Experimental Investigations of Biological Lubrication at the Nanoscale: The Cases of Synovial Joints and the Oral Cavity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
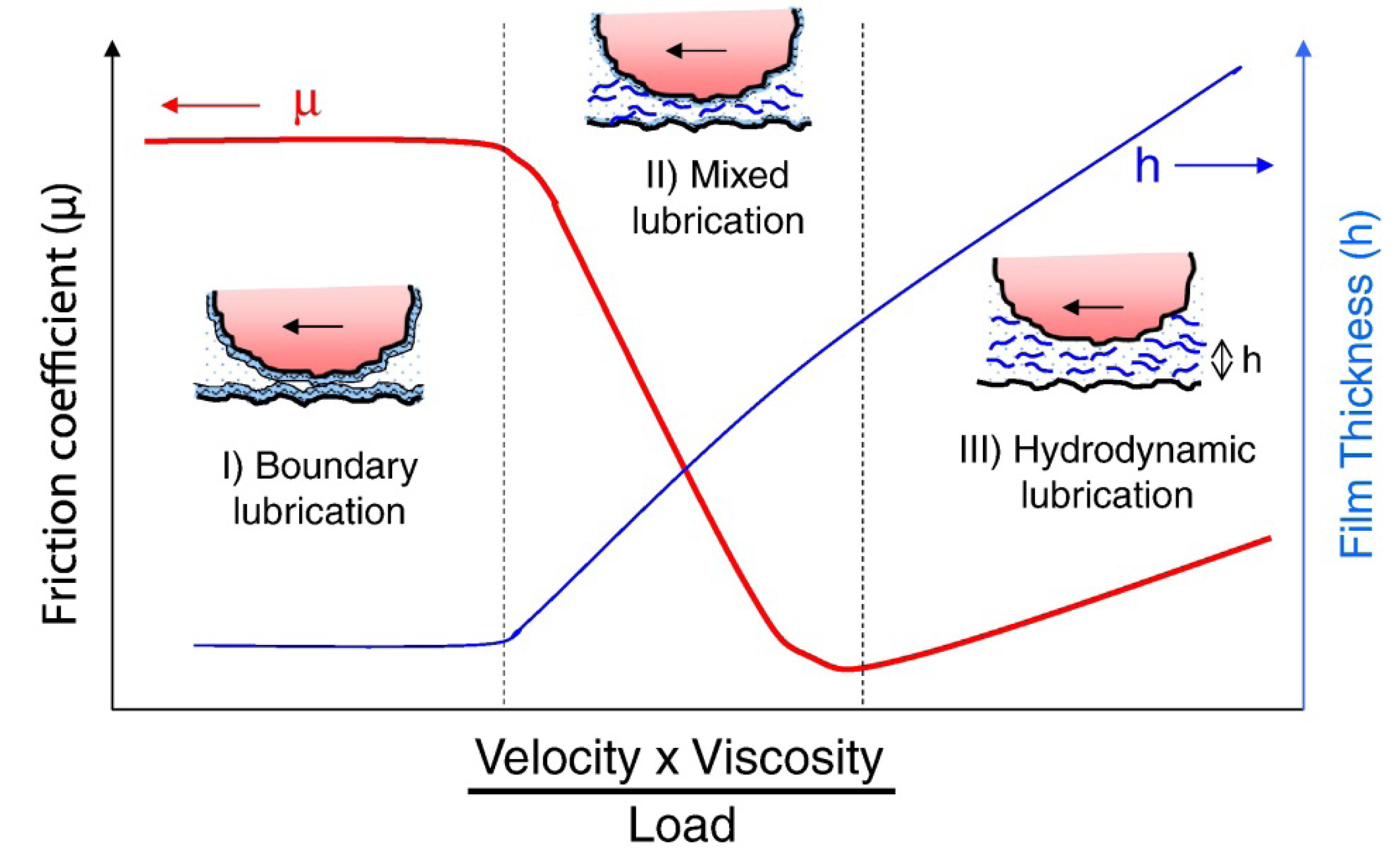
2. Some Basic Tribology Concepts
3. Experimental Techniques for Nanotribological Investigations
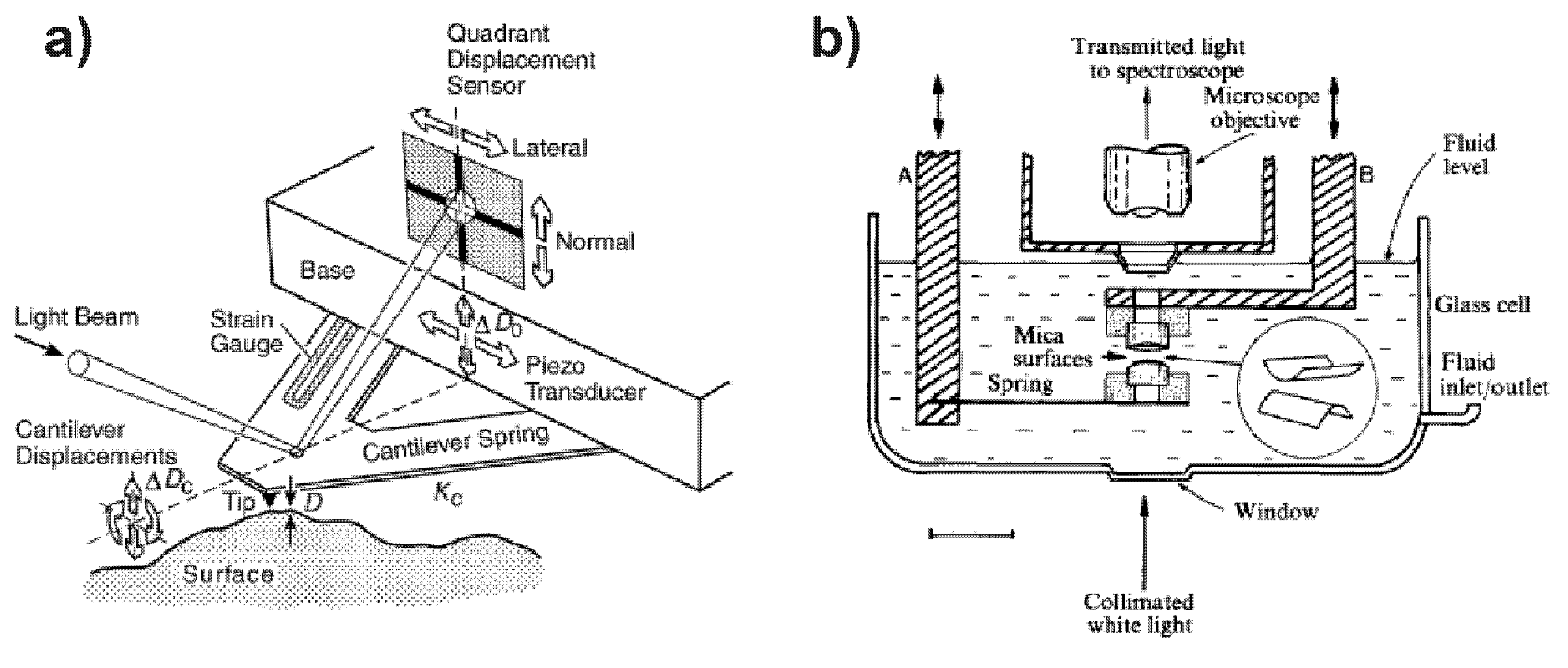
3.1. Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
3.2. Surface Force Apparatus (SFA)
3.3. AFM vs. SFA
4. Lubrication in Synovial Joints
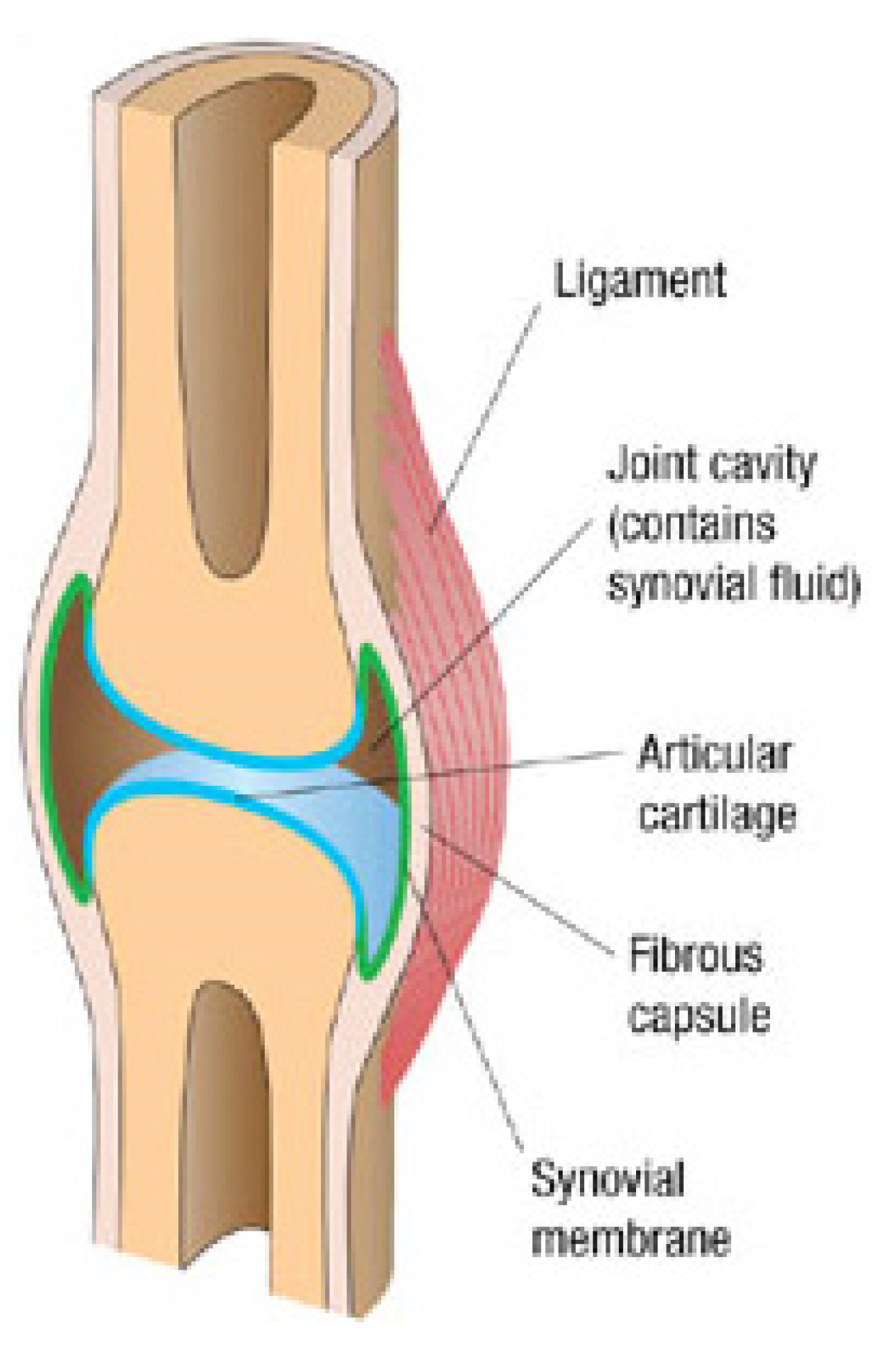
4.1. Physiology and Macrotribology of Synovial Joints
4.2. Nanotribology of Synovial Joints—Cartilage Surfaces
4.3. Nanotribology of Synovial Joints—Reconstituted Model Systems
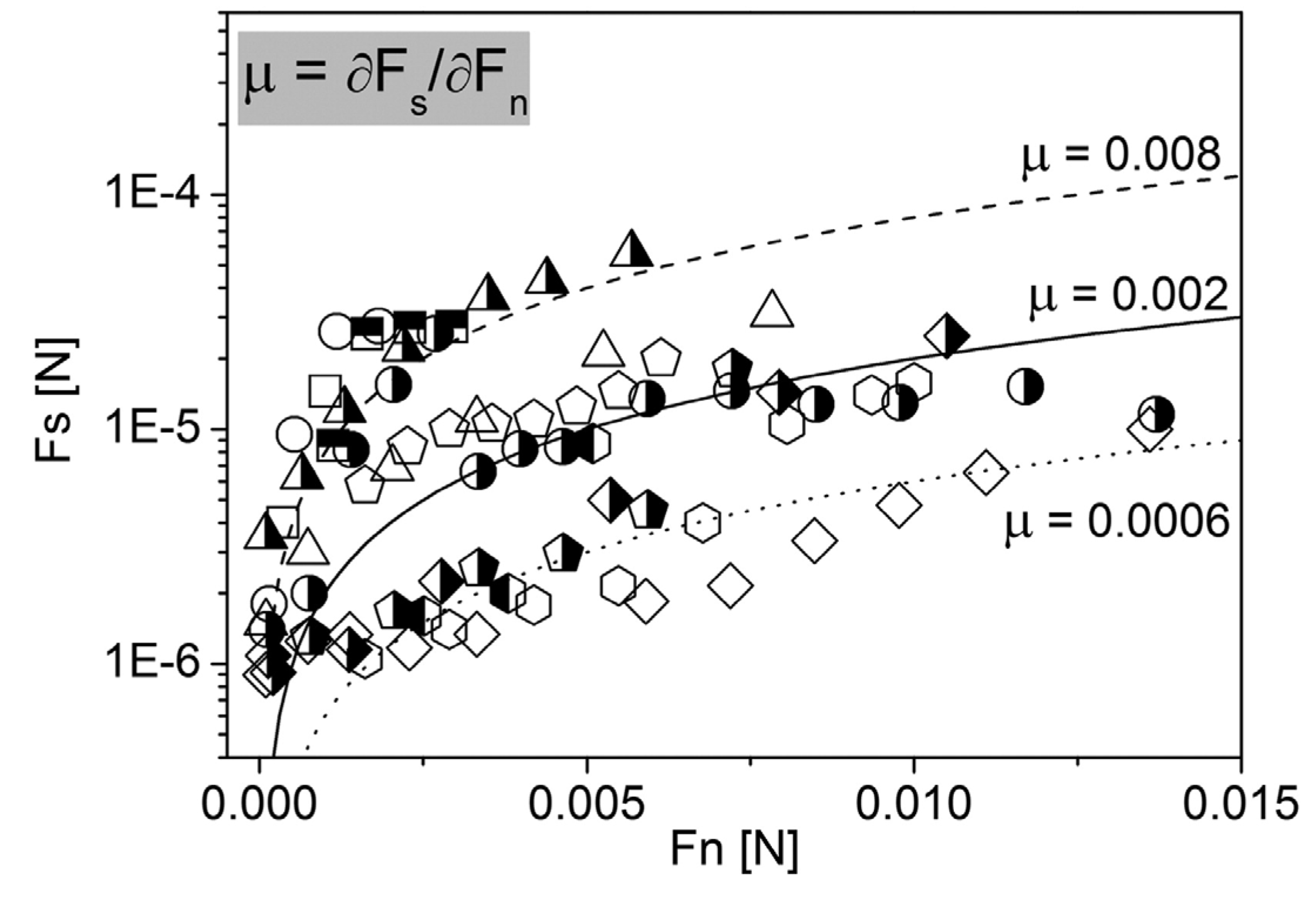
5. Lubrication in the Oral Cavity
5.1. Physiology and Macrotribology of the Oral Cavity
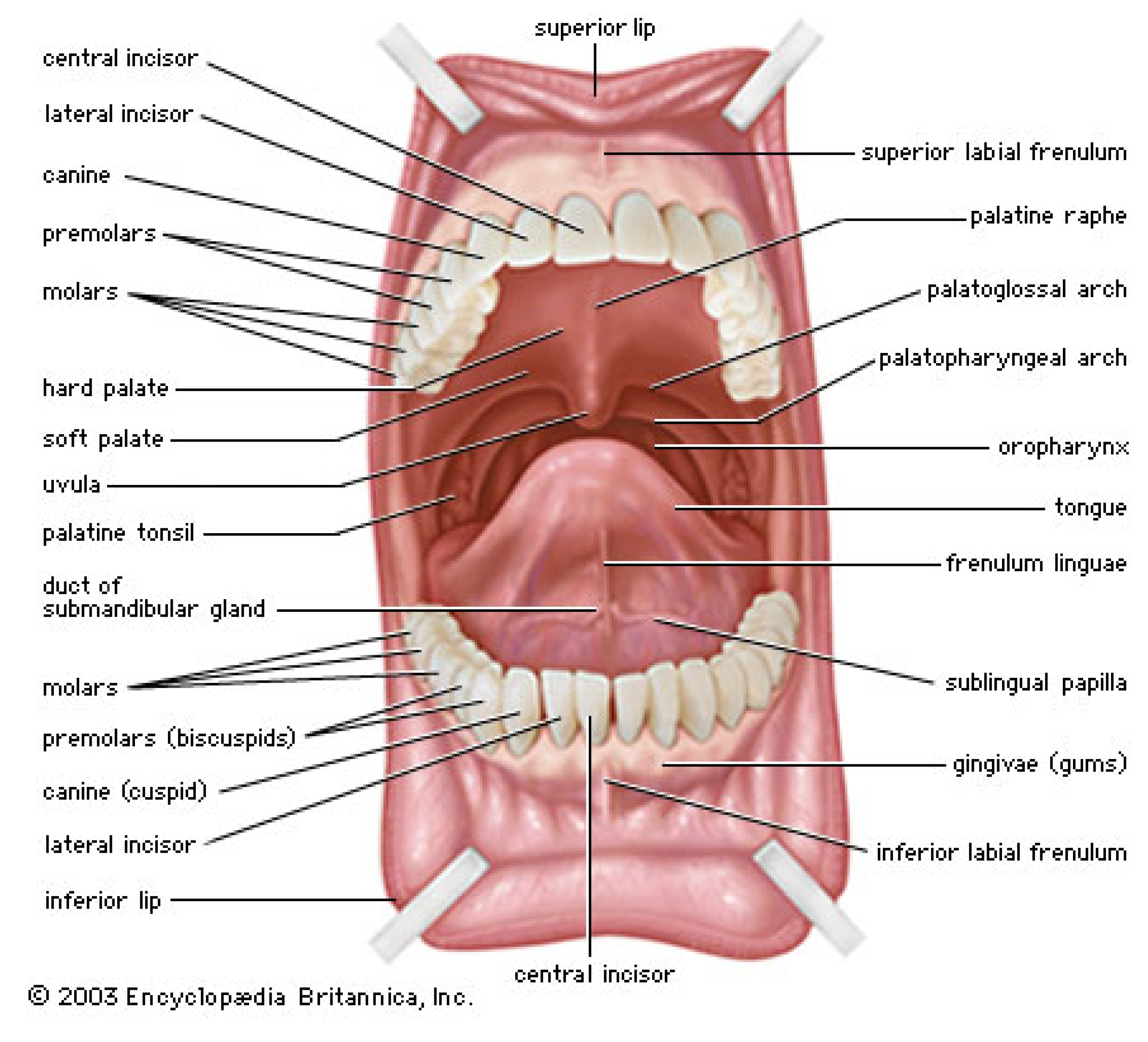
5.2. Nanotribology of the Oral Cavity—Whole Saliva Films


5.3. Nanotribology of the Oral Cavity—Reconstituted Model Systems
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Abbreviations
| AFM | atomic force microscope |
| BSM | bovine submaxillary mucin |
| DOPC | 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| DPPC | 1,2-dihexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| EHL | elastohydrodynamic lubrication |
| GAG | glycosaminoglycan |
| HA | hyaluronic acid |
| HSPC | hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| POPC | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| PRP | proline rich protein |
| SAPL | surface-active phospholipids |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SFA | surface force apparatus |
| SUV | single unilamellar vesicle |
| SZP | superficial zone protein. |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.; Spencer, N.D. Sweet, hairy, soft, and slippery. Science 2008, 319, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, J.; Gregor, B.; Turner, B.; Afdhal, N.H.; Bansil, R.; Erramilli, S. Viscoelastic properties and dynamics of porcine gastric mucin. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, B.A. Boundary lubrication in vivo. J. Eng. Med. 2000, 214, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeri, A.Z. Hydrodynamic and Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. In Modern Tribology Handbook; Bhushan, B., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 383–453. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, J.M.; Chang, D.P.; Zauscher, S. Molecular mechanisms of aqueous boundary lubrication by mucinous glycoproteins. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnig, G.; Quate, C.F.; Gerber, C. Atomic force microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.J.; Cappella, B.; Kappl, M. Force measurements with the atomic force microscope: Technique, interpretation and applications. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2005, 59, 1–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mate, C.M.; McClelland, G.M.; Erlandsson, R.; Chiang, S. Atomic-scale friction of a tungsten tip on a graphite surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 1942–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducker, W.A.; Senden, T.J.; Pashley, R.M. Direct measurement of colloidal forces using an atomic force microscope. Nature 1991, 353, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckband, D.; Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular forces in biology. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2001, 34, 105–267. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, J. Forces between mica surfaces bearing layers of adsorbed polystyrene in cyclohexane. Nature 1980, 288, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Adams, G.E. Measurement of forces between two mica surfaces in aqueous electrolyte solutions in the range 0–100 nm. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1978, 74, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, D.; Winterton, R.H.S. The direct measurement of normal and retarded van der Waals forces. