanisms of DC pulse plasma nitrided austenitic stainless steel in dry reciprocating sliding tests. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, E.A.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Mostafa, A.; Abdel-Rahman, M. Determination of the crystallite size and micro-strain by novel method from XRD profile. Appl. Phys. 2019, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shafi, P.M.; Bose, A.C. Impact of crystalline defects and size on X-ray line broadening: A phenomenological approach for tetragonal SnO2 nanocrystals. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 057137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Electron microscopy and spectroscopy in the analysis of friction and wear mechanisms. Lubricants 2018, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Origin of friction in running-in sliding wear of nitride coatings. Tribo Lett. 2010, 37, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lv, B.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, M.; Yang, S.; Yan, Z. Failure mechanism and worn surface microstructure of high manganese steel and bainite steel crossings. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2008, 44, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emurlaev, K.; Gerasimenko, T.; Abdimazhan, D. Nondestructive evaluation of material state near the friction interface under dry sliding. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 1526–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Polycarpou, A.A. Wear of conventional pearlitic and improved bainitic steels. Wear 2005, 259, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Mei, H.J.; Kitchen, M.; Gao, Y.; Bowen, L. Effect of short-term low-temperature austempering on the microstructure and abrasive wear of medium-carbon low-alloy stee. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 3115–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | C * | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OES | 1.29 ± 0.01 | 17.93 ± 0.06 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 1.87 ± 0.01 | In balance |
| EDX | 1.29 ± 0.01 | 17.88 ± 0.18 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 1.43 ± 0.04 | In balance |
| Time Period | Volume Loss [10−12 m3] | Wear Coefficient [10−16 m3·N−1·m−1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | WC | Steel | WC | |
| 0–40 min | 20.3 ± 2.6 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 275.1 ± 35.5 | 15.5 ± 3.5 |
| 40–400 min | 83.7 ± 5.0 | 6.2 ± 1.0 | 126.3 ± 6.8 | 9.1 ± 1.4 |
| 0–400 min | 104.0 ± 5.0 | 7.3 ± 1.0 | 141.2 ± 6.8 | 9.7 ± 1.4 |
| Property | Position | Mean | Stdev | Diffraction Peak | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A(111) | A(200) | A(220) | A(311) | A(222) | |||||
| β, deg | Bulk | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.27 | |||
| Worn surface | I | 1.22 | 0.45 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 1.17 | 1.91 | 1.38 | |
| II | 3.33 | 0.75 | 2.33 | 2.81 | 3.55 | 4.19 | 3.76 | ||
| ε, % | Bulk | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.07 | |||
| Worn surface | I | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.37 | |
| II | 1.34 | 0.57 | 2.15 | 0.66 | 1.59 | 1.29 | 0.99 | ||
| t, nm | Bulk | 49 | 11 | 38 | 50 | 59 | |||
| Worn surface | I | 11 | 2 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 12 | |
| II | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q.; Zhu, J. Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding. Lubricants 2022, 10, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10030037
Luo Q, Zhu J. Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding. Lubricants. 2022; 10(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Quanshun, and Jingzhi Zhu. 2022. "Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding" Lubricants 10, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10030037
APA StyleLuo, Q., & Zhu, J. (2022). Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding. Lubricants, 10(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10030037






