Phosphate Esters, Thiophosphate Esters and Metal Thiophosphates as Lubricant Additives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
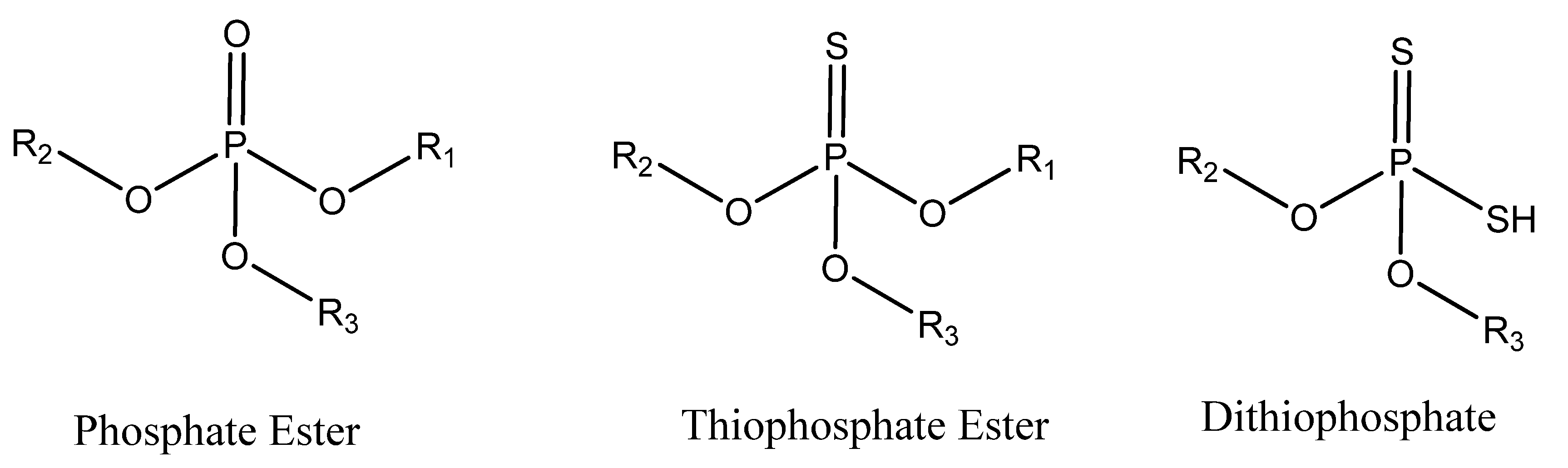
2. Zinc Dialkyldithiophosphate and Other Metal Containing Phosphate Esters

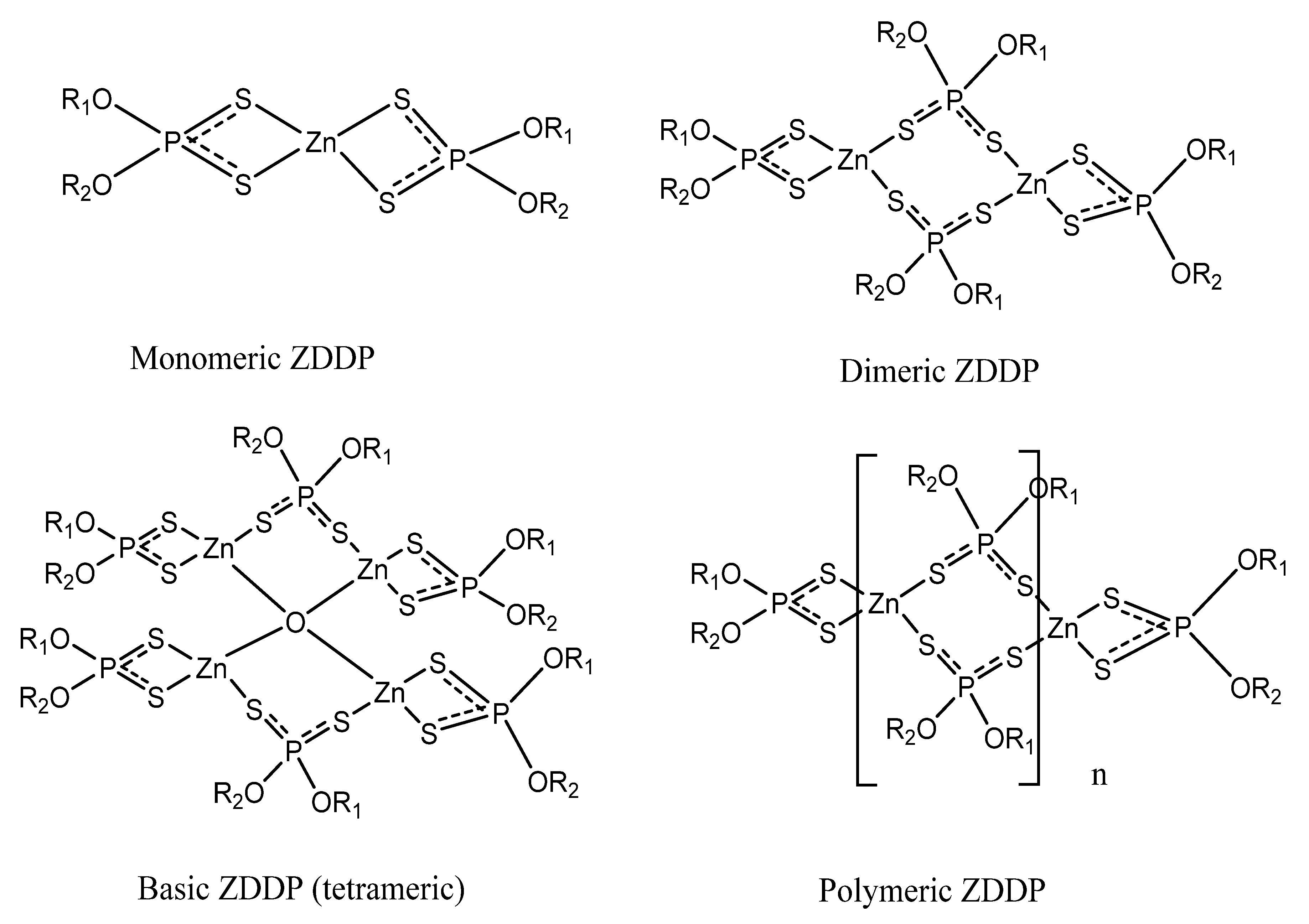
2.1. The Structure of ZDDP in Solution
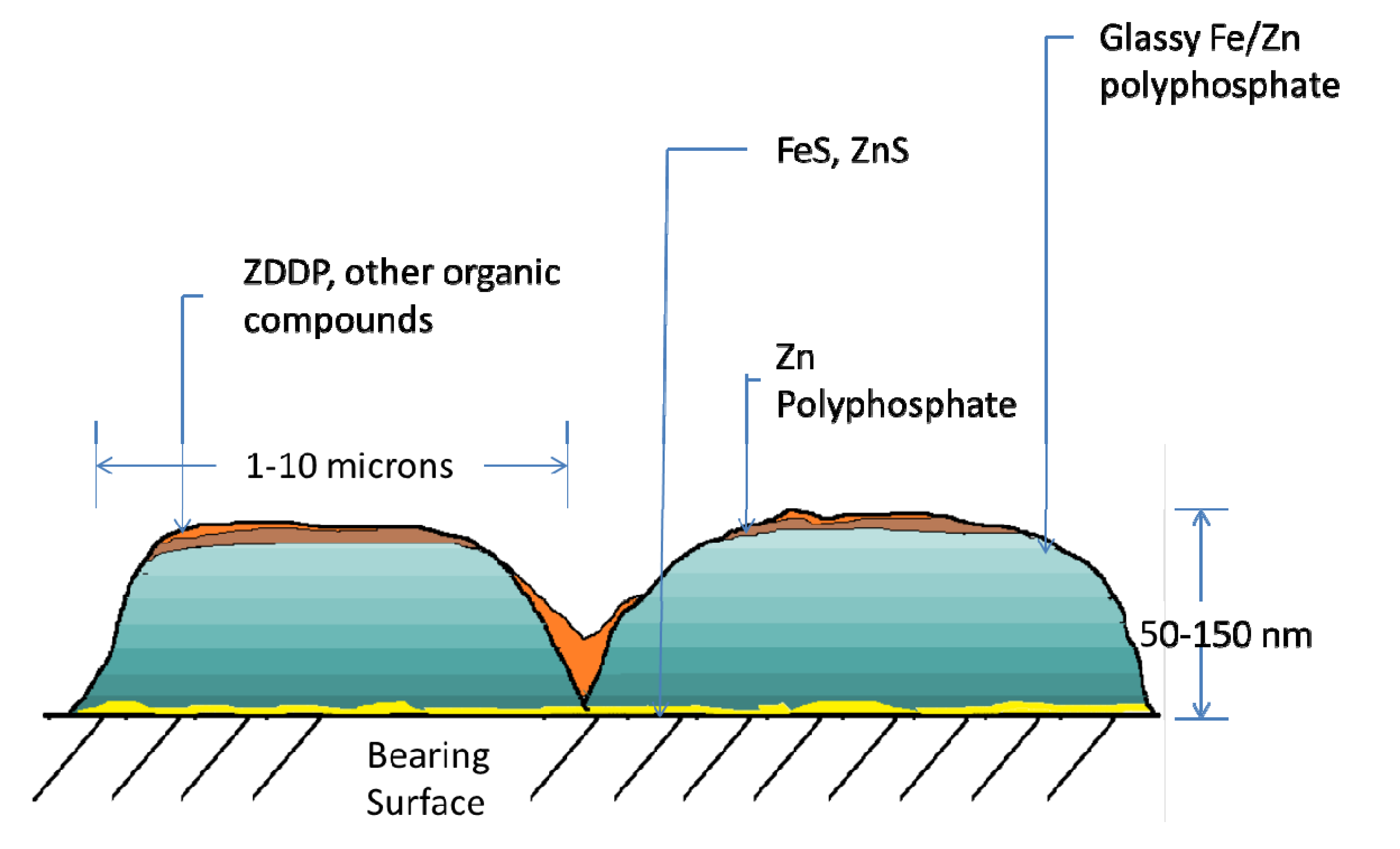
2.2. The Reaction of ZDDP at Surfaces
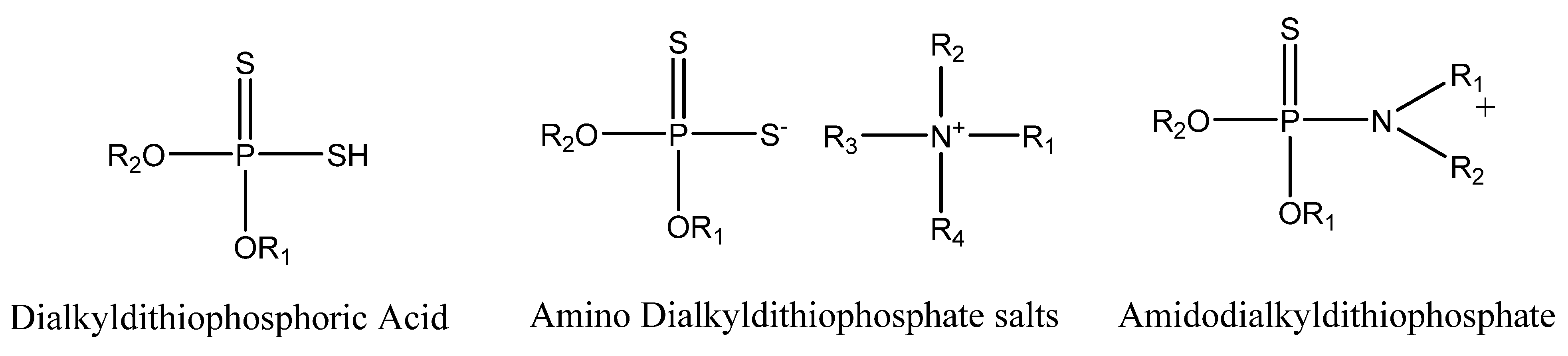
3. Dithiophosphate Ester and Phosphorothionate Ester Additives