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1969, 312, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonck, A.; Georges, J.M.; Loubet, J.L. Measurements of intermolecular forces and the rheology of dodecane between alumina surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 126, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, A.M.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Gee, M.L.; McGuiggan, P.M. Measurements of and relation between the adhesion and friction of two surfaces separated by molecularly thin liquid films. J. Tribol. 1989, 111, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Kumacheva, E. Simple liquids confined to molecularly thin layers. I. Confinement-induced liquid-to-solid phase transitions. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 6996–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Measurement of the viscosity of liquids in very thin films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 110, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, G.; Schmitt, F.-J.; Hill, R.; Israelachvili, J. Thin film rheology and tribology of confined polymer melts: Contrasts with bulk properties. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colchero, J.; Storch, A.; Luna, M.; Gómez Herrero, J.; Baró, A.M. Observation of liquid neck formation with scanning force microscopy techniques. Langmuir 1998, 14, 2230–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crassous, J.; Charlaix, E.; Loubet, J.L. Capillary condensation between high-energy surfaces. An experimental study with a surface force apparatus. In Europhys. Lett.; 1994; Volume 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Gupta, B.K.; Azarian, M.H. Nanoindentation, microscratch, friction and wear studies of coatings for contact recording applications. Wear 1995, 181–183, 743–758. [Google Scholar]
- Beegan, D.; Chowdhury, S.; Laugier, M.T. Comparison between nanoindentation and scratch test hardness (scratch hardness) values of copper thin films on oxidised silicon substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 5804–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotres, J.; Barrantes, A.; Arnebrant, T. Friction force spectroscopy as a tool to study the strength and lateral diffusion of protein layers. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9439–9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappone, B.; Ruths, M.; Greene, G.W.; Jay, G.D.; Israelachvili, J.N. Adsorption, lubrication, and wear of lubricin on model surfaces: Polymer brush-like behavior of a glycoprotein. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 1693–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, W. Of the structure and diseases of articulating cartilages, by William Hunter, surgeon. Phil. Trans. 1742, 42, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dėdinaitė, A. Biomimetic lubrication. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J. Molecular mechanisms of synovial joint lubrication. J. Eng. Tribol. 2006, 220, 691–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.; Morina, A.; Liskiewicz, T.; Yan, Y. Synovial joint lubrication—Does nature teach more effective engineering lubrication strategies? J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2007, 221, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, W.A.; Fijan, R.S.; Carlson, K.L.; Burgess, R.G.; Harris, W.H.; Mann, R.W. Contact pressures in the human hip joint measured in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 2879–2883. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, J. Polymers in living systems: From biological lubrication to tissue engineering and biomedical devices. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, F.C. Lubrication of animal joints: II the mechanism. J. Biomech. 1968, 1, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, V.; Dowson, D. Lubrication and cartilage. J. Anat. 1976, 121, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, H. Anatomy of the Human Body; Lea & Febiger: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1918. [Google Scholar]
- Bole, G.G. Synovial fluid lipids in normal individuals and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1962, 5, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, A.V.; Powell, G.L.; LaBerge, M. Phospholipid composition of articular cartilage boundary lubricant. J. Orthop. Res. 2001, 19, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcutchen, C.W. Boundary lubrication by synovial fluid: Demonstration and possible osmotic explanation. Fed. Proc. 1966, 25, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Ogston, A.G.; Stanier, J.E. The physiological function of hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid; viscous, elastic and lubricant properties. J. Physiol. 1953, 119, 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Schurz, J.; Ribitsch, V. Rheology of synovial fluid. Biorheology 1987, 24, 385–399. [Google Scholar]
- Linn, F.C.; Radin, E.L. Lubrication of animal joints. III. The effect of certain chemical alterations of the cartilage and lubricant. Arthritis Rheum. 1968, 11, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setton, L. Polymer therapeutics: Reservoir drugs. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dintenfass, L. Lubrication in synovial joints. Nature 1963, 197, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.R.; McCutchen, C.W. Experimental evidence for weeping lubrication in mammalian joints. Nature 1959, 184, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnley, J. The lubrication of animal joints in relation to surgical reconstruction by arthroplasty. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1960, 19, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, R. Boundary lubrication in natural articular joints. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 35, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, E.L.; Swann, D.A.; Weisser, P.A. Separation of a hyaluronate-free lubricating fraction from synovial fluid. Nature 1970, 228, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, D.A.; Radin, E.L. The molecular basis of articular lubrication: I. Purification and properties of a lubricating fraction from bovine synovial fluid. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 8069–8073. [Google Scholar]
- Swann, D.A.; Slayter, H.S.; Silver, F.H. The molecular structure of lubricating glycoprotein-I, the boundary lubricant for articular cartilage. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 5921–5925. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.R.C.; Gleghorn, J.P.; Hughes, C.E.; Fitz, L.J.; Zollner, R.; Wainwright, S.D.; Caterson, B.; Morris, E.A.; Bonassar, L.J.; Flannery, C.R. Binding and localization of recombinant lubricin to articular cartilage surfaces. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, G.D.; Torres, J.R.; Warman, M.L.; Laderer, M.C.; Breuer, K.S. The role of lubricin in the mechanical behavior of synovial fluid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6194–6199. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, I.M.; Hills, B.A. Surface-active phospholipid as the lubricating component of lubricin. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 37, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, B.A.; Monds, M.K. Enzymatic identification of the load-bearing boundary lubricant in the joint. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 37, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Jay, G.D.; Cha, C.J. The effect of phospholipase digestion upon the boundary lubricating ability of synovial fluid. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 2454–2457. [Google Scholar]
- Hills, B.A. Identity of the joint lubricant. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 200–201. [Google Scholar]