4. Phosphate Esters
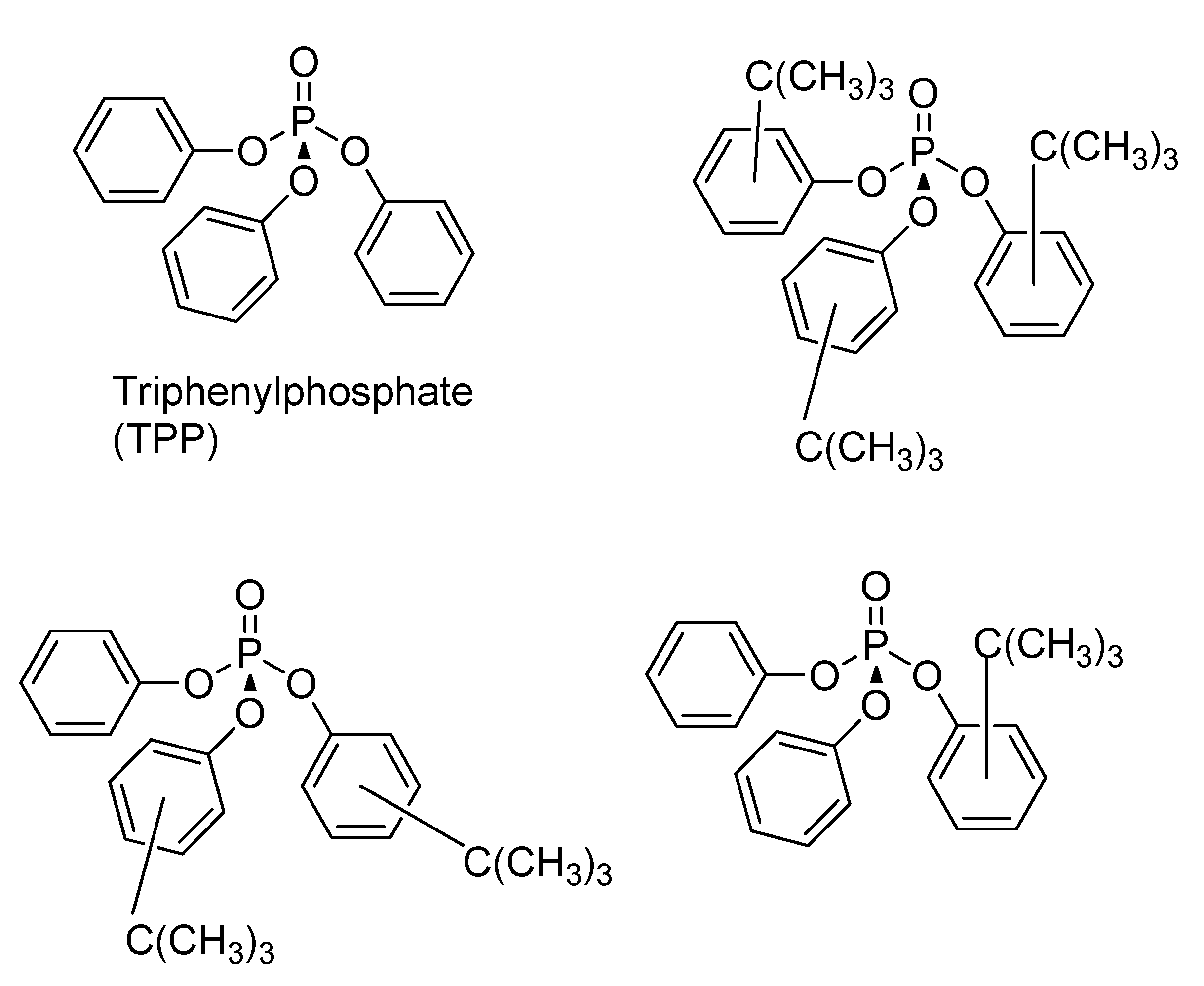
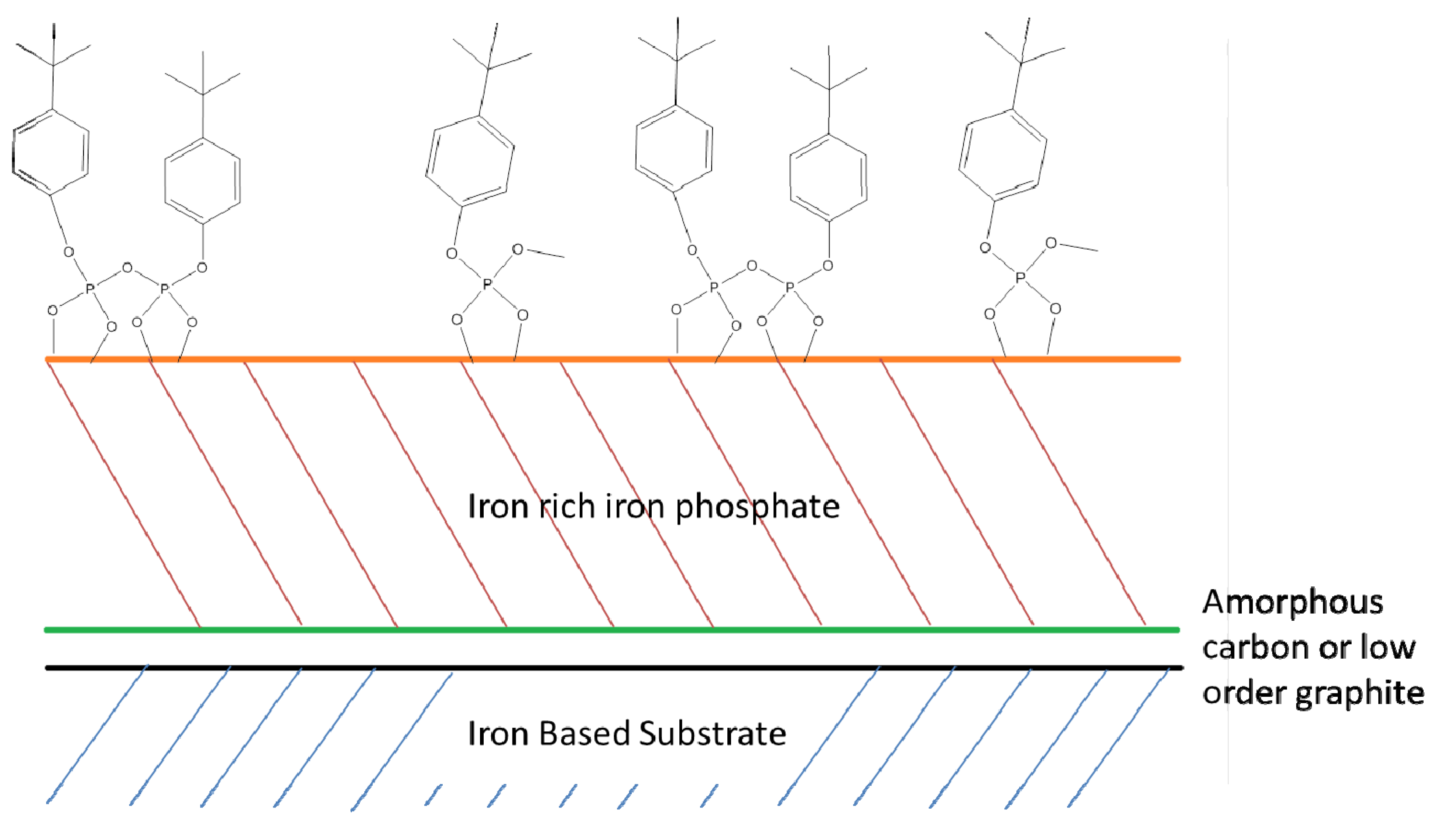
4.1. Mechanism of Phosphate Ester Modification of Metal surfaces

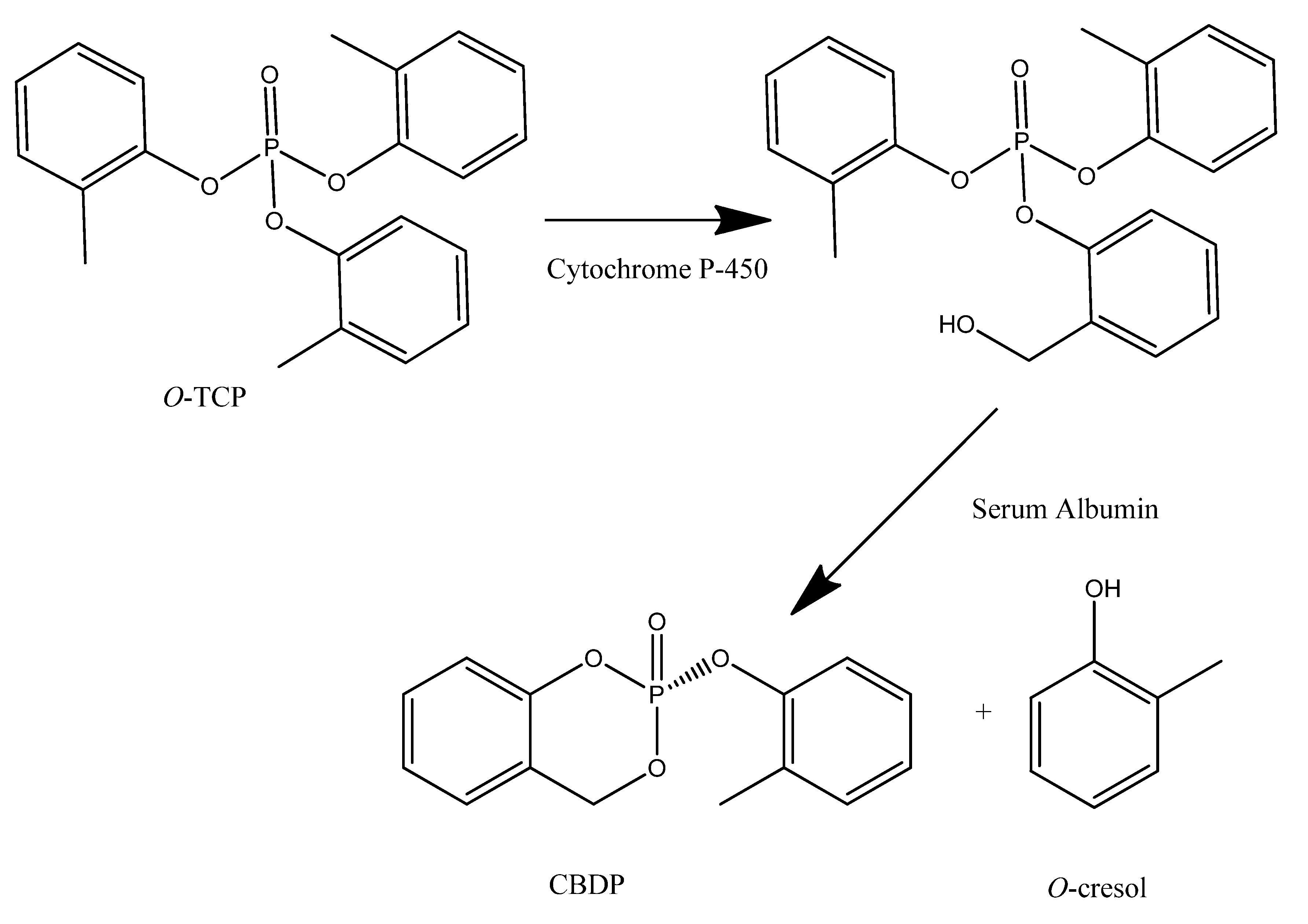
4.2. Safety of Phosphate Esters
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marino, M.P.; Placek, D.C. Phosphate Esters. In Synthetic Lubricants and High Performance Functional Fluids; Rudnick, L.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 103–140. [Google Scholar]
- Moy, P. Aryl phosphate ester fire-retardant additive for low-smoke vinyl applications. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2004, 10, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, D.B.; Bravo, R.; Weerasekera, G.; Caltabiano, L.M.; Whitehead, R.D., Jr.; Olsson, A.O.; Caudill, S.P.; Schober, S.E.; Pirkle, J.L.; Sampson, R.J.; Needham, L.L. Concentrations of dialkyl phosphate metabolites of organophosphorus pesticides in the U.S. population. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 186–200. [Google Scholar]
- Oldenhoveda de Guertechin, L. Surfactants: Classification. In Handbook of Detergents, Surfactant Science Series; Broze, G., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 82, pp. 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, R.A. Zinc Dialkyldithiophosphates, Chemical Industries. In Lubricant Additives: Chemistry and Applications, 2nd ed.; Rudnick, L.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 124, pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Champy, P. Lubricants. Fr. Patent 784803, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Selby, T.W. Analysis of engine oil and phosphorus volatility. Tribotest 2000, 6, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, T.W. Phosphorus volatility of engine oils: Use of the phosphorus emission index. Tribotest 2005, 11, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asseff, P.A. Lubricants Suitable for Internal-Combustion Engines. U.S. Patent 1941.