- Sivan, S.; Schroeder, A.; Verberne, G.; Merkher, Y.; Diminsky, D.; Priev, A.; Maroudas, A.; Halperin, G.; Nitzan, D.; Etsion, I.; et al. Liposomes act as effective biolubricants for friction reduction in human synovial joints. Langmuir 2009, 26, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.S.; Mow, V.C.; Lai, W.M.; Holmes, M.H. An analysis of the squeeze-film lubrication mechanism for articular cartilage. J. Biomech. 1992, 25, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.S.; Sikorski, J.; Dowson, D.; Longfield, M.D.; Wright, V. Features of the synovial fluid film in human joint lubrication. Nature 1970, 225, 956–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Higaki, H.; Sawae, Y.; Ohtsuki, N.; Moriyama, S.; Nakanishi, Y. Adaptive multimode lubrication in natural synovial joints and artificial joints. J. Eng. Med. 1998, 212, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.W.; Batchelor, A.W.; Griffiths, L.J. Friction and wear changes in synovial joints. Wear 1994, 171, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Costa, K.D.; Ateshian, G.A. Microscale frictional response of bovine articular cartilage from atomic force microscopy. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.M.T.; Neu, C.P.; DuRaine, G.; Komvopoulos, K.; Reddi, A.H. Atomic force microscope investigation of the boundary-lubricant layer in articular cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.M.T.; Neu, C.P.; Komvopoulos, K.; Reddi, A.H. Dependence of nanoscale friction and adhesion properties of articular cartilage on contact load. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, J.M.; Blum, J.J.; Jay, G.D.; Darling, E.M.; Guilak, F.; Zauscher, S. In situ friction measurement on murine cartilage by atomic force microscopy. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateshian, G.A. The role of interstitial fluid pressurization in articular cartilage lubrication. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 1163–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, G.W.; Banquy, X.; Lee, D.W.; Lowrey, D.D.; Yu, J.; Israelachvili, J.N. Adaptive mechanically controlled lubrication mechanism found in articular joints. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5255–5259. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.W.; Banquy, X.; Israelachvili, J.N. Stick-slip friction and wear of articular joints. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 567–574. [Google Scholar]
- Crockett, R.; Roos, S.; Rossbach, P.; Dora, C.; Born, W.; Troxler, H. Imaging of the surface of human and bovine articular cartilage with ESEM and AFM. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 19, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, R.; Chen, N.; Israelachvili, J.N. Thin film rheology and lubricity of hyaluronic acid solutions at a normal physiological concentration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, R.; Chen, N.; Israelachvili, J. Normal and shear forces between mica and model membrane surfaces with adsorbed hyaluronan. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 9519–9526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, M.; Chen, N.; Israelachvili, J. Lubrication and wear properties of grafted polyelectrolytes, hyaluronan and hylan, measured in the surface forces apparatus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 71, 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Banquy, X.; Greene, G.W.; Lowrey, D.D.; Israelachvili, J.N. The boundary lubrication of chemically grafted and cross-linked hyaluronic acid in phosphate buffered saline and lipid solutions measured by the surface forces apparatus. Langmuir 2012, 28, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, G.D.; Torres, J.R.; Rhee, D.K.; Helminen, H.J.; Hytinnen, M.M.; Cha, C.-J.; Elsaid, K.; Kim, K.-S.; Cui, Y.; Warman, M.L. Association between friction and wear in diarthrodial joints lacking lubricin. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3662–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappone, B.; Greene, G.W.; Oroudjev, E.; Jay, G.D.; Israelachvili, J.N. Molecular aspects of boundary lubrication by human lubricin: Effect of disulfide bonds and enzymatic digestion. Langmuir 2007, 24, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.P.; Abu-Lail, N.I.; Guilak, F.; Jay, G.D.; Zauscher, S. Conformational mechanics, adsorption, and normal force interactions of lubricin and hyaluronic acid on model surfaces. Langmuir 2008, 24, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.P.; Abu-Lail, N.I.; Coles, J.M.; Guilak, F.; Jay, G.D.; Zauscher, S. Friction force microscopy of lubricin and hyaluronic acid between hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3438–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Banquy, X.; Zappone, B.; Greene, G.W.; Jay, G.D.; Israelachvili, J.N. Synergistic interactions between grafted hyaluronic acid and lubricin provide enhanced wear protection and lubrication. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Dean, D.; Ortiz, C.; Grodzinsky, A.J. Lateral nanomechanics of cartilage aggrecan macromolecules. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 1384–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, J.; Merkher, Y.; Kampf, N.; Collinson, L.; Day, A.J.; Maroudas, A.; Klein, J. Articular cartilage proteoglycans as boundary lubricants: Structure and frictional interaction of surface-attached hyaluronan and hyaluronan-aggrecan complexes. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3432–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, J.; Merkher, Y.; Kampf, N.; Collinson, L.; Day, A.J.; Maroudas, A.; Klein, J. Normal and shear interactions between hyaluronan-aggrecan complexes mimicking possible boundary lubricants in articular cartilage in synovial joints. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3823–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneci, M.-C.; Dekkiche, F.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M.; Meurisse, M.-H.; Berthier, Y.; Rieu, J.P. Tribological properties of fluid phase phospholipid bilayers. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.-M.; Berthier, Y.; Meurisse, M.-H.; Rieu, J.-P. Role of nanomechanical properties in the tribological performance of phospholipid biomimetic surfaces. Langmuir 2008, 24, 8765–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducker, W.A.; Clarke, D.R. Controlled modification of silicon nitride interactions in water via zwitterionic surfactant adsorption. Colloids Surf. A 1994, 93, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducker, W.A.; Luther, E.P.; Clarke, D.R.; Lange, F.F. Effect of zwitterionic surfactants on interparticle forces, rheology, and particle packing of silicon nitride slurries. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 80, 575–583. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, L.M.; Tiberg, F. Normal and lateral forces between lipid covered solids in solution: Correlation with layer packing and structure. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, M.; An, J.; Thormann, E.; Dedinaite, A. Hyaluronan and phospholipids in boundary lubrication. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10241–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, R.; Schroeder, A.; Barenholz, Y.; Klein, J. Interactions between adsorbed hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine (HSPC) vesicles at physiologically high pressures and salt concentrations. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, R.; Schroeder, A.; Silbert, G.; Turjeman, K.; Barenholz, Y.; Klein, J. Boundary lubricants with exceptionally low friction coefficients based on 2D close-packed phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3517–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaisinskaya, A.; Ma, L.; Silbert, G.; Sorkin, R.; Tairy, O.; Goldberg, R.; Kampf, N.; Klein, J. Hydration lubrication: Exploring a new paradigm. Faraday Discuss. 