- Cook, E.W.; Thomas, W.D., Jr. Lubricating-oil Addition Agents. U.S. Patent 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Fruehler, H.C. Antioxidant for Lubricating Oils. U.S. Patent 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Fruehler, H.C. Antioxidant for Lubricating Oils. U.S. Patent 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Varlot, K.; Kasrai, M.; Martin, J.M.; Vacher, B.; Bancroft, G.M.; Yamaguchi, E.S.; Ryason, P.R. Anti-wear film formation from neutral and basic ZDDP, influence of the reaction temperature and concentration. Tribol. Lett. 2000, 8, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Burn, A.J. The mechanism of the antioxidant action of zinc dialkyl dithiophosphates. Tetrahedron 1966, 22, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidwell, J.B.; Williams, R.K. The new look in lubricating oils. SAE Trans. 1955, 63, 349–361. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, C.S.; Larson, R. The performance of zinc dithiophosphates as lubricating oil additives. SAE J. 1958, 107, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Spikes, H. The history and mechanisms of ZDDP. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, A.M.; Bartle, K.D.; Thibon, V.R.A. A review of zinc dialkyldithiophosphates (ZDDPS): Characterization and role in the lubricating oil. Tribol. Int. 2001, 34, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.G.; Kikabhai, T. Proton and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance study of zinc(II) O,O′-dialkyl dithiophosphates in solution. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1987, 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.J.; Chan, C.Y.; Onopchenko, A.; Pradhan, A.R.; Petersen, M. Neutral zinc(II) O,O-dialkyldithiophosphates—Variable temperature 31P NMR and quantum chemical study of the ZDDP monomer-dimer equilibrium. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2008, 46, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Haiduc, I.; Sowerby, D.B.; Shao-Fang, L. Stereochemical aspects of phosphor-1,1-dithiolato metal complexes (dithiophosphates, dithiophosphinates): Coordination patterns, molecular structures and supramolecular associations—I. Polyhedron 1995, 14, 3389–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, E.S.; Primer, R.L.; Aragon, S.R.; Labrador, E.Q. Dynamic light scattering studies of neutral diisobutyl zinc dithiophosphate. Tribol. Transactions 1997, 40, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.R.; Ferrari, E.S.; Roberts, K.J.; Adams, D. An investigation into the molecular stability of zinc di-alkyl-di-thiophosphates (ZDDPs) in relation to their use as anti-wear and anti-corrosion additives in lubricating oils. Wear 1997, 208, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, E.S.; Ryason, P.R.; Labrador, E.Q.; Hansen, T.P. Comparison of the relative performance of neutral and basic ZnDTP salts. Tribol. Trans. 1996, 39, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Hong, S.Z.; Lu, W.Z. The degradation of zinc dialkyldithiophosphate additives in fully formulated engine oil as studied by P-31 NMR spectroscopy. Lubr. Eng. 1994, 50, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Vizintin, J. Oil Surface: Additive Reaction Mechanism. In Surface Modification and Mechanisms; Totten, G.E., Liang, H., Eds.; Marcel Decker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 243–298. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Igarashi, T.; Hagihara, H. The crystal structure of metal diethyldithiophosphates I. Zinc diethyldithiophosphate. Acta Cryst. 1969, 25, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, S.L.; Kokotailo, G.T. The crystal and molecular structures of zinc and cadmium O,O-diisopropylphosphorodithioloates. Inorg. Chem. 1969, 8, 2410–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Antzutkin, O.N.; Larsson, A.C.; Kritijkos, M.; Forsling, W. Polycrystalline and surface O,O′-dialkyldithiophosphate zinc(II) complexes: Preparation, 31P CP/MAS NMR and single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2001, 315, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A.C.; Ivanov, A.V.; Forsling, W.; Antzutkin, O.N.; Abraham, A.E.; de Dios, A.C. Correlations between 31P chemical shift anisotropy and molecular structure in polycrystalline O,O′-dialkyldithiophosphate zinc(II) and nickel(II) complexes: 31P CP/MAS NMR and ab initio quantum mechanical calculation studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suominen-Fuller, M.L.; Kasrai, M.; Bancroft, G.M.; Fyfe, K.; Tan, K.H. Solution decomposition of zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate and its effect on antiwear and thermal film formation by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.J.; Galvin, G.D. The application of photoelectron spectroscopy to the study of EP films on lubricated surfaces. Wear 1976, 37, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, G.M.; Kasrai, M.; Fuller, M.; Yin, Z.; Fyfe, K.; Tan, K.H. Mechanisms of tribochemical film formation: Stability of tribo- and thermally-generated ZDDP films. Tribol. Lett. 1997, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bec, S.; Tonck, A.; Georges, J.M.; Coy, R.C.; Bell, J.C.; Roper, G.W. Relationship between mechanical properties and structure of zinc dithiophosphate antiwear films. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1999, 455, 4181–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, F.M.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Combined in situ (ATR FT-IR) and ex situ (XPS) study of the ZnDTP-iron surface interaction. Tribol. Lett. 2003, 15, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuko, M.; Ohkido, T.; Suzuki, A.; Ueno, T. Fundamental Changes in Friction and Wear Characteristics due to ZnDTP Deterioration in Simulating Engine Oil Degradation during Use. In. In Proceedings of the 30th Leeds-Lyon Symposium on Tribology: Transient Processes in Tribology, Lyon, France, 2–8 September 2003; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 359–356. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, K.L.; Stair, P.C. The surface chemistry of zinc dialkyldithiophosphate, an antiwear additive on oxidized iron and steel foils. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1988, 6, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.; Yin, Z.; Kasrai, M.; Bancroft, G.M.; Yamaguchi, E.S.; Ryason, P.R.; Willermet, P.A.; Tan, K.H. Chemical characterization of tribochemical and thermal films generated from neutral and basic ZDDPs using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Tribol. Int. 1997, 30, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willermet, P.A.; Dailey, D.P.; Carter, R.O., III; Schmitz, P.J.; Zhu, W. Mechanism of formation of antiwear films from zinc dialkyldithiophosphates. Tribol. Int. 1995, 28, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.M. Antiwear mechanisms of zinc dithiophosphate: A chemical hardness approach. Tribol. Lett. 1999, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Kasrai, M.; Fuller, M.; Bancroft, G.M.; Fyfe, K.; Tan, K.H. Application of soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy in chemical characterization of antiwear films generated by ZDDP part I: The effects of physical parameters. Wear 1997, 202, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.L.; Fernandez, L.R.; Massoumi, G.R.; Lennard, W.N.; Kasrai, M.; Bancroft, G.M. The use of X-ray absorption spectroscopy for monitoring the thickness of antiwear films from ZDDP. Tribol. Lett. 2000, 8, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhvorostov, D.; Muserm, M.H.; Song, Y.; Norton, P.R. Smart materials behavior in phosphates: Role of hydroxyl groups and relevance to antiwear films. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, F.C. Catalyzed Lubricant Additives and Catalyzed Lubricant Systems Designed to Accelerate the Lubricant Bonding Reaction. U.S. Patent 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Huq, M.Z.; Chen, X.; Aswath, P.B.; Elsenbaumer, R.L. Thermal degradation behavior of zinc dialkyldithiophosphate in presence of catalysts and detergents in neutral oil. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 19, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, G.N. The effect of FeF3/TiF3 catalysts on the thermal and tribological performance of plain oil ZDDP under extreme pressure loading. Wear 2012, 278–279, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, G. Tribological and thermal characteristics of reduced phosphorus plain ZDDP oil in the presence of PTFE/FeF3/TiF3 under optimized extreme loading condition and a break in period using two different rotational speeds. Wear 2013, 301, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, K.; Chen, X.; Aswath, P.B. Synthesis of fluorinated ZDDP compounds. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 34, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Raza, S.K.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Chemical warfare agents. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2007 on type approval of motor vehicles with respect to emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro. 5 and Euro. 6) and on access to vehicle repair and maintenance information. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32007R0715:EN:NOT (accessed on 12 December 2013).
- Rokosz, M.J.; Chen, A.E.; Lowe-Ma, C.K.; Kucheroz, A.V.; Benson, D.; Paputa Peck, M.C.; McCabe, R.W. Characterization of phosphorus-poisoned automotive exhaust catalysts. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2001, 33, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spikes, H. Low and zero sulfated ash, phosphorus and sulfur anti-wear additives for engine oils. Lubr. Sci. 2008, 20, 103–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borshchevskii, S.B.; Shabanova, E.V.; Markov, A.A.; Yu Rebrov, I. Antifriction and antiwear properties of dialkyldithioaminephosphates. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 1984, 20, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, W.; Xue, Q. The application research on series of ashless P-containing EP and AW additives. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2005, 57, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaskal’ko, P.P.; Parfenova, V.A.; Markov, A.A.; Lesninova, V.A.; Belov, P.S. Amidothiophosphates—Effective antiwear and extreme pressure additives for lubricating oils. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 1976, 12, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boreshchevskii, S.B.; Levitina, I.S.; Shabanova, E.V.; Kotova, G.G. Additives based on dithiophosphoric acids and unsaturated compounds for lubricating oils. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 1992, 27, 326–328. [Google Scholar]
- Chem, X.; Kim, B.; Eisenbaumer, R.L.; Aswath, P.B. Synthesis and antiwear behavior of ashless alkylthioperoxydiphosphates. Tribology 2012, 6, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Najman, M.N.; Kasrai, M.; Bancroft, G.M. Chemistry of antiwear films for ashless thiophosphate oil additives. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Mourhatch, R.; Aswath, P.B. Properties of tribofilms formed with ashless dithiophosphate and zinc dialkyldithiophosphate under extreme pressure conditions. Wear 2010, 268, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangolini, F.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Reactivity of triphenylphosphorothionate in lubricant oil solution. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 35, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangolini, F.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Influence of metallic and oxidized iron/steel on the reactivity of triphenyl phosphorothionate in oil solution. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Jiang, J.C.; Aswath, P.B. Mechanism of wear at extreme load and boundary conditions with ashless anti-wear additives: Analysis of wear surfaces and wear debris. Wear 2011, 270, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Hirano, F. Scuffing resistance of phosphate esters. Wear 1978, 50, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Hirano, F. Effect of different phosphate esters on frictional characteristics. Tribol. Int. 1980, 13, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beek, O.; Givens, J.W.; Williams, E.C. On the mechanism of boundary lubrication. II. Wear prevention by addition agents. Proc. R. Soc. A 1940, 177, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottington, R.L.; Ravner, H. Interactions in neopentyl polyol ester-tricresyl phosphate—Iron system at 500 F. ASLE Trans. 1969, 12, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.L.; Ravner, H.; Cottington, R.L. Inhibition of iron-catalyzed neopentyl polyol ester thermal degradation through passivation of the active metal surface by tricresyl phosphate. ASLE Trans. 1970, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Inauoshi, N.; Tashiro, K. Friction-induced dynamic chemical changes of tricresyl phosphate as lubricant additive observed under boundary lubrication with 2D fast imaging FTIR-ATR spectrometer. Wear 2010, 268, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Gellman, A.J. The surface chemistry of alkyl and arylphosphate vapor phase lubricants on Fe foil. Tribol. Int. 2002, 35, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.E.; Klaus, E.E. Lubrication from the vapor phase at high temperatures. ASLE Trans. 