2012, 156, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkin, R.; Kampf, N.; Dror, Y.; Shimoni, E.; Klein, J. Origins of extreme boundary lubrication by phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5465–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejak, B.; Młotkowski, A.; Romanowicz, M. Finite element analysis of stresses in molars during clenching and mastication. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 90, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlone, R.E.; Proffit, W.R. Correlation between functional lingual pressure and oral cavity size. Cleft Palate J. 1972, 9, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.R.; Zheng, J. Tribology of dental materials: A review. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2008, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goktas, S.; Dmytryk, J.J.; McFetridge, P.S. Biomechanical behavior of oral soft tissues. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, A.; Keskiner, I.; Arici, S.; Sato, S. The effect of periodontal surgery on bite force, occlusal contact area and bite pressure. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2006, 137, 978–983. [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka, O.; Iwasaki, M.; Saito, M.; Morimoto, T. Influence of clenching intensity on bite force balance, occlusal contact area, and average bite pressure. J. Dent. Res. 1999, 78, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieser, J.; Singh, B.; Swain, M.; Ichim, I.; Waddell, J.N.; Kennedy, D.; Foster, K.; Livingstone, V. Measuring intraoral pressure: Adaptation of a dental appliance allows measurement during function. Dysphagia 2008, 23, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuga, K.; Akagawa, Y.; Groher, M. Comparison of three types of tongue pressure measurement devices. Dysphagia 2011, 26, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongue. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Available online: http://www.Britannica.Com/ebchecked/media/68879/anterior-view-of-the-oral-cavity (accessed on 11 July 2013).
- Humphrey, S.P.; Williamson, R.T. A review of saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, W.H. The rheology of saliva. J. Dent. Res. 1987, 66, 660–666. [Google Scholar]
- Christersson, C.E.; Lindh, L.; Arnebrant, T. Film-forming properties and viscosities of saliva substitutes and human whole saliva. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2000, 108, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Haward, S.; Odell, J.; Berry, M.; Hall, T. Extensional rheology of human saliva. Rheol. Acta 2011, 50, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantonen, P.J.; Meurman, J.H. Viscosity of whole saliva. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1998, 56, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Ono, K.; Masuda, W.; Inagaki, T.; Yokota, M.; Inenaga, K. Rheological properties of human saliva and salivary mucins. J. Oral Biosci. 2008, 50, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wickström, C.; Christersson, C.; Davies, J.R.; Carlstedt, I. Macromolecular organization of saliva: Identification of “insoluble” MUC5B assemblies and non-mucin proteins in the gel phase. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickström, C.; Davies, J.R.; Eriksen, G.V.; Veerman, E.C.; Carlstedt, I. MUC5B is a major gel-forming, oligomeric mucin from human salivary gland, respiratory tract and endocervix: Identification of glycoforms and C-terminal cleavage. Biochem. J. 1998, 334, 685–693. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, A.; Mendoza, B.; Reddy, M.S.; Scannapieco, F.A.; Levine, M.J.; Hatton, M.N. Lubrication of selected salivary molecules and artificial salivas. Dysphagia 1989, 4, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongaerts, J.H.H.; Rossetti, D.; Stokes, J.R. The lubricating properties of human whole saliva. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 27, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, J.F.; de Wijk, R.A.; Huntjens, L. Load dependency of the coefficient of friction of oral mucosa. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeh, E.S.; Aguirre, A.; Sakaguchi, R.L.; Rudney, J.D.; Levine, M.J.; Douglas, W.H. Hard tissue lubrication by salivary fluids. Clin. Mater. 1990, 6, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.; Mendoza, B.; Levine, M.J.; Hatton, M.N.; Douglas, W.H. In vitro characterization of human salivary lubrication. Arch. Oral Biol. 1989, 34, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, C.; Jenkins, G.N.; Tonge, C.H. The nomenclature of the integuments of the enamel surface of teeth. Br. Dent. J. 1963, 115, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilakos, N.; Arnebrant, T.; Glantz, P.O. Adsorption of whole saliva onto hydrophilic and hydrophobic solid surfaces: Influence of concentration, ionic stength and pH. Scand. J. Dent. Res. 1992, 100, 346–353. [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen, I.E.; Lindh, L. The composition of enamel salivary films is different from the ones formed on dental materials. Biofouling 2009, 25, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, W.L.; Custodio, W.; McDonald, E.E. New insights into the composition and functions of the acquired enamel pellicle. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannig, M.; Joiner, A. The structure, function and properties of the acquired pellicle. Monogr. Oral Sci. 2006, 19, 29–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lendenmann, U.; Grogan, J.; Oppenheim, F.G. Saliva and dental pellicle—A review. Adv. Dent. Res. 2000, 14, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dédinaité, A. Interfacial Properties of Mucins. In Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, O.; Arnebrant, T. Mucin layers and multilayers—Physicochemical properties and applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, W.H.; Reeh, E.S.; Ramasubbu, N.; Raj, P.A.; Bhandary, K.K.; Levine, M.J. Statherin: A major boundary lubricant of human saliva. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 180, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, M.N.; Loomis, R.E.; Levine, M.J.; Tabak, L.A. Masticatory lubrication. The role of carbohydrate in the lubricating property of a salivary glycoprotein-albumin complex. Biochem. J. 1985, 230, 817–820. [Google Scholar]
- Joiner, A.; Schwarz, A.; Philpotts, C.J.; Cox, T.F.; Huber, K.; Hannig, M. The protective nature of pellicle towards toothpaste abrasion on enamel and dentine. J. Dent. 2008, 36, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macakova, L.; Yakubov, G.E.; Plunkett, M.A.; Stokes, J.R. Influence of ionic strength on the tribological properties of pre-adsorbed salivary films. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, T.; Arnebrant, T.; Glantz, P.O. Interactions between salivary films adsorbed on mica surfaces. Colloids Surf. A 1997, 129–130, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.M.; Yakubov, G.E.; Stokes, J.R.; Klein, J. Lubrication and load-bearing properties of human salivary pellicles adsorbed ex vivo on molecularly smooth substrata. Biofouling 2012, 28, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn Berg, I.C.; Rutland, M.W.; Arnebrant, T. Lubricating properties of the initial salivary pellicle—An AFM study. Biofouling 2003, 19, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, M.; Valle-Delgado, J.J.; Hamit, J.; Rutland, M.W.; Arnebrant, T. Interactions of hydroxyapatite surfaces: Conditioning films of human whole saliva. Langmuir 2008, 24, 7262–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeregowda, D.H.; Busscher, H.J.; Vissink, A.; Jager, D.-J.; Sharma, P.K.; van der Mei, H.C. Role of structure and glycosylation of adsorbed protein films in biolubrication. PLoS One 2012, 7, e42600. [Google Scholar]