1986, 29, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, N.H. Rolling contact testing of vapor phase lubricants—Part III: Surface analysis. Tribol. Trans. 1999, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheaffer, S.K. High temperature reaction of aryl phosphate esters on an iron film. Tribol. Trans. 2003, 46, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, C.S.; Forster, N.H. Reaction of aromatic phosphate esters with metals and their oxides. Tribol. Lett. 2002, 12, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, H.K.; Forster, N.H.; Saba, C.S. Rolling contact fatigue testing of a 3 cSt polyolester lubricant with and without TCP and DODPA/PANA at 177 °C. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 16, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Morrow, S.J.; Forster, N.; Saba, C.S. Vapor-phase lubrication: Reaction of phosphate ester vapors with iron and steel. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3767–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Morrow, S.J. Decomposition of butylated triphenylphosphate on steel surfaces. University of Dayton: Dayton, OH, USA, Unpublished work. 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, D.H.; Chin, H.A.; Klenke, C.; Galbato, A.T.; Ragan, M.A.; Spitzer, R.F. High Temperature Turbine Engine Bearing and Lubrication System Development. In Bearing Steels: Into the 21st Century; Hoo, J.J.C., Green, W.B., Eds.; American Society for Testing and Materials: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1998; pp. 409–435. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, H.K.; Forster, N.H.; Rosado, L. Rolling contact fatigue evaluation of advanced steels with and without the oil anti-wear additive tricresyl phosphate. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Hils, J.E.; Forster, N. Interaction of polyol esters and phosphate esters with metal carbides. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 42, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Iacullo, C.; Hils, J.E. Reaction between polyol-esters and phosphate esters in the presence of metal carbides. Frict. Wear Res. 2013, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.W.; Bachus, M.; Hils, J.E. Interaction between lubricants containing phosphate ester additives and stainless steels. Lubricants 2013, 1, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwender, L.J.; Kramer, D.C.; Lok, B.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Snyder, C.E., Jr.; Sztenderowicz, M.L. Liquid Lubricants and Lubrication. In Modern Tribology Handbook; Bhushan, B., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 361–382. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, F.R.; Wright, P.L.; Gordon, D.E.; Levinskas, G.J.; Radue, R.W.; Graham, P.R. Evaluation of delayed neurotoxicity and dose-response relationships of phosphate esters in the adult hen. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1977, 41, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopfer, L.M.; Furlong, C.E.; Lockridge, O. Development of diagnostics in the search for an explanation of aerotoxic syndrome. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 404, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, S. Contaminated aircraft cabin air. J. Biol. Phys. Chem. 2011, 11, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.E.; Cole, T.B.; Cartwright, M.; Suzuki, S.M.; Thummel, K.E.; Lin, Y.S.; Co, A.L.; Rettie, A.E.; Kim, J.H.; Furlong, C.E. Identifying safer anti-wear triaryl phosphate additives for jet engine lubricant. Chem. Biol. Addit. 2013, 203, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.A.; Brix, K.A. Review of health consequences from high, intermediate and low-level exposure to organophosphorus nerve agents. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1998, 18, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, J.G.; Langworthy, O.R. Jake paralysis: Paralysis following the ingestion of Jamaica ginger extract adulterated with tri-ortho-cresyl phosphate. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1933, 52, 39–65. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, H.V.; Spaulding, J.M.K. Outbreak of paralysis in Morocco due to ortho-cresyl phosphate poisoning. Lancet 1959, 274, 1019–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carletti, E.; Schopfer, L.M.; Colletier, J.P.; Froment, M.T.; Nachon, F.; Weik, M.; Lockridge, O.; Masson, P. Reaction of cresyl salingen phosphate, the organophosphorus agent implicated in aerotoxic syndrome with human cholinesterases: Mechanistic studies employing kinetics, mass spectrometry and X-ray structure analysis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubey, W.A.; Streibich, R.C.; Bush, J.; Centers, P.W.; Wright, R.L. Neurotoxin formations from pilot-scale incineration of synthetic ester turbine lubricants with triaryl phosphate additive. Arch. Toxicol. 1996, 70, 508–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers, P.W. Potential neurotoxin formation in thermally degraded synthetic ester turbine lubricants. Arch. Toxicol. 1992, 66, 679–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, J.F.; Porvezuik, M.; Serve, P.; Hobson, D.; Uddin, D.E. High temperature decomposition of military specification L-23699 synthetic aircraft lubricants. J. Fire Sci. 1987, 5, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, D.W.; Hils, J.E. Phosphate Esters, Thiophosphate Esters and Metal Thiophosphates as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants 2013, 1, 132-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants1040132
Johnson DW, Hils JE. Phosphate Esters, Thiophosphate Esters and Metal Thiophosphates as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants. 2013; 1(4):132-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants1040132
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, David W., and John E. Hils. 2013. "Phosphate Esters, Thiophosphate Esters and Metal Thiophosphates as Lubricant Additives" Lubricants 1, no. 4: 132-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants1040132
APA StyleJohnson, D. W., & Hils, J. E. (2013). Phosphate Esters, Thiophosphate Esters and Metal Thiophosphates as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants, 1(4), 132-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants1040132