- Walz, A.; Stühler, K.; Wattenberg, A.; Hawranke, E.; Meyer, H.E.; Schmalz, G.; Blüggel, M.; Ruhl, S. Proteome analysis of glandular parotid and submandibular-sublingual saliva in comparison to whole human saliva by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proteomics 2006, 6, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeregowda, D.H.; van der Mei, H.C.; de Vries, J.; Rutland, M.W.; Valle-Delgado, J.J.; Sharma, P.K.; Busscher, H.J. Boundary lubrication by brushed salivary conditioning films and their degree of glycosylation. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012, 16, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotres, J.; Lindh, L.; Arnebrant, T. Friction force spectroscopy as a tool to study the strength and structure of salivary films. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13692–13700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotres, J.; Pettersson, T.; Lindh, L.; Arnebrant, T. Nanowear of salivary films vs. substratum wettability. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 973–978. [Google Scholar]
- Carlén, A.; Börjesson, A.C.; Nikdel, K.; Olsson, J. Composition of pellicles formed in vitro on tooth surfaces in different parts of the dentition, and in vitro on hydroxyapatite. Caries Res. 1998, 32, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedinaite, A.; Lundin, M.; Macakova, L.; Auletta, T. Mucin-chitosan complexes at the solid-liquid interface: Multilayer formation and stability in surfactant solutions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9502–9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, T.; Dedinaite, A. Normal and friction forces between mucin and mucin-chitosan layers in absence and presence of SDS. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 324, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, E.; Proust, J.E. Forces between mica surfaces covered with adsorbed mucin across aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 118, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proust, J.E.; Baszkin, A.; Perez, E.; Boissonnade, M.M. Bovine submaxillary mucin (BSM) adsorption at solid/liquid interfaces and surface forces. Colloids Surf. 1984, 10, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, T.; Arnebrant, T.; Glantz, P.O.; Baier, R.E. Interactions between layers of salivary acidic proline rich protein 1 (PRP1) adsorbed on mica surfaces. Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1998, 108, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.M.; Carpenter, G.H.; Proctor, G.B.; Klein, J. Normal and frictional interactions of purified human statherin adsorbed on molecularly-smooth solid substrata. Biofouling 2011, 27, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn Berg, I.C.; Lindh, L.; Arnebrant, T. Intraoral lubrication of PRP-1, statherin and mucin as studied by AFM. Biofouling 2004, 20, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotres, J.; Madsen, J.B.; Arnebrant, T.; Lee, S. Adsorption and nanowear properties of bovine submaxillary mucin (BSM) films on solid surfaces: Influence of solution pH and substrate hydrophilicity. Langmuir 2013. submitted. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sotres, J.; Arnebrant, T. Experimental Investigations of Biological Lubrication at the Nanoscale: The Cases of Synovial Joints and the Oral Cavity. Lubricants 2013, 1, 102-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants1040102
Sotres J, Arnebrant T. Experimental Investigations of Biological Lubrication at the Nanoscale: The Cases of Synovial Joints and the Oral Cavity. Lubricants. 2013; 1(4):102-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants1040102
Chicago/Turabian StyleSotres, Javier, and Thomas Arnebrant. 2013. "Experimental Investigations of Biological Lubrication at the Nanoscale: The Cases of Synovial Joints and the Oral Cavity" Lubricants 1, no. 4: 102-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants1040102
APA StyleSotres, J., & Arnebrant, T. (2013). Experimental Investigations of Biological Lubrication at the Nanoscale: The Cases of Synovial Joints and the Oral Cavity. Lubricants, 1(4), 102-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants1040102